JP4728323B2 - 調整可能なゲート電極の仕事関数を備えたデュアルメタルのcmosトランジスタおよびその製造方法 - Google Patents
調整可能なゲート電極の仕事関数を備えたデュアルメタルのcmosトランジスタおよびその製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4728323B2 JP4728323B2 JP2007510795A JP2007510795A JP4728323B2 JP 4728323 B2 JP4728323 B2 JP 4728323B2 JP 2007510795 A JP2007510795 A JP 2007510795A JP 2007510795 A JP2007510795 A JP 2007510795A JP 4728323 B2 JP4728323 B2 JP 4728323B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- silicon
- metal
- region
- silicide
- work function
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 64
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 title claims description 64
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 36
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title description 6
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical group [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 76
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 76
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 76
- 229910021332 silicide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 67
- FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicide(4-) Chemical group [Si-4] FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 66
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910001092 metal group alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical group [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ruthenium Chemical compound [Ru] KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052702 rhenium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhenium atom Chemical compound [Re] WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910019001 CoSi Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 CoSi Chemical compound 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001010 compromised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- CUILPNURFADTPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N hypobromous acid Chemical compound BrO CUILPNURFADTPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004151 rapid thermal annealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/8238—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/8238—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS
- H01L21/823828—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes
- H01L21/823835—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes silicided or salicided gate conductors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/8238—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS
- H01L21/823828—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes
- H01L21/823842—Complementary field-effect transistors, e.g. CMOS with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes gate conductors with different gate conductor materials or different gate conductor implants, e.g. dual gate structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/28—Manufacture of electrodes on semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/268
- H01L21/28008—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes
- H01L21/28017—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes the insulator being formed after the semiconductor body, the semiconductor being silicon
- H01L21/28026—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes the insulator being formed after the semiconductor body, the semiconductor being silicon characterised by the conductor
- H01L21/28097—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes the insulator being formed after the semiconductor body, the semiconductor being silicon characterised by the conductor the final conductor layer next to the insulator being a metallic silicide
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
Description
Claims (10)
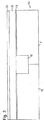
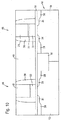
- NMOSデバイス領域とPMOSデバイス領域とにゲート電極を形成するために、ゲート誘電体層上にシリコン領域を形成するステップ、
第1金属あるいは金属合金を前記NMOSデバイス領域の前記シリコン領域に堆積し、第2金属あるいは金属合金を前記PMOSデバイス領域の前記シリコン領域に堆積するステップ、
前記第1金属あるいは金属合金を前記NMOSデバイス領域の前記シリコン領域と反応させ、第1シリサイド領域上に第1金属あるいは金属合金領域が積層された第1ゲート電極構造を形成し、前記第2金属あるいは金属合金を前記PMOSデバイス領域の前記シリコン領域と反応させ、第2シリサイド領域上に第2金属あるいは金属合金領域が積層された第2ゲート電極構造を形成するようにアニールするステップ、を含み、
前記第1シリサイド領域の仕事関数は、シリコンの伝導帯の+/−0.2V内であり、前記第2シリコン領域の仕事関数は、シリコンの価電子帯の+/−0.2V内である、デュアルメタルCMOS配列を形成する方法。 - 前記シリコン領域を形成する前記ステップは、
ゲート誘電体層上にシリコンを堆積するステップ、
シリコンスタックを形成するために前記シリコンをエッチングするステップ、および、
前記シリコンスタックの上部だけを除去し、それにより前記シリコン領域を形成するために前記シリコンスタックを部分的にエッチングするステップを含む、請求項1に記載の方法。 - 前記部分的にエッチングするステップは、エッチングステップ内のシリコンスタックの時間制御されたエッチングである、請求項2に記載の方法。
- 前記シリコンを堆積するステップは、前記ゲート誘電体層上に第1シリコン層を堆積するステップ、前記第1シリコン層上にエッチストップ層を形成するステップ、および、前記エッチストップ層上に第2シリコン層を形成するステップを含む、請求項2に記載の方法。
- 前記部分的にエッチングするステップは、前記第2シリコン層をエッチングし、前記エッチストップ層上でエッチングを停止させるステップ、および、前記エッチストップ層を除去するステップを含む、請求項4に記載の方法。
- 前記第1および第2シリサイド領域の相を制御することによって、前記第1および第2シリサイド領域の仕事関数を制御するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記第1および第2シリサイド領域の相を制御するステップは、前記シリコン領域の厚みを制御するステップを含む、請求項6に記載の方法。
- 前記第1金属あるいは金属合金はタンタルである、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記第2金属あるいは金属合金は、ルテニウム、レニウム、あるいはコバルトのうちのいずれかである請求項1記載の方法。
- 前記第1金属あるいは金属合金はタンタルであり、前記第2金属あるいは金属合金は、ルテニウム、レニウム、あるいはコバルトのうちの1つである、請求項1に記載の方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/833,073 | 2004-04-28 | ||
| US10/833,073 US7078278B2 (en) | 2004-04-28 | 2004-04-28 | Dual-metal CMOS transistors with tunable gate electrode work function and method of making the same |
| PCT/US2005/013240 WO2005109493A1 (en) | 2004-04-28 | 2005-04-19 | Dual-metal cmos transistors with tunable gate electrode work function and method of making the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007535171A JP2007535171A (ja) | 2007-11-29 |
| JP2007535171A5 JP2007535171A5 (ja) | 2008-06-19 |
| JP4728323B2 true JP4728323B2 (ja) | 2011-07-20 |
Family
ID=34966174
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007510795A Active JP4728323B2 (ja) | 2004-04-28 | 2005-04-19 | 調整可能なゲート電極の仕事関数を備えたデュアルメタルのcmosトランジスタおよびその製造方法 |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7078278B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP1741132B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4728323B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101125269B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN100472756C (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE602005016790D1 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI378492B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2005109493A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7645687B2 (en) * | 2005-01-20 | 2010-01-12 | Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing, Ltd. | Method to fabricate variable work function gates for FUSI devices |
| JP2006253316A (ja) * | 2005-03-09 | 2006-09-21 | Sony Corp | 固体撮像装置 |
| JP5015446B2 (ja) * | 2005-05-16 | 2012-08-29 | アイメック | 二重の完全ケイ化ゲートを形成する方法と前記方法によって得られたデバイス |
| JP2007142127A (ja) * | 2005-11-18 | 2007-06-07 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2007157744A (ja) * | 2005-11-30 | 2007-06-21 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US7768072B2 (en) * | 2007-03-27 | 2010-08-03 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Silicided metal gate for multi-threshold voltage configuration |
| US7678694B2 (en) * | 2007-04-18 | 2010-03-16 | Taiwan Semicondutor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method for fabricating semiconductor device with silicided gate |
| US8183137B2 (en) * | 2007-05-23 | 2012-05-22 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Use of dopants to provide low defect gate full silicidation |
| US7642153B2 (en) * | 2007-10-23 | 2010-01-05 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Methods for forming gate electrodes for integrated circuits |
| US8124515B2 (en) * | 2009-05-20 | 2012-02-28 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Gate etch optimization through silicon dopant profile change |
| US8895426B2 (en) * | 2009-06-12 | 2014-11-25 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Metal gate transistor, integrated circuits, systems, and fabrication methods thereof |
| WO2012086102A1 (ja) * | 2010-12-24 | 2012-06-28 | パナソニック株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US8440520B2 (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2013-05-14 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Diffused cap layers for modifying high-k gate dielectrics and interface layers |
| US8722472B2 (en) * | 2011-12-16 | 2014-05-13 | International Business Machines Corporation | Hybrid CMOS nanowire mesh device and FINFET device |
| US8633118B2 (en) | 2012-02-01 | 2014-01-21 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Method of forming thin metal and semi-metal layers by thermal remote oxygen scavenging |
| US8865538B2 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2014-10-21 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Method of integrating buried threshold voltage adjustment layers for CMOS processing |
| CN103515319B (zh) * | 2012-06-20 | 2015-08-19 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | 形成cmos全硅化物金属栅的方法 |
| US8865581B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2014-10-21 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Hybrid gate last integration scheme for multi-layer high-k gate stacks |
| KR102311552B1 (ko) | 2014-12-04 | 2021-10-12 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| KR102214096B1 (ko) | 2015-08-06 | 2021-02-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 장치 제조 방법 |
| CN105097473A (zh) * | 2015-09-28 | 2015-11-25 | 上海集成电路研发中心有限公司 | 一种双金属栅极的形成方法 |
| US10103065B1 (en) | 2017-04-25 | 2018-10-16 | International Business Machines Corporation | Gate metal patterning for tight pitch applications |
| CN110391233B (zh) * | 2018-04-17 | 2022-10-14 | 联华电子股份有限公司 | 半导体元件及其制作方法 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11284179A (ja) * | 1998-03-30 | 1999-10-15 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2001284466A (ja) * | 2000-03-29 | 2001-10-12 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2005019885A (ja) * | 2003-06-27 | 2005-01-20 | Semiconductor Leading Edge Technologies Inc | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2005085949A (ja) * | 2003-09-08 | 2005-03-31 | Semiconductor Leading Edge Technologies Inc | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2005228868A (ja) * | 2004-02-12 | 2005-08-25 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0504390B1 (en) | 1990-10-05 | 1996-01-10 | General Electric Company | Thin film transistor stucture with improved source/drain contacts |
| JPH1117181A (ja) * | 1997-06-26 | 1999-01-22 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US6392302B1 (en) * | 1998-11-20 | 2002-05-21 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Polycide structure and method for forming polycide structure |
| JP4237332B2 (ja) * | 1999-04-30 | 2009-03-11 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP4811895B2 (ja) * | 2001-05-02 | 2011-11-09 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US6475908B1 (en) * | 2001-10-18 | 2002-11-05 | Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing Ltd. | Dual metal gate process: metals and their silicides |
| US6703271B2 (en) * | 2001-11-30 | 2004-03-09 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company | Complementary metal oxide semiconductor transistor technology using selective epitaxy of a strained silicon germanium layer |
| US6770521B2 (en) * | 2001-11-30 | 2004-08-03 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Method of making multiple work function gates by implanting metals with metallic alloying additives |
| US6689676B1 (en) * | 2002-07-26 | 2004-02-10 | Motorola, Inc. | Method for forming a semiconductor device structure in a semiconductor layer |
-
2004
- 2004-04-28 US US10/833,073 patent/US7078278B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2005
- 2005-04-19 CN CNB2005800131825A patent/CN100472756C/zh active Active
- 2005-04-19 JP JP2007510795A patent/JP4728323B2/ja active Active
- 2005-04-19 DE DE602005016790T patent/DE602005016790D1/de active Active
- 2005-04-19 WO PCT/US2005/013240 patent/WO2005109493A1/en active Application Filing
- 2005-04-19 EP EP05736767A patent/EP1741132B1/en active Active
- 2005-04-19 KR KR1020067023670A patent/KR101125269B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2005-04-26 TW TW094113211A patent/TWI378492B/zh active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11284179A (ja) * | 1998-03-30 | 1999-10-15 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2001284466A (ja) * | 2000-03-29 | 2001-10-12 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2005019885A (ja) * | 2003-06-27 | 2005-01-20 | Semiconductor Leading Edge Technologies Inc | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2005085949A (ja) * | 2003-09-08 | 2005-03-31 | Semiconductor Leading Edge Technologies Inc | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2005228868A (ja) * | 2004-02-12 | 2005-08-25 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE602005016790D1 (de) | 2009-11-05 |
| EP1741132B1 (en) | 2009-09-23 |
| EP1741132A1 (en) | 2007-01-10 |
| TW200540961A (en) | 2005-12-16 |
| CN100472756C (zh) | 2009-03-25 |
| KR20070004095A (ko) | 2007-01-05 |
| CN1947243A (zh) | 2007-04-11 |
| KR101125269B1 (ko) | 2012-03-22 |
| WO2005109493A1 (en) | 2005-11-17 |
| US20050245016A1 (en) | 2005-11-03 |
| JP2007535171A (ja) | 2007-11-29 |
| TWI378492B (en) | 2012-12-01 |
| US7078278B2 (en) | 2006-07-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4728323B2 (ja) | 調整可能なゲート電極の仕事関数を備えたデュアルメタルのcmosトランジスタおよびその製造方法 | |
| US7410854B2 (en) | Method of making FUSI gate and resulting structure | |
| US7737009B2 (en) | Method of implanting a non-dopant atom into a semiconductor device | |
| US7229873B2 (en) | Process for manufacturing dual work function metal gates in a microelectronics device | |
| US7879666B2 (en) | Semiconductor resistor formed in metal gate stack | |
| US8198151B2 (en) | Method for fabricating a metal gate structure | |
| US8765586B2 (en) | Methods of forming metal silicide regions on semiconductor devices | |
| JP2009033032A (ja) | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2009181978A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| US7635648B2 (en) | Methods for fabricating dual material gate in a semiconductor device | |
| JP2006156807A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| US20080206973A1 (en) | Process method to optimize fully silicided gate (FUSI) thru PAI implant | |
| US20140051240A1 (en) | Methods of forming a replacement gate structure having a gate electrode comprised of a deposited intermetallic compound material | |
| KR100549006B1 (ko) | 완전한 실리사이드 게이트를 갖는 모스 트랜지스터 제조방법 | |
| US7018887B1 (en) | Dual metal CMOS transistors with silicon-metal-silicon stacked gate electrode | |
| JP2009277961A (ja) | Cmisトランジスタの製造方法 | |
| JP2005294799A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP5194732B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法および半導体装置 | |
| JP2009038350A (ja) | デュアル仕事関数半導体デバイス | |
| US7960280B2 (en) | Process method to fully salicide (FUSI) both N-poly and P-poly on a CMOS flow | |
| JP2003188386A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| TWI390640B (zh) | 半導體製造方法 | |
| JP2006024587A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2010056239A (ja) | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2007214503A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080421 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080421 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20100421 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20100902 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100930 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20101006 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20110106 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20110114 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110207 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110316 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110414 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4728323 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140422 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |