EP1968355B1 - Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées - Google Patents
Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1968355B1 EP1968355B1 EP20070004759 EP07004759A EP1968355B1 EP 1968355 B1 EP1968355 B1 EP 1968355B1 EP 20070004759 EP20070004759 EP 20070004759 EP 07004759 A EP07004759 A EP 07004759A EP 1968355 B1 EP1968355 B1 EP 1968355B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- induction coil
- turns
- flat
- turn
- coil
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 title claims description 85
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 title claims description 17
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 15
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002826 coolant Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004809 Teflon Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920006362 Teflon® Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000859 α-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 50
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 14
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000005755 formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 6
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005672 electromagnetic field Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001879 copper Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010792 warming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B6/00—Heating by electric, magnetic or electromagnetic fields
- H05B6/02—Induction heating
- H05B6/36—Coil arrangements
- H05B6/362—Coil arrangements with flat coil conductors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B6/00—Heating by electric, magnetic or electromagnetic fields
- H05B6/02—Induction heating
- H05B6/36—Coil arrangements
- H05B6/44—Coil arrangements having more than one coil or coil segment
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an induction coil for inductive heating of workpieces, which has a plurality of turns, wherein at least one of the turns is at least partially flat, according to the preamble of patent claim 1.
- the invention relates to a device for inductive heating of workpieces, comprising a high-frequency generator (HF generator) in signal-operative connection with at least one induction coil, according to the preamble of patent claim 11.
- a high-frequency generator HF generator
- Such devices are used for inductive heating of workpieces containing electrically conductive components, and are used for example for the hardening of workpieces, for joining (welding, gluing) of workpieces or for sealing containers.
- Devices for inductive heating basically consist of a high-frequency generator and an induction coil (or in short: coil), which is usually arranged in a processing head.
- the coil is either flat in a plane or three-dimensional, in particular helical or tunnel-shaped, wound. It usually consists either of copper pipe, which is flowed through with water for cooling, or of stranded wire. Coils made of stranded wire can be cooled by air. It is also known to surround the coil with a Ferrritumhüllung that focuses the electromagnetic field in the direction of application.
- the coil is typically incorporated in a series or parallel resonant circuit that is driven near the resonant frequency to produce current spikes in the coil. Due to the electromagnetic field of the induction coil eddy currents are generated in the electrically conductive components of the workpieces, which lead to a warming.
- the machining head which contains the induction coil, is often arranged above a conveying device, with the aid of which the workpieces to be heated under the coil or through it. It is also possible to immerse the workpieces in the coil or coil in the workpieces.
- An induction coil for inductive heating of workpieces having a plurality of turns is known from US 5,156,237 DE 23 31 004 known.
- a planar winding is surrounded in a radially inner region by a single, radially outer winding, wherein both windings are arranged concentrically in a common plane.
- the two windings are also arranged concentrically in a common plane, wherein the outer winding is arranged in a groove of the inner winding.
- the invention has for its object to further develop an induction coil or a device of the type mentioned in each case that a high concentration and gain effect on the magnetic field generated and thus the heating effect and energy efficiency can be improved.
- Efindungsfer is an induction coil for inductive heating of workpieces, which has a plurality of turns, characterized in that the planar winding extends at least over a covered area of the other turns, wherein either the induction coil flat and with a substantially annular, flat Winding under the other, spirally extending turns is formed, wherein the flat winding is parallel to the coil plane of the remaining turns; or the induction coil has helically extending turns, wherein the two-dimensional turn is substantially cylindrical and arranged within the helically extending turns.
- a device for the inductive heating of workpieces, comprising a high-frequency generator in operative signal connection with at least one induction coil, characterized in that the induction coil is designed as an induction coil according to the invention.
- the effect of a concentrator can be increased many times when the concentrator is designed as an additional, at least partially or sectionally planar winding of the induction coil, that is, connected in series with a number of the remaining coil turns.
- the induction coil consists of several turns, wherein at least one of the turns is at least partially flat, and wherein this planar turn or partial turn of at least a portion of the remaining turns inductively, ie by the electromagnetic field of the other turns being affected.
