JP6536522B2 - 信号出力回路 - Google Patents
信号出力回路 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6536522B2 JP6536522B2 JP2016186953A JP2016186953A JP6536522B2 JP 6536522 B2 JP6536522 B2 JP 6536522B2 JP 2016186953 A JP2016186953 A JP 2016186953A JP 2016186953 A JP2016186953 A JP 2016186953A JP 6536522 B2 JP6536522 B2 JP 6536522B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- drive
- output
- current
- circuit
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 71
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 21
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 20
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004043 responsiveness Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/16—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents
- H03K17/161—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents in field-effect transistor switches
- H03K17/162—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents in field-effect transistor switches without feedback from the output circuit to the control circuit
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/08—Circuits specially adapted for the generation of control voltages for semiconductor devices incorporated in static converters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/14—Arrangements for reducing ripples from dc input or output
- H02M1/15—Arrangements for reducing ripples from dc input or output using active elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/06—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using resistors or capacitors, e.g. potential divider
- H02M3/07—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using resistors or capacitors, e.g. potential divider using capacitors charged and discharged alternately by semiconductor devices with control electrode, e.g. charge pumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K4/00—Generating pulses having essentially a finite slope or stepped portions
- H03K4/94—Generating pulses having essentially a finite slope or stepped portions having trapezoidal shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/0003—Details of control, feedback or regulation circuits
- H02M1/0025—Arrangements for modifying reference values, feedback values or error values in the control loop of a converter
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/0003—Details of control, feedback or regulation circuits
- H02M1/0029—Circuits or arrangements for limiting the slope of switching signals, e.g. slew rate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M7/00—Conversion of ac power input into dc power output; Conversion of dc power input into ac power output
- H02M7/42—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal
- H02M7/44—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters
- H02M7/48—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M7/53—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M7/537—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters
- H02M7/5387—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters in a bridge configuration
- H02M7/53871—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters in a bridge configuration with automatic control of output voltage or current
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters
- H02P27/08—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters with pulse width modulation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Electronic Switches (AREA)
- Inverter Devices (AREA)
- Dc-Dc Converters (AREA)
- Power Conversion In General (AREA)
Description
(第1実施形態)
以下、本発明の第1実施形態について図1〜図9を参照して説明する。
IT11=VREFP/R1 …(1)
IH=N×IT11=N×(VREFP/R1) …(2)
IT13=(VB−VREFN)/R2 …(3)
IL=N×IT13=N×((VB−VREFN)/R2) …(4)
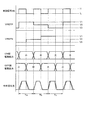
ここでは、駆動能力変更部5がトランジスタT1の駆動周期(PWM周期)の1周期毎に駆動部4の駆動能力を変更する場合における各部の動作状態について、図7を参照して説明する。また、この場合、オン側駆動部6およびオフ側駆動部7の駆動能力をそれぞれ「小」、「中」および「大」の3種類(3段階)に変更することとする。また、変更の順番は、「…小→中→大→小→中→大…」といった具合とする。
本実施形態では、駆動部4の駆動能力が周期的に変更されることにより、台形波出力のスルーレートが周期的に変化する。その結果、台形波出力の立ち上がりおよび立ち下がりに含まれる高調波成分が分散され、ノイズのピーク値が低く抑えられる。この場合、駆動能力、ひいてはスルーレートの変更パターンを増やすほど、ノイズ低減効果が高まる。図8に示すように、スルーレートの種類が2種類である場合に比べ、3種類である場合のほうがノイズ低減の効果が高いことが分かる。
以下、第2実施形態について図10および図11を参照して説明する。
第1実施形態では、電圧生成部14、16により生成される基準電圧VREFP、VREFNの電圧値を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさ、ひいては駆動部4の駆動能力を変更するようになっていた。しかし、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさは、前述した(2)式および(4)式からも明らかなように、基準電圧VREFP、VREFNだけでなく、抵抗R1、R2の抵抗値にも依存する。そこで、本実施形態では、抵抗R1、R2の抵抗値を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさを変更する構成について説明する。
この場合、駆動能力の変更間隔や種類などについては、第1実施形態と同様となっている。そして、この場合、ON側駆動能力は、抵抗R1の抵抗値が低いほど大きくなるため、抵抗R1の抵抗値が「大」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「小」のときに「大」になる。また、OFF側駆動能力は、抵抗R2の抵抗値が低いほど大きくなるため、抵抗R2の抵抗値が「大」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「小」のときに「大」になる。
以下、第3実施形態について図12および図13を参照して説明する。
第1実施形態では、電圧生成部14、16により生成される基準電圧VREFP、VREFNの電圧値を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさ、ひいては駆動部4の駆動能力を変更するようになっていた。しかし、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさは、前述した(2)式および(4)式からも明らかなように、基準電圧VREFP、VREFNだけでなく、カレントミラー回路11、12のミラー比(=N)にも依存する。そこで、本実施形態では、カレントミラー回路11、12のミラー比を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさを変更する構成について説明する。
この場合、駆動能力の変更間隔や種類などについては、第1実施形態と同様となっている。そして、この場合、ON側駆動能力は、ON側カレントミラー比が大きいほど大きくなるため、ON側カレントミラー比が「小」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「大」のときに「大」になる。また、OFF側駆動能力は、OFF側カレントミラー比が大きいほど大きくなるため、OFF側カレントミラー比が「小」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「大」のときに「大」になる。
以下、第4実施形態について図14および図15を参照して説明する。
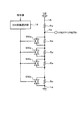
図2に示した第1実施形態の駆動回路3の具体的な構成では、オン側駆動部6の出力段にカレントミラー回路11を設けるとともに、オフ側駆動部7の出力段にカレントミラー回路12を設けた構成となっていたが、オン側駆動部6およびオフ側駆動部7の出力段に単一のトランジスタを設けた構成に変更することもできる。
IH=(VB−VREFP)/R51 …(5)
IL=VREFN/R52 …(6)
この場合、駆動能力の変更間隔や種類などについては、第1実施形態と同様となっている。そして、この場合、ON側駆動能力は、基準電圧VREFPの電圧値が低いほど大きくなるため、基準電圧VREFPの電圧値がV1のときに「小」になり、V2のときに「中」になり、V3のときに「大」になる。また、OFF側駆動能力は、基準電圧VREFNの電圧値が高いほど大きくなるため、基準電圧VREFNの電圧値がV1のときに「大」になり、V2のときに「中」になり、V3のときに「小」になる。
以下、第5実施形態について図16を参照して説明する。
第4実施形態では、電圧生成部14、16により生成される基準電圧VREFP、VREFNの電圧値を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさ、ひいては駆動部4の駆動能力を変更するようになっていた。しかし、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさは、前述した(5)式および(6)式からも明らかなように、基準電圧VREFP、VREFNだけでなく、抵抗R51、R52の抵抗値にも依存する。そこで、本実施形態では、抵抗R51、R52の抵抗値を切り替えることで、駆動電流IH、ILの大きさを変更する構成について説明する。
この場合、駆動能力の変更間隔や種類などについては、第1実施形態と同様となっている。そして、この場合、ON側駆動能力は、抵抗R51の抵抗値が低いほど大きくなるため、抵抗R51の抵抗値が「大」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「小」のときに「大」になる。また、OFF側駆動能力は、抵抗R52の抵抗値が低いほど大きくなるため、抵抗R52の抵抗値が「大」のときに「小」になり、「中」のときに「中」になり、「小」のときに「大」になる。
以下、第6実施形態について図17〜図19を参照して説明する。
図17に示すように、第1実施形態などで説明したスイッチングレギュレータ1において、トランジスタT1がオンオフされる際、回路上の寄生インダクタンス成分などの影響により台形波出力にサージ電圧が発生する。そして、駆動部4の駆動能力が大きくなるほど、上記サージ電圧も大きくなる。
この場合、周期的な駆動能力の変更間隔や種類などについては、第1実施形態と同様となっている。したがって、本実施形態によっても、第1実施形態と同様の効果が得られる。ただし、この場合、図19に示すように、駆動能力の周期的な変更に伴い、ON側駆動能力およびOFF側駆動能力が「大」となる期間Tcの動作が異なっている。
