WO2020071250A1 - ワイピングシート - Google Patents
ワイピングシートInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020071250A1 WO2020071250A1 PCT/JP2019/037998 JP2019037998W WO2020071250A1 WO 2020071250 A1 WO2020071250 A1 WO 2020071250A1 JP 2019037998 W JP2019037998 W JP 2019037998W WO 2020071250 A1 WO2020071250 A1 WO 2020071250A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- fiber
- wiping sheet
- fibers
- sheet according
- less
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A47—FURNITURE; DOMESTIC ARTICLES OR APPLIANCES; COFFEE MILLS; SPICE MILLS; SUCTION CLEANERS IN GENERAL
- A47L—DOMESTIC WASHING OR CLEANING; SUCTION CLEANERS IN GENERAL
- A47L13/00—Implements for cleaning floors, carpets, furniture, walls, or wall coverings
- A47L13/10—Scrubbing; Scouring; Cleaning; Polishing
- A47L13/16—Cloths; Pads; Sponges
- A47L13/17—Cloths; Pads; Sponges containing cleaning agents
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/42—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece
- D04H1/4391—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties characterised by the use of certain kinds of fibres insofar as this use has no preponderant influence on the consolidation of the fleece characterised by the shape of the fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/44—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties the fleeces or layers being consolidated by mechanical means, e.g. by rolling
- D04H1/46—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties the fleeces or layers being consolidated by mechanical means, e.g. by rolling by needling or like operations to cause entanglement of fibres
- D04H1/492—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties the fleeces or layers being consolidated by mechanical means, e.g. by rolling by needling or like operations to cause entanglement of fibres by fluid jet
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a wiping sheet.
- Patent Literatures 1 and 2 are intended for cleaning the surface of a substrate, or for wiping or cosmetics for a person, and collecting dirt when a floor or the like is cleaned. Is not disclosed at all. Further, a nonwoven fabric or the like containing ultrafine fibers has insufficient strength, and as a result, the sheet is likely to break during use.
- the present invention is directed to a wiping sheet that overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art.
- the wiping sheet includes a first fiber and a fiber aggregate including at least a second fiber having a smaller diameter than the first fiber.
- the first fiber and the second fiber are the first fiber, the second fiber, and the first fiber and the second fiber entangled to form the fiber aggregate. That is, the fiber aggregate used for the wiping sheet is a fiber aggregate mainly composed of entanglement of the first and second fibers.
- the wiping sheet may be composed of only the fiber aggregate, or may include, in addition to the fiber aggregate, another sheet material and / or another member.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention may be a fiber aggregate that does not carry a cleaning liquid (hereinafter, this embodiment is also referred to as a “dry type”), or may be a fiber aggregate that carries a cleaning liquid (hereinafter, referred to as a “dry type”). This mode is also referred to as “wet”.)
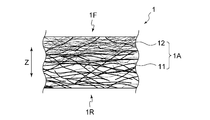
- FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a fiber assembly provided in the wiping sheet of the present invention.
- the fiber aggregate 1A in the wiping sheet 1 is configured to include a first fiber 11 and a second fiber 12 having a smaller diameter than the first fiber.
- the wiping sheet 1 has a first surface 1F and a second surface 1R located on the opposite side of the first surface 1F.
- the wiping sheet 1 mainly includes a second fiber 12 which is a fiber having a small fiber diameter on a first surface 1F in FIG. 1, and a first fiber 11 on a second surface 1R. Is mainly present.
- the first surface 1F serves as a wiping surface when the wiping sheet is used. Note that “mainly present” means that when the wiping sheet 1 is viewed in a vertical cross section along the thickness direction Z, the ratio of any fiber present in the above-described surface is the highest.
- the proportion of the second fibers 12 occupied by the first surface 1F is preferably 40% or more, more preferably 50% or more, and even more preferably 60% or more, expressed as an area ratio. Also, it is preferably at most 100%, more preferably at most 90%, even more preferably at most 85%.
- the abundance ratio of the second fibers 12 in the first surface 1F is preferably 40% or more and 100% or less, more preferably 50% or more and 90% or less, and more preferably 60% or more. More preferably, it is at most 85%. By having such an abundance ratio, it is possible to enhance the performance of collecting fine particle dirt with a dense and low porosity structure formed by the fine fibers, and to enhance the sheet strength during use. In addition, the sustained release of the cleaning solution in the wet mode can be enhanced.
- the abundance ratio of the first fibers 11 on the first surface 1F is preferably 0% or more, more preferably 1% or more, still more preferably 5% or more, expressed as an area ratio. Also, it is preferably at most 60%, more preferably at most 40%, even more preferably at most 35%.
- the proportion of the first fibers 11 occupied by the first fibers 11 on the first surface 1F is preferably 0% or more and 60% or less, more preferably 1% or more and 40% or less, and more preferably 5% or more. More preferably, it is 35% or less.
- the proportion of the second fibers 12 on the second surface 1R occupied by the second fibers 12 is preferably 1% or more, more preferably 3% or more, and more preferably 5% or more in terms of area ratio. Is more preferably 60% or less, more preferably 40% or less, and even more preferably 35% or less.
- the proportion of the second fibers 12 occupied by the second surface 1R in the area ratio is preferably 1% or more and 60% or less, more preferably 3% or more and 40% or less, and more preferably 5% or more. More preferably, it is 35% or less.
- the ratio of the first fiber 11 and the second fiber 12 on each surface can be measured as an area ratio using, for example, a confocal laser microscope.
- the image data is acquired with the first surface 1F or the second surface 1R as the observation target.
- a threshold is set for each of the obtained images at the lightness boundary between the first fiber and the second fiber, and the lightness is binarized. Thereafter, the area having each color is calculated, and the area ratio of each fiber is calculated.
- the existence ratio of the second fiber 12 in the virtual surface is expressed by an area ratio, and is a thickness on the opposite side of the first surface 1F. It is preferred that it decreases stepwise, continuously, or a combination thereof in the direction Z.
- the sheet strength and the dirt collecting property can be enhanced by setting the presence ratio of the second fibers 12 in the range of 50% or more and 100% or less in terms of area ratio. Further, the sustained release property of the cleaning liquid in the wet mode can be enhanced.
- the ratio of the sheet thickness in which the presence ratio of the second fiber is in the range of 50% to 100% is preferably 1% to 90%, more preferably 5% to 70%, and more preferably 7% or more. 50% or less is more preferable.
- This abundance ratio can be calculated as the above-described area ratio by performing Raman imaging in the sheet thickness direction using, for example, a confocal laser microscope.
- At least the first fibers 11 having a large diameter are modified fibers.
- Irregular fibers are those whose cross section is non-circular.
- the non-circular cross section of the fiber means that the cross section of the fiber has a shape other than a perfect circle.
- at least the first fiber 11 having a large diameter is preferably an irregular fiber, and both the first fiber and the second fiber are irregular fibers. More preferably.
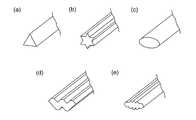
- modified fibers having the cross-sectional shape of such fibers include, for example, triangles shown in FIG. 2 (a), convex polygons such as quadrangular, pentagonal and hexagonal or regular polygons, and FIG. 2 (b).
- Examples include cross-sectional shapes such as a star polygon, an elliptical shape shown in FIG. 2C, a W-shaped shape shown in FIG. 2D, and a multi-leaf shape shown in FIG. There is no particular limitation as long as the effects of the invention are exhibited.
- the first fiber 11 is a modified fiber having preferably at least one, more preferably two or more, and more preferably three or more convex portions having a sharp apex in the cross-sectional shape thereof.
- the sharp peak is defined as (a) one straight line and one straight line when the contour of the convex portion in the cross-sectional shape of the deformed fiber is defined by, for example, (a) two non-parallel straight lines intersecting with each other. And (c) a case where two curves intersect with each other.
- the deformed fiber shown in FIG. 2A has three sharp peaks
- the deformed fiber shown in FIG. 2B has six sharp peaks
- the deformed fiber shown in FIG. It has eight tops.
- one type of modified fiber may be used alone, or two or more types of modified fibers having different cross-sectional shapes may be used in combination.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention has a high tensile modulus due to the fact that the constituent fibers include irregular fibers.
- the tensile elastic modulus of the wiping sheet is preferably equal to or greater than 1.3 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 N / mm 2 and equal to or greater than 1.4 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 N / mm 2. Is more preferably 1.5 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 N / mm 2 or more.
- the upper limit of the tensile modulus is not particularly limited, it is practically 5.0 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 N / mm 2 or less.
- the tensile elastic modulus can be determined from, for example, a difference between two tensile strengths (N / mm) and a difference between displacements (mm) in these tensile strengths.
- the measuring method will be described in detail in Examples described later.
- the fineness (dtex) of the first fiber is preferably higher than the fineness (dtex) of the second fiber.
- the ratio of the fineness (dtex) of the first fiber to the fineness (dtex) of the second fiber is preferably 10 or more, more preferably 15 or more, and preferably 25 or more. More preferably, it is preferably 2000 or less, more preferably 1500 or less, even more preferably 1000 or less.
- the fineness of the first fibers contained in the wiping sheet is preferably 0.5 dtex or more, more preferably 1 dtex or more, further preferably 1.2 dtex or more, and
- the upper limit is preferably 3 dtex or less, more preferably 2.5 dtex or less, even more preferably 2 dtex or less.
- the fineness of the second fiber included in the wiping sheet is preferably 1.5 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 dtex or more, more preferably 2.5 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 dtex or more, and more preferably 4 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 dtex or more. More preferably, it is not less than 0.5 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 dtex.
- the fineness of the second fiber is preferably 3.0 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 1 dtex or less, more preferably 1.0 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 1 dtex or less, and 5.0 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 2 dtex or less. Is more preferable.
- the first fibers 11 and the second fibers 12 constituting the wiping sheet 1 may be any of synthetic fibers and natural fibers. However, from the viewpoint of easy molding and production efficiency of the fibers, at least the first fibers 11 and the second fibers 12 may be used. Is preferably a synthetic fiber made of a thermoplastic resin, and more preferably both fibers 11 and 12 are synthetic fibers made of a thermoplastic resin.
- thermoplastic resin examples include polyolefin resins such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), polyester resins such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide resins, vinyl resins such as polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene, and polyacrylic acids.
- An acrylic resin such as polymethyl methacrylate, a fluororesin such as polyperfluoroethylene, and the like can be given.
- the natural fiber include various cellulose fibers, for example, hydrophilic fibers such as pulp, cotton, rayon, lyocell, and tencel. These fibers can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the fiber length of the first fiber depends on the method of producing the fiber, but is preferably 1 mm or more and 100 mm or less, more preferably 10 mm or more and 90 mm or less, and even more preferably 20 mm or more and 60 mm or less.
- the fiber length of the second fiber depends on the method for producing the fiber, but is preferably 1 mm or more.
- Examples of the method for producing the first fiber 11 and the second fiber 12 include a method such as a spunbond method, a melt blown method, and an electrospinning method (electrospinning method). From the viewpoint of further increasing the production efficiency of the fine fiber, it is preferable that at least the second fiber is a synthetic fiber made of a thermoplastic resin and produced by an electrospinning method.
- the length of the longest line segment was A
- the length of the longest line segment orthogonal to the line segment and crossing the cross section was B.
- the ratio (A / B) of the length A to the length B is preferably 1.2 or more, more preferably 1.5 or more. It is more preferably 2 or more, and the upper limit is preferably 5 or less, more preferably 4 or less, and even more preferably 3 or less.
- the value of A / B is preferably 1.2 or more, 5 or less, more preferably 1.5 or more and 4 or less, and even more preferably 2 or more and 3 or less.
- examples of cross-sectional shapes other than the shapes shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C are as follows.
- the length A is the length of one side of an equilateral triangle
- the length B is the length of a perpendicular drawn from one vertex to one side.
- the length A is the major axis of the ellipse
- the length B is the minor axis of the ellipse.
- the lengths A and B are the average of A and the average of B measured for all types of modified fibers. That is.
- the length A is preferably 1 ⁇ m or more, and more preferably 5 ⁇ m or more on condition that the above-mentioned A / B range is satisfied, from the viewpoint of both the operability at the time of wiping and the collecting property of dirt. More preferably, it is more preferably at least 10 ⁇ m, and the upper limit is preferably at most 80 ⁇ m, more preferably at most 50 ⁇ m, and preferably at most 25 ⁇ m. From the same viewpoint, the length B is preferably 0.2 ⁇ m or more, more preferably 1 ⁇ m or more, and further preferably 2 ⁇ m or more, provided that the above-mentioned range of A / B is satisfied.
- the upper limit is preferably 40 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 20 ⁇ m or less, and preferably 15 ⁇ m or less.
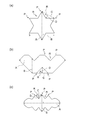
- the contour line in the cross section of the deformed fiber is viewed along the circumferential direction, the plurality of convex portions P and the concave portions located between the adjacent convex portions P.
- the length of a line segment connecting the vertices of adjacent convex portions P is C
- the length of a perpendicular line drawn from the line segment to the lowest position of the concave portion R is D (See FIGS. 3A to 3C)
- the value of C / D is preferably 0.1 or more, more preferably 1 or more, still more preferably 2 or more, and the upper limit thereof. Is preferably 5 or less, more preferably 4 or less, and still more preferably 3 or less.
- the value of C for calculating the value of C / D is all The average value of the values of C is used.
- the value of D for calculating the value of C / D is an average value of all the values of D.
- the value is an average value of C and D.
- the length C is preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more, and more preferably 0.5 ⁇ m or more, provided that the above-described C / D range is satisfied. More preferably, it is more preferably 1 ⁇ m or more, and the upper limit is preferably 20 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 10 ⁇ m or less, and preferably 5 ⁇ m or less. From the same viewpoint, the length D is preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more, more preferably 0.5 ⁇ m or more, and more preferably 1 ⁇ m or more on condition that the above-mentioned C / D range is satisfied. Is more preferable, and the upper limit thereof is preferably 20 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 10 ⁇ m or less, and preferably 5 ⁇ m or less.
- the above-mentioned lengths A to D can be measured by the following measuring methods. That is, the prepared fiber assembly was cut using a razor or the like while maintaining the cross-sectional shape of the fiber, and the cross-section was vacuum-deposited with Pt. Using a scanning electron microscope (JSM-IT100, manufactured by JEOL Ltd.), the cross section of the Pt-deposited fiber assembly was observed at a magnification of 500 to 1000 times, and the above-mentioned fiber cross section was measured using the attached software length measurement tool. The lengths A to D were measured respectively.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention may be composed of only the first fibers 11 and the second fibers 12, and may further contain other fibers in addition to these fibers.
- the other fibers the above-described synthetic fibers and natural fibers can be used. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- Other fibers may be circular (non-irregular) or non-circular (irregular) in cross-section.
- the other fibers are contained in the fiber aggregate at a ratio of preferably 50% by mass or less, more preferably 40% by mass or less, and still more preferably 30% by mass or less.
- the fineness of the fibers is preferably 0.6 dtex or more, and more preferably 1.0 dtex or more, from the viewpoints of operability and dirt collection efficiency during wiping. More preferably, it is more preferably 1.2 dtex or more. Further, it is preferably at most 4.0 dtex, more preferably at most 3.5 dtex, even more preferably at most 3.0 dtex.
- the basis weight of the fiber aggregate constituting the wiping sheet is preferably equal to or greater than 40 g / m 2, more preferably equal to or greater than 45 g / m 2, and further preferably equal to or greater than 50 g / m 2.
- the upper limit thereof is preferably 140 g / m 2 or less, more preferably 100 g / m 2 or less, 80 g / m 2 or less is more preferable.
- the thickness of the wiping sheet is preferably 0.5 mm or more under a load of 40 N / m 2 , more preferably 1.0 mm or more, and the upper limit is 2 mm under the same load. It is preferably at most 0.5 mm, more preferably at most 3 mm.
- the cleaning liquid carried on the sheet water alone or an aqueous solution containing an additive, such as a general composition used for a wet wiping sheet, is used. be able to.
- an additive such as a general composition used for a wet wiping sheet.
- the additive used in the cleaning liquid at least one selected from the group consisting of a surfactant, a bactericide, a fragrance, a fragrance, a deodorant, a pH adjuster, an alcohol, abrasive particles, a gloss imparting agent and a thickener. Is mentioned.
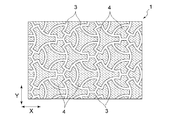
- a pattern concave portion 3 and a pattern convex portion 4 forming a concave and convex portion of a macroscopic pattern are formed on one surface of the wiping sheet 1.
- the boundary between the pattern concave portion 3 and the pattern convex portion 4 has a curved portion when viewed macroscopically.
- the other surface is flat without complementary concave and convex portions derived from the concave and convex portions of the macroscopic pattern.
- the concavo-convex portions of the macroscopic pattern are not limited to the macroscopic pattern shown in the figure.
- the macroscopic pattern shown in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2017-113282 and a graphic such as a straight line, a curve, a circle, and a polygon are appropriately combined. It may be a macroscopic pattern.
- the macroscopically curved shape constitutes a pattern uneven portion except for a curve constituting a micro-scale fine hole and a curve constituting a drainage hole having a diameter of about 1.5 to 2 mm.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention may be constituted by a fiber assembly in which the boundary of the existing region between the first fiber and the second fiber in the sheet thickness direction is not clear when focusing on one fiber assembly.
- it may be constituted by a fiber aggregate having a two-layer structure of a layer containing the first fibers and a layer containing the second fibers.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention is composed of a fiber aggregate having a multilayer structure of three or more layers including a layer containing a first fiber, a layer containing a second fiber, and a layer containing another fiber. Is also good.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention may be composed of only one fiber aggregate (irrespective of a single layer or a multilayer) containing deformed fibers, or a first fiber aggregate containing first and second fibers. And a multi-ply laminate structure in which the second fiber aggregate with or without the deformed fiber or a sheet material other than the fiber aggregate is laminated.
- the sheet material include a nonwoven fabric, a woven fabric, and paper.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention may further include a scrim net for supporting the fiber aggregate constituting the sheet.
- a scrim net is provided, it is preferable that the scrim net is arranged in the central region in the thickness direction of the fiber assembly.
- the scrim net can be integrally entangled with the deformed fiber constituting the fiber assembly, and may be in the form of a net, a grid, a strand, or the like.
- Resin can be used as a raw material constituting the scrim net.
- the resin include polyolefin resins such as polyethylene and polypropylene; polyester resins such as polyethylene terephthalate; polyamide resins such as nylon 6 and nylon 66; acrylonitrile resins such as polyacrylonitrile; vinyl resins such as polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene; A vinylidene-based resin such as vinylidene chloride can be used.
- the diameter of the scrim net (diameter in the cross section) can be appropriately adjusted according to the degree of entanglement of the fiber, but is 10 ⁇ m or more. Is preferably 500 ⁇ m or more, more preferably 2000 ⁇ m or less, and even more preferably 1000 ⁇ m or less.
- the wire diameter of the scrim net may be partially different or the same, and when the wire diameter is partially different, the wire diameter of the scrim is taken to be the average value.
- the basis weight of the scrim net is preferably 1 g / m 2 or more, more preferably 3 g / m 2 or more, preferably 20 g / m 2 or less, and further preferably 10 g / m 2 or less.
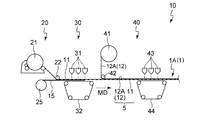
- the water pressure blown from the first water stream nozzle 31 is preferably 30 kg / cm 2 or more and 80 kg / cm 2 or less, more preferably 40 kg / cm 2 or more and 60 kg / cm 2 or less, and the web of the first fibers 11
- the transport speed in the MD direction is preferably 2 m / min or more and 10 m / min or less, more preferably 4 m / min or more and 8 m / min or less.
- the entangled body 12A of the second fiber 12 is laminated on the upper surface thereof, and the fiber aggregate 1A is formed by hydroentanglement (second entanglement step).
- the entangled body of the first fiber 11 is conveyed in the MD direction, and the entangled body 12A of the sheet-like second fiber 12 unwound from the raw roll 41 is placed on the upper surface of the entangled body.
- the layers are laminated to form a laminate 5.
- the constituent fibers of each entangled body are three-dimensionally entangled to form the fiber assembly 1A.
- the fiber assembly 1A may be used as it is as a wiping sheet 1 of a dry type or a wet type, and if necessary, as shown in FIG.
- the uneven portion of the macroscopic pattern may be formed, and this may be used as the wiping sheet 1 in a dry or wet mode.
- ⁇ 21> The wiping sheet according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 20>, wherein the first fibers and the second fibers are both synthetic fibers.
- ⁇ 22> The wiping sheet according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 21>, which has a substantially rectangular shape.
- ⁇ 23> On one surface of the wiping sheet are formed a pattern concave portion and a pattern convex portion that constitute the concave and convex portion of the macroscopic pattern, and the boundary between the pattern concave portion and the pattern convex portion is macroscopically viewed.
- the wiping sheet according to any one of the above ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 22> having a curved portion.
- ⁇ 24> The wiping sheet according to ⁇ 23>, wherein the other surface is flat when the uneven portion is formed on one surface.
- Example 1 As the first fiber, hydroentanglement was performed using a modified fiber (see FIG. 2 (e)) in which the cross-sectional shape of the fiber made of a thermoplastic resin was multilobal, to produce a fiber aggregate.
- the constituent fibers of the fiber assembly are multilobal fibers (made of PET, fineness of 1.7 dtex, average fiber diameter of 13.5 ⁇ m) as the first fibers, and perfect circular fibers (made of PP, fineness of 7.25) as the second fibers. 0 ⁇ 10 ⁇ 3 dtex, average fiber diameter 1 ⁇ m).
- Example 1 As the first fiber, only a fiber made of a thermoplastic resin and having a perfect circular cross section was subjected to hydroentanglement to produce a fiber aggregate.
- the perfect circular fiber as the first fiber was made of PET, had a fineness of 1.45 dtex and an average fiber diameter of 11.5 ⁇ m.
- the other conditions were the same as in Example 1, and a wet wiping sheet was manufactured.
- the wiping sheet of this comparative example does not include the second fiber.
- the tensile modulus of the wiping sheets of the examples and the comparative examples was measured.
- a tensile strength tester AG-IS 100N, manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation
- a dry-type sample having a length of 150 mm and a width of 30 mm was sampled in the length direction at a span of 100 mm and a speed of 300 mm / min.
- the tensile strength (N / mm) and the displacement (mm) at that time were measured.
- the tensile modulus (N / mm 2 ) was calculated by dividing the difference in displacement in tensile strength between the difference in tensile strength between 0 N / mm and 0.17 N / mm. The higher the tensile modulus, the higher the sheet strength. Table 1 shows the results.
- the wiping sheet of the present invention has a high sheet strength, a fine particle stain, and a fiber stain such as hair by containing a modified fiber and a fiber having a smaller diameter than the fiber as constituent fibers. It can be seen that it has a high trapping performance. Further, it can be seen that the wiping sheet of the present invention has a high sustained release property of the cleaning liquid when used in a wet mode, and enables wiping in a wide range.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Cleaning Implements For Floors, Carpets, Furniture, Walls, And The Like (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Polishing Bodies And Polishing Tools (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201980065138.0A CN112788975A (zh) | 2018-10-02 | 2019-09-26 | 擦拭片材 |
| JP2020550370A JPWO2020071250A1 (ja) | 2018-10-02 | 2019-09-26 | ワイピングシート |
| SG11202102900RA SG11202102900RA (en) | 2018-10-02 | 2019-09-26 | Wiping sheet |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018-187761 | 2018-10-02 | ||
| JP2018187761 | 2018-10-02 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020071250A1 true WO2020071250A1 (ja) | 2020-04-09 |
Family
ID=70055194
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/037998 Ceased WO2020071250A1 (ja) | 2018-10-02 | 2019-09-26 | ワイピングシート |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2020071250A1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN112788975A (enExample) |
| SG (1) | SG11202102900RA (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI839394B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2020071250A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022129832A (ja) * | 2021-02-25 | 2022-09-06 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | ロール状ペーパータオル |
| JP2023066249A (ja) * | 2021-10-28 | 2023-05-15 | ライオン株式会社 | シート状化粧料 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009279312A (ja) * | 2008-05-26 | 2009-12-03 | Teijin Fibers Ltd | ワイピングクロスおよびその製造方法 |
| JP2017113282A (ja) * | 2015-12-24 | 2017-06-29 | 花王株式会社 | 湿式清掃用シート |
| WO2018105340A1 (ja) * | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | 花王株式会社 | 湿式ワイピングシート |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19947870C1 (de) * | 1999-10-05 | 2001-05-10 | Freudenberg Carl Fa | Fersenfutter für die Schuhindustrie |
| EP1689008B1 (en) * | 2005-01-26 | 2011-05-11 | Japan Vilene Company, Ltd. | Battery separator and battery comprising the same |
| JP4827528B2 (ja) * | 2005-12-28 | 2011-11-30 | 花王株式会社 | ウエットシート用シート基材 |
| WO2014132690A1 (ja) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-04 | 東レ株式会社 | 不織布 |
| CN105386240A (zh) * | 2015-10-15 | 2016-03-09 | 称道新材料科技(上海)有限公司 | 异截面熔喷纤维无纺布及其制备方法和专用喷丝板 |
-
2019
- 2019-09-26 SG SG11202102900RA patent/SG11202102900RA/en unknown
- 2019-09-26 JP JP2020550370A patent/JPWO2020071250A1/ja active Pending
- 2019-09-26 WO PCT/JP2019/037998 patent/WO2020071250A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2019-09-26 CN CN201980065138.0A patent/CN112788975A/zh active Pending
- 2019-10-02 TW TW108135683A patent/TWI839394B/zh active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009279312A (ja) * | 2008-05-26 | 2009-12-03 | Teijin Fibers Ltd | ワイピングクロスおよびその製造方法 |
| JP2017113282A (ja) * | 2015-12-24 | 2017-06-29 | 花王株式会社 | 湿式清掃用シート |
| WO2018105340A1 (ja) * | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | 花王株式会社 | 湿式ワイピングシート |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022129832A (ja) * | 2021-02-25 | 2022-09-06 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | ロール状ペーパータオル |
| JP7495892B2 (ja) | 2021-02-25 | 2024-06-05 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | ロール状ペーパータオル |
| JP2023066249A (ja) * | 2021-10-28 | 2023-05-15 | ライオン株式会社 | シート状化粧料 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW202020250A (zh) | 2020-06-01 |
| SG11202102900RA (en) | 2021-04-29 |
| CN112788975A (zh) | 2021-05-11 |
| TWI839394B (zh) | 2024-04-21 |
| JPWO2020071250A1 (ja) | 2021-09-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3559533B2 (ja) | 絡合不織布とこれを用いた清拭シートおよび湿潤性シート | |
| AU2014356113B2 (en) | Multi-purpose tough stain removal articles | |
| WO2020071250A1 (ja) | ワイピングシート | |
| JP2005245913A (ja) | 清掃用ワイパー | |
| JP5117152B2 (ja) | フローリングワイパー | |
| CN112261897B (zh) | 擦拭片材 | |
| JP4648724B2 (ja) | 不織布およびその製造方法 | |
| JP5421765B2 (ja) | 清掃シート | |
| JP2023101408A (ja) | ワイパー用不織布およびワイパー | |
| JP7030542B2 (ja) | ワイピングシート | |
| JP3912177B2 (ja) | 起毛様不織布、その製造方法及びそれを用いた繊維製品 | |
| JP7055009B2 (ja) | ワイピングシート及び清掃具 | |
| JP6276921B2 (ja) | 不織布ワイパー | |
| JP7511316B2 (ja) | ワイピングシート | |
| JP7359676B2 (ja) | 湿式ワイピングシート | |
| JP2019154526A (ja) | 清掃用シート | |
| JP2002263043A (ja) | ワイピング用不織布 | |
| JP2019208949A (ja) | ワイピングシート | |
| JP6986940B2 (ja) | ワイピングシート | |
| JP7359677B2 (ja) | 湿式ワイピングシート | |
| JP7566300B2 (ja) | スパンレース不織布 | |
| JP2023143236A (ja) | 不織布およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2025015521A (ja) | 対物ワイパー用不織布および対物ワイパー | |
| JP2005028115A (ja) | ワイパー | |
| TW201920793A (zh) | 擦拭片材及其製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19868315 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2020550370 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2101001886 Country of ref document: TH |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19868315 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |