WO2018116504A1 - 多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 - Google Patents
多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018116504A1 WO2018116504A1 PCT/JP2017/023674 JP2017023674W WO2018116504A1 WO 2018116504 A1 WO2018116504 A1 WO 2018116504A1 JP 2017023674 W JP2017023674 W JP 2017023674W WO 2018116504 A1 WO2018116504 A1 WO 2018116504A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- resin layer
- polystyrene
- resin
- layer
- container
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/30—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin comprising vinyl (co)polymers; comprising acrylic (co)polymers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/32—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin comprising polyolefins
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B5/00—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts
- B32B5/18—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by features of a layer of foamed material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D1/00—Containers having bodies formed in one piece, e.g. by casting metallic material, by moulding plastics, by blowing vitreous material, by throwing ceramic material, by moulding pulped fibrous material, by deep-drawing operations performed on sheet material
- B65D1/22—Boxes or like containers with side walls of substantial depth for enclosing contents
- B65D1/26—Thin-walled containers, e.g. formed by deep-drawing operations
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D1/00—Containers having bodies formed in one piece, e.g. by casting metallic material, by moulding plastics, by blowing vitreous material, by throwing ceramic material, by moulding pulped fibrous material, by deep-drawing operations performed on sheet material
- B65D1/22—Boxes or like containers with side walls of substantial depth for enclosing contents
- B65D1/26—Thin-walled containers, e.g. formed by deep-drawing operations
- B65D1/28—Thin-walled containers, e.g. formed by deep-drawing operations formed of laminated material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D1/00—Containers having bodies formed in one piece, e.g. by casting metallic material, by moulding plastics, by blowing vitreous material, by throwing ceramic material, by moulding pulped fibrous material, by deep-drawing operations performed on sheet material
- B65D1/22—Boxes or like containers with side walls of substantial depth for enclosing contents
- B65D1/26—Thin-walled containers, e.g. formed by deep-drawing operations
- B65D1/30—Groups of containers joined together end-to-end or side-by-side
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D65/00—Wrappers or flexible covers; Packaging materials of special type or form
- B65D65/38—Packaging materials of special type or form
- B65D65/40—Applications of laminates for particular packaging purposes
Definitions
- the present invention is a multilayer sheet having a divided groove in which a polystyrene resin layer and a functional resin layer are bonded via an adhesive resin layer, and the functional resin layer and the adhesive resin layer are cut leaving the polystyrene resin layer.
- a multilayer container obtained by molding the multilayer sheet with a polystyrene resin layer on the outside. This multilayer container is particularly suitable as a food container or a pharmaceutical container.
- Containers with dividing grooves include multiple containers for storing yogurt, tofu, etc. in food, instant noodle containers that tear off the edges and peel off the seal pieces, and coffee milk containers. There are double bags that store liquids and mix them when used.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a tofu container in which a groove for cutting is provided in a connecting portion of two containers.
- polypropylene, polystyrene, polyethylene terephthalate or the like is used for this container.
- the inventors of the present invention have examined a container having a dividing groove such as a multi-container container.
- Polystyrene is easy to break off at the dividing groove part, but the strength is weak in impact strength such as drop strength, and food.
- the strength is weak in impact strength such as drop strength, and food.
- trace amounts of residual styrene monomer, dimer, trimer, etc. may elute and cause health problems.
- the object of the present invention is to solve the problems of these polystyrenes, and to provide a multilayer sheet that is easy to break off at the dividing groove portion but has high impact resistance and no health problems, and a multilayer container using the same. It is to provide.
- the present inventors considered to laminate a functional resin layer on a polystyrene resin layer via an adhesive resin layer in order to solve the above-described problems and enhance the functions required according to the application. And, by dividing the adhesive resin layer from the functional resin layer to reach the polystyrene resin layer by dividing the groove, problems such as easy division, impact resistance of the container, elution of styrene monomer, oligomer, etc. The inventors have found that all can be solved, and have completed the present invention.
- the polystyrene resin layer containing polystyrene as a main component is used as one surface
- the functional resin layer containing a functional resin as a main component is used as the other surface
- the polystyrene resin layer and the functional resin layer are bonded.
- a multilayer sheet bonded through a resin layer, wherein the functional resin layer and the adhesive resin layer are cut and a dividing groove reaching the polystyrene resin layer is provided. .
- the functional resin is polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, polyethylene terephthalate, polyamide, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, polylactic acid, or polybutylene succinate.
- the polystyrene resin is a foamed resin.
- the polystyrene resin layer is composed of three layers of an unfoamed resin layer / foamed resin layer / unfoamed resin layer.
- the adhesive resin is a modified polyolefin in which an unsaturated dicarboxylic acid is grafted to the polyolefin.
- an adhesive resin is extruded from a T die, a polystyrene resin sheet is fed out from one side directly below the T die, and a functional resin film is fed out from the opposite side, and polystyrene is passed through the adhesive resin layer.
- a resin sheet and a functional resin film are laminated, and a dividing groove reaching the polystyrene resin sheet by cutting the functional resin film and the adhesive resin layer is provided.
- a coextruded film comprising an adhesive resin layer and a functional resin layer is prepared, and a polystyrene resin is extruded and laminated on the adhesive resin layer side, and the functional resin layer and The adhesive resin layer is cut to provide a dividing groove reaching the polystyrene resin layer.
- a multi-layer container for foods or medicines formed from a multi-layer sheet.
- the multi-layer container has a flange portion and a dividing groove is provided in the flange portion.
- a multilayer container that is a container for storing dairy products.
- the split groove portion is easy to break off but strong in impact strength
- the polystyrene resin layer is a layer that does not come into contact with the contents.
- a sheet and a multilayer container using the sheet can be provided.
- the multilayer sheet of the present invention supplements the impact strength of the polystyrene resin with an adhesive resin and a functional resin, so the polystyrene sheet can be made significantly thinner, reducing costs and saving resources compared to the case of a single polystyrene resin. Can be achieved.
- the heat insulation can be enhanced.
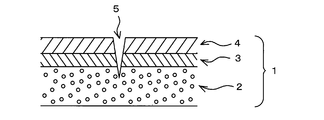
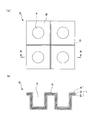
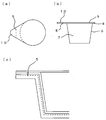
- FIG. 1 It is a fragmentary sectional view of an example in which the division groove part of the multilayer sheet of the present invention entered. It is the figure which showed typically the quadruple container of yogurt which is an example of the multilayer container of this invention, (a) is a top view, (b) is the sectional view on the AA line. It is a figure which shows the milk container for coffee which is another example of the multilayer container of this invention, (a) is a top view, (b) is a side view, (c) is the partial expanded sectional view. It is the figure which showed the simple method of a press-cutting in the 4 series yoghurt cup which is another example of the multilayer container of this invention.
- the multilayer sheet of the present invention comprises a polystyrene resin layer, a functional resin layer, and an adhesive resin layer that adheres both.
- the polystyrene resin layer is a layer mainly composed of polystyrene.
- Polystyrene is called general purpose polystyrene called GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), and HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene), which is made by adding a rubber latex such as polybutadiene during the polymerization of styrene monomers to improve impact resistance.
- GPPS General Purpose Polystyrene
- HIPS High Impact Polystyrene
- MIPS High Impact Polystyrene
- MIPS High Impact Polystyrene
- other components can be blended depending on the application and the like, and the polystyrene content is 70 to 100% by mass, preferably 90 to 100% by mass.
- the MFR is desirably about 1 to 12 g / 10 minutes, preferably about 2 to 10 g / 10 minutes. If it is less than 1 g / 10 minutes, the viscosity is too high during melt extrusion. On the other hand, if it exceeds 12 g / 10 minutes, the neck-in becomes large and the film surface is not stable.
- the foaming method is a physical method of foaming by adding a gas such as carbon dioxide or butane or a volatile liquid such as ether or hexane, or by thermally decomposing a carbonate such as ammonium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate or an azo compound.
- a gas such as carbon dioxide or butane or a volatile liquid such as ether or hexane
- thermally decomposing a carbonate such as ammonium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate or an azo compound.
- a physical method using an inert gas such as carbon dioxide gas or nitrogen gas is particularly preferable for food and pharmaceutical containers because there is no problem such as toxicity.
- the expansion ratio is suitably about 1.1 to 3 times, particularly about 1.4 to 2.5 times.
- One preferable embodiment in the case of foaming polystyrene is a sandwich structure in which unfoamed layers are arranged on both sides of the foamed layer.
- the thickness of the polystyrene resin layer is about 200 to 1000 ⁇ m, particularly about 500 to 700 ⁇ m for the non-foamed layer, and about 300 to 1500 ⁇ m, especially about 400 to 800 ⁇ m for the foamed layer. If the thickness is less than 200 ⁇ m for the non-foamed layer and less than 300 ⁇ m for the foamed layer, the rigidity becomes insufficient. On the other hand, if the thickness exceeds 1000 ⁇ m for the non-foamed layer and 1500 ⁇ m for the foamed layer, the container already satisfies the required performance. Since it becomes too heavy, it is not preferable.
- the unfoamed layer thickness on both sides is about 100 to 500 ⁇ m
- the foamed layer is about 300 to 1500 ⁇ m
- the total of the three layers is about 500 to 2500 ⁇ m.
- the adhesive resin layer is a layer that bonds the polystyrene resin layer and the functional resin layer, and a resin that can bond both layers is used.
- a resin having such a function there are a modified polyolefin in which an unsaturated dicarboxylic acid anhydride is graft-bonded to a polyolefin, and an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer.
- the unsaturated dicarboxylic acid anhydride used in the modified polyolefin include maleic anhydride, phthalic anhydride, itaconic anhydride, citraconic anhydride, mesaconic anhydride, and fumaric anhydride.
- maleic anhydride and phthalic anhydride which are commonly used from the viewpoint of easy handling and heat resistance, are preferred.
- Polypropylene and polyethylene are commonly used as examples of polyolefin. These modified polyolefins are commercially available and can be used.
- a copolymer of ethylene or propylene can be added to the modified polyolefin.
- the ethylene or propylene copolymer is preferably soft, for example, an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, an ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer, an ethylene-acrylic acid alkyl ester copolymer (alkyl is about C 1-6 ).
- alkyl is about C 1-6 .
- ethylene copolymer rubber for example, ethylene-propylene rubber, ethylene-propylene-diene copolymer rubber, etc.
- the addition of these is particularly preferable because the adhesiveness can be improved when the functional resin is polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer or the like.
- the blending ratio with the modified polyolefin is preferably 2 to 100% by mass, preferably 5 to 80% by mass, and about 98 to 0% by mass, preferably 95 to 20% by mass, of ethylene or propylene copolymer. .
- the modified polyolefin is less than 2% by mass, particularly, the adhesive force with the polystyrene resin layer becomes insufficient.
- resins and additives can be blended in the adhesive resin layer, such as hydrogenated styrene / butadiene / block copolymer, alicyclic saturated hydrocarbon resin, and epoxy having two or more epoxy groups in the molecule. Addition of a compound or the like is preferable because it improves the adhesion to the polystyrene resin layer.
- the epoxy compound having two or more epoxy groups in the molecule include epoxidized soybean oil and epoxidized linseed oil. Resins and additives exemplified above are commercially available and can be used.
- the blending ratio is preferably about 2 to 10% by mass, preferably about 4 to 8% by mass of the hydrogenated styrene / butadiene block copolymer, and alicyclic saturated.
- the hydrocarbon resin is an epoxy compound having 0.5 to 10 parts by weight, preferably 1 to 5 parts by weight, and two or more epoxy groups based on 100 parts by weight of a mixed resin of a modified polyolefin and ethylene homopolymer or copolymer. Is from 0.05 to 5 parts by weight, preferably from 0.5 to 2 parts by weight, based on 100 parts by weight of the mixed resin.
- the thickness of the adhesive resin layer is suitably about 10 to 100 ⁇ m, particularly about 30 to 60 ⁇ m.
- the functional resin layer together with the adhesive resin layer, compensates for the weak impact strength of the polystyrene resin layer.
- Polyethylene is not only toxic and highly safe, it is easy to heat-seal, has excellent cold resistance, but also has excellent thermal stability and easy molding, and is widely used as a packaging resin.
- the polyethylene includes low density polyethylene, high density polyethylene, linear low density polyethylene, and the like, and is selected from these depending on required physical properties. As physical properties, those having an MFR of about 0.1 to 8 g / 10 min, preferably about 0.5 to 3 g / 10 min are desirable.
- the above polyethylene resin is used for the standards specified in “Ministerial Ordinance on Component Standards of Milk and Dairy Products (December 27, 1951, Ministry of Health and Welfare Ordinance No. 52)” and “Packaging or containers of food during cooking” It is preferable in terms of food safety that it conforms to the polyethylene standard for products (FDA CFR21 ⁇ 177.1520 (c) 2.2).
- the polyethylene resin that meets such criteria include an additive-free polyethylene resin, that is, a polyethylene that does not contain a resin additive.
- the multilayer container according to the present invention which is a molded product of the multilayer sheet according to the present invention, can contain dairy products that meet the above criteria. is there.
- the layer thickness is about 20 to 250 ⁇ m, particularly about 50 to 150 ⁇ m.
- Polypropylene is often used when heat resistance is required.
- Polypropylene includes, in addition to homopolypropylene, copolymers of propylene and ethylene, which are called random polypropylene, block polypropylene, and the like, and are selected from these according to required physical properties.
- As physical properties those having an MFR of about 0.4 to 12 g / 10 min, preferably about 3 to 8 g / 10 min are desirable.
- the appropriate layer thickness is about 20 to 200 ⁇ m, particularly about 50 to 150 ⁇ m.
- An ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer is widely used as a general packaging resin because it has excellent flexibility and low-temperature properties as well as excellent moldability.
- As physical properties those having an MFR of about 0.5 to 8 g / 10 min, preferably about 1 to 4 g / 10 min are desirable.
- Polyethylene terephthalate is excellent in gas barrier properties and non-adsorptive properties, and recently, a film imparted with heat sealability has been developed, and its uses are widespread.
- This physical property value is generally expressed as an IV value (intrinsic viscosity) and is about 0.5 to 0.9 dl / g, preferably about 0.6 to 0.8 dl / g.
- Polyamide is not only excellent in strength properties such as puncture resistance, but also excellent in chemical resistance and oil resistance, and is widely used as a film for functional packaging materials.
- the polyamide is typically nylon, such as 6-nylon and 66-nylon, and is selected from these depending on the required physical properties.
- the ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer has excellent gas barrier properties and chemical resistance and is used as a functional packaging film.
- the functional resin layer of the present invention is a layer mainly composed of the above functional resin, and can contain other resins and the like as long as the required function is satisfied.
- the total thickness of the multilayer sheet of the present invention is about 230 to 1350 ⁇ m, usually about 600 to 800 ⁇ m when polystyrene is a non-foamed layer, and about 330 to 1850 ⁇ m, usually about 600 to 1000 ⁇ m is appropriate for a foamed layer. .
- the thickness ratio of each layer is about 36 to 98% polystyrene resin layer, about 1 to 31% adhesive resin layer, and about 1 to 54% functional resin layer.
- the method of forming the multilayer sheet is not particularly limited, but the adhesive resin is extruded with a T-die, the polystyrene resin sheet is drawn out from one side immediately below the T-die, and the functional resin film is drawn out from the other side and passed through a pressure-bonding roll and laminated.
- the crimping temperature is preferably 180 to 250 ° C. in order to ensure adhesion.
- the multi-layer sheet of the present invention is provided with a dividing groove, which is divided into individual containers when formed into multiple containers, for example, and when formed into a coffee milk container or the like, the tab piece is broken off. This is for peeling the cover sheet. Therefore, the position of the dividing groove is provided at the connecting portion between the individual containers in the case of multiple containers, and in the tab portion in the case of a milk container for coffee or instant noodle containers. As a rule, the dividing groove is provided over the entire length of the dividing part, and the depth of the groove is provided so that the functional resin layer and the adhesive resin layer are completely cut to reach the polystyrene resin layer. .
- the dividing groove needs to have a strength capable of maintaining the state in which both sides of the groove are connected before dividing. For this reason, both the case where the polystyrene resin layer is a non-foamed layer and a foamed layer are about 1 to 150 ⁇ m, particularly 5 It is preferable that the groove depth is about 100 ⁇ m.
- This dividing groove needs to cut the functional resin layer and the adhesive resin layer to reach the polystyrene resin layer, and the groove depth in the polystyrene resin layer of the dividing groove is 0.1 of the total thickness of the polystyrene resin layer. About 75%, preferably about 0.3-50%.
- the sectional shape of the dividing groove is usually V-shaped so that it can be easily broken.
- the multilayer sheet 1 of the present invention has a polystyrene resin layer 2 (this layer is a foamed layer), an adhesive resin layer 3 and a functional resin layer 4 laminated in this order.
- the dividing groove 5 is provided so as to cut the adhesive resin layer 3 from the functional resin layer 4 side to reach the polystyrene resin layer 2.
- This dividing groove is usually a straight line, but may be a dotted line or a broken line with a part thereof cut completely, or may be a curved line or a jagged broken line.
- the method for providing the dividing groove in the present invention is not particularly limited, but a press cutting blade corresponding to the dividing position is generally used, and the blade used for the cutting groove is also used for a punching die of a thermoformed product.
- a material used for the Thomson blade Swedish steel which is a high-tensile steel plate is preferable.
- the time for providing the dividing groove may be before or after the container is formed, but usually the container is formed first.
- FIG. 4 shows an example of a method for forming the divided grooves. This is an example in which four yogurt cups are provided, and a dividing groove is provided at a set depth by lowering a V-shaped Thomson blade attached in a cross shape on the lower surface of the blade fixing plate by a predetermined distance.
- the shape of the container can vary depending on the application, but the multilayer container of the present invention usually has a flange portion in addition to the chamber for containing the packaged object, and the dividing groove is usually provided in this flange portion. It is done.
- the multilayer container is generally cup-shaped or tray-shaped, and typical examples of the multilayer container of the present invention include a multi-layer container and a portion pack.
- a multi-container is a container in which individual containers are connected via a flange portion or the like, and there are also some in which a considerable number, for example, 20 or 100 are connected from a double container.
- An example of multiple containers is shown in FIG.
- This container is a quadruple container of yogurt, (a) is a plan view with the cover sheet removed, and (b) is a sectional view taken along the line AA.
- the four containers 6 are composed of a storage chamber 7 having the same shape and a substantially bottomed cylindrical shape and a square flange portion 8 extending in the horizontal direction from the outer edge of the upper end thereof. It is connected to the shape of the rice field through.
- this multiple container includes, in addition to containers for storing yogurt, tofu, etc., a container made of two containers in which matcha pudding and black honey are separated and folded between them.
- a portion pack has a flange portion provided at the upper edge of an individual container, protruding into a tab portion, and provided with a dividing groove. The tab portion is opened and the cover sheet bonded thereto is pulled up to open.
- FIG. This container is a milk container for coffee, (a) is a plan view thereof, (b) is a side view, and (c) is a partially enlarged sectional view thereof. As shown in the figure, this container is composed of a tapered frustoconical storage chamber 7 and an annular flange portion 8 extending in the horizontal direction from the outer edge of the upper end thereof, and a tab portion 10 protruding in a substantially triangular shape from one end of the flange portion. Is provided. The tab portion 10 is provided with a dividing groove 5. The upper surface of the container 6 is sealed with a cover sheet 9 bonded thereto.
- This portion pack is used in the food field for instant noodles, milk for coffee, and the like.
- the production method of the multilayer container of the present invention is not particularly limited, but usually vacuum forming or vacuum / pressure forming is used.
- Adhesive Resin A modified polyolefin having an MFR of 1 g / 10 min and a density of 0.91 g / cc in which an unsaturated dicarboxylic acid anhydride was grafted to polypropylene was used.
- EVA Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer
- Molding method (1) Sand extrusion laminating method of adhesive resin Adhesive resin is extruded to a thickness of 50 ⁇ m with a T die, a foamed PS sheet of 600 ⁇ m from one side immediately below the T die, and a low density polyethylene of 100 ⁇ m from the other side. The film is drawn out to form a multilayer sheet.
- the molding equipment used in this case can be any general extrusion laminating machine that has the function of feeding the substrate from both sides directly under the T die. In this case, it has a ⁇ 90 mm extruder. Molded using molding equipment.
- Adhesive resin is extruded 50 ⁇ m with a T-die, and a 600 ⁇ m foam PS sheet is drawn from one side directly below the T-die, and a 25 ⁇ m polyamide film is drawn from the other to produce a multilayer sheet. Mold.
- the molding equipment used in this case can be any general extrusion laminating machine that has the function of feeding the substrate from both sides directly under the T die. In this case, it has a ⁇ 90 mm extruder. Molded using molding equipment.
- Adhesive resin 50 ⁇ m and EVA resin 100 ⁇ m are co-extruded with a T-die (150 ⁇ m), and a 600 ⁇ m foamed PS sheet is formed on the adhesive resin surface side directly under the T-die.
- the multilayer sheet was formed by feeding and welding.
- the molding equipment used in this case can be used as long as it is a general extrusion laminating machine having the function of feeding the substrate from one side directly under the T die, and in this case, two ⁇ 90 mm extruders are used. Molded using a coextrusion molding facility.
- Adhesive resin 50 ⁇ m and polyethylene terephthalate resin 60 ⁇ m are co-extruded with a T-die (110 ⁇ m), and a 600 ⁇ m foamed PS sheet directly on the adhesive resin surface side immediately below the T-die Were fed out and welded to form a multilayer sheet.
- the molding equipment used in this case can be used as long as it is a general extrusion laminating machine having the function of feeding the substrate from one side directly under the T die, and in this case, two ⁇ 90 mm extruders are used. Molded using a coextrusion molding facility.
- Multilayer molding method in which a multilayer film of adhesive resin and polyethylene resin is welded to PS extrusion resin PS foam resin is extruded to a thickness of 600 ⁇ m with a T die, and an adhesive resin layer of 50 ⁇ m from one side directly below the T die And a co-extruded film composed of a low-density polyethylene resin layer of 100 ⁇ m is drawn out so that the adhesive resin comes to the PS surface, and a multilayer sheet is formed.
- the molding equipment used in this case can be used as long as it is a general extrusion laminating machine having a function of feeding the substrate from one side directly under the T die. In this case, a ⁇ 90 mm extruder is used. Molded.
- the functional resin surface of the multilayer sheet is arranged and fixed in correspondence with the blade mold surface.
- the Thomson blade which is fixed to the corresponding blade mold surface and designed in a cut shape, is lowered onto the functional resin surface to form the dividing groove.
- channel formed here was set so that an adhesive resin layer might be cut
- Multi-layer sheets having various configurations were manufactured by the manufacturing method shown in Table 2.
- the thickness of the polystyrene resin layer (hereinafter also referred to as “PS layer”) was 600 ⁇ m
- the thickness of the adhesive resin layer was 50 ⁇ m
- the thickness of the functional resin layer was 100 ⁇ m.
- E indicates that the corresponding resin layer was produced by extrusion molding in the production of the multilayer sheet.
- S indicates that a resin sheet prepared in advance was used as the corresponding resin layer in the production of the multilayer sheet
- “F” represents that the resin layer prepared in advance in the production of the multilayer sheet. It shows that the prepared resin film was used.
- the details of the manufacturing method are as follows.
- “S / E / F” in the “Manufacturing method” column of Table 2 is a polystyrene resin sheet made of a mixture having the composition shown in the “PS layer (foamed layer)” column of Table 2 by a laminating machine according to the sandwich lamination method. (Thickness: 600 ⁇ m) and the resin film (thickness: 100 ⁇ m) shown in the column “PE layer” (shown as “PE layer” because the functional resin is only polyethylene) in Table 2, respectively, While dripping the melt of the resin composition having the composition shown in the column of “Adhesive resin layer” in Table 2, it was heat bonded at 200 ° C. to produce the multilayer sheet.
- the polystyrene resin sheet is a foamed sheet obtained by the same physical foaming method as in Examples 1-5.
- E / E / F in the “Manufacturing method” column of Table 2 is a polystyrene resin having the composition shown in the “PS layer (foamed layer)” column of Table 2 and the adhesive property in accordance with a thermal laminating method and a laminating machine.
- the two-layer sheet obtained by co-extrusion of the resin composition at 260 ° C. and 200 ° C., respectively, and the polyethylene resin film were heat-bonded at 200 ° C. to cool and fix the multilayer sheet.
- the polystyrene resin composition was foamed by a conventional physical foaming method.
- “S / E / E” in the “Manufacturing method” column of Table 2 is a laminating machine according to the thermal laminating method, and the adhesive resin composition and the polyethylene resin having the composition shown in the “PE layer” column of Table 2 are The multilayer sheet was manufactured by thermally bonding the polystyrene resin sheet at 200 ° C. to the adhesive resin composition side of the two-layer sheet obtained by coextrusion at 200 ° C. in both cases.
- E / E / E in the “Manufacturing method” column of Table 2 is obtained by coextruding the polystyrene resin, the adhesive resin composition, and the polyethylene resin at 260 ° C., 200 ° C., and 200 ° C., respectively.
- the multilayer sheet was manufactured by forming a laminate in which the PS layer and the PE layer were bonded via an adhesive resin layer.
- the polystyrene resin composition was foamed by a conventional physical foaming method.
- the obtained multilayer sheet was formed by a vacuum / pressure forming machine (FLC-415PCS, manufactured by Asano Laboratories), and the multilayer container schematically shown in FIG. 2 (a) and FIG.
- a multi-layered multi-layer container provided with dividing grooves in the shape was produced.
- channel corresponds to the groove part 5 in Fig.2 (a) and FIG.2 (b).
- a force was applied to the dividing groove of the obtained multilayer container to test whether the container could be divided along the dividing groove.
- the fracture splitting property was evaluated according to the following five criteria. The results are shown in Table 2. 5: Splitting was possible with relatively weak force. 4: Splitting was possible with a relatively intermediate force. 3: Splitting was possible with relatively strong force. 2: The multilayer sheet could be deformed along the engraved line, but could not be divided. 1: When the applied force was removed, the shape of the multilayer sheet returned to its original shape and could not be divided.
- the depth of the dividing groove” in Table 2 corresponds to the depth of the groove 5.
- the dividing groove penetrates the functional resin layer 4 and the adhesive resin layer 3 which are polyethylene resin layers, and reaches the position of the depth of the polystyrene resin layer of 10 ⁇ m.
- the depth of the dividing groove is 80 ⁇ m, the dividing groove is only provided in a part of the polyethylene resin layer 4 and does not penetrate either the polyethylene resin layer 4 or the adhesive resin layer 3. .
- the depth of the dividing groove is 120 ⁇ m, the dividing groove penetrates the polyethylene resin layer 4 and is provided in a part of the adhesive resin layer 3, but penetrates the adhesive resin layer 3. No.
- the depth of the dividing groove is 0 ⁇ m, no dividing groove is provided.
- the multilayer sheet of the present invention has a polystyrene resin layer as an outer layer when used in a container, so that the leakage of a trace amount of styrene monomer or oligomer contained therein does not affect the package, and breakage is caused.
- a polystyrene resin layer as an outer layer when used in a container, so that the leakage of a trace amount of styrene monomer or oligomer contained therein does not affect the package, and breakage is caused.
- it since it has high strength and excellent splitting ability from the split groove, it can be widely used for multiple containers, potion packs, etc., and is particularly suitable for food and pharmaceutical packaging containers.
Abstract
分割溝部で折取りが容易でありながら、落下強度等における耐衝撃性のある、健康上の問題もない多層シートとそれを用いた多層容器を提供することにある。 上記課題は、ポリスチレンを主成分とするポリスチレン樹脂層を一方の面とし、機能性樹脂を主成分とする機能性樹脂層を他方の面とし、該ポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層が接着性樹脂層を介して接着されている多層シートであって、該機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層が切断された分割溝がポリスチレン樹脂層内に達する様に設けられている多層シートとそれを用いた容器によって解決される。
Description
本発明は、ポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層が接着性樹脂層を介して接着されており、ポリスチレン樹脂層を残して機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層が切断された分割溝を有する多層シートと、該多層シートをポリスチレン樹脂層を外側にして成形した多層容器に関するものである。この多層容器は、特に食品容器、医薬品容器として適する。
食品や医薬品の容器には、その安全性の観点からポリエチレンやポリプロピレンが多用され、最近ではポリエチレンテレフタレートも多用するようになっている。分割溝のある容器は、食品では、ヨーグルトや豆腐等を小分けして収納した多連容器や、端部を折り取ってシール片を剥がす即席麺容器やコーヒー用ミルク容器などがあり、医薬品では2液を収納し使用時に混合するダブルバッグなどがある。
例えば特許文献1には2個の容器の連結部に切取用の溝を設けた豆腐容器が開示されている。この容器には、通常ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリエチレンテレフタレートなどが使用されるとしている。
本発明者らは、多連容器などの分割溝のある容器について検討したところ、ポリスチレンは分割溝部で折取りが容易な反面、強度面では落下強度の様な耐衝撃強度に弱く、また、食品や医薬品容器に使用した場合には、残存している微量のスチレンモノマー、ダイマー、トリマー等が溶出して健康上の問題を惹き起こすおそれがあることも知られている。
本発明の目的は、これらのポリスチレンの問題点を解決して、分割溝部で折取りが容易でありながら、耐衝撃性に強く、健康上の問題もない多層シートとそれを用いた多層容器を提供することにある。
本発明者らは、上記問題点を解決するとともに用途等に応じて要求される機能を高めるために、ポリスチレン樹脂層に接着性樹脂層を介して機能性樹脂層を積層することを考えた。そして、分割溝を機能性樹脂層から接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層内に達するように設けることにより、易分割性、容器の耐衝撃性、スチレンモノマー、オリゴマーの溶出等の問題を全て解決できることを見出し、本発明を完成するに至った。
こうして、本発明は、ポリスチレンを主成分とするポリスチレン樹脂層を一方の面とし、機能性樹脂を主成分をする機能性樹脂層を他方の面とし、該ポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層が接着樹脂層を介して接着されている多層シートであって、該機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層が切断されてポリスチレン樹脂層内に達する分割溝が設けられている多層シートを提供するものである。
本発明の一態様においては、機能性樹脂がポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリアミド、エチレンビニルアルコール共重合体、ポリ乳酸又はポリブチレンサクシネートである。
本発明の別の態様においては、ポリスチレン樹脂が発泡樹脂である。
本発明の別の態様においては、ポリスチレン樹脂層が未発泡樹脂層/発泡樹脂層/未発泡樹脂層の3層よりなっている。
本発明の別の態様においては、接着性樹脂が、不飽和ジカルボン酸がポリオレフィンにグラフト結合している変性ポリオレフィンである。
本発明の別の態様においては、接着性樹脂をTダイから押出し、そのTダイ真下の片側よりポリスチレン樹脂シート、反対側からは機能性樹脂フィルムを繰出して、該接着性樹脂層を介してポリスチレン樹脂シートと機能性樹脂フィルムを積層し、これに該機能性樹脂フィルムと接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂シートに達する分割溝を設けてなる。
本発明の別の態様においては、接着性樹脂層と機能性樹脂層よりなる共押出フィルムを作製し、その接着性樹脂層側にポリスチレン樹脂を押出して積層し、これに該機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達する分割溝を設けてなる。
本発明の別の態様においては、多層シートで成形されている食品又は医薬品の多層容器である。
本発明の別の態様においては、フランジ部を有し、分割溝がフランジ部に設けられている多層容器である。
本発明の別の態様においては、乳製品を収容する容器である多層容器である。
本発明により、分割溝部で折取りが容易でありながら耐衝撃強度に強く、また、ポリスチレン樹脂層を内容物と接触しない層としているので、食品や医薬品に用いても健康上の問題のない多層シートとそれを用いた多層容器を提供することができる。本発明の多層シートはポリスチレン樹脂の耐衝撃強度を接着性樹脂と機能性樹脂で補っているのでポリスチレンシートを大幅に薄くすることができ、ポリスチレン樹脂単体の場合に比べて、コストダウンと省資源を達成できる。
さらにポリスチレン樹脂層を発泡層とした場合は、断熱性も高めることができる。
本発明の多層シートは、ポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層とこの両方を接着させる接着性樹脂層よりなる。
ポリスチレン樹脂層はポリスチレンを主成分とする層である。ポリスチレンにはGPPS(General Purpose Polystyrene)と称される一般用ポリスチレンと、スチレンモノマーの重合の際にポリブタジエンなどのゴムラテックスを添加して耐衝撃性を高めたHIPS(High Impact Polystyrene)と称される耐衝撃性ポリスチレンがあり、この両者をブレンドしたMIPSと称されるその中間の性質のものもあるが、そのいずれも使用することができる。このポリスチレン樹脂層には、用途等に応じてその他の成分を配合することができ、ポリスチレンの含有量は70~100質量%、好ましくは90~100質量%である。その他の成分としては、他の樹脂や添加剤、色素などを挙げることができる。物性面では、MFRは1~12g/10分程度、好ましくは2~10g/10分程度のものが望ましい。1g/10分未満では、溶融押出しの際に粘性が大きすぎ、一方、12g/10分を越えるとネックインが大きくなる外、膜面も安定せず好ましくない。
ポリスチレンは発泡させることによって、断熱性、保温性を高めることができる。さらに、使用樹脂を節減して、軽量化、製造コスト削減、廃棄時の燃焼負荷低減等のメリットも得られる。発泡方法は、炭酸ガスやブタンのような気体あるいはエーテルやヘキサンなどの揮発性液体を添加して発泡させる物理的方法、炭酸アンモニウムや炭酸水素ナトリウム等の炭酸塩とかアゾ化合物などを加熱分解してガスを発生させたり、炭酸塩にクエン酸等を加えて炭酸ガスを発生する化学的方法があり、そのいずれも利用することができる。これらのなかで、炭酸ガスや窒素ガスなどの不活性ガスを用いた物理的方法は毒性等の問題がないので食品や医薬品の容器には特に好ましい。発泡倍率は1.1~3倍程度、特に1.4~2.5倍程度が適当である。ポリスチレンを発泡させる場合の一つの好ましい態様は、発泡層の両側に未発泡層を配置したサンドイッチ構造とすることである。
ポリスチレン樹脂層の厚みは非発泡層の場合は200~1000μm程度、特に500~700μm程度であり、発泡層の場合は300~1500μm程度、特に400~800μm程度が適当である。厚みが非発泡層で200μm未満、発泡層で300μm未満になると剛性が不十分になり、一方、非発泡層で1000μm、発泡層で1500μmを越えると容器が既に要求性能を満足している上に重くなりすぎるので好ましくない。上記の三層構造の場合は、両側の未発泡層の厚みがそれぞれ100~500μm程度、発泡層が300~1500μm程度、3層合わせて500~2500μm程度が適当である。
接着性樹脂層はポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層を接着する層であり、両層を接着できる樹脂が用いられる。このような機能を持つ樹脂として不飽和ジカルボン酸無水物がポリオレフィンにグラフト結合している変性ポリオレフィンとエチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体がある。変性ポリオレフィンに用いられる不飽和ジカルボン酸無水物の例としては、無水マレイン酸、無水フタル酸、無水イタコン酸、無水シトラコン酸、無水メサコン酸、無水フマル酸を挙げることができる。その中でもハンドリングのし易さ、耐熱性等の観点から常用されている無水マレイン酸、無水フタル酸が好ましい。ポリオレフィンの例としては、ポリプロピレンやポリエチレンが常用されている。これらの変性ポリオレフィンは市販品があり、それを用いることができる。
接着性樹脂層には、変性ポリオレフィンにエチレンあるいはプロピレンの共重合体を加えることができる。エチレンあるいはプロピレンの共重合体は軟質のものが好ましく、例えば、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体、エチレン-アクリル酸共重合体、エチレン-アクリル酸アルキルエステル共重合体(アルキルはC1~6程度のもの、例えばメチル、エチル等が好ましい。)、エチレン共重合体ゴム(例えば、エチレン-プロピレンゴム、エチレン-プロピレン-ジエン共重合体ゴム等)などを用いることができる。これらを加えることは、機能性樹脂がポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体等である場合に接着性を改善できる点で特に好ましい。変性ポリオレフィンとの配合割合は、変性ポリオレフィン2~100質量%、好ましくは5~80質量%、エチレンあるいはプロピレンの共重合体98~0質量%程度、好ましくは95~20質量%とすることが好ましい。変性ポリオレフィンが2質量%未満になると、特に、ポリスチレン樹脂層との接着力が不充分になる。
接着性樹脂層には、他の樹脂や添加剤等を配合することができ、水添スチレン・ブタジエン・ブロックコポリマー、脂環族飽和炭化水素樹脂、分子内に2個以上のエポキシ基を有するエポキシ化合物等を加えるとポリスチレン樹脂層との接着性を向上させるので好ましい。分子内に2個以上のエポキシ基を有するエポキシ化合物は、例えば、エポキシ化大豆油、エポキシ化アマニ油などである。上記例示の樹脂や添加剤は市販品があり、それらを利用することができる。ポリスチレン樹脂への接着性向上の観点から好ましい配合率は、水添スチレン・ブタジエン・ブロックコポリマーは、接着性樹脂層の2~10質量%程度、好ましくは4~8質量%程度、脂環族飽和炭化水素樹脂は、変性ポリオレフィンとエチレン単独あるいは共重合体との混合樹脂100質量部に対して0.5~10質量部、好ましくは1~5質量部、2個以上のエポキシ基を有するエポキシ化合物は、混合樹脂100質量部に対して0.05~5質量部、好ましくは0.5~2質量部である。
接着性樹脂層の厚みは10~100μm程度、特に30~60μm程度が適当である。
機能性樹脂層は、接着性樹脂層とともにポリスチレン樹脂層の耐衝撃強度の弱さを補うものであり、容器の用途や要求される物性に応じて、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリアミド、エチレンビニルアルコール共重合体、ポリ乳酸、ポリブチレンサクシネート等から選ばれる。
ポリエチレンは、毒性がなく安全性が高い、ヒートシールしやすい、耐寒性に優れるばかりでなく、熱安定性にも優れ成形加工しやすい等の特徴があり、幅広く包装用樹脂として使用されている。ポリエチレンには、低密度ポリエチレン、高密度ポリエチレン、直鎖状低密度ポリエチレン等があり、要求される物性等によりこれらから選択される。物性値としてはMFRが0.1~8g/10分程度、好ましくは0.5~3g/10分程度のものが望ましい。
上記ポリエチレン樹脂は、「乳及び乳製品の成分規格等に関する省令(昭和26年12月27日厚生省令第52号)」に規定する基準、及び、「調理中の食品の包装又は入れ物に使用する製品用ポリエチレン基準(FDA CFR21 §177.1520(c)2.2)」に適合することが食品安全面では好ましい。このような基準に適合するポリエチレン樹脂としては、例えば、無添加のポリエチレン樹脂、即ち、樹脂添加剤を含まないポリエチレン等が挙げられる。上記ポリエチレン樹脂層中の上記ポリエチレン樹脂が上記基準に適合する場合、本発明に係る多層シートの成形体である本発明に係る多層容器には上記基準に適合した乳製品を収容することが可能である。
機能性樹脂層にポリエチレンを用いた場合の層厚は20~250μm程度、特に50~150μm程度が適当である。
ポリプロピレンは、耐熱性が要求される場合に用いられることが多い。ポリプロピレンには、ホモポリプロピレンの外、ランダムポリプロピレン、ブロックポリプロピレン等と称されるプロピレンとエチレン等との共重合体等があり、要求される物性等によりこれらから選択される。物性値としてはMFRが0.4~12g/10分程度、好ましくは3~8g/10分程度のものが望ましい。
機能性樹脂層にポリプロピレンを用いた場合の層厚は20~200μm程度、特に50~150μm程度が適当である。
エチレン酢酸ビニル共重合体は、柔軟性、低温特性の他、成形加工性にも優れているため幅広く一般包装用樹脂として使用されている。物性値としては、MFRが0.5~8g/10分程度、好ましくは1~4g/10分程度のものが望ましい。
ポリエチレンテレフタレートは、ガスバリア性や非吸着性に優れ、最近ではヒートシール性も付与されたフィルムも開発されて来ており、その用途は広くなっている。この物性値は、一般にIV値(固有粘度)で示され0.5~0.9dl/g程度、好ましくは0.6~0.8dl/g程度のものが望ましい。
ポリアミドは、耐突刺し性等の強度物性に優れる他、耐薬品性や耐油性にも優れ、機能性包材用フィルムとして幅広く使用されている。ポリアミドはナイロンが代表的であり、6-ナイロン、66-ナイロン等があり、要求される物性等によりこれらから選択される。
エチレン-ビニルアルコール共重合体は、ガスバリア性や耐薬品性に優れ、機能性包装用フィルムとして使用されている。
尚、本発明の機能性樹脂層は、上記の機能性樹脂を主成分とする層であって、要求される機能を満足する範囲で他の樹脂等を含むことができる。
本発明の多層シートの全厚は、ポリスチレンが非発泡層の場合は230~1350μm程度、通常600~800μm程度であり、発泡層の場合は330~1850μm程度、通常600~1000μm程度が適当である。各層の厚み比では、ポリスチレン樹脂層36~98%程度、接着性樹脂層1~31%程度、機能性樹脂層1~54%程度である。
多層シートの成形方法は、特に限定されないが、接着性樹脂をTダイで押出し、そのTダイ直下の片側よりポリスチレン樹脂シート、もう一方より機能性樹脂フィルムを繰り出して圧着ロールを通過させて積層するサンドイッチ押出ラミネート法、接着性樹脂と機能性樹脂を共押出してフィルムを成形し、この接着性樹脂層側にポリスチレン樹脂シートを押出成形する方法、接着性樹脂とポリスチレン樹脂を共押出し、この接着性樹脂層側に機能性樹脂フィルムを圧着する方法、ポリスチレン樹脂、接着性樹脂および機能性樹脂を三層共押出しする方法等がある。上記の方法の外、押出されたフィルムを一旦固化後、必要により加熱して他のフィルムと圧着させる方法もある。これらのなかで、接着性樹脂と機能性樹脂を共押出して共押出フィルムを作製し、この接着性樹脂層側にポリスチレン樹脂を押出して積層する方法が、広く使われている既存の設備を利用できる点で有利で最も好ましい。上記いずれの圧着方法においても、圧着温度は180~250℃とするのが接着を確実にするので好ましい。
本発明の多層シートは、分割溝が設けられており、これは、例えば多連容器に成形したときには個々の容器に分割したり、コーヒー用ミルク容器などに成形したときはタブ片を折り取ってカバーシートを剥離するためのものである。従って、分割溝の位置は、多連容器の場合は個々の容器間の連結部に、コーヒー用ミルク容器や即席麺容器などの場合はタブ部に設けられる。分割溝は切り放せるよう、原則として分割部の全長に亘って設けられ、溝の深さは、機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層を完全に切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達するように設けられる。一方、分割溝は、分割する前は溝の両側を連結する状態を維持できる強度が必要であり、そのため、ポリスチレン樹脂層が非発泡層の場合も発泡層の場合も1~150μm程度、特に5~100μm程度の溝深さにすることが好ましい。この分割溝は、機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達するようにする必要があり、分割溝のポリスチレン樹脂層における溝深さはポリスチレン樹脂層全厚の0.1~75%程度、好ましくは0.3~50%程度とするのがよい。分割溝の断面形状は折り取り易いように通常V字形である。すなわち、本発明の多層シート1は、図1に示すように、ポリスチレン樹脂層2(この層は発泡層である。)、接着性樹脂層3および機能性樹脂層4がこの順に積層されており、分割溝5は機能性樹脂層4側から接着性樹脂層3も切断してポリスチレン樹脂層2に達するように設けられている。この分割溝は、通常は直線であるが、一部を完全に切断した点線や破線状にしてもよく、また、曲線やギザギザ状の折れ線にしてもよい。
本発明における分割溝を設ける方法は、特に限定するものではないが、分割位置に対応した押切刃が用いられるのが一般的で、それに用いられる刃は熱成型品の打抜き型でも用いられているトムソン刃で、それに用いられる材質としては、高張力鋼板であるスェーデン鋼が好ましい。分割溝を設ける時期は容器を成形する前であっても後であってもよいが、通常は容器の成形が先である。
この分割溝を形成する方法の一例を図4に示す。これは、4連のヨーグルトカップに設ける例であり、刃固定盤の下面に十字形に取り付けた断面V字形のトムソン刃を所定の距離下降させて設定深さで分割溝を設けている。
容器の形状は用途に応じて種々とりうるが、本発明の多層容器は、被包装物を収容する室に加えて、通常はフランジ部を有しており、分割溝は通常このフランジ部に設けられる。多層容器は、一般にカップ形やトレー形をしており、本発明の多層容器の典型例として多連容器とポーションパックがある。
多連容器は、個々の容器がフランジ部等を介して連結されたものであり、2連容器からかなり多くの数、例えば20個とか100個が連結されたものもある。多連容器の例を図2に示す。この容器はヨーグルトの4連容器であり、(a)はそのカバーシートを外した状態の平面図、(b)はそのA-A線断面図である。同図に示すように、4個の容器6は同形で略有底円筒状の収容室7とその上端外縁から水平方向に延びる正方形のフランジ部8からなり、4個の容器6はフランジ部8を介して田の字形に連結されている。そして、その連結部に分割溝5が設けられ、各容器を折り取ることができるようになっている。各容器は収容室7が深絞りされて形成されているので薄肉になっており、当初の多層シートの厚みが残っているのはフランジ部8のみである。この多連容器は、食品分野では、ヨーグルト、豆腐などを収容する容器の外、抹茶プリンと黒みつを分室してその間を折り取れるようにした2つの容器からなるものなどがある。
ポーションパックは、個別容器の上縁に設けられたフランジ部の一部が突出してタブ部となり、そこに分割溝が設けられているものである。このタブ部を折り取ってそこに接着されているカバーシートを引き上げることにより開口する。このポーションパックの例を図3に示す。この容器はコーヒー用ミルク容器であり、(a)はその平面図、(b)は側面図、(c)はその部分拡大断面図である。同図に示すように、この容器は先細円錐台形の収容室7とその上端外縁から水平方向に延びる円環状のフランジ部8からなり、該フランジ部の一端から略三角形に突出するタブ部10が設けられている。そして、タブ部10には分割溝5が設けられている。容器6の上面はカバーシート9が接着されて封止されている。このポーションパックは食品分野では、即席麺、コーヒー用ミルクなどで使用されている。
医薬品分野でも、2液を収納し使用時に混合するダブルバックなどで使用されている。
本発明の多層容器の製法は特に制限されないが、通常は真空成形や真空圧空成形が利用される。
[実施例1~5]
使用樹脂
ポリスチレン
MFR9g/10分、密度1.04g/ccの一般用ポリスチレン(GPPS)70質量%とMFR2.7g/10分、密度1.04g/ccの耐衝撃性ポリスチレン30質量%の混合樹脂を使用した。発泡ポリスチレンは、この混合樹脂にN2ガスを0.25kg/hの割合で注入し、発泡倍率を1.6倍としたものを用いた。
使用樹脂
ポリスチレン
MFR9g/10分、密度1.04g/ccの一般用ポリスチレン(GPPS)70質量%とMFR2.7g/10分、密度1.04g/ccの耐衝撃性ポリスチレン30質量%の混合樹脂を使用した。発泡ポリスチレンは、この混合樹脂にN2ガスを0.25kg/hの割合で注入し、発泡倍率を1.6倍としたものを用いた。
接着性樹脂
不飽和ジカルボン酸無水物がポリプロピレンにグラフト結合された、MFR1g/10分、密度0.91g/ccの変性ポリオレフィンを用いた。
不飽和ジカルボン酸無水物がポリプロピレンにグラフト結合された、MFR1g/10分、密度0.91g/ccの変性ポリオレフィンを用いた。
機能性樹脂
下記の樹脂を使用した。
(1)低密度ポリエチレン(LDPE)
MFR2g/10分 密度0.919g/cc
樹脂添加剤が無添加で乳等省令1群適合
下記の樹脂を使用した。
(1)低密度ポリエチレン(LDPE)
MFR2g/10分 密度0.919g/cc
樹脂添加剤が無添加で乳等省令1群適合
(2)エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体(EVA)
MFR2g/10分 酢酸ビニル含有4質量%
MFR2g/10分 酢酸ビニル含有4質量%
(3)ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)
固有粘度0.62dl/g 密度1.34g/cc
固有粘度0.62dl/g 密度1.34g/cc
(4)ポリアミド(NY)
ユニチカ製 エンブレムON
ユニチカ製 エンブレムON
成形方法
(1)接着性樹脂のサンド押出しラミ法
接着性樹脂をTダイで50μmの厚みに押出しし、そのTダイの直下の片側より600μmの発泡PSシートを、もう片方より100μmの低密度ポリエチレンフィルムを繰り出しして多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で両サイドから基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機をもつ成形設備を用いて成形した。
(1)接着性樹脂のサンド押出しラミ法
接着性樹脂をTダイで50μmの厚みに押出しし、そのTダイの直下の片側より600μmの発泡PSシートを、もう片方より100μmの低密度ポリエチレンフィルムを繰り出しして多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で両サイドから基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機をもつ成形設備を用いて成形した。
(2)接着性樹脂のサンド押出しラミ法
接着性樹脂をTダイで50μm押出しし、そのTダイ直下の片側より600μmの発泡PSシートを、もう片方より25μmのポリアミドフィルムを繰り出しして多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で両サイドから基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機をもつ成形設備を用いて成形した。
接着性樹脂をTダイで50μm押出しし、そのTダイ直下の片側より600μmの発泡PSシートを、もう片方より25μmのポリアミドフィルムを繰り出しして多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で両サイドから基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機をもつ成形設備を用いて成形した。
(3)接着性樹脂とEVA樹脂の共押出しラミ法
接着性樹脂50μmとEVA樹脂100μmをTダイで共押出し(150μm)し、そのTダイ直下の接着性樹脂面側に600μmの発泡PSシートを繰り出して溶着させ多層シートを成形した。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機2台をもつ共押出し成形設備を用いて成形した。
接着性樹脂50μmとEVA樹脂100μmをTダイで共押出し(150μm)し、そのTダイ直下の接着性樹脂面側に600μmの発泡PSシートを繰り出して溶着させ多層シートを成形した。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機2台をもつ共押出し成形設備を用いて成形した。
(4)接着性樹脂とポリエチレンテレフタレートの共押出しラミ法
接着性樹脂50μmとポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂60μmをTダイで共押出し(110μm)し、そのTダイ直下の接着性樹脂面側に600μmの発泡PSシートを繰り出して溶着させ多層シートを成形した。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機2台をもつ共押出し成形設備を用いて成形した。
接着性樹脂50μmとポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂60μmをTダイで共押出し(110μm)し、そのTダイ直下の接着性樹脂面側に600μmの発泡PSシートを繰り出して溶着させ多層シートを成形した。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機2台をもつ共押出し成形設備を用いて成形した。
(5)接着性樹脂とポリエチレン樹脂の多層フィルムをPS押出し樹脂に溶着させた多層成形法
PS発泡樹脂をTダイで600μmの厚みに押出しし、そのTダイ直下の片側より50μmの接着性樹脂層と100μmの低密度ポリエチレン樹脂層からなる共押出しフィルムをPS面に接着性樹脂が来るように繰り出して多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機を用いて成形した。
PS発泡樹脂をTダイで600μmの厚みに押出しし、そのTダイ直下の片側より50μmの接着性樹脂層と100μmの低密度ポリエチレン樹脂層からなる共押出しフィルムをPS面に接着性樹脂が来るように繰り出して多層シートを成形する。
この場合用いる成形設備は、Tダイ直下で片側から基材を繰り出すことができる機能を持った一般の押出しラミネート成形機であれば使用することができ、今回の場合、φ90mmの押出機を用いて成形した。
多層シートが容器内面に機能性樹脂層が来るように容器成型された後、多層シートの機能性樹脂面を刃型面に対応させて配置・固定する。
これに対応する刃型面に固定され、カット形状にデザインされたトムソン刃を機能性樹脂面に下ろして分割溝を成形する。
なお、ここで形成された分割溝は、機能性樹脂層から接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達するように設定した。
これに対応する刃型面に固定され、カット形状にデザインされたトムソン刃を機能性樹脂面に下ろして分割溝を成形する。
なお、ここで形成された分割溝は、機能性樹脂層から接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達するように設定した。
得られた結果を表1に示す。
使用樹脂
ポリスチレン
PS1:GPPS(MFR9g/10分、密度1040kg/m3)
PS2:HIPS(MFR2.7g/10分、密度1040kg/m3)
接着性樹脂
AD1:無水マレイン酸グラフトポリエチレン(MFR6g/10分、密度900kg/m3)
AD2:無水マレイン酸グラフトポリプロピレン(MFR3.5g/10分、密度900kg/m3)
LD:低密度ポリエチレン(MFR2.0g/10分、密度919kg/m3)
EVA:エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体(酢酸ビニル含有量4.0質量%、MFR2.0g/10分)
SEBS:水添スチレンブタジエンブロックコポリマー(スチレン含有量65質量%)
PR:脂環族飽和炭化水素樹脂(軟化点100℃)
ESO:エポキシ化大豆油
機能性樹脂
LD1:低密度ポリエチレン(MFR2.0g/10分、密度919kg/m3、樹脂添加剤が添加済)
LD2:低密度ポリエチレン(MFR2.0g/10分、密度919kg/m3、樹脂添加剤が無添加で乳等省令に適合)
成形方法
表2に示す製造方法により、各種構成の多層シートを製造した。得られた多層シートにおいて、ポリスチレン樹脂層(以下、「PS層」ともいう。)の厚みは600μm、接着性樹脂層の厚みは50μm、機能性樹脂層の厚みは100μmであった。なお、表2の「製造方法」欄において、「E」は、多層
シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層を押出成形により作製したことを示し、
「S」は、多層シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層として、予め作製しておいた樹脂シートを用いたことを示し、「F」は、多層シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層として、予め作製しておいた樹脂フィルムを用いたことを示す。製造方法の詳細は以下の通りである。
シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層を押出成形により作製したことを示し、
「S」は、多層シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層として、予め作製しておいた樹脂シートを用いたことを示し、「F」は、多層シートの製造において、該当する樹脂層として、予め作製しておいた樹脂フィルムを用いたことを示す。製造方法の詳細は以下の通りである。
表2の「製造方法」欄における「S/E/F」は、サンドイッチラミネート法に従い、ラミネート機で、表2の「PS層(発泡層)」欄に示す組成を有する混合物からなるポリスチレン樹脂シート(厚み:600μm)と、表2の「PE層」(機能性樹脂がポリエチレンのみなので「PE層」と表記した。)欄に示す樹脂フィルム(厚み:100μm)とを各々繰り出し、その層間に、表2の「接着性樹脂層」欄に示す組成を有する樹脂組成物の溶融物を垂下しながら、200℃で熱貼合して、上記多層シートを製造した。なお、上記ポリスチレン樹脂シートは、実施例1~5と同じ物理発泡法により得た発泡シートである。
表2の「製造方法」欄における「E/E/F」は、サーマルラミネート法に従い、ラミネート機で、表2の「PS層(発泡層)」欄に示す組成を有するポリスチレン樹脂及び上記接着性樹脂組成物を、それぞれ260℃及び200℃で共押出して得られた2層シートと、上記ポリエチレン樹脂フィルムとを200℃で熱貼合して冷却固定することで、上記多層シートを製造した。なお、上記共押出の際、常法の物理発泡法により、上記ポリスチレン樹脂組成物を発泡させた。
表2の「製造方法」欄における「S/E/E」は、サーマルラミネート法に従い、ラミネート機で、上記接着性樹脂組成物及び表2の「PE層」欄に示す組成を有するポリエチレン樹脂をいずれも200℃で共押出して得られた2層シートの上記接着性樹脂組成物側に、上記ポリスチレン樹脂シートを200℃で熱貼合して冷却固定することで、上記多層シートを製造した。
表2の「製造方法」欄における「E/E/E」は、上記ポリスチレン樹脂、上記接着性樹脂組成物、及び上記ポリエチレン樹脂を、それぞれ260℃、200℃、及び200℃で共押出して、PS層及びPE層が接着性樹脂層を介して接着している積層体を形成することで、上記多層シートを製造した。なお、上記共押出の際、常法の物理発泡法により、上記ポリスチレン樹脂組成物を発泡させた。
<多層間の接着性の評価>
作製した多層シートの接着強度をJIS Z 1707に準じて測定した。以下の基準に従って、測定後における多層間の接着性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
◎:PS層と接着性樹脂層との界面(以下、「界面1」ともいう。)及び接着性樹脂層とPE層との界面(以下、「界面2」ともいう。)のいずれにおいても、剥離が観察されず、接着性は非常に良好であった。
○:界面1及び界面2のいずれにおいても、剥離が観察されず、接着性は、◎で示す場合より劣るものの、良好であり、実用上、問題ないレベルであった。
△:界面1及び界面2の一方において、剥離が観察され、接着性は、不良であり、実用上、問題のあるレベルであった。
×:界面1及び界面2の両方において、剥離が観察され、接着性は、非常に不良であり、実用上、より問題のあるレベルであった。
作製した多層シートの接着強度をJIS Z 1707に準じて測定した。以下の基準に従って、測定後における多層間の接着性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
◎:PS層と接着性樹脂層との界面(以下、「界面1」ともいう。)及び接着性樹脂層とPE層との界面(以下、「界面2」ともいう。)のいずれにおいても、剥離が観察されず、接着性は非常に良好であった。
○:界面1及び界面2のいずれにおいても、剥離が観察されず、接着性は、◎で示す場合より劣るものの、良好であり、実用上、問題ないレベルであった。
△:界面1及び界面2の一方において、剥離が観察され、接着性は、不良であり、実用上、問題のあるレベルであった。
×:界面1及び界面2の両方において、剥離が観察され、接着性は、非常に不良であり、実用上、より問題のあるレベルであった。
<破断分割性の評価>
得られた多層シートを真空圧空成形機(浅野研究所製、FLC-415PCS)により成形して、図2(a)及び図2(b)に模式的に示す多層容器、即ち、区画間に罫線状に分割溝が設けられた多連状の多層容器を作製した。分割溝は、図2(a)及び図2(b)中の溝部5に該当する。得られた多層容器の分割溝に力を加え、分割溝に沿って容器を分割できるか否かを試験した。以下の5段階の基準に従って、破断分割性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
5:相対的に弱い力で分割可であった。
4:相対的に中間の力で分割可であった。
3:相対的に強い力で分割可であった。
2:刻線に沿って多層シートを変形させることはできたが、分割不可であった。
1:加えた力を除くと多層シートの形状は元に戻り、分割不可であった。
得られた多層シートを真空圧空成形機(浅野研究所製、FLC-415PCS)により成形して、図2(a)及び図2(b)に模式的に示す多層容器、即ち、区画間に罫線状に分割溝が設けられた多連状の多層容器を作製した。分割溝は、図2(a)及び図2(b)中の溝部5に該当する。得られた多層容器の分割溝に力を加え、分割溝に沿って容器を分割できるか否かを試験した。以下の5段階の基準に従って、破断分割性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
5:相対的に弱い力で分割可であった。
4:相対的に中間の力で分割可であった。
3:相対的に強い力で分割可であった。
2:刻線に沿って多層シートを変形させることはできたが、分割不可であった。
1:加えた力を除くと多層シートの形状は元に戻り、分割不可であった。
表2中の「分割溝の深さ」は、溝部5の深さに該当する。分割溝の深さが160μmの場合、分割溝は、ポリエチレン樹脂層である機能性樹脂層4及び接着性樹脂層3を貫通し、ポリスチレン樹脂層の深さ10μmの位置まで達している。これに対し、分割溝の深さが80μmの場合、分割溝はポリエチレン樹脂層4の一部に設けられているにとどまり、ポリエチレン樹脂層4及び接着性樹脂層3のいずれをも貫通していない。また、分割溝の深さが120μmの場合、分割溝は、ポリエチレン樹脂層4を貫通し、かつ、接着性樹脂層3の一部に設けられているものの、接着性樹脂層3を貫通してはいない。なお、分割溝の深さが0μmの場合、分割溝は設けられていない。
<安全衛生性の評価>
(1)「乳及び乳製品の成分規格等に関する省令(昭和26年12月27日厚生省令第52号)」に規定する基準、及び
(2)「調理中の食品の包装又は入れ物に使用する製品用ポリエチレン基準(FDA CFR21 §177.1520(c)2.2)」
に準じて、溶出試験を行い、以下の基準に従って安全衛生性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
合格:上記(1)及び(2)のいずれにも適合した場合、安全衛生性は良好であると評価した。
不合格:上記(1)及び(2)の少なくとも一方に適合しなかった場合、安全衛生性は不良であると評価した。
(1)「乳及び乳製品の成分規格等に関する省令(昭和26年12月27日厚生省令第52号)」に規定する基準、及び
(2)「調理中の食品の包装又は入れ物に使用する製品用ポリエチレン基準(FDA CFR21 §177.1520(c)2.2)」
に準じて、溶出試験を行い、以下の基準に従って安全衛生性を評価した。結果を表2に示す。
合格:上記(1)及び(2)のいずれにも適合した場合、安全衛生性は良好であると評価した。
不合格:上記(1)及び(2)の少なくとも一方に適合しなかった場合、安全衛生性は不良であると評価した。
なお、実施例7~15及び24において、S/E/Fの製造方法に代えて、E/E/F、S/E/E、又はE/E/Eの製造方法を用いた場合においても、S/E/Fの製造方法を用いた場合と同様の結果が得られた。
また、実施例19~23及び比較例6~8において、E/E/Eの製造方法に代えて、S/E/F、E/E/F、又はS/E/Eの製造方法を用いた場合においても、E/E/Eの製造方法を用いた場合と同様の結果が得られた。
本発明の多層シートは、容器に用いた場合に、ポリスチレン樹脂層を外層としているので、そこに含まれる微量のスチレンモノマーやオリゴマーの漏出が被包装物へ影響を与えることがなく、また、破断強度が大きく、一方、分割溝からの分割性にも優れているので、多連容器やポーションパックなどに広く利用でき、特に食品や医薬品の包装容器に適する。
1 多層シート
2 ポリスチレン樹脂層
3 接着性樹脂層
4 機能性樹脂層
5 分割溝(連結部)
6 多層容器
7 収容室
8 フランジ部
9 カバーシート
10 タブ部
2 ポリスチレン樹脂層
3 接着性樹脂層
4 機能性樹脂層
5 分割溝(連結部)
6 多層容器
7 収容室
8 フランジ部
9 カバーシート
10 タブ部
Claims (11)
- ポリスチレンを主成分とするポリスチレン樹脂層を一方の面とし、機能性樹脂を主成分とする機能性樹脂層を他方の面とし、該ポリスチレン樹脂層と機能性樹脂層が接着性樹脂層を介して接着されている多層シートであって、該機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層が切断されてポリスチレン樹脂層内に達する分割溝が設けられている多層シート。
- 機能性樹脂がポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリアミド、エチレンビニルアルコール共重合体、ポリ乳酸又はポリブチレンサクシネートである請求項1記載の多層シート。
- ポリスチレン樹脂が発泡樹脂である請求項1記載の多層シート。
- ポリスチレン樹脂層が未発泡樹脂層/発泡樹脂層/未発泡樹脂層の3層よりなる請求項1記載の多層シート。
- 接着性樹脂が、不飽和ジカルボン酸がポリオレフィンにグラフト結合している変性ポリオレフィンである請求項1記載の多層シート。
- 接着性樹脂層の樹脂が変性ポリオレフィンとエチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体の混合樹脂である請求項1記載の多層シート。
- 接着性樹脂をTダイから押出し、そのTダイ真下の片側よりポリスチレン樹脂シート、反対側からは機能性樹脂フィルムを繰出して、該接着性樹脂層を介してポリスチレン樹脂シートと機能性樹脂フィルムを積層し、これに該機能性樹脂フィルムと接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂シートに達する分割溝を設けてなる請求項1記載の多層シートの製造方法。
- 接着性樹脂層と機能性樹脂層よりなる共押出フィルムを作製し、その接着性樹脂層側にポリスチレン樹脂を押出して積層し、これに該機能性樹脂層と接着性樹脂層を切断してポリスチレン樹脂層に達する分割溝を設けてなる請求項1記載の多層シートの製造方法。
- 請求項1の多層シートで成形されている食品又は医薬品の多層容器。
- フランジ部を有し、分割溝がフランジ部に設けられている請求項9記載の多層容器。
- 乳製品を収容する容器である請求項9記載の多層容器。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015250444 | 2015-12-22 | ||
| JP2016249158A JP6266744B2 (ja) | 2015-12-22 | 2016-12-22 | 多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 |
| JP2016-249809 | 2016-12-22 | ||
| JP2016-249158 | 2016-12-22 | ||
| JP2016249809A JP2017114125A (ja) | 2015-12-22 | 2016-12-22 | 多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018116504A1 true WO2018116504A1 (ja) | 2018-06-28 |
Family
ID=59231755
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/023674 WO2018116504A1 (ja) | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-28 | 多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP6266744B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2018116504A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022131246A1 (ja) * | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | デンカ株式会社 | 多層樹脂シート、及びそれを成形してなる成形容器 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6914543B2 (ja) * | 2019-04-05 | 2021-08-04 | 東京スレート株式会社 | 接着部材及びそれを使用した物品支持システム |
| JP2021154569A (ja) * | 2020-03-26 | 2021-10-07 | 三菱ケミカル株式会社 | 多層フィルム、複合シート、および包装体 |
| JPWO2023204216A1 (ja) * | 2022-04-18 | 2023-10-26 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59190528U (ja) * | 1983-06-03 | 1984-12-18 | 福山パ−ル紙工株式会社 | 容器 |
| JP2000212369A (ja) * | 1999-01-27 | 2000-08-02 | Nippon Synthetic Chem Ind Co Ltd:The | 樹脂組成物およびその用途 |
| JP2006021409A (ja) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Idemitsu Unitech Co Ltd | 積層シート、当該積層シートからなる容器、及び当該容器の製造方法 |
| JP2011051264A (ja) * | 2009-09-02 | 2011-03-17 | Kuraray Co Ltd | 深絞り成形用発泡シート、およびそれを用いてなる発泡容器 |
| JP2011079538A (ja) * | 2009-10-05 | 2011-04-21 | Q P Corp | 分配包装体詰め食品 |
| WO2013122057A1 (ja) * | 2012-02-13 | 2013-08-22 | 電気化学工業株式会社 | 熱可塑性多層樹脂シート及び成形容器 |
| JP2016101758A (ja) * | 2016-01-14 | 2016-06-02 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 蓋材用積層体、蓋材、分配包装容器、及び分配包装体 |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003231515A (ja) * | 2002-02-08 | 2003-08-19 | Idemitsu Unitech Co Ltd | 液体封入用容器 |
| JP5749218B2 (ja) * | 2012-05-31 | 2015-07-15 | 京セラドキュメントソリューションズ株式会社 | 用紙仕分け装置及び画像形成装置 |
-
2016
- 2016-12-22 JP JP2016249158A patent/JP6266744B2/ja active Active
- 2016-12-22 JP JP2016249809A patent/JP2017114125A/ja active Pending
-
2017
- 2017-06-28 WO PCT/JP2017/023674 patent/WO2018116504A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59190528U (ja) * | 1983-06-03 | 1984-12-18 | 福山パ−ル紙工株式会社 | 容器 |
| JP2000212369A (ja) * | 1999-01-27 | 2000-08-02 | Nippon Synthetic Chem Ind Co Ltd:The | 樹脂組成物およびその用途 |
| JP2006021409A (ja) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Idemitsu Unitech Co Ltd | 積層シート、当該積層シートからなる容器、及び当該容器の製造方法 |
| JP2011051264A (ja) * | 2009-09-02 | 2011-03-17 | Kuraray Co Ltd | 深絞り成形用発泡シート、およびそれを用いてなる発泡容器 |
| JP2011079538A (ja) * | 2009-10-05 | 2011-04-21 | Q P Corp | 分配包装体詰め食品 |
| WO2013122057A1 (ja) * | 2012-02-13 | 2013-08-22 | 電気化学工業株式会社 | 熱可塑性多層樹脂シート及び成形容器 |
| JP2016101758A (ja) * | 2016-01-14 | 2016-06-02 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 蓋材用積層体、蓋材、分配包装容器、及び分配包装体 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022131246A1 (ja) * | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | デンカ株式会社 | 多層樹脂シート、及びそれを成形してなる成形容器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017114124A (ja) | 2017-06-29 |
| JP2017114125A (ja) | 2017-06-29 |
| JP6266744B2 (ja) | 2018-01-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018116504A1 (ja) | 多層シート及びこれを用いた多層容器 | |
| US10569948B2 (en) | Thermoforming sheets and thermoformed containers prepared therefrom | |
| EP3946758B1 (en) | Recyclable film for thermoforming | |
| US20090233025A1 (en) | Multi-Seal Method Capable Structures for Gusseted Flexible Containers | |
| MX2010011967A (es) | Lamina para empaque sin cloro con propiedades de resistencia al rasgado. | |
| JP2015160374A (ja) | 易引裂性多層フィルム及び包装材 | |
| US9789670B2 (en) | Heat-sealable laminate and method for producing same | |
| EP3576945B1 (en) | Moldable polyester sheet materials and recyclable barrier packages made therefrom | |
| JP2006021409A (ja) | 積層シート、当該積層シートからなる容器、及び当該容器の製造方法 | |
| KR20130080009A (ko) | 다층 시트, 열성형 용기, 및 개봉 용이성 포장체 | |
| JP2009083926A (ja) | 易切開性多層容器 | |
| JP4121794B2 (ja) | 易開封性シーラントフィルム及びそれを用いた包装材料及び容器 | |
| JP2018090658A (ja) | シーラント用接着剤及び易剥離性フィルム | |
| KR20130127296A (ko) | 박리성을 갖는 접합 구조의 형성 방법 | |
| JP5915211B2 (ja) | 蓋材 | |
| JP2003020070A (ja) | 深絞り包装体 | |
| JP4402489B2 (ja) | 易開封性シーラントフィルム及びそれを用いた包装材料及び容器 | |
| JP2001287323A (ja) | 易開封性積層体およびそれを用いた蓋材および軟包装材 | |
| JP6185341B2 (ja) | 容器 | |
| JP2002088168A (ja) | 熱融着フィルム及びそれからなる包装体 | |
| JP2018131564A (ja) | シーラント用接着剤及び易剥離性フィルム | |
| JP2024053326A (ja) | 多層フィルム、包装用シート、及び、食品用容器 | |
| JP2022054127A (ja) | 多層フイルム、食品包装用シート、および食品容器、ならびに容器製造方法 | |
| JPS6020984A (ja) | シ−ラント用熱接着フイルム | |
| JPH0873615A (ja) | ヒートシーラント層 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17883895 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17883895 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |