WO2013005512A1 - 衝撃吸収構造体及び人体保護具 - Google Patents
衝撃吸収構造体及び人体保護具 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013005512A1 WO2013005512A1 PCT/JP2012/064020 JP2012064020W WO2013005512A1 WO 2013005512 A1 WO2013005512 A1 WO 2013005512A1 JP 2012064020 W JP2012064020 W JP 2012064020W WO 2013005512 A1 WO2013005512 A1 WO 2013005512A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- shape
- elastic spherical
- elastic
- shock absorbing
- absorbing structure
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A42—HEADWEAR
- A42B—HATS; HEAD COVERINGS
- A42B1/00—Hats; Caps; Hoods
- A42B1/04—Soft caps; Hoods
- A42B1/08—Soft caps; Hoods with protection against blows
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A41—WEARING APPAREL
- A41D—OUTERWEAR; PROTECTIVE GARMENTS; ACCESSORIES
- A41D13/00—Professional, industrial or sporting protective garments, e.g. surgeons' gowns or garments protecting against blows or punches
- A41D13/015—Professional, industrial or sporting protective garments, e.g. surgeons' gowns or garments protecting against blows or punches with shock-absorbing means
- A41D13/0156—Professional, industrial or sporting protective garments, e.g. surgeons' gowns or garments protecting against blows or punches with shock-absorbing means having projecting patterns
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A42—HEADWEAR
- A42B—HATS; HEAD COVERINGS
- A42B3/00—Helmets; Helmet covers ; Other protective head coverings
- A42B3/04—Parts, details or accessories of helmets
- A42B3/10—Linings
- A42B3/12—Cushioning devices
- A42B3/124—Cushioning devices with at least one corrugated or ribbed layer
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a shock absorbing structure and a human body protector.
- the buffer body includes a porous body having deformation restoring properties, a bag body that encloses the porous body in an airtight manner, an intake means that sucks gas into the buffer body, and an exhaust that discharges gas to the outside of the buffer body. Means.
- polystyrene foam is conventionally known as a cushioning material for helmets, and is processed and formed to form a uniform hemisphere along the curved surface of the back surface of the helmet, and is provided on the back surface of the helmet.
- the porous body which exhibits the buffer function of the human body protector of the conventional patent document 1 it is excellent in flexibility and light weight, but since it is used by being worn on the human body, it is a material especially worn in summer The rise in temperature causes a decrease in shock absorption and stuffiness at the time of wearing.
- this porous body has low air permeability, there are many inconveniences such as low environmental temperature maintenance (temperature tends to be high) and low shock absorption to relatively sharp objects. .
- foamed polystyrene used as a cushioning material for general helmets has high impact absorption and light weight, but lacks breathability, environmental temperature maintenance performance and flexibility, lowers user comfort, and consequently helmets. It leads to dislike.
- the present invention has been made paying attention to the above-mentioned problems, and the shock absorbing structure and the human body protection satisfying all of the shock absorbing property, flexibility, breathability, light weight, and environmental temperature maintainability at a high level.
- the purpose is to provide ingredients.
- the external shape is spherical, and a plurality of elastic spherical bodies that elastically deform according to the magnitude and direction of external force applied from the outside,
- a structure that is provided between the elastic spheres in which the plurality of elastic spheres are assembled in a planar shape or a linear shape, and that secures a plurality of through gaps by opposing spherical surfaces that are separated from the plurality of elastic spheres, and is applied from the outside
- a soft-coupled structure that is coupled with low rigidity so that the shape of the structure can be deformed according to body deformation force; It is characterized by providing.
- the elastic sphere since the elastic sphere is spherical, it exhibits shock absorbing performance from all directions. Further, high air permeability and light weight can be obtained by the through gap formed between the elastic spherical bodies. Furthermore, since the elastic spheres are “soft-bonded”, high flexibility can be obtained that deforms following the shape of the portion provided with this structure. In addition, since the air permeability is high, problems such as “steaming” and “heat accumulation” due to the low air permeability do not occur, and the environmental temperature around the elastic spherical body suitably exhibits the above-mentioned shock absorption. It is difficult to deviate from the ambient temperature.
- the shock absorbing structure of the present invention can satisfy all of shock absorption, flexibility, breathability, light weight, and environmental temperature maintainability at a high level.
- FIG. 1 It is an external view which shows the protective hat which has the impact-absorbing structure of Example 1. It is a figure which shows the cross section (schematic diagram) of the protective cap of Example 1, and demonstrates an effect
- Example 2 It is a side view of the impact-absorbing structure of Example 2.
- 6 is a plan view showing an impact absorbing structure of Example 3.
- FIG. It is a side view of the impact-absorbing structure of Example 3.
- 6 is a plan view showing an impact absorbing structure of Example 4.
- FIG. It is a side view of the impact-absorbing structure of Example 4.
- It is a performance-evaluation figure which shows the impact-absorbing property by the impact-absorbing structure which concerns on Example 1 of this invention, a softness
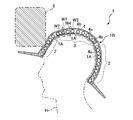
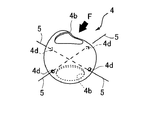
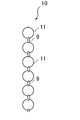
- FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 show a protective cap 1 as a human body protector according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 shows a cross-sectional view of the protective cap 1 of FIG.
- the protective hat 1 is made of a cloth material having good air permeability, a hat main body 1B as a body protecting body, and a sheet-like impact as an impact absorbing sheet provided inside the side and zenith of the hat main body 1B. Absorbing structures 2 and 3 are provided.
- the shock absorbing structure 2 is formed to have a vertical width substantially the same as the height of the side portion of the cap body 1B, and is provided so as to cover the side portion of the hat body 1B. Therefore, the shock absorbing structure 2 is also provided inside the side portion of the cap body 1B (not shown) shown in FIG.
- the shape and size (diameter, etc.) of the disk shape of the shock absorbing structure 3 provided inside the zenith portion of the hat body 1B are set to be substantially the same as the shape and size of the zenith portion of the hat body 1B. They are formed so as to coincide with each other.
- the hat main body 1B has a partially double structure, and this part serves as a seat pocket that functions as a storage part for the shock absorbing structure.
- the seat pocket is formed so as to exhibit a shape obtained by dividing the curved surface shape of the human body H into a plurality of parts.
- the double-structure portion of the cap body 1B is provided with an insertion opening 1A for storage, and the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 can be taken in and out of the seat pocket through the insertion opening 1A.
- ⁇ Shock absorbing structure on the side of the hat> 3A to 3C show the shock absorbing structure 2 provided inside the side portion of the cap body 1B.
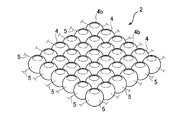
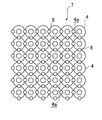
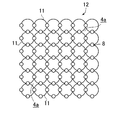
- the shock absorbing structure 2 has a plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 arranged in a plane and a plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 penetrating the elastic spherical bodies 4 vertically. And a synthetic resin yarn 5 bonded to each other in the lateral direction.
- the vertical and horizontal directions are the front, depth, and left and right directions in FIG. 3B.
- a gap 4a is formed between the opposing spherical surfaces facing the elastic spherical bodies 4.
- the gap 4a is formed as a plurality of penetrating gaps by opposing spherical surfaces separated from each other by the elastic spherical bodies 4, and penetrates from the front surface side to the rear surface side of the shock absorption structure 2, so that the shock absorption structure 2 It is a ventilation passage.
- the synthetic resin yarn 5 binds the plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 to each other and suppresses the rigidity to be low so that the shape of the shock absorbing structure 2 can be deformed according to the structure deformation force applied from the outside of the shock absorbing structure 2. Bonded (soft bond).
- soft coupling structures all structures for achieving such soft coupling are referred to as soft coupling structures.
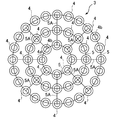
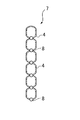
- the shock absorbing structure 3 includes a plurality of elastic spheres 4 arranged in a line in a triple circle and a plurality of circular elastic spheres 4.
- a synthetic resin thread 5 that penetrates in the circumferential direction and is connected to each other to form a bead shape, and further includes a plurality of synthetic resin threads 5A that connect the three parallel synthetic resin threads 5 in the radial direction of the circle. It has a disk shape as a whole.
- the elastic spherical bodies 4 are softly bonded to each other by the synthetic resin threads 5 and 5A.
- a gap 4a is formed between the adjacent elastic spherical bodies 4 and 4 (see FIG. 4A).
- each elastic spherical body 4 constituting each of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 has a spherical outer shape, depending on the magnitude and direction of external force applied from the outside. It is elastically deformed.
- the elastic spherical body 4 is made of polypropylene resin and is hollow.
- the elastic spherical body 4 is formed with vent holes 4b and 4c for communicating the inside and the outside.
- the elastic spherical body 4 has a shell thickness of about 0.3 mm, a sphere diameter of about 11 mm, and vent holes 4 b and 4 c having an opening diameter of about 6 mm.
- each elastic spherical body 4 has its vent holes 4b and 4c facing the front and back sides (upper and lower sides in FIG. 3B) of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3. The orientation is arranged.
- the ventilation holes 4b and 4c and the internal space of the elastic spherical body 4 constitute a ventilation path different from the air gap 4a that connects the front surface side and the back surface side of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3.
- a small thread hole 4d for allowing the synthetic resin thread 5 to pass therethrough is provided at the spherical top where the elastic spherical bodies 4 are close to each other.
- a knot 5n is formed at the end of the synthetic resin yarn 5, and the knot 5n prevents the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 from falling apart.
- shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 of the protective hat 1 of the first embodiment are the “venting action”, “shock absorbing action”, “following deformation action”, “environment temperature maintaining action”, and “lightening action”. This will be explained separately.
- the elastic spherical bodies 4 gather in a flat shape to form a sheet, and because of the spherical shape, there are voids 4a (see FIGS. 3A and 4A) formed between the elastic spherical bodies 4 and 4. It functions as a ventilation path that passes from the front surface side to the rear surface side of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3, and the air permeability of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 is ensured (see arrows W3 and W4 in FIG. 2).
- the ground contact area is reduced because the elastic spherical body 4 and the surface of the human body H and the back surface of the seat pocket of the hat body 1B are substantially point-contacted, thereby ensuring air permeability. (See FIG. 2).
- the elastic spherical body 4 is hollow and passes through each elastic spherical body 4 so as to penetrate from the front side to the back side of the sheet-like shock absorbing structures 2 and 3. Since the pores 4b and 4c are formed, the air permeability is further increased (see arrows W1 and W2 in FIG. 2 and FIG. 6A).
- shock absorption action Since the elastic spherical body 4 is spherical, it exhibits impact absorbing performance from all directions. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 6B, the shock absorbing performance is shown in any input direction (for example, the direction indicated by the black arrow). Unlike conventional honeycomb-shaped blocks and the like, it does not show excellent shock absorption in only one direction, but shows high shock absorption performance in all directions.
- the contact surface increases as a load is applied, and injury caused by local load concentration on the receiving side of the human body (such as the scalp of the human body) can be alleviated.
- the elastic spherical bodies 4 are softly coupled to each other, when the protective cap 1 provided with the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 is worn, the head shape of any person H is also deformed to absorb individual differences. Fit (see FIG. 2). For this reason, when an impact is applied to the head via the protective cap 1, the impact force is dispersed without being concentrated in one place. Further, at this time, the sheet shape of the shock absorbing structure 2 is also deformed following the shape of the corner portion of the object 6, and the impact force is uniformly dispersed.
- the elastic spherical body 4 is hollow, and the formed vent holes 4b and 4c are oriented in both directions of the normal direction of the head of the human body H and the curved surfaces of the head.
- the elastic spherical body 4 is sandwiched between the object 6 and the head surface, and the vent holes 4b and 4c are substantially closed.
- the elastic spherical body 4 itself is also elastically deformed, for example, the elastic spherical body 4 is deformed following the fine irregularities on the body surface.
- the deforming force when a structure deforming force is applied, the deforming force is uniformly dispersed by soft coupling, and the entire body is deformed flexibly and only a part is not bent.
- the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 are reduced in weight by the gap 4a between the elastic spherical bodies 4 and 4.
- the elastic spherical body is as described above. It is reduced in weight by the gap 4a between 4 and 4.
- Example 1 Since the elastic spherical body 4 of Example 1 is hollow, the weight is further reduced accordingly.
- shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 do not require the use of a high-mass resin unlike the conventional honeycomb block in order to maintain the shape, it can be said that the weight is high in this respect.
- the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 are formed in a flexible sheet shape by being penetrated by a plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 in a skewer shape so that the synthetic resin yarns 5 are orthogonal to each other, and further each elastic body is elastic. Since the spherical body 4 has the property of returning to its original shape even when it is crushed, even if the entire shock absorbing structure 2 or 3 is extremely deformed by absorbing the shock, the shock absorbing structure 2 3 can return to its original shape. For this reason, the entire shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 are not irreversibly collapsed like a polystyrene foam or a honeycomb block, and it is not necessary to use a high-mass resin for maintaining the shape.
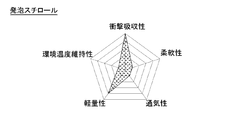
- the foam material shown in FIG. 10B is particularly excellent in flexibility and light weight, but it can be said that the balance of each performance is similarly poor overall because of low shock absorption, environmental temperature maintenance, and air permeability.
- the polystyrene foam is excellent in shock absorption and has a certain amount of lightness, but has extremely low flexibility, air permeability and environmental temperature maintainability, and the overall balance of performance is very poor. It can be said.
- foam materials are required to improve air permeability and environmental temperature maintainability without impairing flexibility and lightness.
- Styrofoam is required to improve flexibility, air permeability and environmental temperature maintainability without impairing shock absorption.
- the shock absorbing structure 2 according to the first embodiment of the present invention has the above-described functions that can solve these problems, and satisfies each performance at a high level (see FIG. 10A).
- the outer shape is spherical and a plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 that are elastically deformed according to the magnitude and direction of external force applied from the outside, and the plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 are assembled into a planar shape or a linear shape
- a plurality of through-gap 4a is secured by opposing spherical surfaces of the plurality of elastic spheres 4 provided between the elastic spheres 4 so that the structure shape can be deformed according to the structure deformation force applied from the outside.
- a soft coupling structure 5 coupled with low rigidity.
- shock absorbing structure according to the present invention instead of the shock absorbing member included in the human body protector such as the conventional protective hat, it is possible to add performance which is insufficient to the conventional one.
- the elastic spherical body 4 has air flow lines W1 and W2 parallel to air flow lines W3 and W4 passing from the front surface side to the back surface side thereof through the through-holes 4a of the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3. Ventilation holes 4b and 4c to be added are provided. For this reason, in addition to the effect of (1), it can be set as the protective hat 1 with further high air permeability.
- the elastic spherical body 4 is a hollow elastic spherical body made of synthetic resin.
- the protective hat 1 which further improved air permeability, shock absorption, and environmental temperature maintenance property by the above-mentioned impact absorption action can be provided.
- the soft bond structure is a structure in which a plurality of elastic spherical bodies 4 assembled in a planar shape or a linear shape are connected by a synthetic resin thread 5. For this reason, in addition to the effects (1) to (3), it is possible to provide the protective cap 1 which has high flexibility and absorbs individual differences in the shape of the head at a higher dimension and can follow and deform.
- a hat that is normally used is a breathable cloth hat main body, a plurality of seat pockets provided on the back surface of the cloth hat main body, each having a curved head shape, and each of the plurality of seat pockets. And an impact absorbing sheet loaded in the container.
- the shock absorbing sheet has a spherical outer diameter, and a plurality of elastic spherical bodies that are elastically deformed according to the magnitude and direction of external force applied from the outside, and the plurality of elastic spherical bodies are planar or linear.
- the plurality of elastic spheres are separated from each other by opposing spherical surfaces, and a plurality of through gaps are secured, and the structure shape can be deformed according to a structure deformation force applied from the outside.
- the shock absorbing structure is provided with a soft coupling structure coupled with low rigidity, and has a predetermined divided sheet shape.
- shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 can be attached to the hats that are usually used to make the protective hat 1 satisfying all of the impact absorption, flexibility, breathability, light weight, and environmental temperature maintenance at a high level. This will not impair the original comfort and design of the hat. Human damage caused by sudden accidents that occur in daily life without wearing a disaster hood, etc. can be minimized.
- a relatively pointed object such as a metal pliers falls on the head from the top and hits you directly.
- the impact can be dispersed and absorbed.
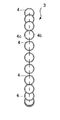
- Example 7A and 7B show an impact absorbing structure 7 of Example 2 according to the present invention.
- the shock absorbing structure 7 includes an elastic spherical body 4 and an adhesive portion 8 that softly bonds the elastic spherical bodies 4 to each other.
- the elastic spherical bodies 4 are softly coupled to each other by the bonding portion 8 to form a soft coupling structure.
- symbol is attached
- the bonding area 8 increases the opening area of the gap 4a between the elastic spherical bodies 4, thereby improving the air permeability and the air permeability of the protective cap 1. As a result, the temperature environment around the elastic spherical body 4 is less likely to change, and the environmental temperature maintainability is also improved.
- the degree of strength of the partial soft bond of the shock absorbing structure 7 can be changed depending on the type of adhesive used for the bonding portion 8, a desired shock absorbing structure 7 having locally different rigidity is obtained. Can do.
- the strength of the soft bond may be locally changed.
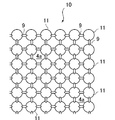
- Example 3 shows an impact absorbing structure 10 of Example 3 according to the present invention.
- the shock absorbing structure 10 includes a solid elastic spherical body 11 and an elongated bonding portion 9 that softly bonds the elastic spherical bodies 11 to each other. Then, the elastic spherical bodies 11 are softly coupled to each other by the adhesive portion 9 to form a soft coupling structure.
- symbol is attached
- the air permeability of the structure is higher.
- the elastic spherical body 11 is solid, the impact absorbing performance of the structure is further improved. Therefore, the air permeability can be improved without impairing the shock absorption of the structure.
- the protective hat 1 provided with the shock absorbing structure 10 ensures high breathability according to demand. be able to.
- the anti-stain property can be improved by making the elastic spherical body 11 solid compared to a hollow one.
- 9A and 9B show an impact absorbing structure 12 of Example 4 according to the present invention.
- the shock absorbing structure 12 includes an elastic spherical body 11 and an adhesive portion 8 as a soft coupling structure that softly bonds the elastic spherical bodies 11 to each other.
- the elastic spherical bodies 11 are softly bonded to each other by the bonding portion 8 to form a soft bond structure.
- symbol is attached
- the opening area of the gap 4a is narrower than that of the third embodiment by the adhesive portion 8 that softly bonds the elastic spherical bodies 11 to each other. , Breathability is low.
- the opening area of the gap 4a is adjusted to absorb the shock.
- the air permeability of the structure is adjusted.
- the impact absorbing structure 12 is formed by using a portion where the elastic spherical body 11 is softly coupled as an adhesive portion 9 in which the gap 4a is narrower than in the third embodiment.
- the protective hat 1 having a high heat retaining property by suitably adjusting the air permeability of the shock absorbing structure.
- the environmental temperature around the elastic spherical body 11 is maintained at an environmental temperature exhibiting high shock absorption, and the shock absorption of the elastic spherical body 11 is not impaired. As a result, a decrease in flexibility of the shock absorbing structure 12 can be suppressed.
- shock absorbing structure according to the present invention has been described based on Examples 1 to 4. However, the configuration can be changed without departing from the gist of the present invention.
- the “soft bond” between the elastic spheres 4 and 11 is realized by a flexible synthetic resin yarn in the shock absorbing structures 2 and 3 of the first embodiment, and a flexible adhesive in the second to fourth embodiments. Is realized. However, the configuration is not limited to these, and any configuration may be used as long as it can be “soft coupled”.
- the thickness, diameter, and vent holes of the elastic spherical body 4 are set to predetermined sizes and lengths, but are not limited to these as long as the desired performance is exhibited.
- the material of the elastic spheres 4 and 11 may be of any kind, and the resin constituting the elastic spheres 4 and 11 is not limited to polypropylene, and is known as a buffer material (other resins other than polypropylene and resins) Any other known material can be used.
- the shape of the elastic spherical bodies 4 and 11 may be any spherical shape, and for example, an elliptical cross section or an oval shape may be used.
- the overall breathability of the shock absorber can be further improved or decreased. Can be adjusted.
- the overall shape of the shock absorbing structure is not limited to that of the first embodiment, and may be any shape (three-dimensional shape or the like).
