WO2015033995A1 - 吸収性物品 - Google Patents
吸収性物品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015033995A1 WO2015033995A1 PCT/JP2014/073315 JP2014073315W WO2015033995A1 WO 2015033995 A1 WO2015033995 A1 WO 2015033995A1 JP 2014073315 W JP2014073315 W JP 2014073315W WO 2015033995 A1 WO2015033995 A1 WO 2015033995A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- absorber
- recess
- sheet
- absorbent
- liquid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/47—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins
- A61F13/475—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means
- A61F13/4758—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means the means preventing fluid flow in a longitudinal direction
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/47—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins
- A61F13/475—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means
- A61F13/4751—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means the means preventing fluid flow in a transversal direction
- A61F13/4756—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means the means preventing fluid flow in a transversal direction the means consisting of grooves, e.g. channels, depressions or embossments, resulting in a heterogeneous surface level
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
- A61F13/51104—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin the top sheet having a three-dimensional cross-section, e.g. corrugations, embossments, recesses or projections
- A61F13/51108—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin the top sheet having a three-dimensional cross-section, e.g. corrugations, embossments, recesses or projections the top sheet having corrugations or embossments having one axis relatively longer than the other axis, e.g. forming channels or grooves in a longitudinal direction
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/56—Supporting or fastening means
- A61F13/5605—Supporting or fastening means specially adapted for sanitary napkins or the like
- A61F13/5611—Supporting or fastening means specially adapted for sanitary napkins or the like using fastening strips, e.g. adhesive, on the undergarment-facing side
Definitions
- the present invention mainly relates to absorbent articles used for incontinence pads, sanitary napkins, cage sheets, medical pads, toiletries, disposable diapers, and the like, and grooves are formed along the longitudinal direction on the surface side.
- the present invention relates to an absorbent article.
- an absorbent body is interposed between a liquid-impermeable back sheet such as a polyethylene sheet or a polyethylene sheet-laminated nonwoven fabric and a liquid-permeable surface sheet such as a nonwoven fabric or a liquid-permeable plastic sheet. It has been known.
- the middle-high portion located at the substantially center portion of the lower layer absorbent body has a recess extending in the longitudinal direction formed at the substantially center on the skin contact surface side, and forms the recess of the middle-high portion.
- the portion has a convex portion on the lower surface of the upper absorbent body that protrudes toward the non-skin contact surface side, and a concave portion on the upper surface of the lower absorbent body that is in contact with the upper absorbent body, and the bottom of the recess is a lower layer absorbent
- an absorbent article which is immersed in the body side, and in which the upper absorbent body and the lower absorbent body are both compacted with an absorbent fiber material in the vicinity of the uneven recess.
- Patent Document 2 discloses an absorbent article in which a recess extending in the longitudinal direction of the absorbent article is formed integrally with the top sheet and the absorbent layer.
- Patent Document 4 an absorbent in which a superabsorbent polymer is mixed inside the absorber, and a part or all of the superabsorbent polymer is unevenly distributed on the peripheral wall and / or bottom surface of the stool pocket.
- a sex product is disclosed.
- Patent Document 5 a first flexible shaft extending along the vertical axis and a pair of second and third flexible shafts extending from the first flexible shaft to both sides in the horizontal axis direction and extending in the vertical axis direction.
- a shaft is located, and the first flexible shaft is a through-hole formed by a non-existing portion of the absorbent fiber between the surface opposite to the body fluid-absorbing surface, and the second and third An absorbent pad is disclosed in which the flexible shaft is a groove formed by a portion where the thickness of the absorbent fiber is thinner than other portions.
- the first flexible shaft is formed by the through-holes, but the top sheet and the back sheet are provided so as to cover the front and back sides of the through-holes. Therefore, there is a problem that it is difficult to maintain the hollow state of the through-holes. That is, there is a possibility that the body fluid cannot be received because the through-hole is crushed only by applying a little external force such as body pressure.
- the users of the incontinence pad in particular vary depending on individual symptoms such as a person who has a small amount of urination at one time but a high frequency, and a person who urinates at a stroke.
- individual symptoms such as a person who has a small amount of urination at one time but a high frequency
- a person who urinates at a stroke For those who have a high frequency, it is troublesome to change the incontinence pad every time urination is performed, so that the absorption performance is not lowered by one urination, and the initial absorption performance is maintained as it is.
- the conventional incontinence pad has a slow absorption speed and often does not provide satisfaction, so it has been required to quickly absorb a large amount of urine discharged at once.
- the main problem of the present invention is to maintain the effect of the groove when absorbing liquid or receiving external force in the absorbent article having a groove formed along the longitudinal direction on the surface side, and reduce the absorption speed.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an absorbent article that does not cause deterioration of wearing feeling.
- an absorbent article in which an absorber is interposed between a liquid-permeable top sheet and a back sheet,
- the absorbent body is formed in a groove shape or a slit shape on the surface of the liquid-permeable surface sheet side along the longitudinal direction of the absorbent article and over a longitudinal range including the body fluid discharge site without being squeezed.
- an absorbent recess By embossing from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet, an embossed portion provided with an embossing width smaller than the groove width of the absorber recess is provided inside the absorber recess along the absorber recess.
- An absorbent article is provided.
- the absorber recess is formed in the absorber without being compressed, and the embossed portion is provided to the absorber recess by embossing from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet. It has been.
- the bottom of the absorber recess is formed when the absorbent recess is formed in a concave groove shape.
- the swell is suppressed to be extremely small as compared with a polymer or pulp having a high density by pressing, and the side surface of the absorbent recess is interspersed with the liquid-permeable surface sheet in the absorbent recess by the embossed portion. Therefore, the expansion of both side surfaces can be kept small. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent the absorbent recess from being blocked by the polymer or the pulp that has expanded during liquid absorption, thereby reducing the absorbability of the body fluid.
- the absorber recess is formed in a slit shape, the absorber does not intervene on the bottom surface of the absorber recess, so that the bottom surface does not expand.
- swelling comes to be suppressed with a liquid-permeable surface sheet similarly to the above-mentioned.
- the emboss width A of the embossed portion is formed smaller than the groove width B of the absorber recess, the liquid-permeable surface sheet interposed in the absorber recess by the embossed portion and the side surface of the absorber recess A gap is provided between them.
- This gap functions as a buffer zone for temporarily storing the body fluid that has passed through the liquid-permeable surface sheet during permeation of the body fluid, and also functions as a buffer region when the absorber absorbs liquid and the side surface of the absorber recess expands. .
- the absorbent concave portion is not formed by pressing, for example, in the case of a concave groove, it is formed by a laminated fiber or a laminated structure of the absorbent, so that compression by the absorbent pressing or hardening by heat fusion, etc. Therefore, the flexibility of the absorbent body can be maintained, and a good wearing feeling can be maintained.
- the embossed portion is provided inside the absorber concave portion by embossing from the surface side of the liquid permeable surface sheet, the liquid permeable surface sheet is interposed in the absorber concave portion, and an external force Even if the liquid is added, the absorber recess for receiving the body fluid is not easily crushed, and the structure for quickly absorbing the body fluid can be maintained.
- the ratio A / B between the emboss width A of the embossed portion and the groove width B of the absorber recessed portion is defined within a certain range, whereby the shape retention of the absorber recessed portion is improved.
- the function of receiving bodily fluids can be further maintained.
- a second sheet is disposed between the liquid-permeable surface sheet and the absorber,
- the embossed portion is provided together with the second sheet.
- one embossed portion is provided at the center in the width direction of the absorber recess, or one embossed portion is provided on each side of the absorber recess. 3.
- An absorbent article according to any one of 3 is provided.
- the invention according to claim 4 defines an arrangement mode of the embossed portion to be provided in the absorber recess. Only one embossed portion may be provided at the center in the width direction of the absorber recess, or one embossed portion may be provided on each side of the absorber recess.
- the absorbent recess is formed only in the center of the absorbent article in the width direction, or is formed in a plurality along the longitudinal direction while being spaced apart in the width direction.
- An absorbent article according to any one of 1 to 4 is provided.
- the arrangement of the absorber recesses formed in the absorber is defined.
- the absorbent body recess can be formed only in the center of the absorbent article in the width direction, or can be formed in a plurality of lines along the longitudinal direction while being separated in the width direction.
- the rear end of the body recess is provided so as to extend to the rear side beyond the hip groove start position on the wearer's crotch side.
- an anti-slip adhesive layer is provided on the outer surface of the back sheet, and the anti-slip adhesive layer is not provided in a region overlapping with the absorber recess.
- An absorbent article as described in 1 above is provided.
- the anti-slip adhesive layer when the anti-slip adhesive layer is provided in a region where the absorber thickness is thin and easily deforms, the absorber recess may be easily deformed with the movement of the underwear. For this reason, in order not to be affected by the movement of the undergarment, an anti-displacement pressure-sensitive adhesive layer is not provided in a region overlapping the absorbent body recess. Moreover, when an adhesive layer is provided in this area
- the effect of the groove can be maintained even when liquid absorption or external force is applied, the absorption speed Does not decrease, and deterioration of the wearing feeling can be prevented.
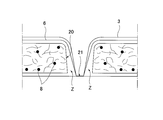
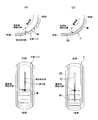
- FIG. 3 is a view taken along line III-III in FIG. It is an expanded sectional view near absorber crevice 20.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of the absorber 4.
- A) is a cross-sectional view showing a permeation state of body fluid
- B) is a cross-sectional view showing an expanded state during liquid absorption. It is an expanded sectional view near absorber crevice 20 concerning other forms.
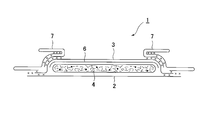
- (A), (B) is a top view of the incontinence pad 1.
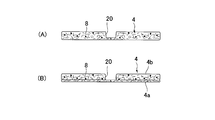
- (A) is a comparative example
- (B) shows the present invention
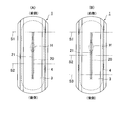
- the upper part is a sectional view of the wearing state
- the lower part is a plan view of the incontinence pad 1 showing the state of wrinkles in the wearing state.
- (A) is a plan view of the incontinence pad 1 showing a folding position in three
- (B) is a folding position in four.
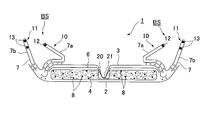
- 2 is a rear view of the incontinence pad 1.
- FIG. It is an expanded sectional view near absorber crevice 20 concerning other forms.
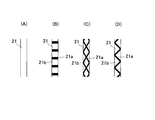
- (A) to (D) are emboss patterns of the embossed portion 21.
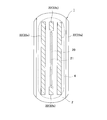
- an incontinence pad 1 includes a liquid-impervious back sheet 2 made of a polyethylene sheet and the like, a liquid-permeable front sheet 3 that allows urine to permeate quickly, and the like.
- An absorbent body 4 made of cotton-like pulp or synthetic pulp interposed between the two sheets 2 and 3 and a hydrophilic substance disposed between the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the absorbent body 4 as necessary.
- the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 and the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 are mainly composed of BS and side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 that form the BS, and at the periphery of the absorbent body 4 at the longitudinal edges.
- the outer edge of the hot melt The liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 and the side nonwoven fabric 7 that are joined by any adhesive or adhesive means such as heat seal and that extend laterally from the absorbent body 4 at both side edges thereof are hot-melted. It is joined by adhesive means such as adhesive or heat seal.
- the absorber 4 can be surrounded by an encapsulating sheet (not shown) such as crepe paper or non-woven fabric in order to maintain the shape and improve the diffusibility.
- the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 is made of a sheet material having at least water-impervious properties such as polyethylene and polypropylene, but in addition to this, a non-woven sheet after securing a substantially liquid-impervious property through a waterproof film.
- a liquid-impervious back sheet is composed of the waterproof film and the nonwoven fabric.
- those having moisture permeability tend to be suitably used from the viewpoint of preventing stuffiness.
- the water- and moisture-permeable sheet material is a microporous material obtained by melting and kneading an inorganic filler in an olefin-based resin such as polyethylene or polypropylene to form a sheet, and then stretching in a uniaxial or biaxial direction.
- a sheet is preferably used.
- the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 is preferably a porous or non-porous nonwoven fabric or a porous plastic sheet.
- the material fibers constituting the nonwoven fabric include synthetic fibers such as polyethylene or polypropylene, synthetic fibers such as polyester and polyamide, recycled fibers such as rayon and cupra, and natural fibers such as cotton.
- a nonwoven fabric obtained by an appropriate processing method such as a lace method, a spun bond method, a thermal bond method, a melt blown method, or a needle punch method can be used. Among these processing methods, the spunlace method is excellent in terms of flexibility and drapeability, and the thermal bond method is excellent in terms of being bulky and soft.
- the absorbent body 4 is composed of, for example, absorbent fibers such as fluffy pulp and the superabsorbent polymer 8, and in the illustrated example, the planar shape is an oblong shape that is long in the longitudinal direction of the pad.
- the superabsorbent polymer 8 is, for example, granular powder, and is dispersed and mixed in the pulp constituting the absorber 4.
- the absorbent body 4 is provided with an absorbent body recess 20 for inflow of body fluid on the surface of the liquid-permeable topsheet 3 side, and this configuration will be described in detail later.
- the pulp examples include chemical fibers obtained from wood, cellulose fibers such as dissolving pulp, and artificial cellulose fibers such as rayon and acetate. It is preferably used in terms of price.
- the encapsulating sheet is interposed between the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the absorbent body 4 as a result, and the above-described excellent absorbency is achieved. The body fluid is quickly diffused by the encapsulating sheet, and the reverse of such urine is prevented.
- the superabsorbent polymer 8 examples include a cross-linked polyacrylate, a self-crosslinked polyacrylate, a saponified acrylate-vinyl acetate copolymer cross-linked product, and a cross-linked isobutylene / maleic anhydride copolymer.
- a crosslinked polysulfonate, and a partially crosslinked water-swellable polymer such as polyethylene oxide and polyacrylamide.
- those based on acrylic acid or acrylate that are excellent in water absorption and water absorption speed are preferred.
- the water-absorbing polymer having the water-absorbing performance can be adjusted in water absorption (absorption capacity) and water absorption speed by adjusting the crosslinking density and the crosslinking density gradient in the production process.
- synthetic fibers may be mixed in the absorber 4.
- synthetic fiber for example, polyolefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene, polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate and polybutylene terephthalate, polyamides such as nylon, and copolymers thereof can be used. It may be a mixture.
- a composite fiber such as a core-sheath fiber, a side-by-side fiber, or a split fiber having a fiber having a high melting point as a core and a fiber having a low melting point as a sheath can also be used.
- hydrophobic fiber it is desirable to use a synthetic fiber that has been surface-treated with a hydrophilizing agent so as to have an affinity for body fluids.
- the second sheet 6 only needs to be hydrophilic to body fluids. Specifically, by using recycled fibers such as rayon and cupra, natural fibers such as cotton, the material itself has hydrophilicity, or synthesis of olefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene, polyesters, polyamides, etc. The fiber which surface-treated with the hydrophilizing agent and provided the hydrophilic property can be used. Further, the second sheet 6 may have a porous film layer on the back surface side (absorbent body 4) in order to give elasticity, and may be a laminated sheet with an encapsulating sheet. You may use the raw material to contain.
- Side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 are provided on both sides of the surface of the incontinence pad 1 along the longitudinal direction and over the entire length of the incontinence pad 1, and the outer portions of the side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 extend laterally.
- the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 is laterally extended, and the side nonwoven fabric 7 portion and the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 portion that are extended to the side are formed by a hot melt adhesive or the like. Joined to form side flaps.
- a water-repellent treated nonwoven fabric or a hydrophilic treated nonwoven fabric can be used from the viewpoint of important functions. For example, if importance is placed on functions such as preventing the penetration of urine, etc. or enhancing the feeling of touch, such as SSMS, SMS, and SMMS coated with a silicon-based, paraffin-based, alkylchromic chloride-based water repellent, etc.
- a water-repellent non-woven fabric It is desirable to use a water-repellent non-woven fabric, and if importance is attached to the absorbability of body fluids, a method of polymerizing a compound having a hydrophilic group, such as an oxidation product of polyethylene glycol, in the synthetic fiber production process, Treating with metal salt such as stannic, partially dissolving the surface to make it porous and making the synthetic fiber swell or porous by applying a metal hydroxide, etc., applying capillary action to impart hydrophilicity It is desirable to use a hydrophilic treated nonwoven fabric. As this side nonwoven fabric 7, what was formed by a proper processing method using natural fiber, synthetic fiber, regenerated fiber, etc. as a raw material can be used.
- a hydrophilic group such as an oxidation product of polyethylene glycol
- the side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 are appropriately folded, and a pair of left and right inner solid gathers 10 and 10 that stand on the skin side with the position near the side edge of the absorbent body 4 as a standing base end, and the inner side relatively
- a pair of left and right outer three-dimensional gathers 11 standing on the skin side formed by the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 and the side nonwoven fabric 7 that are located outside the three-dimensional gather 10 and extend laterally from the absorbent body 4, 11 is a three-dimensional gather BS having a double gather structure.
- the three-dimensional gather BS may have a single gather structure including only the inner three-dimensional gather 10 or the outer three-dimensional gather 11, or a three-dimensional gather standing up on the skin side simply by disposing the side nonwoven fabric 7. It does not have to be formed into a shape.
- the side nonwoven fabric 7 is folded back on both sides in the width direction toward the back side of the pad.
- one or a plurality of double sheet portions 7a and 7b are formed on the outer side, and both ends or appropriate positions in the longitudinal direction are fixed inside the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction.
- One or a plurality of thread elastic elastic members 12 are arranged in the double sheet portion 7b on the outer side in the width direction, and two appropriate positions in the longitudinal direction are fixed.
- the base end portion of the double sheet portion 7 b on the outer side in the width direction extending laterally from the absorbent body 4.
- the inner solid gathers 10 standing on the skin side are formed by the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction, and the skin is formed by the double sheet portion 7b on the outer side in the width direction.
- An outer three-dimensional gather 11 standing on the side is formed. As shown in FIG.
- the side nonwoven fabric 7 is not provided with the elastic elastic members 12 and 13 at both ends in the longitudinal direction of the pad, and the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction is hot. It is joined to the absorber 4 side by a melt adhesive or the like.
- a body fluid inflow groove is formed along the longitudinal direction on the surface side.
- the concave groove receives the bodily fluid discharged on the surface of the liquid-permeable top sheet 3 and temporarily stores the bodily fluid, and induces the diffusion of the bodily fluid in the front-rear direction. As a result, absorption of the bodily fluid into the absorbent body 4 This is to increase the speed and prevent side leakage.
- the said absorber 4 will follow the surface of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 side (surface on the skin side) along a pad longitudinal direction.
- the absorbent body recess 20 formed in a groove shape or a slit shape in the illustrated example without being compressed is provided over a longitudinal range including the body fluid discharge site H.
- the said absorber recessed part 20 is a non-penetrating recessed part which has a bottom face dented from the surrounding absorber to the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 side on the surface on the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 side, and is by compression
- (A) stacked fiber or (B) the lower layer absorber 4a formed with the thickness of the bottom of the absorber recess 20 and a portion corresponding to the absorber recess 20 are opened. It is formed by the laminated structure with the upper layer absorber 4b.
- the embossed portion 21 At least the liquid permeable surface sheet 3 and the absorbent body 4 are laminated by an emboss having a tip width smaller than the groove width of the absorbent body recessed portion 20. It is given from the surface side of the sheet 3.
- the corners formed on the skin side surface of the absorbent body 4 are crushed and rounded by providing the absorbent body recessed portion 20.
- the groove is formed to have a cross-sectional shape having an inclined side surface that is curved so as to bulge inside the concave groove whose width becomes narrower as it goes.
- the concave groove does not disappear completely immediately, but gradually becomes narrower from the bottom surface side, so that the absorption performance of body fluid is somewhat reduced, but to some extent Absorption performance can be maintained.
- the embossed portion 21 is a state in which the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the second sheet 6 are laminated. It is given in one. Further, when the absorbent body 4 is surrounded by the encapsulating sheet, the encapsulating sheet is also embossed with the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3.
- the embossed portion 21 is formed with a smaller dimension in the pad width direction than the absorber concave portion 20. Preferably, it is formed with a small size in the pad width direction and the longitudinal direction, and is provided inside the absorbent body recess 20 without protruding outside the absorbent body recess 20, but may protrude in the longitudinal direction of the pad.
- the embossed portion 21 may be simply applied with pressure without being heat-sealed to the bottom of the absorber recess 20, or contained in the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3, the second sheet 6 and the absorber 4. Synthetic fibers may be heat-sealed or ultrasonically fused, and the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the second sheet 6 may be bonded to the absorber 4.
- the embossed width A of the embossed part 21 is formed smaller than the groove width B of the absorbent body recessed part 20, the surface of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 is formed as shown in FIG. 6 (A).
- the flowing body fluid flows into the embossed portion 21, it passes through the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the second sheet 6 and temporarily enters the buffer zone Z formed between the side surface of the absorber recess 20 and the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3.
- the buffer zone Z formed between the side surface of the absorber recess 20 and the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3.
- the said absorber recessed part 20 is formed without being squeezed, as shown in FIG.6 (B), a bodily fluid osmose
- the said embossed part 21 provided by the embossing from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 is provided with respect to this absorber recessed part 20, both the side surfaces of the absorber recessed part 20 bulge inside.
- liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 interposed in the absorber concave portion 20 acts to firmly press down both side surfaces to be expanded, expansion of both side surfaces can be suppressed to a small level. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent the absorbent recess 20 from being blocked by the polymer 8 or pulp that has expanded during liquid absorption and thus reducing the absorbability of the body fluid.
- the absorbent body recess 20 is formed by the stacked structure of the stacked fibers and the absorbent bodies 4a and 4b without being compressed, so that there is no consolidation due to compression of the absorbent body or hardening due to heat fusion, etc.
- the inherent flexibility of the absorber can be maintained, and a good wearing feeling can be maintained.
- the said embossing part 21 is provided in the inside of the said absorber recessed part 20 by the embossing from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3, the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 interposes in the absorber recessed part 20. In other words, even when an external force is applied, the absorber recess 20 is not easily crushed, and a structure that quickly absorbs body fluid can be maintained.
- the emboss width A of the embossed portion 21 is smaller than the groove width B of the absorber recessed portion 20 (A ⁇ B), and the embossed width A of the embossed portion 21 and the absorber recessed portion 20 are formed.
- the ratio A / B to the groove width B is 0.5 or more and less than 1, and preferably 0.6 or more and less than 0.83.
- surfaces may be formed in an inclined shape in consideration of draft, but in that case, the groove width B of the said absorber recessed part 20 is The width on the bottom side (impermeable liquid back sheet 2 side) of the absorber recess 20 is taken.
- the absorber recess 20 may be formed in the shape of a non-penetrating recess in which the absorber 4 is interposed at the bottom, or as shown in FIG. You may form in the shape of an open penetration type slit which does not intervene from the skin side to the non-skin side.
- the embossed portion 21 is applied to the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3.
- the said absorber recessed part 20 when the said absorber recessed part 20 is formed in the shape of a non-penetrating concave groove, it becomes a press which receives the said embossed part 21, and an embossing enters easily, and an absorber recessed part is more than a through-type slit-shaped thing. This is preferable because the stiffness of 20 becomes strong and is difficult to be crushed.
- one embossed portion 21 is provided at the center in the width direction in the absorber recess 20, or FIG. As shown in FIG. 1, one can be provided on each side of the absorber recess 20. In the latter case, the left and right sides of the absorber recess 20 are restrained by the embossed portions 21 and 21, so that unnecessary portions of the absorber recess 20 are squeezed to prevent the recess 20 from becoming hard.
- the absorbent body recess 20 may be formed with only one strip in the center part of the pad width direction with respect to the absorbent body 4.
- a plurality of strips may be formed along the longitudinal direction.
- the said embossed part 21 is provided with respect to each absorber recessed part 20.
- the dimensions of the absorber recess 20 are preferably such that the length in the longitudinal direction of the pad is 100 to 180 mm and the groove width B is 5 to 30 mm.
- the embossed portion 21 preferably has a length in the pad longitudinal direction of 90 to 170 mm and an emboss width A of 3 to 25 mm.
- the dimension of the embossed portion 21 is formed smaller than the size of the absorber concave portion 20, but if the longitudinal dimension is reduced by about 20 mm and the groove width by about 5 mm for operation, the embossed portion 21 is easily formed.
- the position of the rear end portion of the absorber recess 20 will be described with reference to FIG. 9.
- the incontinence pad 1 is curved along the curve so as to bulge to the non-skin surface side with respect to the longitudinal direction, and a plurality of wrinkles are formed along the width direction on the pad surface side along with the curvature.
- FIG. 9 (A) if the rear end of the absorber concave portion is in front of the hip groove start position on the crotch side of the wearer, the rear end portion of the absorber concave portion and the width direction are aligned.
- the ridges thus formed are continuous, and it is easy to form a recess as if the rear end of the absorber recess extends to both sides in the width direction.
- the body fluid flows through the absorber recess from the body fluid discharge part to the rear side, the body fluid moves in the width direction through the ridge extending from the rear end of the absorber recess before being absorbed by the absorber. As a result, side leakage is likely to occur.
- the rear end of the absorber recess 20 extends beyond the hip groove start position on the crotch side of the wearer to the rear side (the rear side of the crotch portion of the underwear). It is preferable to provide in.
- the absorber thickness of the absorber recess 20 is small, even if the pad is curved along the roundness of the flange portion, the pad recess in the pad width direction is not formed in the absorber recess 20 and the absorber recess 20 Since the body fluid is provided continuously to the rear end portion without being divided by the fluid, the body fluid surely flows to the rear side through the absorber concave portion 20 and is absorbed by the absorber 4 in the process of reaching the rear end. Side leakage and rear leakage will not occur.
- FIG. 10 (A) shows a case where the incontinence pad 1 is folded in three in the width direction folding lines S1 and S2, and FIG. 10 (B) shows a case in which the incontinence pad 1 is folded in the width direction folding lines S1 to S3. It is shown.
- this incontinence pad As shown in FIG. 11, a plurality of misalignment-adhering adhesive layers 22, 22... On the outer surface of the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 by an appropriate application pattern for fixing to the underwear. Is formed.
- the anti-slipping adhesive layer 22 is not provided in a region overlapping the absorber recess 20.
- the region where the absorber recess 20 is formed is a region where the absorber is thin and the rigidity is low, and deformation is likely to occur.
- the absorber recess 20 may be deformed along with the movement of the groove, making it impossible to maintain the shape of the recess, and when the underwear is twisted, the adhesive layer is prevented from slipping and the product is twisted as an absorber recess. There is a high possibility that the function of can not be demonstrated. For this reason, by not providing the anti-displacement adhesive layer 22 in the region overlapping with the absorber recess 20, the groove shape of the absorber recess 20 can be maintained, the product can be prevented from twisting, and the body fluid can be reliably absorbed. become.
- the absorbent body recess 20 is preferably longer in the longitudinal direction than the absorbent body recess 20 on both sides of the absorbent body recess 20.
- One or a plurality of strips of adhesive adhesive layers 22a and 22a in the illustrated example are provided over almost the entire length in the direction, and the center portion in the pad width direction is the front and rear ends of the absorber recess 20 It is preferable to provide the anti-slip adhesive layers 22b and 22b along the pad longitudinal direction before and after the position separated from the portion in the pad longitudinal direction.
- the embossed portion 21 is provided by embossing to a depth substantially equal to the bottom surface of the absorber recess 20, As shown in FIG. 12, the bottom surface of the absorber recess 20 may also be applied to a depth that is squeezed at a predetermined depth. As a result, the rigidity of the absorber recess 20 is increased and deformation is less likely to occur, and the volume of the space in the absorber recess 20 is increased, thereby increasing the amount of body fluid that can be temporarily stored, and further absorbing performance. Will increase. Moreover, although a highly water-absorbing polymer etc.
- the emboss 21 is less likely to expand than when not compressed.
- the height h of the bottom of the absorber recess 20 is preferably less than 50% of the height h 0 of the absorbent body 4.
- the basis weight of the bottom of the absorber recess 20 is preferably 0 to 200 g / m 2 .
- the embossed pattern of the embossed portion 21 is formed by the flat groove pattern of (A), and the high-pressed portion 21a and the low-pressed portion 21b of (B) to (C).
- the high pressing portion 21a arranged in a cross shape or a triangular shape is particularly excellent in that the rigidity against an external force is increased.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Orthopedics, Nursing, And Contraception (AREA)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| BR112016003758-8A BR112016003758B1 (pt) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | Artigo absorvente |
| US14/916,457 US10166152B2 (en) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | Absorbent article |
| CN201480048974.5A CN105517518B (zh) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | 吸收性物品 |
| EP14842149.8A EP3042640B1 (en) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | Absorbent article |
| KR1020167008105A KR102353425B1 (ko) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | 흡수성 물품 |
| RU2016111920A RU2664360C2 (ru) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | Впитывающее изделие |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-182857 | 2013-09-04 | ||
| JP2013182857A JP5992381B2 (ja) | 2013-09-04 | 2013-09-04 | 吸収性物品 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015033995A1 true WO2015033995A1 (ja) | 2015-03-12 |
Family
ID=52628461
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/073315 Ceased WO2015033995A1 (ja) | 2013-09-04 | 2014-09-04 | 吸収性物品 |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10166152B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3042640B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5992381B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102353425B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105517518B (enExample) |
| BR (1) | BR112016003758B1 (enExample) |
| RU (1) | RU2664360C2 (enExample) |
| TR (1) | TR201909770T4 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015033995A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017074281A (ja) * | 2015-10-16 | 2017-04-20 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN108348366A (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2018-07-31 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN108348384A (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2018-07-31 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| WO2020235180A1 (ja) * | 2019-05-21 | 2020-11-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Families Citing this family (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5938440B2 (ja) * | 2014-06-13 | 2016-06-22 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| US10806642B2 (en) * | 2014-08-29 | 2020-10-20 | Daio Paper Corporation | Absorbent article with a concave groove |
| JP6479520B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-20 | 2019-03-06 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6412834B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-24 | 2018-10-24 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6641559B2 (ja) * | 2015-11-27 | 2020-02-05 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6232459B2 (ja) * | 2016-03-03 | 2017-11-15 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6868362B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2021-05-12 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2019090291A1 (en) | 2017-11-06 | 2019-05-09 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent article with conforming features |
| JP2019176925A (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP7119501B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2022-08-17 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN110522563A (zh) * | 2018-05-23 | 2019-12-03 | 文宜平 | 婴儿屎尿裤 |
| JP7097287B2 (ja) * | 2018-12-19 | 2022-07-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP7194585B2 (ja) * | 2018-12-26 | 2022-12-22 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN111374834B (zh) * | 2018-12-29 | 2022-10-21 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品用的吸收体以及吸收性物品 |
| JP7322590B2 (ja) * | 2019-08-21 | 2023-08-08 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| US20240261159A1 (en) * | 2021-05-31 | 2024-08-08 | Sumitomo Seika Chemicals Co., Ltd. | Absorbent article |
| US12186170B2 (en) | 2021-06-10 | 2025-01-07 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Sanitary article comprising shaping elements |
| WO2022258187A1 (en) * | 2021-06-10 | 2022-12-15 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Sanitary article comprising shaping elements |
| USD1092727S1 (en) | 2021-06-21 | 2025-09-09 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Sanitary napkin |
| CN113648135B (zh) * | 2021-08-09 | 2022-07-22 | 山东茁彼母婴用品有限公司 | 一种具有打孔型高分子吸水层的尿不湿芯体 |
| JP2024038676A (ja) * | 2022-09-08 | 2024-03-21 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 生理用吸収性物品 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10234775A (ja) * | 1997-02-28 | 1998-09-08 | Uni Charm Corp | 使い捨ての体液吸収性物品 |
| JPH11216161A (ja) * | 1998-01-30 | 1999-08-10 | Uni Charm Corp | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2007117727A (ja) | 2005-09-30 | 2007-05-17 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2010246896A (ja) * | 2009-03-26 | 2010-11-04 | Daio Paper Corp | 補助吸収性物品 |
| JP4683892B2 (ja) | 2004-09-30 | 2011-05-18 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性パッド |
| JP2012005539A (ja) * | 2010-06-22 | 2012-01-12 | Livedo Corporation | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5105884B2 (ja) | 2007-01-17 | 2012-12-26 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5132264B2 (ja) | 2007-11-07 | 2013-01-30 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5132264B1 (enExample) | 1970-09-30 | 1976-09-11 | ||
| US4624666A (en) * | 1984-07-20 | 1986-11-25 | Personal Products Company | Channeled napkin with dry cover |
| JP3956358B2 (ja) * | 2002-07-19 | 2007-08-08 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | 吸収コアおよびこれを備えた使い捨て吸収性物品 |
| JP5089435B2 (ja) * | 2008-02-29 | 2012-12-05 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5452960B2 (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2014-03-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品及び吸収性物品の製造方法 |
-
2013
- 2013-09-04 JP JP2013182857A patent/JP5992381B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-09-04 EP EP14842149.8A patent/EP3042640B1/en active Active
- 2014-09-04 RU RU2016111920A patent/RU2664360C2/ru active
- 2014-09-04 TR TR2019/09770T patent/TR201909770T4/tr unknown
- 2014-09-04 BR BR112016003758-8A patent/BR112016003758B1/pt active IP Right Grant
- 2014-09-04 KR KR1020167008105A patent/KR102353425B1/ko active Active
- 2014-09-04 CN CN201480048974.5A patent/CN105517518B/zh active Active
- 2014-09-04 WO PCT/JP2014/073315 patent/WO2015033995A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-09-04 US US14/916,457 patent/US10166152B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10234775A (ja) * | 1997-02-28 | 1998-09-08 | Uni Charm Corp | 使い捨ての体液吸収性物品 |
| JPH11216161A (ja) * | 1998-01-30 | 1999-08-10 | Uni Charm Corp | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP3406214B2 (ja) | 1998-01-30 | 2003-05-12 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP4683892B2 (ja) | 2004-09-30 | 2011-05-18 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性パッド |
| JP2007117727A (ja) | 2005-09-30 | 2007-05-17 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5105884B2 (ja) | 2007-01-17 | 2012-12-26 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5132264B2 (ja) | 2007-11-07 | 2013-01-30 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2010246896A (ja) * | 2009-03-26 | 2010-11-04 | Daio Paper Corp | 補助吸収性物品 |
| JP2012005539A (ja) * | 2010-06-22 | 2012-01-12 | Livedo Corporation | 吸収性物品 |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017074281A (ja) * | 2015-10-16 | 2017-04-20 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN108348366A (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2018-07-31 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN108348384A (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2018-07-31 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| TWI703967B (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2020-09-11 | 日商優你 嬌美股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN108348384B (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2020-10-09 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN108348366B (zh) * | 2015-11-09 | 2020-10-30 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| WO2020235180A1 (ja) * | 2019-05-21 | 2020-11-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2020188908A (ja) * | 2019-05-21 | 2020-11-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP7109403B2 (ja) | 2019-05-21 | 2022-07-29 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3042640A1 (en) | 2016-07-13 |
| JP2015047432A (ja) | 2015-03-16 |
| TR201909770T4 (tr) | 2019-07-22 |
| BR112016003758A2 (pt) | 2017-08-01 |
| US10166152B2 (en) | 2019-01-01 |
| RU2664360C2 (ru) | 2018-08-16 |
| EP3042640A4 (en) | 2017-04-12 |
| US20160213525A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 |
| KR20160052599A (ko) | 2016-05-12 |
| BR112016003758B1 (pt) | 2021-12-21 |
| CN105517518B (zh) | 2019-06-14 |
| JP5992381B2 (ja) | 2016-09-14 |
| RU2016111920A (ru) | 2017-10-05 |
| RU2016111920A3 (enExample) | 2018-06-05 |
| CN105517518A (zh) | 2016-04-20 |
| KR102353425B1 (ko) | 2022-01-19 |
| EP3042640B1 (en) | 2019-06-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5992381B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2015047432A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP6031428B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6169338B2 (ja) | 吸収体及びこれを用いた吸収性物品 | |
| JP4653537B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5938440B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| CN109152679B (zh) | 吸收性物品 | |
| JP2015089382A5 (enExample) | ||
| WO2016031668A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2015099121A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品の製造方法 | |
| JP6484416B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6138872B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6081422B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2017029352A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2017169967A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6441621B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2010088528A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6073619B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6254030B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6326229B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP3865565B2 (ja) | 前漏れ防止効果の高い吸収性物品 | |
| JP6152517B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5007187B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14842149 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14916457 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112016003758 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: IDP00201601790 Country of ref document: ID |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167008105 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016111920 Country of ref document: RU Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014842149 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014842149 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112016003758 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20160222 |