以下、第7実施形態について図20および図21を参照して説明する。
上記各実施形態では、本発明の信号出力回路をスイッチングレギュレータ1に適用した例を説明したが、本発明の信号出力回路は、出力トランジスタの駆動を制御することにより、その出力トランジスタの主端子から台形波の出力信号を出力する構成全般に適用することができる。例えば、本発明の信号出力回路は、図20に示すチャージポンプ回路71、図21に示すモータドライブシステム81などに適用することができる。
なお、本発明は上記し且つ図面に記載した各実施形態に限定されるものではなく、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲で任意に変形、組み合わせ、あるいは拡張することができる。
上記各実施形態では、PWM周期の1周期におけるON側駆動能力とOFF側駆動能力とが同一となるように駆動能力の変更を行っていたが、1周期におけるON側駆動能力とOFF側駆動能力とが異なるように駆動能力の変更を行ってもよい。
駆動能力の変更パターンは、3種類に限らずともよく、2種類でもよいし、4種類以上でもよい。
Claims (9)
- 出力トランジスタ(T1、T71、T72、T81〜T86)の駆動を制御することにより、前記出力トランジスタの主端子から台形波の出力信号を出力する信号出力回路(3、51、62、74、82)であって、
前記出力トランジスタを定電流駆動する駆動部(4、75、76、83〜88)と、
前記駆動部の駆動能力を周期的に変更する駆動能力変更部(5、64、77、89)と、
を備え、
前記駆動能力変更部は、前記駆動能力の変更前における前記出力信号のスルーレートと、前記駆動能力の変更後における前記出力信号のスルーレートとの差が、所定の閾値より小さくなるように前記駆動能力を変更し、
前記閾値は、前記駆動能力の変更前における前記出力信号のスルーレートで決定される周波数と、前記駆動能力の変更後における前記出力信号のスルーレートで決定される周波数と、の最小公倍数が所定の周波数以上になるように設定される信号出力回路。 - 出力トランジスタ(T1、T71、T72、T81〜T86)の駆動を制御することにより、前記出力トランジスタの主端子から台形波の出力信号を出力する信号出力回路(3、51、62、74、82)であって、
前記出力トランジスタを定電流駆動する駆動部(4、75、76、83〜88)と、
前記駆動部の駆動能力を周期的に変更する駆動能力変更部(5、64、77、89)と、
を備え、
前記駆動部は、
前記出力トランジスタをオン駆動するオン側駆動部(6)および前記出力トランジスタをオフ駆動するオフ側駆動部(7)を備え、
前記駆動能力変更部は、
前記オン側駆動部によるオン駆動の開始をトリガとして前記オフ側駆動部の駆動能力を変更し、
前記オフ側駆動部によるオフ駆動の開始をトリガとして前記オン側駆動部の駆動能力を変更する信号出力回路。 - 前記駆動部の駆動能力を変更する切替タイミングは、前記出力信号が変化しない期間に設定されている請求項1または2に記載の信号出力回路。
- 前記駆動能力変更部は、
前記出力信号の立ち上がり期間または立ち下がり期間の所定の途中切替タイミングで、前記駆動部の駆動能力を、その時点における駆動能力よりも小さく変更する請求項1に記載の信号出力回路。 - 前記駆動部は、前記出力トランジスタを駆動するための駆動電流を生成する電流生成回路(8、9)を備え、
前記駆動能力変更部は、前記電流生成回路により生成される駆動電流の大きさを変更することにより前記駆動能力を変更する請求項1から4のいずれか一項に記載の信号出力回路。 - 前記電流生成回路は、出力段にカレントミラー回路(11、12)を備えた構成であり、
前記駆動能力変更部は、前記カレントミラー回路の入力側の電流を変更することにより前記駆動電流の大きさを変更する請求項5に記載の信号出力回路。 - 前記電流生成回路は、出力段にカレントミラー回路(41)を備えた構成であり、
前記駆動能力変更部は、前記カレントミラー回路のミラー比を変更することにより前記駆動電流の大きさを変更する請求項5に記載の信号出力回路。 - 前記駆動能力変更部は、前記出力信号の1周期毎に前記駆動能力を変更する請求項1から7のいずれか一項に記載の信号出力回路。
- 前記駆動能力変更部は、前記駆動能力を3種類以上に変更する請求項1から8のいずれか一項に記載の信号出力回路。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016186953A JP6536522B2 (ja) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | 信号出力回路 |
| CN201780058231.XA CN109792201A (zh) | 2016-09-26 | 2017-06-29 | 信号输出电路 |
| PCT/JP2017/023966 WO2018055864A1 (ja) | 2016-09-26 | 2017-06-29 | 信号出力回路 |
| US16/278,278 US20190181853A1 (en) | 2016-09-26 | 2019-02-18 | Signal output circuit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016186953A JP6536522B2 (ja) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | 信号出力回路 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018057072A JP2018057072A (ja) | 2018-04-05 |
| JP2018057072A5 JP2018057072A5 (ja) | 2018-10-25 |
| JP6536522B2 true JP6536522B2 (ja) | 2019-07-03 |
Family
ID=61689554
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016186953A Active JP6536522B2 (ja) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | 信号出力回路 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20190181853A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6536522B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN109792201A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2018055864A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7026531B2 (ja) * | 2018-02-23 | 2022-02-28 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置、半導体システム、及び、制御システム |
| TWI671988B (zh) | 2018-07-10 | 2019-09-11 | 群光電能科技股份有限公司 | 電源轉換裝置及其控制方法 |
| US10848144B2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-11-24 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Switching control circuit |
| CN112585864B (zh) * | 2019-03-14 | 2024-06-14 | 富士电机株式会社 | 功率模块及其电平转换电路 |
| US10771281B1 (en) * | 2019-11-04 | 2020-09-08 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Semi-differential signaling for DSI3 bus enhancement |
| JP7567651B2 (ja) | 2021-05-18 | 2024-10-16 | 株式会社デンソー | スイッチング素子駆動回路 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08340245A (ja) * | 1995-06-13 | 1996-12-24 | Hitachi Ltd | 信号出力回路、及び半導体集積回路 |
| JP3152204B2 (ja) * | 1998-06-02 | 2001-04-03 | 日本電気株式会社 | スルーレート出力回路 |
| US7936189B2 (en) * | 2008-12-04 | 2011-05-03 | Stmicroelectronics S.R.L. | Driver circuit and method for reducing electromagnetic interference |
| JP2012147619A (ja) * | 2011-01-14 | 2012-08-02 | Denso Corp | 電子装置 |
| JP6042091B2 (ja) * | 2011-05-13 | 2016-12-14 | ローム株式会社 | スイッチングレギュレータの制御回路、スイッチングレギュレータおよび電子機器、スイッチング電源装置、テレビ |
| JP5385341B2 (ja) * | 2011-07-05 | 2014-01-08 | 株式会社日本自動車部品総合研究所 | スイッチング素子の駆動装置及びスイッチング素子の駆動方法 |
| US9461640B2 (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2016-10-04 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Switching element drive circuit, power module, and automobile |
| JP6496471B2 (ja) * | 2013-02-28 | 2019-04-03 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | 負荷駆動制御装置 |
| JP6219600B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-30 | 2017-10-25 | ローム株式会社 | スイッチ制御回路、スイッチング電源装置、電子機器 |
-
2016
- 2016-09-26 JP JP2016186953A patent/JP6536522B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-06-29 CN CN201780058231.XA patent/CN109792201A/zh active Pending
- 2017-06-29 WO PCT/JP2017/023966 patent/WO2018055864A1/ja active Application Filing
-
2019
- 2019-02-18 US US16/278,278 patent/US20190181853A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2018055864A1 (ja) | 2018-03-29 |
| JP2018057072A (ja) | 2018-04-05 |
| US20190181853A1 (en) | 2019-06-13 |
| CN109792201A (zh) | 2019-05-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6536522B2 (ja) | 信号出力回路 | |
| US6188590B1 (en) | Regulator system for charge pump circuits | |
| JP4728777B2 (ja) | 電源回路 | |
| JP5456495B2 (ja) | 昇降圧型のスイッチング電源の制御回路、昇降圧型のスイッチング電源、及び昇降圧型のスイッチング電源の制御方法 | |
| US20090015318A1 (en) | Charge pump drive circuit | |
| CN107342685B (zh) | Dcdc转换器 | |
| JP2006136134A (ja) | チャージポンプ回路 | |
| JP2009183111A (ja) | チャージポンプ回路およびそれを備える電子機器 | |
| KR20150024611A (ko) | 전하 펌프 회로 | |
| JP6719242B2 (ja) | レベルシフト回路 | |
| JP5414904B2 (ja) | 制御信号生成回路、チャージポンプ駆動回路、クロックドライバ、チャージポンプの駆動方法 | |
| WO2020250655A1 (ja) | 電源駆動回路 | |
| JP6419024B2 (ja) | 電源回路及び車載用電源システム | |
| JP6794240B2 (ja) | 昇降圧dc/dcコンバータ | |
| CN110277899B (zh) | 脉宽调变控制器及第三态电压产生方法 | |
| JP2010104140A (ja) | 電源回路 | |
| JP4616362B2 (ja) | D/a変換回路 | |
| JP7216539B2 (ja) | スイッチング制御回路 | |
| JP2018182819A (ja) | チャージポンプ回路 | |
| US10491110B2 (en) | Switching control circuit | |
| JP4400145B2 (ja) | 電源装置 | |
| JP6956052B2 (ja) | ゲート制御回路、電源回路及びインバータ回路 | |
| JP4692134B2 (ja) | 出力バッファ回路 | |
| JP5383106B2 (ja) | 電源回路 | |
| JP2007236079A (ja) | チャージポンプ回路、移動通信端末、通信装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180911 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180911 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190507 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20190520 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6536522 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |