WO2018221590A1 - アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステム - Google Patents
アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018221590A1 WO2018221590A1 PCT/JP2018/020769 JP2018020769W WO2018221590A1 WO 2018221590 A1 WO2018221590 A1 WO 2018221590A1 JP 2018020769 W JP2018020769 W JP 2018020769W WO 2018221590 A1 WO2018221590 A1 WO 2018221590A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- communication
- camera
- data
- accessory device
- channel
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/02—Bodies
- G03B17/12—Bodies with means for supporting objectives, supplementary lenses, filters, masks, or turrets
- G03B17/14—Bodies with means for supporting objectives, supplementary lenses, filters, masks, or turrets interchangeably
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/56—Accessories
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/56—Accessories
- G03B17/565—Optical accessories, e.g. converters for close-up photography, tele-convertors, wide-angle convertors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/50—Constructional details
- H04N23/55—Optical parts specially adapted for electronic image sensors; Mounting thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/66—Remote control of cameras or camera parts, e.g. by remote control devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/66—Remote control of cameras or camera parts, e.g. by remote control devices
- H04N23/663—Remote control of cameras or camera parts, e.g. by remote control devices for controlling interchangeable camera parts based on electronic image sensor signals
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B2206/00—Systems for exchange of information between different pieces of apparatus, e.g. for exchanging trimming information, for photo finishing
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an accessory device, a camera, a communication control program, and a camera system.
- a system As a lens interchangeable camera system, a system is known in which a camera performs imaging processing and lens control, and an interchangeable lens as a first accessory device drives a lens in accordance with a control command from the camera body.
- transmission of control commands from the camera body to the interchangeable lens and transmission of lens information from the interchangeable lens to the camera body are performed via a communication channel for exchanging information with each other.
- a camera system in which an intermediate adapter as a second accessory device such as a converter that changes the focal length of the interchangeable lens can be connected between the camera body and the interchangeable lens in order to expand the photographing function.
- an intermediate adapter as a second accessory device such as a converter that changes the focal length of the interchangeable lens can be connected between the camera body and the interchangeable lens in order to expand the photographing function.
- communication between the camera body and the intermediate adapter may be required.
- the camera body specifies a communication partner from the plurality of accessory devices, and performs communication with the specified communication partner.
- Patent Document 1 describes a communication control method using an I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) communication method.
- I2C communication a plurality of communication slaves are connected to a communication master, and communication is performed between a specific communication slave designated by the communication master and the communication master.
- the communication master transmits address information specifying a specific slave to all communication slaves.
- Each communication slave holds address information unique to each communication slave, and the communication slave holding the address information corresponding to the address information transmitted from the communication master is the communication partner of the communication master.
- An object of the present invention is to realize an accessory device and a camera that can perform high-speed communication between the camera and the accessory device.
- the accessory device of the present invention is an accessory device that can be attached to a camera, and notifies the timing of data communication between the camera and the data communication channel used for data communication and the communication performed through the data communication channel.
- An accessory control unit that controls communication using a channel including a notification channel, and the accessory control unit is provided between the camera and a plurality of accessory devices including the accessory device mounted on the camera.
- the first communication method used for communicating with the camera and the voltage level of the notification channel used for communicating with the camera individually while receiving data from the camera are the first communication method.
- the second communication method can be switched to a different second communication method. In the first communication method, the camera of the second communication method can be switched. Switching from the first communication method to the second communication method in response to reception of communication partner designation data indicating that the accessory device has been selected as a communication partner via the data communication channel.
- the camera of the present invention is a camera to which the first accessory device and the second accessory device can be attached, and is used for data communication performed between the first accessory device and the second accessory device.
- a camera control unit configured to control communication using a channel including a data communication channel to be used and a notification channel for notifying a timing of communication performed through the data communication channel;
- a first communication method used to communicate between the accessory device and the second accessory device, and individually communicate with one of the first accessory device and the second accessory device.
- the voltage level of the notification channel is different from that of the first communication method while transmitting data from the camera.
- the camera in the second communication method can be switched to the first accessory device and the second accessory device via the data communication channel in the first communication method. Switching from the first communication method to the second communication method is performed in response to transmission of communication partner designation data indicating the other communication partner.
- an accessory device and a camera that can perform high-speed communication between the camera and the accessory device can be obtained.
- Communication based on a plurality of communication methods is executed between the accessory device and the camera.
- Communication method means a broadcast communication method and a P2P communication method, and in the following, the broadcast communication method may be described as a first communication method, and the P2P communication method may be described as a second communication method.
- the present invention relates to a camera system that appropriately changes the communication method between the camera body and the accessory device.
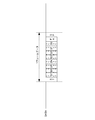
- the present invention is applicable to a camera system in which an intermediate adapter 300 is mounted between the camera 200 and the interchangeable lens 100 as shown in FIG.
- an example in which one intermediate adapter 300 is mounted between the camera 200 and the interchangeable lens 100 will be described.
- a plurality of intermediate adapters are mounted between the camera 200 and the interchangeable lens 100. May be.
- data is transmitted all at once from the camera 200 as a communication master to each accessory device as a communication slave.
- the camera 200 performs P2P communication that is one-to-one communication with a specific accessory device, information indicating the communication partner with the camera 200 in P2P communication is notified to each accessory device in broadcast communication.
- the camera 200 Since the communication partner of the camera 200 is notified to each accessory device at the timing when the P2P communication is started, the camera 200 needs to transmit information for specifying the communication partner to each accessory device in the P2P communication. There is no. In this way, after selecting a communication partner with the camera 200 in broadcast communication, switching to P2P communication, which is a one-to-one communication method between the camera 200 and the selected communication partner, is performed. Communication speed can be improved.
- FIG. 1 shows a configuration of a camera system including a camera 200 according to an embodiment of the present invention, an intermediate adapter 300 that can be attached to the camera 200, and an interchangeable lens 100.
- the camera 200 is configured so that a plurality of accessory devices can be mounted.
- Each of the intermediate adapter 300 and the interchangeable lens 100 is an accessory device that can be attached to the camera 200. Note that both the case where the camera 200 is directly connected and the case where the camera 200 is connected via the intermediate adapter 300 or the like will be described as being mounted on the camera 200.
- the camera 200, the interchangeable lens 100, and the intermediate adapter 300 transmit a control command and internal information via a communication unit included therein.
- Each communication unit supports broadcast communication and P2P communication, and performs communication based on the communication method determined by the camera 200.
- the intermediate adapter 300 and the camera 200 are mechanically and electrically connected via a mount 401 that is a coupling mechanism.
- the intermediate adapter 300 receives power from the camera 200 via a power terminal (not shown) provided on the mount 401 and controls an adapter microcomputer 302 (hereinafter referred to as an adapter microcomputer) 302.
- the interchangeable lens 100 and the intermediate adapter 300 are mechanically and electrically connected via a mount 400 that is a coupling mechanism.
- the interchangeable lens 100 is supplied with power from the camera 200 via a power terminal (not shown) provided on the mount 400 and a power terminal (not shown) provided on the mount 401 described above. Then, using the electric power received from the camera 200, various actuators and a lens microcomputer (hereinafter referred to as a lens microcomputer) 111, which will be described later, are controlled.
- the interchangeable lens 100, the intermediate adapter 300, and the camera 200 communicate with each other via communication terminals (shown in FIG. 2) provided on the mount 400 and the mount 401.
- the interchangeable lens 100 has an imaging optical system.
- the imaging optical system includes, in order from the subject OBJ side, a field lens 101, a zoom lens 102 that performs zooming, an aperture unit 114 that adjusts the amount of light, an image blur correction lens 103, and a focus lens 104 that performs focus adjustment. including.
- variable power lens 102 and the focus lens 104 are held by lens holding frames 105 and 106, respectively.
- the lens holding frames 105 and 106 are guided by a guide shaft (not shown) so as to be movable in the optical axis direction indicated by broken lines in the drawing, and are driven in the optical axis direction by stepping motors 107 and 108, respectively.
- the stepping motors 107 and 108 move the variable power lens 102 and the focus lens 104 in synchronization with the drive pulse, respectively.
- the image blur correction lens 103 moves in a direction orthogonal to the optical axis of the imaging optical system, thereby reducing image blur caused by camera shake or the like.
- the lens microcomputer 111 is an accessory control unit that controls the operation of each unit in the interchangeable lens 100.
- the lens microcomputer 111 receives a control command transmitted from the camera 200 via the lens communication unit 112 as an accessory communication unit, and receives a lens data transmission request.
- the lens microcomputer 111 performs lens control corresponding to the control command, and transmits lens data corresponding to the transmission request to the camera 200 via the lens communication unit 112.
- the lens microcomputer 111 outputs drive signals to the zoom drive circuit 119 and the focus drive circuit 120 in response to commands related to scaling and focusing among the control commands to drive the stepping motors 107 and 108.
- zoom processing for controlling the zooming operation by the zoom lens 102 and autofocus processing for controlling the focus adjustment operation by the focus lens 104 are performed.
- the diaphragm unit 114 is configured to include diaphragm blades 114a and 114b.
- the states of the diaphragm blades 114 a and 114 b are detected by the hall element 115 and input to the lens microcomputer 111 via the amplifier circuit 122 and the A / D conversion circuit 123.
- the lens microcomputer 111 outputs a drive signal to the aperture drive circuit 121 based on the input signal from the A / D conversion circuit 123 to drive the aperture actuator 113. Thereby, the light quantity adjustment operation by the diaphragm unit 114 is controlled.
- the lens microcomputer 111 drives the image stabilization actuator 126 via the image stabilization drive circuit 125 in accordance with a shake detected by a shake sensor (not shown) such as a vibration gyro provided in the interchangeable lens 100. As a result, an image stabilization process for controlling the shift operation of the image blur correction lens 103 is performed.
- the intermediate adapter 300 is an extender for extending the focal length of the interchangeable lens 100.
- the intermediate adapter 300 is not limited to an extender, and may have various functions.
- the intermediate adapter 300 may include a plurality of filters having different light transmittances in the intermediate adapter 300, and an appropriate filter can be selected in accordance with a shooting situation or the like.
- the intermediate adapter 300 in this embodiment includes a variable power lens 301 that extends the focal length of the interchangeable lens 100 and an adapter microcomputer 302 as an accessory control unit that controls the operation of each unit in the intermediate adapter 300.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 receives a control command transmitted from the camera 200 via the adapter communication unit 303 as an accessory communication unit, and performs adapter control corresponding to the control command.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 transmits adapter data corresponding to the transmission request from the camera 200 to the camera 200 via the adapter communication unit 303.
- the camera 200 includes an imaging device 201 such as a CCD sensor or a CMOS sensor, an A / D conversion circuit 202, a signal processing circuit 203, a recording unit 204, a camera microcomputer (hereinafter referred to as camera microcomputer) 205, and a display unit. 206.
- the image sensor 201 photoelectrically converts the subject image formed by the imaging optical system in the interchangeable lens 100 and outputs an electrical signal (analog signal).
- the A / D conversion circuit 202 converts an analog signal from the image sensor 201 into a digital signal.
- the signal processing circuit 203 performs various image processing on the digital signal from the A / D conversion circuit 202 to generate a video signal.
- the signal processing circuit 203 also generates focus information indicating the contrast state of the subject image, that is, the focus state of the imaging optical system, and luminance information indicating the exposure state from the video signal.
- the signal processing circuit 203 outputs the video signal to the display unit 206, and the display unit 206 displays the video signal as a live view image used for checking the composition, focus state, and the like.
- a camera microcomputer 205 serving as a camera control unit controls the camera 200 in response to input from camera operation members such as an imaging instruction switch (not shown) and various setting switches.
- the camera microcomputer 205 transmits a control command related to the zooming operation of the zoom lens 102 to the lens microcomputer 111 via the camera communication unit 208 in accordance with an operation of a zoom switch (not shown).
- the camera microcomputer 205 transmits, via the camera communication unit 208, a control command related to the light amount adjustment operation of the diaphragm unit 114 according to the luminance information and the focus adjustment operation of the focus lens 104 according to the focus information to the lens microcomputer 111.
- the camera microcomputer 205 transmits data to the intermediate adapter 300 and the interchangeable lens 100 simultaneously in broadcast communication, and one-to-one data communication with either the intermediate adapter 300 or the interchangeable lens 100 in P2P communication. I do.
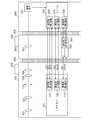
- the camera system of the present embodiment includes a notification channel CS used for communication timing notification and a data communication channel DATA used for data communication.
- the camera 200 and the intermediate adapter 300 are connected via the mount 401.
- the mount 401 is provided with at least two communication terminals.
- the intermediate adapter 300 and the interchangeable lens 100 are connected via a mount 400.
- the mount 400 is provided with at least two communication terminals.
- the notification channel CS and the data communication channel DATA described above are formed by communication terminals provided in each mount.
- the notification channel CS is connected to the camera microcomputer 205, the adapter microcomputer 302, and the lens microcomputer 111, and each microcomputer can detect the signal level (voltage level) of the notification channel CS. Further, the notification channel CS is connected to a power source (not shown) disposed in the camera 200 by pull-up connection. Further, the notification channel CS can be connected to the ground via a ground switch 2081 included in the camera 200, and can be connected to the ground via a ground switch 3031 included in the intermediate adapter 300. The notification channel CS can be connected to the ground via a ground switch 1121 included in the interchangeable lens 100.
- any one of the ground switches included in the camera 200, the intermediate adapter 300, and the interchangeable lens 100 is brought into a connected state (first setting), thereby setting the signal level of the notification channel CS. It can be Low (first level). Also, the signal level of the notification channel CS is set to High (second level) by setting all the ground switches included in the camera 200, the intermediate adapter 300, and the interchangeable lens 100 to the cutoff state (first setting). Is possible.
- Each microcomputer can change the connection state between the notification channel CS and the ground by changing the connection state of the ground switch.
- each microcomputer can set the signal level of the notification channel CS to either High or Low by changing the connection state of the ground switch.
- the camera microcomputer 205 can set the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low by setting the ground switch 2081 included in the camera 200 to the connected state.
- setting the ground switch to the connected state is described as “outputting Low to the notification channel CS”.
- setting the ground switch to the disconnected state is described as “performing the notification channel CS to perform High output”.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low. The role of the notification channel CS during data communication will be described later.
- the data communication channel DATA is a bidirectional data communication channel capable of switching the data propagation direction.
- the data notification channel DATA is connected to the camera microcomputer 205, the adapter microcomputer 302, and the lens microcomputer 111.
- the data communication channel DATA is connected to the camera microcomputer 205 via an input / output changeover switch 2082 included in the camera 200.
- the camera microcomputer 205 is provided with a data output unit for transmitting data and a data input unit for receiving data.
- the data communication channel DATA can be selectively connected to one of the data output unit and the data input unit.
- the data communication channel DATA is connected to the adapter microcomputer 302 via the input / output changeover switch 3032 included in the intermediate adapter 300.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 includes a data output unit for transmitting data and a data input unit for receiving data.
- the data communication channel DATA can be selectively connected to one of the data output unit and the data input unit in accordance with the operation of the input / output changeover switch 3032.
- the data communication channel DATA is connected to the lens microcomputer 111 via the input / output changeover switch 1122 included in the interchangeable lens 100.
- the lens microcomputer 111 is provided with a data output unit for transmitting data and a data input unit for receiving data. Then, in accordance with the operation of the input / output changeover switch 1122, the data communication channel DATA can be selectively connected to one of the data output unit and the data input unit. By adopting such a circuit configuration, it is possible to appropriately switch the data propagation direction of the data communication channel DATA.
- FIG. 3 shows a data format in an asynchronous communication system in which a communication speed is set in advance on both the data transmission side and the data reception side, and data communication is performed at a communication bit rate based on this setting.
- the communication bit rate indicates the amount of data that can be transferred per second, and the unit is expressed in bps (bit per second).
- FIG. 3 shows a signal waveform of one frame which is the minimum communication unit.
- the signal level of the data communication channel DATA is maintained at the high level. Subsequently, in order to notify the data reception side of the start of data transmission, the signal level of the data communication channel DATA is set to Low for one bit period. This one bit period is called a start bit ST, and a data frame is started from the start bit ST. One byte of data is transmitted in an 8-bit period from the second bit to the ninth bit following the start bit ST.
- the bit arrangement of data is MSB (Most Significant Bit) first format, starting from the most significant data D7, followed by the data D6 and the data D5 in order, and ending with the least significant data D0. Then, 1-bit parity information (PA) is added to the 10th bit, and the signal level of the data communication channel DATA is set to High during the stop bit SP indicating the end of one frame. Thereby, the data frame period started from the start bit ST ends.
- the parity information does not need to be 1 bit, and a plurality of bits of parity information may be added. Further, parity information is not essential, and a format to which no parity information is added may be used.
- bit arrangement of the data may be LSB (Least Significant Bit) first format, starting from the lowest-order data D0, followed by data D1 and data D2, and ending with the highest-order data D7.
- LSB east Significant Bit
- 1-byte data is transmitted in an 8-bit period, but 1-byte data may be transmitted in a bit period other than 8 bits.
- Broadcast communication will be described with reference to FIG.
- communication is performed with the camera 200 as a communication master and the intermediate adapter 300 and the interchangeable lens 100 as communication slaves.
- FIG. 4 shows signal waveforms exchanged in broadcast communication.
- the camera microcomputer 205 of the camera 200 that is a communication master notifies the start of broadcast communication to the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 that are communication slaves by performing a Low output to the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205 transmits data to the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 via the data communication channel DATA.
- the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 output Low to the notification channel CS in response to detecting the above-described start bit ST via the data communication channel DATA. Note that, when the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 output Low to the notification channel CS, the signal level of the notification channel CS remains Low because the camera microcomputer 205 outputs Low.
- the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 notify the communication standby request by outputting Low to the notification channel CS.
- the communication standby request is for temporarily stopping communication in the camera system, and the presence or absence of the communication standby request is determined based on the signal level of the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205 outputs High to the notification channel CS after transmitting all data.
- the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 execute analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data. After that, after preparation for executing the next communication is completed, High is output to the notification channel CS.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High when all the components constituting the camera system output High to the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205, the lens microcomputer 111, and the adapter microcomputer 302 confirm that each component constituting the camera system is ready to perform the next communication when the signal level of the notification channel CS returns to High. can do.
- the data transmitted by the camera microcomputer 205 includes a transmission request command for the adapter microcomputer 302, and the data transmission by the adapter microcomputer 302 is performed following the data transmission by the camera microcomputer 205.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 After the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High, the adapter microcomputer 302 outputs Low to the notification channel CS. This notifies the lens microcomputer 111 and the camera microcomputer 205 of the start of broadcast communication. Next, the adapter microcomputer 302 transmits data to the lens microcomputer 111 and the camera microcomputer 205 via the data communication channel DATA.
- the lens microcomputer 111 and the camera microcomputer 205 output Low to the notification channel CS in response to detecting the above-described start bit ST via the data communication channel DATA.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 outputs Low to the notification channel CS, so the signal level of the notification channel CS remains Low.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 outputs High to the notification channel CS after transmitting all data. After receiving the stop bit SP transmitted from the data communication channel DATA, the lens microcomputer 111 and the camera microcomputer 205 execute analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data. After that, after preparation for executing the next communication is completed, High is output to the notification channel CS.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High when all the components constituting the camera system output High to the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205, the lens microcomputer 111, and the adapter microcomputer 302 confirm that each component constituting the camera system is ready to perform the next communication when the signal level of the notification channel CS returns to High. can do.
- the data transmission side notifies the data reception side of the start of broadcast communication by outputting Low to the notification channel CS and changing the signal level of the notification channel CS from High to Low. ing. Further, the data receiving side changes the output to the notification channel CS from Low output to High output, thereby notifying each component of the lens system of the cancellation of the communication standby request.
- FIG. 4 shows an example of a communication waveform of broadcast communication in the present invention
- data transmitted and received in one broadcast communication may be data of a plurality of bytes instead of 1 byte.
- P2P communication as the second communication method in the present invention will be described using FIG.
- the camera 200 serves as a communication master, and one-to-one individual communication is performed with one component selected as a communication slave among the components configuring the camera system.
- FIG. 5 shows signal waveforms exchanged in P2P communication.
- the interchangeable lens 100 is selected as the communication slave.
- Information indicating a communication slave in P2P communication is transmitted by broadcast communication.
- the data transmission side does not output Low to the notification channel CS, and transmits data to the data reception side while maintaining the notification channel CS at High. That is, the voltage level of the notification channel CS during the transmission of data from the camera 200 to the interchangeable lens 100 and the adapter 300 is different between broadcast communication and P2P communication.
- FIG. 5 shows an example in which 2-byte data transmission is performed from the lens microcomputer 111 to the camera microcomputer 205 after the 1-byte data transmission from the camera microcomputer 205 to the lens microcomputer 111.
- the camera microcomputer 205 After the switching from broadcast communication to P2P communication is completed in each component constituting the camera system, the camera microcomputer 205 as a communication master transmits data to the lens microcomputer 111 via the data communication channel DATA. When the data transmission is completed, the camera microcomputer 205 notifies the communication standby request by setting the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low output. Then, the camera microcomputer 205 returns the signal level of the notification channel CS to High output after preparation for receiving data is completed as the data receiving side.
- the lens microcomputer 111 recognizes that the data transmission from the camera microcomputer 205 is completed when the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low, and performs analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data. Execute.
- the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 includes a data transmission request from the lens microcomputer 111 to the camera microcomputer 205, and the lens microcomputer 111 also generates data to be transmitted to the camera microcomputer 205.
- the lens microcomputer 111 that has recognized the cancellation of the communication standby request transmits 2-byte data to the camera microcomputer 205.
- the lens microcomputer 111 When the data transmission ends, the lens microcomputer 111 notifies the communication standby request by setting the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low output. Then, the lens microcomputer 111 returns the signal level of the notification channel CS to High output after preparation for receiving data is completed as the data receiving side. Note that the adapter microcomputer 302 that is not selected as the communication partner of the P2P communication does not change the output to the notification channel CS and does not participate in data transmission / reception.
- the lens microcomputer 111 determines whether P2P communication is continued or switched to broadcast communication based on the data transmission timing from the camera microcomputer 205 after the signal level of the notification channel CS is returned to High. . When data from the camera microcomputer 205 is received while the signal level of the notification channel CS remains High, the lens microcomputer 111 determines that P2P communication is continued. On the other hand, when data from the camera microcomputer 205 is received after the signal level of the notification channel CS changes to Low, the lens microcomputer 111 determines that the P2P communication has been switched to the broadcast communication.
- the data transmission side changes the signal level of the notification channel CS from High output to Low output to notify the data reception side that data transmission by the data transmission side is completed. Yes. Therefore, in P2P communication, a plurality of data frames can be continuously transmitted until the data transmission side changes the signal level of the notification channel CS. Since the system does not have a system configuration in which communication from the communication master is inserted every time a communication slave transmits one data frame, communication between the camera microcomputer 205 and the accessory device such as the lens microcomputer 111 or the adapter microcomputer 302 is performed at high speed. Can be done. Then, the data transmission side notifies the communication standby request by keeping the signal level of the notification channel CS low output until the data reception preparation as the data reception side in the next communication is completed.
- the camera 200 serves as a communication master and performs communication with the intermediate adapter 300 and the interchangeable lens 100. Information indicating a communication partner with the camera body in P2P communication is notified in broadcast communication.
- FIG. 6 shows communication waveforms in communication executed by switching between broadcast communication and P2P communication.
- information indicating that the adapter microcomputer 302 has been selected as a communication partner in P2P communication is transmitted / received in broadcast communication, and then P2P communication is performed between the camera microcomputer 205 and the adapter microcomputer 302.
- communication partner designation data information indicating a communication partner in P2P communication is referred to as communication partner designation data.
- the communication partner designation data itself has a function as a command for switching from broadcast communication to P2P communication.
- switching to P2P communication may be executed by transmitting and receiving a signal instructing switching from broadcast communication to P2P communication.
- the lens microcomputer 111 not selected as the communication partner in the P2P communication After receiving the communication partner designation data, the lens microcomputer 111 not selected as the communication partner in the P2P communication outputs High to the notification channel CS when the analysis of the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 and the internal processing are completed. Then, during the period in which the P2P communication is performed between the camera microcomputer 205 and the adapter microcomputer 302, the setting corresponding to the broadcast communication is maintained without changing the output to the notification channel CS.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 notifies the camera microcomputer 205 of the completion of the switching of the communication method by performing a High output to the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205 also outputs High to the notification channel CS.
- the lens microcomputer 111 that is not selected as the communication partner in the P2P communication outputs High to the notification channel CS when the analysis of the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 and the internal processing are completed.
- the camera microcomputer 205 When the camera microcomputer 205 detects that the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High, the camera microcomputer 205 starts the P2P communication shown in FIG. Since the outline of communication in the P2P communication system is as described with reference to FIG. 5, description of details of P2P communication is omitted here.
- the camera microcomputer 205 transmits communication partner designation data indicating that the lens microcomputer 111 has been selected as a communication partner in the P2P communication by broadcast communication. Thereafter, P2P communication is performed between the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 recognizes that the switching from the P2P communication to the broadcast communication has been executed when the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low before data is transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205.
- FIG. 7 discloses a communication flow of the camera microcomputer 205 as a communication master and a communication flow of the adapter microcomputer 302 as a communication slave. Since the communication flow of the lens microcomputer 111 is substantially the same as the communication flow of the adapter microcomputer 302, the communication flow of the lens microcomputer 111 is not disclosed here.
- the camera microcomputer 205 determines whether or not an event for starting broadcast communication has occurred in S100. If an event for starting broadcast communication has occurred, the process proceeds to S101. If such an event has not occurred, the determination in S100 is repeated.
- the transmission request command is a command for requesting data transmission to the camera microcomputer 205 to the communication slave that has received the data transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205 as the communication master.
- S108 it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become High. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High. When the signal level of the notification channel CS is High, it indicates that the camera system can communicate. When the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High, it is determined in S109 whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become Low. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low.
- the camera microcomputer 205 When the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low, communication from the adapter microcomputer 302 serving as a communication slave to the camera microcomputer 205 is started. After determining that the signal level of the notification channel CS has become Low, the camera microcomputer 205 permits reception of data on the data communication channel DATA in S110. Subsequently, in S111, it is determined whether or not a start bit included in data transmitted from the adapter microcomputer 302 has been received. This determination is continued until a start bit is received.
- the process proceeds to S112, the Low output is performed to the notification channel CS, and it is determined whether or not the stop bit is received in S113. This determination is continued until a stop bit is received.
- the stop bit is received, reception of data on the data communication channel DATA is prohibited in S114, and analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data are executed. After that, in S115, the Low output to the notification channel CS is canceled and the High output is performed.
- S116 it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become High. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High.
- S117 it is determined whether or not the data transmitted in S103 is communication partner designation data. If it is the communication partner designation data, the process proceeds to S118 and a transition to P2P communication is performed. If it is not the communication partner designation data, the broadcast communication is continued.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 determines whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become Low. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low. In response to the signal level of the notification channel CS becoming Low, data transmission from the camera microcomputer 205, which is the communication master, is started. In S201, the adapter microcomputer 302 permits reception of data on the data communication channel DATA.
- S202 it is determined whether or not a start bit has been received. If the start bit has not been received, the process proceeds to S203 to determine whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS is High.
- the processing of S203 and S204 is performed in order to cope with a situation in which P2P communication is performed between the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 and only the adapter microcomputer 302 performs broadcast communication.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 since the adapter microcomputer 302 does not receive data from the camera microcomputer 205, reception of data on the data communication channel DATA is prohibited in S204.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS also changes between High and Low in P2P communication.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS is normally High, and is set to Low in broadcast communication when notifying a communication standby request or notifying the start of communication. In P2P communication, it is set to Low when notifying a communication standby request.
- the first situation is after the camera microcomputer 205 sets the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low and data transmission has not started.
- the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 are performing P2P communication, and the adapter microcomputer 302 is not involved in P2P communication.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS is High unless one of the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 notifies the communication standby request.
- the process basically proceeds from S203 to S204, and reception of data on the data communication channel DATA is prohibited.
- P2P communication when a communication standby request is notified, the process returns from S203 to S202, and the determination in S203 is performed again. Although the determination of S203 may be performed a plurality of times, when the communication standby request is canceled and the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High, the process proceeds from S203 to S204.
- broadcast communication and P2P communication can be used together in the camera system.
- the P2P communication is performed between the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111, while the adapter microcomputer 302 can be put on standby in a state corresponding to broadcast communication.
- the adapter microcomputer 302 starts analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data, and outputs Low to the notification channel CS. Thereby, a communication standby request is notified to each component constituting the camera system.
- S206 it is determined whether or not a stop bit has been received. This determination is continued until a stop bit is received.
- reception of data on the data communication channel DATA is prohibited in S207, and analysis of the received data and internal processing corresponding to the received data are continued.
- the Low output to the notification channel CS is canceled and the High output is performed in S208.
- S209 it is determined whether or not the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 includes a transmission request command.
- the process proceeds to S210, and it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become High. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High. When the signal level of the notification channel CS is High, it indicates that the camera system can communicate. If the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 does not include a transmission request command, the process proceeds to S215 described later.
- S210 If it is determined in S210 that the signal level of the notification channel CS is High, the process proceeds to S211.
- a Low output is performed on the notification channel CS, and the signal level of the notification channel CS is set to Low to notify the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 of the start of broadcast communication.
- the input / output changeover switch 3032 is operated to connect the data communication channel DATA to the data output unit of the adapter microcomputer 302, and data transmission is started in S213.
- the process proceeds to S216.
- S216 it is determined whether or not the data received from the camera microcomputer 205 is communication partner designation data and is selected as the communication partner of the camera microcomputer 205 in P2P communication.
- the process proceeds to S217, and data reception on the data communication channel DATA is permitted.
- S218, a transition from broadcast communication to P2P communication is performed.
- the broadcast communication is continued without executing the transition to the P2P communication.
- FIG. 8 discloses a communication flow of the camera microcomputer 205 as a communication master and a communication flow of the lens microcomputer 111 as a communication slave. Since the communication flow of the adapter microcomputer 302 is almost the same as the communication flow of the lens microcomputer 111, the communication flow of the adapter microcomputer 302 is not disclosed here.
- the camera microcomputer 205 determines whether or not an event for starting P2P communication has occurred in S300. If an event for starting P2P communication has occurred, the process proceeds to S301. If such an event has not occurred, the determination in S300 is repeated.
- the input / output changeover switch 2082 is operated to connect the data communication channel DATA to the data output unit of the camera microcomputer 205, and data transmission is started in S302.
- the data transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205 in S302 includes a transmission request command.
- the transmission request command is a command for requesting the communication slave to transmit data to the camera microcomputer 205.
- the transmission request command is not included in the data transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205 in S302, the data is not transmitted from the lens microcomputer 111.
- the process proceeds from S304 to S305, and it is confirmed whether or not the lens microcomputer 111 has notified the communication standby request.
- step S305 the low output to the notification channel CS in the camera microcomputer 205 is canceled, and in step S306, it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS is low. Thereby, it can be determined whether or not the lens microcomputer 111 has set the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low, that is, whether or not the lens microcomputer 111 has notified the communication standby request.
- the lens microcomputer 111 that has received data from the camera microcomputer 205 notifies the communication standby request by performing a Low output to the notification channel CS for a certain period of time for analysis and internal processing of the data.
- S306 is performed in order to recognize the notification standby request of the lens microcomputer 111.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS may temporarily become High after S305. At this time, it waits until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes Low by performing the determination of S306. After confirming that the signal level of the notification channel CS is Low in S306, the process proceeds to S311.
- the data communication channel DATA is connected to the data input unit of the camera microcomputer 205 by operating the input / output changeover switch 2082.
- the Low output to the notification channel CS is canceled and the High output is performed.
- S311 it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become High. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High.
- the state where the signal level of the notification channel CS is High means that the lens microcomputer 111 as a communication slave is in a state where data communication is possible.
- the process proceeds to S312 and it is determined whether or not an event for transition to broadcast communication has occurred. If a transition event to broadcast communication occurs, the process proceeds to S313, and transition to broadcast communication is performed. If no transition event to broadcast communication has occurred, P2P communication is continued.
- the lens microcomputer 111 executes switching from broadcast communication to P2P communication, the lens microcomputer 111 first receives data transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205. While the data transmitted from the camera microcomputer 205 is being received, the signal level of the notification channel CS is kept high.
- a communication standby request is notified to the camera microcomputer 205 by setting the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low for internal processing or the like on the data received from the camera microcomputer 205.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS is set high in S405, the communication standby request is canceled, and the process proceeds to S411.
- step S403 data transmission to the camera microcomputer 205 is started.
- the input / output changeover switch 1122 is operated to connect the data communication channel DATA to the data input unit of the lens microcomputer 205.
- the Low output to the notification channel CS is canceled and the High output is performed.
- S411 it is determined whether or not the signal level of the notification channel CS has become High. This determination is continuously performed until the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High.
- the state in which the signal level of the notification channel CS becomes High means that the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 can communicate with each other.
- the voltage level of the notification channel CS during the transmission of data from the camera 200 to the interchangeable lens 100 and the adapter 300 is different between broadcast communication and P2P communication.
- the camera 200 communicates with a specific accessory device individually, it is not necessary to notify the communication partner again until the communication partner is changed. Therefore, the camera 200, the interchangeable lens 100, and the adapter are not required. Communication with the accessory device including 300 can be performed at high speed.
- the camera microcomputer 205 outputs Low to the notification channel CS, and notifies each communication slave of the start of broadcast communication by setting the signal level of the notification channel CS to Low.
- FIG. 9 shows a mode in which the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 as communication slaves request the camera microcomputer 205 to start broadcast communication.
- the communication request to the camera microcomputer 205 is that the microcomputer included in the accessory device restarts communication with the camera microcomputer 205 in a state where communication from the camera microcomputer 205 to the microcomputer included in the accessory device is temporarily stopped. When executed.
- This modification is executed when the operation member 304 provided in the intermediate adapter 300 is operated by the user, for example. It can also be executed when the operation member 130 provided in the interchangeable lens 100 is operated by the user.
- the camera microcomputer 205 as the communication master restarts the communication independently. Giving the microcomputer of the accessory device, which is a communication slave, a function of resuming communication may cause communication to resume at an unexpected timing by the camera system 205, which is a communication master. Therefore, it is not preferable to provide the communication slave with a function to resume communication without limitation.
- the microcomputer included in the accessory device makes a communication start request to the camera microcomputer 205, so that the microcomputer of the accessory device that is a communication slave has a function of resuming communication.
- FIG. 9 shows communication waveforms in the broadcast communication of this modification.
- the lens microcomputer 111 and the adapter microcomputer 302 as communication slaves monitor the occurrence of communication events.
- the signal level of the notification channel CS is set to Low by outputting Low to the notification channel CS.
- the camera microcomputer 205 starts broadcast communication after outputting Low to the notification channel CS in response to the signal level of the notification channel CS becoming Low.
- the flow of broadcast communication after performing Low output to the notification channel CS is the same as the flow described with reference to FIG. 4, and thus description thereof is omitted here.
- the embodiment described above can be used in combination with another communication channel in addition to the communication channel including the notification channel CS and the data communication channel DATA.
- FIG. 10 An example will be described with reference to FIG. 10, the same members as those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals, and redundant description is omitted. Further, in FIG. 10, illustration of a part of the members described in FIG. 1 is omitted.
- the notification channel CS and the data communication channel DATA described above are communication lines for communication called third communication.
- the lens microcomputer 111 controls the communication unit 131 for performing the first communication and the communication unit 132 for performing the second communication, in addition to the communication unit 112.
- the camera microcomputer 205 controls the communication unit 209 for performing the first communication and the communication unit 210 for performing the second communication.
- the first communication is communication performed via the communication unit 131 and the communication unit 209.
- the communication unit 131 performs communication via the notification channel CS1, the data communication channel DCL, and the data communication channel DLC based on an instruction from the lens microcomputer 111, and the communication unit 209 based on an instruction from the camera microcomputer 205.
- the communication unit 131 and the communication unit 209 set the voltage level of the notification channel CS1, the communication rate (data amount per unit time) and communication voltage in asynchronous communication. Further, in response to an instruction from the lens microcomputer 111 or the camera microcomputer 205, data is transmitted / received via the data communication channel DCL and the data communication channel DLC.
- the notification channel CS1 is a signal line used for notification of a communication request from the camera body 200 to the interchangeable lens 100.
- the data communication channel DCL is a channel used when data is transmitted from the camera body 200 to the interchangeable lens 100
- the data communication channel DLC is a channel used when data is transmitted from the interchangeable lens 100 to the camera body 200. .
- the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 communicate by clock synchronous communication or start-stop synchronous communication. Initial communication performed when the interchangeable lens 100 is connected to the camera body 200 is also performed by first communication.
- the camera microcomputer 205 and the lens microcomputer 111 communicate the identification information of the interchangeable lens 100, and when it is determined that the interchangeable lens 100 attached to the camera body 200 is compatible with asynchronous communication, communication from clock synchronous communication to asynchronous communication is performed. Switch the method. Further, as a result of the communication of the identification information, the camera microcomputer 205 may identify whether or not the interchangeable lens 100 is compatible with the third communication that performs communication including the adapter 300. If the camera microcomputer 205 determines that the interchangeable lens 100 is compatible with the third communication, the camera microcomputer 205 may perform authentication communication for recognizing the interchangeable lens 100 and the intermediate adapter 300 via P2P communication.
- the second communication is a one-way communication from the interchangeable lens 100 to the camera body 200.
- the second communication is performed via the communication unit 132 and the communication unit 210.
- the communication unit 132 communicates via the notification channel CS2 and the data communication channel DLC2 based on an instruction from the lens microcomputer 111, and the communication unit 210 based on an instruction from the camera microcomputer 205.
- the camera communication unit 208 and the lens communication unit 118 transmit and receive data by clock synchronous communication or asynchronous communication.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Structure And Mechanism Of Cameras (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Accessories Of Cameras (AREA)
- Stroboscope Apparatuses (AREA)
- Exposure Control For Cameras (AREA)
Abstract
カメラ200とアクセサリ装置100、300は、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルとデータ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を行う。アクセサリ装置100、300は、第1通信方式の通信において、カメラ200の通信相手として自身が選択されたことを示す通信相手指定データをデータ通信チャネルを介して受信したことに応じて、第1通信方式から第2通信方式への切り替えを行う。
Description
本発明は、アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステムに関する。
レンズ交換型カメラシステムとして、カカメラが撮像処理やレンズ制御を行い、第1のアクセサリ装置としての交換レンズがカメラ本体からの制御命令に従ってレンズ駆動を行うシステムが知られている。こうしたカメラシステムにおいては、カメラ本体から交換レンズへの制御命令の伝達と交換レンズからカメラ本体へのレンズ情報の伝達は、相互に情報のやりとりをするための通信チャネルを介して行われる。
また、撮影機能を拡張させるために、交換レンズの焦点距離を変化させるコンバータ等の第2のアクセサリ装置としての中間アダプタを、カメラ本体と交換レンズの間に接続可能としたカメラシステムが知られている。このようなカメラシステムにおいては、カメラ本体と交換レンズの間の通信に加えて、カメラ本体と中間アダプタとの間の通信が必要となる場合がある。この場合、カメラ本体は、複数のアクセサリ装置の中から通信相手を特定し、特定された通信相手との通信を行う。
特許文献1には、I2C(Inter-Integrated Circuit)通信方式による通信制御方法が記載されている。I2C通信においては、通信マスタに対して複数の通信スレーブが接続され、通信マスタによって指定された特定の通信スレーブと通信マスタの間で通信が行われる。
I2C通信においては、通信マスタが、特定のスレーブを指定したアドレス情報を全ての通信スレーブに対して送信する。各通信スレーブは、それぞれの通信スレーブに固有のアドレス情報を保持しており、通信マスタから送信されたアドレス情報に対応するアドレス情報を保持している通信スレーブが通信マスタの通信相手となる。
特許文献1にて開示されたI2C通信方式の通信においては、通信スレーブを指定するためのアドレス情報を、通信マスタと通信スレーブの間で通信が行われるたびに送受信する必要がある。また、通信スレーブは、自身が通信マスタの通信相手として選択されているか否かをアドレス情報に基づいて確認する必要がある。
このような通信方式では、データのフォーマットとしてアドレス情報を含ませる必要があり、アドレス情報の分だけ送信可能なデータ量が低減してしまう。また、通信スレーブは、自身が通信相手として選択されているか否かを通信のたびに確認するため、通信が開始されるまでに待ち時間が生じてしまうおそれがある。以上のように、特許文献1にて開示された通信方式では、通信マスタと通信スレーブの間のデータ通信速度を十分に向上させることができないおそれがある。
本発明は、カメラとアクセサリ装置との間の通信を高速に行うことができるアクセサリ装置及びカメラを実現することを目的とする。
本発明のアクセサリ装置は、カメラに対して装着可能なアクセサリ装置であって、前記カメラとの間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するアクセサリ制御部を有し、前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記カメラに装着された、前記アクセサリ装置を含む複数のアクセサリ装置と、前記カメラとの間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記カメラと個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを受信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能であり、前記第1通信方式において、前記第2通信方式における前記カメラの通信相手として前記アクセサリ装置が選択されたことを示す通信相手指定データを前記データ通信チャネルを介して受信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うことを特徴とする。
また、本発明のカメラは、第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置が装着可能なカメラであって、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するカメラ制御部を有し、前記カメラ制御部は、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置のうちの1つのアクセサリ装置と個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを送信する間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能であり、前記第1通信方式において、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置に対して、前記データ通信チャネルを介して前記第2通信方式における前記カメラの通信相手を示す通信相手指定データを送信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うことを特徴とする。
本発明によれば、カメラとアクセサリ装置との間の通信を高速に行うことができるアクセサリ装置及びカメラが得られる。
以下、本発明の交換レンズや中間アダプタを含むアクセサリ装置及びカメラにおける通信制御方法について、添付の図面に基づいて詳細に説明する。アクセサリ装置とカメラの間では、複数の通信方式に基づく通信が実行される。「通信方式」はブロードキャスト通信方式とP2P通信方式を意味し、以下では、ブロードキャスト通信方式を第1通信方式、P2P通信方式を第2通信方式と記載する場合もある。
本発明は、カメラ本体とアクセサリ装置との間の通信方式を適宜変更するカメラシステムに関する発明である。図1で示すようなカメラ200と交換レンズ100の間に中間アダプタ300が装着されたカメラシステムに適用可能な発明である。なお、以下の実施例においては、カメラ200と交換レンズ100の間に1つの中間アダプタ300が装着された例について説明するが、カメラ200と交換レンズ100の間に複数の中間アダプタが装着されていても良い。
本発明では、ブロードキャスト通信において、通信マスタとしてのカメラ200から通信スレーブとしての各アクセサリ装置に対して一斉にデータ送信が行われる。カメラ200が、ある特定のアクセサリ装置との1対1の通信であるP2P通信を行う場合には、P2P通信におけるカメラ200との通信相手を示す情報がブロードキャスト通信において各アクセサリ装置に対して通知される。
P2P通信が開始されるタイミングでは、各アクセサリ装置に対してカメラ200の通信相手が通知されているため、P2P通信において、カメラ200は通信相手を特定するための情報を各アクセサリ装置に送信する必要がない。このように、ブロードキャスト通信においてカメラ200との通信相手を選択した上で、カメラ200と選択された通信相手との1対1の通信方式であるP2P通信への切り替えを行うことで、P2P通信における通信速度を向上させることができる。
<カメラシステムの構成についての説明>
図1には、本発明の実施例のカメラ200と、これに装着可能なアクセサリ装置としての中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を含むカメラシステムの構成を示している。カメラ200は、複数のアクセサリ装置が装着可能に構成されている。また、中間アダプタ300、交換レンズ100のそれぞれは、カメラ200に対して装着可能なアクセサリ装置である。なお、カメラ200に直接的に接続される場合も、カメラ200に対して中間アダプタ300等を介して接続される場合も、カメラ200に装着されている状態として説明する。
図1には、本発明の実施例のカメラ200と、これに装着可能なアクセサリ装置としての中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を含むカメラシステムの構成を示している。カメラ200は、複数のアクセサリ装置が装着可能に構成されている。また、中間アダプタ300、交換レンズ100のそれぞれは、カメラ200に対して装着可能なアクセサリ装置である。なお、カメラ200に直接的に接続される場合も、カメラ200に対して中間アダプタ300等を介して接続される場合も、カメラ200に装着されている状態として説明する。
カメラ200、交換レンズ100及び中間アダプタ300は、それぞれが有する通信部を介して制御命令や内部情報の伝送を行う。それぞれの通信部は、ブロードキャスト通信及びP2P通信に対応しており、カメラ200において決定された通信方式に基づいて通信を行う。
まず、交換レンズ100、中間アダプタ300、及びカメラ200の具体的な構成について説明する。中間アダプタ300とカメラ200は、結合機構であるマウント401を介して機械的および電気的に接続されている。中間アダプタ300は、マウント401に設けられた不図示の電源端子を介してカメラ200から電力の供給を受け、アダプタマイクロコンピュータ(以下、アダプタマイコンという)302の制御を行う。
交換レンズ100と中間アダプタ300は、結合機構であるマウント400を介して機械的および電気的に接続されている。交換レンズ100は、マウント400に設けられた不図示の電源端子と前述したマウント401に設けられた不図示の電源端子を介してカメラ200から電力の供給を受ける。そしてカメラ200から受けた電力を用いて、後述する各種アクチュエータやレンズマイクロコンピュータ(以下、レンズマイコンという)111の制御を行う。また、交換レンズ100、中間アダプタ300及びカメラ200は、マウント400及びマウント401に設けられた通信端子(図2に示す)を介して相互に通信を行う。
次に、交換レンズ100の構成について説明する。交換レンズ100は、撮像光学系を有する。撮像光学系は、被写体OBJ側から順に、フィールドレンズ101と、変倍を行う変倍レンズ102と、光量を調節する絞りユニット114と、像振れ補正レンズ103と、焦点調節を行うフォーカスレンズ104とを含む。
変倍レンズ102とフォーカスレンズ104はそれぞれ、レンズ保持枠105、106により保持されている。レンズ保持枠105、106は、不図示のガイド軸により図中に破線で示した光軸方向に移動可能にガイドされており、それぞれステッピングモータ107、108によって光軸方向に駆動される。ステッピングモータ107、108はそれぞれ、駆動パルスに同期して変倍レンズ102およびフォーカスレンズ104を移動させる。
像振れ補正レンズ103は、撮像光学系の光軸に直交する方向に移動することで、手振れ等に起因する像振れを低減する。
レンズマイコン111は、交換レンズ100内の各部の動作を制御するアクセサリ制御部である。レンズマイコン111は、アクセサリ通信部としてのレンズ通信部112を介して、カメラ200から送信された制御コマンドを受信し、レンズデータの送信要求を受ける。また、レンズマイコン111は、制御コマンドに対応するレンズ制御を行い、レンズ通信部112を介して送信要求に対応するレンズデータをカメラ200に送信する。
また、レンズマイコン111は、制御コマンドのうち変倍やフォーカシングに関するコマンドに応答してズーム駆動回路119およびフォーカス駆動回路120に駆動信号を出力してステッピングモータ107、108を駆動させる。これにより、変倍レンズ102による変倍動作を制御するズーム処理やフォーカスレンズ104による焦点調節動作を制御するオートフォーカス処理を行う。
絞りユニット114は、絞り羽根114a、114bを備えて構成される。絞り羽根114a、114bの状態は、ホール素子115により検出され、増幅回路122およびA/D変換回路123を介してレンズマイコン111に入力される。レンズマイコン111は、A/D変換回路123からの入力信号に基づいて絞り駆動回路121に駆動信号を出力して絞りアクチュエータ113を駆動させる。これにより、絞りユニット114による光量調節動作を制御する。
さらに、レンズマイコン111は、交換レンズ100内に設けられた振動ジャイロ等の不図示の振れセンサにより検出された振れに応じて、防振駆動回路125を介して防振アクチュエータ126を駆動する。これにより、像振れ補正レンズ103のシフト動作を制御する防振処理が行われる。
続いて、中間アダプタ300の構成について説明する。本実施例では、中間アダプタ300は、交換レンズ100の焦点距離を拡張するためのエクステンダである。中間アダプタ300はエクステンダに限らず、種々の機能を有するものが考えられる。例えば、交換レンズ100を透過した光の透過率を変化させるフィルタが内蔵された中間アダプタ300が考えられる。中間アダプタ300の内部に光透過率の異なる複数のフィルタを含み、撮影状況等に応じて適切なフィルタを選択可能な中間アダプタ300であっても良い。
本実施例における中間アダプタ300は、交換レンズ100の焦点距離を拡張する変倍レンズ301と、中間アダプタ300内の各部の動作を制御するアクセサリ制御部としてのアダプタマイコン302を含む。アダプタマイコン302は、アクセサリ通信部としてのアダプタ通信部303を介して、カメラ200から送信された制御コマンドを受信し、制御コマンドに対応するアダプタ制御を行う。また、アダプタマイコン302は、カメラ200からの送信要求に対応するアダプタデータを、アダプタ通信部303を介してカメラ200に送信する。
次に、カメラ200の構成について説明する。カメラ200は、CCDセンサやCMOSセンサ等の撮像素子201と、A/D変換回路202と、信号処理回路203と、記録部204と、カメラマイクロコンピュータ(以下、カメラマイコンという)205と、表示部206とを有する。
撮像素子201は、交換レンズ100内の撮像光学系により形成された被写体像を光電変換して電気信号(アナログ信号)を出力する。A/D変換回路202は、撮像素子201からのアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換する。信号処理回路203は、A/D変換回路202からのデジタル信号に対して各種画像処理を行って映像信号を生成する。
また、信号処理回路203は、映像信号から被写体像のコントラスト状態、つまり撮像光学系の焦点状態を示すフォーカス情報や露出状態を表す輝度情報も生成する。信号処理回路203は、映像信号を表示部206に出力し、表示部206は映像信号を構図やピント状態等の確認に用いられるライブビュー画像として表示する。
カメラ制御部としてのカメラマイコン205は、不図示の撮像指示スイッチおよび各種設定スイッチ等のカメラ操作部材からの入力に応じてカメラ200の制御を行う。また、カメラマイコン205は、カメラ通信部208を介して、不図示のズームスイッチの操作に応じて変倍レンズ102の変倍動作に関する制御コマンドをレンズマイコン111に送信する。さらに、カメラマイコン205は、カメラ通信部208を介して、輝度情報に応じた絞りユニット114の光量調節動作やフォーカス情報に応じたフォーカスレンズ104の焦点調節動作に関する制御コマンドをレンズマイコン111に送信する。
カメラマイコン205は、ブロードキャスト通信においては、中間アダプタ300と交換レンズ100に対してデータを一斉に送信し、P2P通信においては、中間アダプタ300と交換レンズ100のいずれか一方と1対1のデータ通信を行う。
<通信回路の構成についての説明>
次に、図2を用いて、カメラ200、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を含むカメラシステムの間で構成される通信回路について説明する。本実施例のカメラシステムは、通信タイミングの通知に用いられる通知チャネルCSと、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルDATAを含む。
次に、図2を用いて、カメラ200、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を含むカメラシステムの間で構成される通信回路について説明する。本実施例のカメラシステムは、通信タイミングの通知に用いられる通知チャネルCSと、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルDATAを含む。
図1で説明したように、カメラ200と中間アダプタ300は、マウント401を介して接続されている。マウント401には、少なくとも2つの通信端子が設けられている。また、中間アダプタ300と交換レンズ100は、マウント400を介して接続されている。マウント400には、少なくとも2つの通信端子が設けられている。各マウントに設けられた通信端子により、上述した通知チャネルCSとデータ通信チャネルDATAが形成される。
通知チャネルCSは、カメラマイコン205、アダプタマイコン302及びレンズマイコン111に接続されており、各マイコンは、通知チャネルCSの信号レベル(電圧レベル)を検出可能である。また、通知チャネルCSは、カメラ200内に配置された不図示の電源にプルアップ接続されている。さらに、通知チャネルCSは、カメラ200に含まれる接地スイッチ2081を介してグランドと接続可能であり、中間アダプタ300に含まれる接地スイッチ3031を介してグランドと接続可能である。通知チャネルCSは、交換レンズ100に含まれる接地スイッチ1121を介してグランドと接続可能である。
このような回路構成を採用することで、カメラ200、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100に含まれるいずれかの接地スイッチを接続状態(第1の設定)とすることにより、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLow(第1のレベル)とすることが可能である。また、カメラ200、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100に含まれる全ての接地スイッチを遮断状態(第1の設定)とすることにより、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHigh(第2のレベル)とすることが可能である。
各マイコンは、接地スイッチの接続状態を変化させることで、通知チャネルCSとグランドとの接続状態を変化させることができる。換言すれば、各マイコンは接地スイッチの接続状態を変化させることで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHighとLowのいずれかに設定可能である。
例えば、カメラマイコン205は、カメラ200に含まれる接地スイッチ2081を接続状態とすることで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowとすることができる。本発明では、接地スイッチを接続状態とすることを「通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う」と記載する。また、接地スイッチを切断状態とすることを「通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う」と記載する。
つまり、全てのマイコンが通知チャネルCSに対してHigh出力を行うことで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighとなる。一方、いずれかのマイコンが通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行うことで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはLowとなる。なお、データ通信時における通知チャネルCSの役割については後述する。
データ通信チャネルDATAは、データの伝搬方向を切り替え可能な双方向のデータ通信チャネルである。データ通知チャネルDATAは、カメラマイコン205、アダプタマイコン302及びレンズマイコン111に接続されている。
データ通信チャネルDATAは、カメラ200に含まれる入出力切り替えスイッチ2082を介してカメラマイコン205と接続される。カメラマイコン205には、データを送信するためのデータ出力部とデータを受信するためのデータ入力部が備えられている。そして、入出力切り替えスイッチ2082の動作に応じて、データ通信チャネルDATAをデータ出力部とデータ入力部のうちの一方に選択的に接続することができる。
また、データ通信チャネルDATAは、中間アダプタ300に含まれる入出力切り替えスイッチ3032を介してアダプタマイコン302と接続される。アダプタマイコン302には、データを送信するためのデータ出力部とデータを受信するためのデータ入力部が備えられている。そして、入出力切り替えスイッチ3032の動作に応じて、データ通信チャネルDATAをデータ出力部とデータ入力部のうちの一方に選択的に接続することができる。
データ通信チャネルDATAは、交換レンズ100に含まれる入出力切り替えスイッチ1122を介してレンズマイコン111と接続される。レンズマイコン111には、データを送信するためのデータ出力部とデータを受信するためのデータ入力部が備えられている。そして、入出力切り替えスイッチ1122の動作に応じて、データ通信チャネルDATAをデータ出力部とデータ入力部のうちの一方に選択的に接続することができる。このような回路構成を採用することにより、データ通信チャネルDATAのデータの伝搬方向を適切に切り替えることができる。
<データフォーマットの説明>
続いて図3を用いて、データ通信チャネルDATAを介して通信されるデータのフォーマットについて説明する。
続いて図3を用いて、データ通信チャネルDATAを介して通信されるデータのフォーマットについて説明する。
図3は、データ送信側とデータ受信側の双方で通信速度を予め設定し、この設定に基づいた通信ビットレートでデータ通信を行う調歩同期式の通信方式におけるデータフォーマットを示している。通信ビットレートとは、1秒間に転送することができるデータ量を示し、単位はbps(bit per second)で表される。図3は最小通信単位である1フレームの信号波形を示している。
データ通信を行っていない状態では、データ通信チャネルDATAの信号レベルはHighレベルに維持されている。続いて、データの送信開始をデータ受信側に通知するため、データ通信チャネルDATAの信号レベルが1ビット期間の間Lowとされる。この1ビット期間をスタートビットSTと呼び、スタートビットSTからデータフレームが開始される。スタートビットSTに続く2ビット目から9ビット目までの8ビット期間で1バイトのデータが送信される。
データのビット配列はMSB(Most Significant Bit)ファーストフォーマットとして、最上位のデータD7から始まり、順にデータD6、データD5と続き、最下位のデータD0で終了する。そして、10ビット目に1ビットのパリティー情報(PA)を付加し、1フレームの最後を示すストップビットSPの期間、データ通信チャネルDATAの信号レベルがHighとされる。これにより、スタートビットSTから開始されたデータフレーム期間が終了する。なお、パリティー情報は1ビットである必要はなく、複数のビットのパリティー情報が付加されても良い。また、パリティー情報は必須ではなく、パリティー情報が付加されないフォーマットとしても良い。
また、データのビット配列をLSB(Least Significant Bit)ファーストフォーマットとして、最下位のデータD0から始まり、順にデータD1、データD2と続き、最上位のデータD7で終了するようにしても良い。本実施例では、8ビット期間で1バイトのデータが送信されるが、8ビット以外のビット期間で1バイトのデータが送信されるようにしても良い。
<ブロードキャスト通信の説明>
図4を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信について説明する。ブロードキャスト通信では、カメラ200が通信マスタとなり、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を通信スレーブとした通信が行われる。
図4を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信について説明する。ブロードキャスト通信では、カメラ200が通信マスタとなり、中間アダプタ300及び交換レンズ100を通信スレーブとした通信が行われる。
図4は、ブロードキャスト通信においてやり取りされる信号波形を示している。通信マスタであるカメラ200のカメラマイコン205は、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行うことで、通信スレーブであるレンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302に対してブロードキャスト通信の開始を通知する。
次に、カメラマイコン205は、データ通信チャネルDATAを介してレンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302にデータを送信する。
一方、レンズマイコン111とアダプタマイコン302は、データ通信チャネルDATAを介して上述したスタートビットSTを検出することに応じて、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う。なお、レンズマイコン111とアダプタマイコン302が通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う時点で、カメラマイコン205がLow出力を行っているため、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはLowのままである。
レンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302は、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行うことで、通信待機要求を通知する。通信待機要求は、カメラシステムにおける通信を一時停止させるためのものであり、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルにより通信待機要求の有無が判断される。
カメラマイコン205は、全てのデータを送信した後に通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。レンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302は、データ通信チャネルDATAから送信されたストップビットSPを受信した後に、受信したデータの解析及び受信データに対応する内部処理を実行する。その後、次の通信を実行するための準備が整った後に通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。
カメラシステムを構成する全ての構成要素が通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行うことで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighとなる。カメラマイコン205、レンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighに戻ったことにより、カメラシステムを構成する各構成要素が次の通信を実行可能な状態になったことを確認することができる。
図4では、カメラマイコン205が送信するデータに、アダプタマイコン302に対する送信要求命令が含まれており、カメラマイコン205によるデータ送信に続いて、アダプタマイコン302によるデータ送信が行われる。
具体的には、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになった後に、アダプタマイコン302は、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う。これにより、レンズマイコン111及びカメラマイコン205に対してブロードキャスト通信の開始を通知する。次に、アダプタマイコン302は、データ通信チャネルDATAを介してレンズマイコン111及びカメラマイコン205にデータを送信する。
一方、レンズマイコン111とカメラマイコン205は、データ通信チャネルDATAを介して上述したスタートビットSTを検出することに応じて、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う。なお、レンズマイコン111とカメラマイコン205が通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う時点では、アダプタマイコン302が通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行っているため、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはLowのままである。
アダプタマイコン302は、全てのデータを送信した後に通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。レンズマイコン111及びカメラマイコン205は、データ通信チャネルDATAから送信されたストップビットSPを受信した後に、受信したデータの解析及び受信データに対応する内部処理を実行する。その後、次の通信を実行するための準備が整った後に通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。
カメラシステムを構成する全ての構成要素が通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行うことで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighとなる。カメラマイコン205、レンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighに戻ったことにより、カメラシステムを構成する各構成要素が次の通信を実行可能な状態になったことを確認することができる。
以上説明したように、ブロードキャスト通信においては、データ送信側が、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行って通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHighからLowにすることで、ブロードキャスト通信の開始をデータ受信側に通知している。また、データ受信側は、通知チャネルCSへの出力をLow出力からHigh出力に変化させることで、通信待機要求の解除をレンズシステムの各構成要素に通知している。
なお、図4では本発明におけるブロードキャスト通信の通信波形の一例を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、1回のブロードキャスト通信において送受信されるデータを1バイトのデータでなく、複数バイトのデータとしても良い。
また、通信方式をブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信に切り替える場合は、カメラマイコン205からレンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302に対して、通信方式の切り替えを指示するデータの送信のみが行われる。
<P2P通信の説明>
図5を用いて、本発明における第2通信方式としてのP2P通信について説明する。P2P通信では、カメラ200が通信マスタとなり、カメラシステムを構成する構成要素の中で通信スレーブとして選択された1つの構成要素と1対1の個別の通信が行われる。
図5を用いて、本発明における第2通信方式としてのP2P通信について説明する。P2P通信では、カメラ200が通信マスタとなり、カメラシステムを構成する構成要素の中で通信スレーブとして選択された1つの構成要素と1対1の個別の通信が行われる。
図5は、P2P通信においてやり取りされる信号波形を示している。ここでは通信スレーブとして交換レンズ100が選択されている例を示している。P2P通信における通信スレーブを示す情報は、ブロードキャスト通信によって送信される。P2P通信においては、データ送信側が、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行わず、通知チャネルCSをHighに維持したままデータ受信側にデータを送信する。すなわち、カメラ200から交換レンズ100、アダプタ300にデータを送信する間の通知チャネルCSの電圧レベルを、ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信とで異ならせている。
ブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への切り替えが実行されると、最初に通信マスタであるカメラマイコン205からのデータ送信が開始される。
図5は、カメラマイコン205からレンズマイコン111への1バイトのデータ送信後に、レンズマイコン111からカメラマイコン205に対して2バイトのデータ送信が行われる例を示している。
カメラシステムを構成する各構成要素においてブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への切り替えが完了した後に、通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205はデータ通信チャネルDATAを介してレンズマイコン111にデータを送信する。カメラマイコン205は、データ送信が完了すると、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLow出力にして通信待機要求の通知を行う。そして、カメラマイコン205は、データ受信側としてデータを受信する準備が完了した後に通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHigh出力に戻す。
一方、レンズマイコン111は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったことによりカメラマイコン205からのデータ送信が完了したことを認識し、受信したデータの解析や受信したデータに対応する内部処理を実行する。図5の例では、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに、レンズマイコン111からカメラマイコン205へのデータ送信要求が含まれており、レンズマイコン111はカメラマイコン205に送信するデータの生成も行う。
その後、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighに戻ったことにより、通信待機要求の解除を認識したレンズマイコン111は、カメラマイコン205に対して2バイトのデータ送信を行う。
レンズマイコン111は、データ送信が終了すると、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLow出力にして通信待機要求の通知を行う。そして、レンズマイコン111は、データ受信側としてデータを受信する準備が完了した後に通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHigh出力に戻す。なお、P2P通信の通信相手として選択されていないアダプタマイコン302は、通知チャネルCSへの出力を変化させず、データの送受信に関与しない。
レンズマイコン111は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHighに戻した後のカメラマイコン205からのデータ送信タイミングによって、P2P通信が継続されているのか、ブロードキャスト通信への切り替えが行われたのかを判断する。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighのままの状態で、カメラマイコン205からのデータを受信した場合、レンズマイコン111はP2P通信が継続されていると判断する。一方、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowに変化した後に、カメラマイコン205からのデータを受信した場合、レンズマイコン111はP2P通信からブロードキャスト通信に切り換えられたと判断する。
以上説明したように、P2P通信においては、データ送信側が通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHigh出力からLow出力にすることで、データ送信側によるデータの送信が完了したことをデータ受信側に通知している。そのため、P2P通信においては、データ送信側が通知チャネルCSの信号レベルを変化させるまで、複数のデータフレームを連続して送信することができる。通信スレーブが1つのデータフレームを送信する毎に通信マスタからの通信が挿入されるシステム構成ではないため、カメラマイコン205と、レンズマイコン111やアダプタマイコン302等のアクセサリ装置との間の通信を高速に行うことができる。そして、データ送信側は、次の通信におけるデータ受信側としてのデータ受信準備が完了するまで、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLow出力のままとすることで、通信待機要求を通知している。
<通信方式の切り替えについての説明>
図6を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信を切り替えて実行される通信の概要を説明する。ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信のいずれの通信においてもカメラ200が通信マスタとなり、中間アダプタ300や交換レンズ100との通信を実行する。P2P通信におけるカメラ本体との通信相手を示す情報は、ブロードキャスト通信において通知される。
図6を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信を切り替えて実行される通信の概要を説明する。ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信のいずれの通信においてもカメラ200が通信マスタとなり、中間アダプタ300や交換レンズ100との通信を実行する。P2P通信におけるカメラ本体との通信相手を示す情報は、ブロードキャスト通信において通知される。
図6は、ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信を切り替えて実行される通信における通信波形を示している。初めに、P2P通信における通信相手としてアダプタマイコン302が選択されたことを示す情報がブロードキャスト通信において送受信され、その後、カメラマイコン205とアダプタマイコン302の間でP2P通信が行われる。以下、P2P通信における通信相手を示す情報を、通信相手指定データと記載する。
以下、通信相手指定データ自体に、ブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への切り替えコマンドとしての機能を持たせた実施例について説明する。なお、通信相手指定データとは別に、ブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への切り替えを指示する信号を送受信することでP2P通信への切り替えを実行しても良い。
P2P通信における通信相手として選択されていないレンズマイコン111は通信相手指定データを受信した後、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータの解析や内部処理が終了した時点で通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。そして、カメラマイコン205とアダプタマイコン302の間でP2P通信が行われている期間は、通知チャネルCSへの出力を変化させることなく、ブロードキャスト通信に対応した設定を維持する。
具体的には、アダプタマイコン302は、P2P通信への切り替えが完了すると、通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行うことで、通信方式の切り替え完了をカメラマイコン205に通知する。カメラマイコン205も、P2P通信への切り替えが完了すると、通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。上述したように、P2P通信における通信相手として選択されていないレンズマイコン111は、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータの解析や内部処理が終了した時点で通知チャネルCSにHigh出力を行う。
カメラマイコン205は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったことを検出すると、図5で示したP2P通信を開始する。P2P通信方式における通信の概要は図5で説明した通りであるため、ここではP2P通信の詳細についての説明を割愛する。
カメラマイコン205とアダプタマイコン302の間のP2P通信が終了すると、カメラマイコン205はブロードキャスト通信により、P2P通信における通信相手としてレンズマイコン111を選択したことを示す通信相手指定データを送信する。その後、カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111の間でP2P通信が行われる。
なお、アダプタマイコン302は、カメラマイコン205からデータが送信される前に通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったことにより、P2P通信からブロードキャスト通信への切り替えが実行されたことを認識する。
<ブロードキャスト通信における通信フローの説明>
次に、図7を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信における通信フローについて説明する。カメラマイコン205及びアダプタマイコン302は、コンピュータプログラムである通信制御プログラムに従って、図7のフローチャートに示す通信制御を行う。なお、図7において「S」はステップを意味する。図7では通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205の通信フローと、通信スレーブとしてのアダプタマイコン302の通信フローを開示している。レンズマイコン111の通信フローは、アダプタマイコン302の通信フローとほぼ同じであるため、ここではレンズマイコン111の通信フローを開示していない。
次に、図7を用いて、ブロードキャスト通信における通信フローについて説明する。カメラマイコン205及びアダプタマイコン302は、コンピュータプログラムである通信制御プログラムに従って、図7のフローチャートに示す通信制御を行う。なお、図7において「S」はステップを意味する。図7では通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205の通信フローと、通信スレーブとしてのアダプタマイコン302の通信フローを開示している。レンズマイコン111の通信フローは、アダプタマイコン302の通信フローとほぼ同じであるため、ここではレンズマイコン111の通信フローを開示していない。
カメラマイコン205は、S100においてブロードキャスト通信を開始するイベントが発生したか否かの判定を行う。ブロードキャスト通信を開始するイベントが発生した場合はS101に進み、このようなイベントが発生していない場合は、S100の判定を繰り返し行う。
S101では、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行い、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにすることで、レンズマイコン111及びアダプタマイコン302に対してブロードキャスト通信の開始を通知する。続いて、S102において、入出力切り替えスイッチ2082を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをカメラマイコン205のデータ出力部に接続し、S103においてデータ送信を開始する。
S104では、S103でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータに、送信要求コマンドが含まれるか否かの判定を行う。送信要求コマンドとは、通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205から送信されたデータを受信した通信スレーブに対して、カメラマイコン205へのデータ送信を要求するコマンドである。
S103でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれていない場合には、S105に進む。S105では、カメラマイコン205からのデータ送信の完了後に通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、S116に進む。
S103でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれている場合にはS106に進む。S106では、カメラマイコン205からのデータ送信の完了後に、データ通信チャネルDATAをカメラマイコン205のデータ入力部に接続し、S107に進む。S107では、通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。
S108では、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighのときには、カメラシステムが通信可能な状態であることを示している。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになると、S109において通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになるまで継続して行われる。
通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになることに応じて、通信スレーブであるアダプタマイコン302からカメラマイコン205への通信が開始される。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったと判定した後に、カメラマイコン205はS110においてデータ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信を許可する。続いて、S111において、アダプタマイコン302から送信されるデータに含まれるスタートビットを受信したか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、スタートビットを受信するまで継続して行われる。
スタートビットを受信すると、S112に進み、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行い、S113においてストップビットを受信したか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、ストップビットを受信するまで継続して行われる。ストップビットを受信すると、S114においてデータ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信を禁止し、受信したデータの解析や受信したデータに対応する内部処理を実行する。その後、S115において通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。
続いて、S116において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになると、S117において、S103で送信したデータが、通信相手指定データであったか否かの判定を行う。通信相手指定データであった場合には、S118に進み、P2P通信への移行を行う。通信相手指定データでなかった場合には、ブロードキャスト通信を継続する。
次に、アダプタマイコン302における通信フローについて説明する。S200において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになることに応じて、通信マスタであるカメラマイコン205からのデータ送信が開始されるため、S201においてアダプタマイコン302はデータ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信を許可する。
続いて、S202においてスタートビットを受信したか否かの判定を行う。スタートビットを受信していない場合には、S203に進み、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighであるか否かの判定を行う。
ここで、S203及びS204の処理を行うのは、カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111の間でP2P通信が行われ、アダプタマイコン302のみがブロードキャスト通信を行う状況に対応するためである。この状況では、アダプタマイコン302はカメラマイコン205からデータを受信することはないため、S204においてデータ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信を禁止する。
<P2P通信>の欄で説明したように、P2P通信においても通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighとLowの間で変化する。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルは、通常時はHighであり、ブロードキャスト通信においては、通信待機要求を通知する場合や、通信の開始を通知する場合にLowに設定される。P2P通信においては、通信待機要求を通知する場合にLowに設定される。
S202において、アダプタマイコン302がカメラマイコン205からスタートビットを受信していない状況としては、以下の状況が考えられる。
1つ目の状況は、カメラマイコン205が通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにした後であって、データ送信が開始されていない状況である。2つ目の状況は、カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111がP2P通信を行っており、アダプタマイコン302はP2P通信に関与していない状況である。
1つ目の状況の場合には、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighにならないため、S203からS202に戻り、カメラマイコン205からのデータ送信が開始されるまで、S202及びS203の判定を繰り返す。
2つ目の状況の場合には、カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111のいずれかが通信待機要求を通知していない限り、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighになっている。この状況では、基本的にはS203からS204に進み、データ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信が禁止される。なお、P2P通信において、通信待機要求が通知されている場合には、S203からS202に戻り、再びS203の判定が行われることになる。S203の判定が複数回実施されることはあるが、通信待機要求が解除され、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになると、S203からS204に進むことになる。
以上のように、S203及びS204の制御フローを追加することで、カメラシステムの中でブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信を併用することができる。本実施例においては、カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111の間でP2P通信を行う一方で、ブロードキャスト通信に対応した状態でアダプタマイコン302を待機させることができる。
S202の説明に戻る。S202においてスタートビットを受信すると、アダプタマイコン302は、受信したデータの解析や受信したデータに対応する内部処理を開始すると共に、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行う。これにより、カメラシステムを構成する各構成要素に対して通信待機要求を通知する。
次に、S206においてストップビットを受信したか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、ストップビットを受信するまで継続して行われる。ストップビットを受信すると、S207においてデータ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータの受信を禁止し、受信したデータの解析や受信したデータに対応する内部処理を継続する。データの内部処理が完了し、次のデータ通信を実行可能な状態となると、S208において通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。
S209では、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに、送信要求コマンドが含まれるか否かの判定を行う。送信要求コマンドを含む場合には、S210に進み、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighのときには、カメラシステムが通信可能な状態であることを示している。カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれない場合には、後述するS215に進む。
S210において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighであると判定された場合にはS211に進む。S211では、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行い、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにすることで、カメラマイコン205及びレンズマイコン111に対してブロードキャスト通信の開始を通知する。続いて、S212において、入出力切り替えスイッチ3032を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをアダプタマイコン302のデータ出力部に接続し、S213においてデータ送信を開始する。
データ送信が完了すると、S214において、通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。続いて、S215では、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。
通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるとS216に進む。S216では、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータが通信相手指定データであり、かつ、自身がP2P通信におけるカメラマイコン205の通信相手として選択されたか否かの判定を行う。P2P通信におけるカメラマイコン205の通信相手としてアダプタマイコン302が選択された場合には、S217に進み、データ通信チャネルDATAにおけるデータ受信を許可する。そして、S218において、ブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への移行を行う。
カメラマイコン205から受信したデータが通信相手指定データでない場合、またはP2P通信における通信相手としてアダプタマイコン302が選択されていない場合は、P2P通信への移行を実行することなく、ブロードキャスト通信を継続する。
<P2P通信における通信フロー>
次に、図8を用いて、P2P通信における通信フローについて説明する。カメラマイコン205及びレンズマイコン111は、コンピュータプログラムである通信制御プログラムに従って、図8のフローチャートに示す通信制御を行う。なお、図8において「S」はステップを意味する。図8では通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205の通信フローと、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111の通信フローを開示している。アダプタマイコン302の通信フローは、レンズマイコン111の通信フローとほぼ同じであるため、ここではアダプタマイコン302の通信フローを開示していない。
次に、図8を用いて、P2P通信における通信フローについて説明する。カメラマイコン205及びレンズマイコン111は、コンピュータプログラムである通信制御プログラムに従って、図8のフローチャートに示す通信制御を行う。なお、図8において「S」はステップを意味する。図8では通信マスタとしてのカメラマイコン205の通信フローと、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111の通信フローを開示している。アダプタマイコン302の通信フローは、レンズマイコン111の通信フローとほぼ同じであるため、ここではアダプタマイコン302の通信フローを開示していない。
カメラマイコン205は、S300においてP2P通信を開始するイベントが発生したか否かの判定を行う。P2P通信を開始するイベントが発生した場合はS301に進み、このようなイベントが発生していない場合は、S300の判定を繰り返し行う。
S301では、入出力切り替えスイッチ2082を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをカメラマイコン205のデータ出力部に接続し、S302においてデータ送信を開始する。
S303では、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行い、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにする。これにより、カメラマイコン205は、通信スレーブであるレンズマイコン111に対して通信待機要求を行う。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowの期間、レンズマイコン111はカメラマイコン205に対するデータ送信を行わない。
S304では、S302でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータに、送信要求コマンドが含まれるか否かの判定を行う。送信要求コマンドとは、通信スレーブに対して、カメラマイコン205へのデータ送信を要求するコマンドである。S302でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれない場合には、レンズマイコン111からデータが送信されることはない。この場合、S304からS305に進み、レンズマイコン111が通信待機要求を通知しているか否かを確認する。
具体的には、S305において、カメラマイコン205における通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除した上で、S306において通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowであるか否かの判定を行う。これにより、レンズマイコン111が通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにしているか否か、つまり、レンズマイコン111が通信待機要求を通知しているか否かを判定することができる。
一般的に、カメラマイコン205からのデータを受信したレンズマイコン111は、そのデータの解析や内部処理のために、ある程度の期間、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行うことで通信待機要求を通知する。S306は、レンズマイコン111の通知待機要求を認識するために行われる。S305の後に一時的に通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighとなることがある。このときは、S306の判定を行うことで通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowとなるまで待機する。S306で通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowとなったことを確認した上でS311に進む。
S304に戻る。S304において、S302でカメラマイコン205から送信したデータが送信要求コマンドである場合にはS307に進む。
S307では、入出力切り替えスイッチ2082を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをカメラマイコン205のデータ入力部に接続する。さらに、S308において通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。
通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighの状態で、レンズマイコン111からのデータ受信を行い、S309において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったか否かの判定を行う。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったことに応じて、レンズマイコン111のデータ送信が完了したと判断し、S310においてデータ解析を行う。
続いてS311において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighの状態は、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111がデータ通信可能な状態であることを意味している。
通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになると、S312に進み、ブロードキャスト通信への移行イベントが発生した否かの判定を行う。ブロードキャスト通信への移行イベントが発生した場合には、S313に進み、ブロードキャスト通信への移行を行う。ブロードキャスト通信への移行イベントが発生していない場合は、P2P通信を継続して行う。
次に、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111の通信フローについて説明する。レンズマイコン111は、ブロードキャスト通信からP2P通信への切り替えを実行すると、最初にカメラマイコン205から送信されるデータの受信を行う。カメラマイコン205から送信されるデータを受信している期間、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルはHighに保たれている。
続いてS400において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったか否かの判定を行う。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったことに応じて、カメラマイコン205のデータ送信が完了したと判断し、S401においてデータ解析を行う。
続いて、S402において、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowの状態は、カメラマイコン205が通信待機要求を通知している状態である。
通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになると、S403において、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに、送信要求コマンドが含まれるか否かの判定を行う。カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれない場合にはS404に進む。
S404では、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに対する内部処理等のために、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにすることで、カメラマイコン205に対して通信待機要求を通知する。レンズマイコン111が通信可能な状態となると、S405において通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをHighにして、通信待機要求を解除した上でS411に進む。
S403に戻る。S403において、カメラマイコン205から受信したデータに送信要求コマンドが含まれる場合にはS406に進む。S406では、入出力切り替えスイッチ1122を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをレンズマイコン205のデータ出力部に接続する。そしてS407において、カメラマイコン205へのデータ送信を開始する。
カメラマイコン205へのデータ送信が完了した後に、S408において、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行い、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにする。これにより、レンズマイコン111は、通信マスタであるカメラマイコン205に対して通信待機要求を行う。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowの期間、カメラマイコン205はレンズマイコン111に対するデータ送信を行わない。
S409では、入出力切り替えスイッチ1122を動作させることで、データ通信チャネルDATAをレンズマイコン205のデータ入力部に接続し、S410において、通知チャネルCSへのLow出力を解除し、High出力を行う。
S411では、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになったか否かの判定を行う。この判定は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになるまで継続して行われる。通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがHighになった状態は、カメラマイコン205及びレンズマイコン111が通信可能な状態であることを意味している。
以上説明したように、カメラ200から、交換レンズ100、アダプタ300にデータを送信する間の通知チャネルCSの電圧レベルを、ブロードキャスト通信とP2P通信とで異ならせている。このようなシステムにより、カメラ200が特定のアクセサリ装置と個別に通信を行う場合に、通信相手が変更されるまでは通信相手を改めて通知する必要がないため、カメラ200と、交換レンズ100やアダプタ300を含むアクセサリ装置との間の通信を高速に行うことができる。
<変形例>
以下、ブロードキャスト通信における図4とは異なる通信制御方法について説明する。図4のブロードキャスト通信においては、カメラマイコン205が通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行って、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにすることでブロードキャスト通信の開始を各通信スレーブに通知している。
以下、ブロードキャスト通信における図4とは異なる通信制御方法について説明する。図4のブロードキャスト通信においては、カメラマイコン205が通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行って、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにすることでブロードキャスト通信の開始を各通信スレーブに通知している。
図9に示した変形例は、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111やアダプタマイコン302が、ブロードキャスト通信の開始をカメラマイコン205にリクエストする態様を示している。カメラマイコン205への通信リクエストは、カメラマイコン205からアクセサリ装置に含まれるマイコンへの通信が一時停止された状態において、アクセサリ装置に含まれるマイコンが、カメラマイコン205との通信を主体的に再開させるときに実行される。
本変形例は、例えば、中間アダプタ300に備えられた操作部材304がユーザによって操作された場合に実行される。交換レンズ100に供えられた操作部材130がユーザによって操作された場合にも実行されうる。カメラシステムとして通信が一時停止された状態から通信を再開させる場合、基本的には、通信マスタであるカメラマイコン205が主体的に通信を再開させることが適切である。通信スレーブであるアクセサリ装置のマイコンに通信を再開させる機能を持たせることは、通信マスタであるカメラシステム205が予期しないタイミングでの通信再開が行われるおそれがある。それゆえ、通信スレーブに対して、無制限に通信を再開させる機能を持たせることは好ましくない。
そこで、本変形例では、アクセサリ装置に含まれるマイコンが、カメラマイコン205への通信開始リクエストを行うという形で、通信スレーブであるアクセサリ装置のマイコンに、通信を再開させる機能を持たせている。
図9は、本変形例のブロードキャスト通信における通信波形を示している。本変形例の通信制御方法では、通信スレーブとしてのレンズマイコン111やアダプタマイコン302が、通信イベントの発生の有無を監視している。そして、通信イベントが発生した場合には、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行うことで通知チャネルCSの信号レベルをLowにする。
カメラマイコン205は、通知チャネルCSの信号レベルがLowになったことに応じて、通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行った上でブロードキャスト通信を開始する。通知チャネルCSにLow出力を行った後のブロードキャスト通信のフローは、図4で説明したフローと同じであるため、ここでの説明は割愛する。
以上説明した実施例は、通知チャネルCSとデータ通信チャネルDATAを含む通信チャネルに加え、別の通信チャネルと併用可能である。
その一例を、図10を用いて説明する。なお、図10において、図1と同一の部材には同一の符号を付し、重複する説明は省略する。また、図10において、図1に記載されている部材の一部の図示を省略している。前述の通知チャネルCSおよびデータ通信チャネルDATAは、第3通信という通信用の通信線である。
レンズマイコン111は、通信部112に加え、第1通信を行うための通信部131、第2通信を行うための通信部132を制御する。カメラマイコン205は、通信部112に加え、第1通信を行うための通信部209、第2通信を行うための通信部210を制御する。
まず、第1通信について説明する。第1通信は、通信部131と通信部209を介して行われる通信である。通信部131はレンズマイコン111からの指示に基づいて、通信部209はカメラマイコン205からの指示に基づいて、通知チャネルCS1、データ通信チャネルDCL、データ通信チャネルDLCを介して通信を行う。通信部131および通信部209は、通知チャネルCS1の電圧レベル、調歩同期通信の際の通信レート(単位時間当たりのデータ量)や通信電圧の設定をする。さらに、レンズマイコン111やカメラマイコン205からの指示を受けて、データ通信チャネルDCLおよびデータ通信チャネルDLCを介したデータの送受信を行う。
通知チャネルCS1は、カメラ本体200から交換レンズ100への通信要求の通知等に用いられる信号線である。データ通信チャネルDCLは、カメラ本体200から交換レンズ100にデータを送信する際に用いられるチャネルであり、データ通信チャネルDLCは交換レンズ100からカメラ本体200にデータを送信する際に用いられるチャネルである。
カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111は、第1通信では、クロック同期通信または調歩同期通信により通信を行う。交換レンズ100がカメラ本体200に接続された際に行われる初期通信も、まずは第1通信により行う。カメラマイコン205とレンズマイコン111は交換レンズ100の識別情報を通信し、カメラ本体200装着された交換レンズ100が調歩同期通信に対応可能であることが判明すると、クロック同期通信から調歩同期通信に通信方式を切り替える。また、識別情報の通信の結果、カメラマイコン205は、交換レンズ100が、アダプタ300も含めて通信を行う第3通信に対応可能かどうかを識別してもよい。カメラマイコン205は、交換レンズ100が第3通信に対応可能であると判断した場合、交換レンズ100や中間アダプタ300を認識するための認証通信をP2P通信を介して行ってもよい。
次に、第2通信について説明する。第2通信は、交換レンズ100からカメラ本体200への一方向の通信である。第2通信は、通信部132と通信部210を介して行われる。通信部132はレンズマイコン111からの指示に基づいて、通信部210はカメラマイコン205からの指示に基づいて、通知チャネルCS2とデータ通信チャネルDLC2を介して通信を行う。カメラ通信部208とレンズ通信部118は、クロック同期式通信や調歩同期通信によりデータを送受信する。第1通信のデータ通信チャネルDLCと共に第2通信チャネルのデータ通信チャネルDLC2を用いることで、交換レンズ100からカメラ本体200に対して大量のデータを短時間で送信することが可能となる。
以上説明した実施例は代表的な例に過ぎず、本発明の実施に際しては、各実施例に対して種々の変形や変更が可能である。例えば、上記実施例では、アクセサリ装置として交換レンズと中間アダプタを用いた例を示したが、アクセサリ装置として、カメラ本体に直接装着される交換レンズとカメラ本体に直接装着されるストロボ等を用いても良い。
本発明は上記実施の形態に制限されるものではなく、本発明の精神及び範囲から離脱することなく、様々な変更及び変形が可能である。従って、本発明の範囲を公にするために以下の請求項を添付する。
本願は、2017年5月31日提出の日本国特許出願特願2017-108267と2018年5月30日提出の日本国特許出願特願2018-102943を基礎として優先権を主張するものであり、その記載内容の全てをここに援用する。
Claims (21)
- カメラに対して装着可能なアクセサリ装置であって、
前記カメラとの間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するアクセサリ制御部を有し、
前記アクセサリ制御部は、
前記カメラに装着された、前記アクセサリ装置を含む複数のアクセサリ装置と、前記カメラとの間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記カメラと個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを受信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能であり、
前記第1通信方式において、前記第2通信方式における前記カメラの通信相手として前記アクセサリ装置が選択されたことを示す通信相手指定データを前記データ通信チャネルを介して受信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うことを特徴とするアクセサリ装置。 - 前記第1通信方式において前記カメラからデータを受信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルは第1のレベルであり、前記第2通信方式において前記カメラからデータを受信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルは前記第1のレベルよりも高い第2のレベルであることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第1通信方式において、前記カメラからデータを受信した後に、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを変化させてから、前記データ通信チャネルを介して前記カメラにデータ送信を行うことを特徴とする請求項2に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化させ、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1のレベルの状態で、前記カメラに前記データ通信チャネルを介してデータ送信を行うことを特徴とする請求項3に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第1通信方式において、前記データ通信チャネルを介した前記カメラからの通信が停止されている状態で、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化させることで、前記カメラからの通信を再開させることを特徴とする請求項2または3に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第2通信方式において、前記カメラからのデータ受信を開始した後に、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1のレベルから前記第2のレベルに変化したことに応じて、前記カメラに対するデータ送信を開始することを特徴とする請求項2乃至5のいずれか1項に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第2のレベルの状態で前記カメラからのデータ受信を開始し、前記データ受信を開始した後、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化し、再び前記第2のレベルに変化したことに応じて、前記カメラに対するデータ送信を開始することを特徴とする請求項6に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第2通信方式において、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを、前記カメラにデータを送信し始めたときの電圧レベルから、前記カメラにデータを送信し始めたときの電圧レベルとは異なる電圧レベルに変化させることにより、前記アクセサリ装置からのデータ送信が終了したことを前記カメラに通知することを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第2通信方式において、前記カメラに対するデータ送信の後に、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化させることを特徴とする請求項2乃至7のいずれか1項に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、連続して複数のデータフレームを前記カメラに送信可能であることを特徴とする請求項8または9に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記第1通信方式において、前記カメラから受信した通信相手指定データが、前記アクセサリ装置が選択されなかったことを示すデータであった場合は、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行わないことを特徴とする請求項1乃至10のいずれか1項に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- 前記カメラに複数のアクセサリ装置が装着可能であり、前記複数のアクセサリ装置及び前記カメラは、前記通知チャネルを第1の設定と第2の設定にそれぞれ設定可能であり、
前記複数のアクセサリ装置及び前記カメラのいずれかが前記通知チャネルを前記第1の設定した場合と、前記複数のアクセサリ装置及び前記カメラが前記通知チャネルを前記第2の設定とした場合とで、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルは異なり、
前記アクセサリ制御部は、
前記第1通信方式において、前記カメラからデータを受信している間は前記通知チャネルを第1の設定とし、
前記第2通信方式において、前記カメラからデータを受信している間の少なくとも一部の期間で、前記通知チャネルを第2の設定とすることを特徴とする請求項1乃至11のいずれか1項に記載のアクセサリ装置。 - 第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置が装着可能なカメラであって、
前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するカメラ制御部を有し、
前記カメラ制御部は、
前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置のうちの1つのアクセサリ装置と個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを送信する間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能であり、
前記第1通信方式において、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置に対して、前記データ通信チャネルを介して前記第2通信方式における前記カメラの通信相手を示す通信相手指定データを送信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うことを特徴とするカメラ。 - 前記カメラ制御部は、
前記第1通信方式において、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置にデータを送信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを第1のレベルとし、
前記第2通信方式において、前記1つのアクセサリ装置にデータを送信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを前記第1のレベルよりも高い第2のレベルとすることを特徴とする請求項13に記載のカメラ。 - 前記カメラ制御部は、前記第1通信方式において、前記データ通信チャネルを介した前記カメラからの通信が停止されている状態で、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化したことに応じて、前記カメラに装着されたアクセサリ装置へのデータ送信を再開することを特徴とする請求項13または14に記載のカメラ。
- 前記カメラ制御部は、前記第2通信方式において、前記1つのアクセサリ装置に対するデータ送信が完了したことに応じて、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルを前記第2のレベルから前記第1のレベルに変化させることを特徴とする請求項14または15に記載のカメラ。
- 前記カメラ、前記第1のアクセサリ装置、および前記第2のアクセサリ装置のそれぞれは、前記通知チャネルを第1の設定と第2の設定に設定可能であり、
前記カメラ、前記第1のアクセサリ装置、及び前記第2のアクセサリ装置のうち少なくともいずれかが前記通知チャネルを前記第1の設定した場合と、前記カメラ、前記第1のアクセサリ装置、及び前記第2のアクセサリ装置が前記通知チャネルを前記第2の設定とした場合とで、前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルは異なり、
前記カメラ制御部は、
前記第1通信方式において、前記複数のアクセサリ装置へのデータ送信を終了したことに応じて、前記通知チャネルの設定を前記第1の設定から前記第2の設定に切り替え、
前記第2通信方式において、通信相手のアクセサリ装置へのデータ送信を終了したことに応じて、前記通知チャネルの設定を前記第2の設定から前記第1の設定に切り替えることを特徴とする請求項14乃至16のいずれか1項に記載のカメラ。 - 前記カメラ制御部は、連続して複数のデータフレームを前記アクセサリ装置に送信可能であることを特徴とする請求項16または17に記載のアクセサリ装置。
- カメラに対して装着可能であり、前記カメラとの間で、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を行うアクセサリ装置であって、前記カメラに装着された、前記アクセサリ装置を含む複数のアクセサリ装置と前記カメラとの間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記カメラと個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを受信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能なアクセサリ装置のコンピュータに、
前記第2通信方式における前記カメラの通信相手として前記アクセサリ装置が選択されたことを示す通信相手指定データを、前記第1通信方式において前記カメラから受信するステップと、
前記通信相手指定データの受信に応じて前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うステップを実行させることを特徴とする通信制御プログラム。 - 第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置が装着可能であり、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を行うカメラであって、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置との間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置のうちの1つのアクセサリ装置と個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを送信している間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能なカメラのコンピュータに、
前記第1通信方式において、前記第2通信方式における通信相手として選択したアクセサリ装置を示す通信相手指定データを前記複数のアクセサリ装置に送信するステップと、
前記通信相手指定データを送信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うステップを実行させることを特徴とする通信制御プログラム。 - カメラと、それぞれが該カメラに装着可能な第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置を含むカメラシステムであって、
前記カメラは、前記第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置との間で行う、データ通信に用いられるデータ通信チャネルと前記データ通信チャネルを介して行う通信のタイミングを通知する通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するカメラ制御部を有し、
前記第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置のそれぞれは、前記データ通信チャネルと前記通知チャネルとを含むチャネルを用いた通信を制御するアクセサリ制御部を有し、
前記カメラ制御部と第1のアクセサリ装置および第2のアクセサリ装置のそれぞれの前記アクセサリ制御部は、前記複数のアクセサリ装置との間で通信するために用いられる第1通信方式と、前記複数のアクセサリ装置のうちの1つのアクセサリ装置と個別に通信するために用いられ、前記カメラからデータを送信する間の前記通知チャネルの電圧レベルが前記第1通信方式とは異なる第2通信方式と、に切り替え可能であり、
前記カメラ制御部は、前記第1通信方式において、前記第2通信における前記カメラの通信相手を前記カメラの通信相手を示す通信相手指定データを送信したことに応じて、前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行い、
前記第1のアクセサリ装置および前記第2のアクセサリ装置のうち前記通信相手指定データで指定された1つのアクセサリ装置のアクセサリ制御部は、前記通信相手指定データを受信したことに応じて前記第1通信方式から前記第2通信方式への切り替えを行うことを特徴とするカメラシステム。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP24155424.5A EP4354892A3 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-05-30 | Accessory device, camera, communication control program, and camera system |
| CN201880035925.6A CN110692013B (zh) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-05-30 | 配件装置、照相机、通信控制方法、介质和照相机系统 |
| EP18809401.5A EP3611564B1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-05-30 | Accessory device, camera, communication control program, and camera system |
| US16/694,326 US11006031B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2019-11-25 | Accessory device, camera, storage medium, and camera system in which communication is performed via data and notification channels and employs differences in voltage level for the notification channel during a period in which data is received |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017108267 | 2017-05-31 | ||
| JP2017-108267 | 2017-05-31 | ||
| JP2018-102943 | 2018-05-30 | ||
| JP2018102943A JP6427287B1 (ja) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-05-30 | アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステム |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/694,326 Continuation US11006031B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2019-11-25 | Accessory device, camera, storage medium, and camera system in which communication is performed via data and notification channels and employs differences in voltage level for the notification channel during a period in which data is received |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018221590A1 true WO2018221590A1 (ja) | 2018-12-06 |
Family
ID=64397412
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/020769 WO2018221590A1 (ja) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-05-30 | アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11006031B2 (ja) |
| EP (2) | EP3611564B1 (ja) |
| JP (3) | JP6427287B1 (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN113905157A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2018221590A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020024379A (ja) * | 2018-07-31 | 2020-02-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ、中間アクセサリ及びこれらの制御方法 |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3633450B1 (en) * | 2017-05-31 | 2023-08-16 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Accessory device, camera, and communication control program |
| JP7046709B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-17 | 2022-04-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | アクセサリ装置、これを備えるカメラシステム、およびプログラム |
| JP6921896B2 (ja) * | 2018-06-28 | 2021-08-18 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、交換レンズ、中間アクセサリ及びこれらの制御方法 |
| JP7566545B2 (ja) | 2020-09-16 | 2024-10-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ装置および制御方法 |
| JP7293177B2 (ja) | 2020-09-16 | 2023-06-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | アクセサリ装置、撮像装置、撮像システム、通信装置、通信方法、およびプログラム |
| JP7547132B2 (ja) | 2020-09-16 | 2024-09-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ装置および制御方法 |
| JP2023172241A (ja) * | 2022-05-23 | 2023-12-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ装置および通信制御方法 |
| JP2023172239A (ja) * | 2022-05-23 | 2023-12-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ装置および通信制御方法 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007148592A (ja) | 2005-11-24 | 2007-06-14 | Funai Electric Co Ltd | データ通信装置 |
| JP2012037692A (ja) * | 2010-08-06 | 2012-02-23 | Canon Inc | カメラシステムの中間アクセサリおよびカメラシステム |
| WO2013168742A1 (ja) * | 2012-05-08 | 2013-11-14 | 株式会社ニコン | アクセサリ,カメラボディ |
| JP2016167719A (ja) * | 2015-03-10 | 2016-09-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 光学装置 |
| JP2017041833A (ja) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | 電子機器、その制御方法、および制御プログラム |
| WO2017068912A1 (ja) * | 2015-10-20 | 2017-04-27 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | レンズシステム、アクセサリ、通信方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2017108267A (ja) | 2015-12-09 | 2017-06-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像処理装置、撮像装置、画像処理方法、プログラム、記憶媒体 |
| JP2018102943A (ja) | 2011-01-17 | 2018-07-05 | アクティヴパック, インコーポレイテッド | 無菌カートリッジおよび分配装置 |
Family Cites Families (41)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59188622A (ja) * | 1983-04-08 | 1984-10-26 | Minolta Camera Co Ltd | カメラ用中間アクセサリ |
| JP2625701B2 (ja) * | 1987-02-16 | 1997-07-02 | 株式会社ニコン | カメラ用光学系アクセサリ |
| JPH0786586B2 (ja) * | 1990-02-17 | 1995-09-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | カメラシステム,交換レンズ及び光学付属品 |
| US5257058A (en) * | 1990-11-30 | 1993-10-26 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Interchangeable lens system |
| JPH11344764A (ja) | 1998-06-02 | 1999-12-14 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | カメラシステム |
| JP3799169B2 (ja) * | 1998-08-25 | 2006-07-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮影システム及びアダプター装置及びレンズ装置 |
| JP3836685B2 (ja) | 2001-02-28 | 2006-10-25 | ペンタックス株式会社 | レンズ交換式カメラの通信システム |
| JP2002341424A (ja) * | 2001-05-21 | 2002-11-27 | Minolta Co Ltd | 中間アクセサリ、交換レンズ、カメラ本体およびカメラシステム |
| US6812971B2 (en) * | 2001-09-11 | 2004-11-02 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Electronic apparatus, stand and electronic apparatus stand system |
| WO2003028366A1 (fr) * | 2001-09-20 | 2003-04-03 | Nikon Corporation | Camera numerique, systeme de camera numerique, appareil de controle, appareil de stockage d'images, appareil de collecte d'informations, appareil de fourniture de services, appareil de gestion |
| AT413455B (de) | 2002-01-18 | 2006-03-15 | Christian Ing Mag Tschida | System mit einer kamera, passive zubehörkomponente und steuereinrichtung hiefür |
| US6982748B2 (en) * | 2002-02-25 | 2006-01-03 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Automatically switched camera system with indicator for notifying the next subject of the camera system |
| JP4555556B2 (ja) | 2003-10-09 | 2010-10-06 | オリンパス株式会社 | レンズ交換式カメラシステム |
| JP2008216439A (ja) * | 2007-03-01 | 2008-09-18 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | カメラシステム |
| JP2008256847A (ja) * | 2007-04-03 | 2008-10-23 | Nikon Corp | カメラ、アクセサリ装置およびカメラシステム |
| JP5159344B2 (ja) | 2008-02-04 | 2013-03-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | 交換レンズ、カメラおよびカメラシステム |
| JP5094655B2 (ja) * | 2008-09-12 | 2012-12-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置 |
| JP5451260B2 (ja) * | 2009-08-28 | 2014-03-26 | キヤノン株式会社 | 制御装置、制御システム及びコマンド送信方法ならびにプログラム |
| JP5645431B2 (ja) | 2010-03-17 | 2014-12-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | カメラシステム、アクセサリ、及びアクセサリの制御方法 |
| JP5618582B2 (ja) | 2010-03-17 | 2014-11-05 | キヤノン株式会社 | カメラ本体、調整用工具、交換レンズ、アクセサリ、カメラシステム、通信システム、及びアクセサリの制御方法 |
| JP5578951B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-08 | 2014-08-27 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置及び交換レンズ |
| JP5854623B2 (ja) * | 2010-08-06 | 2016-02-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置及びアクセサリ及び撮像装置システム |
| US8755684B2 (en) | 2011-07-22 | 2014-06-17 | Nikon Corporation | Adapter, camera system, and adapter control program |
| US8814449B2 (en) | 2011-07-22 | 2014-08-26 | Nikon Corporation | Adapter, camera system, and adapter control program |
| JP5418552B2 (ja) * | 2011-07-22 | 2014-02-19 | 株式会社ニコン | アダプター、カメラシステム、および、アダプター制御プログラム |
| JP5894397B2 (ja) * | 2011-08-29 | 2016-03-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ及び撮像システム |
| US8714844B2 (en) | 2011-09-20 | 2014-05-06 | Nikon Corporation | Intermediate adapter, camera accessory, and exchangeable lens |
| GB2511679B (en) * | 2011-12-08 | 2016-06-08 | Canon Kk | Image pickup apparatus, method for controlling the same, and program |
| JP5693477B2 (ja) | 2012-01-18 | 2015-04-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | 交換レンズおよびカメラシステム |
| JP5994284B2 (ja) | 2012-02-28 | 2016-09-21 | 株式会社ニコン | 電子機器 |
| JP5709802B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-07 | 2015-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、レンズ装置、および撮像装置の制御方法 |
| JP2014071289A (ja) | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-21 | Nikon Corp | 交換レンズ、アダプタ、カメラシステム |
| US10079968B2 (en) | 2012-12-01 | 2018-09-18 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Camera having additional functionality based on connectivity with a host device |
| KR20150030557A (ko) * | 2013-09-12 | 2015-03-20 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 렌즈 교환식 시스템 카메라의 제어방법 및 제어장치 |
| WO2015068485A1 (ja) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-05-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | カメラシステム、カメラ本体及び通信方法 |
| JP6362490B2 (ja) | 2014-09-12 | 2018-07-25 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、外部機器、撮像システム及びその制御方法 |
| JP2016080732A (ja) | 2014-10-09 | 2016-05-16 | キヤノン株式会社 | レンズユニット及びその制御方法、撮像装置及びその制御方法 |
| KR20160049632A (ko) | 2014-10-28 | 2016-05-10 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 렌즈를 인식하는 전자 장치 및 동작 방법 |
| JP6366621B2 (ja) | 2016-02-12 | 2018-08-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | アクセサリ装置およびアクセサリ装置の制御プログラム |
| EP3633450B1 (en) * | 2017-05-31 | 2023-08-16 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Accessory device, camera, and communication control program |
| JP7046709B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-17 | 2022-04-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | アクセサリ装置、これを備えるカメラシステム、およびプログラム |
-
2018
- 2018-05-30 EP EP18809401.5A patent/EP3611564B1/en active Active
- 2018-05-30 JP JP2018102943A patent/JP6427287B1/ja active Active
- 2018-05-30 CN CN202111072235.8A patent/CN113905157A/zh active Pending
- 2018-05-30 CN CN201880035925.6A patent/CN110692013B/zh active Active
- 2018-05-30 WO PCT/JP2018/020769 patent/WO2018221590A1/ja unknown
- 2018-05-30 EP EP24155424.5A patent/EP4354892A3/en active Pending
- 2018-09-21 JP JP2018177267A patent/JP7129292B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-25 US US16/694,326 patent/US11006031B2/en active Active
-
2022
- 2022-08-09 JP JP2022126946A patent/JP7409623B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007148592A (ja) | 2005-11-24 | 2007-06-14 | Funai Electric Co Ltd | データ通信装置 |
| JP2012037692A (ja) * | 2010-08-06 | 2012-02-23 | Canon Inc | カメラシステムの中間アクセサリおよびカメラシステム |
| JP2018102943A (ja) | 2011-01-17 | 2018-07-05 | アクティヴパック, インコーポレイテッド | 無菌カートリッジおよび分配装置 |
| WO2013168742A1 (ja) * | 2012-05-08 | 2013-11-14 | 株式会社ニコン | アクセサリ,カメラボディ |
| JP2016167719A (ja) * | 2015-03-10 | 2016-09-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 光学装置 |
| JP2017041833A (ja) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | 電子機器、その制御方法、および制御プログラム |
| WO2017068912A1 (ja) * | 2015-10-20 | 2017-04-27 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | レンズシステム、アクセサリ、通信方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2017108267A (ja) | 2015-12-09 | 2017-06-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像処理装置、撮像装置、画像処理方法、プログラム、記憶媒体 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020024379A (ja) * | 2018-07-31 | 2020-02-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、アクセサリ、中間アクセサリ及びこれらの制御方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7129292B2 (ja) | 2022-09-01 |
| CN110692013B (zh) | 2021-09-21 |
| CN110692013A (zh) | 2020-01-14 |
| JP6427287B1 (ja) | 2018-11-21 |
| US11006031B2 (en) | 2021-05-11 |
| JP2018205776A (ja) | 2018-12-27 |
| JP7409623B2 (ja) | 2024-01-09 |
| EP3611564B1 (en) | 2024-03-06 |
| CN113905157A (zh) | 2022-01-07 |
| JP2022161950A (ja) | 2022-10-21 |
| EP3611564A4 (en) | 2021-02-24 |
| JP2018205720A (ja) | 2018-12-27 |
| EP4354892A3 (en) | 2024-07-31 |
| US20200092461A1 (en) | 2020-03-19 |
| EP3611564A1 (en) | 2020-02-19 |
| EP4354892A2 (en) | 2024-04-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7409623B2 (ja) | アクセサリ装置、カメラ、通信制御プログラム、およびカメラシステム | |
| JP6427289B1 (ja) | アクセサリ装置、カメラおよび通信制御プログラム | |
| JP6479242B2 (ja) | カメラおよびその通信制御方法 | |
| JP2024019289A (ja) | カメラ、アクセサリ装置。 | |
| JP6427288B1 (ja) | アクセサリ装置、カメラおよび通信制御プログラム | |
| CN110501857B (zh) | 附件装置、具有该附件装置的照相机系统和存储介质 | |
| EP3705939B1 (en) | Camera, accessory device and control method thereof | |
| WO2018221558A1 (ja) | カメラおよびその通信制御方法 | |
| JP2020034740A (ja) | 撮像装置、アクセサリおよびプログラム | |
| JP7171316B2 (ja) | アクセサリ、カメラおよび通信制御プログラム | |
| JP2023177479A (ja) | アクセサリ装置、撮像装置、撮像システム、制御方法、およびプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18809401 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018809401 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20191114 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |