WO2013140994A1 - オーディオ機器制御プログラム、携帯電話機、記録媒体及び制御方法 - Google Patents
オーディオ機器制御プログラム、携帯電話機、記録媒体及び制御方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013140994A1 WO2013140994A1 PCT/JP2013/055540 JP2013055540W WO2013140994A1 WO 2013140994 A1 WO2013140994 A1 WO 2013140994A1 JP 2013055540 W JP2013055540 W JP 2013055540W WO 2013140994 A1 WO2013140994 A1 WO 2013140994A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- audio device
- incoming call
- unit
- control
- detecting
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 31
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 238000011038 discontinuous diafiltration by volume reduction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000002066 L-histidyl group Chemical group [H]N1C([H])=NC(C([H])([H])[C@](C(=O)[*])([H])N([H])[H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005236 sound signal Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03G—CONTROL OF AMPLIFICATION
- H03G3/00—Gain control in amplifiers or frequency changers
- H03G3/20—Automatic control
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04M—TELEPHONIC COMMUNICATION
- H04M1/00—Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers
- H04M1/72—Mobile telephones; Cordless telephones, i.e. devices for establishing wireless links to base stations without route selection
- H04M1/724—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones
- H04M1/72403—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality
- H04M1/72409—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality by interfacing with external accessories
- H04M1/72415—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality by interfacing with external accessories for remote control of appliances
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03G—CONTROL OF AMPLIFICATION
- H03G3/00—Gain control in amplifiers or frequency changers
- H03G3/20—Automatic control
- H03G3/30—Automatic control in amplifiers having semiconductor devices
- H03G3/3005—Automatic control in amplifiers having semiconductor devices in amplifiers suitable for low-frequencies, e.g. audio amplifiers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03G—CONTROL OF AMPLIFICATION
- H03G3/00—Gain control in amplifiers or frequency changers
- H03G3/20—Automatic control
- H03G3/30—Automatic control in amplifiers having semiconductor devices
- H03G3/3089—Control of digital or coded signals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04M—TELEPHONIC COMMUNICATION
- H04M1/00—Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers
- H04M1/72—Mobile telephones; Cordless telephones, i.e. devices for establishing wireless links to base stations without route selection
- H04M1/724—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones
- H04M1/72484—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones wherein functions are triggered by incoming communication events
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/16—Communication-related supplementary services, e.g. call-transfer or call-hold
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C2201/00—Transmission systems of control signals via wireless link
- G08C2201/90—Additional features
- G08C2201/93—Remote control using other portable devices, e.g. mobile phone, PDA, laptop
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an audio device control program for controlling an audio device from a mobile phone such as a smartphone, a mobile phone equipped with the audio device control program, a recording medium, and a control method.
- a mobile phone such as a smartphone can be provided with a function other than a call, which is a basic function, by installing an application program (a so-called application).
- Some application programs access the AV (Audio / Video) system via a wireless LAN (Local Area Network) (Wi-Fi) to select an input source and adjust the playback volume according to the user's operation. Yes (see Non-Patent Document 1).
- Non-Patent Document 1 By using the application program of Non-Patent Document 1, the user can control the AV system using his / her mobile phone.
- this application program only controls the AV system according to the user's operation, and when the incoming call is a basic function of the mobile phone, the AV system is not disturbed. There was no function to reduce the volume of the.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an audio device control program and a mobile phone for automatically controlling an audio device so as not to disturb a call.
- An audio device control program provided by the first aspect of the present invention provides a control unit for a mobile phone provided with a telephone communication unit, operation detection means for detecting a user operation, and detection of an incoming call to the telephone communication unit.
- the control unit transmits a command message with control contents corresponding to the operation to the audio device.
- the incoming call detection means detects an incoming call, it functions as a command transmission means for sending a command message having a content for controlling the reproduction sound to the audio device.
- control unit of the mobile phone is further operated as an operation state acquisition unit that acquires an operation state of the audio device, and the command transmission unit is detected by the incoming call detection unit. At this time, a command message having a control content corresponding to the operating state of the audio device at that time may be transmitted.
- the operation state obtaining unit obtains an audio source selected in the audio device as an operation state of the audio device, and the command transmission unit is configured to receive an incoming call.
- a command message having a control content corresponding to the audio source selected in the audio device at that time may be transmitted.
- the incoming call detection unit acquires a caller number from the telephone communication unit, and the command transmission unit sets the acquired caller number when the incoming call detection unit detects an incoming call. In response, an individual command message may be transmitted.
- the command message may indicate at least one of volume reduction, mute, playback, and stop of the playback sound.
- the incoming call detection means further detects that the incoming call state or the call state of the telephone has ended, and the command transmission means includes the incoming call detection means that the incoming call detection means has detected the incoming call state or call of the telephone.
- the incoming call detecting means may transmit a command message of control content for returning to the state before detecting the incoming call to the audio device.
- a mobile phone provided by the second aspect of the present invention includes a storage unit that stores the audio device control program, a telephone communication unit that performs telephone communication, and a control unit that executes a program stored in the storage unit And.
- a non-transitory recording medium provided by the third aspect of the present invention stores the audio device control program.
- the control method provided by the fourth aspect of the present invention is a control method of a control unit of a mobile phone provided with a telephone communication unit, wherein the control unit detects an operation of a user, the telephone Communicating with an incoming call detection means for detecting an incoming call to the communication unit, and an audio device for outputting a playback sound, when the operation detection means detects a user operation, a command message of control content corresponding to the operation is sent.
- the incoming call detection means detects an incoming call
- it functions as a command transmission means for transmitting a command message with content for controlling the playback sound to the audio device. It is controlled.
- a control method provided by a fifth aspect of the present invention is a control method for controlling an audio device from a mobile phone including a telephone communication unit, which detects a user operation and receives a call to the telephone communication unit.
- a command message with control content corresponding to the operation is transmitted to the audio device, and the incoming call is detected. Then, a command message having a content for controlling the reproduction sound is transmitted to the audio device.
- the present invention it is possible to control the playback sound of the audio device without the user's operation when the mobile phone is received.
- Configuration diagram of mobile phone and AV system to which the present invention is applied Functional block diagram of an AV controller configured by cooperation of a mobile phone and an AV system control program
- the figure which shows an example of the screen display of AV controller The figure which shows an example of the command table at the time of the incoming call set to memory Flow chart showing operation of AV controller Flow chart showing operation of AV controller Flow chart showing operation of AV controller Flow chart showing operation of AV controller
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone 1 and an AV system 3 to which the present invention is applied.
- the mobile phone 1 is a so-called smartphone.
- a mobile phone (smart phone) 1 has a 3G / 4G communication function, which is a mobile communication network, and also has a wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) communication function, and is connected to the network 2 via an access point 5.
- An AV receiver 4 that is a core of the AV system 3 is also connected to the network 2.
- the cellular phone 1 can control the AV system 3 (AV receiver 4) via the network 2 in response to a user operation by starting an AV controller program 50 that is an application program (application). Also, the mobile phone 1 controls the AV system 3 to reduce the playback volume in response to an incoming call without depending on the user's operation so that the playback sound of the AV system 3 does not hinder the call.
- AV controller program 50 that is an application program (application).
- the mobile phone 1 controls the AV system 3 to reduce the playback volume in response to an incoming call without depending on the user's operation so that the playback sound of the AV system 3 does not hinder the call.
- the AV system 3 has a configuration in which a set top box (STB) 10, a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) player 11, a speaker 12, and a television (TV) 13 are connected to an AV receiver 4 that is a core device. Connected to network 2.
- the AV receiver 4 selects any one of a plurality of AV sources, outputs a reproduction (reception) video of the AV source to the television 13, and outputs a reproduction (reception) sound to the speaker 12.
- AV source selection, volume adjustment, and the like can be performed directly on the operation panel of the AV receiver 4 or the attached infrared remote controller, but can also be performed using the mobile phone 1.
- the configuration of the AV system 3 is not limited to that shown in the figure.
- the network 2 is connected to a router 6, a network storage (NAS) 7, and the like.
- the router 6 is connected to the Internet 8.
- the AV receiver 4 has a function of accessing an internet radio station via the network 2-router 6-internet 8 and reproducing the internet radio.
- the network storage 7 stores music data such as MP3 files.
- the AV receiver 4 has a function of accessing the network storage 7 via the network 2 and reproducing the music data stored in the network storage 7.
- the mobile phone 1 has a control unit 20, an operation unit 30, a media interface 31, a Wi-Fi communication circuit 32, and a 3G / 4G communication circuit 33 on the bus 26.
- the control unit 20 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 21, a ROM (Read Only Memory) (flash memory) 22, a RAM (Random Access Memory) 23, an image processor 24, and an audio processor 25.
- a video RAM (VRAM) 40 is connected to the image processor 24, and a display unit 41 is connected to the VRAM 40.
- the display unit 41 includes a liquid crystal display and displays a standby screen, a telephone number, and the like. In addition, a screen of the AV controller 100 described later is also displayed on the display unit 41.
- An amplifier 42 including a D / A converter is connected to the audio processor 25, and the speaker 16 is connected to the amplifier 42.
- the image processor 24 is provided with a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit, graphics processing unit) that can draw and display a standby screen, a telephone number, and the like on the display unit 41 and generate various videos.
- the image processor 24 generates an image of the AV controller in accordance with an instruction from the CPU 21 and draws it on the VRAM 40.
- the voice processor 25 has a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) that encodes / decodes call voice.
- the audio processor 25 outputs the decoded / generated audio to the amplifier 42.
- the amplifier 42 amplifies this audio signal and outputs it to the speaker 16.
- the Wi-Fi communication circuit 32 performs IEEE802.11g standard wireless communication with the wireless access point 5 and transmits / receives data and messages to / from devices on the network 2 such as the AV receiver 4. Messages are exchanged with the AV receiver 4 in a format defined by DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance).
- the 3G / 4G communication circuit 33 performs a voice call and data communication via a mobile phone communication network. Application programs are downloaded by data communication.
- the operation unit 30 includes a touch panel formed on the display unit 41, and detects a touch operation and a flick operation on the touch panel.
- a memory card 5 is connected to the media interface 31.
- the memory card 5 is, for example, a micro SD card.
- the application program downloaded from the server by the 3G / 4G communication circuit 33 is stored in the memory card 5 or the ROM 22.
- the AV control program 50 is stored in the memory card 5.
- the AV control program 50 includes data necessary for program execution, and a command table 501 and an incoming call command table 502 are stored as data necessary for program execution.
- the command table 501 is a table in which control contents of the AV system 3 are associated with commands representing the contents. As shown in FIG.
- the incoming command table 502 is a table that stores control contents (commands) for the AV system 3 when a telephone call arrives.
- the control contents for each input source selected at that time are as follows. It is stored according to the default setting and the caller (incoming telephone number).
- the control content corresponding to the caller may be set by the user through a setting operation.
- a work area used when the CPU 21 executes the AV controller program 50 is set.
- a system configuration storage area 231 stores the configuration of the AV system 3 acquired from the AV receiver 4.
- the system configuration includes devices connected upstream and downstream of the AV receiver 4, input sources that can be selected by the AV receiver 4, and the like.
- the operation state storage area 232 stores the current operation state of the AV system 3 (AV receiver 4).
- the operating state of the AV system 3 is a selected input source, volume value, name of a song being played back, and the like.
- the incoming flag 233 is a flag that indicates that the mobile phone 1 is receiving a call or is making a call (due to an incoming call).
- the incoming call control register 234 stores the contents of control automatically performed at the time of incoming call.
- the AV controller 100 (see FIG. 2) performs control opposite to this control content at the end of the call and returns the AV system 3 to the original state.
- the ROM 22 stores a basic program for executing calls and application programs of the mobile terminal device 1.
- the ROM 22 is a flash memory that can store a downloaded application program in addition to a basic program.
- the cellular phone 1 configures an AV controller 100 as shown in FIG. 2 in cooperation with the AV controller program 50 stored in the memory card 5, and transmits a command message to the AV receiver 4 via Wi-Fi. To control the AV system 3.
- the AV controller 100 realized by reading the AV controller program 50 of the memory card 5 into the mobile phone 1 (hardware) will be described.
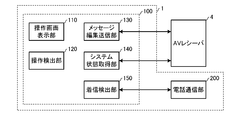
- the AV controller 100 realized by reading the AV controller program 50 into the mobile terminal device 1 includes an operation screen display unit 110, an operation detection unit 120, a message edit transmission unit 130, a system state acquisition unit 140, and an incoming call detection unit 150. Have.
- the operation screen display unit 110 is realized by the cooperation of the control unit 20, the VRAM 40, the display unit 41, and the AV controller program 50, and displays an operation screen as shown in FIG. 3 on the display unit 41 of the mobile phone 1, for example.
- the operation screen shown in FIG. 3 is an example of an input source selection screen.
- the operation detection unit 120 is realized by the cooperation of the control unit 20, the operation unit 30, and the AV controller program 50, and detects an operation on the operation screen displayed on the display unit 41. In FIG. 3, when the user clicks a desired input source (net radio, PC, DOCK, USB, tuner, AV1,...) Displayed on the screen, the operation detection unit 120 detects the operation.
- the operation information is input to the message editing / transmitting unit 130.
- the message editing / transmitting unit 130 is realized by the cooperation of the control unit 20, the Wi-Fi communication circuit 32, and the AV controller program 50, and based on the operation information input from the operation detecting unit 120, a command message corresponding to the operation information. Is transmitted to the AV receiver 4. As will be described later, the message editing / transmitting unit 130 edits a predetermined command message and transmits it to the AV receiver 4 regardless of the operation of the user when a call arrives at the mobile phone 1.
- the system state acquisition unit 140 is realized by the cooperation of the control unit 20, the Wi-Fi communication circuit 32, and the AV controller program 50, and periodically (for example, every 5 seconds) and at the time of editing a command message, the AV receiver 4 Is inquired about the current operating state of the AV system 3.
- the operating state of the AV system 3 is information such as a selectable input source, a selected input source, a song name being played back, a volume value, and the like.
- the incoming call detection unit 150 is a functional unit realized by the cooperation of the control unit 20 and the AV controller program.
- the incoming call detection unit 150 makes an inquiry to the telephone communication unit 200 realized by the mobile phone 1 (hardware) and the basic program, and acquires the call status.
- the call status is information indicating the state of a voice (television) call such as standby, incoming call, outgoing call, or busy.
- the incoming call detection unit 150 notifies the message editing / transmission unit 130 of the change.
- the message editing / transmitting unit 130 edits a command message that controls the playback sound such as lowering the playback volume when the incoming call changes from the standby state to the incoming call state (without depending on the user's operation). Transmit to the receiver 4. This prevents the reproduced sound of the AV system 3 from interfering with the call. Further, when the incoming call (call) ends when the call status changes during an incoming call or during a call to standby, a command message having the opposite content to that of the incoming call is transmitted to the AV receiver 4 to restore the operation of the AV system 3. Return to.
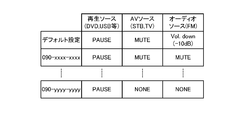
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the configuration of the incoming call command table 502 provided in the message editing / transmitting unit 130 (memory card 5).
- this table the control content for the AV system 3 at the time of incoming call, that is, the content of the command transmitted to the AV receiver 4 is stored.
- commands corresponding to the audio source selected in the AV system 3 when a call is received are stored.
- the selected audio source is a playback source (pauseable) such as DVD or USB, pause is applied.
- the selected audio source is an AV reception source (such as a television) including video, the sound is muted.
- the selected audio source is an audio-only reception source (such as FM), the volume is decreased ( ⁇ 10 dB).
- the command for controlling the AV system 3 is stored with the contents of
- the caller's phone number can be acquired when a call is received, it is possible to set control details for each phone number. If the caller is 090-xxxx-xxxx; If the selected audio source is a playback source, pause. If the selected audio source is an AV reception source, the sound is muted. If the selected audio source is an audio-only receiving source, the sound is muted.
- the command for controlling the AV system 3 is stored with the contents of
- the caller is 090-yyyyy-yyy; If the selected audio source is a playback source, pause. If the selected audio source is an AV reception source, nothing is done. If the selected audio source is an audio-only receiving source, nothing is done.
- the command for controlling the AV system 3 is stored with the contents of
- FIG. 5A to 7 are flowcharts showing the operation of the AV controller 100.
- FIG. FIG. 5A is a flowchart showing an operation at the time of starting the AV controller program 50 which is an application program.
- the AV receiver 4 in the network 2 is searched (S1), and the current system configuration information and the current operation state information are received from the detected AV receiver 4 (S2, S3). Based on the received information, an AV controller screen such as an input source selection screen and a volume slider is constructed (S4).
- FIG. 5B is a flowchart showing the normal operation of the AV controller 100. This operation is repeatedly executed every predetermined period (for example, 10 ms). First, it is determined whether or not there is an operation by the user (S10). If there is no operation (NO in S10), the operation is terminated as it is. When there is an operation by the user (YES in S10), a command for performing control according to the operation is read from the command table 501 (S11), and a command message in which this command is embedded is edited (S12). And transmitted to the AV receiver 4 (S13). Thus, the user can control the AV system 3 using the mobile phone 1.
- S10 command table 501
- S12 command message in which this command is embedded
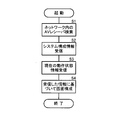
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing a process when an incoming call is received. This process is repeatedly executed every predetermined time (for example, 10 ms). An inquiry is made to the telephone communication unit 200 to determine whether or not an incoming call has been received, that is, whether or not the call status has changed from standby to incoming (S20). If there is no incoming call (NO in S20), the operation is terminated as it is. If there is an incoming call (YES in S20), the operating state of the AV system 3 is acquired (S21). The acquisition of the operating state may be immediately acquired from the AV receiver 4 at this time, but what is periodically acquired may be used as it is. When the current operation state of the AV system 3 is stopped, that is, when no sound is emitted from the speaker 12 (YES in S22), the operation is terminated without doing anything.
- S20 standby to incoming
- the telephone communication unit 200 A caller ID is acquired (S23). If the caller ID can be obtained (YES in S24), the incoming call command table 501 is searched (S25). If there is data corresponding to the acquired caller number (YES in S26), an individual command message is edited for this caller corresponding to the current operating state (S27). On the other hand, if the caller ID cannot be obtained (NO in S24), or if there is no data corresponding to the caller in the incoming call command table 501 (NO in S26), the default command message is edited. (S28).
- the contents of the edited command message that is, the control contents for the AV system 3 are stored in the incoming call control register 234 (S29), and the edited command message is transmitted to the AV receiver 4 (S30). Then, the incoming flag 233 is set. Thereby, when a call arrives at the mobile phone 1, it is possible to perform control such as lowering the reproduction volume of the AV system 3 without depending on the operation of the user.
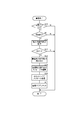
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the operation at the end of the incoming call (call). This process is repeatedly executed every predetermined time (for example, 10 ms). First, it is determined whether or not the incoming flag 233 is set (S40). If the incoming flag 233 is set (YES in S40), it is determined whether or not the incoming call or the call has ended, that is, whether or not the call status has changed from the incoming call or the call to the standby ( S41). If the incoming flag 233 is not set (NO in S40), or if the call status is incoming or in a call (NO in S41), the operation is terminated.
- the operating state of the AV system 3 is acquired (S42).
- the acquisition of the operation state may be immediately acquired from the AV receiver 4 at this time, but what is periodically acquired may be used as it is.
- the current operation state of the AV system 3 is stopped, that is, when no sound is emitted from the speaker 12 (YES in S43), the operation is terminated without doing anything.
- the incoming call control register 234 The content of control performed on the AV system 3 at the time of incoming is read (S44), and a command message for performing control opposite to this control content is edited (S45).
- the reverse control is a control of the content that returns the operation of the AV system 3 to the state before the incoming call.
- the original control content is paused, it is play, and when the original control content is muted, the mute is released.
- the original control content is volume -10 dB, the volume is +10 dB. Then, this command message is transmitted to the AV receiver 4 (S46), the incoming flag 233 is reset (S47), and the operation is terminated.
- the AV system 3 since the user can make a call after controlling the AV system 3 by his / her own operation at the time of outgoing call, the AV system 3 is automatically controlled only at the time of incoming call. You may go. Further, automatic control may be performed not when an incoming call is received but when a response is made (when a call starts). In the manner mode, the operation shown in FIG. 6 may not be performed even when a call is received.
- the AV system including video and audio has been described as an example, but the present invention can also be applied to an audio system including only audio.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
- Transceivers (AREA)
- Selective Calling Equipment (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
通話を妨げないようにオーディオ機器に対する自動制御を行うオーディオ機器制御のアプリケーションプログラムを提供する。電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機の制御部を、ユーザの操作を検出する操作検出手段、前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出する着信検出手段、および、再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記操作検出手段がユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するコマンド送信手段、として機能させる。
Description
この発明は、スマートフォンなどの携帯電話機からオーディオ機器を制御するためのオーディオ機器制御プログラム、このオーディオ機器制御プログラムを搭載した携帯電話機、記録媒体、および制御方法に関する。
スマートフォンなどの携帯電話機は、アプリケーションプログラム(いわゆるアプリ)をインストールすることにより、基本機能である通話以外の機能を持たせることが可能である。アプリケーションプログラムには、無線LAN(Local Area Network)(Wi-Fi)経由でAV(Audio/Video)システムにアクセスして、ユーザの操作に応じた入力ソースの選択や再生音量の調整を行うものがある(非特許文献1参照)。
"ヤマハAVレシーバー専用コントロールApp「AV CONTROLLER」"、[online]、ヤマハ株式会社、[平成24年3月12日検索]、インターネット〈URL:http://jp.yamaha.com/news_events/audio-visual/11040401/〉
非特許文献1のアプリケーションプログラムを用いることにより、ユーザが自分の手持ちの携帯電話機を用いてAVシステムをコントロールすることができる。しかし、このアプリケーションプログラムは、ユーザの操作に応じた制御をAVシステムに対して行うのみのものであり、携帯電話機の基本機能である電話が着信した場合に、通話の妨げにならないようにAVシステムの音量を小さくするなどの機能は備えていなかった。
本発明は、通話を妨げないようにオーディオ機器に対する自動制御を行うオーディオ機器制御プログラムおよび携帯電話機を提供することを目的とする。
本発明の第1の側面によって提供されるオーディオ機器制御プログラムは、電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機の制御部を、ユーザの操作を検出する操作検出手段、前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出する着信検出手段、および、再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記操作検出手段がユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するコマンド送信手段、として機能させることを特徴とする。
上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムにおいて、前記携帯電話の制御部を、前記オーディオ機器の動作状態を取得する動作状態取得手段としてさらに動作させ、前記コマンド送信手段を、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、そのときの前記オーディオ機器の動作状態に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するようにしてもよい。
上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムにおいて、前記動作状態取得手段は、前記オーディオ機器の動作状態として、前記オーディオ機器において選択されているオーディオソースを取得し、前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、そのときの前記オーディオ機器において選択されているオーディオソースに応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するようにしてもよい。
上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムにおいて、前記着信検出手段は、前記電話通信部から発信者番号を取得し、前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、取得した発信者番号に応じて個別のコマンドメッセージを送信するようにしてもよい。
上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムにおいて、前記コマンドメッセージは、前記再生音の音量低下、ミュート、再生、停止の少なくともいずれかを示すようにしてもよい。
さらに、上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムにおいて、前記着信検出手段は、前記電話の着信状態または通話状態が終了したことをさらに検出し、前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が前記電話の着信状態または通話状態が終了したことを検出したとき、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出する前の状態に戻す制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信するものであってもよい。
本発明の第2の側面によって提供される携帯電話機は、上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムを記憶する記憶部と、電話通信を行う電話通信部と、該記憶部に記憶されているプログラムを実行する制御部と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
本発明の第3の側面によって提供される非一過性の記録媒体は、上記オーディオ機器制御プログラムを記憶することを特徴とする。
本発明の第4の側面によって提供される制御方法は、電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機の制御部の制御方法であって、前記制御部が、ユーザの操作を検出する操作検出手段、前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出する着信検出手段、および、再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記操作検出手段がユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するコマンド送信手段、として機能するように制御されることを特徴とする。
本発明の第5の側面によって提供される制御方法は、電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機からオーディオ機器を制御する制御方法であって、ユーザの操作を検出し、前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出し、再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記ユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信することを特徴とする。
この発明によれば、携帯電話の着信時に、ユーザが操作しなくてもオーディオ機器の再生音を制御することが可能になる。
図1は、この発明が適用される携帯電話機1およびAVシステム3の構成を示す図である。
携帯電話機1はいわゆるスマートフォンと言われる機種である。携帯電話機(スマートフォン)1は、携帯通信網である3G/4G通信機能を有するとともに、無線LAN(Wi-Fi)通信機能を有しており、アクセスポイント5を介してネットワーク2に接続される。ネットワーク2には、AVシステム3のコアとなるAVレシーバ4も接続されている。
携帯電話機1は、アプリケーションプログラム(アプリ)であるAVコントローラプログラム50を起動することにより、ユーザの操作に応じてネットワーク2経由でAVシステム3(AVレシーバ4)を制御することができる。また、携帯電話機1は電話の着信に応じて、ユーザの操作に依らずに、AVシステム3に対して再生音量を下げるなどの制御を行い、AVシステム3の再生音が通話の妨げにならないようにする。
AVシステム3は、コア機器であるAVレシーバ4にセットトップボックス(STB)10、DVD(Digital Versatile Disc)プレーヤ11、スピーカ12およびテレビ(TV)13が接続された構成であり、AVレシーバ4がネットワーク2に接続されている。AVレシーバ4は、複数のAVソースからいずれかを選択し、そのAVソースの再生(受信)映像をテレビ13に出力するとともに、再生(受信)音声をスピーカ12に出力する。AVソースの選択、音量の調整等は、AVレシーバ4の操作パネルの直接操作、付属の赤外線リモコンで行うことが可能であるが、携帯電話機1を用いて行うことも可能である。なお、AVシステム3の構成は図示のものに限定されない。
ネットワーク2には、AVレシーバ4、アクセスポイント5以外に、ルータ6、ネットワークストレージ(NAS)7などが接続されている。ルータ6はインターネット8に接続されている。AVレシーバ4は、ネットワーク2-ルータ6-インターネット8を介してインターネットラジオ局にアクセスしてインターネットラジオを再生する機能を備えている。また、ネットワークストレージ7にはMP3ファイルなどの楽曲データが保存されている。AVレシーバ4は、ネットワーク2を介してネットワークストレージ7にアクセスし、ネットワークストレージ7に記憶されている楽曲データを再生する機能を備えている。
携帯電話機1は、バス26上に、制御部20、操作部30、メディアインタフェース31、Wi-Fi通信回路32および3G/4G通信回路33を有している。制御部20は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)21、ROM(Read Only Memory)(フラッシュメモリ)22、RAM(Random Access Memory)23、画像プロセッサ24および音声プロセッサ25を含んでいる。画像プロセッサ24には、ビデオRAM(VRAM)40が接続され、VRAM40には表示部41が接続されている。表示部41は、液晶のディスプレイを含み、待ち受け画面や電話番号などを表示する。また、後述のAVコントローラ100の画面も表示部41に表示される。音声プロセッサ25には、D/Aコンバータを含むアンプ42が接続され、アンプ42にはスピーカ16が接続されている。
画像プロセッサ24は、待ち受け画面や電話番号等を描画して表示部41に表示するとともに、種々の映像を生成可能なGPU(Graphics Processing Unit,グラフィックス・プロセッシング・ユニット)を備えている。画像プロセッサ24は、CPU21の指示に従ってAVコントローラの画像を生成し、VRAM40上に描画する。音声プロセッサ25は、通話音声をエンコード/デコードするDSP(Digital Signal Processor:デジタル・シグナル・プロセッサ)を有している。音声プロセッサ25は、デコード/生成した音声をアンプ42に出力する。アンプ42は、この音声信号を増幅してスピーカ16に出力する。
Wi-Fi通信回路32は、無線アクセスポイント5との間でIEEE802.11g規格の無線通信を行い、AVレシーバ4などのネットワーク2上の機器とデータやメッセージの送受信を行う。AVレシーバ4との間は、DLNA(Digital Living Network Alliance)で規定されたフォーマットでメッセージを交換する。3G/4G通信回路33は、携帯電話通信網を介して、音声通話およびデータ通信を行う。データ通信によってアプリケーションプログラムのダウンロードが行われる。
操作部30は、表示部41上に形成されたタッチパネルを含み、タッチパネル上のタッチ操作、フリック操作を検出する。メディアインタフェース31にはメモリカード5が接続される。メモリカード5は、たとえばマイクロSDカードである。3G/4G通信回路33によってサーバからダウンロードされたアプリケーションプログラムは、メモリカード5またはROM22に保存される。この図では、AVコントロールプログラム50がメモリカード5に保存されている。AVコントロールプログラム50にはプログラムの実行に必要なデータが含まれ、プログラムの実行に必要なデータとして、コマンドテーブル501、着信時コマンドテーブル502が記憶されている。コマンドテーブル501は、AVシステム3の制御内容とその内容を表すコマンドを対応づけたテーブルである。着信時コマンドテーブル502は、図4に示すように、電話が着信した場合のAVシステム3に対する制御内容(コマンド)を記憶したテーブルであり、そのとき選択されている入力ソース別の制御内容が、デフォルト設定、および、発信者(着信電話番号)に応じて記憶される。発信者に応じた制御内容は、ユーザが設定操作で設定すればよい。
RAM23には、CPU21がAVコントローラプログラム50を実行する際に使用されるワークエリアが設定される。ワークエリアとして、システム構成記憶エリア231、動作状態記憶エリア232、着信フラグ233および着信制御レジスタ234などが設定される。システム構成記憶エリア231には、AVレシーバ4から取得したAVシステム3の構成が記憶される。システム構成とは、AVレシーバ4の上流、下流に接続されている機器、AVレシーバ4が選択可能な入力ソースなどである。動作状態記憶エリア232には、現在のAVシステム3(AVレシーバ4)の動作状態が記憶される。AVシステム3の動作状態とは、選択されている入力ソース、ボリューム値、再生中の楽曲名などである。着信フラグ233は、この携帯電話機1に電話が着信中または(着信による)通話中であることを示すフラグである。また、着信制御レジスタ234には、電話着信時に自動で行った制御内容が記憶される。AVコントローラ100(図2参照)は、通話終了時にこの制御内容と逆の制御を行ってAVシステム3を元の状態に戻す。
ROM22には、この携帯端末装置1の通話やアプリケーションプログラムを実行するための基本プログラムが記憶されている。また、ROM22はフラッシュメモリであり、基本プログラムのほか、ダウンロードされたアプリケーションプログラムなどを記憶することも可能である。
携帯電話機1は、メモリカード5に保存されているAVコントローラプログラム50との協働によって、図2に示すようなAVコントローラ100を構成し、Wi-Fi経由でAVレシーバ4にコマンドメッセージを送信してAVシステム3を制御する。
図2の機能ブロック図を参照して、携帯電話機1(ハードウェア)にメモリカード5のAVコントローラプログラム50が読み込まれることによって実現されるAVコントローラ100について説明する。
AVコントローラプログラム50が携帯端末装置1に読み込まれることによって実現されるAVコントローラ100は、操作画面表示部110、操作検出部120、メッセージ編集送信部130、システム状態取得部140および着信検出部150を有している。
操作画面表示部110は、制御部20、VRAM40、表示部41およびAVコントローラプログラム50の協働によって実現され、携帯電話機1の表示部41に、たとえば図3に示すような操作画面を表示する。図3に示した操作画面は、入力ソースの選択画面の例である。また、操作検出部120は、制御部20、操作部30およびAVコントローラプログラム50の協働によって実現され、表示部41に表示された操作画面に対する操作を検出する。図3において、ユーザが画面に表示されている入力ソース(ネットラジオ、PC、DOCK、USB、チューナー、AV1、・・・)のうち希望のものをクリックすると、操作検出部120がその操作を検出し、その操作情報をメッセージ編集送信部130に入力する。
メッセージ編集送信部130は、制御部20、Wi-Fi通信回路32およびAVコントローラプログラム50の協働によって実現され、操作検出部120から入力された操作情報に基づき、その操作情報に対応するコマンドメッセージを編集してAVレシーバ4に送信する。また、後述するように、メッセージ編集送信部130は、この携帯電話機1に電話が着信したとき、ユーザの操作に依らずに所定のコマンドメッセージを編集してAVレシーバ4に送信する。
システム状態取得部140は、制御部20、Wi-Fi通信回路32およびAVコントローラプログラム50の協働によって実現され、定期的(たとえば5秒毎)に、および、コマンドメッセージの編集時に、AVレシーバ4に対して、現在のAVシステム3の動作状態を問い合わせる。AVシステム3の動作状態とは、例えば、選択可能な入力ソース、選択されている入力ソース、再生中の曲名、音量値などの情報である。
着信検出部150は、制御部20およびAVコントローラプログラムの協働によって実現される機能部である。着信検出部150は、携帯電話機1(ハードウェア)と基本プログラムによって実現される電話通信部200に対して問い合わせを行い、通話ステータスを取得する。通話ステータスは、待機中、着信中、発信中、通話中などの音声(テレビ)通話の状態示す情報である。着信検出部150は、通話ステータスが変化すると、その変化をメッセージ編集送信部130に通知する。
メッセージ編集送信部130は、通話ステータスが待機中から着信中に変化した着信時には、再生音量を下げるなどの再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを(ユーザの操作に依らずに)編集してAVレシーバ4に送信する。これにより、AVシステム3の再生音が通話の妨げになることを防止している。また、通話ステータスが、着信中または通話中から待機中に変化した着信(通話)終了時には、着信時とは逆の内容のコマンドメッセージをAVレシーバ4に送信して、AVシステム3の動作を元に戻す。
図4はメッセージ編集送信部130(メモリカード5)に設けられる着信時コマンドテーブル502の構成を示す図である。このテーブルには、電話着信時のAVシステム3に対する制御内容、すなわち、AVレシーバ4に対して送信されるコマンドの内容が記憶されている。このテーブルには、電話着信時にAVシステム3において選択されているオーディオソースに応じたコマンドが記憶されている。
デフォルト設定では;
選択されているオーディオソースがDVDやUSBなどの再生ソース(ポーズ可能)である場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースが映像を含むAV受信ソース(テレビ等)の場合には音声をミュートする。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソース(FM等)の場合にはボリュームを低下(-10dB)する。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
選択されているオーディオソースがDVDやUSBなどの再生ソース(ポーズ可能)である場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースが映像を含むAV受信ソース(テレビ等)の場合には音声をミュートする。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソース(FM等)の場合にはボリュームを低下(-10dB)する。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
また、電話着信時に発信者の電話番号を取得可能であるため、電話番号ごとに制御内容を設定することが可能であり、このテーブルの例では、
発信者が090-xxxx-xxxxの場合には;
選択されているオーディオソースが再生ソースである場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースがAV受信ソースの場合には音声をミュートする。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソースの場合には音声をミュートする。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
発信者が090-xxxx-xxxxの場合には;
選択されているオーディオソースが再生ソースである場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースがAV受信ソースの場合には音声をミュートする。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソースの場合には音声をミュートする。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
発信者が090-yyyy-yyyyの場合には;
選択されているオーディオソースが再生ソースである場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースがAV受信ソースの場合には何もしない。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソースの場合には何もしない。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
選択されているオーディオソースが再生ソースである場合には、ポーズをかける。
選択されているオーディオソースがAV受信ソースの場合には何もしない。
選択されているオーディオソースがオーディオのみの受信ソースの場合には何もしない。
の内容でAVシステム3を制御するコマンドが記憶されている。
図5A~図7は、AVコントローラ100の動作を示すフローチャートである。
図5Aは、アプリケーションプログラムであるAVコントローラプログラム50の起動時の動作を示すフローチャートである。ネットワーク2内のAVレシーバ4を検索し(S1)、検出したAVレシーバ4から現在のシステム構成情報、および、現在の動作状態情報を受信する(S2、S3)。そして、受信した情報に基づいて、入力ソース選択画面やボリュームスライダなどのAVコントローラの画面を構成する(S4)。
図5Aは、アプリケーションプログラムであるAVコントローラプログラム50の起動時の動作を示すフローチャートである。ネットワーク2内のAVレシーバ4を検索し(S1)、検出したAVレシーバ4から現在のシステム構成情報、および、現在の動作状態情報を受信する(S2、S3)。そして、受信した情報に基づいて、入力ソース選択画面やボリュームスライダなどのAVコントローラの画面を構成する(S4)。
図5Bは、AVコントローラ100の通常動作を示すフローチャートである。この動作は所定期間(たとえば10ms)毎に繰り返し実行される。まず、ユーザによる操作があったか否かを判断する(S10)。操作がない場合には(S10でNO)、そのまま動作を終了する。ユーザによる操作があった場合には(S10でYES)、その操作に応じた制御を行うためのコマンドをコマンドテーブル501から読み出し(S11)、このコマンドを埋め込んだコマンドメッセージを編集して(S12)、AVレシーバ4に送信する(S13)。これにより、ユーザが携帯電話機1を用いてAVシステム3をコントロールすることができる。
図6は、電話着信時の処理を示すフローチャートである。この処理は所定時間(たとえば10ms)毎に繰り返し実行される。電話通信部200に問い合わせを行い、電話の着信があったか否か、すなわち、通話ステータスが待機中から着信中に変化したか否かを判断する(S20)。着信がない場合には(S20でNO)、そのまま動作を終了する。着信があった場合は(S20でYES)、AVシステム3の動作状態を取得する(S21)。この動作状態の取得は、このとき即座にAVレシーバ4から取得してもよいが、定期的に取得しているものをそのまま用いてもよい。現在のAVシステム3の動作状態が停止中、すなわち、スピーカ12から音声が放音されていない場合には(S22でYES)、何もしないで動作を終了する。
現在のAVシステム3の動作状態が停止中でない場合、すなわち、何らかのオーディオの再生が行われており、スピーカ12から音声が放音されている場合には(S22でNO)、電話通信部200から発信者番号を取得する(S23)。発信者番号が取得できた場合には(S24でYES)、着信時コマンドテーブル501を検索する(S25)。そして、取得した発信者番号に対応するデータがある場合には(S26でYES)、現在の動作状態に対応するこの発信者に個別のコマンドメッセージを編集する(S27)。一方、発信者番号を取得できなかった場合(S24でNO)、または、着信時コマンドテーブル501にその発信者に対応するデータなかった場合(S26でNO)には、デフォルト設定のコマンドメッセージを編集する(S28)。
そして、編集したコマンドメッセージの内容すなわちAVシステム3に対する制御内容を着信制御レジスタ234に記憶し(S29)、編集したコマンドメッセージをAVレシーバ4に送信する(S30)。そして着信フラグ233をセットする。これにより、携帯電話機1に電話が着信したときは、ユーザの操作に依らないでAVシステム3の再生音量を下げる等の制御をすることができる。
図7は、着信(通話)終了時の動作を示すフローチャートである。この処理は、所定時間(たとえば10ms)毎に繰り返し実行される。まず着信フラグ233がセットしているか否かを判断する(S40)。着信フラグ233がセットしている場合には(S40でYES)、着信または通話が終了したか否か、すなわち、通話ステータスが着信中または通話中から待機中に変化したか否かを判断する(S41)。着信フラグ233がセットしていない場合(S40でNO)、または、通話ステータスが着信中または通話中のままであった場合には(S41でNO)、そのまま動作を終了する。
着信または通話が終了した場合には(S41でYES)、AVシステム3の動作状態を取得する(S42)。この動作状態の取得は、このとき即座にAVレシーバ4から取得してもよいが、定期的に取得しているものをそのま用いてもよい。現在のAVシステム3の動作状態が停止中、すなわち、スピーカ12から音声が放音されていない場合には(S43でYES)、何もしないで動作を終了する。
現在のAVシステム3の動作状態が停止中でない場合、すなわち、何らかのオーディオの再生が行われており、スピーカ12から音声が放音されている場合には(S43でNO)、着信制御レジスタ234から着信時にAVシステム3に対して行った制御内容を読み出し(S44)、この制御内容と逆の制御を行うためのコマンドメッセージを編集する(S45)。逆の制御とは、AVシステム3の動作を着信前の状態に戻す内容の制御であり、元の制御内容がポーズの場合にはプレイであり、元の制御内容がミュートの場合にはミュート解除であり、元の制御内容がボリューム-10dBの場合にはボリューム+10dBである。そして、このコマンドメッセージをAVレシーバ4に送信し(S46)、着信フラグ233をリセットして(S47)、動作を終了する。
この実施形態では、発信時にはユーザが自らの操作でAVシステム3を制御したのち発信することができるため、着信時のみAVシステム3の自動制御を行うようにしているが、発信時にも自動制御を行ってもよい。また、自動制御を着信時ではなく応答時(通話開始時)に行うようにしてもよい。また、マナーモード時には、電話が着信しても図6の動作を行わないようにしてもよい。
また、着信(通話)中にAVレシーバ4が操作された場合には、図7に示した着信(通話)終了時にAVシステム3を元に戻す動作をしないようにしてもよい。
この実施形態では、映像及び音声を含むAVシステムを例にあげて説明したが、音声のみを含むオーディオシステムに対しても適用可能である。
1 携帯電話機
5 メモリカード
20 制御部
41 表示部
50 プログラム
100 AVコントローラ
200 電話通信部
231 システム構成記憶エリア
232 動作状態記憶エリア
233 着信フラグ
234 着信制御レジスタ
501 コマンドテーブル
502 着信時コマンドテーブル
5 メモリカード
20 制御部
41 表示部
50 プログラム
100 AVコントローラ
200 電話通信部
231 システム構成記憶エリア
232 動作状態記憶エリア
233 着信フラグ
234 着信制御レジスタ
501 コマンドテーブル
502 着信時コマンドテーブル
Claims (10)
- 電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機の制御部を、
ユーザの操作を検出する操作検出手段、
前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出する着信検出手段、および、
再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記操作検出手段がユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するコマンド送信手段、
として機能させるオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 前記携帯電話機の制御部を、前記オーディオ機器の動作状態を取得する動作状態取得手段としてさらに動作させ、
前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、そのときの前記オーディオ機器の動作状態に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを送信する
請求項1に記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 前記動作状態取得手段は、前記オーディオ機器の動作状態として、前記オーディオ機器において選択されているオーディオソースを取得し、
前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、そのときの前記オーディオ機器において選択されているオーディオソースに応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを送信する
請求項2に記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 前記着信検出手段は、前記電話通信部から発信者番号を取得し、
前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、取得した発信者番号に応じて個別のコマンドメッセージを送信する
請求項1に記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 前記コマンドメッセージは、前記再生音の音量低下、ミュート、再生、停止の少なくともいずれかを示す
請求項1に記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 前記着信検出手段は、前記電話の着信状態または通話状態が終了したことをさらに検出し、
前記コマンド送信手段は、前記着信検出手段が前記電話の着信状態または通話状態が終了したことを検出したとき、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出する前の状態に戻す制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信する
請求項1乃至5のいずれかに記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラム。 - 請求項1乃至6のいずれかに記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラムを記憶する記憶部と、
電話通信を行う電話通信部と、
該記憶部に記憶されている前記オーディオ機器制御プログラムを実行する制御部と、
を備えた携帯電話機。 - 請求項1乃至6のいずれかに記載のオーディオ機器制御プログラムを記憶するための非一過性の記録媒体。
- 電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機の制御部の制御方法であって、
前記制御部が、
ユーザの操作を検出する操作検出手段、
前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出する着信検出手段、および、
再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記操作検出手段がユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記着信検出手段が電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信するコマンド送信手段、
として機能するように制御される制御方法。 - 電話通信部を備えた携帯電話機からオーディオ機器を制御する制御方法であって、
ユーザの操作を検出し、
前記電話通信部に対する電話の着信を検出し、
再生音を出力するオーディオ機器と通信し、前記ユーザの操作を検出したとき、その操作に応じた制御内容のコマンドメッセージを前記オーディオ機器に対して送信し、前記電話の着信を検出したとき、前記オーディオ機器に対して前記再生音を制御する内容のコマンドメッセージを送信する、
制御方法。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/385,909 US9214914B2 (en) | 2012-03-19 | 2013-02-28 | Audio device control program, mobile telephone, recording medium, and control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-061970 | 2012-03-19 | ||
| JP2012061970A JP5751200B2 (ja) | 2012-03-19 | 2012-03-19 | オーディオ機器制御プログラムおよび携帯電話機 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013140994A1 true WO2013140994A1 (ja) | 2013-09-26 |
Family
ID=49222457
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/055540 WO2013140994A1 (ja) | 2012-03-19 | 2013-02-28 | オーディオ機器制御プログラム、携帯電話機、記録媒体及び制御方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9214914B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5751200B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013140994A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104869206B (zh) | 2014-02-20 | 2018-07-13 | 华为终端(东莞)有限公司 | 一种通信方法及终端 |
| CN104821796A (zh) * | 2015-03-20 | 2015-08-05 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | 一种音量控制方法、播放设备、移动终端及系统 |
| US10531236B2 (en) | 2016-11-03 | 2020-01-07 | International Business Machines Corporation | Universal mute for internet of things enabled devices |
| US20230297322A1 (en) * | 2022-03-21 | 2023-09-21 | Lenovo (United States) Inc. | Device disturbance reduction |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005295272A (ja) * | 2004-03-31 | 2005-10-20 | Dowango:Kk | 携帯端末、外部機器の音量制御方法および外部機器の音量制御プログラム |
| JP2006129219A (ja) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-18 | Toshiba Corp | ネットワーク家電機器制御システムおよび携帯型通信装置 |
| JP2007110388A (ja) * | 2005-10-13 | 2007-04-26 | Funai Electric Co Ltd | 連係動作プログラム及び接続機器 |
| JP2009004823A (ja) * | 2007-06-19 | 2009-01-08 | Nec Corp | 自動車内通話環境制御システム,携帯端末,自動車内通話環境制御方法およびプログラム |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0595392A (ja) * | 1991-06-26 | 1993-04-16 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 電話機 |
| JP2006245799A (ja) * | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-14 | Nec Saitama Ltd | 電子機器、該電子機器における警報出力制御方法及び警報出力制御プログラム |
| EP1724955A3 (en) * | 2005-05-17 | 2007-01-03 | Samsung Electronics Co.,Ltd. | Method for taking a telephone call while receiving a broadcast service, and digital multimedia broadcasting terminal using this method |
| JP4660342B2 (ja) | 2005-10-12 | 2011-03-30 | オリンパス株式会社 | 画像処理システム、画像処理プログラム |
| US8457285B2 (en) * | 2006-08-21 | 2013-06-04 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Communication device |
| JP2009100269A (ja) * | 2007-10-17 | 2009-05-07 | Sharp Corp | リモコン送信機及び音響機器の制御方法 |
-
2012
- 2012-03-19 JP JP2012061970A patent/JP5751200B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2013
- 2013-02-28 US US14/385,909 patent/US9214914B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-02-28 WO PCT/JP2013/055540 patent/WO2013140994A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005295272A (ja) * | 2004-03-31 | 2005-10-20 | Dowango:Kk | 携帯端末、外部機器の音量制御方法および外部機器の音量制御プログラム |
| JP2006129219A (ja) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-18 | Toshiba Corp | ネットワーク家電機器制御システムおよび携帯型通信装置 |
| JP2007110388A (ja) * | 2005-10-13 | 2007-04-26 | Funai Electric Co Ltd | 連係動作プログラム及び接続機器 |
| JP2009004823A (ja) * | 2007-06-19 | 2009-01-08 | Nec Corp | 自動車内通話環境制御システム,携帯端末,自動車内通話環境制御方法およびプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013197812A (ja) | 2013-09-30 |
| JP5751200B2 (ja) | 2015-07-22 |
| US20150079952A1 (en) | 2015-03-19 |
| US9214914B2 (en) | 2015-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101918040B1 (ko) | 스크린 미러링 방법 및 그 장치 | |
| KR101800889B1 (ko) | 음악 재생 장치 및 방법 | |
| JP5708562B2 (ja) | オーディオ・ビデオ制御システム、携帯端末装置およびオーディオ・ビデオ制御プログラム | |
| JP2014131113A (ja) | 再生装置、再生方法、並びに記録媒体 | |
| JP2012248257A (ja) | 映像音声機器、及びそれを備える映像音声システム | |
| JP2005260856A (ja) | 番組録画システム、通信端末、録画再生装置 | |
| KR102585876B1 (ko) | 컨텐트 재생 장치 및 그 동작 방법 | |
| JP5751200B2 (ja) | オーディオ機器制御プログラムおよび携帯電話機 | |
| JP5943050B2 (ja) | 音楽再生装置、及び、音楽再生プログラム | |
| KR101624904B1 (ko) | 휴대용 단말기에서 디엔엘에이를 이용하여 멀티 사운드 채널 컨텐츠를 재생하기 위한 장치 및 방법 | |
| US20140223470A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for reproducing contents | |
| JP6478162B2 (ja) | 携帯端末装置およびコンテンツ配信システム | |
| US20160119573A1 (en) | User terminal apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2013211767A (ja) | 映像記録装置、映像再生装置、及び映像記録再生システム | |
| JP2015122709A (ja) | 音楽再生装置、音楽再生システム、及び音楽再生プログラム | |
| KR20090123236A (ko) | 녹화파일 리스트를 외부로 제공하는 방송수신장치,녹화파일 제공방법 및 녹화파일 제공 시스템 | |
| JPWO2018061836A1 (ja) | 情報処理端末、情報処理方法、およびプログラム | |
| CN107943447A (zh) | 音乐播放方法、系统、可读存储介质及智能终端设备 | |
| US10275139B2 (en) | System and method for integrated user interface for electronic devices | |
| JP6724188B2 (ja) | サーバ、サーバの制御方法およびプログラム | |
| KR20220048670A (ko) | 전자 장치 및 그 동작 방법 | |
| JP2015136157A (ja) | 携帯端末装置 | |
| JP2008252160A (ja) | 放送受信装置及びプログラム | |
| KR101562040B1 (ko) | 동영상 스트리밍 서비스를 이용한 음악 편집 방법 및 이에 사용되는 음악 편집 장치 | |
| WO2012131832A1 (ja) | 音声読み上げシステム、音声読み上げ装置、および音声読み上げ方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13763882 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14385909 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13763882 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |