WO2015162814A1 - カーボンブラックおよびゴム組成物 - Google Patents
カーボンブラックおよびゴム組成物 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015162814A1 WO2015162814A1 PCT/JP2014/081165 JP2014081165W WO2015162814A1 WO 2015162814 A1 WO2015162814 A1 WO 2015162814A1 JP 2014081165 W JP2014081165 W JP 2014081165W WO 2015162814 A1 WO2015162814 A1 WO 2015162814A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- carbon black
- aggregate void
- rubber
- δdmp
- dmp
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/02—Elements
- C08K3/04—Carbon
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60C—VEHICLE TYRES; TYRE INFLATION; TYRE CHANGING; CONNECTING VALVES TO INFLATABLE ELASTIC BODIES IN GENERAL; DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS RELATED TO TYRES
- B60C1/00—Tyres characterised by the chemical composition or the physical arrangement or mixture of the composition
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60C—VEHICLE TYRES; TYRE INFLATION; TYRE CHANGING; CONNECTING VALVES TO INFLATABLE ELASTIC BODIES IN GENERAL; DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS RELATED TO TYRES
- B60C1/00—Tyres characterised by the chemical composition or the physical arrangement or mixture of the composition
- B60C1/0016—Compositions of the tread
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L21/00—Compositions of unspecified rubbers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09C—TREATMENT OF INORGANIC MATERIALS, OTHER THAN FIBROUS FILLERS, TO ENHANCE THEIR PIGMENTING OR FILLING PROPERTIES ; PREPARATION OF CARBON BLACK ; PREPARATION OF INORGANIC MATERIALS WHICH ARE NO SINGLE CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS AND WHICH ARE MAINLY USED AS PIGMENTS OR FILLERS
- C09C1/00—Treatment of specific inorganic materials other than fibrous fillers; Preparation of carbon black
- C09C1/44—Carbon
- C09C1/48—Carbon black
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01P—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO STRUCTURAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF SOLID INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
- C01P2006/00—Physical properties of inorganic compounds
- C01P2006/12—Surface area
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K2201/00—Specific properties of additives
- C08K2201/002—Physical properties
- C08K2201/003—Additives being defined by their diameter
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K2201/00—Specific properties of additives
- C08K2201/002—Physical properties
- C08K2201/006—Additives being defined by their surface area
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K2201/00—Specific properties of additives
- C08K2201/011—Nanostructured additives
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a carbon black capable of imparting low heat build-up to a compounded rubber, particularly a carbon black suitable for a tire tread rubber used under severe driving conditions, and a rubber composition.
- Carbon black for rubber reinforcement there are various varieties depending on the characteristics, and these characteristics are the main factors for determining various performances of rubber. Carbon black has been selected that has properties suitable for component applications.
- rubber members that require a high degree of reinforcement such as tire tread parts, have conventionally had high structures such as SAF (N110) and ISAF (N220), which have a small primary particle diameter, a large specific surface area, and a high structure.
- SAF N110
- ISAF ISAF
- Hard carbon black has been used, but rubber obtained from a rubber composition formed by blending these carbon blacks has a technical problem that heat generation characteristics are likely to increase while providing high reinforcement.
- the rubber composition achieves low heat generation rubber properties by blending carbon black with a large equivalent diameter of secondary particles formed by agglomeration and polymerization of primary particles and a small specific surface area. ing.
- the tread portion of the fuel-efficient tire is required to have a rubber having excellent reinforcement and low heat generation.
- the carbon black compounded to improve the reinforcement and heat generation are improved.
- the particle size and specific surface area are completely different and are in a contradictory relationship, so it is possible to obtain the desired rubber composition by adjusting the particle size and specific surface area of the carbon black to be blended Have difficulty.
- the present invention provides a completely new carbon black that can improve rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties, and a rubber composition that can improve rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties. It is intended to provide.
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp (nm) required by the mercury intrusion method As a result of intensive studies by the present inventors to solve the above technical problem, the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp (nm) required by the mercury intrusion method, the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp (nm) and the mercury intrusion method are used.
- the above technical problem is achieved by the carbon black satisfying a certain relationship between the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution / the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp defined by the half-value width ⁇ Dmp (nm) of the obtained aggregate void diameter distribution.
- the inventors have found that the present invention can be solved, and have completed the present invention based on this finding.
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp obtained by the mercury intrusion method is 25 nm to 60 nm
- Aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp / aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp / aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp determined by mercury intrusion method is 0.30 to Carbon black, characterized by being 0.56
- the carbon black according to the above (1) having a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 60 m 2 / g to 180 m 2 / g and a DBP absorption of 90 ml / 100 g to 140 ml / 100 g
- a rubber composition comprising 30 to 100 parts by mass of the carbon black described in (1) above with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution / aggregate void mode diameter Dmp is appropriately changed to “ ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp”
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution is appropriately changed to“ ⁇ Dmp ”
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp will be referred to as“ mode diameter Dmp ”.
- a completely new carbon black capable of improving rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties is provided, and further a rubber composition capable of improving rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties is provided. be able to.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by a mercury intrusion method of 25 nm to 60 nm, Aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp / aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp / aggregate void diameter distribution half value width ⁇ Dmp determined by mercury intrusion method is 0.30 to It is characterized by 0.56.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by a mercury intrusion method of 25 nm or more, preferably 30 nm or more, and more preferably 35 nm or more.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by a mercury intrusion method of 60 nm or less, preferably 55 nm or less, more preferably 50 nm or less.
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp is obtained when the distribution of the diameters of the voids (aggregate void diameter distribution) formed between the aggregates (aggregates) in which the carbon black basic particles are irregularly and complicatedly fused and bonded is obtained.
- Means the diameter (mode diameter) indicating the maximum frequency, and the mode diameter serves as an index of the form, size, distribution state, and the like of the aggregate.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by the mercury intrusion method that satisfies the above-mentioned definition, it has an agglomerated structure with an essentially developed structure.
- the interaction with the rubber polymer is increased, and the network of carbon black particle aggregates formed in the rubber composition is also increased. Therefore, sufficient reinforcement can be imparted to the rubber composition.
- Carbon black having an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp satisfying the above-mentioned regulations is such that a hydrocarbon gas is supplied into a fluidized bed reactor to generate a gas flow, and the primary particle size separately introduced into the fluidized bed reactor is small.
- the raw material carbon black having a large surface area and a high structure, such as HAF (N330) and ISAF (N220), can be produced by stirring and flowing under heating with the above gas flow.
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp is a mercury porosimeter (micrometer) using a carbon black pellet having a particle size of 250 to 500 ⁇ m dried according to JIS K6218 “Testing method for incidental properties of carbon black for rubber” as a sample. Place 0.14 g of sample in a special cell (3 cm 3 ) of AutoPore IV 9500 made by Tick, pressurize the pressure to 25 to 30000 psi and press in between the mercury inside the cell and the electrode outside the cell This means the void diameter indicating the maximum frequency when the aggregate void diameter distribution is determined from the amount of injected mercury determined from the change in capacitance.
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution obtained by the mercury intrusion method is preferably 12 nm or more, more preferably 13 nm or more, and even more preferably 14 nm or more.
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate pore diameter distribution obtained by the mercury intrusion method is preferably 24 nm or less, more preferably 22 nm or less, and 20 nm or less. Further preferred.
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution obtained by the mercury intrusion method satisfies the above-mentioned definition, the following ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp can be easily controlled within a desired range. can do.
- Carbon black in which the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution satisfies the above-mentioned regulations is the primary particles introduced separately into the fluidized bed reactor by supplying a hydrocarbon gas into the fluidized bed reactor to generate a gas flow.
- Raw material carbon black such as HAF (N330) and ISAF (N220) having a small diameter, a large surface area, and a high structure can be produced by stirring and flowing under heating with the above gas flow.
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution is a frequency that is 50% of the maximum frequency in the aggregate void diameter distribution obtained when the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp is obtained by the above-described method. It means a difference in the aggregate void diameter of two large and small points.
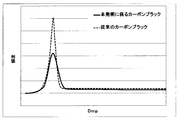
- FIG. 1 shows an aggregate void size distribution of carbon black according to the present invention and an aggregate void size distribution of conventional carbon black.
- the carbon black according to the present invention shows a relatively broad distribution compared to the conventional carbon black
- the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution is also compared with the conventional carbon black. It can be seen that it takes a large value.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by the mercury intrusion method and ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by the half value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution determined by the mercury intrusion method. 30 or more, and preferably 0.31 or more. Further, the carbon black according to the present invention has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by the mercury intrusion method and ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by a half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution determined by the mercury intrusion method. It is 0.56 or less, preferably 0.50 or less, and more preferably 0.45 or less.
- the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp determined by the mercury intrusion method satisfies the above-mentioned definition, and further, the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp required by the mercury intrusion method and the aggregate void mode
- ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the diameter distribution satisfies the above definition
- sufficient reinforcement can be imparted, An increase in heat generation can be suitably suppressed.
- the carbon black according to the present invention preferably has a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 60 m 2 / g or more, more preferably 70 m 2 / g or more, and still more preferably 75 m 2 / g or more. Further, the carbon black according to the present invention preferably has a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 180 m 2 / g or less, more preferably 170 m 2 / g or less, and still more preferably 160 m 2 / g or less. .
- the nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of the carbon black according to the present invention satisfies the above stipulation, sufficient reinforcement is easily imparted to the resulting rubber composition when used as a compounding component of the rubber composition. In addition, the increase in heat generation can be more suitably suppressed.
- nitrogen adsorption specific surface area means the value measured by iodine adsorption amount prescribed
- the carbon black according to the present invention preferably has a DBP (Dibutylphthalate) absorption of 90 ml / 100 g or more, more preferably 95 ml / 100 g or more, and even more preferably 100 ml / 100 g or more.
- the carbon black according to the present invention preferably has a DBP (Dibutylphthalate) absorption of 140 ml / 100 g or less, more preferably 135 ml / 100 g or less, and further preferably 130 ml / 100 g or less.
- the rubber composition obtained by suitably dispersing the carbon black when used as a compounding component of the rubber composition provides sufficient reinforcement.
- DBP absorption amount means a value measured by a method defined in JIS K6217-4 2008 “Basic Test Method for Carbon Black for Rubber”.
- the method for producing carbon black according to the present invention is not particularly limited.
- raw material carbon introduced separately into the fluidized bed reactor by supplying a hydrocarbon gas into the fluidized bed reactor to generate a gas flow.
- Black can be produced by stirring and flowing under heating with the gas flow (a method for producing carbon black according to this method is hereinafter referred to as carbon black production method A).
- the hydrocarbon gas supplied into the fluidized bed reactor may be one or more selected from aromatic hydrocarbon gases such as benzene, toluene, xylene, naphthalene and anthracene.
- the raw material carbon black may be appropriately selected from commercially available products, and preferably, the primary particle diameter of carbon black such as HAF (N330), ISAF (N220) is small and the surface area is large. What is necessary is just to select suitably from the hard type
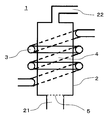
- Examples of the fluidized bed reactor used in the carbon black production method A include those shown in FIG.
- the fluidized bed reactor 1 shown in FIG. 2 has a substantially cylindrical shape, and the furnace axis extends in the vertical direction.
- the fluidized bed reactor 1 shown in FIG. 2 has a gas inlet 21 for supplying hydrocarbon gas from the lower part of the reactor main body 2 toward the upper part and an exhaust port 22 at the upper part of the reactor main body 2. It is.
- the fluidized bed reactor 1 has a heater coil 3 in which a heating wire is spirally wound around the entire outer periphery of the furnace wall of the reactor main body 2, and is provided inside the reactor main body 2.
- the stirring area 4 can be heated.
- a hydrocarbon gas is supplied to a fluidized bed reactor to generate a gas flow.
- the hydrocarbon gas is preferably supplied into the fluidized bed reactor in a preheated state.
- the preheating temperature is preferably 400 ° C. or higher, more preferably 450 ° C. or higher, and further preferably 480 ° C. or higher.
- the preheating temperature is preferably 600 ° C. or lower, more preferably 550 ° C. or lower, and further preferably 520 ° C. or lower.
- the hydrocarbon gas is preferably supplied so as to be 8.5 Nm 3 / hour or less in a fluidized bed reactor per 100 g of the raw material carbon black, and is supplied so as to be 8.0 Nm 3 / hour or less. Is more preferable, and it is more preferable to supply so that it may become 7.8 Nm ⁇ 3 > / hour or less.
- an aggregate having desired voids is formed by controlling the amount of the hydrocarbon gas supplied, and the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp and the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution / aggregate void Carbon black whose mode diameter Dmp is controlled within a desired range can be easily produced.
- the hydrocarbon gas introduced into the fluidized bed reactor is preferably supplied so that the pressure at the gas inlet is 1.0 MPa or more, more preferably 1.1 MPa or more. Preferably, it is more preferable to supply so that it may become 1.2 MPa or more.
- the hydrocarbon gas introduced into the fluidized bed reactor is preferably supplied so that the pressure at the gas inlet is 2.0 MPa or less, more preferably 1.8 MPa or less. More preferably, the supply is performed so that the pressure is 1.5 MPa or less.
- hydrocarbon gas is supplied from the gas inlet 21.
- the hydrocarbon gas may be supplied in a state where the raw material carbon black is previously introduced into the reaction furnace, or after the hydrocarbon gas is supplied into the reaction furnace, it is separately provided in the reaction furnace.
- Raw material carbon black may be introduced from the supply port.
- raw material carbon black those commercially available as HAF (N330), ISAF (N220) or the like can be used as appropriate.
- the raw material carbon black introduced into the reaction furnace is stirred and fluidized under heating by a gas flow of hydrocarbon gas.
- the heating temperature is preferably 500 ° C. or higher, more preferably 550 ° C. or higher, and even more preferably 600 ° C. or higher.
- the heating temperature is preferably 750 ° C. or less, more preferably 720 ° C. or less, and further preferably 700 ° C. or less.
- the stirring and flowing time is preferably 100 seconds or more, more preferably 110 seconds or more, and further preferably 120 seconds or more.
- the stirring and flowing time is preferably 300 seconds or shorter, more preferably 280 seconds or shorter, and further preferably 250 seconds or shorter.
- hydrocarbon gas is supplied into the furnace under heating, and the raw carbon black is stirred and fluidized by the gas flow of the hydrocarbon gas to bring them into contact with each other, thereby thermally decomposing hydrocarbon.
- Gas is deposited on the surface of the aggregate that constitutes the raw material carbon black, and further, fusion and polymerization of the aggregates are promoted by stirring by the gas flow of the hydrocarbon gas, so that the primary particle size of the carbon black is It is considered that carbon black composed of aggregates that are largely agglomerated can be obtained as it is.
- hydrocarbon gas is supplied from the gas inlet 21 at the bottom of the reactor 1 under the heating condition by the heater coil 3, By stirring and flowing the raw material carbon black in the stirring region 4 by the gas flow of the hydrocarbon gas, both are brought into contact with each other, whereby the pyrolyzed hydrocarbon gas is brought into contact with the aggregate surface constituting the raw material carbon black in the stirring region 4. It is considered that the target carbon black of the present invention can be obtained by depositing and further promoting fusion and polymerization between the aggregates by stirring with the gas flow of the hydrocarbon gas.
- the reaction can be stopped by stopping the supply of the hydrocarbon gas, preferably introducing nitrogen gas, and naturally cooling the produced carbon black.
- the nitrogen gas, into the fluidized bed reactor it is preferable to supply such that 6.5 Nm 3 / hr or more, it is more preferable to supply such a 7 ⁇ 0 Nm 3 / h or more, 7.5 nm It is more preferable to supply at 3 / hour or more.
- the nitrogen gas, into the fluidized bed reactor it is preferable to supply such that 8.5 nm 3 / hour or less, it is more preferable to supply such that the 8 ⁇ 0 Nm 3 / hour or less, 7 It is more preferable to supply so that it may become below 8Nm ⁇ 3 > / hour.
- the target carbon black can be recovered by separating and collecting the cooled carbon black particles using a separation and collection device such as a cyclone or a bag filter.
- the carbon black according to the present invention when used as a compounding component of a rubber composition, the carbon black according to the present invention, which can improve the reinforcing property of the resulting rubber and improve the heat generation characteristics, can be easily produced. can do.
- the target carbon black according to the present invention can be easily produced by fusing raw material carbon blacks using a fluidized bed reactor.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention comprises 30 to 100 parts by mass of the carbon black according to the present invention with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component.
- the rubber component is selected from, for example, diene rubbers such as natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, polybutadiene rubber, isoprene rubber, butyl rubber, chloroprene rubber, and acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer rubber. At least one can be mentioned.
- diene rubbers such as natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, polybutadiene rubber, isoprene rubber, butyl rubber, chloroprene rubber, and acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer rubber. At least one can be mentioned.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention contains the carbon black according to the present invention, and the details of the carbon black contained in the rubber composition are as described above.
- the carbon black according to the present invention has a predetermined aggregate void mode diameter Dmp and ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp is within a predetermined range, so that the rubber composition has excellent low heat generation characteristics and reinforcement. I think it can be done.
- the content ratio of the carbon black according to the present invention is 30 parts by mass or more with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component and 35 parts by mass or more with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component. Is more preferable.
- the carbon black content according to the present invention is 100 parts by mass or less with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component and 90 parts by mass or less with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component. It is preferable that it is 80 parts by mass or less with respect to 100 parts by mass of the rubber component.
- the content ratio of the carbon black according to the present invention is a content satisfying the above-mentioned definition, it is possible to obtain a rubber composition excellent in reinforcing property and heat generation property.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention preferably contains 60% by mass or more, more preferably 70% by mass or more, and more preferably 75% by mass or more of the rubber component and the carbon black according to the present invention. More preferably.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention preferably contains 100% by mass or less, more preferably 99% by mass or less, and more preferably 98% by mass or less of the rubber component and the carbon black according to the present invention. More preferably, it is more preferably 97% by mass or less.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention requires commonly used inorganic reinforcing materials, silane coupling agents, vulcanizing agents, vulcanization accelerators, anti-aging agents, vulcanizing aids, softeners, plasticizers, and the like. Ingredients may be included.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention preferably contains 1% by mass or more of the necessary components, more preferably 2% by mass or more, and further preferably 3% by mass or more. Further, the rubber composition according to the present invention preferably contains the above-mentioned necessary components in a total amount of 40% by mass or less, more preferably 30% by mass or less, and further preferably 25% by mass or less. .
- the rubber composition according to the present invention comprises a desired amount of the carbon black and, if necessary, an inorganic reinforcing material, a silane coupling agent, a vulcanizing agent, a vulcanization accelerator, an anti-aging agent, a vulcanizing aid, and a softening agent.
- the desired amount of plasticizer and the like can be obtained by kneading with the rubber component.
- the kneading can be performed using a kneader such as a known mixer or mill.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention can be molded into a predetermined shape and then appropriately heated and cured at 130 to 180 ° C. to obtain a desired rubber molded body.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention can improve the heat generation characteristics of the resulting rubber, and the reinforcing property and heat generation are improved in a well-balanced manner. Therefore, the rubber composition according to the present invention is preferably used as a rubber composition for tire treads. Can do.
- Example 1 Carbon black was produced using a fluidized bed reactor 1 having a substantially cylindrical shape with the furnace axis extending in the vertical direction shown in FIG.
- the fluidized bed reactor 1 shown in FIG. 2 has a casing made of SUS304 and an inner wall made of mullite, and the reactor main body 2 constituting the fluidized bed reactor 1 is carbonized from the bottom toward the top.
- a gas inlet 21 inner diameter: 50 mm
- an exhaust port 22 inner diameter: 30 mm
- the fluidized bed reactor 1 has a heater coil 3 in which a heating wire is spirally wound around the entire outer periphery of the furnace wall of the reactor main body 2, and a stirring region 4 inside the reactor main body 2. It has a structure capable of heating (inner diameter 100 mm, height 200 mm).
- a SUS filter 5 (mesh interval 0.2 mm) was installed at the connecting portion between the reactor main body 2 and the gas inlet 21.
- the stirring zone 4 After introducing 100 g of raw material carbon black 1 (with a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 90 m 2 / g and a DBP absorption of 106 ml / 100 g) into the stirring zone 4 of the fluidized bed reactor 1, the stirring zone 4 is used as a heater coil.
- the hydrocarbon gas (city gas 13A: specific gravity 0.638, CH 4 89.6%, calorific value 45 MJ / m 3 ) heated to 700 ° C. by 3 and then preheated to 500 ° C.
- the obtained carbon black 1 has a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area, DBP absorption, aggregate void mode diameter Dmp, aggregate void diameter distribution half width ⁇ Dmp, and aggregate void mode diameter Dmp and half width of aggregate void diameter distribution.
- Table 1 shows ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by ⁇ Dmp.
- Example 2 to Example 6 The raw material carbon black 1 in Example 1, the raw material carbon black 2 in Example 2 (having a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 120 m 2 / g and the DBP absorption amount of 110 ml / 100 g), and the raw material carbon black in Example 3 3 (one with a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 101 m 2 / g and a DBP absorption of 90 ml / 100 g), in Example 4, the raw material carbon black 4 (a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 75 m 2 / g and a DBP absorption of 99 ml / 100 g) 100 g), raw material carbon black 5 (nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 70 m 2 / g, DBP absorption of 89 ml / 100 g), raw material carbon black 6 (nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 71 m 2 / g, DBP absorption) Except for changing the amount to 84 ml / 100 g
- Example 1 (Comparative Example 1) In Example 1, except that the hydrocarbon gas supply amount was changed from 7.2 Nm 3 / h to 0 Nm 3 / h (no hydrocarbon gas was supplied), the same treatment as in Example 1 was carried out to produce a comparative carbon black 1.
- the obtained comparative carbon black 1 has a nitrogen adsorption specific surface area, a DBP absorption amount, an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp, a half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution, and a half of the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp and the aggregate void diameter distribution.
- Table 2 shows ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by the value width ⁇ Dmp.
- the raw material carbon black 1 in the comparative example 1 is the raw material carbon black 5 in the comparative example 2 (the nitrogen adsorption specific surface area is 126 m 2 / g and the DBP absorption amount is 125 ml / 100 g), and the raw material carbon black in the comparative example 3 6 (nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 62 m 2 / g, DBP absorption amount of 81 ml / 100 g), in Comparative Example 4, raw material carbon black 7 (nitrogen adsorption specific surface area of 100 m 2 / g, DBP absorption amount of 110 ml / 100 g) Comparative carbon black 2 to comparative carbon black 4 were obtained in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1, except that each was changed to 100 g).
- Example 7 to 10 The hydrocarbon gas supply amount in Example 1, 6.7 nm 3 / h in Example 7, 7.5Nm 3 / h in Example 8, 8.0 nm 3 / h in Example 9, Example 10
- carbon black 7 to carbon black 10 were obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the temperature was changed to 8.2 Nm 3 / h.
- Table 3 shows ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by the half-value width ⁇ Dmp.
- Comparative Example 5 to Comparative Example 8 The hydrocarbon gas supply amount in Example 1, 5.0 nm 3 / h in Comparative Example 5, 6.0Nm 3 / h in Comparative Example 6, 9.4Nm 3 / h in Comparative Example 7, Comparative Example 8 Comparative carbon black 5 to comparative carbon black 8 were obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the carbon black was changed to 10.5 Nm 3 / h.
- each obtained rubber composition was vulcanized for 35 minutes under a temperature condition of 145 ° C. to form a vulcanized rubber.
- the dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) and the loss factor (tan ⁇ ) were measured by the following method. The results are shown in Tables 6-9. Tables 6 to 9 show the results of dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) and loss coefficient (tan ⁇ ) for each of the Examples and Comparative Examples in which each carbon black used was obtained.
- ⁇ Dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′), loss coefficient (tan ⁇ )> A test piece cut out from each vulcanized rubber and having a thickness of 2 mm, a length of 35 mm, and a width of 5 mm was used, and a viscoelastic spectrometer (VR-7110, manufactured by Ueshima Seisakusho Co., Ltd.) was used.
- the dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) and loss factor (tan ⁇ ) were measured under the measurement conditions of a strain rate of 1.26% and a measurement temperature of 60 ° C.
- the dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) indicates that the greater the value, the higher the reinforcing property, and the loss coefficient (tan ⁇ ) indicates that the smaller the value, the lower the exothermic property.
- FIG. 4 shows the dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) and loss factor (tan ⁇ ) of vulcanized rubbers produced using the carbon blacks obtained in Examples 1 to 10 and Comparative Examples 1 to 8, respectively. Shown in
- the vulcanized rubber produced using each of the carbon blacks obtained in Examples 1 to 10 has an aggregate void mode diameter Dmp of 25 nm or more as carbon black.
- ⁇ Dmp / mode diameter Dmp defined by the aggregate void mode diameter Dmp and the half-value width ⁇ Dmp of the aggregate void diameter distribution is 0.30 to 0.56. Therefore, both have a high dynamic storage elastic modulus (E ′) and a low loss coefficient (tan ⁇ ). Therefore, both the reinforcing property is high and the heat generation property is low, and both are improved in a well-balanced manner. It turns out that it is.
- a completely new carbon black capable of improving rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties is provided, and further a rubber composition capable of improving rubber properties such as reinforcement and heat generation properties is provided.
- the rubber composition according to the present invention can be suitably used for tire tread rubber used particularly under severe driving conditions.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Tires In General (AREA)
- Pigments, Carbon Blacks, Or Wood Stains (AREA)
Abstract
補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善し得る全く新規なカーボンブラックを提供する。 水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56であることを特徴とするカーボンブラックである。
Description
本発明は、配合ゴムに低発熱性を付与することができるカーボンブラック、特に苛酷な走行条件下に使用されるタイヤトレッドゴム用に好適なカーボンブラックと、ゴム組成物に関する。
ゴム補強用のカーボンブラックとしては、具備特性に応じた多様な品種があり、これらの具備特性がゴムの諸性能を決定付けるための主要な因子となるため、ゴム組成物への配合にあたっては、部材用途に適合する特性を有するカーボンブラックが選定されている。
例えば、タイヤトレッド部のような高度の補強性が要求されるゴム部材には、従来から、SAF(N110)、ISAF(N220)などの、一次粒子径が小さく、比表面積が大きい、高ストラクチャーのハード系カーボンブラックが使用されてきたが、これらのカーボンブラックを配合してなるゴム組成物から得られるゴムは、高度の補強性が付与される反面、発熱特性が増大し易いという技術課題を有していた。
近年、省資源、省エネルギーの社会的要求に対応するため低燃費タイヤの開発要請が強く、低燃費タイヤとして好適な、低発熱なゴム特性を発揮するゴム組成物の開発が盛んに行われるようになっており、一般に、ゴム組成物に対して、一次粒子が凝集、重合して成る二次粒子の等価径が大きく、比表面積の小さなカーボンブラックを配合することにより低発熱のゴム特性を達成している。
このように、低燃費タイヤのトレッド部には、補強性に優れるとともに、発熱性が低いゴムが求められているが、補強性を改善するために配合されるカーボンブラックと、発熱性を改善するために配合されるカーボンブラックでは、その粒子径や比表面積が全く異なり、背反関係にあることから、配合するカーボンブラックの粒子径や比表面積を調整することによって所望のゴム組成物を得ることは困難である。
そこで、従来からゴム補強用のカーボンブラックの基本特性として重視されてきた、粒子径、比表面積、ストラクチャーなどの特性要素に加えて、カーボンブラックのコロイダル特性をよりミクロに評価し、特定の物性を有するカーボンブラックをゴム成分に配合することにより、補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善する技術が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1(特開昭62-192468号公報)等参照) 。
このような状況下、本発明は、補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善し得る全く新規なカーボンブラックを提供するとともに、補強性、発熱特性等のゴム特性を改善し得るゴム組成物を提供することを目的とするものである。
上記技術課題を解決するために本発明者等が鋭意検討した結果、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmp(nm)と、同凝集体空隙モード径Dmp(nm)および水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp(nm)により規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpとがそれぞれ一定の関係を満たすカーボンブラックにより、上記技術課題を解決し得ることを見出し、本知見に基づいて本発明を完成するに至った。
すなわち、本発明は、
(1)水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、
前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56である
ことを特徴とするカーボンブラック、
(2)窒素吸着比表面積が60m2/g~180m2/g、DBP吸収量が90ml/100g~140ml/100gである上記(1)に記載のカーボンブラック、
(3)ゴム成分100質量部に対し、上記(1)に記載のカーボンブラックを30質量部~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物、
(4)ゴム成分100質量部に対し、上記(2)に記載のカーボンブラックを30質量部~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物
を提供するものである。
なお、以下、適宜、「凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmp」を「ΔDmp/モード径Dmp」、「凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp」を「ΔDmp」、「凝集体空隙モード径Dmp」を「モード径Dmp」と称するものとする。
(1)水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、
前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56である
ことを特徴とするカーボンブラック、
(2)窒素吸着比表面積が60m2/g~180m2/g、DBP吸収量が90ml/100g~140ml/100gである上記(1)に記載のカーボンブラック、
(3)ゴム成分100質量部に対し、上記(1)に記載のカーボンブラックを30質量部~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物、
(4)ゴム成分100質量部に対し、上記(2)に記載のカーボンブラックを30質量部~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物
を提供するものである。
なお、以下、適宜、「凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmp」を「ΔDmp/モード径Dmp」、「凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp」を「ΔDmp」、「凝集体空隙モード径Dmp」を「モード径Dmp」と称するものとする。
本発明によれば、補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善し得る全く新規なカーボンブラックを提供するとともに、さらに、補強性、発熱特性等のゴム特性を改善し得るゴム組成物を提供することができる。
先ず、本発明に係るカーボンブラックについて説明する。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、
前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56である
ことを特徴とするものである。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、
前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56である
ことを特徴とするものである。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm以上であるものであり、30nm以上であるものが好ましく、35nm以上であるものがより好ましい。また、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、60nm以下であるものであり、55nm以下であるものが好ましく、50nm以下であるものがより好ましい。
凝集体空隙モード径Dmpは、カーボンブラック基本粒子が不規則で複雑に融着結合した凝集体(アグリゲート)間に形成される空隙の径の分布(凝集体空隙径分布)を求めたときに、最大頻度を示す径(モード径)を意味し、当該モード径は、アグリゲートの形態、大きさ、分布状況等の指標となる。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが上記規定を満たすものであることにより、本質的にストラクチャーの発達した凝集構造を有することから、ゴムへの配合過程でゴムポリマーとの相互作用が大きくなり、さらにゴム組成物中で形成されるカーボンブラック粒子凝集体のネットワークも大きくなって、このために、ゴム組成物に十分な補強性を付与することができるとともに、発熱性の増大を好適に抑制することができると考えられる。
凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが上記規定を満たすカーボンブラックは、流動床反応炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給してガス流を生じさせ、上記流動床反応炉内に別途導入した、一次粒子径が小さく、表面積が大きく、かつ高ストラクチャーであるたとえばHAF(N330)、ISAF(N220)等の原料カーボンブラックを、上記ガス流によって加熱下に攪拌、流動すること等により製造することができる。
なお、本出願書類において、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpは、JIS K6218「ゴム用カーボンブラックの付随的性質の試験法」に従って乾燥した粒度250~500μmのカーボンブラックペレットを試料として、水銀ポロシメーター(マイクロメリティック社製、AutoPore IV 9500)の専用セル(3cm3)中に0.14gの試料を入れ、圧力を25~30000psi に加圧して水銀を圧入しつつ、セル内部の水銀とセル外部の電極間の静電容量を測定し、静電容量の変化から求められる圧入水銀量から、凝集体空隙径分布を求めたときの、最大頻度を示す空隙径を意味する。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpが、12nm以上であるものが好ましく、13nm以上であるものがより好ましく、14nm以上であるものがさらに好ましい。また、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpが、24nm以下であるものが好ましく、22nm以下であるものがより好ましく、20nm以下であるものがさらに好ましい。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpが、上記規定を満たすものであることにより、以下に示すΔDmp/モード径Dmpを所望範囲に容易に制御することができる。
凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpが上記規定を満たすカーボンブラックは、流動床反応炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給してガス流を生じさせ、上記流動床反応炉内に別途導入した、一次粒子径が小さく、表面積が大きく、かつ高ストラクチャーであるたとえばHAF(N330)、ISAF(N220)等の原料カーボンブラックを、上記ガス流によって加熱下に攪拌、流動することにより製造することができる。
なお、本出願書類において、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpは、上述した方法により凝集体空隙モード径Dmpを求めた際に得られた凝集体空隙径分布において、最大頻度の50%の頻度となる大小2点の凝集体空隙径の差を意味する。
図1は、本発明に係るカーボンブラックの凝集体空隙径分布と、従来のカーボンブラックの凝集体空隙径分布を示すものである。図1に示すように、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、従来のカーボンブラックに比較して比較的ブロードな分布を示すために、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpも、従来のカーボンブラックに比較して大きな値を取ることが分かる。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、上記水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが、0.30以上であるものであり、0.31以上であるものが好ましい。また、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、上記水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが、0.56以下であるものであり、0.50以下であるものが好ましく、0.45以下であるものがより好ましい。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが上記規定を満たすものであるとともに、さらに、水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび当該凝集体空隙モード径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが上記規定を満たすものであることにより、ゴム組成物の配合成分として使用したときに、十分な補強性を付与することができるとともに、発熱性の増大を好適に抑制することができる。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、窒素吸着比表面積が、60m2/g以上であるものが好ましく、70m2/g以上であるものがより好ましく、75m2/g以上であるものがさらに好ましい。また、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、窒素吸着比表面積が、180m2/g以下であるものが好ましく、170m2/g以下であるものがより好ましく、160m2/g以下であるものがさらに好ましい。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックの窒素吸着比表面積が上記規定を満たすものであることにより、ゴム組成物の配合成分として使用したときに、得られるゴム組成物により十分な補強性を容易に付与することができるとともに、発熱性の増大をより好適に抑制することができる。
なお、本出願書類において、窒素吸着比表面積は、JIS K6217-2 2001「ゴム用カーボンブラックの基本性能の試験方法」に規定される、よう素吸着量により測定される値を意味する。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、DBP(Dibutylphthalate)吸収量が、90ml/100g以上であるものが好ましく、95ml/100g以上であるものがより好ましく、100ml/100g以上であるものがさらに好ましい。また、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、DBP(Dibutylphthalate)吸収量が、140ml/100g以下であるものが好ましく、135ml/100g以下であるものがより好ましく、130ml/100g以下であるものがさらに好ましい。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックのDBP吸収量が上記規定を満たすものであることにより、ゴム組成物の配合成分として使用したときに、カーボンブラックを好適に分散して得られるゴム組成物により十分な補強性を付与することができるとともに、粘度の上昇を抑制して十分な加工性を容易に付与することができる。
なお、本出願書類において、DBP吸収量は、JIS K6217-4 2008「ゴム用カーボンブラックの基本製の試験法」に規定された方法により測定される値を意味する。
次に、本発明に係るカーボンブラックを製造する方法について説明する。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックを製造する方法は、特に限定されないが、例えば、流動床反応炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給してガス流を生じさせ、前記流動床反応炉内に別途導入した原料カーボンブラックを、前記ガス流によって加熱下に攪拌、流動することにより製造することができる(本法によるカーボンブラックの製造方法を、以下、カーボンブラックの製法Aと称する)。
本発明に係るカーボンブラックを製造する方法は、特に限定されないが、例えば、流動床反応炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給してガス流を生じさせ、前記流動床反応炉内に別途導入した原料カーボンブラックを、前記ガス流によって加熱下に攪拌、流動することにより製造することができる(本法によるカーボンブラックの製造方法を、以下、カーボンブラックの製法Aと称する)。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、流動床反応炉中に供給する炭化水素ガスとしては、ベンゼン、トルエン、キシレン、ナフタレン、アントラセン等の芳香族炭化水素のガス等から選ばれる一種以上が挙げられる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、原料カーボンブラックとしては、市販品等から適宜選択すればよく、好適には、HAF(N330)、ISAF(N220)等の、カーボンブラックの一次粒子径が小さく表面積が大きいものであって、かつ高ストラクチャーであるハード系カーボンブラックから適宜選択すればよい。
カーボンブラックの製法Aで使用する流動床反応炉としては、例えば、図2に示されるものを挙げることができる。
図2に示す流動床反応炉1は概略円筒形状を有し、炉軸が垂直方向に伸びるものである。
図2に示す流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の下部から上部方向に向かって炭化水素ガスを供給するガス導入口21を有するとともに、反応炉本体2の上部に排気口22を有するものである。また、図2に示すように流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の炉壁外周全体に電熱線を螺旋状に巻き付けたヒーターコイル3を有し、反応炉本体2の内部に設けられた攪拌領域4を加熱し得る構造を有している。
図2に示す流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の下部から上部方向に向かって炭化水素ガスを供給するガス導入口21を有するとともに、反応炉本体2の上部に排気口22を有するものである。また、図2に示すように流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の炉壁外周全体に電熱線を螺旋状に巻き付けたヒーターコイル3を有し、反応炉本体2の内部に設けられた攪拌領域4を加熱し得る構造を有している。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、流動床反応炉に炭化水素ガスを供給してガス流を生じさせる。
炭化水素ガスは、予熱した状態で流動床反応炉内に供給することが好ましく、この場合、予熱温度は、400℃以上が好ましく、450℃以上がより好ましく、480℃以上がさらに好ましい。また、この場合、予熱温度は600℃以下が好ましく、550℃以下より好ましく、520℃以下がさらに好ましい。
また、炭化水素ガスは、原料カーボンブラック100gあたり、流動床反応炉中に6.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することが好ましく、7・0Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。また、炭化水素ガスは、原料カーボンブラック100gあたり、流動床反応炉中に8.5Nm3/時以下となるように供給することが好ましく、8・0Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.8Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、上記炭化水素ガスの供給量を制御することによって所望の空隙を有する凝集体を形成し、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが所望範囲に制御されたカーボンブラックを容易に製造することができる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、上記炭化水素ガスの供給量を制御することによって所望の空隙を有する凝集体を形成し、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが所望範囲に制御されたカーボンブラックを容易に製造することができる。
加えて、流動床反応炉中に導入する炭化水素ガスは、ガス導入口の圧力が、1.0MPa以上となるように供給することが好ましく、1.1MPa以上となるように供給することがより好ましく、1.2MPa以上となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。また、流動床反応炉中に導入する炭化水素ガスは、ガス導入口の圧力が、2.0MPa以下となるように供給することが好ましく、1.8MPa以下となるように供給することがより好ましく、1.5MPa以下となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、流動床反応炉として図2に示すものを使用する場合には、ガス導入口21から炭化水素ガスを供給する。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、原料カーボンブラックを予め反応炉内に導入した状態で炭化水素ガスを供給してもよいし、反応炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給した後、反応炉に別途設けた供給口から原料カーボンブラックを導入してもよい。
原料カーボンブラックとしては、HAF(N330)、ISAF(N220)等として市販されているものを適宜使用することができる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、反応炉内に導入された原料カーボンブラックが、炭化水素ガスのガス流によって加熱下に攪拌、流動される。
上記加熱時の温度は、500℃以上が好ましく、550℃以上がより好ましく、600℃以上がさらに好ましい。また、上記加熱時の温度は、750℃以下が好ましく、720℃以下がより好ましく、700℃以下がさらに好ましい。
また、上記攪拌、流動する時間は、100秒間以上が好ましく、110秒間以上がより好ましく、120秒間以上さらに好ましい。上記攪拌、流動する時間は、300秒間以下が好ましく、280秒間以下がより好ましく、250秒間以下がさらに好ましい。
上記加熱時の温度は、500℃以上が好ましく、550℃以上がより好ましく、600℃以上がさらに好ましい。また、上記加熱時の温度は、750℃以下が好ましく、720℃以下がより好ましく、700℃以下がさらに好ましい。
また、上記攪拌、流動する時間は、100秒間以上が好ましく、110秒間以上がより好ましく、120秒間以上さらに好ましい。上記攪拌、流動する時間は、300秒間以下が好ましく、280秒間以下がより好ましく、250秒間以下がさらに好ましい。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、流動床反応炉として図2に示すものを使用する場合には、ガス導入口21から炭化水素ガスを供給した後、ヒーターコイル2によって昇温された攪拌領域4において、原料カーボンブラックを攪拌、混合する。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、加熱下において炉内に炭化水素ガスを供給し、該炭化水素ガスのガス流によって原料カーボンブラックを攪拌、流動することによって両者を接触させることにより、熱分解した炭化水素ガスを原料カーボンブラックを構成するアグリゲートの表面に堆積させ、さらに上記炭化水素ガスのガス流による攪拌によって、アグリゲート同士の融着および重合が促されることにより、カーボンブラックの一次粒子径サイズはそのままに、大きく凝集したアグリゲートによって構成されるカーボンブラックを得ることができると考えられる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいて、図2に示す流動床反応炉1を使用する場合には、ヒーターコイル3による加熱条件下に反応炉1の底部のガス導入口21から炭化水素ガスを供給し、該炭化水素ガスのガス流によって攪拌領域4で原料カーボンブラックを攪拌、流動することによって両者を接触させることにより、攪拌領域4において、熱分解した炭化水素ガスを原料カーボンブラックを構成するアグリゲート表面に堆積させ、さらに上記炭化水素ガスのガス流による攪拌によって、アグリゲート同士の融着および重合が促されることにより、目的とする本発明のカーボンブラックを得ることができると考えられる。
炭化水素ガスによる攪拌後、炭化水素ガスの供給を停止し、好ましくは窒素ガスを導入して、生成したカーボンブラックを自然冷却させることにより反応を停止させることができる。
上記窒素ガスは、流動床反応炉中に、6.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することが好ましく、7・0Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。また、上記窒素ガスは、流動床反応炉中に、8.5Nm3/時以下となるように供給することが好ましく、8・0Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.8Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。
上記窒素ガスは、流動床反応炉中に、6.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することが好ましく、7・0Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.5Nm3/時以上となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。また、上記窒素ガスは、流動床反応炉中に、8.5Nm3/時以下となるように供給することが好ましく、8・0Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがより好ましく、7.8Nm3/時以下となるように供給することがさらに好ましい。
冷却されたカーボンブラック粒子は、サイクロンやバッグフィルター等の分離捕集装置により分離捕集することにより、目的とするカーボンブラックを回収することができる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aによれば、ゴム組成物の配合成分として用いたときに、得られるゴムの補強性を向上させるとともに、発熱特性を向上させることができる本発明に係るカーボンブラックを簡便に製造することができる。
カーボンブラックの製法Aにおいては、流動床反応炉を用い、原料カーボンブラック同士を融着させることにより、目的とする本発明に係るカーボンブラックを容易に製造することができる。
本発明によれば、補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善し得る全く新規なカーボンブラックを提供することができる。
次に、本発明に係るゴム組成物について説明する。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、ゴム成分100質量部に対し、本発明に係るカーボンブラックを30~100質量部含むことを特徴とするものである。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、ゴム成分100質量部に対し、本発明に係るカーボンブラックを30~100質量部含むことを特徴とするものである。
本発明に係るゴム組成物において、ゴム成分としては、例えば、天然ゴム、スチレン-ブタジエンゴム、ポリブタジエンゴム、イソプレンゴム、ブチルゴム、クロロプレンゴム、アクリロニトリル-ブタジエン共重合体ゴムなどのジエン系ゴムから選ばれる少なくとも一種を挙げることができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、本発明に係るカーボンブラックを含むものであり、ゴム組成物中に含まれるカーボンブラックの詳細については上述したとおりである。
そして、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、所定の凝集体空隙モード径Dmpを有し、ΔDmp/モード径Dmpが所定範囲内にあるために、ゴム組成物に優れた低発熱特性と補強性を付与することができると考えられる。
そして、本発明に係るカーボンブラックは、所定の凝集体空隙モード径Dmpを有し、ΔDmp/モード径Dmpが所定範囲内にあるために、ゴム組成物に優れた低発熱特性と補強性を付与することができると考えられる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物において、本発明に係るカーボンブラックの含有割合は、ゴム成分100質量部に対して30質量部以上であり、ゴム成分100質量部に対して35質量部以上であることがより好ましい。また、本発明に係るゴム組成物において、本発明に係るカーボンブラックの含有割合は、ゴム成分100質量部に対して100質量部以下であり、ゴム成分100質量部に対して90質量部以下であることが好ましく、ゴム成分100質量部に対して80質量部以下であることがより好ましい。
本発明に係るゴム組成物において、本発明に係るカーボンブラックの含有割合が上記規定を満たす含有量にあることにより、補強性および発熱性等に優れたゴム組成物を得ることができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物において、本発明に係るカーボンブラックの含有割合が上記規定を満たす含有量にあることにより、補強性および発熱性等に優れたゴム組成物を得ることができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、ゴム成分および本発明に係るカーボンブラックを、合計で、60質量%以上含むものであることが好ましく、70質量%以上含むものであることがより好ましく、75質量%以上含むものであることがさらに好ましい。本発明に係るゴム組成物は、ゴム成分および本発明に係るカーボンブラックを、合計で、100質量%以下含むものであることが好ましく、99質量%以下含むものであることがより好ましく、98質量%以下含むものであることがさらに好ましく、97質量%以下含むものであることが一層好ましい。
また、本発明に係るゴム組成物は、常用される、無機補強材、シランカップリング剤、加硫剤、加硫促進剤、老化防止剤、加硫助剤、軟化剤、可塑剤などの必要成分を含んでもよい。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、上記必要成分を、合計で、1質量%以上含むものであることが好ましく、2質量%以上含むものであることがより好ましく、3質量%以上含むものであることがさらに好ましい。また、本発明に係るゴム組成物は、上記必要成分を、合計で、40質量%以下含むものであることが好ましく、30質量%以下含むものであることがより好ましく、25質量%以下含むものであることがさらに好ましい。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、上記必要成分を、合計で、1質量%以上含むものであることが好ましく、2質量%以上含むものであることがより好ましく、3質量%以上含むものであることがさらに好ましい。また、本発明に係るゴム組成物は、上記必要成分を、合計で、40質量%以下含むものであることが好ましく、30質量%以下含むものであることがより好ましく、25質量%以下含むものであることがさらに好ましい。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、上記カーボンブラックの所望量と、必要に応じ、無機補強材、シランカップリング剤、加硫剤、加硫促進剤、老化防止剤、加硫助剤、軟化剤、可塑剤等の所望量とを、ゴム成分と混練することにより得ることができる。上記混練は、公知のミキサーやミル等の混練機を用いて行うことができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、所定形状に成形した後、適宜、130~180℃で加温して硬化することにより、所望のゴム成形体を得ることができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、得られるゴムの発熱特性を向上させることができ、補強性および発熱性がバランスよく改良されていることから、タイヤトレッド用のゴム組成物として好適に使用することができる。
次に、実施例を挙げて本発明を更に具体的に説明するが、これは単に例示であって、本発明を制限するものではない。
(実施例1)
図2に示す、炉軸が垂直方向に伸びる概略円筒形状を有する流動床反応炉1を用いてカーボンブラックを作製した。
図2に示す流動床反応炉1は、筐体がSUS304、内壁がムライトにより構成されるものであって、流動床反応炉1を構成する反応炉本体2は、下部から上部方向に向かって炭化水素ガスを供給するガス導入口21(内径50mm)を有するとともに、反応炉本体2の上部に排気口22(内径30mm)を有するものである。また、図2に示すように、流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の炉壁外周全体に電熱線を螺旋状に巻き付けたヒーターコイル3を有し、反応炉本体2内部の攪拌領域4(内径100mm、高さ200mm)を加熱し得る構造を有している。
また、反応炉本体2とガス導入口21との連結部には、SUS製フィルタ5(メッシュ間隔0.2mm)を設置した。
図2に示す、炉軸が垂直方向に伸びる概略円筒形状を有する流動床反応炉1を用いてカーボンブラックを作製した。
図2に示す流動床反応炉1は、筐体がSUS304、内壁がムライトにより構成されるものであって、流動床反応炉1を構成する反応炉本体2は、下部から上部方向に向かって炭化水素ガスを供給するガス導入口21(内径50mm)を有するとともに、反応炉本体2の上部に排気口22(内径30mm)を有するものである。また、図2に示すように、流動床反応炉1は、反応炉本体2の炉壁外周全体に電熱線を螺旋状に巻き付けたヒーターコイル3を有し、反応炉本体2内部の攪拌領域4(内径100mm、高さ200mm)を加熱し得る構造を有している。
また、反応炉本体2とガス導入口21との連結部には、SUS製フィルタ5(メッシュ間隔0.2mm)を設置した。
上記流動床反応炉1の攪拌領域4に原料カーボンブラック1(窒素吸着比表面積が90m2/g、DBP吸収量が106ml/100gであるもの)100gを導入した後、上記攪拌領域4をヒーターコイル3によって700℃に加熱し、次いでガス導入口21から500℃に予熱した炭化水素ガス(都市ガス13A:比重0.638、CH489.6%、発熱量45MJ/m3)を7.2Nm3/hで供給してガス導入口の圧力が1.3MPaとなるように供給して、上記原料カーボンブラック1を2分間攪拌、流動した後、ヒーターコイル3による加熱を停止し、室温で冷却することにより、目的とするカーボンブラック1を得た。
得られたカーボンブラック1の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表1に示す。
得られたカーボンブラック1の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表1に示す。
(実施例2~実施例6)
実施例1における原料カーボンブラック1を、実施例2においては原料カーボンブラック2(窒素吸着比表面積が120m2/g、DBP吸収量が110ml/100gであるもの)、実施例3においては原料カーボンブラック3(窒素吸着比表面積が101m2/g、DBP吸収量が90ml/100gであるもの)、実施例4においては原料カーボンブラック4(窒素吸着比表面積が75m2/g、DBP吸収量が99ml/100gであるもの)、原料カーボンブラック5(窒素吸着比表面積が70m2/g、DBP吸収量が89ml/100gであるもの)、原料カーボンブラック6(窒素吸着比表面積が71m2/g、DBP吸収量が84ml/100gであるもの)にそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々カーボンブラック2~カーボンブラック6を得た。
得られたカーボンブラック2~カーボンブラック6の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表1に示す。
実施例1における原料カーボンブラック1を、実施例2においては原料カーボンブラック2(窒素吸着比表面積が120m2/g、DBP吸収量が110ml/100gであるもの)、実施例3においては原料カーボンブラック3(窒素吸着比表面積が101m2/g、DBP吸収量が90ml/100gであるもの)、実施例4においては原料カーボンブラック4(窒素吸着比表面積が75m2/g、DBP吸収量が99ml/100gであるもの)、原料カーボンブラック5(窒素吸着比表面積が70m2/g、DBP吸収量が89ml/100gであるもの)、原料カーボンブラック6(窒素吸着比表面積が71m2/g、DBP吸収量が84ml/100gであるもの)にそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々カーボンブラック2~カーボンブラック6を得た。
得られたカーボンブラック2~カーボンブラック6の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表1に示す。
(比較例1)
実施例1において、炭化水素ガス供給量を7.2Nm3/hから0Nm3/hに変更した(炭化水素ガスを供給しない)以外は、実施例1と同様に処理して比較カーボンブラック1を作製した。得られた比較カーボンブラック1の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表2に示す。
実施例1において、炭化水素ガス供給量を7.2Nm3/hから0Nm3/hに変更した(炭化水素ガスを供給しない)以外は、実施例1と同様に処理して比較カーボンブラック1を作製した。得られた比較カーボンブラック1の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp、および上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表2に示す。
(比較例2~比較例4)
比較例1における原料カーボンブラック1を、比較例2においては原料カーボンブラック5(窒素吸着比表面積が126m2/g、DBP吸収量が125ml/100gであるもの)、比較例3においては原料カーボンブラック6(窒素吸着比表面積が62m2/g、DBP吸収量が81ml/100gであるもの)、比較例4においては原料カーボンブラック7(窒素吸着比表面積が100m2/g、DBP吸収量が110ml/100gであるもの)にそれぞれ変更した以外は、比較例1と同様に処理することにより、各々比較カーボンブラック2~比較カーボンブラック4を得た。
得られた比較カーボンブラック2~比較カーボンブラック4の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表2に示す。
比較例1における原料カーボンブラック1を、比較例2においては原料カーボンブラック5(窒素吸着比表面積が126m2/g、DBP吸収量が125ml/100gであるもの)、比較例3においては原料カーボンブラック6(窒素吸着比表面積が62m2/g、DBP吸収量が81ml/100gであるもの)、比較例4においては原料カーボンブラック7(窒素吸着比表面積が100m2/g、DBP吸収量が110ml/100gであるもの)にそれぞれ変更した以外は、比較例1と同様に処理することにより、各々比較カーボンブラック2~比較カーボンブラック4を得た。
得られた比較カーボンブラック2~比較カーボンブラック4の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表2に示す。
(実施例7~実施例10)
実施例1における炭化水素ガス供給量を、実施例7においては6.7Nm3/h、実施例8においては7.5Nm3/h、実施例9においては8.0Nm3/h、実施例10においては8.2Nm3/hにそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々カーボンブラック7~カーボンブラック10を得た。
得られたカーボンブラック7~カーボンブラック10の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表3に示す。
実施例1における炭化水素ガス供給量を、実施例7においては6.7Nm3/h、実施例8においては7.5Nm3/h、実施例9においては8.0Nm3/h、実施例10においては8.2Nm3/hにそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々カーボンブラック7~カーボンブラック10を得た。
得られたカーボンブラック7~カーボンブラック10の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表3に示す。
(比較例5~比較例8)
実施例1における炭化水素ガス供給量を、比較例5においては5.0Nm3/h、比較例6においては6.0Nm3/h、比較例7においては9.4Nm3/h、比較例8においては10.5Nm3/hにそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々比較カーボンブラック5~比較カーボンブラック8を得た。
得られた比較カーボンブラック5~比較カーボンブラック8の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表4に示す。
実施例1における炭化水素ガス供給量を、比較例5においては5.0Nm3/h、比較例6においては6.0Nm3/h、比較例7においては9.4Nm3/h、比較例8においては10.5Nm3/hにそれぞれ変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に処理することにより、各々比較カーボンブラック5~比較カーボンブラック8を得た。
得られた比較カーボンブラック5~比較カーボンブラック8の窒素吸着比表面積、DBP吸収量、凝集体空隙モード径Dmp、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpおよび上記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpと凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpを表4に示す。
表1~表4に示すように、各実施例および比較例において、凝集体空隙径分布に一定の広がりがあるカーボンブラックを形成することができた。
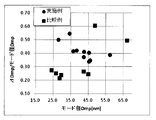
実施例1~実施例10で得られたカーボンブラック1~カーボンブラック10、比較例1~比較例8で得られた比較カーボンブラック1~比較カーボンブラック8において、各凝集体空隙モード径Dmpに対するΔDmp/モード径Dmpの関係を図3に示す。
(ゴム組成物の製造例)
表5に示すように、ゴム成分である天然ゴム(RSS#1)100質量部、上記実施例および比較例で得られた何れかのカーボンブラック45質量部、ステアリン酸3質量部、老化防止剤(川口化学(株)製 アンテージ6C)1質量部、亜鉛華4質量部とを、密閉型ミキサー(神戸製鋼(株)製MIXTRON BB-2)で混練した後、得られた混練物に対し、加硫促進剤(川口化学工業(株)製アクセルNS)0.5質量部と、硫黄1.5質量部とをオープンロールで混練することにより、各々表5に示す組成を有するゴム組成物を得た。
表5に示すように、ゴム成分である天然ゴム(RSS#1)100質量部、上記実施例および比較例で得られた何れかのカーボンブラック45質量部、ステアリン酸3質量部、老化防止剤(川口化学(株)製 アンテージ6C)1質量部、亜鉛華4質量部とを、密閉型ミキサー(神戸製鋼(株)製MIXTRON BB-2)で混練した後、得られた混練物に対し、加硫促進剤(川口化学工業(株)製アクセルNS)0.5質量部と、硫黄1.5質量部とをオープンロールで混練することにより、各々表5に示す組成を有するゴム組成物を得た。
次いで、得られた各ゴム組成物を145℃の温度条件下、35分間加硫して加硫ゴムを形成した。
得られた加硫ゴムを用い、以下に示す方法により、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)、損失係数(tanδ)を測定した。結果を表6~表9に示す。
なお、表6~表9においては、使用した各カーボンブラックが得られた実施例および比較例毎に動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)、損失係数(tanδ)の結果を示している。
得られた加硫ゴムを用い、以下に示す方法により、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)、損失係数(tanδ)を測定した。結果を表6~表9に示す。
なお、表6~表9においては、使用した各カーボンブラックが得られた実施例および比較例毎に動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)、損失係数(tanδ)の結果を示している。
<動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)、損失係数(tanδ)>
得られた各加硫ゴムから切り出した、厚さ2mm、長さ35mm、幅5mmの試験片を用い、粘弾性スペクトロメータ((株)上島製作所製VR-7110)を用い、周波数50Hz、動的歪率1.26%、測定温度60℃の測定条件で、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)および損失係数(tanδ)を測定した。
なお、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)は値が大きいほど補強性が高いことを示し、損失係数(tanδ)は、値が小さいほど発熱性が低いことを示している。
得られた各加硫ゴムから切り出した、厚さ2mm、長さ35mm、幅5mmの試験片を用い、粘弾性スペクトロメータ((株)上島製作所製VR-7110)を用い、周波数50Hz、動的歪率1.26%、測定温度60℃の測定条件で、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)および損失係数(tanδ)を測定した。
なお、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)は値が大きいほど補強性が高いことを示し、損失係数(tanδ)は、値が小さいほど発熱性が低いことを示している。
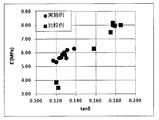
実施例1~実施例10および比較例1~比較例8で得られたカーボンブラックを各々用いて作製された加硫ゴムの動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)および損失係数(tanδ)を図4に示す。
表6、表8および図4の結果から、実施例1~実施例10で得られたカーボンブラックを各々用いて作製された加硫ゴムは、カーボンブラックとして、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが25nm~60nmであるとともに、当該凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが0.30~0.56であるものを用いてなるものであることから、いずれも動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)が高く、損失係数(tanδ)が低いものであり、このため、補強性が高く、発熱性が低いものであって両者がバランス良く改良されてなるものであることが分かる。
一方、表7、表9および図4の結果から、比較例1~比較例8で得られた比較カーボンブラックを各々用いて作製された加硫ゴムは、カーボンブラックとして、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが25nm~60nmの範囲外であるものや(比較例8)、凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定されるΔDmp/モード径Dmpが0.30~0.56の範囲外にあるもの(比較例1~比較例7)を用いてなるものであることから、動的貯蔵弾性率(E’)が低かったり(比較例7、比較例8)、損失係数(tanδ)が高い(比較例1~比較例6)ものであり、このために、補強性が低く、発熱性が高いものであることが分かる。
本発明によれば、補強性、発熱特性などのゴム特性を改善し得る全く新規なカーボンブラックを提供するとともに、さらに、補強性、発熱特性等のゴム特性を改善し得るゴム組成物を提供することができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、特に苛酷な走行条件下に使用されるタイヤトレッドゴム用として好適に使用することができる。
本発明に係るゴム組成物は、特に苛酷な走行条件下に使用されるタイヤトレッドゴム用として好適に使用することができる。
1 流動床反応炉
2 反応炉本体
21 ガス導入口
22 排気口
3 ヒーターコイル
4 攪拌領域
5 フィルタ
2 反応炉本体
21 ガス導入口
22 排気口
3 ヒーターコイル
4 攪拌領域
5 フィルタ
Claims (4)
- 水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、25nm~60nmであるとともに、
前記凝集体空隙モード径Dmpおよび水銀圧入法により求められる凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmpにより規定される、凝集体空隙径分布の半値幅ΔDmp/凝集体空隙モード径Dmpが、0.30~0.56である
ことを特徴とするカーボンブラック。 - 窒素吸着比表面積が60~180m2/g、DBP吸収量が90~140ml/100gである請求項1に記載のカーボンブラック。
- ゴム成分100質量部に対し、請求項1に記載のカーボンブラックを30~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物。
- ゴム成分100質量部に対し、請求項2に記載のカーボンブラックを30~100質量部含むことを特徴とするゴム組成物。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14889916.4A EP3135735A4 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-11-26 | Carbon black and rubber composition |
| US15/305,887 US20170051124A1 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-11-26 | Carbon black and rubber composition |
| CN201480078217.2A CN106232736A (zh) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-11-26 | 炭黑及橡胶组合物 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-088253 | 2014-04-22 | ||
| JP2014088253A JP6233710B2 (ja) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-04-22 | カーボンブラックおよびゴム組成物 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015162814A1 true WO2015162814A1 (ja) | 2015-10-29 |
Family
ID=54331998
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/081165 WO2015162814A1 (ja) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-11-26 | カーボンブラックおよびゴム組成物 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20170051124A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3135735A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6233710B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106232736A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015162814A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7364615B2 (ja) | 2021-04-02 | 2023-10-18 | 住友理工株式会社 | ゴム組成物およびそれを用いたゴム製品、並びにホース |
| WO2024069725A1 (ja) * | 2022-09-27 | 2024-04-04 | 住友理工株式会社 | ゴム組成物およびそれを用いたゴム製品、並びにホース |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107132171B (zh) * | 2017-04-13 | 2019-10-25 | 东北石油大学 | 一种基于压汞-氮吸附联测数据确定致密储层孔径分布的方法 |
| JPWO2019012946A1 (ja) | 2017-07-14 | 2020-07-09 | 株式会社ブリヂストン | ゴム組成物及びタイヤ |
| JP7263090B2 (ja) * | 2019-04-12 | 2023-04-24 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | カーボンブラック、カーボンブラックの製造方法およびゴム組成物 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01201367A (ja) * | 1988-02-05 | 1989-08-14 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | タイヤトレッド用カーボンブラック |
| JPH03121165A (ja) * | 1989-07-13 | 1991-05-23 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | タイヤトレッドゴム用カーボンブラック |
| JPH03149236A (ja) * | 1989-11-06 | 1991-06-25 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴム組成物 |
| JPH07179672A (ja) * | 1993-12-24 | 1995-07-18 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | ゴム組成物 |
| JPH0820674A (ja) * | 1994-07-08 | 1996-01-23 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | 大型タイヤトレッド用ゴム組成物 |
| JPH1036704A (ja) * | 1996-07-22 | 1998-02-10 | Nippon Steel Chem Co Ltd | カーボンブラック及びゴム組成物 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06868B2 (ja) * | 1987-01-21 | 1994-01-05 | 東海カ−ボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP2593113B2 (ja) * | 1991-04-25 | 1997-03-26 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP2729975B2 (ja) * | 1992-12-03 | 1998-03-18 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP3316249B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-04 | 2002-08-19 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP3816541B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-04 | 2006-08-30 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP3283953B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-04 | 2002-05-20 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | ゴム組成物 |
| JP2002327134A (ja) * | 2001-05-07 | 2002-11-15 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | タイヤトレッドゴム用カーボンブラック |
| JP3929838B2 (ja) * | 2002-06-25 | 2007-06-13 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | カーボンブラック及びそのゴム組成物 |
| JP2006022270A (ja) * | 2004-07-09 | 2006-01-26 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | カーボンブラックおよびその製造方法 |
| JP5258010B2 (ja) * | 2004-12-20 | 2013-08-07 | 株式会社ブリヂストン | 天然ゴムマスターバッチおよびその製造方法 |
| JP4947515B2 (ja) * | 2006-10-20 | 2012-06-06 | 東海カーボン株式会社 | 機能性ゴム部品配合用カーボンブラック |
-
2014
- 2014-04-22 JP JP2014088253A patent/JP6233710B2/ja active Active
- 2014-11-26 WO PCT/JP2014/081165 patent/WO2015162814A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2014-11-26 CN CN201480078217.2A patent/CN106232736A/zh active Pending
- 2014-11-26 EP EP14889916.4A patent/EP3135735A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-11-26 US US15/305,887 patent/US20170051124A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01201367A (ja) * | 1988-02-05 | 1989-08-14 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | タイヤトレッド用カーボンブラック |
| JPH03121165A (ja) * | 1989-07-13 | 1991-05-23 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | タイヤトレッドゴム用カーボンブラック |
| JPH03149236A (ja) * | 1989-11-06 | 1991-06-25 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴム組成物 |
| JPH07179672A (ja) * | 1993-12-24 | 1995-07-18 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | ゴム組成物 |
| JPH0820674A (ja) * | 1994-07-08 | 1996-01-23 | Tokai Carbon Co Ltd | 大型タイヤトレッド用ゴム組成物 |
| JPH1036704A (ja) * | 1996-07-22 | 1998-02-10 | Nippon Steel Chem Co Ltd | カーボンブラック及びゴム組成物 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7364615B2 (ja) | 2021-04-02 | 2023-10-18 | 住友理工株式会社 | ゴム組成物およびそれを用いたゴム製品、並びにホース |
| WO2024069725A1 (ja) * | 2022-09-27 | 2024-04-04 | 住友理工株式会社 | ゴム組成物およびそれを用いたゴム製品、並びにホース |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106232736A (zh) | 2016-12-14 |
| EP3135735A4 (en) | 2017-11-29 |
| EP3135735A1 (en) | 2017-03-01 |
| US20170051124A1 (en) | 2017-02-23 |
| JP6233710B2 (ja) | 2017-11-22 |
| JP2015206001A (ja) | 2015-11-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11466139B2 (en) | Carbon and elastomer integration | |
| WO2015162814A1 (ja) | カーボンブラックおよびゴム組成物 | |
| JP5813985B2 (ja) | ゴム物品補強用炭化物の製造方法 | |
| JP5652296B2 (ja) | タイヤ用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP6684607B2 (ja) | カーボンブラック、カーボンブラックの製造方法およびゴム組成物 | |
| JP2017031356A (ja) | スタッドレスタイヤ用ゴム組成物 | |
| NL2020868A (en) | Carbon black and rubber compounds incorporating same | |
| JP5632661B2 (ja) | ゴム補強用炭素材料及びその製造方法 | |
| JP5771686B2 (ja) | ゴム組成物及びタイヤ | |
| JP5672427B2 (ja) | カーボンブラック、カーボンブラックの製造方法およびゴム組成物 | |
| JP2017031381A (ja) | 繊維被覆用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP2003096332A (ja) | ハード系カーボンブラック | |
| JP2005272734A (ja) | タイヤトレッドゴム配合用カーボンブラック | |
| JP6149347B2 (ja) | タイヤ用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP2017031355A (ja) | ビードインシュレーション用ゴム組成物 | |
| WO2015011796A1 (ja) | カーボンブラック、カーボンブラックの製造方法およびゴム組成物 | |
| JP2003292822A (ja) | カーボンブラック及びゴム組成物 | |
| JP7154008B2 (ja) | ゴム組成物および空気入りタイヤ | |
| JP2017075242A (ja) | タイヤベルトクッション用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP2012158659A (ja) | タイヤトレッド用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP2011057904A (ja) | スタッドレスタイヤ用ゴム組成物 | |
| JP2011084695A (ja) | ゴム組成物及び空気入りタイヤ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14889916 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014889916 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014889916 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15305887 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |