EP2620736B1 - Wärmetauscher und Klimaanlagenvorrichtung damit - Google Patents
Wärmetauscher und Klimaanlagenvorrichtung damit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2620736B1 EP2620736B1 EP12182717.4A EP12182717A EP2620736B1 EP 2620736 B1 EP2620736 B1 EP 2620736B1 EP 12182717 A EP12182717 A EP 12182717A EP 2620736 B1 EP2620736 B1 EP 2620736B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- pipe
- aluminum
- heat exchanger
- unit
- refrigerant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004378 air conditioning Methods 0.000 title claims description 18
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 116
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 113
- 239000003507 refrigerant Substances 0.000 claims description 61
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 claims description 52
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 47
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 47
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 47
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 45
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 45
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- 229910000881 Cu alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011241 protective layer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000007743 anodising Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 44
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- JPVYNHNXODAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cu2+ Chemical compound [Cu+2] JPVYNHNXODAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 230000001143 conditioned effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000005057 refrigeration Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910001431 copper ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- -1 aluminum ions Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007791 dehumidification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000006023 eutectic alloy Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000005496 eutectics Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011162 core material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 2
- PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Manganese Chemical compound [Mn] PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010001267 Protein Subunits Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011572 manganese Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F1/00—Room units for air-conditioning, e.g. separate or self-contained units or units receiving primary air from a central station
- F24F1/0007—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units
- F24F1/0071—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units with means for purifying supplied air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F21/00—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials
- F28F21/08—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials of metal
- F28F21/081—Heat exchange elements made from metals or metal alloys
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F1/00—Room units for air-conditioning, e.g. separate or self-contained units or units receiving primary air from a central station
- F24F1/0007—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units
- F24F1/0068—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by the arrangement of refrigerant piping outside the heat exchanger within the unit casing
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F19/00—Preventing the formation of deposits or corrosion, e.g. by using filters or scrapers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F19/00—Preventing the formation of deposits or corrosion, e.g. by using filters or scrapers
- F28F19/02—Preventing the formation of deposits or corrosion, e.g. by using filters or scrapers by using coatings, e.g. vitreous or enamel coatings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/02—Header boxes; End plates
- F28F9/0246—Arrangements for connecting header boxes with flow lines
- F28F9/0256—Arrangements for coupling connectors with flow lines
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F1/00—Room units for air-conditioning, e.g. separate or self-contained units or units receiving primary air from a central station
- F24F1/0007—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units
- F24F1/0043—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by mounting arrangements
- F24F1/0057—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by mounting arrangements mounted in or on a wall
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F13/00—Details common to, or for air-conditioning, air-humidification, ventilation or use of air currents for screening
- F24F13/30—Arrangement or mounting of heat-exchangers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D21/00—Heat-exchange apparatus not covered by any of the groups F28D1/00 - F28D20/00
- F28D2021/0019—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for
- F28D2021/0068—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for for refrigerant cycles
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F21/00—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials
- F28F21/08—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials of metal
- F28F21/081—Heat exchange elements made from metals or metal alloys
- F28F21/084—Heat exchange elements made from metals or metal alloys from aluminium or aluminium alloys
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F21/00—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials
- F28F21/08—Constructions of heat-exchange apparatus characterised by the selection of particular materials of metal
- F28F21/081—Heat exchange elements made from metals or metal alloys
- F28F21/085—Heat exchange elements made from metals or metal alloys from copper or copper alloys
Definitions
- Patent literature 2 discloses for example a heat exchanger having the features in the preamble of claim 1.
- Heat exchangers equipped with heat exchangers having heat transfer pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy are known.
- the heat transfer pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy or refrigerant pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy and connected to the heat transfer pipes.
- These pipes are referred to as “aluminum pipes” hereafter) of such a heat exchanger are connected to refrigerant pipes formed of copper or a copper alloy (hereafter, referred to as “copper pipes”), thereby incorporating the heat exchanger in a refrigeration cycle.
- An air-conditioning apparatus includes a main body of the air-conditioning apparatus, a compressor, and a securing member that secures a refrigeration cycle unit to the main body of the air-conditioning apparatus.
- the refrigeration cycle unit includes a heat exchanger formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy and a refrigerant pipe, which is formed of copper or a copper alloy and connected to the heat exchanger.
- Patent Literature 1 An entire portion of the refrigerant pipe above the heat exchanger serves as a water droplet prevention pipe portion, which is inclined downward from the heat exchanger toward the refrigerant pipe, so that water droplets flow downward along the refrigerant pipe, thereby preventing electrolytic corrosion of the heat exchanger due to copper ions from occurring" (see, for example, Patent Literature 1).
- Patent Literature 2 Another technology has been proposed according the first part of claim 1 (see Patent Literature 2).
- connection pipes including connection unit in which the aluminum side and the copper side are connected to each other
- connection pipes need to be covered with a thermally insulating material so as to suppress condensation.
- condensation cannot be completely prevented even by covering the connection pipes with the thermally insulating material, and accordingly, a small amount of water having condensed on the connection pipes stays in a small gap between the thermally insulating material and the connection pipes.
- connection pipes being formed of copper or a copper alloy diffuse toward the side of the connection pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy through water, which has condensed and stays.
- electrolytic corrosion galvanic corrosion
- An object of the present invention is to provide a heat exchanger and an air-conditioning apparatus including the heat exchanger, in which progress of electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) of aluminum or an aluminum alloy can be suppressed.
- Electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) of aluminum or an aluminum alloy is caused by diffusion of copper ions to connection pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy through water having condensed and staying in a small gap between the thermally insulating material and the connection pipe unit.
- a heat exchanger includes a heat transfer pipe formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy; and a connection pipe unit through which a refrigerant flowing out of the heat transfer pipe and a refrigerant flowing into the heat transfer pipe pass, the connection pipe unit including a gas pipe through which the refrigerant in a gaseous state flows, and a liquid pipe through which the refrigerant in a liquid state or in a two-phase gas-liquid state flows, the gas pipe and the liquid pipe each having a first refrigerant pipe formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy, and a second refrigerant pipe formed of copper or a copper alloy, the first refrigerant pipe and the second refrigerant pipe being connected to each other, the first refrigerant pipe having a fall portion connected to the heat transfer pipe, the fall portion extending downward relative to the heat transfer pipe.
- each connection portion between the first refrigerant pipe and the second refrigerant pipe is disposed in the fall portion of the first refrigerant pipe, the connection pipe unit is covered with a thermally insulating material, and anti-corrosion treatment is applied to each first refrigerant pipe covered with the thermally insulating material, this anti-corrosion treatment comprising the formation of a protective layer.
- An air-conditioning apparatus includes the heat exchanger.
- connection portion in each of the gas pipe and the liquid pipe of the connection pipe unit, the connection portion, in which the first refrigerant pipe (refrigerant pipe formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy) and the second refrigerant pipe (refrigerant pipe formed of copper or a copper alloy) are connected to each other, is disposed in the fall portion of the first refrigerant pipe.
- the connection pipe unit is covered with the thermally insulating material, and anti-corrosion treatment is applied to the first refrigerant pipe (a refrigerant pipe formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy) covered with the thermally insulating material.
- the heat exchanger can have a long life.
- the air-conditioning apparatus includes the heat exchanger, progress of corrosion of the first refrigerant pipe (a refrigerant pipe formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy) can be suppressed, and accordingly, the air-conditioning apparatus can have a long life.
- a heat exchanger according to the present invention installed in an indoor unit of an air-conditioning apparatus will be described.
- An example of the indoor unit according to the present invention is a wall-mounting indoor unit.
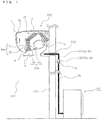
- Fig. 1 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a state in which the air-conditioning apparatus according to Embodiment of the present invention is installed.
- the air-conditioning apparatus includes an indoor unit 100 and an outdoor unit 101.
- the indoor unit 100 is mounted on a wall 111 of a conditioned space 110.
- the outdoor unit 101 is installed outside the conditioned space 110.
- the indoor unit 100 includes components such as a housing 1, a fan 5, and an indoor heat exchanger 10.
- the housing 1 has, for example, a substantially rectangular box shape and has an air inlet 2 formed on an upper portion thereof and an air outlet 3 formed on a lower portion thereof.
- the air inlet 2 is provided with a filter 2a, which collects dust and the like from indoor air sucked into the housing 1.
- the air outlet 3 is provided with a wind direction adjustment mechanism 4, which adjust directions of conditioned air being blown through the air outlet 3.
- the fan 5 includes, for example, a cross flow fan disposed in the housing 1.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 is disposed so as to cover a front, top, and rear sides of the fan 5.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 includes fin-tube heat exchangers.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 includes a plurality of heat exchangers 10a and a plurality of heat exchangers 10b.
- the heat exchangers 10a include cylindrical heat transfer pipes 12.
- the heat exchangers 10b include flat heat transfer pipes 16.
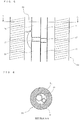
- Each heat exchanger 10a includes a plurality of fins 11 and the plurality of heat transfer pipes (cylindrical pipes) 12.
- the fins 11 are formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the heat transfer pipes 12 are formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the fins 11 are stacked so as to be spaced apart from one another by a specified gap.
- the heat transfer pipes (cylindrical pipes) 12 extend through the stacked fins 11.
- Each heat exchanger 10b includes a plurality of fins 15 and the plurality of heat transfer pipes (flat pipes) 16.
- the fins 15 are formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the heat transfer pipes 16 are formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the fins 15 are stacked so as to be spaced apart from one another by a specified gap.
- the heat transfer pipes (flat pipes) 16 extend through the stacked fins 15.
- the fan 5 When the fan 5 is driven, room air in the conditioned space 110 is sucked into the housing 1 through the air inlet 2.
- the room air is heated or cooled into conditioned air while flowing through the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- the conditioned air is blown through the air outlet 3.
- the heat exchangers 10a using the cylindrical heat transfer pipes 12 are located upstream in an air flow direction
- the heat exchangers 10b using the flat heat transfer pipes 16 are located downstream in the air flow direction.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 has a capability of having a plurality of independent refrigerant circuits, so that the indoor heat exchanger 10 can be thermally divided into, for example, two sections (for example, a section of the heat exchangers 10a and a section of the heat exchangers 10b).
- a pressure reducing device for reheat dehumidification 8 (for example, an expansion valve: Fig. 2 ) is connected between thermally divided two sections of heat exchangers. This can cause, while, for example, cooling operation is being performed, part of the indoor heat exchanger 10 to function as a condenser and part of the remaining part of the indoor heat exchanger 10 to function as an evaporator.
- the temperature of the conditioned air to be blown through the air outlet 3 can be prevented from being excessively decreased.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 includes connection pipe unit 20.
- An end of the connection pipe unit 20 is connected to the heat transfer pipes (connected to either the heat transfer pipes 12 or the heat transfer pipes 16, or the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16) of the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- the connection pipe unit 20 is formed of copper or a copper alloy and is routed to the outdoor side through a hole 112 formed in the wall 111.
- a flare nut connection unit 29 is provided at the other end of the connection pipe unit 20. By connecting the flare nut connection unit 29 to a flare nut connection unit 51 of an extended pipe unit 50, which is connected to the outdoor unit 101, the indoor unit 100 is connected to the outdoor unit 101.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 is connected to elements of a refrigeration cycle (such as an outdoor heat exchanger and a compressor, both of which are not shown), the elements being provided in the outdoor unit 101, thereby forming the refrigeration cycle.
- elements of a refrigeration cycle such as an outdoor heat exchanger and a compressor, both of which are not shown
- connection pipe unit 20 includes two pipes (a gas pipe 30 and a liquid pipe 40).
- the flare nut connection unit 29 includes two flare nut connection sub-units (a flare nut connection sub-unit 39 for the gas pipe 30 and a flare nut connection sub-unit 49 for the liquid pipe 40).
- the extended pipe unit 50 also includes two pipes and the flare nut connection unit 51 of the extended pipe unit 50 includes two flare nut connection sub-units.
- connection pipe unit 20 Next, the details of the connection pipe unit 20 will be described.
- Fig. 2 includes perspective views of the heat exchanger according to Embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 3 is an enlarged front view of the main part of the heat exchanger.
- Fig. 4 is a side view of the heat exchanger.
- Fig. 2 includes separate views (a) and (b) for description of the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40, the views (a) and (b) are the same except for reference numerals.
- the details of the connection pipe unit 20 according to Embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to Figs. 2 to 4 .
- connection pipe unit 20 includes the gas pipe 30 and and the liquid pipe 40.
- the gas pipe 30 is a refrigerant pipe through which mainly the refrigerant in a gaseous state flows.
- the refrigerant having flowed through the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 flows out of the indoor unit 100 through the gas pipe 30.
- the refrigerant to flow through the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 flows into the indoor unit 100 through the gas pipe 30.
- the liquid pipe 40 is a refrigerant pipe through which mainly the refrigerant in a liquid state flows.
- the refrigerant to flow through the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 flows into the indoor unit 100 through the liquid pipe 40.
- the refrigerant having flowed through the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 flows out of the indoor unit 100 through the liquid pipe 40.
- the refrigerant having flowed through a pressure reducing device which is an element of the refrigeration cycle, may flow through the liquid pipe 40 depending on the configuration of the refrigeration cycle.
- the refrigerant flowing through the liquid pipe 40 is a liquid-rich two-phase gas-liquid refrigerant.
- the gas pipe 30 is made of an aluminum pipe 31 formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy and a copper pipe 32 formed of copper or a copper alloy.
- the liquid pipe 40 is made of an aluminum pipe 41 formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy and a copper pipe 42 formed of copper or a copper alloy.
- the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 correspond to a first refrigerant pipe
- the copper pipes 32 and 42 correspond to a second refrigerant pipe.
- pipes on one side of connection each have an internal thread portion
- pipes on the other side of the connection for example, the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40
- Each internal thread portion has an internal thread formed in an inner surface thereof and a through hole communicating with a space in which the internal thread is formed.
- the external thread portion is brazed to the end of each pipe on the other side of the connection (for example, the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40).
- the external thread portions and the respective internal thread portions are screwed to each other.
- each end of the pipes at which the flares is formed (for example, the pipe of the extended pipe unit 50) on the one side of the connection is firmly held between the corresponding one of the internal thread portions and the corresponding one of the external thread portions.
- the extended pipe unit 50 is connected to the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40.
- the external and the internal thread portions are formed of brass with consideration of, for example, suitability of the material for brazing and workability.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed only of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 has the brass external thread portion, it is difficult for the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 to be brazed to the aluminum pipe 31.
- metal materials of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 are different from each other, and accordingly, electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) as described later occurs in a portion where the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 are connected to each other.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed only of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 has the brass internal thread portion
- metal materials of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 are different from each other, and accordingly, electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) as described later occurs in a portion where the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 are in contact with each other.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed only of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 has the external thread portion formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy
- the strength of the screw thread of the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 is insufficient.
- the flare nut connection unit 51 of the copper extended pipe unit 50 has the brass internal thread portions, electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) as described later occurs between the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 and the flare nut connection unit 51 of the extended pipe unit 50.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed only of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 has the internal thread portion formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy, the strength of the screw thread of the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 is insufficient. Furthermore, when forming a flare at an end of the aluminum pipe 31, there is a concern that the end of the aluminum pipe 31 may crack. Since the flare nut connection unit 51 of the copper extended pipe unit 50 has the brass external thread portions, electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) as described later occurs between the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 and the flare nut connection unit 51 of the extended pipe unit 50.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed only of the aluminum pipe 31 and the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 and the flare nut connection unit 51 of the extended pipe unit 50 are formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy, the strengths of the screw threads of the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 and the flare nut connection unit 51 are insufficient.
- the flare nut connection sub-unit 39 of the gas pipe 30 has the internal thread portion, when forming the flare at the end of the aluminum pipe 31, there is a concern that the end of the aluminum pipe 31 may crack.
- the pipes of the extended pipe unit 50 need to be formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the flare nut connection unit 51 of the extended pipe unit 50 has the internal thread portions, when forming the flares at the end of the pipes of the extended pipe unit 50, there is a concern that the end of the pipes of the extended pipe unit 50 may crack.
- the gas pipe 30 is formed of the aluminum pipe 31 and the copper pipe 32.
- the brass flare nut connection sub-unit 39 having an internal or external thread portion is provided at an end of the copper pipe 32, thereby preventing the strength of the screw thread from becoming insufficient and the end of the pipe from cracking, which might otherwise occur when the flare is formed.
- the liquid pipe 40 is formed of the aluminum pipe 41 and the copper pipe 42, and the brass flare nut connection sub-unit 49 having an internal or external thread portion is provided at an end of the copper pipe 42, thereby preventing the strength of the screw thread from becoming insufficient and the end of the pipe from cracking, which might otherwise occur when the flare is formed.
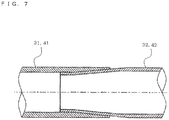
- the aluminum pipe 31 and the copper pipe 32 are connected to each other at a connection portion 37 by eutectic bonding (bonding in which metals are contacted with each other at a certain temperature so as to form a eutectic alloy).
- the end of the aluminum pipe 31 opposite to the connection portion 37 is connected to one of the heat transfer pipes 12 or one of the heat transfer pipes 16 by, for example, brazing.
- the aluminum pipe 41 and the copper pipe 42 are connected to each other at a connection portion 47 by eutectic bonding (bonding in which metals are contacted with each other at a certain temperature so as to form a eutectic alloy).
- the end of the aluminum pipe 41 opposite to the connection portion 47 is connected to one of the heat transfer pipes 12 or one of the heat transfer pipes 16 by, for example, brazing.
- connection portion 37 in which the aluminum pipe 31 and the copper pipe 32 are connected to each other
- connection portion 47 in which the aluminum pipe 41 and the copper pipe 42 are connected to each other
- the ends of the copper pipes 32 and 42 are respectively inserted into the ends of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 so as to be connected to each other by eutectic bonding (bonding in which metals are contacted with each other at a certain temperature so as to form a eutectic alloy).
- connection portions 37 and 47 When water adheres to the connection portions 37 and 47, in particular, adheres to the ends of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41, into which the copper pipes 32 and 42 are inserted, electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) occurs in the connection portions 37 and 47 (in particular, parts of the connection portions 37 and 47 formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy) in accordance with a principle, which will be described later.
- electrolytic corrosion galvanic corrosion
- the connection portions 37 and 47 in particular, parts of the connection portions 37 and 47 formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy
- the connection pipe unit 20 gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40
- the connection pipe unit 20 is routed to the outdoor side through the hole 112 formed in the wall 111.
- the position of the hole 112 of the wall 111 and an installation position of the indoor unit 100 change in accordance with the installation environment.
- lower curved portions 36 and 46 are repeatedly bent and stretched.
- the lower curved portions 36 and 46 are formed of copper or a copper alloy, which have strengths higher than that of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
- the aluminum pipe 31 of ⁇ 9.52 mm x t1.0 mm and the copper pipe 32 of ⁇ 9.52 mm x t0.8 mm are connected to each other so as to form the gas pipe 30, and the aluminum pipe 41 of ⁇ 7.00 mm x t0.75 mm and the copper pipe 42 of ⁇ 7.00 mm x t0.60 mm are connected to each other so as to form the liquid pipe 40.
- the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40 are formed to have the following shapes.
- the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40 in between upper curved portions 34 and 44 and the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 are inclined such that droplets of water having condensed flow toward the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- connection portions 37 and 47 are located closer to the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10 than the upper curved portions 34 and 44 are, water droplets including copper ions flow toward the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- electrolytic corrosion galvanic corrosion
- connection portion 37 is disposed in a linear portion 35, which is in a substantially vertical portion of the gas pipe 30, such that an upper part of the linear portion 35 is to be the aluminum pipe 31 and the lower part of the linear portion 35 of the gas pipe 30 is to be the copper pipe 32.
- connection portion 47 is disposed in a linear portion 45, which is in a substantially vertical portion of the liquid pipe 40, such that an upper part of the linear portion 45 is to be the aluminum pipe 41 and the lower part of the linear portion 45 of the liquid pipe 40 is to be the copper pipe 42.
- connection portions 37 and 47 are located above the lower curved portions 36 and 46 in the linear portions 35 and 45 of fall portions 33 and 43.
- fall portions 33 and 43 are substantially vertical in Embodiment, it is clear that the fall portions 33 and 43 may be inclined.
- connection portion 37 of the gas pipe 30 and the connection portion 47 of the liquid pipe 40 are desirably located at the same height level because, in many cases, the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40 are disposed so as to be close to each other.
- connection portion 37 of the gas pipe 30 and the connection portion 47 of the liquid pipe 40 are disposed so as to be close to each other.
- condensation is suppressed by covering the connection pipe unit 20 with a thermally insulating material 60 in order to prevent leakage of water droplets having condensed on the connection pipe unit 20 to the outside of the air-conditioning apparatus.
- Fig. 5 is a longitudinal sectional view of the connection portion of the aluminum pipe and the copper pipe according to Embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 6 is a cross-sectional view (arrow sectional view taken along line A-A in Fig. 5 ) of the connection portion.
- connection pipe unit 20 With the thermally insulating material 60 as described above.
- a small amount of water having condensed stays in a small space 70 ( Figs. 5 and 6 ) between the thermally insulating material 60 and the connection pipe unit 20.
- the water having condensed and staying in the small space 70 covers surfaces of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 and the copper pipes 32 and 42 in a continuous manner.
- copper ions Cu2+ of the copper pipes 32 and 42 diffuse toward the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 against gravity through the water having condensed and staying, thereby causing electrolytic corrosion (galvanic corrosion) of aluminum or an aluminum alloy to occur.
- Embodiment even when copper ions Cu2+ of the copper pipes 32 and 42, which are formed of copper or an copper alloy, diffuse against gravity toward the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 through the water having condensed and staying in the small space 70, a zinc diffusion layer is formed on the surface of each of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 so that corrosion of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 can be suppressed. By doing this, progress of corrosion of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy can be suppressed, and accordingly, reliability of measures against leakage of the refrigerant can be improved.
- the heat shrinkable tubes or coatings attached or applied to the connection portions 37 and 47 may be applied or attached entirely to ranges of the aluminum pipes 31 and 41, the ranges being covered by the thermally insulating material 60, in order to prevent water from adhering to the connection portions 37 and 47.
- the heat shrinkable tubes are attached or coatings be applied to the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 while the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 are still connection pipes in an assembled state before being brazed to the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 may be anodized or plated with metal such as zinc or manganese. Also in this case, it is desirable that the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 be anodized or plated while the aluminum pipe 31 and 41 are connection pipes in an assembled state before being brazed to the heat transfer pipes 12 and 16 of the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- a clad material which is formed of a core material and a high corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy (for example, A7072) superposed on the core material, may be used for the aluminum pipes 31 and 41 as the material to which the anti-corrosion treatment is applied.
- A7072 high corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy
- an example of the heat exchanger according to the present invention is installed in the indoor unit 100.
- the heat exchanger according to the present invention may be installed in the outdoor unit 101. That is, in above-described Embodiment, an example of the heat exchanger according to the present invention is used as the indoor heat exchanger 10. However, it is clear that the heat exchanger according to the present invention may be used as an outdoor heat exchanger.
- an example of the cylindrical heat transfer pipes 12 and the flat heat transfer pipes 16 are used in the indoor heat exchanger 10.
- the indoor heat exchanger 10 may use either the heat transfer pipes 12 or the heat transfer pipes 16.
- an example of the heat exchanger includes fin-tube heat exchangers.
- the present invention is applicable to a variety of heat exchangers. That is, the present invention can be implemented by connecting the gas pipe 30 and the liquid pipe 40, which have been described in Embodiment of the present invention, to a heat exchanger equipped with heat transfer pipes formed of aluminum or an aluminum alloy.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Heat-Exchange Devices With Radiators And Conduit Assemblies (AREA)
- Air Filters, Heat-Exchange Apparatuses, And Housings Of Air-Conditioning Units (AREA)
- Preventing Corrosion Or Incrustation Of Metals (AREA)
- Protection Of Pipes Against Damage, Friction, And Corrosion (AREA)
Claims (5)
- Wärmetauscher (10), aufweisend:ein Wärmeübertragungsrohr (12,16), das aus Aluminium oder einem Aluminiumgemisch ausgebildet ist; undeine Verbindungsrohreinheit (20), durch welche ein Kältemittel, das aus dem Wärmeübertragungsrohr (12,16) strömt, und ein Kältemittel, das in das Wärmeübertragungsrohr (12,16) strömt, verläuft,wobei die Verbindungsrohreinheit (20) umfasst:ein Gasrohr (30), durch welche das Kältemittel in einem gasförmigen Zustand strömt, undein Flüssigkeitsrohr (40), durch welches das Kältemittel in einem flüssigen Zustand oder in einem zweiphasigen Gas-Flüssigkeitszustand strömt,wobei das Gasrohr (30) und das Flüssigkeitsrohr (40) jeweils aufweisen:ein erstes Kältemittelrohr (31,41), das aus Aluminium oder einem Aluminiumgemisch ausgebildet ist, undein zweites Kältemittelrohr (32,42), das aus Kupfer oder einem Kupfergemisch ausgebildet ist,
wobei das erste Kältemittelrohr (31,41) und das zweite Kältemittelrohr (32,42) miteinander verbunden sind,wobei das erste Kältemittelrohr (31,41) einen Neigungsabschnitt (33,43) aufweist, der mit dem Wärmeübertragungsrohr (12,16) verbunden ist, wobei sich der Neigungsabschnitt (33,43) relativ zu dem Wärmeübertragungsrohr (12,16) abwärts erstreckt, wobeijeder Verbindungsabschnitt (37,47) zwischen dem ersten Kältemittelrohr (31,41) und dem zweiten Kältemittelrohr (32,42) in dem Neigungsabschnitt (33,43) des ersten Kältemittelrohrs (31,41) angeordnet ist,die Verbindungsrohreinheit (20) mit einem thermisch isolierenden Material (60) abgedeckt ist,dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine Antikorrosionsbehandlung auf jedes mit dem thermisch isolierenden Material (60) abgedeckten ersten Kältemittelrohr (31,41) angewendet wird, wobei diese Antikorrosionsbehandlung die Ausbildung einer Schutzschicht aufweist. - Wärmetauscher (10) nach Anspruch 1, wobei
die Ausbildung einer Schutzschicht durch ein Verfahren durchgeführt wird, das aus einem Anodisieren, einem Umhüllen, einem Plattieren oder einer Diffusion ausgewählt ist. - Wärmetauscher (10) nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, wobeidas Gasrohr (30) und das Flüssigkeitsrohr (40) jeweils einen gekrümmten Abschnitt (36,46) in einem unteren Teil des Neigungsabschnitts (33,43) des ersten Kältemittelrohrs (31,41) aufweisen, undjeder Verbindungsabschnitt (37,47) über den korrespondierenden gekrümmten Abschnitten (36,46) angeordnet ist.
- Wärmetauscher (10) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, wobei
der Verbindungsabschnitt (37) des Gasrohrs (30) und der Verbindungsabschnitt (47) des Flüssigkeitsrohrs (40) auf demselben Höhepegel angeordnet sind. - Klimaanlagenvorrichtung, aufweisend:
den Wärmetauscher (10) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012014875A JP5881435B2 (ja) | 2012-01-27 | 2012-01-27 | 熱交換器及びこれを備えた空気調和機 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2620736A2 EP2620736A2 (de) | 2013-07-31 |
| EP2620736A3 EP2620736A3 (de) | 2018-03-14 |
| EP2620736B1 true EP2620736B1 (de) | 2019-10-23 |
Family
ID=46799116
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12182717.4A Active EP2620736B1 (de) | 2012-01-27 | 2012-09-03 | Wärmetauscher und Klimaanlagenvorrichtung damit |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2620736B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5881435B2 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN103225847A (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2756774T3 (de) |
| MY (1) | MY166580A (de) |
| RU (1) | RU2509969C1 (de) |
| SG (1) | SG192323A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6079619B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-27 | 2017-02-15 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空調室内機 |
| JP5861723B2 (ja) * | 2014-01-30 | 2016-02-16 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空気調和機の室内ユニット |
| JP6452961B2 (ja) * | 2014-06-05 | 2019-01-16 | 日立ジョンソンコントロールズ空調株式会社 | 空気調和機 |
| CN104390393A (zh) * | 2014-10-29 | 2015-03-04 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | 换热器及包含该换热器的空调器 |
| WO2017081735A1 (ja) * | 2015-11-09 | 2017-05-18 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 冷凍サイクル装置及び冷媒漏洩検知方法 |
| JP6719394B2 (ja) * | 2017-01-16 | 2020-07-08 | 日立ジョンソンコントロールズ空調株式会社 | 熱交換器の接続配管構造、及び、空気調和機 |
| JP6673318B2 (ja) * | 2017-12-05 | 2020-03-25 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空調機 |
| US11549041B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2023-01-10 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Composition containing refrigerant, use of said composition, refrigerator having said composition, and method for operating said refrigerator |
| US11506425B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-11-22 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Refrigeration cycle apparatus |
| US11820933B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2023-11-21 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Refrigeration cycle apparatus |
| US11493244B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-11-08 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Air-conditioning unit |
| US11441819B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-09-13 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Refrigeration cycle apparatus |
| US11441802B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-09-13 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Air conditioning apparatus |
| US11906207B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2024-02-20 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Refrigeration apparatus |
| WO2019123897A1 (ja) * | 2017-12-18 | 2019-06-27 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 冷凍サイクル装置 |
| US11365335B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-06-21 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Composition comprising refrigerant, use thereof, refrigerating machine having same, and method for operating said refrigerating machine |
| EP3730574B1 (de) | 2017-12-18 | 2023-08-30 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Zusammensetzung mit kältemittel, verwendung davon, kältemaschine damit und verfahren zum betreiben der kältemaschine |
| US11549695B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2023-01-10 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Heat exchange unit |
| US11435118B2 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2022-09-06 | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Heat source unit and refrigeration cycle apparatus |
| CN111479910A (zh) | 2017-12-18 | 2020-07-31 | 大金工业株式会社 | 制冷剂用或制冷剂组合物用的制冷机油、制冷机油的使用方法、以及作为制冷机油的用途 |
| US11466891B2 (en) | 2018-12-25 | 2022-10-11 | Gd Midea Air-Conditioning Equipment Co., Ltd. | Air conditioner indoor unit and air conditioner |
| CN209263169U (zh) * | 2018-12-25 | 2019-08-16 | 广东美的制冷设备有限公司 | 空调室内机及空调器 |
| WO2021064442A1 (en) * | 2019-09-30 | 2021-04-08 | Daikin Industries (Thailand) Ltd. | Indoor unit for an air conditioner |
| JPWO2021186491A1 (de) * | 2020-03-16 | 2021-09-23 | ||
| JP7410418B2 (ja) | 2021-09-30 | 2024-01-10 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 室内機および空気調和機 |
| JP7518052B2 (ja) * | 2021-09-30 | 2024-07-17 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 室内機および空気調和機 |
| JP7323819B2 (ja) | 2021-09-30 | 2023-08-09 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 室内熱交換器の製造方法 |
| JP7133076B1 (ja) | 2021-09-30 | 2022-09-07 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 熱交換ユニットおよび空気調和機 |
| JP7525798B2 (ja) * | 2022-09-27 | 2024-07-31 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空気調和装置の構成ユニット |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH081348B2 (ja) * | 1987-02-09 | 1996-01-10 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 冷却装置 |
| JPH04359797A (ja) * | 1991-06-05 | 1992-12-14 | Showa Alum Corp | 熱交換器 |
| JP2877658B2 (ja) * | 1993-04-15 | 1999-03-31 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 空気調和機 |
| JPH09133389A (ja) * | 1995-11-08 | 1997-05-20 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 空気調和機 |
| JP3197251B2 (ja) * | 1998-09-22 | 2001-08-13 | カルソニックカンセイ株式会社 | 熱交換器用犠牲防食アルミニウム合金、および熱交換器用高耐食性アルミニウム合金複合材 |
| JP4474781B2 (ja) * | 2001-03-19 | 2010-06-09 | 株式会社富士通ゼネラル | 空気調和機 |
| TWI280340B (en) * | 2002-02-20 | 2007-05-01 | Showa Denko Kk | Heat exchanger with receiver tank, receiver tank connecting member, receiver tank mounting structure of heat exchanger and refrigeration system |
| JP2005055081A (ja) * | 2003-08-05 | 2005-03-03 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 熱交換器及び熱交換器を備えた自動販売機 |
| JP2005090761A (ja) * | 2003-09-12 | 2005-04-07 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 空気調和機 |
| JP2009092274A (ja) * | 2007-10-05 | 2009-04-30 | Hitachi Appliances Inc | 空気調和機 |
| CN201110733Y (zh) * | 2007-10-26 | 2008-09-03 | 浙江亚技联节能设备有限公司 | 一种铜铝复合管管壳式换热器 |
| CN201964811U (zh) * | 2010-09-07 | 2011-09-07 | 万建红 | 分离式柔性常压热管换热器 |
| CZ21751U1 (cs) * | 2010-10-08 | 2011-02-14 | Lloyd Coils Europe, S.R.O. | Pevný spoj medené a hliníkové trubky chladicího okruhu |
| CN201983654U (zh) * | 2011-02-10 | 2011-09-21 | 广东万和新电气股份有限公司 | 燃气热水器的铜铝热交换器 |
-
2012
- 2012-01-27 JP JP2012014875A patent/JP5881435B2/ja active Active
- 2012-08-30 SG SG2012064432A patent/SG192323A1/en unknown
- 2012-09-03 ES ES12182717T patent/ES2756774T3/es active Active
- 2012-09-03 EP EP12182717.4A patent/EP2620736B1/de active Active
- 2012-09-18 MY MYPI2012004114A patent/MY166580A/en unknown
- 2012-09-19 RU RU2012140170/06A patent/RU2509969C1/ru active
- 2012-09-20 CN CN2012103516484A patent/CN103225847A/zh active Pending
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013155892A (ja) | 2013-08-15 |
| EP2620736A2 (de) | 2013-07-31 |
| EP2620736A3 (de) | 2018-03-14 |
| SG192323A1 (en) | 2013-08-30 |
| MY166580A (en) | 2018-07-17 |
| ES2756774T3 (es) | 2020-04-27 |
| CN103225847A (zh) | 2013-07-31 |
| RU2509969C1 (ru) | 2014-03-20 |
| JP5881435B2 (ja) | 2016-03-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2620736B1 (de) | Wärmetauscher und Klimaanlagenvorrichtung damit | |
| EP2423609B1 (de) | Wärmetauscher und Klimaanlage, auf der der Wärmetauscher montiert ist | |
| CN1961192B (zh) | 钎焊的散热片热交换器 | |
| CN104011470B (zh) | 制冷装置的室外单元 | |
| EP2863159B1 (de) | Wärmetauscher, herstellungsverfahren dafür und kältekreislaufvorrichtung | |
| US20110042047A1 (en) | Heat exchanger drip tube | |
| JP2005090761A (ja) | 空気調和機 | |
| JP6074648B2 (ja) | 管部材の接合体、及び冷凍サイクル装置の熱交換器 | |
| JP2009250562A (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| WO2015033542A1 (ja) | 熱交換器及びそれを用いた冷却装置 | |
| US11698213B2 (en) | Heat exchanger, indoor unit for air-conditioner, and refrigeration device | |
| JP4980128B2 (ja) | 熱交換器及びその熱交換器を用いた冷凍回路 | |
| JP2005133966A (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| CN107270589B (zh) | 换热器及家用电器 | |
| EP3249339B1 (de) | Klimatisierungsvorrichtung | |
| JP2018009742A (ja) | 冷凍サイクル装置の熱交換器 | |
| JP6873252B2 (ja) | 熱交換器、空気調和装置の室外機及び空気調和装置 | |
| EP3249338B1 (de) | Wärmetauscher und verfahren zur herstellung davon | |
| JP2018115804A (ja) | 熱交換器および空気調和機の室外機 | |
| CN115127382A (zh) | 热交换器以及制冷循环装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F24F 13/30 20060101ALI20180206BHEP Ipc: F28F 9/02 20060101AFI20180206BHEP Ipc: F28F 19/02 20060101ALI20180206BHEP Ipc: F28F 19/00 20060101ALI20180206BHEP Ipc: F28F 21/08 20060101ALI20180206BHEP |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20180822 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20190417 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602012065033 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1194118 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20191115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2756774 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20200427 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200224 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200124 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200123 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200123 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200224 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602012065033 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG2D | Information on lapse in contracting state deleted |
Ref country code: IS |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200223 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1194118 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20200724 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 602012065033 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20200903 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20200930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200903 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20210401 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200930 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200930 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200903 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200903 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191023 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230512 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20230810 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20230808 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20231003 Year of fee payment: 12 |