EP0260546B1 - Machine à forger - Google Patents
Machine à forger Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0260546B1 EP0260546B1 EP87112936A EP87112936A EP0260546B1 EP 0260546 B1 EP0260546 B1 EP 0260546B1 EP 87112936 A EP87112936 A EP 87112936A EP 87112936 A EP87112936 A EP 87112936A EP 0260546 B1 EP0260546 B1 EP 0260546B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- ram
- tie rod
- cylinder
- crosspiece
- piston
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000005242 forging Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 22
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21J—FORGING; HAMMERING; PRESSING METAL; RIVETING; FORGE FURNACES
- B21J7/00—Hammers; Forging machines with hammers or die jaws acting by impact
- B21J7/02—Special design or construction
- B21J7/14—Forging machines working with several hammers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21J—FORGING; HAMMERING; PRESSING METAL; RIVETING; FORGE FURNACES
- B21J13/00—Details of machines for forging, pressing, or hammering
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21J—FORGING; HAMMERING; PRESSING METAL; RIVETING; FORGE FURNACES
- B21J13/00—Details of machines for forging, pressing, or hammering
- B21J13/02—Dies or mountings therefor
- B21J13/03—Die mountings
Definitions
- the invention relates to a forging machine known as a radial forming machine, with four x-shaped arranged in a working plane and radial to the system axis, i.e. along the axis along which the workpiece passes through the forging machine, movable impacts with tools.
- the tools in the stroke diameters of the plungers form a closed caliber
- the tools are connected to the plungers by crosspieces which form a support and which are adjustable across the plungers in the working plane, the adjustment depending on the setting of the stroke end position in such a way
- the extent is such that each workpiece with that part of its working surface which exceeds the caliber dimension in the stroke end position is covered by a side surface of one neighboring tool and even with its side surface which covers the part of the working surface of the other neighboring tool which exceeds the caliber dimension in the stroke end position.
- the cross pieces are connected to the plungers by releasable clamping devices which prevent the cross piece and plunger from being mutually braced by the force of a spring and the loosening of the clamping device by a piston acting against the spring force. Effect cylinder unit.
- a forging machine of this type is known from EP-A 0 228 030. This document falls under Article 54 (3) EPC and is therefore of no importance for the question of inventive step.
- the clamping device of the above Forging machines require a considerable amount of construction, and their arrangement in the vicinity of the tools and the workpiece with its heat radiation is disadvantageous, while the adjustment of the crosspiece relative to the plunger takes place via a shaft which, because of the larger space requirement on the plunger side facing away from the crosspiece arranged drive of the adjusting device connects to the cross piece on the end face of the plunger and penetrates an axial bore in the plunger.
- the object of the invention is a clamping and adjusting device between the cross piece and its plunger, which is structurally less complex and removed from the area of direct heat radiation.
- This object is achieved on the basis of the forging machine mentioned at the outset in that each plunger and the crosspiece assigned to it are penetrated by a tie rod provided with collars, which with the bundles the crosspiece, the plunger and a tensioned spring underlaid on the collar on the free plunger side when tensioned of the cross piece against the plunger comprises that on the collar supported by the spring there is a piston which can be acted upon by the spring force in a cylinder connected to the plunger and then releases the tension of the cross piece against the plunger, and that the tie rod is above that supported by the spring
- the collar also extends and is non-rotatably coupled with a rotary drive supported on the machine frame via the crossbeam, the stopper or the cylinder for adjusting the stroke position, but is axially displaceable.
- the spring and the piston which can be acted upon against the spring force, can act as elements of the clamping device on the side of the plunger facing away from the tool with a crosspiece, that is to say in the space that is less distant from heat radiation and less constricted Area must be relocated.
- the collar of the tie rod associated with the cross piece which braces the cross piece against the plunger, is designed according to a further feature of the invention as a lever arm which is provided with a pin parallel to the tie rod and a pivot piece on the pin, the cross piece having a is provided transversely to its sliding direction guide, in which the link piece engages.
- the cross piece with the link guide, the lever with the link piece and the tie rod are particularly suitable in this design to transmit high clamping and displacement forces.
- the surface of the cross piece which is only occupied by the one collar of the tie rod, and which is protected by a cover carrying the tool, also permits a simple, robust design of the connection of the cross piece with the plunger in terms of production technology.
- the cross piece is guided opposite the plunger by guide blocks which lie in grooves in one part (plunger, cross piece) and lead in the adjustment of the cross piece to provide space in the other part.
- form-locking bodies are provided which lie in recesses in the plunger and the cross piece and are provided on their opposing end faces with fine toothings which engage with one another when the cross piece is clamped against the plunger.
- a spring cup which can be connected to the plunger is provided according to a further development of the invention, in which the spring or the spring assembly is arranged between spring plates and the axial bearings that support them the cover to the spring cup is designed as an annular cylinder in which there is an annular piston which is in operative connection with the axial bearing which is associated with the spring plate connected to the collar of the tie rod.
- the arrangement of the axial bearing enables the tie rod to be rotated to adjust the crosspiece laterally relative to the plunger as soon as the spring or spring assembly is compressed by actuation of the piston, the crosspiece is pressed off the plunger and the fine toothing of the form-locking body is disengaged.
- the tie rod in addition to bracing the cross piece in a simple manner to the same
- it is provided with a multi-spline pin at its end which projects outward from the tappet and with which it engages in a multi-spline hub which has a coupling with a rotary drive which compensates for radial misalignment connected is.
- a gearwheel moved by two counter-rotating plungers via racks is provided as the rotary drive.
- a ram can be provided with a cylinder which is axially movably guided in the machine frame and provided with a central shaft, the ring piston associated with the cylinder and surrounding the shaft being supported by a crossbar which is adjustable relative to the stroke position relative to the machine frame.
- a plunger which is guided in the bore of a cylinder connected to the machine frame and provided with a shaft can also be provided, a plug surrounding the piston shaft and closing the cylinder bore being supported by a crossbar which can be adjusted relative to the stroke position relative to the machine frame.
- a piston guided by a cylinder and provided with a shaft passing through the cylinder base can be provided as the tappet, the cylinder being adjustable in the machine frame for adjusting the stroke position.
- a central shaft which is guided in the machine frame and is provided with an annular flange, can act on the piston-cylinder units, the piston-cylinder units using a crossbar that is adjustable relative to the machine frame for adjusting the stroke position are supported.
- the shaft whether it is part of a piston or part of a cylinder, or whether it forms the tappet itself, is drilled through to receive the tie rod.
- the rotary actuator connected to the tie rod is suitably stored in a bracket for the cross member so that it participates in the stroke position adjustment with the cross member, so that between the tie rod and its rotary actuator only the working stroke has to be compensated and not the total stroke as it is when the rotary actuator is supported would be required directly on the machine frame.
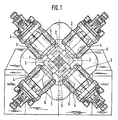
- a forging 1 can be seen in cross section in FIG.
- the cross-sectional size is determined from the respective stroke end position of the tools 2 and the position of the tools 2 relative to one another, with the unused width of the working surface of a tool 2 being covered by the side surface of the adjacent tool 2 in a stroke end position. Shown in dashed lines in FIG. 1 are the largest cross section, determined by the tool width and the smallest, by the greatest possible mutual overlap of the tools 2.
- the tools 2 are carried and moved by rams 3, which are arranged in the machine frame 4 so as to be axially movable.
- plungers 3 are provided, which are x-shaped in a plane perpendicular to the system axis, i.e. he axis along which the workpiece 1 passes through the forging machine, is arranged and moved radially to the workpiece 1.
- the setting of the tools 1 to the plungers 3 is carried out by cross pieces 5, which form 3 supports for the plungers, so that the cross pieces 5 can be adjusted and locked transversely to the plunger axes in the working plane.
- the stroke end position of a tool 2 which is dependent on the desired cross section, determines the adjustment dimension of an adjacent tool that covers the working surface of the first tool 2 with its unused width with its side surface.
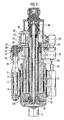
- the plunger 3 is designed as a cylinder 6, which in the machine frame 4 in guide pieces 7 and 8, which can be designed as round or surface guides - the latter around the cylinder 6 in the machine frame 4 against rotation secure - is led.
- a shaft 9 is inserted into the perforated cylinder base, which is connected to the cylinder 6 by a threaded nut 10.
- An annular piston 11 surrounding the shaft 9 is supported on the machine frame 4 via a crossmember 12.
- 4 anchors are used in the machine frame, which are extended to form spindles 13 with threaded shafts 14.
- In the crossbeams 12 are externally toothed 19 and internally threaded nuts 20 rotatably supported and held by split bearing plates 21.
- the four nuts 20 of a cross member 12 are rotated together by a ring gear 22 which can be rotated with balls 23 on a bearing ring 24 centered and fastened on the cross member 12.
- a motor 28 with pinion is provided to drive the ring gear 22.
- a plate 31 is placed on the cross member 12, into which the cylinders 32 are incorporated, which the retracting piston 30 on take and a further cross member 33 is connected to the shaft 9, via which the pistons 30 limit the stroke of the plunger 3 and cause its retraction.
- the shaft 9 is drilled through its entire length and receives in its bore 35 a tie rod 36 which is provided with collars 37 and 38.
- the tie rod 36 also passes through the cross piece 5 placed on the end face of the plunger 3.
- the collar 37 placed on the end of the tie rod 36 and connected to it by wedges 39 abuts the cross piece 5.
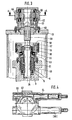
- the collar 37 is designed as a lever which, with a pin 40 and a link piece 41 placed on the pin 40, engages in one leg of a T-shaped opening of the cross piece 5 designed as a link guide 42, while the other leg 43 penetrates the tie rod 36 designed.
- Guide blocks 44 which guide the cross piece 5 provided with a guide groove 45, are embedded in cutouts on the end face of the plunger 3.
- Form-fit bodies 46 are inserted into further cutouts on the end face of the plunger 3 and corresponding cutouts in the cross piece 5, which are provided with fine teeth 47 on their opposite end faces.
- the recess in the cross piece 5, which receives the collar 37, is closed by a cover 48 which encloses the collar 37 and at the same time serves as a support plate for the tool 2.
- a spring head 50 On the shaft 9, a spring head 50 is attached, which receives a spring assembly 51.
- Spring plates 52 and 53 support the spring assembly 51 via axial bearings 54 and 55 on the one hand on the bottom of the spring cup 50 and on the one hand on the collar 38 of the armature 36.
- a cover 56 of the spring cup 50 is designed as an annular cylinder 57 in which an annular piston 58 is guided, in the case of which Actuation over the collar 38 of the armature 36 is axially displaced.
- the tie rod 36 presses the cross piece 5 off the plunger 3 above the cover 48, the fine toothing 47 of the form-locking body 46 disengaging, and by rotating the tie rod 36 over the collar 37 of the pin 40 and the link piece 41, the cross piece 5 in the working plane can be moved transversely to the ram axis.
- the tie rod 36 is extended and designed as a splined pin 59, and this engages in a splined hub 60 which is axially fixed in a bracket 61 with radial play.
- the console 61 is placed on the cross member 16.
- a gear 62 is also mounted, which is rotatably connected to the splined hub 60 via an Oldham coupling 63.
- the gear 62 is driven by two oppositely operating plungers 64 and 65 which are connected to racks 66 which engage in the gear 62.
- the actuation of the turning device i.e. it is only possible to apply the pistons 64 when the annular piston 58 is also acted on.
- the displacement of the tools 2 by acting on the pistons 64 and 65 takes place in dependence on the stroke position setting of the adjacent plunger 3 via the motor 28 as described.
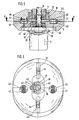
- FIGS. 7 to 8 show further exemplary embodiments in a schematic illustration, the same reference numerals being used for the corresponding parts.
- the machine frame 4 is designed as a cylinder or is permanently connected to the cylinder.
- the plunger 3a is designed as a piston 68 and the cylinder is closed by a plug 15 which is penetrated by the shaft 69 of the piston 68.
- the plug 15 is connected to a crossbar 17 which is adjustable along the spindles 13 for adjusting the stroke position.
- the plunger 3b designed as a piston 70 is guided in the embodiment shown in FIG. 8 in a cylinder 71 which is guided and adjustable in the machine frame 4, for which purpose the cylinder 71 is provided with a neck 72 which is threaded by one in the machine frame mounted nut 73 is adjustable for adjusting the stroke position.
- the plunger 3c is guided directly in the machine frame 4.
- the piston-cylinder units 74 moving the plunger 3c, which are connected to the plunger 3c via an annular flange 75, are supported on the machine frame 4 by means of a traverse 76, for which purpose the crossbar 76 can be adjusted along spindles in order to adjust the stroke position.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Forging (AREA)
- Disintegrating Or Milling (AREA)
- Formation And Processing Of Food Products (AREA)
- Photoreceptors In Electrophotography (AREA)
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT87112936T ATE58657T1 (de) | 1986-09-16 | 1987-09-04 | Schmiedemaschine. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3631439 | 1986-09-16 | ||
| DE3631439 | 1986-09-16 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0260546A2 EP0260546A2 (fr) | 1988-03-23 |
| EP0260546A3 EP0260546A3 (en) | 1988-09-07 |
| EP0260546B1 true EP0260546B1 (fr) | 1990-11-28 |
Family
ID=6309661
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP87112936A Expired - Lifetime EP0260546B1 (fr) | 1986-09-16 | 1987-09-04 | Machine à forger |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4813263A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0260546B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPH0761521B2 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE58657T1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3766454D1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6956032B1 (en) * | 1986-04-18 | 2005-10-18 | Carnegie Mellon University | Cyanine dyes as labeling reagents for detection of biological and other materials by luminescence methods |
| DE4143175A1 (de) * | 1991-12-30 | 1993-07-01 | Hasenclever Maschf Sms | Schmiedemaschine |
| DE4143176A1 (de) * | 1991-12-30 | 1993-07-01 | Hasenclever Maschf Sms | Schmiedemaschine |
| DE4444498A1 (de) * | 1993-12-16 | 1995-06-22 | Hasenclever Maschf Sms | Schmiedemaschine |
| JPH07121429B2 (ja) * | 1993-12-16 | 1995-12-25 | エス エム エス ハーゼンクレヴァー ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | 鍛造機 |
| DE4444493A1 (de) * | 1993-12-16 | 1995-06-22 | Hasenclever Maschf Sms | Schmiedemaschine |
| US20080307709A1 (en) * | 2007-06-15 | 2008-12-18 | Stull Edward J | Dual swing powered gate actuator |
| CN102601280A (zh) * | 2011-01-24 | 2012-07-25 | 西安宝信冶金技术有限公司 | 一种多锤头高频精密径向同步锻造方法 |
| CN107931500A (zh) * | 2017-11-14 | 2018-04-20 | 江苏海威锻造有限公司 | 环形支撑式液压径向锻造机 |
| IT201900012960A1 (it) * | 2019-07-26 | 2021-01-26 | Mecolpress S P A | Apparecchiatura per lo stampaggio di materiali. |
| WO2021064740A1 (fr) * | 2019-10-03 | 2021-04-08 | Shyam Newar | Presse hydraulique à combinaison périphérique pour la forge et son procédé de fabrication |
| CN113680941B (zh) * | 2021-08-03 | 2024-01-12 | 新余市本通特锻有限公司 | 一种双向锤击式锻压机 |
| CN113828694B (zh) * | 2021-10-29 | 2024-04-12 | 领先科技(东台)有限公司 | 一种调节限位式马达顶压成型机构 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE555710A (fr) * | 1956-03-19 | |||
| GB1187587A (en) * | 1966-09-13 | 1970-04-08 | Davy & United Eng Co Ltd | Improvements in or relating to the Securing of a Press Tool in a Press |
| DE1908362A1 (de) * | 1969-02-20 | 1970-09-10 | Sack Gmbh Maschf | Schmiedemaschine mit verstellbaren Schmiedesaetteln |
| DE1908361A1 (de) * | 1969-02-20 | 1970-09-10 | Sack Gmbh Maschf | Schmiedemaschine |
| DE1960418A1 (de) * | 1969-12-02 | 1971-06-24 | Horst Schenk | Werkzeug fuer Schmiedemaschine |
| AT329349B (de) * | 1973-11-15 | 1976-05-10 | Gfm Fertigungstechnik | Schnellaufende kurzhub-schmiedepresse |
| EP0228030B1 (fr) * | 1986-01-02 | 1991-04-24 | SMS Hasenclever GmbH | Machine de forgeage |
-
1987
- 1987-09-04 AT AT87112936T patent/ATE58657T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1987-09-04 EP EP87112936A patent/EP0260546B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-09-04 DE DE8787112936T patent/DE3766454D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-09-16 US US07/096,998 patent/US4813263A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1987-09-16 JP JP62229946A patent/JPH0761521B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE58657T1 (de) | 1990-12-15 |
| EP0260546A3 (en) | 1988-09-07 |
| EP0260546A2 (fr) | 1988-03-23 |
| DE3766454D1 (de) | 1991-01-10 |
| JPS6376732A (ja) | 1988-04-07 |
| US4813263A (en) | 1989-03-21 |
| JPH0761521B2 (ja) | 1995-07-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE10026829C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Festspannen eines Werkstücks mit unebener Oberfläche | |
| EP2258495B1 (fr) | Tête de découpage fin hydraulique pour une presse et procédé pour mouvoir cette dernière | |
| EP0260546B1 (fr) | Machine à forger | |
| EP0228030B1 (fr) | Machine de forgeage | |
| EP3875215B1 (fr) | Plaque de serrage à point zéro, machine-outil pourvue d'une telle plaque de serrage et dispositif de serrage | |
| DE2231579B2 (de) | Schmiedepresse, insbesondere Gesenkschmiedepresse | |
| EP0742063B1 (fr) | Tourelle porte-outil | |
| EP3569354A1 (fr) | Dispositif de fixation de pièces à usiner et installation d'usinage | |
| DE3804163A1 (de) | Druckmittelbetriebene stell- oder arbeitsvorrichtung | |
| EP0228658B1 (fr) | Machine de forgeage | |
| CH656574A5 (de) | Formenschliesseinheit einer spritzgiessmaschine. | |
| DE2655284A1 (de) | Pneumatisch oder hydraulisch und einseitig oder doppelt beaufschlagbare kolben-zylinder-vorrichtung | |
| DE4446692C2 (de) | Formschließeinrichtung für eine Kunststoffspritzgießmaschine | |
| DE3729631A1 (de) | Schmiedemaschine | |
| EP0549825B1 (fr) | Machine à forger | |
| EP0659501B1 (fr) | Machine à forger | |
| DE3738217C2 (de) | Schmiedemaschine | |
| DE4444498A1 (de) | Schmiedemaschine | |
| DE19833113A1 (de) | Lagerung für einen Zylinder in einer Druckmaschine | |
| DE1752698B2 (de) | Vorrichtung fuer den laengsvorschub eines schlanken, gegen ausknicken zu sichernden druckerzeugungsstempels fuer das hydrostatische strangpressen o.dgl. maschinenelementes bzw. werkstueckes | |
| DE3316364A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum sichern des stoessels einer werkzeugmaschine, insbesondere einer grosspresse | |
| DE4143175A1 (de) | Schmiedemaschine | |
| EP0653258B1 (fr) | Machine à forger | |
| DE4143176A1 (de) | Schmiedemaschine | |
| DE8624743U1 (de) | Schmiedemaschine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870904 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB IT SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB IT SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19890307 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: SMS HASENCLEVER GMBH |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB IT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19901128 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 58657 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19901215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3766454 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19910110 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19910311 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19940817 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19940825 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19940831 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19940906 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19950904 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19950904 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19950904 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19960531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19960601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050904 |