- the inductive influencing is preferably carried out in that at least a portion of the remaining turns is arranged directly adjacent, parallel or enveloping to the flat (partial) winding, ie, characterized in that the flat winding at least one of the supernatant turns covered area extends.
- the at least one planar (partial) winding is referred to as a "planar winding" in places, without expressing that this winding is completely, in accordance with the invention. must be formed flat in a whole.
- the concentration of the magnetic field of an induction coil according to the invention is preferably further improved by the fact that the flat winding of the coil has a shape, e.g. has a recess or bulge with smaller dimensions than the flat turn itself, which extends in the direction of the workpiece.
- the effect of the magnetic field is focused in this way in the area of the molding on the workpiece.
- Induction coils with such integrated concentrator, which forms one of the coil turns, can have different geometric embodiments:
- the induction coil is planar and formed with a substantially annular, flat winding under the other, spirally extending turns, wherein the planar winding is parallel to the coil plane of the other turns.
- the induction coil is designed as a helical coil with a cylindrical concentrator winding, ie, the planar winding is substantially cylindrical and formed within the arranged helically extending turns, wherein the two-dimensional turn inside for concentration purposes may have a rectangular or conical shape in cross-section.
- the two-dimensional turn extends inwards beyond the remaining turns, so that only a relatively small-scale recess in the form of a small hole for receiving a workpiece remains inside the flat turn. This causes a strong concentration of energy input at this point in the workpiece.
- the induction coil is designed as a tunnel coil, each having a flat partial turn on the two parallel sides of the coil (coil halves), wherein the planar winding for concentrating the field without limiting the generality has a rectangular in cross section molding inward.
- an induction coil in development of the invention is either designed so that one of the remaining turns is soldered to the flat winding, so that these two windings act as a common turn, so are effective, in particular electrically connected.
- the flat winding is contacted only at its two ends by one of the remaining turns and thus acts as an additional turn of the coil, which is connected in series with all other windings.
- an insulating layer can be arranged in a further development of the invention, preferably in the form of a Teflon foil.
- At least the flat winding and particularly preferably all turns of the induction coil according to the invention consist of copper.
- the formations of the flat winding can be flowed through in the invention as well as the other windings for cooling with water or another cooling medium.
- Fig. 1 shows a basic schematic representation of an inventive device 1 for inductive heating of workpieces, For example, for sealing containers or containers 2.
- the device 1 has a high-frequency generator (HF generator) 3 in conjunction with a resonant circuit 4.
- the oscillating circuit 4 comprises a capacitor 5 which is connected in series with an induction coil (inductance) 6 in order to achieve a current increase.
- the capacitance can also be arranged parallel to the inductance and then together with this form a parallel resonant circuit.
- At least the induction coil 6 is arranged in a movable or fixed machining head 1a of the device 1.
- the movable machining head 1a is movable as a whole in the direction of the double arrows A, A 'in order to adapt the device 1 to different dimensions of the workpieces to be heated, in this case the container 2 to be sealed. It is alternatively also possible that the workpiece 2 moves and the machining head 1 is fixed.
- the induction coil 6 In the current-carrying state, the induction coil 6 generates an (electro) magnetic field H, in the region of which a container 2 to be sealed is arranged with a container opening or a sealing film 7 present on the container opening.
- the container 2 is typically moved by means of a conveyor 8, such as a conveyor belt, through the area of the magnetic field H. Thereby, the sealing film 7 is heated and fused with the material of the container 2, so that it is sealed.
- the scope of the device 1 is by no means limited to the sealing of containers or containers, but can be extended to any type of induction heating of workpieces.
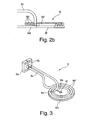
- Fig. 2a shows an overall perspective view of a first embodiment of the inventive induction coil 6.
- the induction coil 6 has connection jaws 6a, 6b, which are connected to a conductor 6c in the form of a copper tube.
- the conductor 6c or the copper tube are in the operation of the induction coil 6 for cooling purposes by a cooling medium, in particular water, flows through.
- the conductor 6c Starting from the connecting jaw 6a, the conductor 6c initially has a straight course, is then angled downwards and then arranged in the form of a planar spiral, that is to say in the form of helical spiral windings 6c ', 6c "with decreasing diameter or winding radius 6c 'of the conductor 6c is then returned to the connection jaw 6b essentially parallel to the initial course of the conductor 6c from the connection jaw 6a.
- a further turn of the induction coil 6 is arranged, which is referred to as a planar winding 6d is formed with a relative to the other conductor 6c enlarged (top) surface is formed.
- the flat winding 6d is formed in the form of an open ring made of copper and has corresponding at 6e a slot and an inner space 6f (recess), the Recording of workpieces to be heated (not shown here) serve
- a considerable concentration and amplification of the magnetic field generated by the induction coil 6 takes place in the region of the free space 6f and below the coil turns.
- the workpieces to be heated are arranged either below the induction coil 6 or within the free space 6f. Further details of the induction coil 6 according to Fig. 2a are in Fig. 2b shown.
- Fig. 2b shows a sectional view of the induction coil 6 according to Fig. 2a along the line II in Fig. 2a ,
- a Teflon film may be arranged.
- the inner spiral turn 6c 'does not contact the two-dimensional turn 6d over the slit 6e, so that the two-dimensional turn 6d effectively cooperates with the inner spiral turn 6c' as one turn of the induction coil 6.
- it functions as a concentrator, through which the magnetic field of the induction coil 6 concentrates on the region below the spiral turns as well as within the free space 6f and noticeably strengthened in this area.
- the inner spiral turn 6c ' also serves to cool the flat turn 6d, which itself is not flowed through by water.
- Fig. 3 shows an overall perspective view of another embodiment of the induction coil 6 according to the invention substantially corresponds to the embodiment according to the FIGS. 2a . b , so that in this case only on relevant differences will be discussed in more detail. While the flat turn 6d in the embodiment according to the FIGS. 2a . b is formed limited by one of the remaining (spiral) turns 6c ', 6c "covered area, the embodiment according to Fig. 3 In that the planar winding 6d extends beyond an area covered by the remaining (spiral) windings 6c ', 6c " Fig.
- the flat winding 6d extends inwardly over the course of the inner spiral turn 6c ', so that at an inner end of the slit 6e only one opposite to the embodiment of FIGS. 2a . b in its dimensions greatly reduced space 6f remains in the form of a hole. This serves to accommodate workpieces of smaller dimensions, with a correspondingly increased concentration of the magnetic field of the induction coil 6 takes place in this area.
- Fig. 4a shows a perspective view of a further embodiment of the induction coil 6 according to the invention.
- this has an angle-shaped holding part 6g, on which the conductor 6c is guided in isolation.
- the windings 6c ', 6c "of the induction coil 6 extend in a helical manner, the two-dimensional turn 6d being substantially cylindrical and arranged within the helically extending remaining windings 6c', 6c" of the induction coil 6.
- the annular planar winding of the embodiments according to the FIGS. 2a . b and 3 also indicates the two-dimensional turn 6d of the embodiment Fig. 4a a slot 6e.
- the two-dimensional turn 6d is electrically insulated by an insulating layer 6h in the form of a Teflon foil, the latter having openings at 6i and 6j at which the two inner of the remaining coil turns 6c 'are electrically conductive with the flat turn 6d connected to both sides of the slot 6 e, preferably soldered, are, so that the flat winding 6 d effectively acts as an additional turn of the induction coil 6.
- Fig. 4b shows the induction coil 6 according to Fig. 4a according to a section along the line II-II in Fig. 4a
- the planar winding 6d has an encircling hollow formation 6k that extends inwards, that is to say in the region of the free space 6f, with respect to the remaining windings 6c ', 6c ", which is rectangular in cross section
- Formations 6k is thus again provided with an area of lesser dimension (smaller diameter) so that a magnetic field generated by the induction coil 6 is concentrated and amplified in the free space 6f, in particular between the formations 6k of the planar coil 6d Fig. 4a and Fig.
- the inner, hollow coil turns 6c ' connected to the openings 6i and 6j with the hollow shape 6k, so that during operation of the induction coil 6, the cooling medium, preferably water, both the coil turns 6', 6c "and the formation 6k and the conductor 6c flows through in a common cooling circuit.
- the cooling medium preferably water
- Fig. 5 shows by means of a representation, the perspective of those in Fig. 4b corresponds to a further embodiment of the induction coil 6 according to the invention.
- the flat winding 6d of the induction coil 6 has an inwardly extending hollow formation 6k, which is cone-shaped in cross-section. This way is opposite to in Fig. 4b shown embodiment of the induction coil 6 reaches a reinforced cooling effect on the flat turn 6d.
- a cylindrical Ferrritumhüllung 9 is shown with a U-shaped inner profile, which surrounds the induction coil 6 and additionally focuses the magnetic field of the coil on the coil interior.
- Analogously designed ferrite cladding can also be used in all other induction coils according to the invention shown.
- the internal formation of the flat turn 6d or its shape 6k is not based on the embodiments according to FIGS FIGS. 4b and 5 limited.
- Various further shaping geometries for generating correspondingly concentrated magnetic fields in the free space 6f of the induction coil 6 are possible without departing from the scope of the present invention.
- Fig. 6 shows an induction coil 6, which is formed as a tunnel coil with two substantially parallel coil halves 6 ', 6 ".
- (Coil) conductor 6c consists of stranded wire and forms in the region of the two coil halves 6', 6" in each case a number of parallel conductor sections which are connected to coil windings via conductor loops 6I, 6I '.
- a planar partial turn 6d, 6d' is arranged, which is contacted at points 6i 'and 6j' (and analogously for the coil half 6", not visible here) through the conductor 6c (eg screwed or soldered to it) so as to act as an additional partial turn of the corresponding coil half 6 ', 6 ".
- the two planar partial turns 6d, 6d' have on their inner side, that is to say, their side facing the respective other coil half hollow shape 6k, 6k ', which according to the present example is rectangular in cross-section, deviating configurations of the formations 6k, 6k' are of course possible, in particular a conical configuration according to FIG Fig. 5 What the expert readily recognizes.
- the formation 6k, 6k ' is in the operation of the induction coil 6 by a cooling medium, preferably of water, flows through.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- General Induction Heating (AREA)
Claims (12)
- Bobine d'induction (6) pour le chauffage par induction de pièces usinées (2), qui présente une pluralité d'enroulements (6c', 6c", 6d),
sachant qu'au moins un (6d) des enroulements est réalisé au moins pour partie plat, caractérisée en ce que l'enroulement plat s'étend au moins sur une région recouverte par les autres enroulements (6c', 6c"), sachant que
soit la bobine d'induction (6) est plane et est réalisée avec un enroulement plat (6d) de forme essentiellement annulaire sous les autres enroulements (6c', 6c") s'étendant en spirale, l'enroulement plat (6d) s'étendant parallèlement au plan de bobine des autres enroulements (6c', 6c"),
soit la bobine d'induction (6) présente des enroulements (6c', 6c") s'étendant en hélice, l'enroulement plat (6d) étant réalisé essentiellement cylindrique et disposé à l'intérieur des enroulements (6c', 6c") s'étendant en hélice. - Bobine d'induction (6) selon la revendication précédente, caractérisée en ce que, pour l'action par induction, au moins une partie des autres enroulements (6c', 6c") est disposée dans le voisinage direct de l'enroulement plat (6d, 6d'), parallèlement à ce dernier et/ou en l'enveloppant.
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisée en ce que l'enroulement plat (6d, 6d') présente une région (6f) ayant des dimensions inférieures à une dimension totale de l'enroulement plat, région qui est destinée à recevoir une pièce usinée.
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que l'enroulement plat annulaire (6d) est ouvert au moyen d'une fente (6e).
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que l'enroulement plat (6d) est réalisé en étant essentiellement limité à une région recouverte par les autres enroulements (6c', 6c").
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisée en ce que l'enroulement plat (6d) est réalisé en s'étendant au-delà d'une région recouverte par les autres enroulements (6c', 6c").
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce qu'un (6c') des autres enroulements est fonctionnellement relié à l'enroulement (partiel) plat (6d), en particulier par brasage.
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce qu'une couche isolante, en particulier sous la forme d'un film de Téflon, est disposée entre l'enroulement (partiel) plat (6d) et les autres enroulements (6c', 6c").
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce qu'au moins l'enroulement (partiel) plat (6d) et en particulier tous les enroulements (6c', 6c" ; 6d) sont réalisés en cuivre.
- Bobine d'induction (6) selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que les autres enroulements (6c', 6c") sont réalisés creux, en particulier tubulaires, et traversés en fonctionnement par un flux de réfrigérant.
- Dispositif (1) pour le chauffage par induction de pièces usinées (2), qui présente un générateur haute fréquence (3) fonctionnellement relié pour la transmission de signaux à au moins une bobine d'induction (6), caractérisé en ce que la bobine d'induction (6) est réalisée selon l'une des revendications précédentes.
- Dispositif (1) pour le chauffage par induction de pièces usinées (2) selon la revendication précédente, caractérisé en ce que la bobine d'induction (6) est entourée, sur son côté opposé à la pièce usinée (2), par une enveloppe (9) en matériau bon conducteur magnétique et mauvais conducteur électrique, notamment en ferrite.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20070004759 EP1968355B1 (fr) | 2007-03-08 | 2007-03-08 | Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20070004759 EP1968355B1 (fr) | 2007-03-08 | 2007-03-08 | Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1968355A1 EP1968355A1 (fr) | 2008-09-10 |
| EP1968355B1 true EP1968355B1 (fr) | 2013-02-27 |
Family
ID=38294109
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20070004759 Active EP1968355B1 (fr) | 2007-03-08 | 2007-03-08 | Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1968355B1 (fr) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102018208400A1 (de) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-11-28 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zum Erwärmen eines Bauteilmaterials, additive Herstellungsanlage und Verfahren zur additiven Herstellung |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011004530A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-06-21 | Mahle International Gmbh | Heizvorrichtung |
| JP6886685B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-27 | 2021-06-16 | トクデン株式会社 | 過熱水蒸気生成装置及び当該装置に用いられる導体管の製造方法 |
| US10917946B2 (en) * | 2017-05-26 | 2021-02-09 | Illinois Tool Works Inc. | Induction heating methods and apparatus |
| DE102018201452A1 (de) * | 2018-01-31 | 2019-08-01 | MTU Aero Engines AG | Vorrichtung zur additiven Herstellung zumindest eines Bauteilbereichs eines Bauteils, Induktionsheizvorrichtung für eine solche Vorrichtung, Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Vorrichtung und Bauteil für eine Strömungsmaschine |
| DE102018203273A1 (de) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | MTU Aero Engines AG | Induktionsheizvorrichtung, Vorrichtung zur additiven Herstellung zumindest eines Bauteilbereichs eines Bauteils mit einer solchen Induktionsheizvorrichtung, Verfahren zum induktiven Erwärmen eines Bauteilbereichs und Bauteil für eine Strömungsmaschine |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE918158C (de) | 1943-11-18 | 1954-09-20 | Siemens Ag | Vorrichtung zum induktiven Erhitzen von flachen Werkstuecken |
| US3017485A (en) * | 1957-11-19 | 1962-01-16 | Asea Ab | Means for electric vacuum furnaces |
| DE1132671B (de) | 1960-11-24 | 1962-07-05 | Telefunken Patent | Vorrichtung zur Erhitzung eines elektrisch leitenden Koerpers im magnetischen Hochfrequenzfeld |
| DE1802524B1 (de) * | 1968-10-11 | 1970-06-04 | Siemens Ag | Vorrichtung zum tiegelfreien Zonenschmelzen eines kristallinen Stabes,insbesondere Halbleiterstabes |
| DE2331004C3 (de) | 1973-06-18 | 1982-02-04 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | Induktionsheizspule zum tiegelfreien Zonenschmelzen |
| DE2357688C2 (de) | 1973-11-19 | 1982-11-18 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | Induktionsheizspule zum tiegelfreien Zonenschmelzen |
| US5048260A (en) | 1989-10-17 | 1991-09-17 | Wm. Wrigley, Jr. Company | Induction sealing machine and package wrapper useful therewith |
| FR2792158B1 (fr) * | 1999-04-09 | 2001-05-18 | Jaeger Regulation | Foyer de cuisson par induction modulable a rayonnement reduit et procede de realisation |
-
2007
- 2007-03-08 EP EP20070004759 patent/EP1968355B1/fr active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102018208400A1 (de) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-11-28 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zum Erwärmen eines Bauteilmaterials, additive Herstellungsanlage und Verfahren zur additiven Herstellung |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1968355A1 (fr) | 2008-09-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1968355B1 (fr) | Bobine d'induction et dispositif destinés au réchauffement par induction de pièces usinées | |
| DE2200489C3 (de) | Induktorvorrichtung für die Hochfrequenz-Induktionserhitzung von Werkstücken | |
| DE102005061670B4 (de) | Verfahren zum induktiven Erwärmen eines Werkstücks | |
| DE10046275A1 (de) | Magnetspule | |
| DE3032118C2 (de) | Matrizenschweißspule | |
| EP2272072B1 (fr) | Bobine et procédé de fabrication d une bobine | |
| DE3836415A1 (de) | Elektromagnetische vorrichtung mit kuehleinrichtung | |
| EP1849169B1 (fr) | Noyau de transformateur a blindage magnetique | |
| EP3924985A1 (fr) | Bobine et procédé de production de cette bobine | |
| EP3876669B1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'un dispositif de chauffage électrique et dispositif de chauffage électrique | |
| EP3329739B1 (fr) | Inductance et dispositif d'inductance | |
| DE102013112325B4 (de) | Ringspule und Herstellungsverfahren für eine Ringspule | |
| EP3529054B1 (fr) | Soudage par induction de tuyaux en matière plastique au moyen d'un agencement de bobines comportant plusieurs bobines | |
| WO2008011907A1 (fr) | Dispositif de soudage pour soudage à l'arc avec amorçage par arc tiré | |
| EP3724360B1 (fr) | Inducteur et procédé pour durcir des crémaillères | |
| EP1614783B1 (fr) | noyau d'inductance pour une galette à chauffer | |
| WO2011054747A1 (fr) | Dispositif de chauffage par induction de pièces constituées d'un matériau électroconducteur | |
| DE102019216194A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Verschweißen von Kantstäben aus einem Kupfermaterial | |
| DE2312555C3 (de) | Induktor zur Druckverformung von Werkstücken mittels eines impulsförmigen Magnetfeldes | |
| DE29601328U1 (de) | Elektromagnetische Induktionsspule | |
| DE3418173A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum elektro-induktiven erhitzen von metallischen werkstuecken | |
| DE2153179C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen induktiven Längs- oder Spiralnahtschweißen von Metallrohren | |
| DE2023869C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Längs- oder SpiralnahtschweiBen von Metallrohren mittels MF-Stromes | |
| DE1145728B (de) | Niedertemperaturheizeinrichtung fuer induktive Erwaermung | |
| DE2609217A1 (de) | Induktor zur druckverformung von metallen durch impulsfoermige magnetfelder |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK RS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20090303 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20090414 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502007011349 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130425 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: TRUMPF HUETTINGER GMBH + CO. KG |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502007011349 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: KOHLER SCHMID MOEBUS PATENTANWAELTE, DE Effective date: 20130801 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502007011349 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: TRUMPF HUETTINGER GMBH + CO. KG, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: HUETTINGER ELEKTRONIK GMBH + CO. KG, 79111 FREIBURG, DE Effective date: 20130801 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502007011349 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: KOHLER SCHMID MOEBUS PATENTANWAELTE PARTNERSCH, DE Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20131128 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502007011349 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20131128 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20220321 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20230308 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230308 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230308 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240320 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240321 Year of fee payment: 18 |