WO2019107201A1 - 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 - Google Patents
硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019107201A1 WO2019107201A1 PCT/JP2018/042663 JP2018042663W WO2019107201A1 WO 2019107201 A1 WO2019107201 A1 WO 2019107201A1 JP 2018042663 W JP2018042663 W JP 2018042663W WO 2019107201 A1 WO2019107201 A1 WO 2019107201A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- curable resin
- resin composition
- polyisocyanate
- composition according
- meth
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/28—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the compounds used containing active hydrogen
- C08G18/40—High-molecular-weight compounds
- C08G18/42—Polycondensates having carboxylic or carbonic ester groups in the main chain
- C08G18/44—Polycarbonates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/73—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates acyclic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/28—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the compounds used containing active hydrogen
- C08G18/30—Low-molecular-weight compounds
- C08G18/32—Polyhydroxy compounds; Polyamines; Hydroxyamines
- C08G18/3203—Polyhydroxy compounds
- C08G18/3206—Polyhydroxy compounds aliphatic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/28—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the compounds used containing active hydrogen
- C08G18/40—High-molecular-weight compounds
- C08G18/62—Polymers of compounds having carbon-to-carbon double bonds
- C08G18/6216—Polymers of alpha-beta ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acids or of derivatives thereof
- C08G18/622—Polymers of esters of alpha-beta ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acids
- C08G18/6225—Polymers of esters of acrylic or methacrylic acid
- C08G18/6229—Polymers of hydroxy groups containing esters of acrylic or methacrylic acid with aliphatic polyalcohols
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/74—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic
- C08G18/76—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic aromatic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/74—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic
- C08G18/76—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic aromatic
- C08G18/7657—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic aromatic containing two or more aromatic rings
- C08G18/7664—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic aromatic containing two or more aromatic rings containing alkylene polyphenyl groups
- C08G18/7671—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates cyclic aromatic containing two or more aromatic rings containing alkylene polyphenyl groups containing only one alkylene bisphenyl group
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/77—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates having heteroatoms in addition to the isocyanate or isothiocyanate nitrogen and oxygen or sulfur
- C08G18/78—Nitrogen
- C08G18/79—Nitrogen characterised by the polyisocyanates used, these having groups formed by oligomerisation of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/791—Nitrogen characterised by the polyisocyanates used, these having groups formed by oligomerisation of isocyanates or isothiocyanates containing isocyanurate groups
- C08G18/792—Nitrogen characterised by the polyisocyanates used, these having groups formed by oligomerisation of isocyanates or isothiocyanates containing isocyanurate groups formed by oligomerisation of aliphatic and/or cycloaliphatic isocyanates or isothiocyanates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/77—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates having heteroatoms in addition to the isocyanate or isothiocyanate nitrogen and oxygen or sulfur
- C08G18/78—Nitrogen
- C08G18/79—Nitrogen characterised by the polyisocyanates used, these having groups formed by oligomerisation of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/797—Nitrogen characterised by the polyisocyanates used, these having groups formed by oligomerisation of isocyanates or isothiocyanates containing carbodiimide and/or uretone-imine groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/70—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen characterised by the isocyanates or isothiocyanates used
- C08G18/72—Polyisocyanates or polyisothiocyanates
- C08G18/80—Masked polyisocyanates
- C08G18/8003—Masked polyisocyanates masked with compounds having at least two groups containing active hydrogen
- C08G18/8006—Masked polyisocyanates masked with compounds having at least two groups containing active hydrogen with compounds of C08G18/32
- C08G18/8009—Masked polyisocyanates masked with compounds having at least two groups containing active hydrogen with compounds of C08G18/32 with compounds of C08G18/3203
- C08G18/8012—Masked polyisocyanates masked with compounds having at least two groups containing active hydrogen with compounds of C08G18/32 with compounds of C08G18/3203 with diols
- C08G18/8016—Masked aliphatic or cycloaliphatic polyisocyanates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D175/00—Coating compositions based on polyureas or polyurethanes; Coating compositions based on derivatives of such polymers
- C09D175/04—Polyurethanes
- C09D175/06—Polyurethanes from polyesters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09J—ADHESIVES; NON-MECHANICAL ASPECTS OF ADHESIVE PROCESSES IN GENERAL; ADHESIVE PROCESSES NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE; USE OF MATERIALS AS ADHESIVES
- C09J133/00—Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by only one carboxyl radical, or of salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, imides, or nitriles thereof; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers
- C09J133/04—Homopolymers or copolymers of esters
- C09J133/14—Homopolymers or copolymers of esters of esters containing halogen, nitrogen, sulfur or oxygen atoms in addition to the carboxy oxygen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09J—ADHESIVES; NON-MECHANICAL ASPECTS OF ADHESIVE PROCESSES IN GENERAL; ADHESIVE PROCESSES NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE; USE OF MATERIALS AS ADHESIVES
- C09J169/00—Adhesives based on polycarbonates; Adhesives based on derivatives of polycarbonates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K3/00—Materials not provided for elsewhere
- C09K3/10—Materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a curable resin composition and an electrical component using the same.
- curable resin compositions containing a polyol and a polyisocyanate are known.
- Patent Document 1 is obtained by polymerizing a radically polymerizable monomer at a polymerization temperature of 150 to 350 ° C., a hydroxyl value of 5 to 55 mg KOH / g, a glass transition temperature of ⁇ 70 to 10 ° C.
- a curable resin composition for a sealing material which comprises a copolymer having an average molecular weight of 500 to 20,000 and a polyoxyalkylene compound having two or more isocyanate groups at its terminal.
- an acrylic polyol and an isocyanate compound are included, and the acrylic polyol is a polyol having a glass transition temperature of ⁇ 20 to 20 ° C. obtained by polymerizing a polymerizable monomer, and the isocyanate compound is A curable resin composition is disclosed which comprises both an isocyanate having no aromatic ring and an isocyanate having an aromatic ring. The said curable resin composition is used for the adhesive agent for lamination sheets.
- the cured product of the curable resin composition described in Patent Document 1 is degraded by hydrolysis or the like in a high-temperature, high-humidity environment as required for electrical components mounted in vehicles such as automobiles. It has no heat and moisture resistance.
- the curable resin composition of patent document 2 is used for the adhesive agent for lamination sheets. Therefore, the glass transition temperature of the acrylic polyol is as high as ⁇ 20 to 20 ° C. Therefore, since the cured product of this curable resin composition is inferior in flexibility in a low temperature environment required for a vehicle, high stress may be generated at the time of use at low temperature, which may cause cracking or peeling. is there. Moreover, when applying a hardened
- the present disclosure provides a curable resin composition having moisture-heat resistance, sufficient flexibility at low temperature, and capable of obtaining a cured product with good initial strength, and an electrical component using the same. With the goal.
- One aspect of the present disclosure is a (meth) acrylic polyol.
- the (meth) acrylic polyol is A polymer which is liquid at a hydroxyl value of 5 mg KOH / g to 150 mg KOH / g, a glass transition temperature of -70 ° C. to -40 ° C., a number average molecular weight of 500 to 20000, and 25 ° C. It is in the curable resin composition.
- Another aspect of the present disclosure is an electrical component having a sealing material composed of a cured product of the curable resin composition.
- Yet another aspect of the present disclosure includes an adhesive layer bonding the case and the lid,
- the said adhesive layer exists in the electrical component comprised from the hardened
- the curable resin composition forms a urethane bond by curing to form a polyurethane-based cured product.
- the cured product has moisture and heat resistance, has sufficient flexibility at low temperature, and has good initial strength, because the curable resin composition has the above-described configuration. Further, since this cured product uses a polycarbonate-based polyol having heat resistance, the heat resistance is also high.
- the sealing material has moisture and heat resistance, has sufficient flexibility at low temperature, and has good initial strength. Have. Therefore, this electric component is excellent in long-term insulation reliability, and can be suitably used for vehicles, such as a car.
- the adhesive layer has moisture and heat resistance and heat resistance, has sufficient flexibility at low temperatures, and has good initial strength Have. Therefore, this electric component is excellent in long-term insulation reliability, and can be suitably used for vehicles, such as a car.
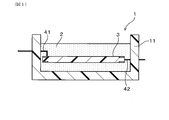
- FIG. 1 is an overall cross-sectional view showing a schematic configuration of an electronic control unit as an example of an electrical component having a sealing material composed of a cured product of a curable resin composition according to Embodiment 1.
- the electric component 1 of the present embodiment is, for example, an electronic control unit (that is, an ECU) for vehicle use, and the curable resin composition of the present embodiment is for the electric component 1. It is used as the sealing material 2.
- the electrical component 1 includes a case 11 made of resin, a substrate 3 housed in the case 11, and a sealing material 2.
- various electronic components including an IC chip and a capacitor are mounted on the substrate 4.
- the sealing material 2 is made of a cured product in which the curable resin composition is injected into the case 11 and cured, and covers the entire substrate 3 including the electronic component.
- the substrate 3 is made of, for example, a known printed wiring board, and external connection terminals 41 and 42 are provided on the outer peripheral portion of the substrate 3 and penetrate the wall of the case 11 and extend to the outside.
- a cured product of a curable resin composition includes a case in which a substrate on which various electronic components are mounted is accommodated, a lid attached to the case, and a case and a lid It can also be used as an adhesive layer in an electronic component such as an electronic control unit having an adhesive layer for bonding.
- the curable resin composition described above contains a (meth) acrylic polyol, a polycarbonate polyol, and a polyisocyanate.
- the curable resin composition may be a two-component mixture type or a one-component moisture-curable type.
- the two-liquid mixed type a two-liquid mixed type in which a main agent containing a (meth) acrylic polyol and a polycarbonate-based polyol and a curing agent containing a polyisocyanate are mixed, (meth) acrylic polyol
- a two-component mixture type in which a urethane prepolymer having an isocyanate group at an end and a (meth) acrylic polyol are mixed.
- a urethane prepolymer having an isocyanate group at the end which is obtained by reacting a (meth) acrylic polyol, a polycarbonate polyol, and a polyisocyanate, is reacted with moisture in the air.
- a liquid moisture curing type etc. can be illustrated.
- the term "(meth) acrylic” in the term “(meth) acrylic polyol” is meant to include not only acrylic but also methacrylic.
- the (meth) acrylic polyol has a hydroxyl value of 5 mg KOH / g to 150 mg KOH / g, a glass transition temperature of -70 ° C. to -40 ° C., a number average molecular weight of 500 to 20000, and 25 It is composed of a polymer which is liquid at ° C.
- not only a polymer but an oligomer is contained in the polymer said above.
- the polymer referred to above may be either a homopolymer or a copolymer.
- the polymer is preferably a copolymer from the viewpoint of easy control of physical properties of the cured product.
- the hydroxyl value when the hydroxyl value is less than 5 mg KOH / g, the curability may be reduced, and a cured product having poor moist heat resistance may be obtained.
- the hydroxyl value may be preferably 8 mg KOH / g or more, more preferably 12 mg KOH / g or more, and even more preferably 15 mg KOH / g or more from the viewpoint of securing moist heat resistance and the like.
- the hydroxyl value exceeds 150 mg KOH / g, the cured product may become brittle due to excessive curing.
- the hydroxyl value can be preferably 145 mg KOH / g or less, more preferably 140 mg KOH / g or less, and even more preferably 135 mg KOH / g or less, from the viewpoint of securing flexibility at low temperature and the like.
- the hydroxyl value is a value measured in accordance with JIS-K1557-1.
- the glass transition temperature is preferably as low as possible from the viewpoint of securing flexibility in a low temperature environment after curing.
- the glass transition temperature is set to ⁇ 70 ° C. or higher from the viewpoint of the availability of the (meth) acrylic polyol and the like.
- the glass transition temperature is preferably ⁇ 45 ° C. or less, more preferably ⁇ 50 ° C. or less, and still more preferably ⁇ 55 ° C. or less from the viewpoint of securing sufficient flexibility at a low temperature, etc. it can.
- the measuring method of a glass transition temperature is a value based on JISK7121 and is a value measured as an inflexion point of DSC.
- a (meth) acrylic polyol when the number average molecular weight is less than 500, the crosslink density of the cured product is increased and the elastic modulus of the cured product is increased, so the possibility of cracking or peeling in a cold environment is increased.
- the number average molecular weight can be preferably 600 or more, more preferably 800 or more, and even more preferably 1000 or more from the viewpoint of suppressing an increase in the elastic modulus of the cured product.
- the number average molecular weight exceeds 20000, there is a possibility that the workability of the curable resin composition may be lowered due to the increase in viscosity.
- the number average molecular weight can be preferably 18000 or less, more preferably 16000 or less, and even more preferably 14000 or less from the viewpoint of facilitating retention of the low viscosity of the curable resin composition.
- the number average molecular weight is a value measured by a GPC method (gel permeation chromatography method) using a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF).
- the (meth) acrylic polyol is liquid at 25 ° C.
- the (meth) acrylic polyol is solid at 25 ° C., it needs to be dissolved with a solvent at the time of preparation of the curable resin composition.
- the (meth) acrylic polyol is liquid at 25 ° C., it is not necessary to dissolve with a solvent at the time of preparation of the curable resin composition, and the (meth) acrylic polyol can be mixed without solvent. .
- the deterioration of the workability such as the necessity of mixing while heating does not occur at the time of the preparation, and the composition can be prepared relatively easily at room temperature, Workability is good.
- polycarbonate-based polyol in the curable resin composition examples include polyols obtained by carbonate-modifying a single or a mixture of aliphatic diols such as hexanediol, pentanediol, butanediol and propanediol. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more. More specifically, examples of polycarbonate-based polyols include diols obtained by subjecting a mixture of hexanediol and pentanediol to carbonate modification and having hydroxyl groups at both ends.
- the polycarbonate-based polyol can have a hydroxyl value of 20 mg KOH / g or more and 300 mg KOH / g or less. According to this configuration, the viscosity at normal temperature is low, the workability is excellent, and a cured product having a high initial strength can be easily obtained.
- the hydroxyl value of the polycarbonate-based polyol is preferably 25 mg KOH / g or more and 280 mg KOH / g or less, more preferably 30 mg KOH / g or more and 260 mg KOH / g or less, and still more preferably 35 mg KOH / g from the viewpoint of adjusting physical properties of the cured product. It can be made into g or more and 250 mgKOH / g or less.
- the hydroxyl value of the polycarbonate polyol is a value measured according to JIS-K1557-1.
- the mass ratio of the (meth) acrylic polyol to the polycarbonate polyol can be 95: 5 to 20:80. According to this configuration, it is possible to obtain a cured product having moisture heat resistance, sufficient flexibility at low temperatures, and good initial strength.
- the mass ratio of the (meth) acrylic polyol to the polycarbonate polyol is preferably 93: 7 to 25:75, more preferably 90:10 to 27:73, still more preferably 85: 5 to 30:70. It can be done.
- the polyisocyanate can include an aliphatic polyisocyanate. According to this configuration, the heat and moisture resistance of the cured product can be easily secured. Moreover, according to this configuration, there is also an advantage that it becomes easy to impart flexibility to the cured product. In addition, in curable resin composition, 1 type, or 2 or more types of polyisocyanate can be used together.
- aliphatic polyisocyanates include hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), derivatives thereof (modified products etc.) and the like.
- HDI hexamethylene diisocyanate
- IPDI isophorone diisocyanate
- derivatives thereof modified products etc.
- suitable hexamethylene diisocyanate
- hexamethylene diisocyanate and hexamethylene diisocyanate derivatives have high reactivity because the number of substituents that cause steric hindrance around the isocyanate group which is a reaction point is small. Therefore, according to this configuration, it is possible to form a cured product in a shorter time. Moreover, according to this configuration, there is also an advantage that the curing temperature can be easily set lower.
- hexamethylene diisocyanate derivatives include biuret-modified hexamethylene diisocyanate, isocyanurate-modified hexamethylene diisocyanate, adduct-modified hexamethylene diisocyanate, prepolymer of hexamethylene diisocyanate, and the like. At least one selected from the group consisting of a mixture of and the like can be mentioned as suitable. According to this configuration, it is possible to obtain a cured product having moisture heat resistance, sufficient flexibility at low temperatures, and good initial strength. Moreover, according to this configuration, there is also an advantage that physical properties of the cured product can be easily controlled.
- the polyisocyanate can contain an aromatic polyisocyanate in addition to the aliphatic polyisocyanate. According to this configuration, it is possible to improve the initial breaking strength and the adhesive strength of the cured product, as compared to the case where an aliphatic polyisocyanate is used alone as the polyisocyanate. For example, by increasing the proportion of aromatic polyisocyanate, the initial breaking strength of the cured product is increased, and the adhesion is also improved.
- aromatic polyisocyanate examples include diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) such as 2,2'-, 2,4'- or 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, 2,2'-, 2,6 Examples thereof include '-toluene diisocyanate (TDI), derivatives thereof (modified products etc.) and the like.
- MDI diphenylmethane diisocyanate
- TDI '-toluene diisocyanate
- derivatives thereof modified products etc.
- the aromatic polyisocyanate diphenylmethane diisocyanate, and at least one of diphenylmethane diisocyanate derivatives can be mentioned as preferable. According to this configuration, it is possible to react with the polyol with less heat to form a cured product. Moreover, according to this configuration, there are also advantages such as the breaking strength of the cured product and the improvement of the adhesive strength.
- diphenylmethane diisocyanate derivatives include biuret-modified diphenylmethane diisocyanate, isocyanurate-modified diphenylmethane diisocyanate, adduct-modified diphenylmethane diisocyanate, prepolymer of diphenylmethane diisocyanate, and a mixture thereof At least one selected from the above and the like can be mentioned as suitable. According to this configuration, it is easier to adjust the initial breaking strength of the cured product. Moreover, according to this configuration, there is also an advantage that it is easy to further improve the breaking strength and the adhesive strength of the cured product.
- the molar ratio of the aliphatic polyisocyanate and the aromatic polyisocyanate can be 9: 1 to 5: 5. According to this structure, it becomes easy to obtain the hardened
- the molar ratio of aliphatic polyisocyanate to aromatic polyisocyanate is preferably 8: 2 to 5: 5, more preferably 7: 3 to 5: 5, still more preferably 6: 4 to 5: 5. can do.
- the polyisocyanate may be composed of a bifunctional polyisocyanate or may be composed of a trifunctional polyisocyanate, or a bifunctional polyisocyanate and a trifunctional polyisocyanate. May be included.
- the polyisocyanate contains both of difunctional polyisocyanate and trifunctional polyisocyanate, it becomes easy to adjust the hardness of the cured product.
- the molar ratio of the difunctional polyisocyanate to the trifunctional polyisocyanate is 1: 9 to 9: 1.
- the molar ratio of difunctional polyisocyanate to trifunctional polyisocyanate is preferably 2: 8 to 8: 2, more preferably 3: 7 to 7: 3, still more preferably 6: 4 to 4: It can be six.
- bifunctional polyisocyanate may be selected from aliphatic polyisocyanate, and may be selected from aromatic polyisocyanate.
- the trifunctional polyisocyanate may be selected from aliphatic polyisocyanates or may be selected from aromatic polyisocyanates.
- a diol having a molecular weight of less than 300 for example, a plasticizer, a catalyst, an additive added to a polyurethane-based curable resin composition, and the like can be exemplified. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the curable resin composition contains a diol having a molecular weight of less than 300, the following advantages can be obtained. Diols having a molecular weight of less than 300 can function as diluents because they are small molecules. Therefore, in the above case, there is an advantage that it is easy to adjust the viscosity before the curable resin composition is cured.
- a diol having a molecular weight of less than 300 there is also an advantage that during curing of the curable resin composition by crosslinking, the distance between crosslinking points becomes short, and the strength of the cured product can be easily improved.
- the molecular weight of the diol can be preferably 250 or less, more preferably 230 or less, and still more preferably 200 or less, from the viewpoint of improving the strength of the cured product and the like.
- the molecular weight of the diol can be preferably 60 or more from the viewpoint of suppressing volatilization at high temperatures.
- the diol having a molecular weight of less than 300 examples include octanediol, nonanediol, hexanediol, butanediol, ethylene glycol and the like.
- the plasticizer specifically, for example, phthalic acid ester represented by dioctyl phthalate, dinonyl phthalate, adipate ester represented by dioctyl adipate, dinonyl adipate, trimellitic acid tris (2 And trimellitic acid such as -ethylhexyl, and phosphoric acid ester such as triethyl phosphate.
- an amine compound, a tin compound, a bismuth compound etc. can be illustrated specifically, for example.
- the curable resin composition contains a diol having a molecular weight of less than 300
- the curable resin composition contains 0 diol having a molecular weight of less than 300 with respect to 100 parts by mass in total of the (meth) acrylic polyol and the polycarbonate polyol. .5 parts by mass or more and 30 parts by mass or less can be included.
- the curable resin composition contains a plasticizer
- the curable resin composition contains 3 to 200 parts by mass of a plasticizer based on 100 parts by mass of the (meth) acrylic polyol and the polycarbonate polyol.
- the curable resin composition contains a catalyst
- the curable resin composition contains 0.0001 to 5 parts by mass of the catalyst per 100 parts by mass of the (meth) acrylic polyol and the polycarbonate polyol. The following can be included.
- Polyacrylic polyol composed of a copolymer ⁇ (Meth) acrylic polyol (2) (manufactured by Toagosei Co., Ltd., “ARUFON UH-2041”, hydroxyl value: 122 mg KOH / g, glass transition temperature Tg: ⁇ 60 ° C., number average molecular weight: about 2000, liquid at 25 ° C.
- Polyacrylic polyol composed of a copolymer ⁇ (Meth) acrylic polyol (3) (synthetic, hydroxyl value: 26 mg KOH / g, glass transition temperature Tg: 15 ° C., number average molecular weight: about 7000, solid copolymer at 25 ° C.) Poly acrylic polyol)
- the (meth) acrylic polyol (3) was synthesized as follows. A flask was charged with 100 g of ethyl acetate (reagent) and 1 g of 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as a polymerization initiator, and the mixture was refluxed at 80 ° C.
- AIBN 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile
- Polycarbonate-based polyol- ⁇ Polycarbonate-based polyol (1) (manufactured by Asahi Kasei Corporation, "Duranol T5651”, polycarbonate diol, hydroxyl value: 110 mg KOH / g, liquid) ⁇ Polycarbonate-based polyol (2) (manufactured by Asahi Kasei Corp., “Duranol T5650E”, polycarbonate diol, hydroxyl value: 223 mg KOH / g, liquid)
- octanediol, a plasticizer, and a catalyst are compounded with respect to a total of 100 parts by mass of a predetermined (meth) acrylic polyol and a predetermined polycarbonate polyol, and each main agent was prepared.
- predetermined polyisocyanates were weighed, and mixed as needed (in the case of blending using plural types of polyisocyanates), to prepare each curing agent. Then, the predetermined resin and the predetermined curing agent were sufficiently mixed at 25 ° C. to obtain a curable resin composition of each sample.
- each of the obtained curable resin compositions was poured into a No. 3 dumbbell-shaped mold of rubber and cured at 120 ° C. for 3 hours to obtain a cured product of each sample.
- the storage modulus E ′ retention was calculated from the formula 100 ⁇ (storage modulus E ′ of cured product after pressure cooker test) / (storage modulus E ′ of cured product before pressure cooker test).
- a + is regarded as having excellent heat and humidity resistance
- the storage elastic modulus E ′ retention is 60% or more and less than 90%.
- C was determined as having no moisture-heat resistance.
- the flexibility at low temperature is excellent as "A +", and when the Tg is more than -50 ° C and -40 ° C or less, the flexibility at low temperature is good.
- cured material in which the determination of "A +" and "A” was made is considered to have sufficient flexibility at low temperature.
- Tables 1 and 2 collectively show detailed blending of the curable resin composition, evaluation results of the cured product, and the like.
- the cured products of Samples 1 to 13 obtained by curing the curable resin composition having the configuration of Samples 1 to 13 have moisture heat resistance, and are sufficiently flexible at low temperatures. It can be seen that it has good initial strength. Therefore, if this is used, for example, as a sealing material or an adhesive layer in an electrical component of a vehicle, it can be said that it is advantageous for improving the long-term insulation reliability of the electrical component.
- the curable resin composition of sample 1C contains a (meth) acrylic polyol alone as a polyol and does not contain a polycarbonate polyol. Therefore, the curable resin composition of sample 1C was a cured product inferior in initial strength.
- the curable resin composition of sample 2C contains a polycarbonate-based polyol alone as a polyol and does not contain a (meth) acrylic-based polyol. Therefore, the curable resin composition of sample 2C was a cured product having no heat and moisture resistance.
- the curable resin composition of Sample 3C had poor workability at the time of preparation of the composition.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Polyurethanes Or Polyureas (AREA)
- Sealing Material Composition (AREA)
- Adhesives Or Adhesive Processes (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/886,070 US20200291170A1 (en) | 2017-11-28 | 2020-05-28 | Curable resin composition and eletrical component using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017-228316 | 2017-11-28 | ||
| JP2017228316A JP6958297B2 (ja) | 2017-11-28 | 2017-11-28 | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/886,070 Continuation US20200291170A1 (en) | 2017-11-28 | 2020-05-28 | Curable resin composition and eletrical component using the same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019107201A1 true WO2019107201A1 (ja) | 2019-06-06 |
Family
ID=66664538
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/042663 Ceased WO2019107201A1 (ja) | 2017-11-28 | 2018-11-19 | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20200291170A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6958297B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2019107201A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6919529B2 (ja) | 2017-11-28 | 2021-08-18 | 株式会社デンソー | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 |
| EP3670560A1 (en) | 2018-12-20 | 2020-06-24 | Sika Technology Ag | Two-component polyurethane composition |
| WO2024194971A1 (ja) | 2023-03-20 | 2024-09-26 | Kfケミカル株式会社 | 一液型湿気硬化性ウレタン樹脂組成物およびそれを用いた塗料 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006182904A (ja) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Nippon Polyurethane Ind Co Ltd | ポリウレタン樹脂コーティング剤 |
| JP2011105819A (ja) * | 2009-11-16 | 2011-06-02 | Toyo Ink Mfg Co Ltd | 積層シート用接着剤組成物 |
| JP2012212805A (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-01 | Toyo Ink Sc Holdings Co Ltd | 太陽電池用裏面保護シート |
| US20140255560A1 (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-11 | H.B. Fuller Company | Gas transmitting polyurethane adhesive |
| JP2017066214A (ja) * | 2015-09-29 | 2017-04-06 | オリジン電気株式会社 | 耐移行性、密着性に優れた塗料組成物及び塗装製品の製造方法 |
-
2017
- 2017-11-28 JP JP2017228316A patent/JP6958297B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-11-19 WO PCT/JP2018/042663 patent/WO2019107201A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2020
- 2020-05-28 US US16/886,070 patent/US20200291170A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006182904A (ja) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Nippon Polyurethane Ind Co Ltd | ポリウレタン樹脂コーティング剤 |
| JP2011105819A (ja) * | 2009-11-16 | 2011-06-02 | Toyo Ink Mfg Co Ltd | 積層シート用接着剤組成物 |
| JP2012212805A (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-01 | Toyo Ink Sc Holdings Co Ltd | 太陽電池用裏面保護シート |
| US20140255560A1 (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-11 | H.B. Fuller Company | Gas transmitting polyurethane adhesive |
| JP2017066214A (ja) * | 2015-09-29 | 2017-04-06 | オリジン電気株式会社 | 耐移行性、密着性に優れた塗料組成物及び塗装製品の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2019099597A (ja) | 2019-06-24 |
| US20200291170A1 (en) | 2020-09-17 |
| JP6958297B2 (ja) | 2021-11-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5886957B2 (ja) | 導電性接着剤組成物、導電性接着フィルム、接着方法及び回路基板 | |
| WO2019107199A1 (ja) | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 | |
| JP5381707B2 (ja) | 熱可塑性ポリウレタンを含む樹脂組成物およびホットメルト接着剤 | |
| CN106062116B (zh) | 用于照明器具的湿气固化性热熔粘合剂 | |
| CN102906210B (zh) | 硅烷湿固化性热熔黏合剂 | |
| US20210062056A1 (en) | Thermally reversible cross-linked hot-melt adhesive | |
| KR20130049423A (ko) | 이방 전도성 접착 필름용 조성물 및 이를 이용한 이방 전도성 접착 필름 | |
| US20200291170A1 (en) | Curable resin composition and eletrical component using the same | |
| JP2013075972A (ja) | ポリエステル−ポリカルボジイミド共重合体樹脂組成物 | |
| JP6935734B2 (ja) | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 | |
| CN111433244A (zh) | 增韧的氰基丙烯酸酯组合物 | |
| US11795325B2 (en) | Curable resin composition and electrical component using the same | |
| JP2019099599A (ja) | 硬化性樹脂組成物およびこれを用いた電装部品 | |
| WO2017188050A1 (ja) | 硬化性ポリウレタン系樹脂組成物及びそれを用いた電装部品 | |
| KR102405505B1 (ko) | 습기 경화형 폴리우레탄 핫멜트 수지 조성물, 및, 그것을 사용한 물품 | |
| JP6084145B2 (ja) | 異方導電性接着組成物およびこれを用いた異方導電性接着フィルム | |
| CN116376500A (zh) | 一种液体橡胶改性湿固化聚氨酯热熔胶及其制备方法 | |
| KR20110073587A (ko) | 내열성 일액형 습기 경화형 폴리카보네이트 수지용 접착제 조성물 | |
| JP7698861B2 (ja) | 二液型硬化性組成物 | |
| KR20210071563A (ko) | 이액형 수지 조성물 | |
| JP4232094B2 (ja) | 高温剪断接着性能に優れた軟質樹脂成形体用組成物及びそれから得られた軟質樹脂成形体 | |
| WO2023276146A1 (ja) | ウレタン系ホットメルト接着剤 | |
| CN108728034B (zh) | 聚酯聚醚粘合剂 | |
| JP2020186280A (ja) | ホットメルト組成物 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18882656 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18882656 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |