CN1235675C - 催化反应器 - Google Patents
催化反应器 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1235675C CN1235675C CNB018063683A CN01806368A CN1235675C CN 1235675 C CN1235675 C CN 1235675C CN B018063683 A CNB018063683 A CN B018063683A CN 01806368 A CN01806368 A CN 01806368A CN 1235675 C CN1235675 C CN 1235675C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- gas flow
- catalytic reactor
- flow channels
- gas
- reaction
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J19/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J19/32—Packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit or module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J19/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J19/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J19/248—Reactors comprising multiple separated flow channels
- B01J19/249—Plate-type reactors
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J8/00—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes
- B01J8/02—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes with stationary particles, e.g. in fixed beds
- B01J8/0207—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes with stationary particles, e.g. in fixed beds the fluid flow within the bed being predominantly horizontal
- B01J8/0214—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes with stationary particles, e.g. in fixed beds the fluid flow within the bed being predominantly horizontal in a cylindrical annular shaped bed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J8/00—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes
- B01J8/02—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes with stationary particles, e.g. in fixed beds
- B01J8/06—Chemical or physical processes in general, conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles; Apparatus for such processes with stationary particles, e.g. in fixed beds in tube reactors; the solid particles being arranged in tubes
- B01J8/067—Heating or cooling the reactor
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B3/00—Hydrogen; Gaseous mixtures containing hydrogen; Separation of hydrogen from mixtures containing it; Purification of hydrogen
- C01B3/02—Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen
- C01B3/32—Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen by reaction of gaseous or liquid organic compounds with gasifying agents, e.g. water, carbon dioxide, air
- C01B3/34—Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen by reaction of gaseous or liquid organic compounds with gasifying agents, e.g. water, carbon dioxide, air by reaction of hydrocarbons with gasifying agents
- C01B3/38—Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen by reaction of gaseous or liquid organic compounds with gasifying agents, e.g. water, carbon dioxide, air by reaction of hydrocarbons with gasifying agents using catalysts
- C01B3/384—Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen by reaction of gaseous or liquid organic compounds with gasifying agents, e.g. water, carbon dioxide, air by reaction of hydrocarbons with gasifying agents using catalysts the catalyst being continuously externally heated
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2/00—Preparation of hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons containing a smaller number of carbon atoms
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2208/00—Processes carried out in the presence of solid particles; Reactors therefor
- B01J2208/00008—Controlling the process
- B01J2208/00017—Controlling the temperature
- B01J2208/00106—Controlling the temperature by indirect heat exchange
- B01J2208/00309—Controlling the temperature by indirect heat exchange with two or more reactions in heat exchange with each other, such as an endothermic reaction in heat exchange with an exothermic reaction
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2208/00—Processes carried out in the presence of solid particles; Reactors therefor
- B01J2208/00008—Controlling the process
- B01J2208/00017—Controlling the temperature
- B01J2208/00389—Controlling the temperature using electric heating or cooling elements
- B01J2208/00398—Controlling the temperature using electric heating or cooling elements inside the reactor bed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2208/00—Processes carried out in the presence of solid particles; Reactors therefor
- B01J2208/00008—Controlling the process
- B01J2208/00017—Controlling the temperature
- B01J2208/00389—Controlling the temperature using electric heating or cooling elements
- B01J2208/00415—Controlling the temperature using electric heating or cooling elements electric resistance heaters
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/00049—Controlling or regulating processes
- B01J2219/00051—Controlling the temperature
- B01J2219/00074—Controlling the temperature by indirect heating or cooling employing heat exchange fluids
- B01J2219/00117—Controlling the temperature by indirect heating or cooling employing heat exchange fluids with two or more reactions in heat exchange with each other, such as an endothermic reaction in heat exchange with an exothermic reaction
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2451—Geometry of the reactor
- B01J2219/2453—Plates arranged in parallel
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2451—Geometry of the reactor
- B01J2219/2456—Geometry of the plates
- B01J2219/2458—Flat plates, i.e. plates which are not corrugated or otherwise structured, e.g. plates with cylindrical shape
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2451—Geometry of the reactor
- B01J2219/2456—Geometry of the plates
- B01J2219/2459—Corrugated plates
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2461—Heat exchange aspects
- B01J2219/2465—Two reactions in indirect heat exchange with each other
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2461—Heat exchange aspects
- B01J2219/2467—Additional heat exchange means, e.g. electric resistance heaters, coils
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2476—Construction materials
- B01J2219/2477—Construction materials of the catalysts
- B01J2219/2479—Catalysts coated on the surface of plates or inserts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2476—Construction materials
- B01J2219/2477—Construction materials of the catalysts
- B01J2219/2482—Catalytically active foils; Plates having catalytically activity on their own
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2476—Construction materials
- B01J2219/2483—Construction materials of the plates
- B01J2219/2485—Metals or alloys
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2476—Construction materials
- B01J2219/2483—Construction materials of the plates
- B01J2219/2485—Metals or alloys
- B01J2219/2486—Steel
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2491—Other constructional details
- B01J2219/2492—Assembling means
- B01J2219/2493—Means for assembling plates together, e.g. sealing means, screws, bolts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2491—Other constructional details
- B01J2219/2492—Assembling means
- B01J2219/2496—Means for assembling modules together, e.g. casings, holders, fluidic connectors
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2491—Other constructional details
- B01J2219/2497—Size aspects, i.e. concrete sizes are being mentioned in the classified document
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/24—Stationary reactors without moving elements inside
- B01J2219/2401—Reactors comprising multiple separate flow channels
- B01J2219/245—Plate-type reactors
- B01J2219/2491—Other constructional details
- B01J2219/2498—Additional structures inserted in the channels, e.g. plates, catalyst holding meshes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/32—Details relating to packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit of module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
- B01J2219/322—Basic shape of the elements
- B01J2219/32203—Sheets
- B01J2219/32206—Flat sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/32—Details relating to packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit of module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
- B01J2219/322—Basic shape of the elements
- B01J2219/32203—Sheets
- B01J2219/3221—Corrugated sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/32—Details relating to packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit of module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
- B01J2219/322—Basic shape of the elements
- B01J2219/32203—Sheets
- B01J2219/32213—Plurality of essentially parallel sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/32—Details relating to packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit of module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
- B01J2219/324—Composition or microstructure of the elements
- B01J2219/32466—Composition or microstructure of the elements comprising catalytically active material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J2219/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J2219/32—Details relating to packing elements in the form of grids or built-up elements for forming a unit of module inside the apparatus for mass or heat transfer
- B01J2219/324—Composition or microstructure of the elements
- B01J2219/32466—Composition or microstructure of the elements comprising catalytically active material
- B01J2219/32475—Composition or microstructure of the elements comprising catalytically active material involving heat exchange
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J23/00—Catalysts comprising metals or metal oxides or hydroxides, not provided for in group B01J21/00
- B01J23/38—Catalysts comprising metals or metal oxides or hydroxides, not provided for in group B01J21/00 of noble metals
- B01J23/40—Catalysts comprising metals or metal oxides or hydroxides, not provided for in group B01J21/00 of noble metals of the platinum group metals
- B01J23/46—Ruthenium, rhodium, osmium or iridium
- B01J23/464—Rhodium
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J37/00—Processes, in general, for preparing catalysts; Processes, in general, for activation of catalysts
- B01J37/0009—Use of binding agents; Moulding; Pressing; Powdering; Granulating; Addition of materials ameliorating the mechanical properties of the product catalyst
- B01J37/0027—Powdering
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J37/00—Processes, in general, for preparing catalysts; Processes, in general, for activation of catalysts
- B01J37/02—Impregnation, coating or precipitation
- B01J37/024—Multiple impregnation or coating
- B01J37/0242—Coating followed by impregnation
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B2203/00—Integrated processes for the production of hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/02—Processes for making hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/0205—Processes for making hydrogen or synthesis gas containing a reforming step
- C01B2203/0227—Processes for making hydrogen or synthesis gas containing a reforming step containing a catalytic reforming step
- C01B2203/0233—Processes for making hydrogen or synthesis gas containing a reforming step containing a catalytic reforming step the reforming step being a steam reforming step
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B2203/00—Integrated processes for the production of hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/08—Methods of heating or cooling
- C01B2203/0805—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/0811—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas by combustion of fuel
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B2203/00—Integrated processes for the production of hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/08—Methods of heating or cooling
- C01B2203/0805—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/0838—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas by heat exchange with exothermic reactions, other than by combustion of fuel
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B2203/00—Integrated processes for the production of hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/08—Methods of heating or cooling
- C01B2203/0805—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas
- C01B2203/0838—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas by heat exchange with exothermic reactions, other than by combustion of fuel
- C01B2203/0844—Methods of heating the process for making hydrogen or synthesis gas by heat exchange with exothermic reactions, other than by combustion of fuel the non-combustive exothermic reaction being another reforming reaction as defined in groups C01B2203/02 - C01B2203/0294
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P20/00—Technologies relating to chemical industry
- Y02P20/50—Improvements relating to the production of bulk chemicals
- Y02P20/52—Improvements relating to the production of bulk chemicals using catalysts, e.g. selective catalysts
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physical Or Chemical Processes And Apparatus (AREA)
- Hydrogen, Water And Hydrids (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Catalysts (AREA)
- Devices And Processes Conducted In The Presence Of Fluids And Solid Particles (AREA)
Abstract
一种催化反应器(10)包括许多流体不可渗透的元件(管或板)(12),在它们之间限定流动通道(15)。紧配合在每个流动通道(15)内的是波纹材料的片(16),它的表面用催化剂材料涂覆。在反应器(10)的每一端是将气体混合物供给流动通道(15)的头部(18),各头部与被分离的相邻通道连通。反应器(10)能将不同的气体混合物供给相邻的通道(15),各气体混合物可在不同压力下,和相应的化学反应也是不同的。其中一个反应是吸热的而另一个反应是放热的,通过分离相邻通道(15)的管(12)的壁从放热反应向吸热反应传热。在紧凑的设备中可以使用反应器(10)进行蒸汽/甲烷转化,从催化甲烷燃烧获得所需的热量,也可从费-托合成取得热量。
Description
技术领域
本发明涉及适合用于在升高的压力下进行气相反应的催化反应器,特别但不是专门用于进行吸热反应,并涉及使用催化反应器的化学方法。
背景技术
应用支持在金属衬底上的催化材料是众所周知的技术。例如英国专利GB 1490 977描述一种催化剂,它包括含铝的铁素体合金衬底,涂覆一层耐熔的氧化物,如氧化铝、二氧化钛或氧化锆,接着涂覆催化的铂系金属。如在GB 1 531 134和GB 1 546 097中描述的那样,催化剂本体可以包括这种材料的基本平的片和有波纹的片,它们交替排列以便限定通过本体的通道,或者几个这样的片排列成一叠层,或者两个这样的片缠绕在一起形成盘管。在这些例子中,平片和波纹片两者都有叠加在它们上面的小尺度的波纹以便有助于涂层的形成。描述的这种催化剂本体适合用于处理车辆的排放气体。
在WO 99/64146(DBB Fuel Cell Engines GmbH)中描述一种紧凑催化反应器的结构,其中由布置成叠层的板中的凹槽限定气体的流动通道,和其中板是连接在一起(使用焊接)。至少某些凹槽在其壁上可以含有催化剂,而将传热介质供给另一组凹槽;如果所需的反应是吸热的,热量可由另一组凹槽中燃料的催化氧化直接供给。例如它可用于烃的水蒸汽转化。这样的反应器称为微型反应器,和凹槽称为微型结构;例如所述的板本身其厚度在0.3到0.5mm之间,所以凹槽有非常小的横截面积。对许多化学过程来说这样小尺寸的流动通道是不利的,只是因为使流体沿着它们流动必然需要压力降。EP 0 885 653A(Friedrich等人)描述了另一种类型的催化反应器,其中通道有较大的横截面,由单张长片折叠成手风琴状或锯齿形而限定,以便形成许多平行的流动路径,并有波纹箔放在每个流动路径中。该箔可用合适的催化剂涂覆。该箔可以拆除。这样的反应器不适合用于相邻的流动通道之间有很大压力差的情况,因为每个流动通道的整个面积必须承受任何压力差;和因为每个流动通道的一侧和两端都是开口的。US 6 098 396=DE 19 923 431(Wen等人)描述与内燃机组合使用的一种催化反应器,包括在相反的表面上有不同催化剂的几个波纹箔,一个催化放热反应,另一个催化吸热反应;燃料/空气混合物在两个表面上流过,吸热反应防止催化剂过热。在各个箔的两个相反侧上的气体之间不存在压力差,因为供应到各个侧的是同一气体混合物。
发明内容
根据本发明,提供一种催化反应器,它包括多个金属片,这些金属片布置成限定在相邻片之间的第一气体流动通道,限定接近第一气体流动通道的第二气体流动通道的装置,该装置这样布置以便保证在第一和第二气体流动通道中的气体之间有良好的热接触,在每个流动通道内的至少某些表面上的催化剂材料,和将气体混合物供应给气体流动通道的头部,头部使得不同的气体混合物可以供应给第一和第二气体流动通道,金属片大致上平坦,气体流动通道至少部分是由沟槽限定出来的,沟槽的宽度令到在第一和第二气体流动通道中的气体压力相差数个大气压,在沟槽之间的部分片与邻近的金属片接触并且提供热接触,以及将金属片粘结在一起形成整体结构,特征在于波纹箔设置在至少第一气体流动通道中,箔是由带铝的铁钢制成,当在空气中受热时形成附合氧化铝氧化覆层,箔在其至少部分表面上有催化材料。
也可在金属片之间限定第二气体流动通道,在连续的这种片之间交替地限定第一和第二气体流动通道。
在每个气体流动通道内通过夹入波纹状的金属箔提高相邻流动通道中气体之间的良好热接触。这种箔也可以作为催化剂材料的载体使用。可将相邻的金属片压在一起,或者可将它们例如通过扩散结合而结合在一起。为了保证所需的良好热接触,第一和第二气体流动通道两者在横截于气体流动方向的至少一个方向上最好有小于5mm的宽度。更优选地第一和第二气体流动通道两者在至少一个这样的方向上有小于2mm的宽度。
横过片的表面可加工出槽,反应器包括这种带槽片的叠层,在相邻板中的槽跟随不同的路径。例如槽本身可以是20mm宽,每个槽容纳涂覆催化剂材料的波纹片或箔。为了保证气体流动通道是气密的,希望各板或片结合在一起。
在使用催化反应器时,供应给每个环形通道的气体混合物与供应给相邻通道的气体混合物不同,那么相应的化学反应也不同。优选地一个反应是吸热的,而另一个反应是放热的。在那种情况下热量通过分隔相邻通道的管或片的壁从放热反应传到吸热反应。
最好,本身也用合适的催化剂材料涂覆。
这种反应器特别合适于进行甲烷/蒸汽转化(它是吸热反应,生成氢和一氧化碳),而交替的通道可以含有甲烷/空气混合物,从而使放热氧化反应为吸热转化反应提供必需的热量。对氧化反应可以使用几种不同的催化剂,例如在陶瓷支承件上的钯或铂;例如在镧稳定的氧化铝支承件上的铂,或在氧化锆上的钯。氧化反应优选的催化剂是稳定的氧化铝上的铂。对转化反应也可以使用几种不同的催化剂,例如镍、铂、钯、钌或铑,它们可在陶瓷涂层上使用;转化反应优选的催化剂是氧化铝上的铑或铂/铑。氧化反应基本上可在大气压力下进行,而转化反应优选地是在升高的压力下进行,该压力例如高至2MPa(20大气压),更普通的是300KPa或500KPa。
将能理解制成反应器的材料在使用中将经受严重腐蚀性的气氛,例如温度可能高至900℃,尽管更普通的是在750℃左右。反应器可由金属例如含铝的铁素体钢制成,特别是称为Fecralloy(商标)的这类钢,它是含高至20%的铬、0.5-12%铝、和0.1-3%钇的铁。例如它可以包括含15%铬、4%铝、和0.3%钇的铁。当在空气中加热这种金属时它形成氧化铝的附着的氧化物涂层,该涂层防止该合金进一步氧化。在将这种金属用作催化剂衬底,和用结合有催化剂材料的陶瓷层涂覆这种金属时,相信金属上的氧化铝氧化物层会与氧化物涂层接合,从而保证催化剂材料附着到金属衬底。
根据本发明,还提供了一种用于处理甲烷以便生产较高分子重量烃的方法,该方法包括在具有第一和第二气体流动通道的第一催化反应器中,通过在升高的压力下将蒸汽和甲烷供给第一催化反应器的第一气体流动通道,进行蒸汽/甲烷转化,并在第一催化反应器的第二气体流动通道内进行甲烷燃烧以便产生热量;将蒸汽/甲烷转化产生的气体混合物供给第二催化反应器来进行费-托合成;并且冷凝由费-托合成产生的流体混合物中的液体组份;其中至少所述第一催化反应器是如前面所述的本发明的催化反应器。
现在通过仅以示例子的方式和参考附图进一步更具体地描述本发明。
附图说明
图1是不属于本发明的催化反应器的纵向剖面图;
图2是图1的反应器的横剖面图;
图3是用图1和2的反应器可以进行的化学过程的流程图;
图4是形成本发明催化反应器的层叠板的剖面图;
图5是用于形成一个代替的催化反应器的板的平面图;
图6是用于形成另一个代替的催化反应器的板的平面图。
具体实施方式
参考图1,不属于本发明的催化反应器10包括Fecralloy钢制的几个套装的同心压力管12,每个壁厚为0.5mm(在图中仅表示4个,但实际上管12的数目可以比方说是15或16)。最内部的管12包括电加热元件14。如在图2中所示,在管12之间的环形通道15定位有波纹状Fecralloy钢的箔16,它的波纹一般是2.0mm高(峰到峰)有2.0mm的间距。
当已经装配好所有的管12和波纹箔16时,用氧化锆溶胶涂覆第1、第3、第5等环形通道15a的表面,和用氧化铝溶胶涂覆第2、第4、第6等环形通道15b的表面。这可以通过例如用蜡暂时堵塞一组环形通道的端部,并将组件浸没到合适的溶胶中进行。然后慢慢干燥该组件,接着烧结,例如在空气炉中,经过4小时将温度升到例如1100℃然后保持该组件于那个温度再经过4小时。在冷却该涂覆的组件之后,接着例如以适宜的金属的盐的形式引入催化剂材料:在这个例子中将钯引入到通道15a中氧化锆涂层上,和将铑引入到通道15b中氧化铝涂层上。通过热处理使盐分解(或还原)然后生成催化剂金属。
然后将环形端帽18激光焊接到每个环形通道15的端部上,每个端帽18与入口或出口导管20连通。所得的反应器10的外直径是50mm,和它的长度是500mm。
反应器10特别适合进行蒸汽/甲烷的转化反应,也就是这个反应:
这个反应是吸热反应,被通道15b中的铑催化剂催化。使这个反应进行所需的热量可由甲烷的燃烧提供,也就是说:
它是放热反应,由通道15a中的钯催化剂催化。由这个燃烧反应产生的热量通过管12的壁传导到相邻的通道15b中。因此在使用中,反应器10首先用电加热元件14加热。在接近大气压下将甲烷和空气的混合物供应给所有的15a通道,在那里进行催化燃烧。将蒸汽和甲烷混合物供应给另一组通道15b,在那里产生蒸汽/甲烷转化反应;最好蒸汽和甲烷混合物是在升高的压力下,因为这提高质量流速从而能处理较大量的甲烷气。例如这些15b通道可以处于1Mpa压力下。
然后可以用蒸汽/甲烷转化产生的气体混合物进行费-托(Fischer-Tropsch)合成,也就是说:
它是放热反应,在升高的温度如320℃和升高的压力(如1.8-2.2Mpa)下,在催化剂如铁、钴或熔融的磁铁矿存在,用钾作助催化剂时发生反应。反应生成的有机化合物的精确特性取决于温度、压力、和催化剂、以及一氧化碳和氢的比例。可以使用由这个合成反应生成的热量,提供蒸汽/甲烷转化反应所需的至少部分热量,例如可以使用传热流体如氦从发生费-托合成的反应器传出热量,使用该热量来预热至少一个供应给反应器10的气流。
现在参考图3,以流程图表示整个化学过程。大多数流体都处于升高的压力10巴(1Mpa)。进给气24主要包括甲烷,有小百分比含量(如10%)的乙烷和丙烷,压力为10巴。将气体通过热交换器25使它的温度约为400℃,然后通过流体涡流混合器26将它供给第一催化反应器28;在混合器26中进给气与也是温度约为400℃和压力为10巴的蒸汽流混合,这些气流通过切向入口进入到混合器26和跟随螺旋的路径到轴向出口,从而使它们彻底混合。反应器28的第一部分是在400℃下具有镍甲烷化催化剂的预转化器29,其中将高级链烷烃与蒸汽反应生成甲烷(和一氧化碳)。反应器28的第二部分是具有铂/铑催化剂的转化器30,在那里甲烷和蒸汽反应生成一氧化碳和氢。这个反应可以在800℃下进行,由甲烷在钯(或铂)催化剂上燃烧提供热量。由转化器30来的灼热气体然后通过热交换器31急冷,以提供供应到涡流混合器26的热蒸汽,接着通过热交换器25,在那里它们把热量传给进给气。
接着将一氧化碳和氢气流供给第三反应器32,在那里一氧化碳和氢反应,进行费-托合成生成烷烃或类似的化合物。这个反应是放热反应,优选地是在约350℃下发生,用该热量预热供给热交换器31的蒸汽,使用热交换流体如氦,氦在反应器32和蒸汽发生器33中的热交换通道之间循环。在这个合成中气体的体积减小,所以这个过程也在升高的压力10巴下进行。然后将所得的气体通入到冷凝器34中,在那里它们首先在25℃与水热交换。高级链烷烃(如C5或以上)冷凝成液体,水也是一样,将这个液体混合物送到重力分离器35;接着可以取出分离的高级链烷烃作为所需的产品,而水通过热交换器33和31回到混合器26。任何低级链烷烃或甲烷和剩下的氢气通过冷凝器34,接着供给到冷却的冷凝器36,在那里气体和蒸汽被冷却到约5℃。将剩余的气体,主要包括氢、二氧化碳、甲烷和乙烷,通过释放压力的通气阀37到放空燃烧装置38。将冷凝的蒸汽,主要包括丙烷、丁烷和水,送到重力分离器39,从那里水与从分离器35来的再循环的水汇合,而链烷烃再循环到费-托合成反应器32的入口。
在第一冷凝器34中蒸汽降低到的温度决定冷凝的并且也是作为产品排出的链烷烃的分子量。因此通过改变供给冷凝器34的水温可以修改产品的特征。上面的反应流程依赖于蒸汽/甲烷的比例,该比例接近于转化器30化学计量的需要,铑催化剂是特别耐结焦;这有如下好处,在转化器30中生成数量可以忽略不计的二氧化碳,从而不需要进一步处理气体(应用相反的水煤气变换反应)以将二氧化碳再转换成一氧化碳。将还能理解如果进给气只包括甲烷,那么预转化器29可以省略。
当应用这种形式时,过程的最终结果是将甲烷转换成分子量较大的烃,它们一般在环境温度和压力下呈液态。可以在油或气井使用该过程将天然气转换成容易运输的液态烃。
将能理解可以应用图1和2的反应器10进行各种化学过程,和在每个通道15内的催化剂必须适合相应的过程。
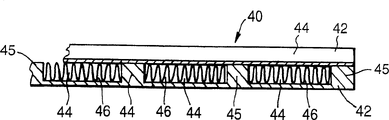
现在参考图4,本发明的一种反应器40包括一板42的叠层,每个板是Fecralloy钢,在这种情况下该板是200mm的方形和3mm厚(在图中以剖面形式仅表示两块板的一部分)。宽8mm和深2.5mm的槽44平行于一侧延伸跨过每块板42的整个宽度,由宽度3mm的槽脊45分隔,槽44是机械加工的。Fecralloy钢的载体箔46用含有催化剂材料的陶瓷涂层涂覆50μm厚,和有波纹2.5mm高,将其放入到每个这样的槽44中。装配这样的带有催化剂箔46的板42的叠层,在顺序的板42中槽44的取向相差90°,并用Fecralloy钢的平顶板覆盖;然后在惰性气氛中将该叠层加热到温度600℃到1200℃范围内,把该叠层扩散结合在一起。或者在这个阶段或者其后可以在该板叠层上装设头部。这样,由槽44限定气体流动通道,一组通道譬如说在叠层中从右边延伸到左边,而另一组通道(在另一些板42中)从叠层的前面延伸到后面。
将能理解沉积在气体流动通道中波纹箔46上的陶瓷类型在叠层中连续的各板42中可以是不同的,因此,催化剂材料也可以不同。例如(用图1和2的反应器10)在一个气体流动通道中陶瓷可以包括氧化铝,而其它气体流动通道的陶瓷可以包括氧化锆。
最好是,在扩散结合之后,该板叠层42保持在约900℃并让氧化气流通过所有限定气体流动通道的槽44。这促进在通道的表面上生成富含氧化铝的氧化物层。在这个氧化步骤之后,将该叠层冷却到室温,将或者氧化铝或者氧化锆溶胶的水悬浮液泵送通过槽44,然后排干(这样在通道的壁上留下溶胶的涂层);通过改变溶胶悬浮液的pH值或浓度可以调节溶胶悬浮液的粘度,而除去多余的溶胶可以依靠在重力下排干,或可以泵送来进行,这取决于粘度。接着在氧化的气氛中在温度例如接近800℃下烧结该叠层,这样将氧化铝溶胶颗粒烧结在Fecralloy钢表面上的氧化物层上,从而形成陶瓷的催化剂载体层。这层希望的厚度是在10-50μm范围,如果需要可以重复用合适的溶胶涂覆然后烧结的步骤,以便达到所需的厚度。最后泵送合适的催化剂金属盐的溶液通过通道44,接着在还原(或氧化)的气氛中干燥和热处理该叠层,以便产生在气体流动通道44内催化剂金属分散在陶瓷载体层上的所需形式。
与反应器10一样,由板42构成的反应器将适合进行蒸汽/甲烷的转化,例如使用铑催化剂。可用甲烷燃烧提供使这个反应进行所需的热量,燃烧可由钯催化剂催化。因为构成叠层的板42是结合在一起,所以气体流动通道是气密的(除了在每端用头部连通之外),和在另外的气体流动通道中的压力也可以不同,如有关反应器10叙述的那样。
将能理解这样窄的气体流动通道的优点是,扩散路径的长度短,和因为边界层的影响较小使热和质量的传递速率增加。化学反应要求反应的物质扩散以与催化剂表面接触,因此化学反应的速率提高,和在放热反应与吸热反应之间的传热速率也提高。因此这样的催化反应器可以提供高的功率密度。
如上所述,陶瓷涂层可以从溶胶形式的材料沉积而成,也就是说分散包含颗粒的颗粒尺寸为1nm到1μm。对具体的溶胶,如氧化铝溶胶,制备溶胶的方式确定颗粒的尺寸。某些氧化铝溶胶有各个分离的颗粒作为主要的溶胶颗粒(所谓不团聚的),而某些氧化铝溶胶有更小颗粒团聚成的溶胶颗粒。一般来说,团聚类型的溶胶比不团聚的溶胶将产生更加多孔的陶瓷涂层。因此通过选择所用溶胶的类型,或通过混合不同数量的不同类型溶胶,可以控制陶瓷涂层的孔隙率。通过调节陶瓷的孔隙率和催化剂材料的装载,可以控制陶瓷涂层的催化剂活性。在制作进行强放热反应的催化反应器时,可能要求沿着流动路径调节催化剂的活性,例如开始时提供的催化剂活性较低,沿着流动路径进一步提高催化剂的活性,以便防止热点形成。例如在进行费-托合成的反应器中这可能是合适的方法。在使用氧化锆溶胶构成氧化锆陶瓷涂层时要应用相类似的考虑;此外它可能要求包含阳离子如钇,以便形成稳定的氧化锆,特别是在操作时可能达到高温的陶瓷涂层处,因为稳定的氧化锆提供稳定的表面区域。
现在再参考图4,将能理解气体流动通道44可以沿着它们的长度改变宽度和深度,以便改变流体流动条件和传热或传质的系数,以便控制在反应器40内不同地方的化学反应。这特别可以应用到费-托合成的反应器,在该反应器中气体体积减小,例如通过适当地收缩通道44使在反应进行时可以维持气体的速度。还有,波纹箔46的节距或图案沿着反应通道44可以改变,以便调节催化剂的活性,从而对反应器40内不同点的温度或反应速率提供控制。例如还可以使波纹箔46成形有穿孔,以便促进在通道44内流体的混合。
现在参考图5,另一种反应器70包括一Fecralloy钢板71的叠层,每块板基本上是矩形,125mm长和82mm宽,2mm厚。沿着每块板71的中心部分机械加工成7个平行的矩形槽72,每个深0.75mm,在每一端有相同深度的头部槽74,头部槽74延伸到板71的一侧边缘。在图示的板71的顶表面上,在底端的头部槽74延伸到板71的右手边缘,而在顶端的头部槽延伸到板71的左手边缘。在板71的相反表面上的槽是相同的,但头部(用虚线表示)延伸到板71的相反侧。连续的板71使它们的头部槽74是镜象布置,以便相邻的槽74延伸到该叠层的相同侧。在每个矩形槽72内是三个波纹Fecralloy箔76a、b和c,每个50μm厚并且其波纹1.8mm高,但它们波纹的节距或波长不同。为了保证在装配时板71的精确对齐,在每端设置孔75,使定位销位于孔中。在扩散结合时将板71和箔76的叠层装配和压缩,从而将箔压缩成1.5mm高。然后将气体流动压力通风装置78钎焊到叠层的每一角,每个压力通风装置78与一组头部槽74连通。
现在参考图6,另一种反应器80有些类似于反应器70,包括一Fecralloy钢板81的叠层,每块板基本是矩形,125mm长和90mm宽以及2mm厚。沿着每块板81的中心部分,机械加工成7个平行的矩形槽82,每个宽4mm和深0.75mm,间距5mm,在每一端有相同深度的头部槽84,头部槽84延伸到靠近板81一侧边缘的头部开孔83。在图中表示的板81的顶表面上,因此气体流动是从底部左边的开孔83到顶部右边的开孔83。在板81相反表面上的槽是相同的,但头部(用虚线表示)延伸到靠近板81相反侧的头部开孔87。连续的各板81使它们的头部槽84是镜象布置的,所以相邻的槽84与相同的各对头部开孔83或87连通。在每个矩形槽82内有3个波纹状的Fecralloy箔86a、b和c,每个50μm厚并且其波纹1.8mm高,但其波纹的节矩或波长不同。为了保证在装配时板81的精确对齐,在每一端设置孔85,定位销位于其中。在扩散结合时将该板叠层81和箔86装配和压缩,从而箔被压缩到1.5mm高。接着将气体流动连接到叠层顶部的开孔83和87,这些开孔在叠层的底部是封闭的。反应器80与反应器70不同之处不仅在于具有由开孔83和87(代替压力通风装置78)限定的成整体的头部,而且在矩形槽82之间的每个槽脊中限定穿过板81的7个缝88,每个缝82是1mm宽和6mm长。在叠层装配之后,这些缝88为第3气流例如预热的气流提供流动路径。
Claims (12)
1.一种催化反应器,其包括多个金属片材,这些金属片材布置成在相邻片材之间限定第一气体流动通道,限定接近第一气体流动通道的第二气体流动通道的装置,该装置布置成能够保证在第一和第二气体流动通道中的气体之间有良好的热接触,在每个流动通道内的至少某些表面上的催化剂材料,以及将气体混合物供给气体流动通道的头部,头部布置成将不同的气体混合物供给第一和第二气体流动通道,金属片材基本上是平的,并且通过这些片材中的槽这样限定气体流动通道,使第一和第二气体流动通道内的气体的压力可以相差几个大气压,并且在槽之间的该片材部分与相邻金属片材接触,从而提供热接触,并且金属片材结合在一起成为一叠层,其特征在于,在气体流动通道内设置波纹状的箔,该箔是含铝的铁素体钢,在空气中加热时该钢形成氧化铝的附着的氧化物涂层,并且该箔在其表面上具有催化剂材料。
2.如权利要求1所述的催化反应器,其特征在于,波纹状金属箔被压缩在流动通道内。
3.如权利要求1所述的催化反应器,其特征在于,在沿着流动通道的连续的各位置设置不同节矩、波长或图案的波纹。
4.如权利要求1所述的催化反应器,其特征在于,使波纹状的箔成形以便促进在流动通道内的流体的混合。
5.如权利要求1所述的催化反应器,其特征在于,至少某些气体流动通道沿着其长度改变宽度或深度。
6.一种进行气体之间的化学反应的方法,其中供给第一气体流动通道的气体混合物不同于供给第二气体流动通道的气体混合物,每种气体混合物都经历反应,并且一种反应是吸热的,而另一种反应是放热的,因此在相邻通道之间传热,并且其特征在于,使用如前述权利要求中任一项所述的反应器。
7.如权利要求6所述的方法,其特征在于,吸热反应是甲烷/蒸汽转化。
8.如权利要求7所述的方法,其特征在于,转化反应在200kPa和2MPa之间的高压下进行。
9.一种用于处理甲烷以便生产较高分子重量烃的方法,该方法包括在具有第一和第二气体流动通道的第一催化反应器中,通过在升高的压力下将蒸汽和甲烷供给第一催化反应器的第一气体流动通道,进行蒸汽/甲烷转化,并在第一催化反应器的第二气体流动通道内进行甲烷燃烧以便产生热量;将蒸汽/甲烷转化产生的气体混合物供给第二催化反应器来进行费-托合成;并且冷凝由费-托合成产生的流体混合物中的液体组份;其中至少所述第一催化反应器是如权利要求1至5中任一项所述的催化反应器。
10.如权利要求9所述的方法,其特征在于,其还包括传递在费-托合成期间放出的热量以便预热供给第一催化反应器的气体。
11.如权利要求9或10所述的方法,其特征在于,其还包括传递来自蒸汽/甲烷转化产生的气体混合物的热量以便预热供给第一催化反应器的气体。
12.如权利要求9或10所述的方法,其特征在于,其还包括从费-托合成产生的流体混合物中提取短链烃,并且将这些短链烃再循环到第二催化反应器以便再次经历费-托合成。
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB0000473.9 | 2000-01-11 | ||
| GBGB0000473.9A GB0000473D0 (en) | 2000-01-11 | 2000-01-11 | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0006620A GB0006620D0 (en) | 2000-03-20 | 2000-03-20 | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0006620.9 | 2000-03-20 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2005101193905A Division CN100415358C (zh) | 2000-01-11 | 2001-01-10 | 催化反应器 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1416361A CN1416361A (zh) | 2003-05-07 |
| CN1235675C true CN1235675C (zh) | 2006-01-11 |
Family
ID=26243366
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB018063683A Expired - Lifetime CN1235675C (zh) | 2000-01-11 | 2001-01-10 | 催化反应器 |
Country Status (14)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US7300635B2 (zh) |
| EP (4) | EP1905508A3 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP4704649B2 (zh) |
| KR (2) | KR100718831B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1235675C (zh) |
| AP (1) | AP1457A (zh) |
| AU (1) | AU2001223877A1 (zh) |
| BR (1) | BR0107557B1 (zh) |
| CA (1) | CA2396191C (zh) |
| DK (2) | DK1248675T3 (zh) |
| MX (1) | MXPA02006855A (zh) |
| NO (2) | NO332058B1 (zh) |
| OA (1) | OA12158A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2001051194A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (104)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6451864B1 (en) | 1999-08-17 | 2002-09-17 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Catalyst structure and method of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis |
| AU2001223877A1 (en) * | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-24 | Aea Technology Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| MX2007008365A (es) * | 2001-01-10 | 2007-09-21 | Compactgtl Plc | Reactor catalitico. |
| DE10108380A1 (de) * | 2001-02-21 | 2002-09-05 | Deg Intense Technologies & Ser | Reaktor zur Durchführung von katalysierten Reaktionen |
| JP4267325B2 (ja) * | 2001-03-02 | 2009-05-27 | インテリジェント・エネルギー・インコーポレーテッド | アンモニアベース水素発生装置および同装置の使用方法 |
| GB0116894D0 (en) * | 2001-07-11 | 2001-09-05 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| JP4923360B2 (ja) * | 2001-09-04 | 2012-04-25 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 薄板積層構造を有する水蒸気混合装置を備えた燃料改質装置、水蒸気混合装置、及び、水蒸気混合装置の製造方法 |
| AU2002331937B2 (en) * | 2001-10-12 | 2007-07-05 | Compactgtl Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0125035D0 (en) * | 2001-10-18 | 2001-12-12 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0125000D0 (en) * | 2001-10-18 | 2001-12-05 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0124999D0 (en) * | 2001-10-18 | 2001-12-05 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0129054D0 (en) * | 2001-12-05 | 2002-01-23 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor and process |
| WO2003048034A1 (en) * | 2001-12-05 | 2003-06-12 | Gtl Microsystems Ag | Process an apparatus for steam-methane reforming |
| AUPR981702A0 (en) * | 2002-01-04 | 2002-01-31 | Meggitt (Uk) Limited | Steam reformer |
| US7967878B2 (en) * | 2002-01-04 | 2011-06-28 | Meggitt (Uk) Limited | Reformer apparatus and method |
| US7179313B2 (en) * | 2002-08-02 | 2007-02-20 | Catacel Corp. | Regenerative autothermal catalytic steam reformer |
| US20040060238A1 (en) * | 2002-08-02 | 2004-04-01 | Retallick William B. | Autothermal catalytic steam reformer |
| US7014835B2 (en) | 2002-08-15 | 2006-03-21 | Velocys, Inc. | Multi-stream microchannel device |
| US7250151B2 (en) * | 2002-08-15 | 2007-07-31 | Velocys | Methods of conducting simultaneous endothermic and exothermic reactions |
| GB0314790D0 (en) * | 2003-06-25 | 2003-07-30 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor and process |
| GB0304949D0 (en) | 2003-03-05 | 2003-04-09 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor and process |
| AU2004218208A1 (en) * | 2003-03-05 | 2004-09-16 | Compactgtl Plc | Producing longer-chain hydrocarbons from natural gas |
| WO2004082823A1 (ja) * | 2003-03-19 | 2004-09-30 | Tosoh Corporation | 微小流路構造体 |
| US7220699B2 (en) * | 2003-03-31 | 2007-05-22 | Intelligent Energy, Inc. | Catalyst incorporation in a microreactor |
| DE10317451A1 (de) * | 2003-04-16 | 2004-11-18 | Degussa Ag | Reaktor für heterogen katalysierte Reaktionen |
| US8580211B2 (en) * | 2003-05-16 | 2013-11-12 | Velocys, Inc. | Microchannel with internal fin support for catalyst or sorption medium |
| US7763217B2 (en) | 2003-05-16 | 2010-07-27 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Rapid start fuel reforming systems and techniques |
| US8821832B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2014-09-02 | UltraCell, L.L.C. | Fuel processor for use with portable fuel cells |
| US7462208B2 (en) * | 2003-06-27 | 2008-12-09 | Ultracell Corporation | Planar micro fuel processor |
| US20060156627A1 (en) * | 2003-06-27 | 2006-07-20 | Ultracell Corporation | Fuel processor for use with portable fuel cells |
| GB0315180D0 (en) * | 2003-06-28 | 2003-08-06 | Accentus Plc | Combustion of gaseous fuel |
| JP2005103399A (ja) * | 2003-09-29 | 2005-04-21 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | 反応装置及び反応方法 |
| US20050142049A1 (en) * | 2003-12-31 | 2005-06-30 | Amsden Jeffrey M. | Multi-tubular reactors with monolithic catalysts |
| DE102004007344A1 (de) * | 2004-02-14 | 2005-09-01 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Integrierter Reaktor zur thermischen Kopplung von Reaktionen und Verfahren zur Steuerung des Temperaturfeldes in einem solchen Reaktor |
| DE112005000391T5 (de) * | 2004-02-17 | 2007-12-27 | Modine Manufacturing Co., Racine | Integrierte Brennstoffverarbeitungsanlage für eine dezentrale Wasserstoffproduktion |
| JP4580664B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-01 | 2010-11-17 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | マイクロリアクターおよびその製造方法 |
| KR100542201B1 (ko) * | 2004-03-03 | 2006-01-10 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 연료 전지 시스템의 개질기 및 이를 채용한 연료 전지시스템 |
| GB0405796D0 (en) | 2004-03-16 | 2004-04-21 | Accentus Plc | Converting natural gas to longer-chain hydrocarbons |
| GB0405786D0 (en) | 2004-03-16 | 2004-04-21 | Accentus Plc | Processing natural gas to form longer-chain hydrocarbons |
| US8062623B2 (en) * | 2004-10-15 | 2011-11-22 | Velocys | Stable, catalyzed, high temperature combustion in microchannel, integrated combustion reactors |
| US7063910B2 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2006-06-20 | Angstrom Power | Compact chemical reactor with reactor frame |
| JP5567251B2 (ja) * | 2004-04-06 | 2014-08-06 | ソシエテ ビック | 化学反応装置及びその製造方法 |
| US7195652B2 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2007-03-27 | Angstrom Power | Method for forming compact chemical reactors with reactor frames |
| US7052795B2 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2006-05-30 | Angstrom Power | Compact chemical reactor |
| US7458997B2 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2008-12-02 | Angstrom Power Incorporated | Method for making compact chemical reactors |
| US7067217B2 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2006-06-27 | Angstrom Power | Compact fuel cell layer |
| GB0408896D0 (en) * | 2004-04-20 | 2004-05-26 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| US20050282100A1 (en) * | 2004-06-07 | 2005-12-22 | Arlo Lin | Catalyzer for gas-consuming device |
| US7743499B2 (en) * | 2004-12-20 | 2010-06-29 | Gm Global Technology Operations, Inc. | Reactor manufacturing method for a fuel cell processor |
| KR20060080385A (ko) * | 2005-01-05 | 2006-07-10 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 연료 전지 시스템, 개질기, 반응 기판 및 그 반응 기판의제조 방법 |
| GB0501731D0 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2005-03-02 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| US7514387B2 (en) * | 2005-02-15 | 2009-04-07 | Umicore Ag & Co. Kg | Reformer and method of making the same |
| GB0504622D0 (en) | 2005-03-05 | 2005-04-13 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactors |
| US20060225347A1 (en) * | 2005-04-12 | 2006-10-12 | Dong-Uk Lee | Reformer for fuel cell system |
| GB0515276D0 (en) | 2005-07-26 | 2005-08-31 | Accentus Plc | Catalyst |
| ITRM20050532A1 (it) * | 2005-10-26 | 2007-04-27 | Technip Kti S P A | Apparato di combustione catalitica controllata accoppiata a reazioni endotermiche. |
| GB0603609D0 (en) | 2006-02-23 | 2006-04-05 | Accentus Plc | Catalyst structure |
| US7789920B2 (en) * | 2006-04-07 | 2010-09-07 | Chart Industries, Inc. | Supercritical process, reactor and system for hydrogen production |
| GB0608277D0 (en) | 2006-04-27 | 2006-06-07 | Accentus Plc | Process for preparing liquid hydrocarbons |
| GB0608927D0 (en) * | 2006-05-08 | 2006-06-14 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic Reactor |
| EA201101623A1 (ru) | 2006-05-08 | 2012-09-28 | КОМПАКТДЖТЛ ПиЭлСи | Способ осуществления быстрой реакции в компактном каталитическом реакторе |
| KR100810965B1 (ko) * | 2006-05-29 | 2008-03-10 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 다단계 반응용 마이크로 채널 반응 장치 |
| US7820725B2 (en) | 2006-09-05 | 2010-10-26 | Velocys, Inc. | Integrated microchannel synthesis and separation |
| WO2008089376A2 (en) | 2007-01-19 | 2008-07-24 | Velocys Inc. | Process and apparatus for converting natural gas to higher molecular weight hydrocarbons using microchannel process technology |
| US20080260575A1 (en) * | 2007-04-17 | 2008-10-23 | Honeywell International Inc. | Two-stage catox apparatus and process |
| CA2698140A1 (en) | 2007-10-02 | 2009-04-09 | Compactgtl Plc | Gas-to-liquid plant using parallel units |
| DE102008005839A1 (de) * | 2008-01-24 | 2009-07-30 | Borit Leichtbau-Technik Gmbh | Verfahren zur thermischen Integration eines Brennstoffzellensystems und Brennstoffzellensystem |
| DE102008017342A1 (de) * | 2008-04-04 | 2009-10-08 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Kompaktreaktor |
| US7976797B2 (en) * | 2008-04-08 | 2011-07-12 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Advanced materials for regenerative pyrolysis reactors, methods, and reactors using the same |
| US8100996B2 (en) | 2008-04-09 | 2012-01-24 | Velocys, Inc. | Process for upgrading a carbonaceous material using microchannel process technology |
| WO2009126765A2 (en) | 2008-04-09 | 2009-10-15 | Velocys Inc. | Process for converting a carbonaceous material to methane, methanol and/or dimethyl ether using microchannel process technology |
| ITVR20080069A1 (it) * | 2008-06-18 | 2009-12-19 | I C I Caldaie S P A | Dispositivo catalizzatore |
| AU2009302276B2 (en) | 2008-10-10 | 2015-12-03 | Velocys Inc. | Process and apparatus employing microchannel process technology |
| US8278231B2 (en) * | 2008-11-24 | 2012-10-02 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Heat stable formed ceramic, apparatus and method of using the same |
| US8450552B2 (en) | 2009-05-18 | 2013-05-28 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Pyrolysis reactor materials and methods |
| JP5581028B2 (ja) * | 2009-09-16 | 2014-08-27 | 住友精密工業株式会社 | 触媒反応器 |
| KR101112662B1 (ko) * | 2010-04-05 | 2012-02-15 | 주식회사 아모그린텍 | 대용량 금속 촉매 담체 및 이를 이용한 촉매 컨버터 |
| GB201007196D0 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2010-06-16 | Compactgtl Plc | Gas-to-liquid technology |
| US20120051993A1 (en) * | 2010-08-25 | 2012-03-01 | L'air Liquide Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Mitigation System In A Steam Methane Reformer Plant |
| GB201118465D0 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2011-12-07 | Compactgtl Plc | Gas-to-liquid technology |
| GB201120327D0 (en) | 2011-11-24 | 2012-01-04 | Compactgtl Plc | Oil well product treatment |
| WO2013093423A1 (en) | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | Compactgtl Limited | Process for the regeneration of a fischer tropsch catalyst |
| WO2013093428A1 (en) | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | Compactgtl Limited | Operation of a fischer - tropsch catalytic process |
| GB201122193D0 (en) * | 2011-12-22 | 2012-02-01 | Compact Gtl Plc | Catalytic reactor and catalyst structure |
| US11607657B2 (en) | 2012-02-06 | 2023-03-21 | Helbio S.A. | Heat integrated reformer with catalytic combustion for hydrogen production |
| JP6002249B2 (ja) * | 2012-02-06 | 2016-10-05 | ヘルビオ ソシエテ アノニム ハイドロジェン アンド エナジー プロダクション システムズ | 水素生成のための触媒燃焼式熱統合型改質器 |
| WO2013132276A1 (en) * | 2012-03-08 | 2013-09-12 | Helbio Societé Anonyme Hydrogen And Energy Production Systems | Catalytically heated fuel processor with replaceable structured supports bearing catalyst for fuel cell |
| EP2653765B1 (de) * | 2012-04-20 | 2019-02-27 | TI Automotive (Heidelberg) GmbH | Rohrleitung für ein zu temperierendes fluides Medium |
| US8574501B1 (en) | 2012-05-16 | 2013-11-05 | Greenway Innovative Energy, Inc. | Natural gas to liquid fuels |
| US20150263366A1 (en) * | 2012-08-01 | 2015-09-17 | Kyushu University, National University Corporation | Paper-structured catalyst, paper-structured catalyst array body, and solid oxide fuel cell provided with paper-structured catalyst or paper-structured catalyst array body |
| JP6084394B2 (ja) * | 2012-08-09 | 2017-02-22 | 株式会社Ti | 水素発生装置の反応セル構造 |
| KR101401355B1 (ko) | 2012-11-21 | 2014-06-02 | 한국과학기술연구원 | 탄화수소 개질용 마이크로 채널 반응기 |
| JP6408754B2 (ja) * | 2013-02-06 | 2018-10-17 | 株式会社Ihi | リアクタ |
| US9676623B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2017-06-13 | Velocys, Inc. | Process and apparatus for conducting simultaneous endothermic and exothermic reactions |
| GB2527592A (en) * | 2014-06-27 | 2015-12-30 | Compactgtl Ltd | Catalytic reactors |
| JP6728739B2 (ja) * | 2016-02-12 | 2020-07-22 | 株式会社Ihi | 反応装置 |
| CN106076220A (zh) * | 2016-08-02 | 2016-11-09 | 杭州沈氏节能科技股份有限公司 | 一种气固相微反应器 |
| JP7010940B2 (ja) * | 2016-10-25 | 2022-02-10 | テクニップ フランス | 改質のための触媒管 |
| CN107115828A (zh) * | 2017-06-17 | 2017-09-01 | 福建德兴节能科技有限公司 | 高效催化器及其用途 |
| KR101980631B1 (ko) | 2017-08-25 | 2019-05-21 | 국방과학연구소 | 연료의 흡열성능을 시험하기 위한 열 교환 장치 및 흡열성능시험방법 |
| EP3710399A4 (en) * | 2017-11-16 | 2021-07-21 | Societé de Commercialisation des Produits de la Recherche Appliquée SOCPRA Sciences et Génie S.E.C | INTEGRATED SOLAR MICROREACTORS FOR HYDROGEN SYNTHESIS BY STEAM REFORMING OF METHANE |
| US10822233B2 (en) * | 2018-05-11 | 2020-11-03 | Doosan Fuel Cell America, Inc. | Reformer including catalyst in an inlet plenum |
| CN108636301B (zh) * | 2018-07-05 | 2023-07-25 | 鄂尔多斯应用技术学院 | 一种化工实验室固定床模块化反应装置 |
| JP7107387B2 (ja) | 2018-11-26 | 2022-07-27 | 株式会社Ihi | 反応装置 |
Family Cites Families (51)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3127247A (en) * | 1964-03-31 | Alternate annular isothermal reactor | ||
| GB1490977A (en) | 1973-12-10 | 1977-11-09 | Atomic Energy Authority Uk | Catalysts |
| GB1546097A (en) | 1975-08-20 | 1979-05-16 | Atomic Energy Authority Uk | Fabricating catalyst bodies |
| SE422744B (sv) * | 1975-08-20 | 1982-03-29 | Atomic Energy Authority Uk | Katalysatorkropp med genomgaende kanaler jemte sett for dess tillverkning |
| GB1531134A (en) * | 1975-08-20 | 1978-11-01 | Atomic Energy Authority Uk | Methods of fabricating bodies and to bodies so fabricated |
| JPS5556823A (en) * | 1978-10-19 | 1980-04-26 | Daikin Ind Ltd | Catalytic oxidation apparatus |
| CA1146148A (en) | 1981-06-30 | 1983-05-10 | James Den Hartog | Ordered bed packing module |
| JPS61171870A (ja) * | 1985-01-28 | 1986-08-02 | Houyuu:Kk | 改質天然ガスを用いた内燃機関 |
| GB8626532D0 (en) * | 1986-11-06 | 1986-12-10 | British Petroleum Co Plc | Chemical process |
| DK156701C (da) * | 1987-08-27 | 1990-01-29 | Haldor Topsoe As | Fremgangsmaade til gennemfoerelse af heterogene katalytiske kemiske reaktioner |
| US4815534A (en) * | 1987-09-21 | 1989-03-28 | Itt Standard, Itt Corporation | Plate type heat exchanger |
| KR940005668B1 (ko) * | 1988-08-13 | 1994-06-22 | 우스이 고꾸사이 산교 가부시끼가이샤 | 배기가스 정화용 촉매를 담지하기 위한 금속제 담지모체(擔持母體) |
| FR2657273B1 (fr) * | 1990-01-19 | 1992-05-15 | Inst Francais Du Petrole | Enceinte reactionnelle comprenant un reacteur calandre et des moyens de stratification du courant d'un fluide caloporteur. |
| DE4016276C1 (zh) * | 1990-05-21 | 1991-06-20 | Behr Gmbh & Co | |
| JPH0815559B2 (ja) | 1990-11-13 | 1996-02-21 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 耐熱応力・耐熱疲労特性の優れたレーストラック型自動車排ガス触媒用金属担体 |
| JPH05105405A (ja) * | 1991-10-21 | 1993-04-27 | Ishikawajima Harima Heavy Ind Co Ltd | プレート型リフオーマ |
| JPH05196386A (ja) * | 1991-11-22 | 1993-08-06 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 積層プレート式熱交換器 |
| US5846494A (en) * | 1992-04-30 | 1998-12-08 | Gaiser; Gerd | Reactor for catalytically processing gaseous fluids |
| US5328359A (en) * | 1992-05-19 | 1994-07-12 | W. R. Grace & Co.-Conn. | Ignition stage for a high temperature combustor |
| US5250270A (en) * | 1992-07-17 | 1993-10-05 | The M. W. Kellogg Company | Catalytic reactor bed |
| SE470581B (sv) | 1993-02-26 | 1994-10-03 | Sandvik Ab | Bärarkropp av metallfolie för katalysator |
| JP3512186B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-19 | 2004-03-29 | イー・アイ・デユポン・ドウ・ヌムール・アンド・カンパニー | 化学処理及び製造のための一体構造及び方法、並びにその使用方法及び製造方法 |
| US5534328A (en) * | 1993-12-02 | 1996-07-09 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Integrated chemical processing apparatus and processes for the preparation thereof |
| US5600052A (en) * | 1994-05-02 | 1997-02-04 | Uop | Process and apparatus for controlling reaction temperatures |
| DE59503581D1 (de) * | 1994-06-15 | 1998-10-22 | Dbb Fuel Cell Engines Gmbh | Zweistufige Methanol-Reformierung |
| US5611214A (en) * | 1994-07-29 | 1997-03-18 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Microcomponent sheet architecture |
| US5811062A (en) | 1994-07-29 | 1998-09-22 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Microcomponent chemical process sheet architecture |
| JPH08106197A (ja) * | 1994-10-06 | 1996-04-23 | Toshiba Corp | 画像形成装置 |
| US5681538A (en) * | 1995-02-01 | 1997-10-28 | Engelhard Corporation | Metallic monolith and plates for the assembly thereof |
| DE19524158A1 (de) * | 1995-07-03 | 1997-01-09 | Degussa | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Blausäure |
| CN1166032A (zh) * | 1995-12-29 | 1997-11-26 | 奎德/技术公司 | 包装计算机盘的方法 |
| DE19617396C2 (de) * | 1996-05-02 | 1998-03-26 | Dornier Gmbh | Strömungsmodul |
| JPH10151356A (ja) * | 1996-11-21 | 1998-06-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 燃焼用触媒部材 |
| DE19654361A1 (de) | 1996-12-24 | 1998-06-25 | Behr Gmbh & Co | Reaktor in Stapelbauweise |
| JPH10273304A (ja) * | 1997-03-28 | 1998-10-13 | Sekiyu Sangyo Kasseika Center | 熱交換型改質反応器 |
| DE19725378A1 (de) * | 1997-06-16 | 1998-12-17 | Gerhard Friedrich | Kompakter Festbettreaktor für katalytische Reaktionen mit integriertem Wärmeaustausch |
| DE19725665A1 (de) * | 1997-06-18 | 1998-12-24 | Lubo Maschf | Vorrichtung zum Sortieren von Abfallmaterialien |
| US6200536B1 (en) | 1997-06-26 | 2001-03-13 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Active microchannel heat exchanger |
| DE19743673C2 (de) | 1997-10-02 | 2002-05-08 | Xcellsis Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur Wasserstofferzeugung aus Kohlenwasserstoffen und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Katalysators |
| DE19746251C2 (de) * | 1997-10-20 | 1999-09-09 | Dbb Fuel Cell Engines Gmbh | Anlage zur Wasserdampfreformierung eines Kohlenwasserstoffs und Betriebsverfahren hierfür |
| DE19754012C2 (de) * | 1997-12-05 | 1999-11-11 | Dbb Fuel Cell Engines Gmbh | Anlage zur Wasserdampfreformierung eines Kohlenwasserstoffs |
| ZA99313B (en) | 1998-01-20 | 1999-07-19 | Shell Int Research | Catalyst suitable for the preparation of hydrogen and carbon monoxide from a hydrocarbonaceous feedstock |
| US6098396A (en) | 1998-05-27 | 2000-08-08 | Solar Turbines Inc. | Internal combustion engine having a catalytic reactor |
| DE19825102C2 (de) | 1998-06-05 | 2001-09-27 | Xcellsis Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines kompakten katalytischen Reaktors |
| US6168765B1 (en) * | 1998-09-08 | 2001-01-02 | Uop Llc | Process and apparatus for interbed injection in plate reactor arrangement |
| US6180846B1 (en) * | 1998-09-08 | 2001-01-30 | Uop Llc | Process and apparatus using plate arrangement for combustive reactant heating |
| US6284217B1 (en) | 1999-08-17 | 2001-09-04 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Method and catalyst structure for steam reforming of a hydrocarbon |
| AU2001223877A1 (en) * | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-24 | Aea Technology Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| AU2002331937B2 (en) * | 2001-10-12 | 2007-07-05 | Compactgtl Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0125000D0 (en) * | 2001-10-18 | 2001-12-05 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
| GB0408896D0 (en) * | 2004-04-20 | 2004-05-26 | Accentus Plc | Catalytic reactor |
-
2001
- 2001-01-10 AU AU2001223877A patent/AU2001223877A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2001-01-10 KR KR1020027008896A patent/KR100718831B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-01-10 WO PCT/GB2001/000077 patent/WO2001051194A1/en active Application Filing
- 2001-01-10 US US10/169,901 patent/US7300635B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-01-10 BR BRPI0107557-8A patent/BR0107557B1/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-01-10 AP APAP/P/2002/002574A patent/AP1457A/en active
- 2001-01-10 MX MXPA02006855A patent/MXPA02006855A/es active IP Right Grant
- 2001-01-10 CA CA002396191A patent/CA2396191C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-01-10 EP EP08100024A patent/EP1905508A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2001-01-10 DK DK01900200T patent/DK1248675T3/da active
- 2001-01-10 CN CNB018063683A patent/CN1235675C/zh not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-01-10 DK DK05007275T patent/DK1559475T3/da active
- 2001-01-10 EP EP06125827A patent/EP1764150A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2001-01-10 EP EP05007275A patent/EP1559475B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-01-10 OA OA1200200207A patent/OA12158A/en unknown
- 2001-01-10 KR KR1020067023012A patent/KR100771391B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-01-10 JP JP2001551604A patent/JP4704649B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-01-10 EP EP01900200A patent/EP1248675B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2002
- 2002-07-09 NO NO20023320A patent/NO332058B1/no not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2006
- 2006-10-30 NO NO20064969A patent/NO20064969L/no not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2007
- 2007-11-27 US US11/987,136 patent/US7670393B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2008
- 2008-01-29 US US12/010,754 patent/US7695694B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1235675C (zh) | 催化反应器 | |
| RU2415701C2 (ru) | Каталитический реактор | |
| US7201883B2 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| US7186388B2 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| US20040251001A1 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| AU2002314372A1 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| AU2002331937A1 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| US20080194712A1 (en) | Process an apparatus for steam-methane reforming | |
| JP2003519563A5 (zh) | ||
| US7189271B2 (en) | Catalytic reactor | |
| CN1772368A (zh) | 催化反应器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right |
Owner name: HACKETT CAMPANELLA GTL LTD. Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ASHANTES CO. LTD. Effective date: 20070316 |
|
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20070316 Address after: Oxfordshire Patentee after: Gtl Microsystems AG Address before: Oxfordshire Patentee before: Ashats Co., Ltd. |
|
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Granted publication date: 20060111 |