WO2016208309A1 - 車両制御装置及び車両制御方法 - Google Patents
車両制御装置及び車両制御方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016208309A1 WO2016208309A1 PCT/JP2016/065301 JP2016065301W WO2016208309A1 WO 2016208309 A1 WO2016208309 A1 WO 2016208309A1 JP 2016065301 W JP2016065301 W JP 2016065301W WO 2016208309 A1 WO2016208309 A1 WO 2016208309A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- detection
- vehicle control
- detected
- vehicle
- unit
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 215
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 claims description 41
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 21
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 15
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000004522 Pentaglottis sempervirens Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W30/00—Purposes of road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. of systems using conjoint control of vehicle sub-units
- B60W30/08—Active safety systems predicting or avoiding probable or impending collision or attempting to minimise its consequences
- B60W30/095—Predicting travel path or likelihood of collision
- B60W30/0956—Predicting travel path or likelihood of collision the prediction being responsive to traffic or environmental parameters
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W30/00—Purposes of road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. of systems using conjoint control of vehicle sub-units
- B60W30/08—Active safety systems predicting or avoiding probable or impending collision or attempting to minimise its consequences
- B60W30/09—Taking automatic action to avoid collision, e.g. braking and steering
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
- G08G1/166—Anti-collision systems for active traffic, e.g. moving vehicles, pedestrians, bikes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R22/00—Safety belts or body harnesses in vehicles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R2300/00—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle
- B60R2300/30—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle characterised by the type of image processing
- B60R2300/301—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle characterised by the type of image processing combining image information with other obstacle sensor information, e.g. using RADAR/LIDAR/SONAR sensors for estimating risk of collision
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R2300/00—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle
- B60R2300/80—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle characterised by the intended use of the viewing arrangement
- B60R2300/8093—Details of viewing arrangements using cameras and displays, specially adapted for use in a vehicle characterised by the intended use of the viewing arrangement for obstacle warning
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T7/00—Brake-action initiating means
- B60T7/12—Brake-action initiating means for automatic initiation; for initiation not subject to will of driver or passenger
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T7/00—Brake-action initiating means
- B60T7/12—Brake-action initiating means for automatic initiation; for initiation not subject to will of driver or passenger
- B60T7/22—Brake-action initiating means for automatic initiation; for initiation not subject to will of driver or passenger initiated by contact of vehicle, e.g. bumper, with an external object, e.g. another vehicle, or by means of contactless obstacle detectors mounted on the vehicle
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/02—Ensuring safety in case of control system failures, e.g. by diagnosing, circumventing or fixing failures
- B60W50/0205—Diagnosing or detecting failures; Failure detection models
- B60W2050/0215—Sensor drifts or sensor failures
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2420/00—Indexing codes relating to the type of sensors based on the principle of their operation
- B60W2420/40—Photo, light or radio wave sensitive means, e.g. infrared sensors
- B60W2420/403—Image sensing, e.g. optical camera
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2420/00—Indexing codes relating to the type of sensors based on the principle of their operation
- B60W2420/40—Photo, light or radio wave sensitive means, e.g. infrared sensors
- B60W2420/408—Radar; Laser, e.g. lidar
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2554/00—Input parameters relating to objects
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60Y—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO ASPECTS CROSS-CUTTING VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
- B60Y2300/00—Purposes or special features of road vehicle drive control systems
- B60Y2300/08—Predicting or avoiding probable or impending collision
- B60Y2300/095—Predicting travel path or likelihood of collision
- B60Y2300/0954—Predicting travel path or likelihood of collision the prediction being responsive to traffic or environmental parameters
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a vehicle control technology that detects an object around the host vehicle using a plurality of sensors and performs vehicle control in accordance with the possibility of collision between the detected object and the host vehicle.
- Patent Document 1 when the object is in a state of being shielded by a shielding object (shielding state), the time required for the collision determination with the object is shortened compared to the case where the object is not in the shielding state. . Thereby, in patent document 1, the presence or absence of a collision is determined at an early stage with respect to an object in a shielded state.
- the shielding state described in the prior art is one of the phenomena caused by the poor scene of the sensor.
- an object that is not detected in a weak scene of a sensor can be detected by eliminating the poor scene of the sensor.
- an object that has not been detected in a poor scene cannot always be detected when the poor scene is resolved. In this case, the vehicle control for the object becomes unnecessary.
- Patent Document 1 when the time required for the collision determination is shortened only on the condition that the poor scene of the sensor has been eliminated, there is a possibility that unnecessary vehicle control is performed on the object. there were.
- the present disclosure aims to provide a vehicle control device that can suppress unnecessary vehicle control on an object, and a vehicle control method executed by the vehicle control device.
- the vehicle control device is applied to a vehicle including a plurality of detection units (20) that detect objects existing around the host vehicle (50) by different methods, and based on detection information of the plurality of detection units.
- a vehicle control device that performs vehicle control for collision avoidance or collision suppression with respect to the object, wherein the detection ability of the detection part decreases in any one of the plurality of detection parts. It is determined by the first determination unit that determines that a reduction situation has occurred based on the detection information of the detection unit or another detection unit and the first determination unit that the detection capability reduction situation has occurred.
- a second determination unit that determines that the detection capability reduction situation has been eliminated later, and the detection capability reduction within a predetermined time after the second determination unit determines that the detection capability reduction situation has been eliminated.
- the collision avoidance or the collision is less than the time when the detection unit detects the object without causing the detection capability degradation state.
- An operation control unit that shortens an operation time until the vehicle control for suppression is performed.
- the vehicle control device of the present disclosure on the condition that the object is detected by the detection unit in which the detection capability reduction situation is resolved within a predetermined time after the detection capability reduction situation of the detection unit is eliminated, the vehicle The operation time (time required for determining collision with an object) until the control is performed is shortened. Specifically, when an object is detected by the detection unit in which the detection capability reduction situation has been eliminated, compared to the time when the detection unit detects the object without the detection capability reduction situation occurring, The operation time until the vehicle control for collision avoidance or collision suppression is set short. Thereby, in the vehicle control device of the present disclosure, it is possible to suppress unnecessary vehicle control from being performed on the object when the detection capability reduction state of the detection unit is resolved.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of the vehicle control device.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart regarding the collision determination process.
- FIG. 3A is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 3B is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 4A is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 4B is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 5A is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 5B is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 6A is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 6B is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an execution example of the collision determination process.
- FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of operation time setting.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 is mounted on a vehicle (own vehicle) and detects an object existing around the front of the traveling direction of the own vehicle.
- the vehicle control device 100 performs various controls for avoiding or reducing the collision between the detected object and the host vehicle.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 according to the present embodiment functions as a PCS (Pre-crash safety system).
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 includes an ECU 10, various sensors 20, a controlled object 30, and the like.
- Various sensors 20 include, for example, an image sensor 21, a radar sensor 22, a yaw rate sensor 23, a vehicle speed sensor 24, and the like.
- the various sensors 20 function as a plurality of detection units mounted on the vehicle.
- the image sensor 21 is configured using, for example, a CCD camera, a monocular camera, a stereo camera, or the like, and is provided at a predetermined height (near the upper end of the windshield, etc.) in the center of the host vehicle in the vehicle width direction.
- the image sensor 21 captures an image of a region (photographable region) that extends over a range of a predetermined angle toward the front of the host vehicle from a bird's eye view at predetermined time intervals, and acquires a captured image. Then, the image sensor 21 performs predetermined image processing on the acquired captured image.
- the image sensor 21 acquires the shape (size) of the object detected in front of the host vehicle, the distance (relative position and relative distance) from the host vehicle to the object, and the like as the target information.
- the target information acquired by the image sensor 21 is input to the ECU 10.
- the image sensor 21 functions as a second detection unit that detects an object present around the host vehicle by image processing of the captured image.
- the image sensor 21 performs predetermined image processing such as template matching on the captured image. Thereby, the image sensor 21 specifies the type of a predetermined object (for example, another vehicle, a pedestrian, a road obstacle, etc.) existing within the detection range (within the shooting angle of view).
- a plurality of dictionary data image pattern data
- These dictionary data are stored in a predetermined storage area of a storage device provided in the vehicle control device 100.
- As the dictionary data whole body dictionary data in which features of the entire object are patterned and half-body dictionary data in which partial features of the object are patterned are stored. Information on the type of object recognized by the image sensor 21 is input to the ECU 10.
- the radar sensor 22 detects an object in front of the host vehicle using a directional electromagnetic wave such as a millimeter wave or a laser.
- the radar sensor 22 is provided at the front end of the host vehicle, and is attached so that the optical axis of the radar faces the front of the host vehicle.
- the radar sensor 22 transmits an exploration wave at a predetermined time and scans with a radar signal in a region (detectable region) that extends over a range of a predetermined angle toward the front of the host vehicle.
- the radar sensor 22 receives the electromagnetic wave (reflected wave from the object) reflected on the surface of the object outside the vehicle, and based on the reception result, the distance and speed (relative position, relative distance, And relative speed) are acquired as target information.
- the target information acquired by the radar sensor 22 is input to the ECU 10.
- the radar sensor 22 functions as a first detection unit that detects an object existing around the host vehicle by using a reflected wave.
- the yaw rate sensor 23 detects the turning angular velocity (yaw rate) of the host vehicle.
- the vehicle speed sensor 24 detects the traveling speed (vehicle speed) of the host vehicle based on the rotational speed of the wheels. Detection results by these sensors 23 and 24 are input to the ECU 10.
- the ECU 10 is an electronic control unit that controls the entire vehicle control apparatus 100.
- ECU10 is provided with CPU, memory (for example, ROM, RAM, etc.), I / O, etc.
- ECU10 has each function regarding vehicle control.
- the CPU executes a program installed in, for example, a ROM to realize each function.
- Each function of the ECU 10 will be described.
- the ECU 10 functions as, for example, a recognition unit that recognizes an object, a determination unit that determines the possibility of collision with an object, and a control processing unit that controls the operation of the controlled object 30.
- the ECU 10 recognizes an object (for example, another vehicle, a pedestrian, a road obstacle, etc.) ahead of the host vehicle based on information (detection result) input from the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22. Specifically, the ECU 10 fuses the target information (first position information) from the image sensor 21 and the target information (second position information) from the radar sensor 22 for the same object. At this time, the ECU 10 associates information located in the vicinity as position information of the same object. For example, when the position indicated by the second position information exists in the vicinity of the position indicated by the first position information, there is a possibility that an object actually exists at the position indicated by the first position information. high.
- a state in which the position of the object can be acquired with high accuracy by the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22 is referred to as a “fusion state”.
- ECU10 recognizes an object based on a fusion result. That is, the ECU 10 functions as an object recognition unit that recognizes an object by fusing a plurality of pieces of position information. Then, the ECU 10 determines whether or not the own vehicle may collide with the recognized object (collision possibility). As a result, when the ECU 10 determines that the possibility of a collision is high, the ECU 10 activates the controlled object 30 such as a safety device for avoiding or suppressing collision of the host vehicle with respect to the object.
- the controlled object 30 such as a safety device for avoiding or suppressing collision of the host vehicle with respect to the object.
- the controlled object 30 is, for example, a speaker, a seat belt, a brake, or the like.
- the ECU 10 determines that there is a high possibility that the host vehicle will collide with an object, the ECU 10 performs the following control on these controlled objects 30.
- the operation of the speaker is controlled so as to send an alarm to the driver (notify the danger).
- the operation of the seat belt is controlled so as to wind up the belt and protect the driver from the impact at the time of collision.
- the operation of the brake is controlled so as to reduce the collision speed by a braking support function, an automatic braking function, or the like. In this way, the ECU 10 controls the operation of the controlled object 30 such as a safety device for avoiding or suppressing collision between the host vehicle and the object.
- the object in front of the vehicle For example, there are two objects in front of the host vehicle. Of these, one is a moving object, and the other is a shielding object that shields the moving object. In this case, a sudden situation change such as a sudden appearance of a moving object from behind the shield is conceivable. In such a case, if the movement trajectory of the moving object is statistically processed, the possibility of collision may not be determined in time.
- shielding state when there is a risk that the object suddenly appears, such as when the moving object is shielded by the shielding object (hereinafter referred to as “shielding state”), the object is Compared with the case where the object is not in the shielding state, the time required for the object collision determination is shortened. Thereby, the presence or absence of a collision is determined at an early stage with respect to the object in the shielding state.
- the sensor 20 used at the time of object detection has a detection capability reduction situation (hereinafter referred to as “poor scene” for convenience) in which the detection capability of the object is reduced in accordance with the characteristics.
- the object detection capability is also reduced.
- the “object detection capability” referred to here means detection accuracy when the sensor 20 detects an object, possibility of whether or not the sensor 20 can detect an object, and the like.
- the radar sensor 22 cannot distinguish between the shielding object and the moving object. For this reason, the situation where the moving object is shielded is a poor scene of the radar sensor 22. Therefore, in the scene where the radar sensor 22 is not good, the object is detected only by the image sensor 21.
- the poor scene of the sensor 20 If the poor scene of the sensor 20 is eliminated, it is possible to detect an object that the sensor 20 could not detect in the poor scene. However, depending on the sensor 20, even if the weak scene is eliminated, an object that is not detected by the poor scene cannot always be detected. Therefore, on the condition that the poor scene of the sensor 20 has been eliminated, when the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is shortened, the collision possibility between the host vehicle and the object is low. Vehicle control for collision avoidance or collision suppression may be performed. That is, in the conventional apparatus, there is a possibility that unnecessary vehicle control is performed on the object.
- An object that may collide with the host vehicle has a feature that is detected by the sensor 20 in which the poor scene is eliminated immediately before the collision with the host vehicle. Therefore, in the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment, the collision determination is performed on the condition that an object that has not been detected in a scene where the sensor 20 is not good is detected along with the cancellation of the sensor 20's weak scene. The time required for the operation (operation time until vehicle control is performed) is shortened.
- the vehicle control device 100 an object that was not detected in the poor scene (before cancellation) is detected by the sensor 20 within a predetermined time after the weak scene of the certain sensor 20 is resolved. If this happens, the time required for collision determination is reduced (time reduction processing is performed). On the other hand, in the vehicle control device 100, when an object that is not detected in the poor scene is not detected again by the sensor 20 within a predetermined time after the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved, the collision determination is performed. Does not reduce the time required to complete (does not perform time reduction processing). Thus, in the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment, unnecessary vehicle control for an object having a low possibility of collision with the host vehicle is suppressed.
- the value of the “predetermined time” is a value (reference value) calculated based on, for example, experiments. This value may be set in advance.
- the time required for the collision determination is increased. Shorten. That is, in the present embodiment, if the radar sensor 22 detects an object that has been detected only by the image sensor 21 within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the time for collision determination is shortened. On the other hand, if an object that has not been detected in the poor scene is not detected again by the radar sensor 22 within a predetermined time after the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 is resolved, the time required for collision determination is shortened. do not do. That is, in the present embodiment, the collision determination time is not shortened unless the radar sensor 22 detects an object that has been detected only by the image sensor 21 within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved.
- the collision determination process (determination process of the collision determination calculation time) executed by the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- This process is executed at predetermined intervals (for example, about 50 ms) set in advance by the ECU 10 included in the vehicle control device 100.
- the vehicle control device 100 detects an object existing around the front in the traveling direction of the host vehicle (S11). At this time, the vehicle control device 100 fuses the target information from the image sensor 21 and the target information from the radar sensor 22 for the same object, and detects the object. In addition, when the target information can be acquired only from one of the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22, the object is detected using the acquired target information.
- the vehicle control device 100 recognizes the detected object (S12).
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 uses template data such as a half-body dictionary or a whole body dictionary stored in advance in a predetermined storage area such as a ROM, for example, to perform template matching for specifying an object with respect to a captured image. I do.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 specifies the type (type) of the object.
- the vehicle control device 100 associates the recognition history of the object so far with the recognition result of the current object and stores it in a predetermined storage area such as a RAM.
- the vehicle control device 100 determines whether or not the current object detection state (detection condition) is a scene that the radar sensor 22 or the image sensor 21 is not good (detection ability reduction state) (S13).
- the weak scene is predetermined for each sensor 20. Therefore, when the object is detected only by the image sensor 21 and not detected by the radar sensor 22 under the predetermined detection condition, this detection condition corresponds to the condition of the poor scene of the radar sensor 22. Further, when the object is detected only by the radar sensor 22 and not detected by the image sensor 21 under the predetermined detection condition, this detection condition corresponds to the condition of the poor scene of the image sensor 21.
- the above conditions are set in advance as conditions (occurrence conditions) of poor scenes for each sensor 20, and the poor scenes are determined based on these settings.
- the conditions of the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 or the image sensor 21 are not limited to the above conditions.
- the radar sensor 22 or the image sensor 21 is also used. It may be a condition of the poor scene.
- the vehicle control device 100 determines that the scene is not good in the determination process (S13: YES), the vehicle control device 100 turns on the weak flag (S14). On the other hand, if it is determined in the determination process that the scene is not a poor scene (S13: NO), the vehicle control device 100 turns off the weak flag (S15).
- the “bad flag” indicates whether the current object detection status is a poor scene of the sensor 20 and whether or not the poor scene has been resolved by turning on / off the flag. That is, the ECU 10 functions as a first determination unit that determines whether or not the object detection state is a poor scene of the sensor 20 by executing the processing from step S13 to step S15. Also, it functions as a second determination unit that determines whether or not the weak scene has been resolved.
- the vehicle control device 100 measures an elapsed time after the weak flag is switched from on to off, and determines whether or not the measured elapsed time is within a predetermined time (S16). As a result, when it is determined that the elapsed time is not within the predetermined time (S16: NO), the vehicle control device 100 sets the normal mode that does not reduce the time required for the collision determination with the object (S19). That is, when it is determined that the elapsed time exceeds the predetermined time, the normal mode that does not shorten the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is set.
- the vehicle control device 100 detects an object that has not been detected before the weak scene is eliminated by the sensor 20 in which the poor scene is eliminated. It is determined whether or not (S17). That is, in this process, it is determined whether or not an object that could not be detected before the cancellation was detected by either the radar sensor 22 or the image sensor 21 in which the weak scene was eliminated. As a result, when it is determined that the sensor 20 in which the poor scene has been resolved has detected an object that has not been detected before the cancellation (S17: YES), the vehicle control device 100 reduces the time required for the collision determination with the object.
- the shortening mode to be set is set (S18).
- the shortening mode that shortens the operation time until the vehicle control is performed.
- the criterion condition used when determining the possibility of collision with an object is relaxed. Thereby, in the shortening mode, the time required for the collision determination with the object (time until the determination is completed) is set short.
- the determination criterion conditions include, for example, the number of target information samples used when calculating the movement trajectory of the object, the movement distance of the object in the lateral direction perpendicular to the traveling direction of the host vehicle, and the like. Moreover, it is the reliability etc.
- the relaxation of the determination criterion condition represents, for example, reducing the number of samplings when the determination criterion condition is the sampling number, and reducing the value of the movement distance when the determination criterion condition is the movement distance.
- the determination criterion condition is the reliability
- the vehicle control device 100 sets the normal mode (S19) when the sensor 20 in which the weak scene has been resolved determines that an object that has not been detected before the cancellation is not detected (S17: NO). That is, when the elapsed time is within a predetermined time and an object that has not been detected by the sensor 20 in which the weak scene has been eliminated is not detected, the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is not shortened. Set to normal mode. As described above, the ECU 10 executes the processes from step S16 to step S19, thereby shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed as compared with the time when the poor scene of the sensor 20 does not occur. Functions as an operation control unit.
- 3A to 5B are examples of poor scenes that occur due to a positional relationship in which a plurality of objects are close to each other.
- 6A and 6B are examples of poor scenes that occur due to the presence of an object outside the detection range of each sensor 20.
- FIG. 7 is an example of a poor scene that occurs due to a state where the host vehicle and an object are approaching (approaching state).
- the image sensor 21 detects an object at a position equidistant from the rear end of the vehicle 60.
- the above situation is determined as the poor scene 1 of the radar sensor 22.
- the weak flag is turned on.
- the pedestrian 61 is separated from the vehicle 60 (when the cancellation condition is satisfied), as shown in FIG.
- the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 is eliminated. Specifically, for example, using a photographed image of the image sensor 21, the difference between the angle ⁇ 2 of the vehicle 60 with respect to the axle O of the host vehicle 50 and the angle ⁇ 1 of the pedestrian 61 with respect to the axle O becomes a predetermined value or more. If it is detected that the radar sensor 22 is not good at the scene 1, it is determined that the poor scene 1 of the radar sensor 22 has been resolved.
- the difference between the relative distance / relative position (lateral position) of the vehicle 60 relative to the host vehicle 50 and the relative distance / relative position of the pedestrian 61 relative to the host vehicle 50 is equal to or greater than a predetermined value (constant). May be determined that the poor scene 1 of the radar sensor 22 has been eliminated. Thus, in the present embodiment, when the poor scene 1 is resolved, the weak flag is switched from on to off.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 61 is shortened. Done in mode.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 61 is performed in the normal mode.
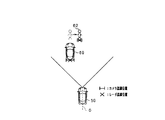
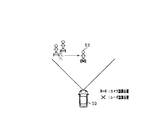
- the vehicle 60 stops at a distance d ahead of the traveling direction of the host vehicle 50, and a pedestrian 62 exists at the front end position (near the front) of the vehicle 60. That is, the pedestrian 62 is positioned in front of the traveling direction of the host vehicle 50 across the vehicle 60 and is in a shielding state.
- the image sensor 21 detects the vehicle 60 by image processing (template matching) based on the whole body dictionary data, and detects the pedestrian 62 by image processing based on the half-body dictionary data.
- the radar sensor 22 when there is an object (pedestrian 62) that is shielded by the vehicle 60 (when the image sensor 21 detects a shielded object ahead of the traveling direction of the host vehicle 50), the radar sensor 22 This is determined as the condition for scene 2 that is not good for.
- the above situation is determined as the poor scene 2 of the radar sensor 22.
- the weak flag is turned on.
- the poor scene 2 of the radar sensor 22 is detected. Is resolved. Specifically, for example, when the dictionary data used in the image processing performed by the image sensor 21 for the pedestrian 62 is switched from the half-body dictionary data to the whole body dictionary data, the poor scene 2 of the radar sensor 22 is eliminated.
- the image sensor 21 detects that the pedestrian 62 has moved to the detection range (detectable angle) of the radar sensor 22, it is determined that the poor scene 2 of the radar sensor 22 has been eliminated. May be.
- the poor flag is switched from on to off.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 62 is shortened. Done in mode.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 62 is performed in the normal mode.
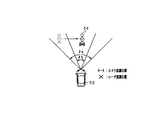
- the above situation is determined as the scene 3 that the radar sensor 22 is not good at.
- the weak flag is turned on.
- at least one pedestrian 63 among the plurality of pedestrians in the predetermined area S has left the predetermined area S as shown in FIG. If this is detected, the scene 3 that the radar sensor 22 is not good at is eliminated.
- an angle between a line segment connecting the pedestrian and the host vehicle 50 in the predetermined area S and a line segment connecting the pedestrian 63 and the host vehicle 50 is predetermined.
- the poor scene 3 of the radar sensor 22 When it is detected that the value is greater than or equal to (away from a certain angle), it is determined that the poor scene 3 of the radar sensor 22 has been eliminated. In addition to this, the difference between the relative distance / relative position (lateral position) of the pedestrian in the predetermined area S with respect to the own vehicle 50 and the relative distance / relative position of the pedestrian 63 with respect to the own vehicle 50 is equal to or greater than a predetermined value. May be determined that the poor scene 3 of the radar sensor 22 has been resolved. As described above, in the present embodiment, when the weak scene 3 is eliminated, the poor flag is switched from on to off.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 63 is shortened. Done in mode.
- the radar sensor 22 does not detect the pedestrian 63 within a predetermined time after the weak scene 3 is resolved, the collision determination with the pedestrian 63 is performed in the normal mode.
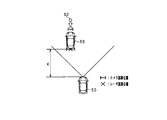
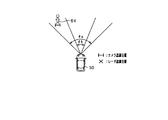
- the detection angle ⁇ a of the image sensor 21 is larger than the detection angle ⁇ b (an angle indicating the detectable area) of the radar sensor 22 ( ⁇ b ⁇ a).
- the detection range is shown.
- the pedestrian 64 exists outside the detection angle ⁇ b of the radar sensor 22 (outside the detection range).
- the image sensor 21 detects the pedestrian 63.
- the pedestrian 64 is not detected from the radar sensor 22.
- the detection angle ⁇ a of the image sensor 21 is larger than the detection angle ⁇ b of the radar sensor 22, there is an object outside the detection angle ⁇ b (outside the detection range) (the image sensor 21 is a radar). (When an object is detected outside the detection range of the sensor 22) is determined as a condition of the poor scene of the radar sensor 22.
- the above situation is determined as a poor scene of the radar sensor 22.
- the weak flag is turned on.
- the weak flag is switched from on to off.
- the collision determination with the pedestrian 64 is performed in a shortened mode. Done in On the other hand, when the radar sensor 22 does not detect the pedestrian 64 within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the collision determination with the pedestrian 64 is performed in the normal mode.
- the radar sensor 22 detects an object based on the reflection point of the electromagnetic wave. Therefore, the radar sensor 22 detects the preceding vehicle 70 even when the host vehicle 50 and the preceding vehicle 70 are in an approaching state (regardless of the inter-vehicle distance). On the other hand, when the host vehicle 50 and the preceding vehicle 70 are in an approaching state (in the case of a short distance), the preceding vehicle 70 (a part of or the entire rear end of the vehicle) is detected by the image sensor 21 (shooting angle of view). There is a possibility that it will come off.
- the above situation is determined as a poor scene of the image sensor 21.
- the image sensor 21 when it is detected that the inter-vehicle distance between the preceding vehicle 70 and the host vehicle 50 is equal to or less than the first distance d1 (approaching to a certain distance), the image sensor 21 It is determined that the scene is weak. At this time, the weak flag is turned on. Thereafter, when it is detected that the inter-vehicle distance between the host vehicle 50 and the preceding vehicle 70 is equal to or greater than a predetermined distance (away from a certain distance) in a situation where the image sensor 21 is determined to be a poor scene. It is determined that the weak scene has been resolved.
- the detection result of the radar sensor 22 is used to detect that the inter-vehicle distance between the host vehicle 50 and the preceding vehicle 70 is equal to or greater than the second distance d2, and the preceding image processing by the image sensor 21 is performed.
- the vehicle 70 it is determined that the poor scene of the image sensor 21 has been eliminated.
- the weak flag is switched from on to off.
- the collision determination with the preceding vehicle 70 is performed in the shortened mode. Done in On the other hand, when the image sensor 21 does not detect the preceding vehicle 70 within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the collision determination with the preceding vehicle 70 is performed in the normal mode.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 according to the present embodiment has the following excellent effects due to the above configuration.
- the operation time until the vehicle control for avoiding or suppressing the collision with the object is performed ( Assume that the time required for collision determination is increased. In this case, there is a delay in the determination of the possibility of collision, and there is a possibility that the alarm output to the driver who prompts the collision avoidance or collision suppression with the object may not be in time. Therefore, in the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment, when the object detection state is a poor scene of the sensor 20, such as when the object is hidden behind a shield, the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is shortened. .
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 it is possible to eliminate the inconvenience that the delay in determining the possibility of collision is suppressed and the warning output to the driver who prompts the collision avoidance or collision suppression with the object is not in time.
- the sensor 20 depending on the sensor 20, an object that is not detected in a poor scene is not always detected when the poor scene is resolved. In this case, an unnecessary warning for the object is output (unnecessary vehicle control is performed). As a result, the driver of the host vehicle 50 may feel the outputted alarm uncomfortable.
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is increased. It is set short. Specifically, the vehicle control device 100 sets the operation time until vehicle control is performed on the condition that an object that has not been detected before cancellation of the poor scene is detected by the sensor 20 after cancellation of the poor scene. Reduce (perform time reduction processing). At this time, the vehicle control device 100 sets the operation time to be shorter than the time when the object is detected by the sensor 20 without causing a poor scene. Thereby, in the vehicle control apparatus 100 which concerns on this embodiment, when the weak scene of the sensor 20 is eliminated, implementation of the unnecessary vehicle control with respect to an object can be suppressed.
- the condition of the poor scene in the sensor 20 and the condition (resolving condition) for eliminating the poor scene are determined in advance (conditions are set in advance).
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 according to the present embodiment can appropriately determine for each sensor 20 whether or not the current object detection state is a poor scene, and the cancellation of the poor scene.
- the image sensor 21 can distinguish and detect the first object and the second object.
- the object detection capability decreases. Therefore, in the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment, when the image sensor 21 detects a second object that is close to the first object, the object detection state is determined to be a poor scene of the radar sensor 22. That is, in the vehicle control device 100, the case where the image sensor 21 detects the second object close to the first object is set in advance as a determination condition for the poor scene of the radar sensor 22.
- the radar sensor 22 It is determined that the weak scene has been resolved. That is, in the vehicle control device 100, a case where the image sensor 21 detects that the proximity state between the first object and the second object has been canceled is set in advance as a condition for canceling the poor scene of the radar sensor 22. . Then, in the vehicle control apparatus 100, when the radar sensor 22 detects the second object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after determining that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been canceled, the second object And the host vehicle 50 may collide with each other.
- the vehicle control device 100 performs the collision determination with the second object in the shortened mode, and shortens the operation time until the vehicle control is performed.
- the vehicle control device 100 when the radar sensor 22 does not detect the second object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after determining that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been canceled, It is assumed that there is a low possibility that two objects and the host vehicle 50 will collide. As a result, the vehicle control device 100 performs the collision determination with the second object in the normal mode and does not shorten the operation time until the vehicle control is performed.
- the vehicle control device 100 when the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 occurs due to the positional relationship between a plurality of objects, the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment performs the following process.
- the vehicle control device 100 if both the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22 do not detect the second object within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is not shortened. .
- unnecessary vehicle control is performed on an object with low reliability (an object with low reliability of detection accuracy). Can be suppressed.
- the detection angles ⁇ a and ⁇ b (detection range) of the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22 are different, and the detection angle ⁇ b (first detection range) of the radar sensor 22 is different from the detection angle ⁇ a (second detection range) of the image sensor 21. ) And the detection angle ⁇ b is included in the range of the detection angle ⁇ a.
- the third object that is outside the detection angle ⁇ b (outside the detection range of the radar sensor 22) and within the detection angle ⁇ a (in the detection range of the image sensor 21) is the image sensor 21. Is detected but is not detected by the radar sensor 22.
- the object detection status is weak in the radar sensor 22. It is determined that it is a scene. That is, in the vehicle control device 100, a case where the image sensor 21 detects a third object that is outside the detection range of the radar sensor 22 is set in advance as a determination condition for the poor scene of the radar sensor 22. Thereafter, in the vehicle control device 100, when the third object is detected within the range of the detection angle ⁇ b of the radar sensor 22 by the image sensor 21, it is determined that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been eliminated.
- the vehicle control device 100 the case where the image sensor 21 detects the third object within the detection range of the radar sensor 22 is set in advance as a condition for canceling the poor scene of the radar sensor 22. Then, in the vehicle control device 100, when the radar sensor 22 detects a third object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after determining that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been canceled, the third object The collision is determined in the shortened mode. As a result, the vehicle control apparatus 100 shortens the operation time until the vehicle control is performed.
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 when the radar sensor 22 does not detect the third object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after determining that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been canceled, Judgment of collision with three objects is performed in the normal mode. As a result, the vehicle control apparatus 100 does not shorten the operation time until the vehicle control is performed. As described above, when a scene in which the radar sensor 22 is not good occurs due to the presence of an object outside the detection range, the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment performs the following processing. In the vehicle control device 100, if both the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22 do not detect the third object within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is not shortened. . Thereby, in the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment, when the weak scene of the radar sensor 22 is resolved, unnecessary vehicle control is performed on an object with low reliability (an object with low reliability of detection accuracy). Can be suppressed.
- the radar sensor 22 detects an approaching fourth object (a fourth object located at a short distance) whose distance from the host vehicle 50 is equal to or less than a predetermined distance. In addition, it is determined that the object detection state is a poor scene of the image sensor 21.
- the case where the radar sensor 22 detects a fourth object that is in close proximity to the host vehicle 50 is set in advance as the determination condition for the poor scene of the image sensor 21. Thereafter, in the vehicle control device 100, when the radar sensor 22 detects that the approaching state of the fourth object to the host vehicle 50 has been canceled (the objects are separated by a certain distance or more), It is determined that the weak scene has been resolved. That is, in the vehicle control device 100, a case where the radar sensor 22 detects that the approach state between the host vehicle 50 and the fourth object has been canceled is set in advance as a condition for canceling the poor scene of the image sensor 21. .
- the vehicle control apparatus 100 when the image sensor 21 detects the 4th object which was not detected before cancellation within the predetermined time after the weak scene of the image sensor 21 is canceled, Collision determination is performed in the shortened mode. As a result, the vehicle control apparatus 100 shortens the operation time until the vehicle control is performed. On the other hand, in the vehicle control device 100, when the image sensor 21 does not detect the fourth object that has not been detected before the cancellation within the predetermined time after the weak scene of the image sensor 21 is canceled, the fourth object Judgment is made in normal mode. As a result, the vehicle control apparatus 100 does not shorten the operation time until the vehicle control is performed.
- the vehicle control device 100 when the poor scene of the image sensor 21 occurs due to the approaching state between the host vehicle 50 and the object, the vehicle control device 100 according to the present embodiment performs the following process.
- the vehicle control device 100 unless both the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22 detect the fourth object within a predetermined time after the weak scene is resolved, the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is not shortened. .
- unnecessary vehicle control is performed on an object with low reliability (an object with low reliability of detection accuracy). Can be suppressed.
- vehicle control device 100 of the present disclosure is not limited to the contents of the above embodiment.
- the same reference numerals are given to the same components as those in the above embodiment, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
- an object that may collide with the host vehicle 50 has a feature that is detected immediately before the collision (feature that allows the entire object to be detected) as the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved.
- feature that allows the entire object to be detected the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved.
- the time required for the collision determination may be shortened on the condition that the entire object that has not been detected before the elimination is detected by the image sensor 21. Note that whether or not the entire object has been detected can be determined by image processing (template matching) based on whole body dictionary data.
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is determined according to the time required from the determination that the object detection state is the poor scene of the sensor 20 to the determination that the poor scene has been resolved.
- the degree of shortening may be changed (variably set).
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is set. Specifically, the shorter the time T1 until the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved, the smaller the degree of shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed. That is, the operation time is set longer. On the other hand, the longer the time T1 until the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved, the greater the degree of shortening. That is, the operation time is set short.
- the vehicle control is more appropriately performed in consideration of the situation when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is eliminated (the positional relationship between the host vehicle 50 and the object when the poor scene is eliminated). Can be implemented.
- the degree of shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is changed according to the elapsed time from when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved until the object is detected by the sensor 20. It may be set.
- the operation time until vehicle control is performed is set as follows. Specifically, the shorter the elapsed time from when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved until the object is detected, the greater the degree of shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed. That is, the operation time is set short. On the other hand, the longer the elapsed time from when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved until the object is detected, the smaller the degree of shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed. That is, the operation time is set longer.
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed may not be shortened after a certain time has elapsed since the scene in which the sensor 20 is not good. Thereby, in a modification, the vehicle control can be more appropriately performed in consideration of a situation in which an object is detected after the weak scene is resolved.
- the radar sensor 22 can detect the distance to an object existing ahead of the traveling direction of the host vehicle 50 regardless of the difference in brightness (contrast).
- the image sensor 21 has a low object detection capability when the amount of light is small (when the difference in brightness is small), such as at night. Therefore, in the modified example, a case where the difference in brightness is small is determined as a condition for the poor scene of the image sensor 21.
- the detection range of the object detected by the radar sensor 22 is outside the irradiation range of the low beam (passing headlight) in the host vehicle 50 and the high beam (traveling headlight) What is necessary is just to determine that the weak scene of the image sensor 21 has been eliminated on the condition that it is within the irradiation distance. Then, when the image sensor 21 detects an object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after the weak scene of the image sensor 21 is canceled, the collision determination with the object is performed in the shortened mode.
- the detection range (detection angle ⁇ b) of the radar sensor 22 is larger than the detection range (detection angle ⁇ a) of the image sensor 21, the image sensor 21 is outside the detection range (detection) of the image sensor 21.
- An object existing outside (angle ⁇ a) cannot be detected. Therefore, in the modified example, the case where the radar sensor 22 detects an object that exists outside the detection range of the image sensor 21 is determined as a condition for the poor scene of the image sensor 21. In this case, for example, on the condition that the object has moved into the detection range of the image sensor 21 on the basis of changes in the vehicle speed of the host vehicle 50 or the movement speed of the object (pedestrian or the like), the image sensor 21. What is necessary is just to determine that the weak scene of has been eliminated.
- a plurality of large vehicles such as trucks
- large vehicles such as trucks
- small vehicles for example, minicars, two-wheeled vehicles, etc.
- the small vehicles are located at the same distance from the rear end of the large vehicle.
- the difference between the relative distance / relative position (lateral position) of the large vehicle with respect to the own vehicle 50 and the relative distance / relative position of the small vehicle with respect to the own vehicle 50 has become a predetermined value or more ( It may be determined that the weak scene of the radar sensor 22 has been resolved on the condition that the radar sensor 22 is separated by a certain distance or more. If the radar sensor 22 detects a vehicle that has not been detected before the resolution within a predetermined time after it is determined that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been resolved, the collision determination with the vehicle is performed in the shortened mode. Do. On the other hand, if the radar sensor 22 does not detect a vehicle that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after it is determined that the weak scene has been canceled, the collision determination with the vehicle is performed in the normal mode.
- such a situation is defined as a condition for the poor scene of the radar sensor 22.
- a condition for the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 for example, on the condition that the pedestrian has moved over the guardrail into the road and the distance between the guardrail and the pedestrian is more than a predetermined distance (more than a certain distance).
- the collision judgment with the pedestrian is shortened. Do in mode.
- the radar sensor 22 does not detect a pedestrian that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after it is determined that the poor scene has been canceled, the collision determination with the pedestrian is performed in the normal mode.
- the radar sensor 22 detects a pedestrian that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after it is determined that the weak scene has been canceled, and the detected pedestrian is in the own vehicle 50.
- the time required for collision determination may be shortened on the condition that the vehicle is moving in the approaching direction.
- the above-described processes can be applied even when the object ahead of the traveling direction of the host vehicle 50 is a bicycle. If the object is a bicycle, the radar sensor 22 may not be able to detect the bicycle due to the low tracking accuracy due to the fast moving speed of the bicycle. Therefore, in the modified example, a condition where the bicycle is detected by the image sensor 21 and the movement speed of the detected bicycle is equal to or higher than a predetermined speed is determined as a condition of the poor scene of the radar sensor 22. In this case, for example, it may be determined that the poor scene of the radar sensor 22 has been eliminated on the condition that the moving speed of the bicycle is less than a predetermined speed.
- the radar sensor 22 becomes a poor scene in which the detection capability of the object decreases when the distance to the object becomes a close distance (for example, less than 2 m). Therefore, in a modification, for example, a sensor 20 such as a sonar or a laser that can detect an object at a closer distance than the radar sensor 22 is mounted on the host vehicle 50. In the modified example, a case where an object that is not detected by the radar sensor 22 is detected by the sensor 20 that can detect an object at a close distance is determined as a condition of the poor scene of the radar sensor 22.
- the radar sensor 22 can detect a guardrail from an array of objects having a predetermined reflection intensity. Therefore, in the modified example, the case where the guardrail is detected by the radar sensor 22 is determined as a condition of the poor scene of the monocular camera (image sensor 21). In the modified example, it is determined that the poor scene of the monocular camera has been resolved on the condition that the monocular camera detects a pedestrian and the detected pedestrian is moving toward the road.
- the time required for the collision determination is increased. Shorten.
- the time required for collision determination is not shortened.
- the shortening mode or the normal mode may be set according to the type (type) of the object detected when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved. Specifically, for example, when the object detected within a predetermined time after it is determined that the poor scene of the sensor 20 has been resolved is a moving object such as a pedestrian or a vehicle, the vehicle control is performed. Set the mode to shorten the operating time. On the other hand, when the object detected within a predetermined time after it is determined that the poor scene of the sensor 20 has been resolved is a stationary object such as a manhole, the operation mode until the vehicle control is performed is not shortened. Set.
- the determination threshold used for determining whether or not the weak scene has been eliminated may be changed according to the type of the object. Specifically, for example, when the object is a two-wheeled vehicle having a moving speed faster than that of a pedestrian, the determination threshold value is decreased and the determination criterion is set lower. Further, for example, in the case of a pedestrian, it is determined that the poor scene has been eliminated when detection by image processing based on whole body dictionary data is performed. On the other hand, in the case of a two-wheeled vehicle, it may be determined that the poor scene has been eliminated when detection by image processing based on half-body dictionary data is performed. By doing in this way, in a modification, according to the kind of object, the cancellation of the weak scene of sensor 20 can be judged more appropriately.
- the degree (shortening rate) of shortening the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is changed and set according to the type of the object detected when the poor scene of the sensor 20 is resolved. Also good. Specifically, for example, when the object is a two-wheeled vehicle having a moving speed faster than that of a pedestrian, the degree is set so as to shorten the operation time. By doing in this way, in a modification, according to the kind of object detected with cancellation of the poor scene of sensor 20, vehicle control can be carried out at a more suitable timing.
- the host vehicle 50 may be configured to include a sonar in addition to the image sensor 21 and the radar sensor 22.
- the predetermined time may be set by changing according to the type of poor scene or the type of object. That is, in the modification, the ECU 10 may function as a setting unit that variably sets the predetermined time. Specifically, for example, the predetermined time is set to a different value in each of the poor scenes generated due to the positional relationship of the plurality of objects. The predetermined time is set to a different value depending on whether the object is the host vehicle 50 or a pedestrian.
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed when the sensor 20 detects an object that has not been detected before the cancellation within a predetermined time after it is determined that the poor scene of the sensor 20 has been canceled is not limited to this.
- the operation time until the vehicle control is performed is set to be short on the condition that the sensor 20 detects an object that has not been detected before the cancellation. You may be made to do.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Regulating Braking Force (AREA)
Abstract
周囲の物体をそれぞれ異なる方式で検出する複数のセンサ20の検出情報に基づいて、物体に対する衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施する車両制御装置100は、いずれかのセンサにおいて物体の検出能力が低下する検出能力低下状況が生じていることを、当該センサ又は他のセンサの検出情報に基づき判定する。そして、生じた検出能力低下状況が解消されたことが判定された後の所定時間内に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消されたセンサにより物体が検出された場合には、検出能力低下状況が生じることなくセンサにより物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する。
Description
本開示は、複数のセンサを用いて自車両周囲の物体を検出し、その検出された物体と自車両との衝突可能性に応じて車両制御を行う車両制御技術に関する。
車両制御装置では、自車両と周囲の物体との衝突可能性を早期に判定する必要がある。一方で、衝突可能性が正確に判定されない場合には、不要な車両制御(不必要な制御)の増加につながる。そこで、従来では、物体の移動軌跡を統計処理し、物体の位置の検出精度を高めることによって、不要な車両制御を抑制することが知られている。
しかし、物体が遮蔽物の陰から突然現れる等の場合には、物体の移動軌跡を統計処理していると、衝突可能性の判定が間に合わなくなるおそれがある。
そこで特許文献1では、物体が遮蔽物で遮蔽された状態(遮蔽状態)である場合には、物体が遮蔽状態ではない場合と比較して、物体との衝突判定に要する時間を短縮している。これにより、特許文献1では、遮蔽状態の物体に対して早期に衝突の有無が判定されるようにしている。
ところで、複数のセンサを用いて物体を検出する場合には、物体の検出能力がセンサごとに低下する検出能力低下状況(苦手シーン)が生じる。なお、従来技術に記載の遮蔽状態は、センサの苦手シーンに起因して生じる現象の1つであると言える。
例えば、あるセンサの苦手シーンで検出されなかった物体は、そのセンサの苦手シーンが解消されることで検出可能となる。しかし、センサによっては、苦手シーンにおいて検出されなかった物体が、苦手シーンの解消に伴って検出できるとは限らない。この場合、その物体に対する車両制御は不要となる。
そのため、特許文献1に記載のように、センサの苦手シーンが解消されたことのみを条件として、衝突判定に要する時間が短縮された場合には、物体に対する不要な車両制御が行われる可能性があった。
本開示は、物体に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる車両制御装置、及び、車両制御装置が実行する車両制御方法を提供することを目的とする。
本開示の車両制御装置は、自車両(50)の周囲に存在する物体をそれぞれ異なる方式で検出する複数の検出部(20)を備える車両に適用され、前記複数の検出部の検出情報に基づいて、前記物体に対する衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施する車両制御装置であって、前記複数の検出部のうち、いずれかの検出部において、前記物体の検出能力が低下する検出能力低下状況が生じていることを、当該検出部又は他の検出部の前記検出情報に基づき判定する第1判定部と、前記第1判定部により前記検出能力低下状況が生じていると判定された後に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消されたことを判定する第2判定部と、前記第2判定部により前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により前記物体が検出された場合に、前記検出能力低下状況が生じることなく前記検出部により前記物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、前記衝突回避又は前記衝突抑制のための前記車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する作動制御部と、を備える。
本開示の車両制御装置では、検出部の検出能力低下状況が解消された後の所定時間以内に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消された検出部によりその物体が検出されたことを条件として、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間(物体との衝突判定に要する時間)を短縮している。具体的には、検出能力低下状況が解消された検出部により物体が検出された場合には、当該検出能力低下状況が生じることなく検出部によりその物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短く設定する。これにより、本開示の車両制御装置では、検出部の検出能力低下状況が解消された際に、物体に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる。
以下、各実施形態を図面に基づいて説明する。なお、以下の各実施形態において、互いに同一もしくは均等である部分には、図中、同一符号を付しており、同一符号の部分についてはその説明を援用する。
本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100は、車両(自車両)に搭載され、自車両の進行方向前方等の周囲に存在する物体を検出する。そして、車両制御装置100は、検知したその物体と自車両との衝突を回避、又は、軽減するための各種制御を行う。このように、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100は、PCS(Pre-crash safety system)として機能する。
図1は、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100のブロック図である。図1に示すように、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100は、ECU10、各種センサ20、被制御対象30等を備えている。
各種センサ20としては、例えば、画像センサ21、レーダセンサ22、ヨーレートセンサ23、車速センサ24等を備えている。なお、各種センサ20は、車両が搭載する複数の検出部として機能する。
画像センサ21は、例えばCCDカメラ、単眼カメラ、ステレオカメラ等を用いて構成され、自車両の車幅方向中央の所定の高さ(フロントガラスの上端付近等)に設けられている。画像センサ21は、自車両前方に向かって、所定の角度の範囲に亘って広がる領域(撮影可能領域)を、所定時間ごとに俯瞰視点から撮像し、撮影画像を取得する。そして、画像センサ21は、取得した撮影画像に対して所定の画像処理を行う。これにより、画像センサ21は、自車両前方に検知した物体の形状(大きさ)や、自車両から物体までの距離(相対位置及び相対距離)等を物標情報として取得する。画像センサ21が取得した物標情報は、ECU10に入力される。なお、画像センサ21は、撮影画像の画像処理により、自車両の周囲に存在する物体を検出する第2検出部として機能する。
また、画像センサ21は、撮影画像に対して、テンプレートマッチング等の所定の画像処理を行う。これにより、画像センサ21は、検出範囲内(撮影画角内)に存在する所定の物体の種類(例えば他車両、歩行者、路上障害物等)を特定する。本実施形態では、各物体の種類(種別)を特定するためのテンプレートとして、物体ごとの特徴を示す画像パターンである複数の辞書データ(画像パターンデータ)を有する。これらの辞書データは、車両制御装置100が備える記憶装置の所定の記憶領域に記憶されている。なお、辞書データとしては、物体全体の特徴をパターン化した全身辞書データと、物体の部分的な特徴をパターン化した半身辞書データとを記憶している。画像センサ21が認識した物体の種類の情報は、ECU10に入力される。
レーダセンサ22は、例えばミリ波やレーザ等の指向性を有する電磁波を利用して自車両前方の物体を検出する。レーダセンサ22は、自車両の前端部に設けられ、レーダの光軸が自車両前方を向くように取り付けられている。レーダセンサ22は、自車両前方に向かって、所定の角度の範囲に亘って広がる領域(検出可能領域)を、所定時間ごとに探査波を送信し、レーダ信号で走査する。その結果、レーダセンサ22は、車外の物体の表面で反射された電磁波(物体からの反射波)を受信し、受信結果に基づいて、自車両に対する物体の距離や速度(相対位置、相対距離、及び相対速度)等を物標情報として取得する。レーダセンサ22が取得した物標情報は、ECU10に入力される。なお、レーダセンサ22は、反射波により、自車両の周囲に存在する物体を検出する第1検出部として機能する。
ヨーレートセンサ23は、自車両の旋回角速度(ヨーレート)を検出する。車速センサ24は、車輪の回転速度に基づき自車両の走行速度(車速)を検出する。これらのセンサ23,24による検出結果は、ECU10に入力される。
ECU10は、車両制御装置100全体の制御を行う電子制御ユニットである。ECU10は、CPU、メモリ(例えばROMやRAM等)、I/O等を備えている。ECU10は、車両制御に関する各機能を有している。ECU10は、CPUが、例えばROMにインストールされているプログラムを実行し、各機能を実現する。ECU10が有する各機能について説明する。ECU10は、例えば、物体を認識する認識部、物体との衝突可能性を判定する判定部、及び、被制御対象30の作動を制御する制御処理部等として機能する。ECU10は、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22から入力された情報(検出結果)に基づいて、自車両前方の物体(例えば他車両、歩行者、路上障害物等)を認識する。具体的には、ECU10は、画像センサ21からの物標情報(第1位置情報)と、レーダセンサ22からの物標情報(第2位置情報)とを、同一物体について融合する。このときECU10は、近傍に位置する情報同士を、同じ物体の位置情報として対応付ける。例えば、上記第1位置情報で示される位置の近傍に、上記第2位置情報で示される位置が存在する場合には、第1位置情報で示される位置に、実際に物体が存在する可能性が高い。このように、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22により、物体の位置が精度良く取得できている状態を「フュージョン状態」という。これにより、ECU10は、融合結果に基づいて、物体を認識する。つまり、ECU10は、複数の位置情報を融合することで、物体を認識する物体認識部として機能する。そして、ECU10は、自車両が、認識した物体と衝突する可能性があるか否か(衝突可能性)を判定する。その結果、ECU10は、衝突する可能性が高いと判定した場合には、物体に対する自車両の衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための安全装置等の被制御対象30を作動させる。
被制御対象30としては、例えばスピーカ、シートベルト、ブレーキ等である。ECU10は、自車両が物体に衝突する可能性が高いと判定した場合、これらの被制御対象30に対して次のような制御を行う。例えばスピーカについては、運転者に警報を発信(危険性を報知)するように作動が制御される。また、シートベルトについては、ベルトを巻き上げ、衝突時の衝撃から運転者を守るように作動が制御される。また、ブレーキについては、制動支援機能や自動制動機能等によって衝突速度を低減するように作動が制御される。このように、ECU10は、自車両と物体との衝突回避又は衝突抑制するための安全装置等の被制御対象30の作動を制御する。
ところで、自車両と物体との衝突回避又は衝突抑制のためには、自車両と物体との衝突可能性を早期に判定する必要がある。一方、衝突可能性が正確に判定されない場合には、不要な車両制御(不必要な制御)の増加につながる。そこで、これまでの装置では、物体の移動軌跡を統計処理で算出し、物体の位置の検出精度を高めることによって、衝突可能性の判定精度の向上を図っていた。
しかし、自車両前方の物体には、次のような状況も想定される。例えば、自車両前方に2つの物体が存在している。そのうち、一方は移動物であり、他方は移動物を遮蔽する遮蔽物であったとする。この場合には、移動物が遮蔽物の陰から突然現れる等の突発的な状況変化が考えられる。このような場合には、移動物の移動軌跡を統計処理していると、衝突可能性の判定が間に合わなくなるおそれがある。そこで、これまでの装置では、さらに、移動物が遮蔽物で遮蔽された状態(以下「遮蔽状態」という)である場合等のように、物体が突然現れる危険性がある場合には、物体が遮蔽状態でない場合と比較して、物体の衝突判定に要する時間を短縮する。これにより、遮蔽状態の物体に対して早期に衝突の有無が判定されるようにしている。
一方で、物体検出時に用いるセンサ20は、その特性に応じて物体の検出能力が低下する検出能力低下状況(以下便宜上「苦手シーン」という)が生じる。これにより、苦手シーンにおいて、複数のセンサ20を用いて物体を検出する場合には、物体の検出能力も低下する。なおここで言う「物体の検出能力」とは、センサ20が物体を検出する際の検出精度や、センサ20が物体を検出可能か否かの可能性等を意味する。
例えば、移動物が遮蔽状態の場合、レーダセンサ22は、遮蔽物と移動物とを区別して検出できない。そのため、移動物が遮蔽された状況は、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンとなる。よって、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンにおいては、画像センサ21のみで物体が検出されることにとなる。
センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されれば、そのセンサ20が苦手シーンの際に検出できなかった物体が検出可能となる。しかし、センサ20によっては、苦手シーンが解消されたとしても、その苦手シーンによって検出されなかった物体が検出できるとは限らない。そのため、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたことのみを条件として、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間が短縮された場合には、自車両と物体との衝突可能性が低いにも関わらず、衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御が行われる可能性がある。つまり、これまでの装置では、物体に対する不要な車両制御が行われる可能性があった。
自車両と衝突する可能性がある物体は、自車両との衝突直前に苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20によって検出される特徴を有する。そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、あるセンサ20の苦手シーンの際に検出されなかった物体が、そのセンサ20の苦手シーンの解消に伴って検出されたことを条件に、衝突判定に要する時間(車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間)を短縮する。
具体的には、車両制御装置100では、あるセンサ20の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、苦手シーンの際(解消前)に検出されなかった物体が、当該センサ20によって検出された場合に、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮する(時間短縮処理を行う)。一方、車両制御装置100では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、苦手シーンの際に検出されなかった物体が、当該センサ20によって再び検出されなかった場合に、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮しない(時間短縮処理を行わない)。このようにして、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、自車両との衝突可能性が低い物体に対する不要な車両制御を抑制する。なお、上記「所定時間」の値は、例えば実験等に基づき算出した値(基準値)である。この値は、予め設定しておけばよい。
上述した例では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、苦手シーンの際に検出されなかった物体が、当該レーダセンサ22によって検出された場合、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮する。つまり、本実施形態では、レーダセンサ22が、苦手シーン解消後の所定時間以内に、画像センサ21のみで検出されていた物体を検出すれば、衝突判定の時間短縮を行う。一方、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、苦手シーンの際に検出されなかった物体が、当該レーダセンサ22によって再び検出されなかった場合、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮しない。つまり、本実施形態では、レーダセンサ22が、苦手シーン解消後の所定時間以内に、画像センサ21のみで検出されていた物体を検出しなければ、衝突判定の時間短縮を行わない。
次に、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100が実行する衝突判定処理(衝突判定の演算時間の判定処理)について図2を用いて説明する。本処理は、車両制御装置100が備えるECU10によって、予め設定された所定周期(例えば約50ms)ごとに実行される。
図2において、車両制御装置100は、自車両の進行方向前方の周囲に存在する物体を検出する(S11)。このとき車両制御装置100は、画像センサ21からの物標情報と、レーダセンサ22からの物標情報とを、同一物体について融合し、物体を検出する。なお、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22の一方からしか物標情報が取得できなった場合には、取得できた物標情報を用いて、物体を検出する。
次に、車両制御装置100は、検出した物体を認識する(S12)。このとき車両制御装置100では、例えばROM等の所定の記憶領域に予め記憶しておいた半身辞書や全身辞書等の辞書データを用いて、撮影画像に対して、物体を特定するためのテンプレートマッチングを行う。これにより、車両制御装置100では、物体の種類(種別)を特定する。そして、車両制御装置100は、これまでの物体の認識履歴と、今回の物体の認識結果とを対応付けて、例えばRAM等の所定の記憶領域に記憶する。
次に、車両制御装置100は、現在の物体の検出状況(検出条件)が、レーダセンサ22又は画像センサ21の苦手シーン(検出能力低下状況)であるか否かを判定する(S13)。なお、苦手シーンについては、センサ20ごとに予め定められる。よって、所定の検出条件において、物体が、画像センサ21のみで検出され、レーダセンサ22で検出されていない場合には、この検出条件がレーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件に相当する。また、所定の検出条件において、物体が、レーダセンサ22のみで検出され、画像センサ21で検出されていない場合には、この検出条件が画像センサ21の苦手シーンの条件に相当する。このように、車両制御装置100では、上記条件を、センサ20ごとの苦手シーンの条件(発生条件)として予め設定しておき、これらの設定に基づいて、上記苦手シーンの判定を行う。なお、レーダセンサ22又は画像センサ21の苦手シーンの条件は、上記条件に限らない。例えば、レーダセンサ22及び画像センサ21の両方で検出されているが、一方が非遮蔽状態での検出結果であり、他方が遮蔽状態での検出結果である場合も、レーダセンサ22又は画像センサ21の苦手シーンの条件としてもよい。
車両制御装置100は、上記判定処理において、苦手シーンであると判定した場合(S13:YES)、苦手フラグをオンにする(S14)。一方、車両制御装置100は、上記判定処理において、苦手シーンでないと判定した場合(S13:NO)、苦手フラグをオフにする(S15)。なおここで言う「苦手フラグ」は、現在の物体の検出状況がセンサ20の苦手シーンか否か、また、その苦手シーンが解消されたか否かを、フラグのオン・オフによって示している。つまり、ECU10は、ステップS13からS15までの処理を実行することで、物体の検出状況がセンサ20の苦手シーンか否かを判定する第1判定部として機能する。また、その苦手シーンが解消されたか否かの判定を行う第2判定部として機能する。
車両制御装置100は、苦手フラグをオフすると、苦手フラグがオンからオフに切り替わってからの経過時間を計測し、計測した経過時間が所定時間以内であるか否かを判定する(S16)。その結果、車両制御装置100は、経過時間が所定時間以内ではないと判定した場合(S16:NO)、物体との衝突判定に要する時間を短縮しない通常モードに設定する(S19)。つまり、経過時間が所定時間を超過していると判定した場合には、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない通常モードに設定する。
一方、車両制御装置100は、経過時間が所定時間以内であると判定した場合(S16:YES)、苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20によって、苦手シーンの解消前に検出されなかった物体を検出したか否かを判定する(S17)。つまり、本処理では、苦手シーンが解消されたレーダセンサ22又は画像センサ21のいずれか一方によって、解消前に検出できなかった物体を検出したか否かを判定する。その結果、車両制御装置100は、苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20が、解消前に検出されなかった物体を検出したと判定した場合(S17:YES)、物体との衝突判定に要する時間を短縮する短縮モードに設定する(S18)。つまり、経過時間が所定時間以内で、かつ、苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20により解消前に検出されなかった物体を検出した場合には、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する短縮モードに設定する。本実施形態に係る短縮モードでは、物体との衝突可能性を判定する際に用いる判定基準条件を緩和する。これにより、短縮モードでは、物体との衝突判定に要する時間(判定が終了するまでの時間)を短く設定する。なお、上記判定基準条件とは、例えば、物体の移動軌跡を算出する際に用いる物標情報のサンプリング数や、自車両の進行方向に対して直行する横方向における物体の移動距離等である。また、車両制御の対象物標として確定するか否かを判定するための信頼度等である。上記判定基準条件の緩和とは、例えば、判定基準条件が上記サンプリング数である場合、サンプリング数を減らすことを表し、判定基準条件が上記移動距離である場合、移動距離の値を小さくすることを表す。また、判定基準条件が上記信頼度である場合には、信頼度を判定するための閾値を小さくすることを表す。このようにすることで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、物体との衝突判定に要する時間を短縮できる。
一方、車両制御装置100は、苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20が、解消前に検出されなかった物体を検出しなかったと判定した場合(S17:NO)、通常モードに設定する(S19)。つまり、経過時間が所定時間以内で、かつ、苦手シーンが解消されたセンサ20により解消前に検出されなかった物体を検出しなかった場合には、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない通常モードに設定する。このように、ECU10は、上記ステップS16からS19までの処理を実行することで、センサ20の苦手シーンが発生しなかった場合の時間に比べて、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する作動制御部として機能する。
次に、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100による上記処理の実行例(具定例)を図3A~7を用いて説明する。
図3A~図5Bは、複数の物体が相互に近接している位置関係に起因して発生する苦手シーンの例である。図6A及び図6Bは、各センサ20の検出範囲外に物体が存在することに起因して発生する苦手シーンの例である。図7は、自車両と物体とが接近している状態(接近状態)に起因して発生する苦手シーンの例である。
<複数物体の位置関係に起因して発生する苦手シーン1>
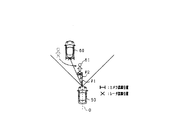
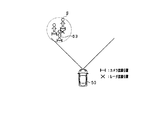
図3Aに示す例では、自車両50の進行方向前方に車両60が停車しており、車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に歩行者61が存在している。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、車両60及び歩行者61を個別に検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、互いに等距離dに存在する車両60及び歩行者61(複数の物体)を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に物体(歩行者61)が存在する場合(画像センサ21が車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1(レーダセンサ22の検出能力が低下する状況)の条件(発生条件)として定める。
図3Aに示す例では、自車両50の進行方向前方に車両60が停車しており、車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に歩行者61が存在している。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、車両60及び歩行者61を個別に検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、互いに等距離dに存在する車両60及び歩行者61(複数の物体)を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に物体(歩行者61)が存在する場合(画像センサ21が車両60の後端と等距離dの位置に物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1(レーダセンサ22の検出能力が低下する状況)の条件(発生条件)として定める。
これにより、本実施形態では、上記状況が、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1として判定される。このとき、苦手フラグがオンになる。その後、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1と判定された状況下において、図3Bに示すように、車両60から歩行者61が離れたことを検出した場合(解消条件が満たされた場合)には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消される。具体的には、例えば、画像センサ21の撮影画像を用いて、自車両50の車軸Oに対する車両60の角度θ2と、車軸Oに対する歩行者61の角度θ1との差が、所定値以上となったこと(一定の角度以上離れたこと)を検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1が解消されたと判定する。これ以外にも、自車両50に対する車両60の相対距離/相対位置(横位置)と、自車両50に対する歩行者61の相対距離/相対位置との差が、所定値以上となったこと(一定の距離以上離れたこと)を検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1が解消されたと判定してもよい。このように、本実施形態では、苦手シーン1が解消されると、苦手フラグはオンからオフに切り替わる。
そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン1が解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者61をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、歩行者61との衝突判定が短縮モードで行われる。一方、苦手シーン1が解消された後の所定時間以内に、歩行者61をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、歩行者61との衝突判定が通常モードで行われる。
<複数物体の位置関係に起因して発生する苦手シーン2>
図4Aに示す例では、自車両50の進行方向前方の距離dに車両60が停車しており、車両60の前端の位置(前方付近)に歩行者62が存在している。つまり、歩行者62は、車両60を挟んで自車両50の進行方向前方に位置し、遮蔽状態となっている。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、車両60を全身辞書データに基づく画像処理(テンプレートマッチング)により検出し、歩行者62を半身辞書データに基づく画像処理により検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、車両60及び歩行者62を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、車両60によって遮蔽状態の物体(歩行者62)が存在する場合(画像センサ21が自車両50の進行方向前方に遮蔽状態の物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2の条件として定める。
図4Aに示す例では、自車両50の進行方向前方の距離dに車両60が停車しており、車両60の前端の位置(前方付近)に歩行者62が存在している。つまり、歩行者62は、車両60を挟んで自車両50の進行方向前方に位置し、遮蔽状態となっている。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、車両60を全身辞書データに基づく画像処理(テンプレートマッチング)により検出し、歩行者62を半身辞書データに基づく画像処理により検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、車両60及び歩行者62を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、車両60によって遮蔽状態の物体(歩行者62)が存在する場合(画像センサ21が自車両50の進行方向前方に遮蔽状態の物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2の条件として定める。
これにより、本実施形態では、上記状況が、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2として判定される。このとき、苦手フラグがオンになる。その後、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2と判定された状況下において、図4Bに示すように、車両60の前方から歩行者62が現れたことを検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2が解消される。具体的には、例えば、画像センサ21が歩行者62に対して行う画像処理で用いる辞書データが、半身辞書データから全身辞書データに切り替わった場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2が解消されたと判定する。これ以外にも、レーダセンサ22の検出範囲(検出可能な角度)に歩行者62が移動したことを、画像センサ21が検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2が解消されたと判定してもよい。このように、本実施形態では、苦手シーン2が解消されると、苦手フラグはオンからオフに切り替わる。
そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン2が解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者62をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、歩行者62との衝突判定が短縮モードで行われる。一方、苦手シーン2が解消された後の所定時間以内に、歩行者62をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、歩行者62との衝突判定が通常モードで行われる。
<複数物体の位置関係に起因して発生する苦手シーン3>
図5Aに示す例では、所定エリアS内に複数の歩行者が存在している。つまり、自車両50の進行方向前方には、人ごみが形成されている。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、全身辞書データ又は半身辞書データに基づく画像処理を行うことで、複数の歩行者を個別に検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、複数の歩行者を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、自車両50の進行方向前方に人ごみが存在する場合(画像センサ21が所定エリアS内に複数の歩行者を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3の条件として定める。
図5Aに示す例では、所定エリアS内に複数の歩行者が存在している。つまり、自車両50の進行方向前方には、人ごみが形成されている。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、全身辞書データ又は半身辞書データに基づく画像処理を行うことで、複数の歩行者を個別に検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、複数の歩行者を区別して検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、自車両50の進行方向前方に人ごみが存在する場合(画像センサ21が所定エリアS内に複数の歩行者を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3の条件として定める。
これにより、本実施形態では、上記状況が、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3として判定される。このとき、苦手フラグがオンになる。その後、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3と判定された状況下において、図5Bに示すように、所定エリアS内の複数の歩行者のうち、少なくとも1人の歩行者63が、所定エリアSから離れたことを検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3が解消される。具体的には、例えば、画像センサ21の撮影画像を用いて、所定エリアSの歩行者及び自車両50を結ぶ線分と、歩行者63及び自車両50を結ぶ線分との角度が、所定値以上となったこと(一定の角度以上離れたこと)を検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3が解消されたと判定する。これ以外にも、自車両50に対する所定エリアSの歩行者の相対距離/相対位置(横位置)と、自車両50に対する歩行者63の相対距離/相対位置との差が、所定値以上となったこと(一定の距離以上離れたこと)を検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3が解消されたと判定してもよい。このように、本実施形態では、苦手シーン3が解消されると、苦手フラグはオンからオフに切り替わる。
そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーン3が解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者63をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、歩行者63との衝突判定が短縮モードで行われる。一方、苦手シーン3が解消された後の所定時間以内に、歩行者63をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、歩行者63との衝突判定が通常モードで行われる。
<検出範囲外に物体が存在することに起因して発生する苦手シーン>
図6Aに示す例では、画像センサ21の検出角θa(撮影可能領域を示す角度)が、レーダセンサ22の検出角θb(検出可能領域を示す角度)よりも大きい(θb<θa)という、異なる検出範囲が示されている。また、本例では、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの外側(検出範囲外)に歩行者64が存在している。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、歩行者63を検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、歩行者64が検出されない。そこで、本実施形態では、画像センサ21の検出角θaがレーダセンサ22の検出角θbよりも大きいときに、検出角θbの外側(検出範囲外)に物体が存在する場合(画像センサ21がレーダセンサ22の検出範囲外に物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。
図6Aに示す例では、画像センサ21の検出角θa(撮影可能領域を示す角度)が、レーダセンサ22の検出角θb(検出可能領域を示す角度)よりも大きい(θb<θa)という、異なる検出範囲が示されている。また、本例では、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの外側(検出範囲外)に歩行者64が存在している。この場合には、画像センサ21(撮影画像から)は、歩行者63を検出する。一方、レーダセンサ22からは、歩行者64が検出されない。そこで、本実施形態では、画像センサ21の検出角θaがレーダセンサ22の検出角θbよりも大きいときに、検出角θbの外側(検出範囲外)に物体が存在する場合(画像センサ21がレーダセンサ22の検出範囲外に物体を検出した場合)を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。
これにより、本実施形態では、上記状況が、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンとして判定される。このとき、苦手フラグがオンになる。その後、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンと判定された状況下において、図6Bに示すように、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの内側(検出範囲内)に歩行者64が移動したことを検出した場合には、苦手シーンが解消される。具体的には、例えば、画像センサ21の撮影画像を用いて、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの内側に歩行者64が横移動したことを検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。または、レーダセンサ22が検出角θb内側に存在する歩行者64を検出した場合には、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定してもよい。このように、本実施形態では、苦手シーンが解消されると、苦手フラグはオンからオフに切り替わる。
そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者64をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、歩行者64との衝突判定を短縮モードで行われる。一方、苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、歩行者64をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、歩行者64との衝突判定が通常モードで行われる。
<自車両50と物体との接近状態に起因して発生する苦手シーン>
図7に示す例では、レーダセンサ22は、電磁波の反射点に基づいて、物体を検出している。そのため、レーダセンサ22は、自車両50と先行車両70とが接近状態であっても(車間距離に関わらず)、先行車両70を検出する。一方、自車両50と先行車両70とが接近状態の場合(近距離の場合)には、先行車両70(車両後端の一部または全体)が、画像センサ21の検出範囲(撮影画角)から外れてしまう可能性がある。そのため、画像センサ21(撮影画像)からは、全身辞書データ又は半身辞書データに基づく画像処理により先行車両70を検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、自車両50に対して接近状態の物体が存在する場合(レーダセンサ22が自車両50との距離が所定距離以下である接近状態の物体を検出した場合)を、画像センサ21の苦手シーン(画像センサ21の検出能力が低下する状況)の条件として定める。
図7に示す例では、レーダセンサ22は、電磁波の反射点に基づいて、物体を検出している。そのため、レーダセンサ22は、自車両50と先行車両70とが接近状態であっても(車間距離に関わらず)、先行車両70を検出する。一方、自車両50と先行車両70とが接近状態の場合(近距離の場合)には、先行車両70(車両後端の一部または全体)が、画像センサ21の検出範囲(撮影画角)から外れてしまう可能性がある。そのため、画像センサ21(撮影画像)からは、全身辞書データ又は半身辞書データに基づく画像処理により先行車両70を検出することが困難となる。そこで、本実施形態では、自車両50に対して接近状態の物体が存在する場合(レーダセンサ22が自車両50との距離が所定距離以下である接近状態の物体を検出した場合)を、画像センサ21の苦手シーン(画像センサ21の検出能力が低下する状況)の条件として定める。
これにより、本実施形態では、上記状況が、画像センサ21の苦手シーンとして判定される。図7に示すように、例えば、先行車両70と自車両50との車間距離が第1距離d1以下となったこと(一定の距離まで接近したこと)を検出した場合には、画像センサ21の苦手シーンであると判定する。このとき、苦手フラグがオンになる。その後、画像センサ21の苦手シーンと判定された状況下において、自車両50と先行車両70との車間距離が所定距離以上となったこと(一定の距離以上離れたこと)を検出した場合には、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。具体的には、例えば、レーダセンサ22の検出結果を用いて、自車両50と先行車両70との車間距離が第2距離d2以上となったことを検出し、画像センサ21の画像処理により先行車両70が検出可能となった場合には、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定される。このように、本実施形態では、苦手シーンが解消されると、苦手フラグはオンからオフに切り替わる。
そして、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった先行車両70を画像センサ21が検出した場合には、先行車両70との衝突判定が短縮モードで行われる。一方、苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、先行車両70を画像センサ21が検出しなかった場合には、先行車両70との衝突判定が通常モードで行われる。
本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、上記構成により、以下の優れた効果を奏する。
・例えば、センサ20の苦手シーン(検出能力低下状況)において、当該センサ20による物体の検出能力を高めるために、物体との衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間(衝突判定に要する時間)を長くしたとする。この場合には、衝突可能性の判定に遅れが生じ、物体との衝突回避又は衝突抑制を促す運転者への警報出力が間に合わなくなるおそれがある。そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、物体が遮蔽物の陰に隠れている等、物体の検出状況がセンサ20の苦手シーンの場合、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、衝突可能性の判定遅れを抑制し、物体との衝突回避又は衝突抑制を促す運転者への警報出力が間に合わなくなる不都合を解消できる。しかし、センサ20によっては、苦手シーンにおいて検出されなかった物体が、苦手シーンの解消に伴って検出されるとは限らない。この場合には、当該物体に対する不要な警報が出力される(不要な車両制御が行われる)。その結果、自車両50の運転者は、出力された警報を不快に感じる可能性がある。
そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、次のような条件が満たされた場合、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短く設定している。具体的には、車両制御装置100では、苦手シーンの解消前に検出されなかった物体が、苦手シーン解消後のセンサ20によって検出されたことを条件に、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する(時間短縮処理を行う)。このとき、車両制御装置100では、苦手シーンが生じることなく、センサ20によって物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、作動時間を短く設定する。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された際に、物体に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる。
・本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、センサ20における苦手シーンの条件と、その苦手シーンが解消される条件(解消条件)とを予め定めておく(条件を予め設定しておく)。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、現在の物体の検出状況が苦手シーンか否か、また、その苦手シーンの解消を、センサ20ごとに適切に判定できる。
・例えば、互いに近接している第1物体及び第2物体が存在する場合、画像センサ21は、第1物体及び第2物体を区別して検出できる。一方、レーダセンサ22は、第1物体及び第2物体(近接状態の複数の物体)を区別して検出することが困難であるため、物体の検出能力が低下する。そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、第1物体に近接する第2物体を検出した場合に、物体の検出状況がレーダセンサ22の苦手シーンであると判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、第1物体に近接する第2物体を検出した場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの判定条件として予め設定しておく。その後、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21によって、第1物体に対する第2物体の近接状態が解消されたこと(物体同士が一定の距離以上離れたこと)を検出した場合に、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、第1物体と第2物体との近接状態が解消されたことを検出した場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの解消条件として予め設定しておく。そして、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定した後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第2物体をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合に、第2物体と自車両50とが衝突する可能性があるとする。その結果、車両制御装置100では、第2物体との衝突判定を短縮モードで行い、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する。一方、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定した後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第2物体をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合に、第2物体と自車両50とが衝突する可能性が低いとする。その結果、車両制御装置100では、第2物体との衝突判定を通常モードで行い、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。このように、複数物体の位置関係に起因してレーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが発生した場合、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、次のような処理を行う。車両制御装置100では、苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22の両方が第2物体を検出しなければ、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消された際に、信頼度の低い物体(検出精度の信頼度が低い物体)に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる。
・例えば、画像センサ21とレーダセンサ22との検出角θa,θb(検出範囲)が異なり、レーダセンサ22の検出角θb(第1検出範囲)が画像センサ21の検出角θa(第2検出範囲)よりも小さく、検出角θbが検出角θaの範囲内に含まれるとする。この場合において、検出角θbの範囲外(レーダセンサ22の検出範囲外)であり、且つ、検出角θaの範囲内(画像センサ21の検出範囲内)に存在する第3物体は、画像センサ21では検出されるが、レーダセンサ22では検出されない。そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの範囲外に存在する第3物体を検出した場合に、物体の検出状況がレーダセンサ22の苦手シーンであると判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、レーダセンサ22の検出範囲外に存在する第3物体を検出した場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの判定条件として予め設定しておく。その後、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21によって、レーダセンサ22の検出角θbの範囲内で第3物体を検出した場合に、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21が、レーダセンサ22の検出範囲内に第3物体を検出した場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの解消条件として予め設定しておく。そして、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定した後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第3物体をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合に、第3物体との衝突判定を短縮モードで行う。その結果、車両制御装置100では、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する。一方、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定した後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第3物体をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合に、第3物体との衝突判定を通常モードで行う。その結果、車両制御装置100では、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。このように、検出範囲外に物体が存在することに起因してレーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが発生した場合、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、次のような処理を行う。車両制御装置100では、苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22の両方が第3物体を検出しなければ、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消された際に、信頼度の低い物体(検出精度の信頼度が低い物体)に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる。
・例えば、自車両50と第4物体とが接近状態の場合(近距離の場合)には、第4物体の一部(上下左右の端)又は全体が、画像センサ21の検出範囲から外れてしまうため、画像センサ21による物体の検出能力が低下する。そこで、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22が、自車両50との距離が所定距離以下である接近状態の第4物体(近距離に位置する第4物体)を検出した場合に、物体の検出状況が画像センサ21の苦手シーンであると判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22が、自車両50と接近状態の第4物体を検出した場合を、画像センサ21の苦手シーンの判定条件として予め設定しておく。その後、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22によって、自車両50に対する第4物体の接近状態が解消されたこと(物体同士が一定の距離以上離れたこと)を検出した場合に、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。つまり、車両制御装置100では、レーダセンサ22が、自車両50と第4物体との接近状態が解消されたことを検出した場合を、画像センサ21の苦手シーンの解消条件として予め設定しておく。そして、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第4物体を画像センサ21が検出した場合に、第4物体との衝突判定を短縮モードで行う。その結果、車両制御装置100では、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する。一方、車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった第4物体を画像センサ21が検出しなかった場合に、第4物体との衝突判定を通常モードで行う。その結果、車両制御装置100では、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。このように、自車両50と物体との接近状態に起因して画像センサ21の苦手シーンが発生した場合、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、次のような処理を行う。車両制御装置100では、苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、画像センサ21及びレーダセンサ22の両方が第4物体を検出しなければ、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない。これにより、本実施形態に係る車両制御装置100では、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消された際に、信頼度の低い物体(検出精度の信頼度が低い物体)に対する不要な車両制御の実施を抑制できる。
また、本開示の車両制御装置100は、上記実施形態の内容に限定されない。例えば、以下のように実施してもよい。なお、以下の説明においては、上記実施形態と同様の構成には同一の参照符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
・上記実施形態において、自車両50と衝突する可能性がある物体は、センサ20の苦手シーンの解消に伴って、衝突直前に検出される特徴(物体全体が検出可能な状態となる特徴)を有している。そこで、変形例では、苦手シーンが解消された場合に、解消前に検出されなかった物体全体が画像センサ21によって検出されたことを条件に、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮してもよい。なお、物体全体が検出されたか否かの判定は、全身辞書データに基づく画像処理(テンプレートマッチング)によって行える。
・変形例では、物体の検出状況がセンサ20の苦手シーンであると判定されてから、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定されるまでに要する時間に応じて、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合い(短縮率)を変化させて設定(可変設定)してもよい。変形例では、例えば、図8に示すように、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を設定する。具体的には、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されるまでの時間T1が短いほど、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合いを小さくする。すなわち、作動時間を長めに設定する。一方、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されるまでの時間T1が長いほど、短縮する度合いを大きくする。すなわち、作動時間を短めに設定する。これにより、変形例では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたときの状況(苦手シーンが解消された時点での自車両50と物体との位置関係)を考慮して、車両制御をより適切に実施できる。
・変形例では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されてから、当該センサ20により物体が検出されるまでの経過時間に応じて、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合いを変化させて設定してもよい。変形例では、例えば次のようにして、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を設定する。具体的には、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されてから物体が検出されるまでの経過時間が短いほど、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合いを大きくする。すなわち、作動時間を短めに設定する。一方、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されてから物体が検出されるまでの経過時間が長いほど、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合いを小さくする。すなわち、作動時間を長めに設定する。なお、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されてから一定時間が経過した後は、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間の短縮を実施しないようにしてもよい。これにより、変形例では、苦手シーンの解消後に物体が検出される状況を考慮して、車両制御をより適切に実施できる。
・レーダセンサ22は、明暗の差(コントラスト)の大小に関わらず、自車両50の進行方向前方に存在する物体までの距離を検出できる。一方、画像センサ21は、夜間等のように光量が少ない場合(明暗の差が小さい場合)、物体の検出能力が低下する。そこで、変形例では、明暗の差が小さい場合を、画像センサ21の苦手シーンの条件として定める。この場合には、例えば、レーダセンサ22によって検出された物体の検出範囲が、自車両50におけるロービーム(すれ違い用前照灯)の照射範囲外であり、且つ、ハイビーム(走行用前照灯)の照射距離内であることを条件に、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定すればよい。そして、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった物体を画像センサ21が検出した場合には、物体との衝突判定が短縮モードで行われる。
・上記実施形態において、画像センサ21の検出範囲(検出角θa)よりレーダセンサ22の検出範囲(検出角θb)が大きい場合には、画像センサ21は、当該画像センサ21の検出範囲外(検出角θaの外側)に存在する物体を検出できない。そこで、変形例では、画像センサ21の検出範囲外に存在する物体をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合を、画像センサ21の苦手シーンの条件として定める。この場合には、例えば、自車両50の車速や物体(歩行者等)の移動速度等の変化に基づいて、物体が画像センサ21の検出範囲内に移動してきたことを条件に、画像センサ21の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定すればよい。
・例えば、片側複数車線の道路において、自車両50の進行方向前方を、複数の大型車両(トラック等)が並走している。さらに、大型車両の間には小型車両(例えば、軽自動車や二輪車等)が存在し、その小型車両は大型車両の後端と等距離に位置しているとする。このような場合には、レーダセンサ22が、大型車両及び小型車両を区別して検出することが困難となる。そのため、変形例では、このような状況を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。この場合には、例えば、自車両50に対する大型車両の相対距離/相対位置(横位置)と、自車両50に対する小型車両の相対距離/相対位置との差が、所定値以上となったこと(一定の距離以上離れたこと)を条件に、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定してもよい。そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった車両をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、車両との衝突判定を短縮モードで行う。一方、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった車両をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、車両との衝突判定を通常モードで行う。
・例えば、ガードレール(クラッシュバリア)付近に歩行者等の物体が存在し、ガードレールと物体との間隔が狭いとする。このような場合には、レーダセンサ22が、ガードレール及び物体を区別して検出することが困難となる。そのため、変形例では、このような状況を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。この場合には、例えば、歩行者がガードレールを超えて走行道路内に移動し、且つ、ガードレールと歩行者との間隔が所定間隔以上に離れたこと(一定の距離以上離れたこと)を条件に、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定してもよい。そして、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者をレーダセンサ22が検出した場合には、歩行者との衝突判定を短縮モードで行う。一方、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者をレーダセンサ22が検出しなかった場合には、歩行者との衝突判定を通常モードで行う。なお、変形例では、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった歩行者をレーダセンサ22が検出し、且つ、検出した歩行者が自車両50に接近する方向に移動していることを条件に、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮してもよい。
・変形例では、自車両50の進行方向前方の物体が自転車の場合にも、上記各処理を適用できる。なお、物体が自転車である場合には、自転車の移動速度が速いことによる追跡精度の低さに起因して、レーダセンサ22によって自転車の検出ができなくなるおそれがある。そのため、変形例では、画像センサ21によって自転車を検出し、且つ、検出した自転車の移動速度が所定速度以上である場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。この場合には、例えば、自転車の移動速度が所定速度未満となったことを条件に、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定してもよい。
・レーダセンサ22は、物体との距離が至近距離(例えば2m未満)になると、物体の検出能力が低下する苦手シーンとなる。そこで、変形例では、例えば、レーダセンサ22よりも至近距離の物体を検出可能なソナーやレーザ等のセンサ20を自車両50に搭載する。そして、変形例では、至近距離の物体を検出可能なセンサ20によって、レーダセンサ22で検出されていない物体が検出された場合を、レーダセンサ22の苦手シーンの条件として定める。
・画像センサ21が単眼カメラの場合には、例えば、ガードレール付近に存在する歩行者を撮影できない。一方、レーダセンサ22は、所定の反射強度の物体の並びからガードレールを検出できる。そこで、変形例では、レーダセンサ22によってガードレールが検出された場合を、単眼カメラ(画像センサ21)の苦手シーンの条件として定める。そして、変形例では、単眼カメラが歩行者を検出し、且つ、検出した歩行者が走行道路に向かって移動していることを条件に、単眼カメラの苦手シーンが解消されたと判定する。この場合には、変形例では、単眼カメラの苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、全身辞書データに基づく画像処理によって歩行者を検出した場合に、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮する。一方、歩行者を検出しなかった場合には、衝突判定に要する時間を短縮しない。
・変形例では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された際に検出された物体の種類(種別)に応じて、短縮モードか通常モードかを設定してもよい。具体的には、例えば、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に検出された物体が歩行者や車両等の移動物の場合には、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する短縮モードに設定する。一方、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に検出された物体がマンホール等の静止物の場合には、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しない通常モードに設定する。
・変形例では、物体の種類に応じて、苦手シーンが解消されたか否かの判定に用いる判定閾値を変更してもよい。具体的には、例えば、物体が歩行者に比べて移動速度の速い二輪車の場合には、判定閾値を小さくし、判定基準を低めに設定する。また、例えば、歩行者の場合には、全身辞書データに基づく画像処理による検出が行われた際に、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定される。これに対して、二輪車の場合には、半身辞書データに基づく画像処理による検出が行われた際に、苦手シーンが解消されたと判定してもよい。このようにすることで、変形例では、物体の種類に応じて、センサ20の苦手シーンの解消をより適切に判定できる。
・変形例では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された際に検出された物体の種類に応じて、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する度合い(短縮率)を変化させて設定してもよい。具体的には、例えば、物体が歩行者に比べて移動速度の速い二輪車の場合には、度合いを大きくし、作動時間がより短縮されるように設定する。このようにすることで、変形例では、センサ20の苦手シーンの解消に伴って検出された物体の種類に応じて、より適切なタイミングで車両制御を実施できる。
・変形例では、車両の周囲に存在する物体をそれぞれ異なる方式によって検出するセンサ20を、少なくとも3つ以上備えていてもよい。具体的には、例えば、自車両50は、画像センサ21やレーダセンサ22に加えて、ソナー等を備えた構成であってもよい。
・上記では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった物体を当該センサ20が検出した場合に、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮している。なお上記所定時間は、苦手シーンの種類や物体の種類に応じて変化させて設定されてもよい。つまり、変形例では、ECU10を、所定時間を可変設定する設定部として機能させてもよい。具体的には、例えば、所定時間は、上記の複数物体の位置関係に起因して発生する苦手シーンのそれぞれにおいて異なる値に設定する。また、物体が自車両50の場合と歩行者の場合とでは、所定時間を異なる値に設定する。
・上記では、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、解消前に検出されなかった物体を当該センサ20が検出した場合に、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮しているが、これに限らない。他の例としては、センサ20の苦手シーンが解消された時点で、解消前に検出されなかった物体を当該センサ20が検出したことを条件に、車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間が短く設定されるようにしてもよい。
10…ECU、21…画像センサ、22…レーダセンサ、50…自車両、100…車両制御装置。
Claims (12)
- 自車両(50)の周囲に存在する物体をそれぞれ異なる方式で検出する複数の検出部(20)を備える車両に適用され、前記複数の検出部の検出情報に基づいて、前記物体に対する衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施する車両制御装置であって、
前記複数の検出部のうち、いずれかの検出部において、前記物体の検出能力が低下する検出能力低下状況が生じていることを、当該検出部又は他の検出部の前記検出情報により判定する第1判定部と、
前記第1判定部により前記検出能力低下状況が生じていると判定された後に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消されたことを判定する第2判定部と、
前記第2判定部により前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により前記物体が検出された場合に、前記検出能力低下状況が生じることなく前記検出部により前記物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、前記衝突回避又は前記衝突抑制のための前記車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する作動制御部と、
を備える車両制御装置。 - 前記複数の検出部により前記物体を検出する状況下において、前記検出部で生じる前記検出能力低下状況の条件を前記検出部ごとに定めておくとともに、当該検出能力低下状況が解消される解消条件を定めておき、
前記第1判定部は、前記検出部ごとの前記検出能力低下状況の条件が成立する場合に、前記検出能力低下状況が生じていることを判定し、
前記第2判定部は、前記解消条件が成立する場合に、前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたことを判定する、請求項1に記載の車両制御装置。 - 前記作動制御部は、前記第1判定部により、前記検出部が前記検出能力低下状況であると判定されてから、前記第2判定部により、前記解消条件が成立し、前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定されるまでの時間に応じて、前記作動時間の短縮率を可変設定する、請求項2に記載の車両制御装置。
- 前記作動制御部は、前記第2判定部により、前記解消条件が成立し、前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定されてから、前記検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により、前記物体が検出されるまでの時間に応じて、前記作動時間の短縮率を可変設定する、請求項2又は3に記載の車両制御装置。
- 前記作動制御部は、前記第2判定部により、前記解消条件が成立し、前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定されてから、前記検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により、前記物体が検出された際、検出された前記物体の種類に応じて、前記作動時間の短縮率を可変設定する、請求項2乃至4のいずれか1項に記載の車両制御装置。
- 前記複数の検出部として、反射波により、前記自車両の周囲の前記物体を検出する第1検出部(22)と、撮影画像の画像処理により、前記自車両の周囲の前記物体を検出する第2検出部(21)と、を備えており、
前記第1判定部は、前記第2検出部の前記画像処理により、互いに近接状態の第1物体及び第2物体が検出された場合に、前記第1検出部が前記検出能力低下状況であると判定し、
前記第2判定部は、前記第2検出部の前記画像処理により、前記第1物体と前記第2物体との前記近接状態が解消されたことが検出された場合に、前記第1検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定し、
前記作動制御部は、前記第1検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の前記所定時間以内に、前記第1検出部により前記第2物体が検出された場合に、前記作動時間を短縮し、一方、前記所定時間以内に、前記第1検出部により前記第2物体が検出されなかった場合に、前記作動時間を短縮しない、請求項1乃至5のいずれか1項に記載の車両制御装置。 - 前記第1検出部が前記物体を検出可能な第1検出範囲と、前記第2検出部が前記物体を検出可能な第2検出範囲とが異なり、前記第1検出範囲が前記第2検出範囲内に含まれる場合において、
前記第1判定部は、前記第2検出部により、前記第1検出範囲外に第3物体が検出された場合に、前記第1検出部が前記検出能力低下状況であると判定し、
前記第2判定部は、前記第2検出部により、前記第1検出範囲内に前記第3物体が検出された場合に、前記第1検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定し、
前記作動制御部は、前記第1検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の前記所定時間以内に、前記第1検出部により前記第3物体が検出された場合に、前記作動時間を短縮し、一方、前記所定時間以内に、第1検出部により前記第3物体が検出されなかった場合に、前記作動時間を短縮しない、請求項6に記載の車両制御装置。 - 前記第1判定部は、前記第1検出部により、前記自車両に対して近距離に位置し、接近状態である第4物体が検出された場合に、前記第2検出部が前記検出能力低下状況であると判定し、
前記第2判定部は、前記第1検出部により、前記自車両と前記第4物体との距離が所定距離以上離れたことが検出された場合に、前記第2検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定し、
前記作動制御部は、前記第2検出部の前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の前記所定時間以内に、前記第2検出部により前記第4物体が検出された場合に、前記作動時間を短縮し、一方、前記所定時間以内に、前記第2検出部により前記第4物体が検出されなかった場合に、前記作動時間を短縮しない、請求項6又は7に記載の車両制御装置。 - 前記第1検出部と前記第2検出部とで取得された前記物体の位置情報を融合することで、前記物体を認識する物体認識部を備える、請求項6乃至8のいずれか1項に記載の車両制御装置。
- 前記作動制御部は、前記第2判定部により前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された時点で、当該検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により前記物体が検出されたことを条件に、前記作動時間を短く設定する、請求項1乃至9のいずれか1項に記載の車両制御装置。
- 前記検出能力低下状況の種類、又は、前記物体の種類に応じて、前記所定時間を可変設定する設定部を備える、請求項1乃至10のいずれか1項に記載の車両制御装置。
- 自車両(50)の周囲に存在する物体をそれぞれ異なる方式で検出する複数の検出部(20)を備える車両に適用され、前記複数の検出部の検出情報に基づいて、前記物体に対する衝突回避又は衝突抑制のための車両制御を実施する車両制御装置により実行される車両制御方法であって、
前記車両制御装置が、
前記複数の検出部のうち、いずれかの検出部において、前記物体の検出能力が低下する検出能力低下状況が生じていることを、当該検出部又は他の検出部の前記検出情報により判定する第1判定ステップと、
前記検出能力低下状況が生じていると判定された後に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消されたことを判定する第2判定ステップと、
前記検出能力低下状況が解消されたと判定された後の所定時間以内に、当該検出能力低下状況が解消された前記検出部により前記物体が検出された場合に、前記検出能力低下状況が生じることなく前記検出部により前記物体が検出される場合の時間に比べて、前記衝突回避又は前記衝突抑制のための前記車両制御を実施するまでの作動時間を短縮する作動制御ステップと、
を実行する、車両制御方法。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/738,513 US10654475B2 (en) | 2015-06-26 | 2016-05-24 | Vehicle control apparatus and vehicle control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015128606A JP6361592B2 (ja) | 2015-06-26 | 2015-06-26 | 車両制御装置 |
| JP2015-128606 | 2015-06-26 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016208309A1 true WO2016208309A1 (ja) | 2016-12-29 |
Family
ID=57585509
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/065301 WO2016208309A1 (ja) | 2015-06-26 | 2016-05-24 | 車両制御装置及び車両制御方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10654475B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6361592B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016208309A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6649178B2 (ja) | 2016-05-24 | 2020-02-19 | 株式会社東芝 | 情報処理装置、および、情報処理方法 |
| KR101996419B1 (ko) * | 2016-12-30 | 2019-07-04 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 센서 융합 기반 보행자 탐지 및 보행자 충돌 방지 장치 및 방법 |
| JP6664360B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-08 | 2020-03-13 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 判定装置および車両 |
| KR102037324B1 (ko) * | 2017-11-30 | 2019-10-28 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 자율주행 차량 및 그 제어 방법 |
| JP7077606B2 (ja) * | 2017-12-22 | 2022-05-31 | 株式会社デンソー | 衝突判定装置 |
| JP6661695B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-09 | 2020-03-11 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 移動体検出装置、車両制御システム、移動体検出方法および車両制御方法 |
| JP6930512B2 (ja) * | 2018-10-19 | 2021-09-01 | 株式会社デンソー | 物体検知装置、物体検知方法およびプログラム |
| CN111086508A (zh) * | 2018-10-24 | 2020-05-01 | 罗伯特·博世有限公司 | 自动躲避或减轻碰撞的方法及控制系统、存储介质和汽车 |
| JP6820958B2 (ja) * | 2019-01-22 | 2021-01-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 車両の制御装置および制御方法 |
| US11577741B1 (en) * | 2019-04-05 | 2023-02-14 | Zoox, Inc. | Systems and methods for testing collision avoidance systems |
| US11210946B2 (en) * | 2019-07-15 | 2021-12-28 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Content sharing between vehicles based on a peer-to-peer connection |
| KR102585557B1 (ko) * | 2021-11-29 | 2023-10-06 | 주식회사 와이즈오토모티브 | 자율 주행 차량의 장애물 인지 성능 평가 장치 및 방법 |
| KR102677416B1 (ko) * | 2021-12-08 | 2024-06-24 | 사이텍 주식회사 | 자율주행차량 시험데이터수집장치 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005280538A (ja) * | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 走行安全装置 |
| JP2007091207A (ja) * | 2005-08-31 | 2007-04-12 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両の走行安全装置 |
| JP2012064026A (ja) * | 2010-09-16 | 2012-03-29 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両用対象物検出装置、およびその方法 |
| JP2012247829A (ja) * | 2011-05-25 | 2012-12-13 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両周辺監視装置 |
| JP5641271B1 (ja) * | 2013-05-31 | 2014-12-17 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両の運転支援装置及び車載コンピュータ |
| JP2015078926A (ja) * | 2013-10-17 | 2015-04-23 | 株式会社デンソー | 物標検出装置 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9091762B2 (en) * | 2011-10-27 | 2015-07-28 | Gulfstream Aerospace Corporation | Methods and systems for avoiding a collision between an aircraft on a ground surface and an obstacle |
| US9643576B2 (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2017-05-09 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Collision avoidance assist device and collision avoidance assist method |
| JP2014099019A (ja) * | 2012-11-14 | 2014-05-29 | Denso Corp | 車両の衝突予防装置 |
| DE102013113054B4 (de) | 2012-12-03 | 2022-01-27 | Denso Corporation | Zielerfassungsvorrichtung zum Vermeiden einer Kollision zwischen einem Fahrzeug und einem durch einen an dem Fahrzeug montierten Sensor erfassten Ziel |
| DE102013102608A1 (de) * | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-18 | Audi Ag | Kollisionsschutzvorrichtung für eine schwenkbare Klappe eines Kraftfahrzeugs, Klappe, Kraftfahrzeug und entsprechendes Verfahren |
| JP5729416B2 (ja) | 2013-04-26 | 2015-06-03 | 株式会社デンソー | 衝突判定装置、および衝突緩和装置 |
| JP5778236B2 (ja) * | 2013-10-18 | 2015-09-16 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両衝突判定装置 |
| US9875661B2 (en) * | 2014-05-10 | 2018-01-23 | Aurora Flight Sciences Corporation | Dynamic collision-avoidance system and method |
| US9776589B2 (en) * | 2014-06-26 | 2017-10-03 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Vehicle control system and method of using the same |
| CN111762136A (zh) * | 2015-05-12 | 2020-10-13 | 深圳市大疆创新科技有限公司 | 识别或检测障碍物的设备和方法 |
-
2015
- 2015-06-26 JP JP2015128606A patent/JP6361592B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-05-24 US US15/738,513 patent/US10654475B2/en active Active
- 2016-05-24 WO PCT/JP2016/065301 patent/WO2016208309A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005280538A (ja) * | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 走行安全装置 |
| JP2007091207A (ja) * | 2005-08-31 | 2007-04-12 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両の走行安全装置 |
| JP2012064026A (ja) * | 2010-09-16 | 2012-03-29 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両用対象物検出装置、およびその方法 |
| JP2012247829A (ja) * | 2011-05-25 | 2012-12-13 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両周辺監視装置 |
| JP5641271B1 (ja) * | 2013-05-31 | 2014-12-17 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両の運転支援装置及び車載コンピュータ |
| JP2015078926A (ja) * | 2013-10-17 | 2015-04-23 | 株式会社デンソー | 物標検出装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US10654475B2 (en) | 2020-05-19 |
| JP2017010498A (ja) | 2017-01-12 |
| JP6361592B2 (ja) | 2018-07-25 |
| US20180178786A1 (en) | 2018-06-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2016208309A1 (ja) | 車両制御装置及び車両制御方法 | |
| CN107408345B (zh) | 物标存在判定方法以及装置 | |
| US9460627B2 (en) | Collision determination device and collision mitigation device | |
| EP2302412B1 (en) | System and method for evaluation of an automotive vehicle forward collision threat | |
| JP6539228B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置、及び車両制御方法 | |
| JP6729282B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置 | |
| US10665107B2 (en) | Moving object control apparatus and method of controlling moving object | |
| JP6669090B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置 | |
| US8248295B2 (en) | Pre-crash safety system | |
| EP3007149B1 (en) | Driving assistance device for vehicles and onboard computer | |
| US20190061750A1 (en) | Collision mitigation control device | |
| JP2019114030A (ja) | 衝突判定装置 | |
| JP6855776B2 (ja) | 物体検出装置、及び物体検出方法 | |
| US10787170B2 (en) | Vehicle control method and apparatus | |
| JP6358017B2 (ja) | 運転支援装置 | |
| KR102106345B1 (ko) | 후측방 경보 시스템 및 그 제어 방법 | |
| US11634121B2 (en) | Driving assistance apparatus and driving assistance method for vehicle | |
| JP6432538B2 (ja) | 衝突予測装置 | |
| WO2016204213A1 (ja) | 車両制御装置、及び車両制御方法 | |
| CN114987455A (zh) | 碰撞避免辅助装置 | |
| JP2017194926A (ja) | 車両制御装置、車両制御方法 | |
| CN113544031A (zh) | 驾驶辅助装置 | |
| JP6733616B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置 | |
| KR20200009760A (ko) | 차량용 위험 검출 및 대응 장치와 방법 | |
| EP3774500B1 (en) | Method for obstacle identification |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16814080 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15738513 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16814080 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |