WO2010008011A1 - 画質改善装置及び方法 - Google Patents
画質改善装置及び方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010008011A1 WO2010008011A1 PCT/JP2009/062787 JP2009062787W WO2010008011A1 WO 2010008011 A1 WO2010008011 A1 WO 2010008011A1 JP 2009062787 W JP2009062787 W JP 2009062787W WO 2010008011 A1 WO2010008011 A1 WO 2010008011A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- low
- component signal
- signal
- frequency
- frequency component
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 18
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 20
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 9
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000002238 attenuated effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N1/00—Scanning, transmission or reproduction of documents or the like, e.g. facsimile transmission; Details thereof
- H04N1/40—Picture signal circuits
- H04N1/409—Edge or detail enhancement; Noise or error suppression
- H04N1/4092—Edge or detail enhancement
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/14—Picture signal circuitry for video frequency region
- H04N5/20—Circuitry for controlling amplitude response
- H04N5/205—Circuitry for controlling amplitude response for correcting amplitude versus frequency characteristic
- H04N5/208—Circuitry for controlling amplitude response for correcting amplitude versus frequency characteristic for compensating for attenuation of high frequency components, e.g. crispening, aperture distortion correction
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/73—Deblurring; Sharpening
- G06T5/75—Unsharp masking
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N1/00—Scanning, transmission or reproduction of documents or the like, e.g. facsimile transmission; Details thereof
- H04N1/40—Picture signal circuits
- H04N1/407—Control or modification of tonal gradation or of extreme levels, e.g. background level
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10016—Video; Image sequence
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an image quality improving apparatus and method for improving image quality by correcting an edge (contour) of a video signal.
- an enhancement process has been performed to add a shoot component to the edge of the video signal to sharpen the edge and improve the sharpness of the video.
- An enhancer that performs this enhancement processing extracts a high frequency component of a video signal using a high-pass filter with a relatively short tap length of several to a dozen taps, and generates a shoot component based on the extracted high frequency component. This is added to the video signal.
- Patent Document 1 describes such an enhancer (image quality improvement apparatus).
- the high-frequency component is extracted by the high-pass filter, but in reality, the mid-high frequency component including the mid-range may be extracted to emphasize the mid-high frequency component of the video signal.
- the peak frequency of the pass band of the high-pass filter is shifted to the middle band side, the middle and high band components are emphasized.
- the mid frequency component is extracted along with the high frequency component, and as a result, the mid high frequency component is emphasized.
- the conventional enhancer will be described as enhancing the high frequency component even when the high frequency component including the mid frequency component of the video signal is emphasized.
- the present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide an image quality improving apparatus and method capable of improving the sense of contrast. It is another object of the present invention to provide an image quality improving apparatus and method capable of improving both sharpness and contrast.
- a first low-pass filter having a first cutoff frequency and extracting a low-frequency component signal of an input video signal.
- a subtractor that subtracts the low-frequency component signal from the input video signal to extract a high-frequency component signal; and a second cutoff frequency that is higher than the first cutoff frequency, and the high-frequency component
- a second low-pass filter that extracts a low-frequency high-frequency component signal that is a low-frequency signal in the signal; a multiplier that multiplies the low-frequency high-frequency component signal by a predetermined gain to generate a correction component signal; And an adder that adds the correction component signal to the input video signal.
- the first low-pass filter having a first cutoff frequency and extracting a low-frequency component signal of the input video signal, and the input video signal
- a subtractor that subtracts a low-frequency component signal to extract a first high-frequency component signal; a second cutoff frequency that is higher than the first cutoff frequency; and a low-frequency region in the first high-frequency component signal
- a first low-pass filter that extracts a low-frequency high-frequency component signal, which is a signal on the side, and a first gain that is multiplied by a first gain by the low-frequency high-frequency component signal to generate a first correction component signal
- a multiplier a high-pass filter that extracts a second high-frequency component signal from the input video signal, and a second gain are multiplied by the second high-frequency component signal to generate a second correction component signal A second multiplier and the input movie Image quality improving device characterized by comprising an adder for adding the first and second correction component signal to signal.
- a high-pass filter that extracts a first high-frequency component signal from the input video signal, a first gain multiplied by the first high-frequency component signal, A first multiplier that generates one correction component signal; a first adder that adds the first correction component signal to the input video signal; and a first cut-off frequency.
- a first low-pass filter that extracts a low-frequency component signal of the video signal output from the detector, and a second high-frequency component signal that is subtracted from the video signal output from the adder And a second subtractor having a second cutoff frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and extracting a low-frequency high-frequency component signal that is a low-frequency signal in the second high-frequency component signal Low pass filter and low frequency
- a second multiplier that multiplies the minute signal by a second gain to generate a second correction component signal; and a second multiplier that adds the second correction component signal to the video signal output from the adder.
- a first low-pass filter having a first cut-off frequency and extracting a low-frequency component signal of the input video signal, and the input video signal
- a first low-pass filter that extracts a low-frequency high-frequency component signal that is a low-frequency signal, and a first gain that multiplies the low-frequency high-frequency component signal by a first gain to generate a first correction component signal.
- an image quality improving apparatus comprising a second adder.
- a first step of extracting a low frequency component signal of a video signal by a first low-pass filter having a first cutoff frequency, and the low frequency component from the video signal A second step of subtracting the signal to extract a high frequency component signal and a second low-pass filter having a second cutoff frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency, A third step of extracting a low-frequency high-frequency component signal, a fourth step of generating a first correction component signal by multiplying the low-frequency high-frequency component signal by a first gain, A fifth step of adding the first correction component signal to the video signal and outputting a corrected video signal in which the band component of the low frequency side high frequency component signal in the band of the video signal is emphasized.
- Image quality improving method characterized the door is provided.
- the image quality improving apparatus and method of the present invention it is possible to improve the sense of contrast. Moreover, both sharpness and contrast can be improved.
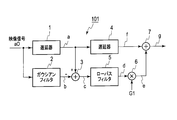
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a first embodiment of the present invention.
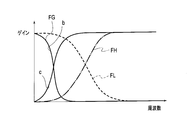
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating the frequency characteristics of each filter used in each embodiment.
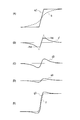
- FIG. 3 is a waveform diagram for explaining the first embodiment.
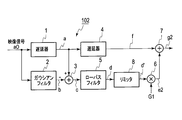
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a second embodiment of the present invention.
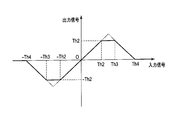
- FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a first example of the limiting characteristics of the limiter used in each embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a second example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter used in each embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a third example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter used in each embodiment.
- FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a fourth example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter used in each embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating the frequency characteristics of each filter used in each embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is a waveform diagram for explaining the first embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing a third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 is a waveform diagram for explaining the third embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a fifth embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 13 is a block diagram showing a sixth embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a first embodiment of an image quality improving apparatus according to the present invention.
- the configuration and operation of the image quality improvement apparatus 101 according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to the frequency characteristics of each filter shown in FIG. 2 and the waveform diagram shown in FIG.
- a video signal a 0 is input to a delay device 1 and a Gaussian filter 2.
- the video signal a0 may be a luminance signal or a color signal.
- the Gaussian filter is a low-pass filter that extracts a very low frequency component using a Gaussian function.
- the frequency characteristic FG of the Gaussian filter 2 has a very low cutoff frequency as shown in FIG.
- a low-pass filter having a very low cutoff frequency and a long tap length may be used.
- the delay device 1 delays the input video signal a0 by the time required for processing in the Gaussian filter 2 to obtain the video signal a.
- the Gaussian filter 2 extracts a low frequency component signal b from the input video signal a0.
- the video signal a is an edge signal as indicated by a solid line in FIG. 3A
- the low frequency component signal b has a waveform indicated by a broken line in FIG.
- the band of the low frequency component signal b is a band limited by the frequency characteristic FG.
- the subtracter 3 subtracts the low frequency component signal b from the video signal a and outputs a high frequency component signal c shown in FIG. Since the subtracter 3 subtracts the low frequency component signal b from the video signal a of the entire band, the band of the high frequency component signal c is as shown in FIG.
- the high frequency component signal c output from the subtractor 3 is input to the low pass filter 5.
- the frequency characteristic FL of the low-pass filter 5 is as shown in FIG. 2, and the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter 5 is higher than the cutoff frequency of the Gaussian filter 2.
- the output signal d of the low-pass filter 5 is a signal obtained by extracting the low frequency side signal in the high frequency component signal c by the frequency characteristic FL, and has a waveform shown in FIG.
- the output signal d is referred to as a low frequency side high frequency component signal.
- the low frequency side high frequency component signal d is input to the multiplier 6.
- the multiplier 6 multiplies the low frequency side high frequency component signal d by the gain G1 to generate a correction component signal e shown in FIG.
- the gain G1 is for adjusting the image quality improvement effect by the image quality improvement apparatus 101 of the first embodiment, and is normally a positive number less than 1 exceeding 0.
- the delay unit 4 further delays the video signal a output from the delay unit 1 by a time required for processing in the low-pass filter 5 and the multiplier 6 to obtain a video signal f.
- the adder 7 receives the video signal f output from the delay unit 4 and the correction component signal e output from the multiplier 6.
- the waveform of the video signal f is the same as that of the video signal a as shown in FIG.
- the adder 7 outputs a corrected video signal g indicated by a solid line in FIG. 3E by adding the correction component signal e to the video signal f.
- the image quality improving apparatus 101 of the first embodiment it is possible to emphasize the low frequency component (the band component of the low frequency side high frequency component signal d) rather than the high frequency component emphasized by the conventional enhancer. A relatively wide chute component is added to the. Then, the difference in signal level perceived by a person becomes larger than the difference in actual signal level, and the contrast can be improved. Therefore, according to the image quality improving apparatus 101 of the first embodiment, it is possible to obtain an image quality improving effect different from that of the conventional enhancer, that is, an improvement in contrast perceived by a person.
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a second embodiment of the image quality improving apparatus of the present invention.
- the low frequency side high frequency component signal d output from the low pass filter 5 is input to the limiter 8.
- the limiter 8 limits the low-frequency high-frequency component signal d based on the characteristics described later and outputs it as a low-frequency high-frequency component signal d ′.
- the multiplier 6 multiplies the low frequency side high frequency component signal d ′ by the gain G1 and outputs a correction component signal e2.
- the adder 7 adds the correction component signal e2 to the video signal f and outputs a corrected video signal g2.
- FIG. 5 is a first example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter 8.
- the limiting characteristic shown in FIG. 5 is that if the positive or negative input signal (that is, the low frequency side high frequency component signal d) is a value up to the threshold values Th1 and -Th1, the value of the input signal is output as it is. If the value exceeds the value Th1 and ranges up to the value 2Th1, the value of the input signal is attenuated. If the value exceeds the threshold -Th1 and ranges from the value -2Th1, the value of the input signal is amplified, and the value 2Th1,- The characteristic is to hold at 0 when it exceeds 2Th1. In this example, the attenuation slope from the threshold value Th1 to the value 2Th1 and the amplification slope from the threshold value -Th1 to the value -2Th1 are set to -1, but the absolute value of the slope may be smaller than 1.
- FIG. 6 is a second example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter 8.
- the input signal is the threshold value Th2, -Th2
- the value of the input signal is output as it is, and the range from the threshold value Th2 to the threshold value Th3 and the range from the threshold value -Th2 to the threshold value -Th3
- hold the values Th2 and -Th2 and attenuate the input signal value in the range from the threshold Th3 to the value Th4, and the input signal value in the range from the threshold -Th3 to the value -Th4.
- the characteristic is amplified and held at 0 when the value Th4, -Th4 is exceeded.
- the limiting characteristics shown in FIG. 6 are obtained by limiting the value of the output signal of the limiting characteristics shown in FIG. 5 with values Th2 and -Th2, thereby converting the triangular characteristics into trapezoidal characteristics in the positive and negative directions. .
- FIG. 7 shows a third example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter 8.
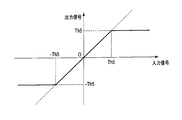
- the limiting characteristic shown in FIG. 7 is a characteristic in which the value of the input signal is output as it is until the input signal reaches the threshold Th5, -Th5, and is held at the value Th5, -Th5 when the threshold exceeds the threshold Th5, -Th5.
- FIG. 8 is a fourth example of the limiting characteristic of the limiter 8.
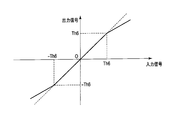
- the limiting characteristic shown in FIG. 8 is that the value of the input signal is output as it is until the input signal reaches the threshold Th6, -Th6, and when the threshold signal Th6 is exceeded, the value of the input signal is changed with a slope of less than 1 exceeding 0.
- the value of the input signal is amplified with a slope of less than 1 exceeding 0.
- the threshold values in FIGS. 5 to 8 may be appropriately set according to the magnitude of the low-frequency high-frequency component signal d output from the low-pass filter 5.
- the limiter 8 since the limiter 8 is provided, when the difference in the signal level of the edge portion in the video signal a0 is large, it is not included in the low frequency side high frequency component signal d. Necessary high-frequency components can be suppressed, and the image quality improvement effect can be improved as compared with the image quality improvement apparatus 101 of the first embodiment.
- the limiter 8 When the low-pass filter 5 cannot secure a sufficient tap length, it is preferable to provide the limiter 8. Of the limiting characteristics shown in FIGS. 5 to 8, the limiting characteristics shown in FIGS. 7 and 8 are preferable.
- FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing a third embodiment of the image quality improving apparatus of the present invention.
- the image quality improving apparatus 103 according to the third embodiment is obtained by switching the order of the low-pass filter 5 and the limiter 8 in the image quality improving apparatus 102 according to the second embodiment.
- the high frequency component signal c output from the subtractor 3 is input to the limiter 8.
- the limiter 8 limits the high-frequency component signal c based on any of the limiting characteristics shown in FIGS. 5 to 8 described above and outputs it as a high-frequency component signal c ′.
- the low-pass filter 5 extracts a low-frequency signal in the input high-frequency component signal c ′ by the frequency characteristic FL and outputs a low-frequency high-frequency component signal d3.
- the multiplier 6 multiplies the low frequency side high frequency component signal d3 by the gain G1 and outputs a correction component signal e3.
- the adder 7 adds the correction component signal e3 to the video signal f and outputs a corrected video signal g3.
- FIG. 10 shows signal waveforms when the limiting characteristic of the limiter 8 in the image quality improvement apparatus 103 is as shown in FIG.
- the high frequency component signal c since the amplitude of the high frequency component signal c is limited by the threshold values Th5 and -Th5, the high frequency component signal c 'has a waveform indicated by a solid line.
- the low-frequency high-frequency component signal d3 output from the low-pass filter 5 is as shown in FIG. 10C
- the correction component signal e3 output from the multiplier 6 is as shown in FIG. 10D.
- the corrected video signal g3 output from the adder 7 is as shown by a solid line in FIG.
- the image quality improving apparatus 103 according to the third embodiment can achieve the same effects as the image quality improving apparatus 102 according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing a fourth embodiment of the image quality improving apparatus of the present invention.
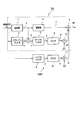
- the image quality improving apparatus 104 of the fourth embodiment shown in FIG. 11 the same reference numerals are given to substantially the same parts as those of the image quality improving apparatus 102 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. To do.
- the image quality improving apparatus 104 according to the fourth embodiment includes a low frequency image quality improving unit 104L for enhancing the low frequency component of the video signal and a high frequency for enhancing the high frequency component of the video signal.
- the image quality improvement unit 104H is provided in parallel.
- the high frequency image quality improvement unit 104H emphasizes the high frequency component, but also includes the case where the high frequency component is emphasized including the mid frequency component of the video signal.
- the low frequency image quality improvement unit 104L has the same configuration as the image quality improvement apparatus 102 of the second embodiment.
- the high-pass filter 9, the limiter 10, the multiplier 11, and the adder 7 which is also a part of the low-frequency image quality improvement unit 104L constitute a high-frequency image quality improvement unit 104H.
- the high frequency image quality improvement unit 104H has a configuration equivalent to that of a general enhancer.
- the video signal input to the low frequency image quality improvement unit 104L is also input to the high pass filter 9 in parallel.
- the frequency characteristic FH of the high-pass filter 9 is as shown in FIG. 2, and the high-pass filter 9 extracts the high frequency component of the video signal and supplies the high frequency component signal h to the limiter 10.
- the limiting characteristic of the limiter 10 is the same as that of the limiter 8, and the input high frequency component signal h is limited and output as a high frequency component signal h '.
- the multiplier 11 multiplies the high frequency component signal h 'by the gain G2 to generate a high frequency correction component signal i4.
- the adder 7 adds the low-frequency correction component signal e2 and the high-frequency correction component signal i4 output from the multiplier 6 to the video signal f output from the delay device 4, and outputs a corrected video signal g4. To do.
- the image quality improving apparatus 104 of the fourth embodiment since the low frequency component can be emphasized by the low frequency image quality improving unit 104L, it is possible to improve the sense of contrast, and at the same time, the high frequency image quality improving unit 104H. Since the high frequency component can be emphasized by this, sharpness can be improved. Therefore, according to the image quality improving apparatus 104 of the fourth embodiment, a higher image quality improving effect can be obtained as compared with the conventional enhancer.
- the low-frequency image quality improvement unit 104L has the same configuration as the image quality improvement device 102 of the second embodiment, but may have the same configuration as the image quality improvement device 103 of the third embodiment. In some cases, the limiters 8 and 10 may be deleted.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a fifth embodiment of the image quality improving apparatus of the present invention.
- the image quality improving apparatus 105 of the fifth embodiment shown in FIG. 12 emphasizes the high frequency image quality improving unit 105H for enhancing the high frequency component (or middle high frequency component) of the video signal and the low frequency component of the video signal.
- a low-frequency image quality improvement unit 105L is provided in series in this order.
- the high frequency image quality improvement unit 105H includes a high pass filter 9, a limiter 10, a multiplier 11, a delay unit 12, and an adder 13.
- the low frequency image quality improvement unit 105L has the same configuration as the image quality improvement apparatus 102.
- the video signal a0 is input to the delay device 12 and the high-pass filter 9.
- the high pass filter 9 extracts the high frequency component of the video signal a0 and supplies the high frequency component signal h5 to the limiter 10.
- the limiter 10 limits the input high frequency component signal h5 and outputs it as a high frequency component signal h5 '.
- the multiplier 11 multiplies the high frequency component signal h5 'by the gain G2 to generate a high frequency correction component signal i5.
- the gain G2 is a positive number exceeding 0 and may exceed 1.
- the delay unit 12 delays the input video signal a0 by a time required for processing in the high-pass filter 9, the limiter 10, and the multiplier 11 to obtain a video signal j5.
- the adder 13 adds the correction component signal i5 to the video signal j5 and outputs the video signal k5 in which the high frequency component is emphasized.
- the video signal k5 in which the high frequency component is emphasized is input to the low frequency image quality improvement unit 105L.
- the delay device 1 delays the video signal k5 to be a video signal a5, and the delay device 4 delays the video signal a5 to be a video signal f5.
- the Gaussian filter 2 extracts the low frequency component signal b5 from the video signal k5, and the subtractor 3 outputs the high frequency component signal c5.
- the low pass filter 5 extracts the low frequency side high frequency component signal d5 from the high frequency component signal c5.
- the limiter 8 limits the low frequency side high frequency component signal d5 to a low frequency side high frequency component signal d5 '.
- the multiplier 6 multiplies the low frequency side high frequency component signal d5 'by the gain G1 to generate a correction component signal e5.
- the adder 7 adds the correction component signal e5 to the video signal f5 and outputs a video signal g5 in which both the high frequency component and the low frequency component are emphasized.
- the same effect as that of the image quality improving apparatus 104 of the fourth embodiment can be obtained.
- the low-frequency image quality improvement unit 105L has the same configuration as that of the image quality improvement apparatus 102 of the second embodiment, but may have the same configuration as the image quality improvement apparatus 103 of the third embodiment.
- the limiters 8 and 10 may be deleted.
- FIG. 13 is a block diagram showing a sixth embodiment of the image quality improving apparatus of the present invention.
- the image quality improving apparatus 105 of the sixth embodiment shown in FIG. 13 the same reference numerals are given to the substantially same parts as those of the image quality improving apparatus 102 of the second embodiment and the image quality improving apparatus 105 of the fifth embodiment shown in FIG. The description thereof will be omitted as appropriate.
- the image quality improving apparatus 106 of the sixth embodiment emphasizes the low frequency image quality improving unit 106L for enhancing the low frequency component of the video signal and the high frequency component (or middle high frequency component) of the video signal.
- the high-frequency image quality improvement unit 106H for this purpose is provided in series in this order.
- the corrected video signal g in which the low frequency component output from the adder 7 of the low frequency image quality improvement unit 106L is emphasized is input to the high frequency image quality improvement unit 106H.
- the delay unit 12 delays the input video signal g by a time required for processing in the high-pass filter 9, the limiter 10, and the multiplier 11 to obtain a video signal j 6.
- the high pass filter 9 extracts a high frequency component of the video signal g and supplies a high frequency component signal h6 to the limiter 10.
- the limiter 10 limits the input high frequency component signal h6 and outputs it as a high frequency component signal h6 '.
- the multiplier 11 multiplies the high frequency component signal h6 'by the gain G2 to generate a high frequency correction component signal i6.
- the adder 13 adds the correction component signal i6 to the video signal j6 and outputs a video signal k6 in which both the low frequency component and the high frequency component are emphasized.
- the same effects as those of the image quality improving apparatus 104 of the fourth embodiment and the image quality improving apparatus 105 of the fifth embodiment can be obtained.
- the low-frequency image quality improvement unit 106L has the same configuration as that of the image quality improvement apparatus 102 of the second embodiment, but may have the same configuration as the image quality improvement apparatus 103 of the third embodiment.
- the limiters 8 and 10 may be deleted.
- the present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above, and various modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the present invention.
- the present invention may be configured by hardware or software. Further, both may be mixed.
- the image quality improving apparatus and method of the present invention it is possible to improve the sense of contrast. Moreover, both sharpness and contrast can be improved.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Picture Signal Circuits (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Facsimile Image Signal Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
Description
図1は本発明の画質改善装置の第1実施形態を示すブロック図である。第1実施形態の画質改善装置101の構成及び動作について、図2に示す各フィルタの周波数特性及び図3に示す波形図を参照しながら説明する。図1において、映像信号a0は遅延器1及びガウシアンフィルタ2に入力される。映像信号a0は輝度信号でも色信号でもよい。ガウシアンフィルタとは、ガウス関数を利用して極めて低い周波数成分を抽出するローパスフィルタのことである。ガウシアンフィルタ2の周波数特性FGは図2に示すように、極めて低い遮断周波数を有する。ガウシアンフィルタ2の代わりに、極めて低い遮断周波数を有し、タップ長の長いローパスフィルタを用いてもよい。
図4は本発明の画質改善装置の第2実施形態を示すブロック図である。図4に示す第2実施形態の画質改善装置102において、図1に示す第1実施形態の画質改善装置101と同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明を適宜省略することとする。図4において、ローパスフィルタ5より出力された低域側高周波成分信号dはリミッタ8に入力される。リミッタ8は低域側高周波成分信号dを後述する特性に基づいて制限して低域側高周波成分信号d’として出力する。乗算器6は低域側高周波成分信号d’にゲインG1を乗算して補正成分信号e2を出力する。加算器7は、映像信号fに補正成分信号e2を加算して補正映像信号g2を出力する。
図9は本発明の画質改善装置の第3実施形態を示すブロック図である。図9に示す第3実施形態の画質改善装置103において、図4に示す第2実施形態の画質改善装置102と実質的に同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明を適宜省略することとする。第3実施形態の画質改善装置103は第2実施形態の画質改善装置102におけるローパスフィルタ5とリミッタ8との順序を入れ替えたものである。図9において、減算器3より出力された高周波成分信号cはリミッタ8に入力される。リミッタ8は高周波成分信号cを上述した図5~図8のいずれかの制限特性に基づいて制限して高周波成分信号c’として出力する。
図11は本発明の画質改善装置の第4実施形態を示すブロック図である。図11に示す第4実施形態の画質改善装置104において、図4に示す第2実施形態の画質改善装置102と実質的に同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明を適宜省略することとする。図11に示すように、第4実施形態の画質改善装置104は、映像信号の低域成分を強調するための低域画質改善部104Lと、映像信号の高域成分を強調するための高域画質改善部104Hとを並列に設けたものである。ここでは、高域画質改善部104Hは高域成分を強調するとしているが、映像信号の中域成分を含めて高域成分を強調する場合も含むものとする。
図12は本発明の画質改善装置の第5実施形態を示すブロック図である。図12に示す第5実施形態の画質改善装置105において、図4に示す第2実施形態の画質改善装置102及び第4実施形態の画質改善装置104と実質的に同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明を適宜省略することとする。図12に示すように、第5実施形態の画質改善装置105は、映像信号の高域成分(または中高域成分)を強調するための高域画質改善部105Hと映像信号の低域成分を強調するための低域画質改善部105Lとをこの順で直列に設けたものである。高域画質改善部105Hは、ハイパスフィルタ9,リミッタ10,乗算器11,遅延器12,加算器13を備える。低域画質改善部105Lは画質改善装置102と同等の構成である。
図13は本発明の画質改善装置の第6実施形態を示すブロック図である。図13に示す第6実施形態の画質改善装置105において、図4に示す第2実施形態の画質改善装置102及び第5実施形態の画質改善装置105と実質的に同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明を適宜省略することとする。図13に示すように、第6実施形態の画質改善装置106は、映像信号の低域成分を強調するための低域画質改善部106Lと映像信号の高域成分(または中高域成分)を強調するための高域画質改善部106Hとをこの順で直列に設けたものである。
2 ガウシアンフィルタ
3 減算器
5 ローパスフィルタ
6,11 乗算器
7,13 加算器
8,10 リミッタ
9 ハイパスフィルタ
101~ 106 画質改善装置
104L,105L,106L 低域画質改善部
104H,105H,106H 高域画質改善部
Claims (20)
- 第1の遮断周波数を有し、入力された映像信号の低周波成分信号を抽出する第1のローパスフィルタと、
前記入力された映像信号より前記低周波成分信号を減算して、高周波成分信号を抽出する減算器と、
前記第1の遮断周波数よりも高い第2の遮断周波数を有し、前記高周波成分信号における低域側の信号である低域側高周波成分信号を抽出する第2のローパスフィルタと、
前記低域側高周波成分信号に所定のゲインを乗算して、補正成分信号を生成する乗算器と、
前記入力された映像信号に前記補正成分信号を加算する加算器と
を備えることを特徴とする画質改善装置。 - 前記第1のローパスフィルタはガウシアンフィルタであることを特徴とする請求項1記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記第2のローパスフィルタの後段に、前記低域側高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記乗算器に供給するリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記減算器の後段に、前記高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第2のローパスフィルタに供給するリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の画質改善装置。
- 第1の遮断周波数を有し、入力された映像信号の低周波成分信号を抽出する第1のローパスフィルタと、
前記入力された映像信号より前記低周波成分信号を減算して、第1の高周波成分信号を抽出する減算器と、
前記第1の遮断周波数よりも高い第2の遮断周波数を有し、前記第1の高周波成分信号における低域側の信号である低域側高周波成分信号を抽出する第2のローパスフィルタと、
前記低域側高周波成分信号に第1のゲインを乗算して、第1の補正成分信号を生成する第1の乗算器と、
前記入力された映像信号より第2の高周波成分信号を抽出するハイパスフィルタと、
前記第2の高周波成分信号に第2のゲインを乗算して、第2の補正成分信号を生成する第2の乗算器と、
前記入力された映像信号に前記第1及び第2の補正成分信号を加算する加算器と
を備えることを特徴とする画質改善装置。 - 入力された映像信号より第1の高周波成分信号を抽出するハイパスフィルタと、
前記第1の高周波成分信号に第1のゲインを乗算して、第1の補正成分信号を生成する第1の乗算器と、
前記入力された映像信号に前記第1の補正成分信号を加算する第1の加算器と、
第1の遮断周波数を有し、前記加算器より出力された映像信号の低周波成分信号を抽出する第1のローパスフィルタと、
前記加算器より出力された映像信号より前記低周波成分信号を減算して、第2の高周波成分信号を抽出する減算器と、
前記第1の遮断周波数よりも高い第2の遮断周波数を有し、前記第2の高周波成分信号における低域側の信号である低域側高周波成分信号を抽出する第2のローパスフィルタと、
前記低域側高周波成分信号に第2のゲインを乗算して、第2の補正成分信号を生成する第2の乗算器と、
前記加算器より出力された映像信号に前記第2の補正成分信号を加算する第2の加算器と
を備えることを特徴とする画質改善装置。 - 第1の遮断周波数を有し、入力された映像信号の低周波成分信号を抽出する第1のローパスフィルタと、
前記入力された映像信号より前記低周波成分信号を減算して、第1の高周波成分信号を抽出する減算器と、
前記第1の遮断周波数よりも高い第2の遮断周波数を有し、前記第1の高周波成分信号における低域側の信号である低域側高周波成分信号を抽出する第2のローパスフィルタと、
前記低域側高周波成分信号に第1のゲインを乗算して、第1の補正成分信号を生成する第1の乗算器と、
前記入力された映像信号に前記第1の補正成分信号を加算する第1の加算器と、
前記第1の加算器より出力された映像信号より第2の高周波成分信号を抽出するハイパスフィルタと、
前記第2の高周波成分信号に第2のゲインを乗算して、第2の補正成分信号を生成する第2の乗算器と、
前記第1の加算器より出力された映像信号に前記第2の補正成分信号を加算する第2の加算器と
を備えることを特徴とする画質改善装置。 - 前記第1のローパスフィルタはガウシアンフィルタであることを特徴とする請求項5ないし7のいずれか1項に記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記第2のローパスフィルタの後段に、前記低域側高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第1の乗算器に供給する第1のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項5または7に記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記第2のローパスフィルタの後段に、前記低域側高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第2の乗算器に供給する第1のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項6記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記減算器の後段に、前記第1の高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第2のローパスフィルタに供給する第1のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項5または7に記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記減算器の後段に、前記第2の高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第2のローパスフィルタに供給する第1のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項6記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記ハイパスフィルタの後段に、前記第2の高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第2の乗算器に供給する第2のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項5または7に記載の画質改善装置。
- 前記ハイパスフィルタの後段に、前記第1の高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限して前記第1の乗算器に供給する第2のリミッタを備えることを特徴とする請求項6記載の画質改善装置。
- 第1の遮断周波数を有する第1のローパスフィルタによって映像信号の低周波成分信号を抽出する第1のステップと、
前記映像信号より前記低周波成分信号を減算して、高周波成分信号を抽出する第2のステップと、
前記第1の遮断周波数よりも高い第2の遮断周波数を有する第2のローパスフィルタによって前記高周波成分信号における低域側の信号である低域側高周波成分信号を抽出する第3のステップと、
前記低域側高周波成分信号に第1のゲインを乗算して、第1の補正成分信号を生成する第4のステップと、
前記映像信号に前記第1の補正成分信号を加算して、前記映像信号の帯域における前記低域側高周波成分信号の帯域成分が強調された補正映像信号を出力する第5のステップと
を含むことを特徴とする画質改善方法。 - 前記第1のローパスフィルタはガウシアンフィルタであることを特徴とする請求項15記載の画質改善方法。
- 前記低域側高周波成分信号または前記高周波成分信号の値を所定の制限特性で制限する第6のステップを含むことを特徴とする請求項15または16に記載の画質改善方法。
- 前記映像信号の帯域における高域成分を強調するための第2の補正成分信号を生成する第7のステップを含み、
前記第5のステップは、前記映像信号に前記第1及び第2の補正成分信号の双方を加算して、前記低域側高周波成分信号の帯域成分及び前記高域成分が強調された補正映像信号を出力することを特徴とする請求項15ないし17のいずれか1項に記載の画質改善方法。 - 前記映像信号の帯域における高域成分を強調するための第2の補正成分信号を生成する第7のステップと、
前記映像信号に前記第2の補正成分信号を加算して、前記映像信号の帯域における前記高域成分が強調された補正映像信号を出力する第8のステップとを含み、
前記第1~第5のステップを、前記第7及び第8のステップの後段で行うことを特徴とする請求項15ないし17のいずれか1項に記載の画質改善方法。 - 前記映像信号の帯域における高域成分を強調するための第2の補正成分信号を生成する第7のステップと、
前記映像信号に前記第2の補正成分信号を加算して、前記映像信号の帯域における前記高域成分が強調された補正映像信号を出力する第8のステップとを含み、
前記第1~第5のステップを、前記第7及び第8のステップの前段で行うことを特徴とする請求項15ないし17のいずれか1項に記載の画質改善方法。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020117001587A KR101235605B1 (ko) | 2008-07-15 | 2009-07-15 | 화질 개선 장치 및 방법 |
| EP09797936.3A EP2320638B1 (en) | 2008-07-15 | 2009-07-15 | Device for improving image quality and method therefor |
| US13/054,012 US8363166B2 (en) | 2008-07-15 | 2009-07-15 | Image quality improving device and method |
| CN2009801275973A CN102100061B (zh) | 2008-07-15 | 2009-07-15 | 画质改善装置及方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008183520A JP4453777B2 (ja) | 2008-07-15 | 2008-07-15 | 画質改善装置及び方法 |
| JP2008-183520 | 2008-07-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010008011A1 true WO2010008011A1 (ja) | 2010-01-21 |
Family
ID=41550413
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/062787 WO2010008011A1 (ja) | 2008-07-15 | 2009-07-15 | 画質改善装置及び方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8363166B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2320638B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4453777B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101235605B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102100061B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010008011A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20140086632A (ko) | 2012-12-28 | 2014-07-08 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 영상 처리 장치 및 그것을 포함하는 표시 장치 |
| CN104809694B (zh) * | 2014-01-23 | 2020-04-03 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | 一种数字图像处理方法和装置 |
| US10057566B2 (en) * | 2014-04-04 | 2018-08-21 | Tektronix, Inc. | Depth of field indication using focus-peaking picture markers |
| JP6551048B2 (ja) | 2015-08-24 | 2019-07-31 | 株式会社Jvcケンウッド | 水中撮影装置、水中撮影装置の制御方法、水中撮影装置の制御プログラム |
| CN105447830B (zh) * | 2015-11-27 | 2018-05-25 | 合一网络技术(北京)有限公司 | 动态视频图像清晰度强化方法及装置 |
| JP7101539B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-22 | 2022-07-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、及びプログラム |
| CN110518455B (zh) * | 2019-08-06 | 2021-01-19 | 西安交通大学 | 一种消除外腔可调谐半导体激光器内腔非线性的硬件电路 |
| EP4274207A4 (en) * | 2021-04-13 | 2024-07-10 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND ITS CONTROL METHOD |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH024367U (ja) * | 1988-06-20 | 1990-01-11 | ||
| JPH04973A (ja) * | 1990-04-18 | 1992-01-06 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 映像信号処理装置 |
| JPH0422224A (ja) * | 1990-05-16 | 1992-01-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Yc分離回路 |
| JPH05167889A (ja) * | 1991-04-25 | 1993-07-02 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | 画像信号処理装置 |
| JPH05344385A (ja) | 1992-06-09 | 1993-12-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調回路 |
| JPH05344386A (ja) * | 1992-06-09 | 1993-12-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調器 |
| JPH07177386A (ja) * | 1993-12-21 | 1995-07-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調装置 |
| JPH08111792A (ja) * | 1994-10-13 | 1996-04-30 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調器 |
| JP2002190968A (ja) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-05 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 垂直輪郭補正装置 |
| JP2004120741A (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-04-15 | Eastman Kodak Co | デジタル画像鮮鋭化方法 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03285472A (ja) * | 1990-03-31 | 1991-12-16 | Toshiba Corp | 水平輪郭強調回路 |
| KR950012192B1 (ko) * | 1993-06-29 | 1995-10-14 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 콤브 필터와 회전제어장치 |
| KR100206319B1 (ko) * | 1995-12-13 | 1999-07-01 | 윤종용 | 비디오 신호의 로컬 콘트라스트 개선을 위한 방법및장치 |
| KR100343744B1 (ko) | 2000-09-30 | 2002-07-20 | 엘지전자주식회사 | 영상신호의 콘트라스트 향상 장치 |
| US7177481B2 (en) * | 2000-12-19 | 2007-02-13 | Konica Corporation | Multiresolution unsharp image processing apparatus |
| US7274828B2 (en) * | 2003-09-11 | 2007-09-25 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for detecting and processing noisy edges in image detail enhancement |
| KR20070029176A (ko) * | 2004-05-25 | 2007-03-13 | 코닌클리케 필립스 일렉트로닉스 엔.브이. | 비디오 신호의 선명도를 향상하는 방법 및 시스템 |
| KR20060091637A (ko) * | 2005-02-16 | 2006-08-21 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 고주파 성분을 조절하여 영상의 선명도를 조절할 수 있는영상 보정 회로 |
| JP4555207B2 (ja) * | 2005-10-18 | 2010-09-29 | Necディスプレイソリューションズ株式会社 | 画質改善装置および画質改善方法 |
| WO2009083926A2 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-09 | Nxp B.V. | Arrangement and approach for image data processing |
-
2008
- 2008-07-15 JP JP2008183520A patent/JP4453777B2/ja active Active
-
2009
- 2009-07-15 EP EP09797936.3A patent/EP2320638B1/en active Active
- 2009-07-15 KR KR1020117001587A patent/KR101235605B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2009-07-15 CN CN2009801275973A patent/CN102100061B/zh active Active
- 2009-07-15 WO PCT/JP2009/062787 patent/WO2010008011A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2009-07-15 US US13/054,012 patent/US8363166B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH024367U (ja) * | 1988-06-20 | 1990-01-11 | ||
| JPH04973A (ja) * | 1990-04-18 | 1992-01-06 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 映像信号処理装置 |
| JPH0422224A (ja) * | 1990-05-16 | 1992-01-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Yc分離回路 |
| JPH05167889A (ja) * | 1991-04-25 | 1993-07-02 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | 画像信号処理装置 |
| JPH05344385A (ja) | 1992-06-09 | 1993-12-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調回路 |
| JPH05344386A (ja) * | 1992-06-09 | 1993-12-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調器 |
| JPH07177386A (ja) * | 1993-12-21 | 1995-07-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調装置 |
| JPH08111792A (ja) * | 1994-10-13 | 1996-04-30 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 画像輪郭強調器 |
| JP2002190968A (ja) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-05 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 垂直輪郭補正装置 |
| JP2004120741A (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-04-15 | Eastman Kodak Co | デジタル画像鮮鋭化方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2320638A4 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20110022689A (ko) | 2011-03-07 |
| JP4453777B2 (ja) | 2010-04-21 |
| EP2320638A1 (en) | 2011-05-11 |
| EP2320638B1 (en) | 2015-03-04 |
| KR101235605B1 (ko) | 2013-02-21 |
| CN102100061A (zh) | 2011-06-15 |
| JP2010028178A (ja) | 2010-02-04 |
| CN102100061B (zh) | 2013-11-13 |
| EP2320638A4 (en) | 2011-08-03 |
| US8363166B2 (en) | 2013-01-29 |
| US20110267540A1 (en) | 2011-11-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2010008011A1 (ja) | 画質改善装置及び方法 | |
| KR100343744B1 (ko) | 영상신호의 콘트라스트 향상 장치 | |
| US9153015B2 (en) | Image processing device and method | |
| JP2007208399A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、画像処理方法のプログラム及び画像処理方法のプログラムを記録した記録媒体 | |
| JP4538358B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置 | |
| EP1883225A1 (en) | Dynamic gain adjustment method based on brightness and apparatus thereof | |
| KR20010069143A (ko) | 영상 신호 보정 장치 및 방법 | |
| US5491520A (en) | Contour correcting circuit for sharpening rising and falling edges of video signals | |
| EP1754369A1 (en) | Method and system for enhancing the sharpness of a video signal. | |
| JP3364342B2 (ja) | 雑音除去装置 | |
| US6990250B2 (en) | Image signal processing apparatus | |
| WO1999011055A1 (fr) | Appareil de correction de contours verticaux | |
| JP5349204B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置及び方法、並びに画像表示装置及び方法 | |
| WO2017082286A1 (ja) | 輪郭強調処理回路、輪郭強調処理方法、及びテレビジョンカメラ | |
| JP4454375B2 (ja) | 画像エッジ補正装置、映像表示装置、及び画像エッジ補正方法 | |
| JP5247627B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置及び方法、並びに画像表示装置 | |
| JPH11136541A (ja) | 垂直輪郭補正装置 | |
| JP3242934B2 (ja) | 輪郭補正装置 | |
| US8718395B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, display apparatus provided with same, and image processing method | |
| JP2001148474A (ja) | 固体撮像素子 | |
| US8184203B1 (en) | Video enhancement with separate and distinct methods of enhancement for single transitions and double transitions of opposite polarity | |
| JP3233331B2 (ja) | 輪郭補正回路 | |
| JP2755112B2 (ja) | 輪郭補正回路 | |
| JP2004343645A (ja) | 輪郭補正装置および輪郭補正方法 | |
| JP5225144B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置及び方法、並びに画像表示装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980127597.3 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09797936 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13054012 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117001587 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009797936 Country of ref document: EP |