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Professional, Industrial, Or Sporting Protective Garments (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011-148026 | 2011-07-04 | ||
| JP2011148026A JP5433642B2 (ja) | 2011-07-04 | 2011-07-04 | 衝撃吸収構造体及び人体保護具 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013005512A1 true WO2013005512A1 (ja) | 2013-01-10 |
Family
ID=47436870
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2012/064020 Ceased WO2013005512A1 (ja) | 2011-07-04 | 2012-05-31 | 衝撃吸収構造体及び人体保護具 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5433642B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2013005512A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3634905A1 (de) | 1986-10-14 | 1988-04-28 | Bomag Menck Gmbh | Tauchfaehige rammvorrichtung |
| EP0301116B1 (de) | 1987-07-28 | 1991-07-03 | Menck Gmbh | Tauchfähige elektrohydraulische Antriebseinheit für zum Unterwassereinsatz ausgelegte Ramm- und Arbeitsgeräte |
| EP0301114B1 (de) | 1987-07-28 | 1991-07-03 | Menck Gmbh | Verfahren zum Eintreiben von Rammteilen unter Wasser |
| JP2013057138A (ja) * | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-28 | Tokushu Iryo:Kk | 保護帽子 |
| GB201303048D0 (en) * | 2013-02-21 | 2013-04-03 | Wood John | Impact absorbing structure |
| JP6174431B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-13 | 2017-08-02 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 衝撃吸収構造体の製造方法 |
| JP6247061B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-13 | 2017-12-13 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 衝撃吸収構造体、保護具及びその製造方法 |
| JP7506910B2 (ja) * | 2020-06-12 | 2024-06-27 | 株式会社セフト研究所 | 帽体内換気装置及び換気装置付き帽体 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007107176A (ja) * | 2006-10-16 | 2007-04-26 | Nisshin Kikaku:Kk | スポーツ用衣服 |
| JP2007224450A (ja) * | 2006-02-23 | 2007-09-06 | Nisshinbo Ind Inc | 衣料及び帽子 |
| JP3149676U (ja) * | 2009-01-16 | 2009-04-09 | 金子 博 | 帽子 |
| JP2010084314A (ja) * | 2008-10-01 | 2010-04-15 | Dong Il Sin | 頭保護用帽子 |
-
2011
- 2011-07-04 JP JP2011148026A patent/JP5433642B2/ja active Active
-
2012
- 2012-05-31 WO PCT/JP2012/064020 patent/WO2013005512A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007224450A (ja) * | 2006-02-23 | 2007-09-06 | Nisshinbo Ind Inc | 衣料及び帽子 |
| JP2007107176A (ja) * | 2006-10-16 | 2007-04-26 | Nisshin Kikaku:Kk | スポーツ用衣服 |
| JP2010084314A (ja) * | 2008-10-01 | 2010-04-15 | Dong Il Sin | 頭保護用帽子 |
| JP3149676U (ja) * | 2009-01-16 | 2009-04-09 | 金子 博 | 帽子 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013014855A (ja) | 2013-01-24 |
| JP5433642B2 (ja) | 2014-03-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5433642B2 (ja) | 衝撃吸収構造体及び人体保護具 | |
| CN105050439B (zh) | 冲击吸收设备 | |
| US4422183A (en) | Protective body shield | |
| US20060260026A1 (en) | Protective padding and protective padding systems | |
| JP5878202B2 (ja) | 産業用安全帽 | |
| WO2010082537A1 (ja) | アンダーキャップ | |
| JP2018500478A (ja) | スポーツ用、特にスキーをするときに使用する保護ヘルメット | |
| JP6449360B2 (ja) | プロテクター | |
| JP2009120983A (ja) | 乗車用および作業用ヘルメット | |
| KR100925855B1 (ko) | 방탄모 및 안전모 겸용 내피 | |
| TWM630463U (zh) | 具有透氣吸震功能之頭盔 | |
| KR20150128363A (ko) | 충격 흡수 기능을 갖는 헬멧 | |
| KR20060089967A (ko) | 안전모용 내피 및 이를 구비한 안전모 | |
| JP6236243B2 (ja) | ヘルメット用ハンモック | |
| CN214407176U (zh) | 一种减震透气的军警防弹头盔 | |
| JP2009024289A (ja) | 胸部保護パッド、及び、その製造方法 | |
| JP2002339140A (ja) | 頭部保護キャップ | |
| JP3843120B2 (ja) | 保護帽子 | |
| JP2014234563A (ja) | 帽子用保護具及び帽子 | |
| KR20200041690A (ko) | 두부 보호용 헬멧 | |
| KR20090011189U (ko) | 헬멧의 통풍구조 | |
| KR200474963Y1 (ko) | 코르크로 제작된 헬멧 | |
| JP2021147731A (ja) | ヘルメット | |
| KR101996536B1 (ko) | 통풍기능을 구비한 완충 헬멧 | |
| CN223183014U (zh) | 一种防护性好的安全帽 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12807646 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 12807646 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |