EP2612308B1 - Funkfernsteuerung mit lagesensorik - Google Patents
Funkfernsteuerung mit lagesensorik Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2612308B1 EP2612308B1 EP10757578.9A EP10757578A EP2612308B1 EP 2612308 B1 EP2612308 B1 EP 2612308B1 EP 10757578 A EP10757578 A EP 10757578A EP 2612308 B1 EP2612308 B1 EP 2612308B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- machine
- remote control
- radio remote
- control system
- designed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 claims description 155
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001447 compensatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002457 bidirectional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003813 thumb Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C17/00—Arrangements for transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link
- G08C17/02—Arrangements for transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link using a radio link
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C2201/00—Transmission systems of control signals via wireless link
- G08C2201/30—User interface
- G08C2201/32—Remote control based on movements, attitude of remote control device
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C2201/00—Transmission systems of control signals via wireless link
- G08C2201/50—Receiving or transmitting feedback, e.g. replies, status updates, acknowledgements, from the controlled devices
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a radio remote control of a crane, a boom, a loading bridge and / or a hoist with various moving components (machine) with at least one controllable by the radio remote machine drive a movable machine part, comprising a machine associated with the radio receiving device, a handset with a control unit , a transmitting device and at least one motion sensor, wherein the control unit is adapted to transmit control commands caused by a user to the transmitting device and to cause the transmitting device for transmitting the control commands to the receiving device, and wherein by means of the motion sensor movements of the handset in the room by at least a tilting or tilting axis (KA, DA) can be detected, such that in a movement operating mode the detected movements can be converted by the control unit into control commands which are sent to the machine by F unkübertragung between transmitting device and receiving device can be transmitted, wherein the movement mode of operation can be activated by a user input on the handset.
- KA, DA tilting or tilting axis
- a particularly preferred although not exclusive field of application of the present invention is the control of cranes and hoists.
- a jib crane such as a construction crane, e.g. the orientation of the boom (rotation angle), the movement of the cat and the movement of the hook are controlled with a suitably designed radio remote control according to the invention.
- Position sensors are also installed today, for example, in mobile phones, so that the orientation of such a device, in particular its display can be determined to adjust the display in the display according to the orientation of the device.
- radio remote controls are from the US 2005/0212911 A1 , of the DE 10 2004 009 561 A1 and the US 2008/0150749 A1 known.
- the US 2005/0212911 A1 discloses in general the configuration or use of a handheld device, for example a mobile telephone, as a radio remote control for all possible devices, partly with movable divider and the radio remote control corresponds in its functionality to the other features of the preamble of claim 1.
- the DE 10 2004 009 561 A1 discloses the use of a smartphone as a remote control for controlling a device detected by the camera by means of movements of the smartphone.
- the US 2008/0150749 A1 discloses a remote control for a reclining or seating device, for example a hospital bed, the lying or Sirzflä- has several elements, each of which is separately adjustable by a liner motor. The operating state of the respective linear motors is sent back to the remote control.
- the object of the invention is to improve a generic radio remote control in terms of intuitive operation by a user.
- the receiving device has a feedback transmitter and is adapted to activate the feedback transmitter for the transmission of feedback information upon receipt of control commands, and wherein the handset set up for receiving the return information and connected to the control unit feedback receiver and controlled by the control unit having acoustic and / or haptic display device by means of which operating function information of the radio remote control in accordance with the reception of feedback signals from the feedback transmitter can be displayed.
- control unit it is possible to determine the current reference position in a comfortable hand position for a user.
- a handset of a radio remote control is often not kept exactly horizontal, but a natural attitude of the human hand causes the handset is held with a slight inclination in the upward direction.
- This natural posture can then be defined as the current reference position or as a kind of neutral position, so that movements detected by the motion sensor, such as turning, tilting or tilting of the handset, can be detected and converted into control commands.
- Based on such a natural position of the human hand also results in an optimal utilization of the possible movements by the user for the purpose of controlling a corresponding machine drive.
- the radio remote control is set up such that upon activation of the motion mode, the current position of the handset is detected in space and compared with a predetermined reference position, and that detected movements are only as control commands to the machine can be transmitted, if the radio remote control has been brought at least approximately in the predetermined reference position, wherein for the generation of control commands movements are detected relative to the predetermined reference position.
- the predetermined reference position may be, for example, a substantially horizontal orientation of the handset in space. This predetermined reference position must be reached or adjusted starting from a position of the handset in the room in which the motion control is activated. Once the handset has been brought into a current position or is already in activating the motion control, which corresponds approximately to the predetermined reference position, d. H. meets this predetermined reference position within a tolerance range, then further movements of the handset are detected based on the predetermined reference position and converted into control commands that can be transmitted to the machine.
- the invention allows intuitive operation and control of a machine by means of a hand-held device that contains motion sensors and whose control unit allows transmission of detected movements as a control command to the machine.
- a radio remote control In this regard, reference should be made to two different control operation possibilities that may be implemented in respective embodiments of a radio remote control according to the present invention.
- a first control mode the activation of the motion mode is performed by operating a switch.
- a switch preferably any existing safety relay or the like.
- the machine is unlocked and it follows the referencing of the handset according to one of the aforementioned referencing options.
- By moving the handset relative to the detected reference position is then the specification of the controlled movement of the machine part, whereby by opposite directions of movement of the handset relative to the reference position control commands can be generated, which also cause the machine part to move in corresponding opposite directions.
- the amount of the movement to be controlled for example the speed amount or the acceleration amount, can then also be specified.
- An example of this is provided, for example, by specifying both the direction and the amount of the movement of the machine part to be controlled by rotating the handset relative to a reference position detected when the motion mode is activated by +/- 30 °, for example Plus area represents a direction of movement and the minus area represents the opposite direction of movement of the machine part.
- a second control mode provides that e.g. two contacts or push buttons are provided, which are to be actuated to activate the movement mode of operation, wherein one of the keys associated with a direction of movement of the machine part, whereas the other button is associated with the opposite direction of movement of the machine part.
- the movement of the handset relative to the respective reference position would then be e.g. specify only the amount of the controlled speed of the machine part.
- the motion mode of operation is triggered by actuation of a switch on the handset and maintained by continued contact of that switch to control the movement of the machine part. Releasing this switch will then result in no further control commands being transmitted to control the movement of the machine part. It is therefore a kind of deadman circuit.
- latching switches are provided for user input on the handset, by means of which the user can activate the movement mode of operation by an active switching operation on such a latching switch.
- the output perceivable to the user of the handset improves the intuitive remote control of a machine.
- the user will be supported in an intuitive way in the machine operation by means of movements of the handset.
- the output is a kind of feedback to the user, so that the human-machine interface can be optimized.
- the output means are set up such that the output perceptible to the user is generated as a function of signals output by the motion sensor.
- the output means may be arranged to generate the output perceptible to the user in a stepwise manner in response to the achievement of certain signal strengths output by the motion sensor.
- another signal could be output when an extreme value of the possible motion is reached.
- the output means may be arranged to generate the output perceptible to the user in proportion to the signal strength output by the motion sensor.
- the output means may be arranged to generate the output perceptible to the user in proportion to the signal strength output by the motion sensor.
- the output perceptible to the user may be a predetermined one Characteristic are generated in accordance with the signal strength output by the motion sensor.
- the characteristic curve can be optimized depending on the type of control, so that the dependence of the output perceptible on the user of the signal strength output by the motion sensor is directly proportional, ie linear, or degressive or progressive. In particular, a logarithmic characteristic also comes into question.
- the perceptible for the user output of at least one output means is differentially, so only when the signal strength output by the motion sensor changes.
- a differential or dynamic output normally provides the user with a sufficient subjective feedback feeling of the radio remote control and, on average, places a relatively small burden on the power supply of the handset since during the phases of constant signal output of the motion sensor the output means need not be activated.
- the control unit is preferably set up in such a way that movements detected by the movement sensor or a movement sensor in a working rotation or tilting range of a maximum of about -45 ° to + 45 °, in particular -30 ° to + 30 °, cause an associated horizontal rotation or tilting movement .
- Tilting axis are converted into control commands for the machine.
- Such a limitation of the range of motion convertible into control commands for the machine serves, on the one hand, for ergonomic handling of the handheld device since movements in a larger angular range are inconvenient by means of the human hand.
- an angular range defined in this way can also be used to define positions of the handheld device in which the motion control is switched off by means of the handheld device and no further ones Control commands are sent to the machine more due to detected movements.
- the output means is set up in such a way that it indicates an approximation to the maximum rotational or tilting movement and / or leaving the working rotary or tilting range by a corresponding output perceptible to the user.
- control unit can be set up in such a way that no further control commands due to detected movements are generated when leaving the work turning or tilting area until further notice.
- safety-related control commands e.g. Stop commands are sent from the handset to the machine when the working turn or tilt range is exited.
- leaving a preferred angular range or movement range preferably affects only the machine control by means of movement of the handset, but not the activation of the machine by means of any other controls on the handset, such as push buttons, joystick or the like
- leaving the working rotation or tilting range in the machine control it is determined whether the machine will then remain in its current state or be brought into a neutral position. It is also to be determined whether the movements of all controllable by the radio remote machine parts in the case of leaving the Häitch- or tilting should be stopped or whether only those drives which are controlled by the motion control, stopped.
- Such operating concepts can be determined taking into account corresponding security concepts and standards.
- the receiving device has a feedback transmitter and is configured to activate the feedback transmitter for the transmission of feedback information upon receipt of control commands, wherein the handset for receiving the Having feedback information set up and connected to the control unit feedback receiver.
- the receiving device with feedback transmitter and the transmitting device of the handset with feedback receiver thus form a bidirectional radio remote control system with improved security features.
- the handset has an audible and / or optical and / or haptic display device controlled by the control unit, by means of which operating function information of the radio remote control in accordance with the reception of feedback signals can be displayed by the feedback transmitter.
- Such a display device thus represents an output means which can inform the user about faults.
- the aspect of the radio feedback, in particular in combination with the aforementioned display device and the features of the preamble of claim 1 is possibly independent inventive importance, and the applicant reserves the right to make a corresponding independent claim.
- a further advantageous aspect of the invention is given by the features of claim 5, namely that a data on the respective actual position of the movable machine part and / or on the movement state detecting sensor device - and the data of this sensor device as a feedback information sending feedback message is provided on the machine , and that the handset has a set up to receive the feedback information and connected to the control device feedback receiver.
- the hand-held device preferably has an optical unit controlled by the control unit, the respective actual position and / or the actual deviation of the actual position from the desired position determined by the current position of the hand-held device and / or the optical speed of the moving machine part. and acoustic and / or haptic display device.
- the display device can therefore inform the user about the respective position, direction of movement and speed of movement of the machine part.
- the display device comprises a display, eg LCD display, on which the information is displayed graphically as pictures or pictograms or videos or / and numerically representable as numbers and letters.
- the predetermined reference position in the embodiment of the radio remote control according to claim 2 can be e.g. each time the controller is switched on, each time it is determined as a function of the instantaneous position of the movable machine part.
- the handset first interrogates the feedback information from the acknowledgment transmitter on the machine before sending out new control commands.
- control unit is set up to modify control commands for the machine as a function of the received feedback information.
- modify control commands for the machine could be that, when the movable machine part approaches its nominal position, an automatic reduction of the speed of the machine part or / and a greater resolution of the control characteristic takes place in the sense of a more sensitive control.
- further feedback options may be provided in the radio remote control according to the invention or a machine equipped therewith, such as the display of certain machine reactions or specific dynamic states of movement of the machine or the movable machine part, which eg by control operations or switching operations from another Control source as the radio remote control conditional.
- a machine may be to control in which the movable machine part between two opposite end positions is movable and in which a limit switching off the machine drive as soon as the movable machine part reaches the end position or this approaching to a small distance.
- the approximation of the machine part to the end position can according to a development of the present invention via a feedback signal per Radio transmitted to the handset and there lead to a relevant optical and / or acoustic and / or haptic display, so that the user is made aware of the situation of the machine.
- oversteering feedback is, for example, a crane or hoist with a so-called load oscillation damping, in which the trolley or possibly the crane boom automatically executes compensatory movements in order to counteract an undesired oscillation of the load hanging on the crane.
- Such compensatory movements can be displayed to the latter via wireless feedback from the crane to the handset.
- a haptic and / or acoustic display on the handset is advantageous in order to inform the user accordingly.
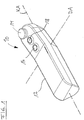
- Fig. 1 shows in a simplified schematic perspective view of a handset 10 of a radio remote control for a machine.
- a machine devices are understood to have moving components that can be changed by appropriate control in their respective situation. It is particularly intended for the remote control of cranes, boom of concrete pumps, hydraulically powered loading bridges on trucks and the like.
- the handset 10 comprises in its housing 12 at least one sensor, not shown, by means of which movements of the handset 10 in space can be detected.
- the motion sensor or the motion sensors can or can detect rotational movements about a rotational or tilting axis DA and tilting movements about a tilting axis KA.
- the detection of the movements of the Handset 10 can be done by means of appropriate angle and position sensors.
- the position or movement sensors used react to gravity or gravitational attraction and therefore have an angle-dependent resolution or maximum signal strength depending on the rotational or tilting movement of the hand-held device.
- the output signal may be maximum at deflection about the horizontal and increasingly be close to zero when turning or tilting in the vertical.
- the hand-held device shown purely by way of example here can have a type of joystick 14, which can generally be operated with a thumb of a user's hand in order to remotely control corresponding machine parts.
- two operation buttons 16, 18 are shown, which can be actuated to activate further control options.
- One of these operating buttons 16, 18 can be used, for example, to activate a movement operating mode in which movements detected by the motion sensors, not shown, are actually converted into control commands in order to be able to control the machine as a function of performed movements.
- This button can be assigned in the manner of a flip-flop circuit on re-pressing and switching off this motion mode of operation. Alternatively, the switching on or off can be done via different control buttons.
- On a handset 10 may also be provided an emergency stop switch, which is not shown in the present example, however.
- the hand-held device shown is purely exemplary and can be configured differently both with regard to its external shape and with regard to further or other operating elements.
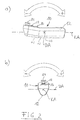
- the handset 10 can be rotated or pivoted about its axis of rotation DA (tilt axis), which is indicated by the double arrow. Furthermore, the handset 10 (FIG. Fig. 2 b) ) can also be tilted or pivoted about its tilt axis KA, which is also indicated by the double arrow.
- the movements about the axis of rotation DA or Tilting axis KA are detected by the motion sensor (s) and, when the motion operating mode is activated accordingly, converted into control signals, which are transmitted to the machine to be remotely controlled.
- Fig. 3 shows a schematic rectangular representation different positions of movement of the handset 10 about its axis of rotation DA.
- a current position I of the handset 10 in space can be assumed as the reference position. How out Fig. 3 can be seen, this reference position I slightly inclined in the example to a horizontal. A comfortable position of such a handheld device is usually in an angular range of +/- 20 ° around the horizontal.
- a so-called movement operating mode for example by pressing an actuating button 16 or 18 (FIG. Fig. 1 )
- the current position I of the handset 10 detected in space and adopted as a reference position for the subsequent motion detection.
- Rotary or pivotal movements of the handset 10 about the axis of rotation DA in positions II and III can then be evaluated with reference to the reference position I and converted into control commands, which are transmitted to the machine to be remotely controlled.
- the movement position IV illustrates a position of the handset 10 in which a maximum angle of rotation has been exceeded with respect to the reference position I.
- the generation of control commands due to the detected movements can be interrupted (termination of the motion mode).
- IV can be achieved, for example, when a user, who holds the handset 10 in his hand while angling his arm, stretches it down so that the handset is oriented substantially vertically toward the ground.
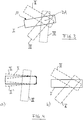
- Fig. 4 shows in the sub-figures a) and b) another type of control or another control mode.
- the handset must first be brought into a movement position II or II ', which corresponds approximately to a preset reference position I of the hand-held device 10.
- the movements of the hand-held device then detected are again converted into control commands, which can be transmitted to the machine. This is in Fig. 2 b) indicated by the movement positions III and V.
- Switching off the motion mode of operation, so that the detected movements are no longer converted into control commands can be done by operating a control knob 16, 18 on the handset 10 or, as above with reference to the Fig. 3 described by leaving a predetermined angle range and the handset is brought, for example, in the movement position IV.
- Fig. 5 shows a simplified flowchart for a control according to Fig. 3 , in which a current position in space is determined as the reference position.
- a control unit which is normally housed in the housing 12 of the handset 10, whether the motion mode is turned on, for example by pressing a button on the operation buttons 16, 18.
- the current position (see I in Fig. 3 ) of the handset in the room as a reference position determined (step 22).
- step 24 the current position is detected and set in relation to the reference position I.
- An action is taken at step 26 Inquire whether the motion mode has been turned off.
- step 28 it is checked in step 28 whether the movement of the handset has taken place within a predetermined turning / tilting range. If the spin / tilt region has been left (N), the motion mode is turned off in step 34 and, if applicable, a user detectable signal is generated on the handset 10. If the movement is within the turning / tilting range (J) in step 28, a control command calculated as a function of the detected movement is generated in step 30 and transmitted to the machine to be remotely controlled or to a machine component to be driven. The steps 24-30 are usually repeated several times in succession with the motion operating mode switched on in order to be able to detect continuously changing movement positions of the handheld device 10 and to be able to generate corresponding control commands. This loop is indicated by the arrow 31.
- the handset also comprises an output means, not shown in the figures, which is arranged to generate, in response to sensed movements, at least one output perceptible to the user, in particular an optical and / or audible and / or haptic signal on the handset.
- an output means not shown in the figures, which is arranged to generate, in response to sensed movements, at least one output perceptible to the user, in particular an optical and / or audible and / or haptic signal on the handset.
- This step 32 extends the multiple sweep loop of steps 24-32, which is indicated by the dashed arrows 33, circumventing the arrow 31.
- a perceptible for the user signal By generating a perceptible for the user signal can during the one Winkelaustsch generating Rotational or tilting movement of the handset 10 and the control command thus generated the user audibly or tactile or visually perceptible feedback can be given, which gives a subjectively experienced by the user control security, such as this by remote control by joystick or push buttons or the like knows and was used to.
- the generation of a perceptible for the user signal can, for. B. when leaving the reference position and when reaching a first stage, which corresponds for example to a speed of the machine part to be remotely controlled.
- a second stage of a speed control fast speed
- speed level II is left again and returned to level I, this can also be made perceptible to the user by means of a corresponding signal.
- the user perceivable signal is haptically and / or acoustically configured, the user may be visually focused on the remote components of the machine when remotely controlling the machine and is not required to direct his gaze to the handset 10.
- the movements he makes with the handset 10 are brought to his perception by acoustic or / and haptic signals in a kind of feedback so that he can perform further movements or countermovements with the handset 10 according to the sensed signals to the desired Remote control of the machine to make.
- such signals can also be output in proportion to the detected movements. It is conceivable, for example, that this makes the enlargement or reduction of the detected turning or tilting angle acoustically / haptically tangible, it being entirely possible for a different signal to be output for the enlargement of the angle than for the reduction of the angle. If the handset is held steady in a certain angular position, the corresponding signal will not be output, but only when the handset is set in motion. Alternatively, it is conceivable that an acoustic and / or haptic signal is output constantly during the entire movement operating mode and is preferably also configured proportionally to the detected rotational or tilting angle.
- the proportional output of a user perceivable signal is not limited to a direct proportional dependence between sensed motion and signal strength. Rather, it is also thought of a logarithmic signal distribution, which is better suited for human perception.
- Both the acoustic and the haptic or vibration feedback signal can consist of vibration impulses or short burst chains of vibration impulses, for example, whose spacing decreases as the rotational or tilting angle increases and thus their perceived intensity increases.
- An acoustic and / or haptic and / or optical output on the handset can also be output when the reference position is reached or when a shutdown situation is reached, for example, when reaching angles of about +/- 45 ° with respect to the reference position.
- the handset 10 includes a return receiver, which is adapted to receive feedback information from the machine to be controlled, in which case it is assumed that such feedback information sending return message transmitter is provided on the machine.
- the receiving device on the machine may comprise a check-back transmitter which acknowledges the receipt of control commands, so that the feedback information is confirmation of the receipt of control commands. If these expected radio reception acknowledgments are not registered by the handset 10, a respective output means of the handset 10 may alert the user to any trouble.
- this has a data on the respective actual position of the movable machine part and / or on the motion state detecting sensor device - and the data of this sensor device as feedback information sending feedback to the machine, wherein the feedback receiver of Handellas receive this feedback information and can pass it to the control unit.
- the latter can then according to a variant of the invention modify control commands for the machine in dependence on the received feedback information.
- the output means can be designed in the form of a display device so that they represent the respective actual position and / or the current deviation of the actual position of the determined by the current position of the handset target position and / or the speed of movement of the movable machine part , Also in this regard is an optical and / or acoustic and / or haptic display or output in question.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Selective Calling Equipment (AREA)
- Toys (AREA)
- Telephonic Communication Services (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2010/062706 WO2012028175A1 (de) | 2010-08-31 | 2010-08-31 | Funkfernsteuerung mit lagesensorik |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2612308A1 EP2612308A1 (de) | 2013-07-10 |
| EP2612308B1 true EP2612308B1 (de) | 2017-04-05 |
Family
ID=44166489
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10757578.9A Active EP2612308B1 (de) | 2010-08-31 | 2010-08-31 | Funkfernsteuerung mit lagesensorik |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8866597B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP2612308B1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP2013536660A (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN103069463A (zh) |
| DK (1) | DK2612308T3 (zh) |
| ES (1) | ES2624862T3 (zh) |
| PL (1) | PL2612308T3 (zh) |
| RU (1) | RU2534934C2 (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2012028175A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130293362A1 (en) * | 2012-05-03 | 2013-11-07 | The Methodist Hospital Research Institute | Multi-degrees-of-freedom hand controller |
| EP2813910A1 (de) * | 2013-06-10 | 2014-12-17 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Bedienhandgerät mit kombinierter Signalauswertung |
| CN104639966A (zh) * | 2015-01-29 | 2015-05-20 | 小米科技有限责任公司 | 遥控方法及装置 |
| CN105678990A (zh) * | 2015-12-31 | 2016-06-15 | 赵旭 | 一种遥控器及其检测、控制方法 |
| JP1587436S (zh) * | 2016-05-10 | 2017-10-02 | ||
| EP3279881A1 (de) * | 2016-08-05 | 2018-02-07 | Alexander Hakenjos | Fernbedienung und verfahren zu deren kontrolle |
| EP3506645B1 (en) * | 2016-08-23 | 2023-09-06 | Sony Group Corporation | Control system, control apparatus, and control method |
| US10331233B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-06-25 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Camera and sensor controls for remotely operated vehicles and virtual environments |
| US10198086B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-02-05 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Dynamically balanced, multi-degrees-of-freedom hand controller |
| US10331232B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-06-25 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Controller with situational awareness display |
| US10520973B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-12-31 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Dynamically balanced multi-degrees-of-freedom hand controller |
| US10324487B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-06-18 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Multi-axis gimbal mounting for controller providing tactile feedback for the null command |
| WO2018081662A1 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2018-05-03 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | Dynamically balanced multi-degrees-of-freedom hand controller |
| CN106683384B (zh) * | 2017-02-28 | 2023-11-24 | 国网山东省电力公司烟台供电公司 | 智能遥控器、家用电器及方法 |
| EP3396478B1 (en) * | 2017-04-28 | 2023-06-14 | Deere & Company | Apparatus, method and computer programme for controlling a machine |
| CN111512114B (zh) | 2017-10-27 | 2022-04-05 | 流体技术股份有限公司 | 用于对空指令提供触觉反馈的控制器的多轴常平架安装座 |
| WO2019084506A1 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2019-05-02 | Fluidity Technologies, Inc. | CONTROL DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH A DISPLAY DEVICE FOR KNOWING THE SITUATION |
| CN111566579A (zh) | 2017-10-27 | 2020-08-21 | 流体技术股份有限公司 | 用于远程操作的交通工具和虚拟环境的相机和传感器控件 |
| EP3771458A1 (en) * | 2019-07-29 | 2021-02-03 | TRUMPF Medizin Systeme GmbH + Co. KG | Remote control for a medical apparatus, system of the remote control and the medical apparatus, and method for operating the medical apparatus |
| US11908574B2 (en) * | 2019-07-29 | 2024-02-20 | Trumpf Medizin Systeme Gmbh + Co. Kg | Remote control for a medical apparatus, system of the remote control and the medical apparatus and method for operating the medical apparatus |
| US11599107B2 (en) | 2019-12-09 | 2023-03-07 | Fluidity Technologies Inc. | Apparatus, methods and systems for remote or onboard control of flights |
| WO2021115505A1 (de) * | 2019-12-11 | 2021-06-17 | Ged Gesellschaft Für Elektronik Und Design Mbh | Vorrichtung zur ertüchtigung des gleichgewichtssinns |
| CN112991705B (zh) * | 2019-12-12 | 2024-09-10 | 无疆(武汉)技术有限公司 | 一种手握式遥控器 |
| US11614766B2 (en) * | 2020-04-09 | 2023-03-28 | Caterpillar Inc. | Machine joystick with comfort and accessibility features |
| IT202000028481A1 (it) * | 2020-11-26 | 2022-05-26 | Aisa Di Zanette Dino | Dispositivo di comando a distanza portatile preferibilmente per uso in ambito domestico |
| US11662835B1 (en) | 2022-04-26 | 2023-05-30 | Fluidity Technologies Inc. | System and methods for controlling motion of a target object and providing discrete, directional tactile feedback |
| US11696633B1 (en) | 2022-04-26 | 2023-07-11 | Fluidity Technologies Inc. | System and methods for controlling motion of a target object and providing discrete, directional tactile feedback |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5444462A (en) * | 1991-12-16 | 1995-08-22 | Wambach; Mark L. | Computer mouse glove with remote communication |
| US5598187A (en) * | 1993-05-13 | 1997-01-28 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Spatial motion pattern input system and input method |
| JP3373423B2 (ja) * | 1998-03-13 | 2003-02-04 | 三菱電機株式会社 | リモコンシステム |
| US6346891B1 (en) * | 1998-08-31 | 2002-02-12 | Microsoft Corporation | Remote control system with handling sensor in remote control device |
| JP4298941B2 (ja) * | 2001-09-26 | 2009-07-22 | ヤマハ株式会社 | リモコン装置 |
| SE521051C2 (sv) * | 2001-11-16 | 2003-09-23 | Volvo Penta Ab | Fjärrmanövreringssystem för ett fordon. |
| JP2004120577A (ja) * | 2002-09-27 | 2004-04-15 | Alps Electric Co Ltd | 機器制御装置 |
| JP2004173003A (ja) * | 2002-11-20 | 2004-06-17 | Toshiba Corp | 放送受信装置とコード信号出力装置及びその制御方法 |
| JP4064255B2 (ja) * | 2003-01-30 | 2008-03-19 | 日本放送協会 | リモコン信号送信装置 |
| DE102004009561A1 (de) | 2003-02-27 | 2004-11-11 | Karlheinz Lederer | Fernbedienungssystem und Verfahren zum Fernbedienen |
| US7173604B2 (en) * | 2004-03-23 | 2007-02-06 | Fujitsu Limited | Gesture identification of controlled devices |
| KR100853605B1 (ko) * | 2004-03-23 | 2008-08-22 | 후지쯔 가부시끼가이샤 | 핸드헬드 장치에서의 경사 및 평행 이동 운동 성분들의구별 |
| US20060036970A1 (en) * | 2004-08-16 | 2006-02-16 | Charles Rich | System for configuring and controlling home appliances |
| RU55760U1 (ru) * | 2006-03-22 | 2006-08-27 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Научно-производственное предприятие "КОМПЛЕКСЫ и СИСТЕМЫ" (ООО НПП "КОМПЛЕКСЫ и СИСТЕМЫ") | Система дистанционного управления грузоподъемными кранами (сду) |
| US20080150749A1 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2008-06-26 | Tai-Hung Lin | Wireless control system for controlling linear actuators |
| JP4940118B2 (ja) | 2007-12-10 | 2012-05-30 | 株式会社キトー | 走行クレーンの操作制御装置 |
| JP5074227B2 (ja) * | 2008-02-18 | 2012-11-14 | 日立マクセル株式会社 | マッサージ機 |
| JP5011169B2 (ja) | 2008-03-05 | 2012-08-29 | 株式会社キトー | 走行クレーンの操作制御装置 |
| JP5011170B2 (ja) | 2008-03-05 | 2012-08-29 | 株式会社キトー | 走行クレーンの操作制御装置、操作制御方法 |
| US8503932B2 (en) * | 2008-11-14 | 2013-08-06 | Sony Mobile Comminications AB | Portable communication device and remote motion input device |
| JP5348760B2 (ja) * | 2009-05-08 | 2013-11-20 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 作業機の遠隔操作装置 |
-
2010
- 2010-08-31 ES ES10757578.9T patent/ES2624862T3/es active Active
- 2010-08-31 PL PL10757578T patent/PL2612308T3/pl unknown
- 2010-08-31 WO PCT/EP2010/062706 patent/WO2012028175A1/de active Application Filing
- 2010-08-31 RU RU2013114302/08A patent/RU2534934C2/ru active
- 2010-08-31 JP JP2013526321A patent/JP2013536660A/ja active Pending
- 2010-08-31 DK DK10757578.9T patent/DK2612308T3/en active
- 2010-08-31 CN CN2010800688473A patent/CN103069463A/zh active Pending
- 2010-08-31 US US13/818,148 patent/US8866597B2/en active Active
- 2010-08-31 EP EP10757578.9A patent/EP2612308B1/de active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103069463A (zh) | 2013-04-24 |
| RU2013114302A (ru) | 2014-10-10 |
| EP2612308A1 (de) | 2013-07-10 |
| ES2624862T3 (es) | 2017-07-17 |
| WO2012028175A1 (de) | 2012-03-08 |
| US20130147611A1 (en) | 2013-06-13 |
| JP2013536660A (ja) | 2013-09-19 |
| PL2612308T3 (pl) | 2017-09-29 |
| RU2534934C2 (ru) | 2014-12-10 |
| DK2612308T3 (en) | 2017-07-31 |
| US8866597B2 (en) | 2014-10-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2612308B1 (de) | Funkfernsteuerung mit lagesensorik | |
| EP2139803B1 (de) | Verfahren zum steuern einer lastbewegungsvorrichtung und steuerung einer lastbewegungsvorrichtung | |
| DE112011101930B4 (de) | Verfahren, Steuerungssystem und Bewegungvorgabemittel zum Programmieren oder Vorgeben von Bewegungen oder Abläufen eines Industrieroboters | |
| EP3099618B2 (de) | Kransteuerung | |
| EP1926069B1 (de) | Funkfernsteuerung | |
| EP3389943B1 (de) | Handwerkzeugmaschine mit einem schlagwerk | |
| EP2652566B1 (de) | Steuervorrichtung für eine werkzeugmaschine und verfahren zum steuern der werkzeugmaschine | |
| DE102015215664A1 (de) | Fernbedienung und Benutzerschnittstelle zum Betreiben einer Winde | |
| WO2021023794A1 (de) | Eingabegerät und eingabesystem sowie verfahren zum betreiben eines eingabegeräts | |
| EP3665117B1 (de) | Fernsteuerungsanordnung und verfahren zum betrieb der fernsteuerungsanordnung | |
| WO2017084984A1 (de) | Elektromotorischer möbelantrieb, möbel und verfahren zum steuern eines elektromotorischen möbelantriebs | |
| WO2008083775A2 (de) | Bedien- und anzeigesystem für ein niveauregelungssystem eines fahrzeugs, insbesondere für einen reisebus oder ein nutzfahrzeug | |
| DE102015226091A1 (de) | Handwerkzeugmaschine mit einem Schlagwerk | |
| EP3705682A1 (de) | System mit einer erdbohrvorrichtung und einer eingabeeinrichtung, verfahren zum steuern eines betriebs einer erdbohrvorrichtung und verwendung einer erdbohrvorrichtung | |
| WO2018210750A1 (de) | Steuerschalter, steuersystem und verfahren zur bedienung eines krans | |
| EP3878520B1 (de) | Verfahren zum betreiben eines rettungssystems mit einem mobilen rettungsgerät | |
| EP2769282A1 (de) | Bedieneinrichtung für fahrzeuge | |
| DE102018109234A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Steuerung eines Kransystems | |
| WO2021099374A1 (de) | Bau- und/oder materialumschlagsmaschine | |
| DE102009006137A1 (de) | Arbeitsmaschine mit einem Bedienelement zur Steuerung eines beweglichen Arbeitsarms | |
| EP3706092A1 (de) | Bedienvorrichtung für ein nutzfahrzeug | |
| DE102011050831A1 (de) | Bedienteil |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20130227 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20160407 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: BRENDEL HOLDING GMBH & CO. KG |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: BRENDEL HOLDING GMBH & CO. KG |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: BRENDEL, WOLFGANG |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20161028 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 882460 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20170415 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: E. BLUM AND CO. AG PATENT- UND MARKENANWAELTE , CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010013430 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2624862 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20170717 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 Effective date: 20170725 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NO Ref legal event code: T2 Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170706 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170805 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170705 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010013430 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20180108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20100831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20230825 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: NO Payment date: 20230824 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20230825 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20230821 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20230902 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20230822 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20230821 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20230817 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20231027 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20240821 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20240821 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240729 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20240829 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240826 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20240821 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240829 Year of fee payment: 15 |