WO2014156183A1 - 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法および製造装置 - Google Patents
酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法および製造装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014156183A1 WO2014156183A1 PCT/JP2014/001824 JP2014001824W WO2014156183A1 WO 2014156183 A1 WO2014156183 A1 WO 2014156183A1 JP 2014001824 W JP2014001824 W JP 2014001824W WO 2014156183 A1 WO2014156183 A1 WO 2014156183A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- acidic gas
- humidity
- gas separation
- film
- roll
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0002—Organic membrane manufacture
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/22—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by diffusion
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0002—Organic membrane manufacture
- B01D67/0009—Organic membrane manufacture by phase separation, sol-gel transition, evaporation or solvent quenching
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0002—Organic membrane manufacture
- B01D67/0009—Organic membrane manufacture by phase separation, sol-gel transition, evaporation or solvent quenching
- B01D67/00091—Organic membrane manufacture by phase separation, sol-gel transition, evaporation or solvent quenching by evaporation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0081—After-treatment of organic or inorganic membranes
- B01D67/0095—Drying
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0081—After-treatment of organic or inorganic membranes
- B01D67/0097—Storing or preservation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D69/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by their form, structure or properties; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D69/10—Supported membranes; Membrane supports
- B01D69/107—Organic support material
- B01D69/1071—Woven, non-woven or net mesh
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D69/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by their form, structure or properties; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D69/14—Dynamic membranes
- B01D69/141—Heterogeneous membranes, e.g. containing dispersed material; Mixed matrix membranes
- B01D69/142—Heterogeneous membranes, e.g. containing dispersed material; Mixed matrix membranes with "carriers"
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/30—Polyalkenyl halides
- B01D71/32—Polyalkenyl halides containing fluorine atoms
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/38—Polyalkenylalcohols; Polyalkenylesters; Polyalkenylethers; Polyalkenylaldehydes; Polyalkenylketones; Polyalkenylacetals; Polyalkenylketals
- B01D71/381—Polyvinylalcohol
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/40—Polymers of unsaturated acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. salts, amides, imides, nitriles, anhydrides, esters
- B01D71/401—Polymers based on the polymerisation of acrylic acid, e.g. polyacrylate
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/76—Macromolecular material not specifically provided for in a single one of groups B01D71/08 - B01D71/74
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/22—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by diffusion
- B01D2053/221—Devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2323/00—Details relating to membrane preparation
- B01D2323/42—Details of membrane preparation apparatus
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a production method and a production apparatus for an acid gas separation composite having an acid gas separation function.
- the composite for carbon dioxide separation used in the membrane separation method contains a carbon dioxide carrier in a carbon dioxide separation layer on a support, and this carrier transports carbon dioxide to the opposite side of the membrane, so-called facilitated transport.
- a carbon dioxide carrier in a carbon dioxide separation layer on a support
- this carrier transports carbon dioxide to the opposite side of the membrane, so-called facilitated transport.
- Dissolving diffusion membrane performs separation based on the difference in solubility in the membrane and the diffusivity in the membrane between carbon dioxide and the substance to be separated, so if the material and physical properties of the membrane are determined, the degree of separation Is uniquely determined, and the permeation rate of the mixed gas increases as the film thickness decreases. Therefore, the dissolution diffusion film is generally manufactured as a thin film having a thickness of 1 ⁇ m or less by using a manufacturing method such as a layer separation method or an interfacial polymerization method.
- the facilitated transport membrane dramatically increases the solubility of carbon dioxide by the carbon dioxide carrier in the membrane and transports carbon dioxide in the membrane at a high concentration.
- the carbon dioxide has a high degree of separation, and the carbon dioxide has a high permeation rate.
- the concentration of carbon dioxide in the membrane is high, it is rare that the diffusion rate of carbon dioxide in the membrane becomes rate limiting. Rather, it has a thickness of 10 ⁇ m or more in order to increase the degree of separation from the substance to be separated. A film is preferred.
- Patent Document 1 discloses that an uncrosslinked vinyl alcohol-acrylate copolymer aqueous solution is applied in a film form onto a carbon dioxide permeable support, and the uncrosslinked vinyl alcohol-acrylic acid is applied onto the support. After forming a liquid film of the salt copolymer aqueous solution, the liquid film is heated and cross-linked to form a water-insoluble film, and the water-insoluble film contains a carbon dioxide carrier (a substance having an affinity for carbon dioxide). A method for producing a composite for separating carbon dioxide by absorbing an aqueous solution into a hydrogel membrane is described.
- Patent Document 2 a gelling agent such as agar is added to a coating solution containing a polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylic acid copolymer and an alkali metal carbonate, and a coating solution prepared at 50 ° C. or more is coated on a support. Thereafter, a method for producing a composite for carbon dioxide separation in which a liquid film is cooled and cured is described.
- a step of applying a vinyl alcohol-acrylate copolymer aqueous solution containing no carbon dioxide carrier on a carbon dioxide permeable support At least three steps of forming a water-insolubilized film by heating and crosslinking and absorbing the aqueous solution containing carbon dioxide carrier in the water-insolubilized film are required. Therefore, there is a problem that production efficiency is low, production cost is expensive, and variations in each process are overlapped, so that variation in performance as a composite for carbon dioxide separation has to be large.
- a hydrophilic compound such as a polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylic acid copolymer and an alkali metal carbonate are used. Since the gelling agent is added to the aqueous solution containing the carrier, a gelling agent introduction step and a coating film cooling step are required. Therefore, the manufacturing process tends to be long, and the simplification and efficiency of the process are problems.
- the facilitated transport membrane is composed of a hydrophilic compound such as a hydrophilic polymer and a carbon dioxide carrier such as an alkali metal carbonate, and these are materials having a very large water absorption amount. Even if a dry film is obtained after coating on a support, various problems in production occur in a high humidity environment. For example, when the carbon dioxide separation membrane is produced by roll-to-roll, the gel membrane that has absorbed water during the winding process from the drying furnace outlet sticks to the surface of the pass roll contacting the gel membrane, causing film peeling and process contamination ( Causes adhesion of gel film, wet roll with alkaline aqueous solution, wiping work by painting, film deformation by grip effect).
- a hydrophilic compound such as a hydrophilic polymer
- a carbon dioxide carrier such as an alkali metal carbonate
- the gel film that has absorbed water comes into contact with the support opposite to the coated surface (back surface of the support), causing the gel film and the back surface of the support to stick to each other. It has been clarified by the present inventors that desired performance as a facilitated transport film cannot be obtained due to scratches or irregularities on the film surface.
- the above problems are not limited to the production of a carbon dioxide separation complex having a carbon dioxide separation function, but are common problems in the production of other acid gas separation complexes having a separation function of acid gas.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and the number of steps in which the complex for acidic gas separation having an acidic gas separation promoting layer having a high degree of separation of a predetermined acidic gas in which membrane defects are suppressed is small, and the efficiency is low. It aims at providing the manufacturing method of the complex for acidic gas separation manufactured well, and its manufacturing apparatus.
- the method for producing a complex for acidic gas separation of the present invention rolls a complex for acidic gas separation comprising an acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane having a function of separating acidic gas in a raw material gas on a porous support.
- a drying step in which the liquid film previously applied is dried in a drying furnace to form an acid gas facilitated transport film;
- the humidity of the winding process unit that performs the winding process is measured and managed so that the humidity is 10% or more and 60% or less, and the winding process is performed under the controlled humidity condition.
- humidity is relative humidity.
- the hydrophilic compound is preferably a hydrophilic polymer.
- the hydrophilic polymer is preferably a polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylic acid copolymer.
- the acidic gas carrier contains a compound containing at least one selected from alkali metal carbonates.
- the liquid film is preferably dried by adjusting the temperature so as to gradually increase in the range from 60 ° C. to 120 ° C. from the drying furnace inlet side to the discharge side.
- the production apparatus for producing a complex for acidic gas separation comprises a complex for acidic gas separation comprising an acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane having a function of separating acidic gas in a raw material gas on a porous support.
- Manufacturing equipment for manufacturing a roll-to-roll system An application part for applying a coating solution for forming an acidic gas facilitated transport film on a support in a liquid film thickness of 0.3 mm to 3.0 mm, comprising a hydrophilic compound, an acidic gas carrier and water;
- a drying section for drying the liquid film applied in a drying furnace to form an acidic gas facilitated transport film;
- a winding process unit that winds a complex for acidic gas separation in which an acidic gas facilitated transport film is formed on a support on a winding roll;
- the humidity adjusting means for adjusting the humidity to be 10% or more and 60% or less, Control means for controlling adjustment by the humidity adjusting means.
- the humidity of the winding process unit for winding the complex for acidic gas separation by the winding roll is managed and managed. Since the winding process is performed in a high humidity environment, the acidic gas separation-enhanced transport membrane with high water absorption can be controlled so that it does not absorb too much water, and the acidic gas separation-enhanced transport membrane adheres to the pass roll surface, causing film peeling and process contamination.
- the production method of the present invention does not require a gelling agent such as agar, the addition of the gelling agent and the cooling step after coating the coating liquid required in Patent Document 2 are unnecessary, and the process is simplified. In addition, more efficient manufacturing is possible.
- the method for producing a complex for acidic gas separation of the present invention rolls a complex for acidic gas separation comprising an acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane having a function of separating acidic gas in a raw material gas on a porous support.
- a manufacturing method for manufacturing by the to-roll method including a hydrophilic compound, an acidic gas carrier and water, and a coating liquid adjusting step for adjusting a coating liquid for forming an acidic gas facilitated transport film, and a coating liquid for forming the coating liquid
- an acidic gas separation layer forming coating liquid containing a hydrophilic compound such as a hydrophilic polymer, an acidic gas carrier and water is prepared.
- the viscosity of the coating solution is preferably 0.5 to 5 Pa ⁇ s (500 to 5000 cp), more preferably 1 to 2 Pa ⁇ s (1000 to 2000 cp) from the viewpoint of surface properties after coating and high speed.
- the viscosity at this time is a value at 60 rpm and a liquid temperature of 25 ° C. in a B-type viscometer. If the viscosity is 0.5 Pa ⁇ s or more, the flow of the film after coating can be suppressed and the film thickness can be made uniform. On the other hand, if the viscosity exceeds 5 Pa ⁇ s, it is difficult to remove bubbles from the coating solution, and it becomes difficult to make the film thickness uniform.
- the prepared coating solution for forming an acid gas facilitated transport film is coated on the porous support with a liquid film thickness of 0.3 mm to 3.0 mm. If the liquid membrane is 0.3 mm or more, a sufficient acidic gas separation function can be obtained in the formed acidic gas facilitated transport membrane. Moreover, if a liquid film is 3.0 mm or less, generation
- the thickness of the liquid film is more preferably in the range of 1.0 mm to 2.5 mm, and particularly preferably in the range of 1.0 mm to 2.0 mm.
- the support it is particularly preferable to use a laminated film of a hydrophobic porous film and a nonwoven fabric as an auxiliary support film. Since the mechanical strength can be improved by providing an auxiliary support film, there is an effect that the support film does not wrinkle even when handled in a roll-to-roll coating apparatus, and productivity can also be improved. .
- the coating method is not particularly limited as long as the coating liquid having the above viscosity can be coated with the above thickness. Because of its high viscosity and thick thickness, the most suitable are post-measuring methods such as roll coating and blade coating, in which a large amount of coating solution is transferred onto the support immediately before it is adjusted to the desired thickness by subsequent mechanics. ing. As other coating methods, an extrusion coating method, a dip coating method, a bar coating method, a curtain coating method, or the like may be employed. A plurality of coating methods may be combined. The roll coating method and the blade coating method are also preferable because they are inexpensive in terms of production equipment.
- drying means removing at least a portion of water contained in the liquid film of the coating solution for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film formed on the support in the coating step.
- temperature of the drying furnace is appropriately determined in the range of 60 to 120 ° C. If it is 60 degreeC or more, drying time can be restrained to practical time.
- the high temperature side can be determined as appropriate mainly according to the heat resistance of the support, and is about 120 ° C. here.
- the temperature of the drying furnace is preferably 60 to 90 ° C., more preferably 70 to 80 ° C. from the stability of the film surface.
- various drying methods such as a drying method using warm air and a drying method using an infrared heater can be applied.
- the temperature in the drying furnace may not be uniform as long as it is 60 to 120 ° C.
- the vicinity of the drying furnace inlet is set to 70 ° C.
- the vicinity of the drying furnace center is set to 80 ° C.
- the vicinity of the drying furnace outlet is set to 90 ° C.
- the winding step is a step of winding an acidic gas separation composite formed by forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film on a support on a winding roll.
- the humidity of the winding process section including from the exit of the drying furnace to the winding roll is controlled, and the winding process is performed in an environment where the humidity is 10% or more and 60% or less. . More preferably, the environmental humidity in the winding process is controlled to be 10% or more and 40 or less. If the humidity is 10% or more, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of film cracking in the acidic gas separation facilitated transport film produced after drying.
- the moisture content in the acidic gas separation promoting transport film can be suppressed to 20% or less, so that problems such as the application surface sticking to the transport roll surface can be suppressed. And the occurrence of film defects can be suppressed.
- the moisture content is as follows, assuming that the mass of a 10 cm square facilitated transport membrane in a dew point-20 ° C environment is A, and the mass of a 10 cm square facilitated transport membrane in a 25 ° C, 20% relative humidity environment is B. It is a value calculated by a calculation formula. (BA) ⁇ B ⁇ 100
- the humidity of the winding process part from the drying furnace exit to the winding roll may not be uniform, the winding process passes under the environment where the coating film passes and exists where the humidity is 10% or more and 60% or less. Need to do.
- the ambient temperature is 15 to 35 ° C., preferably 20 to 30 ° C.
- the mass ratio of the water-absorbing polymer and the acidic gas carrier is preferably 1: 9 or more and 2: 3 or less.
- the mass ratio of the hydrophilic polymer to the acidic gas carrier is 1: 9 or more and 2: 3 or less, which means that the coating solution is subjected to temperature conditions of 15 ° C. or more and 35 ° C. or less.
- a viscosity measured value at a rotational speed of 60 rpm is applied to a support at a viscosity of 0.5 Pa ⁇ s to 10 Pa ⁇ s to form a liquid film of an acid gas forming coating solution on the support.
- coating process to perform is enabled.
- the mass ratio of the hydrophilic polymer and the acidic gas carrier is less than 1: 9
- the viscosity measurement value at a rotation speed of 60 rpm is 0.5 Pa ⁇ s or more in the B-type viscosity measurement in a temperature range of 15 ° C. or more and 35 ° C. or less. It is difficult to obtain a coating solution exhibiting viscosity.
- the mass ratio of the hydrophilic polymer to the acidic gas carrier is larger than 2: 3
- the solid content contained in the coating solution becomes cloudy without being uniformly mixed, and in some cases, the fluidity suitable for coating. Will run out.
- the coating solution is applied under a temperature condition of 15 ° C. or more and 35 ° C.
- an acidic gas having a uniform film thickness is applied in the coating process It becomes difficult to form a separation-enhanced transport membrane, and it is difficult to obtain an acid-gas separation-enhanced transport membrane having excellent performance with high acid gas separation efficiency and high acid gas permeation rate. Furthermore, since the mass ratio of the hydrophilic polymer and the acidic gas carrier is 1: 9 or more and 2: 3 or less, the separation degree of the acidic gas with respect to the substance to be separated is high, and the permeation rate of the acidic gas is fast and excellent. An acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane having performance can be obtained.
- the coating step is performed by applying a coating solution for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film in a range of 15 ° C. to 35 ° C. -It is coated on the support with a viscosity of s to 9 Pa.s, and in a particularly preferred embodiment, the viscosity measured at a rotational speed of 60 rpm in the range of 15 to 35 ° C and B-type viscosity is 1 Pa.s or more. It is coated on the support with a viscosity of 5 Pa ⁇ s or less.
- the viscosity measurement value at a rotational speed of 60 rpm in the B-type viscosity measurement is 0.5 Pa ⁇ s or more and 10 Pa ⁇ It becomes easy to apply a coating solution having a viscosity of s or less.
- a roll-to-roll production apparatus using a belt-like (web-like) support has few membrane defects and is high.
- a complex for separating acidic gas with high performance can be produced by a method with high production efficiency and low production cost.
- the winding process is performed in a winding process where the acidic gas separation complex is wound by the winding roll, and the winding process is performed in a controlled humidity environment. Can be controlled so that the acidic gas separation-enhanced transport membrane having a large water content does not absorb too much water.
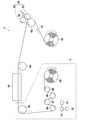
- FIG. 1 schematically shows an example of an apparatus configuration used in the production process of the acidic gas separation composite according to the present invention.
- the apparatus 100 is provided with a feed roll 10 for feeding a belt-like support 12 and a coater 20 for applying a coating solution 30 for forming an acidic gas separation layer on the support 12 (in FIG. 1, it rotates in the direction of the arrow in the figure).
- a drying unit including a drying furnace 40 for drying a membrane (not shown) and a winding process unit 5 including a winding roll 50 that winds up the obtained acidic gas separating composite 52 are provided. Further, transport rolls 62 (also functioning as backup rolls for the roll coater in FIG. 1) and 64 to 69 for transporting the support 12 to the respective parts 20, 40, 50 are arranged.
- a roll-to-roll that is, a support 12 is sent out from the feed roll 10 and the coating process is performed while the support 12 is conveyed, and The drying step is sequentially performed, and the obtained acidic gas separating composite 52 can be wound on the take-up roll 50, and the acidic gas separating composite 52 can be continuously and efficiently manufactured.
- a humidity detector 71 that detects the humidity of the winding A process unit 5 in order to perform humidity management of the winding process unit 5 from the discharge port of the drying furnace 40 to the winding roll 50. And when the humidity detected by the humidity detector 71 is 10% or more and 60% or less, dehumidification or humidification is performed in the process unit 5. And a control unit 73 for controlling the humidity adjusting device 72 so that the humidity of the liquid crystal is 10% to 60%, preferably 10% to 40%.
- only the winding process part 5 may be arrange
- one humidity detector 71 is provided in the winding process unit 5, but a plurality of humidity detectors 71 may be provided in the winding process unit 5. If the humidity in the winding process unit 5 is substantially uniform, one humidity detector 71 may be provided. However, if the humidity varies depending on the location in the winding process unit 5, for example, the outlet of the drying furnace 40 It is preferable to arrange the humidity detectors 71 at a plurality of locations, for example, in the vicinity of the vicinity of the take-up roll 50 or in the vicinity of the rollers of the conveyance path. Even if the humidity environment is not uniform in the winding process section 5, it is sufficient that the humidity is in the range of 10% to 60%.
- the winding process unit 5 surrounded by a dotted line in FIG. 1 may be disposed in a casing that can be humidity controlled separately from the coating and drying processes, and the humidity of the winding process unit 5 is 10% or more. As long as it can be controlled within a range of 60% or less, it may be exposed in an indoor facility.
- the humidity adjusting device 72 has a dehumidifying function and a humidifying function, but may be provided with only a dehumidifier or only a humidifier according to the natural environment of the area where the manufacturing is performed.
- the control unit 73 may be linked with a computer that controls the manufacturing apparatus 1 itself. When the humidity of the winding process unit 5 is 10% or more and 60% or less, the control unit 73 manufactures the complex 52 for acid gas separation. You may make it cancel.
- the acidic gas separation facilitated transport which is a gel film having a very high water absorption property. Problems caused by the film absorbing water in the ambient atmosphere can be suppressed, and sticking of the film to the transport roll in contact with the coating surface can be suppressed. Thereby, since contamination of the process path can be suppressed, efficient production is possible, and an acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane with few defects can be obtained.
- a mobile simple dehumidifier is installed in the vicinity of the winding roll 50, for example, and a form in which a high humidity is pressed (humidity adjustment) is adopted. May be.
- a simple hygrometer may be installed on the transport roll 68 or the take-up roll 50 and the overall air conditioning by the humidity adjusting device and the control unit may be adjusted by looking at the value.
- the humidity may be controlled to some extent by the air conditioning of the winding process unit or the entire manufacturing apparatus, and a hygrometer may be installed on the transport roll 68 and the winding roll 50 to make further adjustment of the air conditioning.
- a coating solution for forming an acidic gas separation facilitating transport film (hereinafter also referred to as “coating solution” for short) containing a hydrophilic compound, an acidic gas carrier, and water is prepared.
- coating solution a hydrophilic compound and an acidic gas carrier are respectively added to water in appropriate amounts.
- hydrophilic polymer is mentioned as a hydrophilic compound contained in a coating liquid.
- the hydrophilic polymer functions as a binder.
- the hydrophilic polymer retains moisture in the acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane and exerts a function of separating acidic gas by an acidic gas carrier.
- the hydrophilic polymer preferably has high water absorption from the viewpoint that the acidic gas separation facilitating transport membrane has high water absorption (retainability), and has a water absorption of 0.5 g / g or more in physiological saline.
- it has a water absorption of 1 g / g or more, more preferably 5 g / g or more, and particularly preferably 10 g / g or more. Further, it is most preferable to have a water absorption of 20 g / g or more.
- hydrophilic polymer contained in the coating solution a conventionally known hydrophilic polymer can be used.
- a conventionally known hydrophilic polymer can be used.
- these copolymers are also preferred, and these copolymers can also be preferably used.
- polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer particularly preferred is a polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer.
- the polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer has a high water absorption capacity and also has a high hydrogel strength even at high water absorption.
- the content of polyacrylate in the polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer is, for example, 1 to 95 mol%, preferably 2 to 70 mol%, more preferably 3 to 60 mol%, and particularly preferably 5 to 50 mol%. Mol%.
- polyacrylic acid salts include alkali metal salts such as sodium salt and potassium salt, as well as ammonium salts and organic ammonium salts.
- polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer sodium salt
- Crustomer AP20 trade name: manufactured by Kuraray Co., Ltd.
- Two or more hydrophilic polymers may be mixed and used.
- the content of the hydrophilic polymer in the coating liquid depends on the type, but from the viewpoint of forming a membrane as a binder and allowing the acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane to sufficiently retain moisture, 0.5% by mass
- the content is preferably 50% by mass or less, more preferably 1% by mass or more and 30% by mass or less, and particularly preferably 2% by mass or more and 15% by mass or less.
- the acid gas carrier means one that indirectly reacts with the acid gas or one that itself reacts directly with the acid gas.
- the acid gas carrier various water-soluble inorganic and organic substances showing basicity are used. Examples of the substance that reacts indirectly with the acid gas include those that react with other gases contained in the supply gas, show basicity, and react with the basic compound and the acid gas. More specifically react with steam OH - to the release, the OH - refers to alkali metal compounds can be incorporated selectively CO 2 in the film by reacting with CO 2 . Examples of those that react directly with acid gas include basic compounds such as nitrogen-containing compounds and sulfur oxides.
- alkali metal compound examples include at least one selected from alkali metal carbonates, alkali metal bicarbonates, or alkali metal hydroxides.
- alkali metal an alkali metal element selected from cesium, rubidium, potassium, lithium, and sodium is preferably used.
- an alkali metal compound is used in the meaning containing the salt and its ion other than alkali metal itself.
- Examples of the alkali metal carbonate include lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, rubidium carbonate, and cesium carbonate.
- Examples of the alkali metal bicarbonate include lithium hydrogen carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate, rubidium hydrogen carbonate, and cesium hydrogen carbonate.
- Examples of the alkali metal hydroxide include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, cesium hydroxide, and rubidium hydroxide. Among these, alkali metal carbonates are preferable, and compounds containing cesium, rubidium, and potassium having high solubility in water are preferable. Moreover, you may mix and use 2 or more types of acidic gas carriers. For example, what mixed cesium carbonate and potassium carbonate can be mentioned suitably.
- nitrogen-containing compounds include amino acids such as glycine, alanine, serine, proline, histidine, taurine, and diaminopropionic acid, hetero compounds such as pyridine, histidine, piperazine, imidazole, and triazine, monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and triazine.
- Alkanolamines such as ethanolamine, monopropanolamine, dipropanolamine, tripropanolamine, cyclic polyetheramines such as cryptand [2.1] and cryptand [2.2], cryptand [2.2.1] Bicyclic polyetheramines such as cryptand [2.2.2], porphyrin, phthalocyanine, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and the like can be used.
- amino acids such as cystine and cysteine, polythiophene, dodecylthiol and the like can be used.
- the content of the acidic gas carrier in the coating liquid is 0.3 to 30% by mass in order to prevent salting out before coating and to ensure the separation function of acidic gas, depending on the type. It is preferably 0.5 to 25% by mass, more preferably 1 to 20% by mass.
- the coating solution preferably contains a hydrophilic polymer and an acidic gas carrier in a mass ratio of 1: 9 to 2: 3. More preferably, it is in the range of 1: 4 or more and 2: 3 or less, more preferably 3: 7 or more and 2: 3 or less.
- Thickener Coating liquid composition for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film, comprising a hydrophilic polymer, an acidic gas carrier, and water, wherein the mass ratio of the hydrophilic polymer to the acidic gas carrier is from 1: 9 to 2: 3.
- a thickener may be further used in the coating solution composition.
- any compound may be used as long as it can increase the viscosity of the coating liquid composition within a temperature range of 15 ° C. or more and 35 ° C. or less.
- Carboxymethyl cellulose that can be suitably used has a degree of etherification in the range of 0.6 to 1.5, and a viscosity measurement value at a rotation speed of 60 rpm in a B-type viscosity measurement when the aqueous solution is 1% by mass is 1 Pa ⁇ It is in the range of s to 10 Pa ⁇ s.
- carboxymethylcellulose When such carboxymethylcellulose is used, a coating liquid composition for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film having a desired viscosity can be easily obtained with a small amount of content, and at least components other than the solvent contained in the coating liquid can be obtained. There is also little risk that a part of the coating solution cannot be dissolved and deposited.
- carboxymethylcellulose can be obtained from commercial products, and preferred examples include CMC2280 manufactured by Daicel Finechem Co., Ltd.
- the prepared coating solution for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film has a viscosity measurement value of 0.5 Pa ⁇ s or more at a rotation speed of 60 rpm in B-type viscosity measurement at any temperature within the range of 15 ° C. or more and 35 ° C. or less. Whether one of the viscosities in the range of 10 Pa ⁇ s or less is exhibited can be confirmed as follows. That is, the prepared coating solution for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film is put into a stainless steel container (for example, 4 cm in inner diameter and 12 cm in height) so that the viscometer cylinder (rotor) is sufficiently immersed in the coating solution. .
- the stainless steel container is immersed in a temperature-adjustable water tank, and while adjusting the temperature of the applied coating solution in the range of 15 ° C. to 35 ° C., a B-type viscometer (BL2 1-100,000 mPa, manufactured by Techjam) S / KN3312481) is operated, the value for each temperature at a rotational speed of 60 rpm is read, and the viscosity of the coating solution is measured according to JIS Z8803.
- a B-type viscometer BL2 1-100,000 mPa, manufactured by Techjam
- the content of the thickener in the composition (coating liquid) is 0.5 Pa ⁇ s at a rotation speed of 60 rpm in the B-type viscosity measurement at any temperature within the range of 15 ° C. to 35 ° C. If it can be adjusted to show any viscosity within the range of 10 Pa ⁇ s or less, it is preferably as small as possible. As a general index, it is preferably 10% by mass or less, more preferably 0.1% by mass or more and 5% by mass or less, and most preferably 0.1% by mass or more and 2% by mass or less.
- the hydrophilic polymer can be crosslinked by a conventionally known method such as thermal crosslinking, ultraviolet crosslinking, electron beam crosslinking, or radiation crosslinking. It is preferable that the composition of this invention contains a crosslinking agent. In particular, it preferably contains a cross-linking agent having two or more functional groups capable of reacting with the polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer and thermally cross-linking, and includes polyvalent glycidyl ether, polyhydric alcohol, polyvalent isocyanate, polyvalent aziridine, Examples include haloepoxy compounds, polyhydric aldehydes, polyhydric amines, and the like.
- polyvalent glycidyl ether for example, ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, glycerol polyglycidyl ether, diglycerol polyglycidyl ether, polyglycerol polyglycidyl ether, sorbitol polyglycidyl ether, pentaerythritol poly Examples thereof include glycidyl ether, propylene glycol glycidyl ether, and polypropylene glycol diglycidyl ether.
- polyhydric alcohol examples include ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, tetraethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol glycerin, polyglycerin, propylene glycol, diethanolamine, triethanolamine, polyoxypropyl, and oxyethylene oxypropylene block. Copolymers, pentaerythritol, sobitol and the like can be mentioned.
- examples of the polyvalent isocyanate include 2,4-toluylene diisocyanate and hexamethylene diisocyanate.
- examples of the polyvalent aziridine include 2,2-bishydroxymethylbutanol-tris [3- (1-acylidinyl) propionate], 1,6-hexamethylenediethyleneurea, diphenylmethane-bis-4,4′- N, N′-diethylene urea and the like can be mentioned.
- Examples of the haloepoxy compound include epichlorohydrin and ⁇ -methylchlorohydrin.
- Examples of the polyvalent aldehyde include glutaraldehyde and glyoxal.
- Examples of the polyvalent amine include ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine, tetraethylenepentamine, pentaethylenehexamine, and polyethyleneimine.
- glutaraldehyde is particularly preferred as the thermal crosslinking agent for the polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylate copolymer.
- the coating liquid can contain one or more other components (additives) other than the hydrophilic polymer, the acidic gas carrier, and the thickener as long as the coating properties and gas separation characteristics are not adversely affected.
- other components include, in addition to the above-described crosslinking agent, for example, surfactants, catalysts, moisturizing (water absorbing) agents, auxiliary solvents, film strength adjusting agents, and defect detecting agents.
- the coating liquid is prepared by adding the above-mentioned hydrophilic polymer, acidic gas carrier, and, if necessary, other additives including a thickener and a crosslinking agent to water (room temperature water or warm water) in appropriate amounts. It is performed with sufficient agitation, and if necessary, dissolution is accelerated by heating with agitation.
- a hydrophilic polymer and an acidic gas carrier may be separately added to water, or those previously mixed may be added.
- the hydrophilic polymer and the thickener are added by gradually adding a hydrophilic polymer and an acidic gas carrier thereto and stirring. Precipitation (salting out) can be effectively prevented.
- the coating liquid for forming an acidic gas separation promoting transport film is fed out from the feed roll 10 to the belt-like support 12 and conveyed to the coater 20 of the coating section.
- the measured viscosity value at a rotational speed of 60 rpm is applied on the support 12 at a viscosity of 0.5 Pa ⁇ s or more and 10 Pa ⁇ s or less, and a liquid film of the coating solution is provided on the support 12.
- the support 12 supports the acidic gas separation facilitated transport membrane, has an acid gas permeability, and is coated with an acidic gas separation facilitated transport membrane forming composition (coating liquid) so as to facilitate the acidic gas separation facilitated transport membrane.
- an acidic gas separation facilitated transport membrane forming composition coating liquid
- the film can be formed and the film can be supported.
- the material of the support 12 paper, fine paper, coated paper, cast coated paper, synthetic paper, and further, cellulose, polyester, polyolefin, polyamide, polyimide, polysulfone aramid, polycarbonate, metal, glass, ceramics and the like are preferable. Can be used.
- resin materials such as polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyphenyl sulfide, polyether imide, polyether ether ketone, polysulfone, polyether sulfone, polyethylene terephthalate, polytetrafluoroethylene, and polyvinylidene fluoride are preferable.
- polyolefins and fluorides thereof can be particularly preferably used from the viewpoint of stability over time.
- a woven fabric, a non-woven fabric, a porous membrane or the like can be adopted. In general, a support having a high self-supporting property and a high porosity can be suitably used.
- Polysulfone, cellulose membrane filter membrane, polyamide, polyimide interfacial polymerized thin film, polytetrafluoroethylene, high molecular weight polyethylene stretched porous membrane has high porosity, low acid gas diffusion inhibition, strength, suitability for manufacturing, etc.
- a stretched film of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is particularly preferable.
- the support 12 it is particularly preferable to use a laminated film of a hydrophobic porous film and a nonwoven fabric as an auxiliary support film. Since the mechanical strength can be improved by providing an auxiliary support film, there is an effect that the support film does not wrinkle even when handled in a roll-to-roll coating apparatus, and productivity can also be improved. . In this case, it is particularly preferable to use PTFE as the hydrophobic porous film and polypropylene (PP) which is inexpensive and has high mechanical strength as the nonwoven fabric.
- PP polypropylene
- the hydrophobic porous membrane means that the surface of the porous membrane on the side in contact with the facilitated transport membrane is a hydrophobic surface. If the surface is hydrophilic, the facilitated transport film containing moisture in the use environment is likely to penetrate into the porous portion, and there is a concern that the film thickness distribution and performance deterioration with time may occur.
- the term “hydrophobic” means that the contact angle of water at room temperature (25 ° C.) is about 80 ° C. or more.
- the thickness of the support is preferably 30 to 500 ⁇ m, more preferably 50 to 300 ⁇ m, and even more preferably 50 to 200 ⁇ m.
- the Young's modulus of the support is preferably 0.4 GPa or more so that the support is not distorted or broken in the production of Roll-to-Roll.
- the porous film thickness is about 5 to 100 ⁇ m and the nonwoven film thickness is about 50 to 300 ⁇ m.
- the transport speed of the support 12 depends on the type of the support 12 and the viscosity of the composition (coating liquid), but if the transport speed of the support is too high, the film thickness uniformity of the coating film in the coating process is reduced. If it is too slow and productivity is too low, the productivity may decrease, and the viscosity of the composition may increase before the cooling step, which may reduce the uniformity of the coating film.
- the conveying speed of the support 12 may be determined according to the type of the support 12 and the viscosity of the composition in consideration of the above points, but is preferably 1 m / min or more. Furthermore, 10 m / min or more and 200 m / min or less is more preferable, and further 20 m / min or more and 200 m / min or less is particularly preferable.
- a roll coater or a blade coater is particularly preferable.
- the roll coater combines one or more rolls to control the amount of coating liquid held on the surface of the roll (applicator roll) arranged closest to the support, and the coating liquid on the (applicator roll) Is a coater that transfers a certain amount of the above to the support surface.
- Suitable roll coaters include a direct gravure coater, an offset gravure coater, a single roll kiss coater, a three reverse roll coater, and a forward rotation roll coater.
- a three reverse roll coater suitable for application of a coating solution having a medium viscosity to a high viscosity of 3 Pa ⁇ s or more and 20 Pa ⁇ s or less is preferable.
- the blade coater is a coater that, after applying an excessive amount of coating solution on a support, scrapes off the excess amount of the coating solution on the support with a blade.
- the drying step at least a part of water as a solvent contained in the coating film of the acidic gas separation layer forming coating solution formed on the support in the coating step is removed in the drying furnace 40.
- a drying step is performed by heating the support on which the coating film is held, blowing dry air on the coating film, or both.
- the temperature is more preferably 60 ° C. or higher and 90 ° C. or lower, and further preferably 70 ° C. or higher and 80 ° C. or lower.
- the film surface temperature is preferably 15 ° C. or higher and 80 ° C. or lower, more preferably 30 ° C. or higher and 70 ° C. or lower.
- the crosslinking step may be performed simultaneously with the drying step or may be performed separately.
- a well-known crosslinking method can be used for the crosslinking method.
- the acidic gas separation promoting transport membrane may be heated and crosslinked by heating means such as an infrared heater after the drying step, or may be crosslinked together with drying by warm air in the drying step.
- Thermal crosslinking can be performed by heating to about 100 to 150 ° C., for example.
- UV or electron beam crosslinking may be applied to the liquid film of the coating solution formed on the support and then dried.
- the acidic gas separation composite 52 in which the liquid film of the coating liquid for forming the acidic gas separation facilitated transport film applied in the coating step on the support is dried in a drying furnace to form the acidic gas separation facilitated transport film. Is wound up by a winding roll. At this time, the humidity of the winding process unit 5 is measured by the humidity detector 71, and the control unit 73 controls the humidity adjusting device 72 to adjust the humidity of the winding process unit 5 according to the measured humidity. Is performed in an environment of 10% to 60%.
- the composite for acidic gas separation according to the present invention is obtained through the above steps.
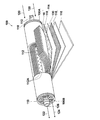
- FIG. 2 is a schematic block diagram showing a spiral-shaped acidic gas separation module 100 according to the first embodiment of the acidic gas separation module of the present invention, which is partially cut away.
- the acidic gas separation module 100 has a basic structure in which the outermost periphery of the laminate 114 is wound around a permeate gas collecting pipe 112 in a state where one or more laminates 114 described below are wound. Covered with a covering layer 116, telescope prevention plates 118 are attached to both ends of these units.
- the module 100 having such a configuration, when the source gas 120 containing an acidic gas is supplied to the laminate 114 from the one end 100A side, the source gas 120 is mixed with the acid gas 122 and the remaining gas by the configuration of the laminate 114. It is separated into 124 and discharged separately to the other end 100B side.
- the permeate gas collecting pipe 112 is a cylindrical pipe having a plurality of through holes 112A formed in the pipe wall.
- the one end side (one end 100A side) of the permeate gas collecting pipe 112 is closed, and the other end side (the other end 100B side) of the permeate gas collecting pipe 112 is opened and penetrates the laminate to collect from the through hole 112A.
- a discharge port 126 from which acidic gas 122 such as gas is discharged is provided.
- the shape of the through hole 112A is not particularly limited, but it is preferable that a circular hole with a diameter of 1 to 20 mm ⁇ is opened. Further, it is preferable that the through holes 112A are arranged uniformly with respect to the surface of the permeate gas collecting pipe 112.
- the covering layer 116 is formed of a blocking material capable of blocking the raw material gas 120 passing through the acidic gas separation module 100.
- This blocking material preferably further has heat and humidity resistance.
- heat resistance in the heat and humidity resistance means having a heat resistance of 80 ° C. or higher.
- the heat resistance of 80 ° C. or higher means that the shape before storage is maintained even after being stored for 2 hours under a temperature condition of 80 ° C. or higher, and curling that can be visually confirmed by heat shrinkage or heat melting does not occur.
- “moisture resistance” of the heat and humidity resistance is a curl that can be visually confirmed by heat shrinkage or heat melting even after being stored at 40 ° C. and 80% RH for 2 hours. It means not occurring.
- the telescope prevention plate 118 is preferably made of a heat and moisture resistant material.
- the laminated body 114 is formed by laminating a permeating gas flow path member 16, an acidic gas separation complex 110, a supply gas flow path member 130, and an acidic gas separation complex 110. It is wound around the permeating gas collecting pipe 112. By laminating these films, the source gas 120 containing the acid gas 122 is supplied from the end of the supply gas flow path member 130 and is separated through the acid gas separation complex 110 partitioned by the coating layer 116.
- the acidic gas 122 collected in the permeated gas collecting pipe 112 is collected through the permeated gas flow path member 16 and the through hole 112A, and is collected from the discharge port 126 connected to the permeated gas collecting pipe 112. Further, the residual gas 124 from which the acidic gas 122 has been separated that has passed through the gap or the like of the supply gas flow path member 130 is discharged from the end of the acidic gas separating mogas separation complex 110.
- the complex for acidic gas separation 110 is produced by the production method of the present invention, and is a porous support formed by laminating a porous membrane and an auxiliary support membrane, on the porous membrane side of the porous support. It is composed of an acidic gas separation promoting transport film including an acidic gas carrier that reacts with at least the hydrophilic polymer and the acidic gas in the raw material gas.
- the number of the laminated body 114 wound around the permeate gas collecting pipe 112 is not particularly limited, and may be single or plural. By increasing the number (number of laminated layers), the membrane area of the facilitated transport film can be improved. Thereby, the quantity which can isolate
- the supply gas flow path member 130 is a member to which a source gas containing an acid gas is supplied from one end of the acid gas separation module, has a function as a spacer, and causes a turbulent flow in the source gas. Therefore, a net-like member is preferably used. Since the gas flow path changes depending on the shape of the net, the shape of the unit cell of the net is selected from shapes such as rhombus and parallelogram according to the purpose. Assuming that a raw material gas containing water vapor is supplied at a high temperature, the supply gas flow path member preferably has moisture and heat resistance in the same manner as the acidic gas separation layer described later.
- the material of the supply gas flow path member 130 is not limited in any way, but paper, fine paper, coated paper, cast coated paper, synthetic paper, cellulose, polyester, polyolefin, polyamide, polyimide, polysulfone, aramid, Examples thereof include resin materials such as polycarbonate and inorganic materials such as metal, glass and ceramics.
- the resin materials include polyethylene, polystyrene, polyethylene terephthalate, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethersulfone (PES), polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), polysulfone (PSF), polypropylene (PP), polyimide, polyetherimide, poly Suitable examples include ether ether ketone and polyvinylidene fluoride.
- preferable materials from the viewpoint of heat and humidity resistance include inorganic materials such as ceramics, glass, and metals, organic resin materials having heat resistance of 100 ° C. or higher, high molecular weight polyester, polyolefin, heat resistant polyamide, polyimide, and the like.
- Polysulfone, aramid, polycarbonate, metal, glass, ceramics and the like can be suitably used. More specifically, at least one selected from the group consisting of ceramics, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinylidene fluoride, polyethersulfone, polyphenylene sulfide, polysulfone, polyimide, polypropylene, polyetherimide, and polyetheretherketone. It is preferable that it is comprised including these materials.
- the thickness of the supply gas flow path member is not particularly limited, but is preferably 100 ⁇ m or more and 1000 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 150 ⁇ m or more and 950 ⁇ m or less, and further preferably 200 ⁇ m or more and 900 ⁇ m or less.
- the permeating gas channel member 16 is a member in which the acidic gas that has reacted with the carrier and permeated the acidic gas separating complex 110 flows toward the through hole.
- the permeate gas flow path member 16 has a function as a spacer, and also has a function of causing the permeated acidic gas to flow inside the permeate gas flow path member 16.
- An example is a tricot knitting shape.
- the material of the permeating gas flow path member can be the same as that of the supply gas flow path member.
- the permeate gas channel member has moisture and heat resistance in the same manner as the acidic gas separation layer.
- polyesters such as epoxy-impregnated polyester, polyolefins such as polypropylene, and fluorines such as polytetrafluoroethylene.
- the thickness of the permeating gas channel member is not particularly limited, but is preferably 100 ⁇ m or more and 1000 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 150 ⁇ m or more and 950 ⁇ m or less, and further preferably 200 ⁇ m or more and 900 ⁇ m or less.
- the complex for acid gas separation produced by the production method of the present invention may be installed as a flat membrane, a spiral type known as a reverse osmosis membrane module, for example, JP 2010-279885 A, etc. It can also be used after being processed into a pleated mold having a shape as described in 1. Furthermore, the carbon dioxide separation module according to the present invention can be used by being set in a carbon dioxide separator.
- Example 1 (Preparation process) 5% cesium carbonate aqueous solution, 2.5% PVA-PAA copolymer (Kuraray; Clastomer AP) and 0.3% glutaraldehyde (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) are heated and stirred to separate acidic gases. As the coating solution, a coating solution for carbon dioxide separation was prepared.
- the blade coating method was selected, and the coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 0.3 mm by adjusting the blade height to 0.3 mm.
- drying process In the coating step, the liquid film was dried in a drying furnace. Drying was a method of volatilizing water from the liquid membrane by passing continuously through a 3.0 m drying zone by a hot air method, and a carbon dioxide separation membrane was formed on the support.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 60 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 80 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 90 ° C.
- thermo-hygrometer ONDOTORI JC-M3200, manufactured by Nippon Keiki Kogyo Co., Ltd.
- the temperature and humidity were controlled.
- the wind-up part from the drying outlet can be adjusted in the common low humidity package 5.
- Air with adjusted temperature and humidity at a setting of 25 ° C. and 35% was supplied from the drying outlet to the winding unit. Specifically, the air whose humidity has been adjusted by the package is supplied between the roll 65 and the roll 66 in FIG. At this time, the humidity detected by the hygrometer was 40% at the drying outlet and 38% at the winding part.
- Example 2 Coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 1.5 mm by adjusting the blade height in Example 1 to 1.5 mm.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 70 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 90 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 100 ° C.
- the temperature and humidity conditions at the take-up portion from the drying outlet were the same as in Example 1.
- Example 3 By adjusting the blade height in Example 1 to 3.0 mm, coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 3.0 mm.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 80 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 100 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 110 ° C.
- the temperature and humidity conditions at the take-up portion from the drying outlet were the same as in Example 1.
- Example 4 By adjusting the blade height in Example 1 to 3.0 mm, coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 3.0 mm.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 80 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 100 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 110 ° C.
- the set value of the package in the winding part was set to 25 ° C. and 50%, and air adjusted in temperature and humidity was supplied from the drying outlet to the winding part.
- Example 5 In Example 1, air whose temperature and humidity were adjusted from the drying outlet to the winding portion was set to 25 ° C. and 10% from the drying outlet to the winding portion.
- Example 6 In Example 4, air whose temperature and humidity were adjusted at a set value of the package at the winding portion from the drying outlet of 25 ° C. and 59% was supplied from the drying outlet to the winding portion.
- Example 1 By adjusting the blade height to 0.1 mm in Example 1, coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 0.1 mm.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 60 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 80 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 90 ° C. From the drying outlet, air whose temperature and humidity were adjusted at a set value of the package in the winding part at 25 ° C. and 35% was supplied from the drying outlet to the winding part.
- Example 2 Coating was performed with a liquid film thickness of 4.0 mm by adjusting the blade height in Example 1 to 4.0 mm.
- the drying zone 1-2 was 80 ° C.
- the drying zone 3-4 was 100 ° C.
- the drying zone 5-7 was 110 ° C. From the drying outlet, air whose temperature and humidity were adjusted at a set value of the package in the winding part at 25 ° C. and 35% was supplied from the drying outlet to the winding part.
- Comparative Example 3 In Comparative Example 2, the drying zone 1-2 was 90 ° C., the drying zone 3-4 was 110 ° C., and the drying zone 5-7 was 130 ° C.
- the permeated gas was analyzed with a gas chromatograph, and the CO 2 permeation rate (P (CO 2 )) was calculated. Production and performance evaluation of a carbon dioxide separation membrane were carried out 5 times, and evaluated according to the following criteria.
- C Average value is less than 20 GPU
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Separation Using Semi-Permeable Membranes (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201480017975.3A CN105120989B (zh) | 2013-03-29 | 2014-03-28 | 酸性气体分离用复合体的制造方法和制造装置 |
| EP14773491.7A EP2979744A4 (en) | 2013-03-29 | 2014-03-28 | METHOD OF MANUFACTURING AND MANUFACTURING APPARATUS FOR ACID GAS SCALING COMPLEXES |
| US14/862,646 US10022675B2 (en) | 2013-03-29 | 2015-09-23 | Method of producing composite for acid gas separation and apparatus for producing same |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-072015 | 2013-03-29 | ||
| JP2013072015A JP6046537B2 (ja) | 2013-03-29 | 2013-03-29 | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法および製造装置 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/862,646 Continuation US10022675B2 (en) | 2013-03-29 | 2015-09-23 | Method of producing composite for acid gas separation and apparatus for producing same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014156183A1 true WO2014156183A1 (ja) | 2014-10-02 |
Family
ID=51623194
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/001824 Ceased WO2014156183A1 (ja) | 2013-03-29 | 2014-03-28 | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法および製造装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10022675B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2979744A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6046537B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105120989B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014156183A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5490281B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-20 | 2014-05-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 酸性ガス分離モジュール、及び酸性ガス分離システム |
| US10507434B2 (en) | 2014-08-11 | 2019-12-17 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Composition for CO2 gas separation membrane, CO2 gas separation membrane and method for producing same, and CO2 gas separation membrane module |
| WO2016080400A1 (ja) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-26 | 住友化学株式会社 | 二酸化炭素ガス分離膜及びその製造方法、並びに二酸化炭素ガス分離膜モジュール |
| JP2016117045A (ja) * | 2014-12-23 | 2016-06-30 | 住友化学株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離膜の製造方法、二酸化炭素分離膜用樹脂組成物、二酸化炭素分離膜モジュール及び二酸化炭素分離装置 |
| JP6917155B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-14 | 2021-08-11 | 住友化学株式会社 | 促進輸送膜の包装方法 |
| JPWO2019059368A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-25 | 2020-12-03 | 株式会社クラレ | 炭酸ガス吸収体およびそれを含む非水電解質蓄電池、並びに炭酸ガスの分離回収方法 |
| CN110636896B (zh) * | 2017-09-29 | 2022-03-25 | 住友化学株式会社 | 螺旋型气体分离膜元件、气体分离膜模块以及气体分离装置 |
| JP2019091577A (ja) * | 2017-11-13 | 2019-06-13 | 株式会社クラレ | 炭酸ガス発生剤およびそれを用いた非水電解質蓄電池 |
| WO2019168138A1 (ja) * | 2018-02-28 | 2019-09-06 | 東レ株式会社 | 複合半透膜および複合半透膜エレメント |
| WO2019190404A1 (en) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-03 | Singapore University Of Technology And Design | A porous membrane fabrication system |
| JP7691863B2 (ja) * | 2021-06-22 | 2025-06-12 | 次世代型膜モジュール技術研究組合 | ガス分離膜 |
| GB2621880A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2024-02-28 | Dyson Technology Ltd | Filter Media |
| WO2024197068A2 (en) * | 2023-03-21 | 2024-09-26 | Captura Corp. | Direct removal of carbon dioxide from oceanwater based on a composite membrane |
| WO2025193867A1 (en) * | 2024-03-12 | 2025-09-18 | Ohio State Innovation Foundation | Polyguanidine-containing membranes and methods of using thereof |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07102310A (ja) | 1993-09-30 | 1995-04-18 | Shinko Flex:Kk | 精錬用複合造滓剤 |
| JP2010279885A (ja) | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-16 | Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corp | 気体分離装置 |
| JP2011235204A (ja) * | 2010-05-06 | 2011-11-24 | Toyobo Co Ltd | 中空糸膜 |
| WO2012096055A1 (ja) * | 2011-01-12 | 2012-07-19 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離膜形成用組成物、二酸化炭素分離膜及びその製造方法、並びに二酸化炭素分離装置 |
| WO2012096114A1 (ja) * | 2011-01-12 | 2012-07-19 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法及び製造装置 |
| WO2013018659A1 (ja) * | 2011-08-01 | 2013-02-07 | 株式会社ルネッサンス・エナジー・リサーチ | Co2促進輸送膜及びその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5389724A (en) * | 1992-04-23 | 1995-02-14 | Rohm And Haas Company | Polymer blends |
| US5445669A (en) | 1993-08-12 | 1995-08-29 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Membrane for the separation of carbon dioxide |
| JPH07102310B2 (ja) | 1993-10-19 | 1995-11-08 | 工業技術院長 | 二酸化炭素分離ゲル膜及びその製造方法 |
| CN1180878C (zh) * | 2002-11-14 | 2004-12-22 | 天津大学 | 用于分离酸性气体的固定载体复合膜制备方法 |
| JP2006243025A (ja) * | 2005-02-28 | 2006-09-14 | Nippon Oil Corp | 液晶用配向膜および該配向膜より得られる液晶性光学フィルム |
| JP2009001009A (ja) * | 2007-05-22 | 2009-01-08 | Nippon Synthetic Chem Ind Co Ltd:The | 液圧転写印刷用ベースフィルム、液圧転写印刷用ベースフィルムの製造方法および液圧転写方法 |
| CN103432910A (zh) * | 2008-01-24 | 2013-12-11 | 株式会社新生能源研究 | Co2促进输送膜及其制造方法 |
| EP2365869B1 (en) * | 2008-11-21 | 2017-10-04 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Method for forming a microporous membrane |
| CN102631843A (zh) * | 2011-02-14 | 2012-08-15 | 同济大学 | 可用于分离气体中co2的离子液体支撑液膜的制备方法 |
| JP5738710B2 (ja) * | 2011-07-29 | 2015-06-24 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離膜の製造方法及び二酸化炭素分離モジュール |
| JP6159624B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-02 | 2017-07-05 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 酸性ガス分離膜の製造方法 |
-
2013
- 2013-03-29 JP JP2013072015A patent/JP6046537B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-03-28 CN CN201480017975.3A patent/CN105120989B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-03-28 WO PCT/JP2014/001824 patent/WO2014156183A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-03-28 EP EP14773491.7A patent/EP2979744A4/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2015
- 2015-09-23 US US14/862,646 patent/US10022675B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07102310A (ja) | 1993-09-30 | 1995-04-18 | Shinko Flex:Kk | 精錬用複合造滓剤 |
| JP2010279885A (ja) | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-16 | Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corp | 気体分離装置 |
| JP2011235204A (ja) * | 2010-05-06 | 2011-11-24 | Toyobo Co Ltd | 中空糸膜 |
| WO2012096055A1 (ja) * | 2011-01-12 | 2012-07-19 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離膜形成用組成物、二酸化炭素分離膜及びその製造方法、並びに二酸化炭素分離装置 |
| WO2012096114A1 (ja) * | 2011-01-12 | 2012-07-19 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法及び製造装置 |
| JP2012143711A (ja) | 2011-01-12 | 2012-08-02 | Fujifilm Corp | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法及び製造装置 |
| WO2013018659A1 (ja) * | 2011-08-01 | 2013-02-07 | 株式会社ルネッサンス・エナジー・リサーチ | Co2促進輸送膜及びその製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014195760A (ja) | 2014-10-16 |
| US20160008764A1 (en) | 2016-01-14 |
| EP2979744A1 (en) | 2016-02-03 |
| US10022675B2 (en) | 2018-07-17 |
| CN105120989B (zh) | 2017-09-29 |
| CN105120989A (zh) | 2015-12-02 |
| JP6046537B2 (ja) | 2016-12-14 |
| EP2979744A4 (en) | 2016-07-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6046537B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法および製造装置 | |
| JP6156837B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法 | |
| JP6156838B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法 | |
| WO2012096055A1 (ja) | 二酸化炭素分離膜形成用組成物、二酸化炭素分離膜及びその製造方法、並びに二酸化炭素分離装置 | |
| JP5865201B2 (ja) | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法、二酸化炭素分離用複合体及び二酸化炭素分離用モジュール | |
| WO2014156185A1 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離複合膜の製造方法及び酸性ガス分離膜モジュール | |
| JP6001013B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用スパイラル型モジュール | |
| JP2016137462A (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用スパイラル型モジュール | |
| JP5840574B2 (ja) | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法、二酸化炭素分離用複合体、及び二酸化炭素分離用モジュール | |
| WO2014010377A1 (ja) | 二酸化炭素分離用複合体の製造方法、二酸化炭素分離用複合体、二酸化炭素分離モジュール、二酸化炭素分離装置、及び二酸化炭素分離方法 | |
| JP6276598B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用モジュール | |
| JP6159624B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離膜の製造方法 | |
| JP2016117045A (ja) | 二酸化炭素分離膜の製造方法、二酸化炭素分離膜用樹脂組成物、二酸化炭素分離膜モジュール及び二酸化炭素分離装置 | |
| JP6145431B2 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離モジュールの製造方法および酸性ガス分離モジュール | |
| JP2015136634A (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用スパイラル型モジュールおよび製造方法 | |
| WO2014050226A1 (ja) | 酸性ガス分離用複合体の製造方法、酸性ガス分離用複合体、及び酸性ガス分離モジュール | |
| JP5975951B2 (ja) | 促進輸送型分離膜の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14773491 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014773491 Country of ref document: EP |