EP1731460B1 - Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée - Google Patents
Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1731460B1 EP1731460B1 EP06017757A EP06017757A EP1731460B1 EP 1731460 B1 EP1731460 B1 EP 1731460B1 EP 06017757 A EP06017757 A EP 06017757A EP 06017757 A EP06017757 A EP 06017757A EP 1731460 B1 EP1731460 B1 EP 1731460B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cylindrical body
- conical elements
- diameter
- effective diameter
- conical
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims description 5
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 14
- 101100450591 Human adenovirus B serotype 3 PVIII gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 101100294463 Human adenovirus E serotype 4 L2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004323 axial length Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010073 coating (rubber) Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002996 emotional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012804 iterative process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007645 offset printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H20/00—Advancing webs
- B65H20/02—Advancing webs by friction roller
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H29/00—Delivering or advancing articles from machines; Advancing articles to or into piles
- B65H29/20—Delivering or advancing articles from machines; Advancing articles to or into piles by contact with rotating friction members, e.g. rollers, brushes, or cylinders
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/40—Shafts, cylinders, drums, spindles
- B65H2404/41—Details of cross section profile
- B65H2404/411—Means for varying cross-section
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2511/00—Dimensions; Position; Numbers; Identification; Occurrences
- B65H2511/20—Location in space
- B65H2511/22—Distance
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2515/00—Physical entities not provided for in groups B65H2511/00 or B65H2513/00
- B65H2515/30—Forces; Stresses
- B65H2515/32—Torque e.g. braking torque
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a cylindrical body of a printing material processing machine according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the present invention relates to a method for changing the effective diameter of a cylindrical body of a printing machine according to the preamble of claim 10.
- a body and such a method are from the US-A-180169 known.
- many different types of cylinders are used, eg inking rollers, dampening rollers, plate cylinders, blanket cylinders and web-guiding cylinders.
- a method for changing a diameter of a cylinder in a printing press is z.
- a circumferentially-variable rotating body for rotary printing presses is described, which comprises a shaft on which a circumferentially adjustable cylinder-like support element is arranged.
- a cylindrical coil spring is disposed over the support member and connected at one side directly or indirectly to the shaft. On the other side of the coil spring is a means for relative movement of the turns of the spring in the circumferential direction to selectively change the diameter of the coil spring.
- the cylinder may be used as a blanket cylinder, a diverter cylinder for diverting a web of material having a diameter adaptable to different paper thicknesses, or as a belt pulley for varying the speed for flat belt transmissions.
- Springs urge segments against the frusto-conical rotating element under the coil spring. By an axial displacement of the rotational movement, the segments are shifted, so that the diameter changes. There are gaps in the outer circumference of the coil spring and between the elements.
- the DE 1 097 452 describes a printing cylinder consisting of a conical support cylinder and an internally conical, detachable jacket for rotary printing machines with two cooperating cylinders.
- a pressure fluid in a helical groove By a pressure fluid in a helical groove, the sleeve is stretched to remove or postpone it to the support cylinder.
- the sleeve fits snugly on the support cylinder when it is not pressurized.
- the pressurized fluid system is complicated and no axial motion device is disclosed.
- An alternative or additional object of the invention is to provide better control of the torque for cylindrical bodies in printing presses.
- a cylindrical body according to the invention of a variable diameter substrate processing machine comprises a plurality of first conical elements and a plurality of second conical elements cooperating with the first conical elements and axially movable with respect to the first conical elements, the effective diameter of the cylindrical body being in Dependent on the axial movement between the first and second conical elements is variable, and is characterized in that the first and second conical elements define the outer surface of the cylindrical body.
- variable effective diameter over the effective width of the cylindrical body is substantially the same for a given positioning of the conical elements.
- Cylindrical here refers to a substantially cylindrical outer surface, which, however, does not have to be completely cylindrically shaped. If the conical elements are moved away from their zero position, z. B. arise a slight rosette shape.
- the first conical elements may have first contact surfaces, which contact second contact surfaces of the second conical elements at least in sections, wherein the first conical elements and the second conical elements are arranged alternately in the circumferential direction of the cylindrical body.
- first and second contact surfaces are in contact over the entire effective width of the cylindrical body.
- the cylindrical body is preferably a rotating cylindrical body, the surface of which in particular has no openings.
- the effective diameter can be adjusted in a simple manner, wherein an outer surface is provided without openings, so that the inventive body z. B. as Paint roller can be used, on the outer surface of which color is transported.
- the cylindrical body is preferably connected to a torque control by means of which the torque of a motor driving the body can be changed or controlled by changing the diameter of the body.
- the cylindrical body according to the invention can, for. Example, as a plate cylinder and a blanket cylinder of a printing press are used, both of which have a variable diameter and are driven independently of each other by a separate motor.
- a plate cylinder and a blanket cylinder of a printing press are used, both of which have a variable diameter and are driven independently of each other by a separate motor.
- the torque of the two motors driving the cylinders can be changed to distribute the torque in an appropriate manner to the two motors.
- This arrangement can help to solve the torque distribution problem that occurs in printing presses with cylinders driven by separate motors driven by each other.
- the number of first and second conical elements is preferably odd and z. B. 3, 5, 7 or 9.
- the cylindrical body according to the invention can be used as a blanket cylinder, as a plate cylinder or as another press cylinder, e.g. Example, as an inking roller or a dampener, be formed whose diameter z. B. for removing, pulling and secure fastening a tubular blanket, a pressure plate or other pressure sleeve on the outer surface of the cylindrical body or to change the amount of liquid supplied (eg., Dampening agent or color) should be adjustable.
- liquid supplied eg., Dampening agent or color
- the cylindrical body may also have an outer gap into which both ends of a pressure plate or blanket placed around the cylindrical body are inserted can be. Subsequently, the effective diameter can be increased to secure the flat pressure plate securely.
- the cylindrical body can also be used to form a web or signatures either directly or via an elastic element, e.g. B. a blanket to contact.
- the cylindrical body may act as a driving roller or a contact driven cylindrical variable radius roller offering the possibility of finely adjusting a rotational speed or varying a section length.
- the web tension can be controlled in an exit area or an entry area or in an area between two transfer columns. With superimposed webs it is also possible to control the speed of the upper and lower webs.
- the diameter of the cylindrical body by changing the diameter of the cylindrical body, it may be brought into contact or out of contact with another object, or the contact pressure between the cylindrical body and another object may be changed.
- the diameter adjuster of a group of conical elements may comprise a motor with an internally threaded shaft and with a second internally threaded shaft fixedly connected to the conical elements.
- a coupling may be provided, which allows in the engaged state, a common rotation of the two shafts and in the disengaged state, the implementation of a setting operation.
- a printing device comprises a first rotating cylindrical body having a plurality of first conical elements and a plurality of second conical elements cooperating therewith relative to the first conical elements Axially movable elements, wherein the first and second conical elements define an outer surface of the body, the diameter of which is variable in dependence on the axial movement between the first and second conical elements.
- the apparatus of the present invention may include a second rotating cylindrical body forming a transfer nip with the first rotating cylindrical body, a first motor for driving the first cylindrical body, a second motor for driving the second cylindrical body, and a torque controller for distributing the torque between comprise first and second motors in response to an effective diameter of the first rotating cylindrical body.
- the second cylindrical body is also preferably a cylindrical body of variable diameter.
- the cylindrical body of variable diameter is preferably laterally register adjustable.
- the effective diameter may be changeable by less than 10% or less than 1% of a minimum effective diameter.
- An inventive method for changing the effective diameter of a cylindrical body in a printing machine wherein the effective diameter of the body is changed by axially moving a plurality of first conical elements with respect to these cooperating second conical elements, provides that a substantially closed outer surface by means of the outwardly facing surfaces of the first and second conical elements is formed.
- the cylindrical body can be rotated and be part of a printing press.
- the torque of a drive motor for the cylindrical body is changed by a change in the effective diameter.
- the method may further comprise a change in the ink or fountain solution supply depending on the diameter of the cylindrical body.
- a printing forme, z As a blanket or a printing plate supported by a change in the effective diameter of the cylindrical body is applied to the cylindrical body.
- the slip at a transfer nip, the web speed, the web tension between two transfer nips and / or the web tension in an exit or entrance area can be controlled.
- the method according to the invention can also be used to bring the surface of the cylindrical body into contact with another object or to remove it and / or to change the contact pressure between the cylindrical body and another object.
- an inventive body can be used as a cutting, folding, or collecting cylinder.
- the method may also provide that the cylindrical body is moved laterally by moving the first and second conical elements in the same direction when the first and second conical elements are independently driven.
- a combination of change in diameter and lateral movement is possible with the body according to the invention or the method according to the invention.
- printing form means any cover of a printing press cylinder, e.g. As a blanket, a printing plate or other roller cover.
- a printing press according to the invention comprises a first cylindrical body of variable diameter comprising opposing first and second conical elements.
- the printing machine further preferably includes a second cylindrical body forming a transfer nip with the first cylindrical body, a first motor driving the first cylindrical body and a second motor driving the second cylindrical body, and torque control for distributing the torque between the first and second motors depending on the diameter of the cylindrical body of variable diameter.
- both cylindrical bodies have a variable diameter.
- variable diameter cylindrical body of the present invention can also be used for side register inspection of a web by moving the first and second conical elements in the same direction without changing the diameter.
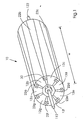
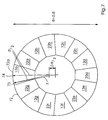
- Fig. 1 shows a cylindrical body 10 with a width (axial length) w and with first conical elements 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d, 12e, 12f and 12g and second conical elements 22a, 22b, 22c, 22d, 22e, 22f and 22g.
- the first conical elements 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d, 12e, 13f and 12g are respectively connected on their inner surface, ie on their surface directed towards the axis of rotation, to a first common actuator 112 which comprises seven arms corresponding to the number of first conical elements. on each of which one of the first conical elements are arranged in the axial direction in such a way that a radial position change is possible.
- the second Conical elements 22a, 22b, 22c, 22d, 22e, 22f and 22g are attached to a second common actuator 122 in the same manner.
- the first and second conical elements are interconnected in such a way that they are movable or displaceable relative to each other, for. B. via a dovetail guide or Profilnutharm 30th
- Fig. 4 is a possible embodiment of an actuator 112 shown schematically in more detail.
- the arms 212 of the actuator 112 are fixedly connected to the first conical elements and to a plate 312, which in turn is fixedly connected to a shaft 412.
- the shaft 412 has an external thread 413 at one end.
- the actuator 112 further includes a drive motor 60 having a drive shaft 62 connected to a female threaded portion 63.
- the internal thread 63 cooperates with the thread 413 of the shaft 412.
- a coupling 64 for selectively engaging and disengaging the shaft 62 with respect to the shaft 412 Fig. 1 shown cylindrical body 10 is to be driven, the clutch 64 is engaged, so that the two shafts 62 and 412 rotate together.
- the motor 60 is preferably stationary so that the shaft 62, with the motor 60 and disengaged clutch 64 disengaged via the female threaded portion 63, causes the male thread 413 to move the shaft 412, plate 312 and arms 212 away from or toward the motor 60 emotional.
- a further drive or motor can also be provided for the rotational driving of the body 10.
- the actuator 122 for the second conical elements may have a mirror-inverted arrangement compared to the actuator 112. However, the actuator 122 may be formed stationary in the axial direction and have no motor, in which case only the first conical elements are axially movable.
- the actuator 112 can therefore cause an axial movement of the first conical elements with disengaged clutch 64 via the motor 60.
- the clutch 64 When the clutch 64 is engaged, the entire cylinder can be driven by the motor 60 or by both Motors are driven when the second actuator 122 is also a motor is arranged.
- actuators there are also other actuators conceivable. However, in one mode of operation, they must enable common rotation of the first and second conical elements and, in a cylinder adjustment mode, axial movement of the first conical elements relative to the second conical elements.
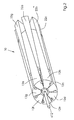
- Fig. 2 shows the cylindrical body 10 of Fig. 1 in a state where the shaft 412 and the first tapered elements 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d, 12e, 12f and 12g are displaced away from the second tapered elements.
- Adjacent conical elements are thereby moved or displaced in opposite axial directions, the movements taking place such that the adjacent conical elements do not touch or overlap in the region of the cone base in order to reduce the diameter of the cylindrical body.
- the effective circumference decreases slightly, so that the diameter also slightly reduces depending on the angle of the slope or the conicity of the elements and the length of the movement path. So very fine diameter adjustments, z. In the range of 1% or less. This reduces the effective width of the cylindrical body, ie the width that can be used during operation.
- Fig. 3 is the in Fig. 1 shown cylinder 10 in a state in which the shaft 412 and the first conical elements 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d, 12e, 12f, 12g have been moved to the second conical elements.
- adjacent conical elements are moved or displaced in opposite axial directions in such a way that the elements do not touch or overlap in the region of the cone tip.
- the effective circumference of the cylinder 10 has thereby increased slightly, so that the effective Diameter is slightly larger. In this case also the effective width of the cylindrical body is reduced.
- the element 12a has an end 88.
- the cylinder may comprise any number of first conical elements, but preferably an odd number, and in particular 3, 5, 7 or 9 conical elements. The same number of second conical elements can be provided.
- a preferred taper of the elements can be determined by drawing a distance of a length L representing an axis. L corresponds to the width of the cylinder to be produced or is greater than this. At one end, a plane orthogonal to the line L is drawn. In the plane, a circle is drawn whose center lies on the axis. At a uniform distance from one another, an odd number n of points on the circumference of the circle corresponding to the desired number of first conical elements is distributed. Any one of these points is connected by two straight lines A, B to the two farthest points on the circle. The two planes formed by the straight lines A and B, respectively, and the midpoint of the path L define the sides of a conical element, but the ends of the conical element can be cut off.
- the length L can z. B. be chosen so that it is three times the actual length of the cylinder, so that two thirds are cut off.
- a 2n corresponding number of conical elements must be prepared and z. B. are positioned slidably together via a dovetail guide or a profile groove, so that they form the cylinder 10.
- the length L can be determined on the basis of design requirements, eg based on the consideration of how much the diameter should be variable and how wide (axial extent) the cylinder should be.
- the contact surfaces of the conical elements are preferably displaceable relative to each other in such a way that the surfaces remain constantly in contact with each other over the effective width of the cylinder.
- a rosette shape may be formed when the first and second conical elements are displaced relative to each other to increase or decrease the diameter.
- This rosette shape the based on Fig. 6 and 7 is explained in detail, however, remains negligible and does not affect the print quality in a printing press.
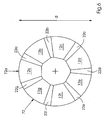
- Fig. 6 shows the end of the in Fig. 1 shown cylindrical body 10 in the zero position with an effective diameter d.
- the outer surface of the body 10 formed by the outer surface of the conical elements 12a, 22a, 12b, 22b, etc. is completely cylindrical.
- the surface portion 72a formed by the element 12a and the outer surface 72 accordingly have the same curvature.
- Fig. 7 shows the end or side 88 of the cylindrical body 10 in FIG Fig. 3 shown state.
- the elements 12a, 12b, 12c, etc. have been moved outwardly toward each other by a movement of the elements towards each other, so that the effective diameter is now d + ⁇ d.
- the effective diameter is formed by the centers 74 of the circular arc line of the conical elements 12a, 22a, 12b, 22b, etc., since these points are farthest from the center of the body 10.
- the distance z of the points 73 remote from the points 74 from the center of the body 10 is slightly smaller than the distance of the points 74 from the center of the body 10, which is evident from the fact that z is smaller than (d + ⁇ d) / 2.
- the outer surface remains substantially cylindrical and therefore remains suitable for almost all applications in a printing press, since the conical elements have little, e.g. B. in the percentage range or less (that is, for example, less than one percent of their axial extent) are shifted from each other.
- the conical elements are constructed in such a way that the effective diameter remains the same over a change over the entire effective width of the body.
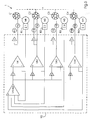
- Fig. 5 is a schematic representation of an embodiment of a printing unit of a printing machine 1.
- a first plate cylinder C1 is at a transfer nip with a first blanket cylinder C2 in operative contact.
- the blanket cylinder C2 forms with a second blanket cylinder C3 a transfer nip through which a Material web, z. B. a paper web is performed.
- a second plate cylinder C4 is in operative contact with the second blanket cylinder C3.
- Each cylinder C1, C2, C3, C4 is driven by its own motor M1, M2, M3, M4.
- Each of the motors has a specified rated power K1, K2, K3 or K4, where Ktotal is the sum of the rated power.
- Each of the cylinders C1, C2, C3, C4 has a variable diameter and preferably comprises similar to the conical elements of FIG Fig. 1 shown cylinder 10 formed conical elements, but with two position controls are provided at each end.
- the power distribution can be z. B. occur when starting the printing press or after several seconds of data acquisition by means of a low-frequency controller with a relatively large dead time.
- the motors M1, M2, M3 and M4 all have the same rated power, and the motor M1 drives all the cylinders since the contact pressure at the transfer nip is so strong that the torque currents I2, I3 and I4 have a very low or no value exhibit.
- P1 would be set to -I1 / Ktotal + I1 / K1, giving a positive number
- P2 would be the negative value of that amount (i.e., multiplied by -1).
- the diameter of the cylinder C1 would be reduced
- P3, P5 and P7 would be set to -I1 / Ktotal
- P4, P6, P8 to I1 / Ktotal so that the cylinder diameter would be increased.
- the torque would be more evenly distributed to the engines, since the contact pressure at the transmission gap formed between the cylinders C1 and C2 would be reduced.
- the values calculated for P1-P8 represent adjustment values which have to be added to the control variables. to achieve the same current in all motors when the scale factor between position and torque or current is 1.
- P3, P5 and P7 would be set to -1 / 4I1 / K1, and P2, P4 and P6 would be set to the negative of that amount.
- I1 / K1 100%.
- a feedback circuit may also be provided to alter the diameter, for example, in an iterative process and thereby equalize the torque currents I1, I2, I3, I4 in motors of similar rated power.
- the side register of the plates can be adjusted by moving the first and second conical elements of a cylinder in the same direction, the diameter remaining unchanged.
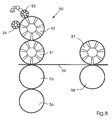
- Fig. 8 shows an offset printing machine 50 with a blanket cylinder 51, a plate cylinder 52, an inking roller 53 and a fountain solution applicator roll 54.
- a blanket cylinder 51 On the blanket cylinder 51, an axially removable, sleeve-shaped blanket be applied, which can be applied by increasing its diameter. Such a blanket is z. B. in the US 5,813,336 described.
- a flat pressure plate On the plate cylinder, a flat pressure plate may be applied, which extends at both ends in an axially extending gap in the cylinder 52 inside. Subsequently, the diameter of the plate cylinder 52 is increased.
- a sleeve-shaped pressure plate may be used, or the cylinder may be formed as a cylinder with a directly imageable outer surface.
- the rollers 53 and 54 may have an outer rubber coating or be uncoated. By changing the diameter of the rollers, the inking and fountain solution supply can be changed, and the rollers 53, 54 can be turned off the printing plate so that they no longer contact them.
- the printing machine 50 further comprises a second blanket cylinder 55 and a second plate cylinder 56, which may be similar to the cylinders 51 and 52, respectively.
- a web 59 - or more superimposed web strands - is or are formed by a between the two blanket cylinders 51, 55 Transmission gap led.
- the web can also be passed through a gap formed between cylindrical bodies 57, 58, wherein the cylindrical bodies 57, 58 may be blanket cylinders of another printing unit.
- the tension in the web between the two columns can be controlled by changing the diameter of the cylindrical bodies, since the tension at the entrance and exit of the nip is controllable.
- the cylindrical body according to the invention can also be used to change the section length in a folder and to change a trajectory of a folding cylinder in response to a change in the cylinder diameter. As a result, signatures of different section lengths can be generated or folded.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Rotary Presses (AREA)
- Rolls And Other Rotary Bodies (AREA)
- Registering, Tensioning, Guiding Webs, And Rollers Therefor (AREA)
- Printing Methods (AREA)
- Winding Of Webs (AREA)
- Advancing Webs (AREA)
Claims (11)
- Corps cylindrique (10) au diamètre variable (d) avec une pluralité de premiers éléments coniques (12a-g) et une pluralité de seconds éléments coniques (22a-g) qui coagissent avec les premiers éléments coniques (12a-g) et peuvent être déplacés axialement par rapport aux premiers éléments coniques (12a-g), sachant que le diamètre effectif (d) du corps cylindrique (10) peut être modifié en fonction du mouvement axial entre les premiers et seconds éléments coniques (12a-g. 22a-g), sachant que
les premiers et seconds éléments coniques (12a-g, 22a-g) définissent la surface extérieure du corps cylindrique (10), caractérisé en ce que le corps cylindrique est un corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée et caractérisé par un second corps cylindrique rotatif qui forme une fente de transfert avec le premier corps cylindrique rotatif (10), par un premier moteur (M1) destiné entraîner le premier corps cylindrique (10), par un second moteur (M2) destiné à entraîner le second corps cylindrique et par une commande de couple destinée à distribuer le couple entre le premier et le second moteur (M1, M2) en fonction d'un diamètre effectif (d) du premier corps cylindrique rotatif (10). - Corps cylindrique selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que le diamètre effectif variable (d) est sensiblement identique sur la largeur effective (w) du corps cylindrique (10) en cas de positionnement donné des éléments coniques (12a-g, 22a-g).
- Corps cylindrique selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que les premiers éléments coniques (12a-g) présentent des premières surfaces de contact qui touchent au moins partiellement des secondes surfaces de contact des seconds éléments coniques (22a-g), sachant que les premiers éléments coniques (12a-g) et les seconds éléments coniques (22a-g) sont disposés alternativement dans le sens périphérique du corps cylindrique (10).
- Corps cylindrique selon la revendication 3, caractérisé en ce que les premières et secondes surfaces de contact sont en contact sur toute la largeur effective du corps cylindrique (10).
- Corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérise par un dispositif de réglage de diamètre (112, 122) pour la commande du diamètre effectif (d) du corps cylindrique (10) par le déplacement des premiers éléments coniques (12a-d) par rapport aux seconds éléments coniques (22a-d).
- Corps cylindrique selon la revendication 5, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de réglage du diamètre (112) comporte un arbre (412) avec un filetage (413).
- Corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que le corps cylindrique (10) est réalisé comme un cylindre porte-plaque (52, 56), un cylindre de blanchet (51, 55), un rouleau encreur (53) ou un rouleau mouilleur (54) d'une machine à imprimer.
- Corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que le registre du corps cylindrique (10) au diamètre variable est réglable latéralement en déplaçant les premiers et seconds éléments coniques du corps dans la même direction.
- Corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que le diamètre effectif (d) peut être modifié de moins de 10 % ou moins d'1% d'un diamètre effectif minimal.
- Procédé de modification du diamètre effectif (d) d'un corps cylindrique (10), sachant que le diamètre effectif (d) du corps est modifié par le déplacement axial d'une pluralité de premiers éléments coniques (12a-g) par rapport aux seconds éléments coniques (22a-g) coagissant avec ceux-ci, comprenant l'étape de procédé suivante :formation d'une surface extérieure sensiblement fermée à l'aide des surfaces tournées vers l'extérieur des premiers et seconds éléments coniques (12a-g, 22a-g), caractérisé en ce que le corps cylindrique est un corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 9, et en ce que le couple du moteur d'entraînement (M1-4) du corps cylindrique (10) est modifié en changeant le diamètre effectif (d).
- Machine à imprimer, en particulier presse rotative à imprimer, caractérisée par un corps cylindrique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 9.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/845,556 US6546867B1 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2001-04-30 | Variable-diameter cylindrically-shaped body |
| EP02007374A EP1254856B1 (fr) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-04-09 | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée |
Related Parent Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02007374A Division EP1254856B1 (fr) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-04-09 | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée |
| EP02007374.8 Division | 2002-04-09 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1731460A1 EP1731460A1 (fr) | 2006-12-13 |
| EP1731460B1 true EP1731460B1 (fr) | 2012-01-25 |
Family
ID=25295507
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02007374A Expired - Lifetime EP1254856B1 (fr) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-04-09 | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée |
| EP06017757A Expired - Lifetime EP1731460B1 (fr) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-04-09 | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02007374A Expired - Lifetime EP1254856B1 (fr) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-04-09 | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6546867B1 (fr) |
| EP (2) | EP1254856B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP4404519B2 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1298532C (fr) |
| AT (2) | ATE349391T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE50209045D1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1262320A3 (fr) * | 2001-05-25 | 2005-02-09 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Aktiengesellschaft | Machine recto-verso comprenant des cylindres porte-blanchet à rayons différents |
| US6684783B2 (en) * | 2001-08-17 | 2004-02-03 | Creo Inc. | Method for imaging a media sleeve on a computer-to-plate imaging machine |
| US20030136643A1 (en) * | 2002-01-18 | 2003-07-24 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Dynamically variable diameter, drive roller mounting system for companioned-belt speed synchronization, and a method of operating the same |
| JP3814546B2 (ja) * | 2002-03-05 | 2006-08-30 | 富士写真フイルム株式会社 | 回転ドラム及び画像記録装置 |
| DE10331943A1 (de) * | 2003-07-15 | 2005-02-17 | Nexpress Solutions Llc | Verfahren zum Wechseln einer Manschette an einem Zylinder und Zylinder mit einer Manschette |
| CN100581966C (zh) * | 2003-12-12 | 2010-01-20 | 三菱重工业株式会社 | 轮转印刷机的折叠机 |
| WO2006032514A2 (fr) * | 2004-09-24 | 2006-03-30 | Hannecard Nv | Ensemble de rouleaux |
| US7871361B2 (en) * | 2005-09-23 | 2011-01-18 | Slyne William J | Rotating roller to shape moving webs |
| US7617773B2 (en) * | 2006-06-01 | 2009-11-17 | Goss International Americas, Inc. | Blanket size verification using drive torque feedback |
| EP2232462B1 (fr) * | 2007-12-21 | 2015-12-16 | Leddartech Inc. | Système et procédé de gestion de stationnement utilisant un système d'éclairage |
| US8250977B2 (en) * | 2008-08-22 | 2012-08-28 | Goss International Americas, Inc. | Printing press with replaceable sleeve shell segments for a cylinder |
| DE102010046962A1 (de) * | 2010-09-29 | 2012-04-26 | Eastman Kodak Co. | Transportanordnung für Bedruckstoffe in einer Druckmaschine |
| US8985016B2 (en) * | 2010-11-25 | 2015-03-24 | Esko-Graphics Imaging, Gmbh | Printing plate sleeve loading and unloading apparatus and method |
| CN102161254B (zh) * | 2011-03-25 | 2012-08-15 | 南京信息工程大学 | 一种卷筒胶印机的印刷滚筒 |
| EP3335879B1 (fr) | 2012-01-31 | 2020-07-01 | HP Indigo B.V. | Application d'un revêtement sur un support |
| CN103434879B (zh) * | 2013-08-30 | 2015-11-18 | 无锡宝南机器制造有限公司 | 夹纸辊结构 |
| EP3110697B1 (fr) | 2014-02-24 | 2019-03-27 | Pregis Innovative Packaging LLC | Dispositif de manipulation de film gonflable |
| CN104355152A (zh) * | 2014-10-30 | 2015-02-18 | 无锡市羊尖盛裕机械配件厂 | 收卷机卷取辊 |
| CN105155240B (zh) * | 2015-10-23 | 2017-09-15 | 绍兴柯桥科强化纤有限公司 | 一种验布机的传动装置 |
| CN106273012B (zh) * | 2016-08-08 | 2017-11-03 | 保定爱廸新能源股份有限公司 | 一种可调直径导轮 |
| CN108244698A (zh) * | 2016-12-29 | 2018-07-06 | 贵州中烟工业有限责任公司 | 卷接机组水松纸的切纸长度调整方法、装置及供给系统 |
| WO2018173703A1 (fr) * | 2017-03-24 | 2018-09-27 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | Appareil de commande |
| CN108975009A (zh) * | 2017-06-05 | 2018-12-11 | 惠州瑞德新材料科技股份有限公司 | 具有张力调整与卷料夹持结构的卷取设备 |
| CN107233959A (zh) * | 2017-06-21 | 2017-10-10 | 河池市森机械有限责任公司 | 辊式破碎机 |
| CN109484007B (zh) * | 2018-07-04 | 2021-01-29 | 重庆宏声印务有限责任公司 | 一种胶印工艺中的可变套筒 |
| CN109179036B (zh) * | 2018-08-24 | 2023-12-29 | 天津市天塑滨海氟塑料制品有限公司 | 一种车削膜张力辊 |
| CN109291671B (zh) * | 2018-09-21 | 2021-01-05 | 杭州钱塘彩印包装有限公司 | 一种增加胶与印刷产品附着力的彩箱制造方法 |
| CN109397733B (zh) * | 2018-10-12 | 2024-02-27 | 北京晟智科技发展有限公司 | 一种带自动控制的有机废弃物挤压装置 |
| CN111270634A (zh) * | 2020-03-25 | 2020-06-12 | 安徽安康塑业有限公司 | 一种可变扫路刷总成 |
| CN111702820B (zh) * | 2020-05-21 | 2022-04-15 | 无锡宏义高分子材料科技有限公司 | 一种水果包装pvc吸塑材料分切机 |
| CN112048839A (zh) * | 2020-09-14 | 2020-12-08 | 董续军 | 一种用于丝绸面料服装缝制的防褶皱辅助装置 |
| CN112309913A (zh) * | 2020-09-28 | 2021-02-02 | 晶澳(扬州)太阳能科技有限公司 | 一种用于湿法刻蚀的带液滚轮及湿法刻蚀方法 |
| CN112297605A (zh) * | 2020-10-10 | 2021-02-02 | 山东华冠智能卡有限公司 | 一种基于石墨烯导电浆料的rfid天线印刷设备 |
| CN113199849A (zh) * | 2021-04-28 | 2021-08-03 | 江苏友迪电气有限公司 | 一种制版机的滚筒组件 |
| CN113211938B (zh) * | 2021-06-11 | 2021-11-30 | 丰县鑫牧网络科技有限公司 | 印刷机用导辊 |
| KR102612721B1 (ko) * | 2023-08-02 | 2023-12-13 | 김현균 | 반도체부품 제조장치 |
| CN117565551B (zh) * | 2024-01-15 | 2024-04-05 | 昆山侨通印务有限公司 | 一种可调节的标签印刷设备 |
| CN117841512B (zh) * | 2024-03-08 | 2024-05-31 | 泉州百胜包装有限公司 | 具有适应性润版系统的瓦楞纸印刷机 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US598107A (en) * | 1898-02-01 | moody | ||
| US180169A (en) * | 1876-07-25 | Improvement in expanding mandrels | ||
| US763251A (en) * | 1904-03-07 | 1904-06-21 | Joseph H Breck | Expansible roll. |
| DE504304C (de) * | 1929-02-21 | 1930-08-19 | Julius Fischer Fa | Relief-Walzendruckmaschine |
| GB445733A (en) * | 1935-01-18 | 1936-04-17 | John Arthur Mumford | An adjustable weave-correcting winch for materials which are in open widths and long lengths |
| US2715024A (en) * | 1951-03-07 | 1955-08-09 | Johnson & Johnson | Strip feeding device |
| DE1097452B (de) * | 1955-03-30 | 1961-01-19 | George Edmond Brackenbury Abel | Druckzylinder fuer Rotationsdruckmaschinen |
| CH345023A (de) * | 1955-03-30 | 1960-03-15 | Brackenburry Abell George Edmo | Rotationsdruckmaschine |
| GB1203320A (en) * | 1968-12-24 | 1970-08-26 | Pako Corp | Improvements in or relating to rollers for transporting sheet material |
| CH557451A (de) * | 1972-10-26 | 1974-12-31 | Escher Wyss Ag | Druckwalze. |
| US4141517A (en) * | 1978-03-22 | 1979-02-27 | Martin Automatic, Inc. | Apparatus for adjusting the lateral position of a rolled web |
| AU525559B2 (en) * | 1979-04-17 | 1982-11-11 | Dusan Sava Lajovic | Printing drum with adjustable blankets |
| USD267016S (en) | 1980-03-07 | 1982-11-23 | Hermes Precisa International S.A. | Noise abatement cover for typewriter |
| DE3024893A1 (de) * | 1980-07-01 | 1982-01-28 | Continental Gummi-Werke Ag, 3000 Hannover | Walze fuer die druckbehandlung von warenbahnen |
| EP0110751B1 (fr) * | 1982-10-29 | 1988-01-07 | Newtec International | Dispositif d'étirage |
| DE19541541A1 (de) | 1995-11-08 | 1997-05-15 | Focke & Co | Verpackung für insbesondere Zigaretten sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen derselben |
| US5813336A (en) | 1995-12-22 | 1998-09-29 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Printing unit with axially removable printing sleeves |
| US5711222A (en) * | 1996-06-14 | 1998-01-27 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Method and apparatus for mounting a flat printing plate on a cantilevered plate cylinder of a printing press |
| DE19649324C2 (de) * | 1996-11-28 | 1998-09-17 | Koenig & Bauer Albert Ag | Umfangsveränderbarer Rotationskörper |
| US6110093A (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2000-08-29 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Variable diameter roller |
-
2001
- 2001-04-30 US US09/845,556 patent/US6546867B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2002
- 2002-04-05 CN CNB021061637A patent/CN1298532C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-04-09 DE DE50209045T patent/DE50209045D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-09 AT AT02007374T patent/ATE349391T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-04-09 AT AT06017757T patent/ATE542765T1/de active
- 2002-04-09 EP EP02007374A patent/EP1254856B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-09 EP EP06017757A patent/EP1731460B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-10 DE DE10215705A patent/DE10215705A1/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2002-04-30 JP JP2002128562A patent/JP4404519B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1254856B1 (fr) | 2006-12-27 |
| CN1383980A (zh) | 2002-12-11 |
| US6546867B1 (en) | 2003-04-15 |
| DE50209045D1 (de) | 2007-02-08 |
| DE10215705A1 (de) | 2002-10-31 |
| ATE542765T1 (de) | 2012-02-15 |
| EP1254856A2 (fr) | 2002-11-06 |
| JP2003040496A (ja) | 2003-02-13 |
| CN1298532C (zh) | 2007-02-07 |
| JP4404519B2 (ja) | 2010-01-27 |
| ATE349391T1 (de) | 2007-01-15 |
| EP1254856A3 (fr) | 2004-01-21 |
| EP1731460A1 (fr) | 2006-12-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1731460B1 (fr) | Corps cylindrique d'une machine de traitement de matériau de bande imprimée | |
| DE19742461C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Antrieb einer Bogendruckmaschine mit Mehrmotorenantrieb | |
| EP3043994B1 (fr) | Machine à imprimer pour impression de papiers-valeur et procédé pour remplacer une forme imprimante et pour démarrage de la presse | |
| EP1493563A2 (fr) | Machine d'impression offset | |
| DE20221937U1 (de) | Rollenrotationsdruckmaschine | |
| EP0970807B1 (fr) | Rouleau avec un diamètre variable | |
| EP0355595A2 (fr) | Appareil pour plier | |
| EP1393901A2 (fr) | Dispositif de réglage d'une pression d'impression d'un rouleau monté de facon réglable | |
| EP0956973A2 (fr) | Blanchet pour l'impression avec transfert complet de l'encre | |
| DE3789351T2 (de) | Apparat zum Steuern der Papiergeschwindigkeit in einer Druckstation einer Formulardruckmaschine. | |
| EP0516649B1 (fr) | Machine rotative d'impression avec appareil de pliage | |
| EP3431291B1 (fr) | Machine d'impression avec des groupes d'impression flexographique arrangés en série et procédé pour opérer une telle machine d'impression | |
| EP1291175B1 (fr) | Cylindre porte-plaque pour plusieurs images | |
| DD249887A5 (de) | Kupplung fuer bogendruckrotationsmaschinen | |
| EP0453788B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'enclenchement, de déclenchement et de réglage des rouleaux d'encrage | |
| DE10202385A1 (de) | Druckwerk mit variabler Drucklänge und Umfangsregisterverstellung | |
| EP0019697B1 (fr) | Dispositif de réglage du repérage latéral et circonférentiel sur les machines à imprimer rotatives | |
| EP3287281B1 (fr) | Outil d'usinage et machine à imprimer d'étiquettes pourvue d'un tel outil d'usinage | |
| EP1871603B1 (fr) | Systemes d'encrage d'une presse d'imprimerie et procede permettant de faire fonctionner un systeme d'encrage | |
| DE19616629A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Umstellung eines produktführenden Zylinders am Falzapparat | |
| EP3287280B1 (fr) | Outil d'usinage et machine à imprimer d'étiquettes pourvue d'un tel outil d'usinage | |
| DE102017203560B4 (de) | Druckmaschine | |
| EP3370965B1 (fr) | Entraînement pour presses à feuilles rotatives | |
| EP2759397A2 (fr) | Dispositif de matriçage rotatif avec système de serrage et réglage d'angle | |
| EP2090435A1 (fr) | Entraînement rotatif et axial, en particulier pour un cylindre distributeur d'encre |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060825 |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 1254856 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20070724 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 1254856 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 542765 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 50215365 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120329 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Owner name: GOSS INTERNATIONAL AMERICAS, INC. Free format text: GOSS INTERNATIONAL AMERICAS, INC.#121 BROADWAY STREET#DOVER, NH 03820 (US) -TRANSFER TO- GOSS INTERNATIONAL AMERICAS, INC.#121 TECHNOLOGY DRIVE#DURHAM, NH 03824 (US) Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: KIRKER & CIE S.A. |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120525 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120426 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20120423 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: GOSS INTERNATIONAL AMERICAS, INC. Effective date: 20120430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120430 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20121026 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 50215365 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20121026 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120506 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 542765 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120409 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20130429 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20130409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120125 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120409 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20140429 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20140417 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140430 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50215365 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20151231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50215365 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: LAVOIX MUNICH, DE |