WO2012067155A1 - Dispositif de transport - Google Patents
Dispositif de transport Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012067155A1 WO2012067155A1 PCT/JP2011/076426 JP2011076426W WO2012067155A1 WO 2012067155 A1 WO2012067155 A1 WO 2012067155A1 JP 2011076426 W JP2011076426 W JP 2011076426W WO 2012067155 A1 WO2012067155 A1 WO 2012067155A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- chain
- support member
- key material
- rail
- transport
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/30—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor
- H05K3/32—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits
- H05K3/34—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits by soldering
- H05K3/3494—Heating methods for reflowing of solder
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K1/00—Soldering, e.g. brazing, or unsoldering
- B23K1/0008—Soldering, e.g. brazing, or unsoldering specially adapted for particular articles or work
- B23K1/0016—Brazing of electronic components
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K1/00—Soldering, e.g. brazing, or unsoldering
- B23K1/008—Soldering within a furnace
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K3/00—Tools, devices, or special appurtenances for soldering, e.g. brazing, or unsoldering, not specially adapted for particular methods
- B23K3/08—Auxiliary devices therefor
- B23K3/087—Soldering or brazing jigs, fixtures or clamping means
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K13/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or adjusting assemblages of electric components
- H05K13/0015—Orientation; Alignment; Positioning
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2101/00—Articles made by soldering, welding or cutting
- B23K2101/36—Electric or electronic devices
- B23K2101/42—Printed circuits
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a transport device used for transporting a substrate of a soldering apparatus for soldering a substrate.
- the second support member that supports the upper part of the chain is disposed in the second groove part of the rail part so as to be movable through a gap, so that the chain can be stably absorbed by absorbing the vibration and expansion of the chain. It is intended to run.
- the soldering apparatus When soldering a printed circuit board and an electronic component, a soldering device is generally used.
- the soldering apparatus can be roughly classified into a reflow method and a flow method.
- the reflow soldering apparatus includes a transport device that transports a substrate and a tunnel-like reflow device body (muffle).
- a preheating zone, a main heating zone, and a cooling zone are provided inside the reflow apparatus main body.
- hot air is blown against the board transported by the transporting device to solder the solder paste. Is melted to fix an electronic component or the like to the electrode of the substrate.
- the substrate heated in the preheating zone and the main heating zone is cooled to solidify the solder.
- the printed circuit board is soldered by such a series of processes.
- a chain with a bush is generally used.
- the chain with the bush is configured as a pair to support both ends of the substrate, and runs along the tunnel of the reflow apparatus main body.
- a plurality of holding pins for holding the substrate are provided on the opposing plate surfaces of the pair of chains with bushes, and the substrate is placed on the holding pins so that the substrate is placed in the tunnel of the reflow apparatus main body. Transported to the zone.
- the distance between the pair of chains may increase during traveling or the vibration of the chain may intensify, and the printed circuit board placed on the holding pin will fall.
- the soldering process may be affected due to poor conveyance of the substrate.
- the reflow soldering apparatus disclosed in Patent Document 1 has the following problems.
- the upper chain guide is in contact with the upper part of the chain and is integrally formed with the upper support part
- the intermediate chain guide is in contact with the lower part of the chain and fixed to the support member. It is fixed with no gap between it and the chain guide. Therefore, when the chain vibrates while traveling, there is a problem that the chain vibration cannot be absorbed by the upper chain guide and the intermediate chain guide, and the chain operation is stopped by the vibration.
- the chain is pressed by expansion due to the material of the upper chain guide and the middle chain guide, and the operation of the chain is stopped.
- the flow type soldering apparatus is an apparatus for performing soldering by jetting solder that has been melted in advance upward and bringing the printed circuit board into contact with the jet surface and carrying the same as the above-described reflow apparatus. Having the device has the same problem. Further, regardless of the soldering apparatus, this type of conveying apparatus has the same problem.
- an object of the present invention is to solve the above-described problems and to provide a transport device that can stabilize the traveling of a chain that transports a substrate.
- a conveyance chain a first guide portion provided below the chain, and a second guide portion provided above the chain are provided, and the chain is transported in the substrate direction.
- a rail portion that travels along the rail, a first support member that is attached to the first guide portion of the rail portion and that supports the lower portion of the chain, and a second guide portion that is movably disposed on the rail portion. And a second support member that supports the upper part of the first support member.
- the second support member is disposed in the second guide portion via a gap and is configured to be movable within the gap. Therefore, when the chain vibrates during traveling, the vibration of the chain is absorbed by the second support member, and stable traveling of the chain is ensured. Further, even when the second support member or the chain is expanded by its material, it is possible to avoid a situation in which the expansion is absorbed in the gap by the second support member and the operation of the chain is stopped.
- the vibration of the chain can be absorbed by the second support member when the chain vibrates during traveling.
- the chain can be driven stably.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of the transport device shown in FIG. 3. It is sectional drawing which shows the structural example of the principal part of the conveying apparatus shown in FIG.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line BB of the transport device shown in FIG.
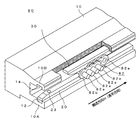
- FIG. 1 shows an example of the configuration of the reflow apparatus 100.
- the reflow device 100 includes a reflow device main body 40, a transport device 80, a heater 50, a fan 60, and a motor 62.
- the reflow device main body 40 is a tunnel-like housing having a carry-in port 40a and a carry-out port 40b, and includes a preheating zone Z1 and a main heating zone Z2 along a transfer path H1 from the carry-in port 40a to the carry-out port 40b. And a cooling zone Z3.
- the transport device 80 transports the printed circuit board 70 along the transport path H ⁇ b> 1 in the reflow device main body 40, and includes an endless chain 82 with a bush (hereinafter referred to as a chain 82) and a sprocket 86.
- the chain 82 is stretched by four sprockets 86 to which the rotational force of a driving motor (not shown) is transmitted, and the transport path H1 in the tunnel of the reflow device main body 40, the side and the lower side of the reflow device main body 40. It is laid to go around.
- the transport device 80 will be described later.
- the heater 50, the fan 60, and the motor 62 are installed in each of the preheating zone Z1 and the main heating zone Z2, and are arranged to face each other in the vertical direction of the transfer device 80.
- the heater 50 heats the gas inside the reflow apparatus main body 40 and generates hot hot air.
- the fan 60 is composed of, for example, a sirocco fan, and blows hot air heated by the heater 50 by rotation of the motor 62 from above and below the printed circuit board 70. As a result, the solder of the printed circuit board 70 is melted, and electronic components and the like are fixed to the electrodes of the printed circuit board 70.
- the heater 50, the fan 60, and the motor 62 installed in the preheating zone Z1 and the main heating zone Z2 have the same configuration.
- the cooling unit 92 includes, for example, a cooling member, a fan, a motor, and the like, and is installed in the cooling zone Z3.
- the cooling unit 92 solidifies the molten solder by cooling the printed circuit board 70 heated in the preheating zone Z1 and the main heating zone Z2.
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view illustrating an example of a main part of the configuration of the transport device 80.
- FIG. 3 is a plan view illustrating a configuration example of the transport device 80.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of the transport device 80 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a configuration example of a main part of the transport device 80 illustrated in FIG. 4.
- FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line BB of the transport device 80 shown in FIG.
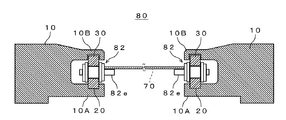
- the transport device 80 includes a transport rail (rail portion) 10, a chain 82, a lower key material 20, and an upper key material 30, as shown in FIGS.
- the transport rail 10 is composed of a pair of transport rails 10 and 10 arranged to face each other in the width direction of the printed circuit board 70, and the reflow apparatus main body 40. Are laid along the longitudinal direction (conveyance path H1).
- a metal material such as aluminum is used for the transport rail 10.
- the pair of transport rails 10 and 10 has a substantially U-shaped side surface opened on opposite sides, and has a lower rail 10A provided below the chain 82 and an upper rail 10B provided above the chain 82. is doing.
- a groove 12 for attaching the lower key material 20 is formed in the inner surface of the lower rail 10 ⁇ / b> A facing the upper rail 10 ⁇ / b> B along the longitudinal direction of the transport rail 10.
- the width W ⁇ b> 1 of the groove 12 is selected to be substantially the same as the width W ⁇ b> 2 of the lower key material 20, and the depth D ⁇ b> 1 is the chain 82 when the chain 82 is placed on the upper surface of the lower key material 20.
- the depth is such that the lower end of the inner plate 82a is not in contact with the inner surface of the lower rail 10A.
- the groove part 12 comprises an example of a 1st guide part.
- a groove 14 for attaching the upper key material 30 is formed along the longitudinal direction of the transport rail 10.
- the width W3 of the groove portion 14 is selected to be slightly larger than the width W4 of the upper key member 30, and a gap A1 is formed between the groove portion 14 and the upper key member 30.
- the depth D2 of the groove portion 14 is selected so that a slight gap A2 is formed between the upper surface of the upper key material 30 and the groove upper surface of the groove portion 14 when the upper key material 30 is disposed on the bush 82c of the chain 82.
- the groove part 14 comprises an example of a 2nd guide part.
- the chain 82 has a pair of inner plates 82a, 82a, a pair of outer plates 82b, 82b, a bush 82c, a pin 82d, and a holding pin 82e.
- the two inner plates 82a and 82a are press-fitted through a bush 82c and coupled.
- the pin 82d is inserted inside the bush 82c, and outer plates 82b and 82b are press-fitted and coupled to both ends of the pin 82d and outside the inner plates 82a and 82a, respectively.
- the holding pin 82e holds the printed circuit board 70, and is provided so as to protrude from the plate surface side of the outer plate 82b disposed on the transport rail 10 side facing each other.
- the printed circuit board 70 is placed on the holding pins 82e and is transported along the transport path H1.
- a pair of chains 82 is shown, but actually, a plurality of inner links having an inner plate 82a and a bush 82c and a plurality of outer links having an outer plate 82b and a pin 82d are alternately arranged. Concatenated and configured.
- the lower key member 20 is a long columnar body as shown in FIGS. 2 to 6, and is made of a metal material having excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance, such as stainless steel (SUS).
- the lower key material 20 is fitted into the groove portion 12 so that the upper side of the lower key material 20 is exposed from the groove portion 12 and supports the bush 82c of the traveling chain 82 slidably on the upper surface portion thereof. Further, the lower key material 20 is fitted into the groove portion 12 without a gap, and is fixed to the groove portion 12 so as not to move in the transport path H1 and the direction orthogonal thereto.
- the width W2 of the lower key member 20 is selected to be substantially the same as the length of the bush 82c in the longitudinal direction.
- the lower key material 20 constitutes an example of a first support member.
- the lower key material 20 is divided into a plurality of key materials 20A, 20B, 20C, and 20D, and adjacent key materials 20A and 20B, key materials 20B and 20C, and key materials 20C and 20D. Is fitted into the groove 12 with a predetermined interval X1.
- the interval X1 is selected based on the expansion coefficient of the lower key material 20 and the like.
- the key materials 20B and 20C are shown for the sake of convenience as an example in which adjacent key materials are separated.
- the example which comprised the lower key material 20 by four is shown, it is not limited to this.
- a taper portion 22 that is inclined downward from the upper surface portion is provided at each of both ends in the longitudinal direction of the lower key material 20.
- a tapered portion 22a is provided at the end of the key member 20A on the carry-in port 40a side
- a tapered portion 22d is provided at the end of the key member 20D on the carry-out port 40b side.
- These tapered portions 22a and 22d function as guide portions for smoothly transporting the chain 82 inside and outside the tunnel of the reflow apparatus main body 40.
- a tapered portion 22b is provided at an end portion of the key material 20B facing the key material 20C
- a tapered portion 22c is provided at an end portion of the key material 20C facing the key material 20B.
- each lower key member 20 is fixed on the upstream side with respect to the conveyance path H1 of the printed circuit board 70, and the downstream side is a free end.
- a stopper 23 provided on the lower key material 20 is fixed by being inserted into the recess 11 of the groove 12. This is because when the lower key material 20 expands due to heat, the lower key material 20 is configured to expand in the transport direction side.
- the running direction of the chain 82 and the extending direction of the lower key material 20 coincide with each other, and therefore, the extension of the lower key material 20 is not subjected to stress due to the running of the chain 82. There will be no hindrance to the 82.
- the chain 82 travels to cause vibration of the lower key material 20 with the fixed side as a base point.
- the free end of the lower key material 20 is transferred to the transport path.
- the lower key material 20 is stretched in the direction opposite to the conveying direction due to the force that is lifted inward and hinders the chain traveling or due to heat, the chain 82 is traveling in the conveying direction.
- the extension of the lower key material 20 affects the travel of the chain 82, as stress is applied to the lower key material along with the expansion, and the lower key material 20 swells in the transport path and impedes the travel of the chain 82. May affect.
- the upper key material 30 is a long columnar body like the lower key material 20, and is made of a metal material having excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance, such as stainless steel (SUS).
- the upper key member 30 is inserted into a space formed by the groove portion 14 and the chain 82, and is placed on the bush 82c of the chain 82 by its own weight. As a result, the bush 82c of the chain 82 slides in contact with the lower surface portion of the upper key member 30, and the inner plate 82a of the chain 82 is supported by the upper key member 30, thereby restricting the traveling direction of the chain 82. .
- a gap A1 is provided between the peripheral surface of the upper key member 30 and the groove peripheral surface of the groove portion 14, and between the upper surface of the upper key member 30 and the groove upper surface of the groove portion 14.
- a gap A2 is provided, and the upper key member 30 is disposed in the groove portion 14 with play. That is, the upper key member 30 is disposed in the groove portion 14 so as to be movable up and down and left and right through the gaps A1 and A2.
- the upper key member 30 constitutes an example of a second support member.
- the upper key member 30 is divided into a plurality of key members 30A, 30B, and 30C (support members). This is because the upper key member 30 is divided and smoothly attached to the groove portion 14.
- the plurality of key members 30A, 30B, and 30C are attached by sequentially inserting the lower key member 20 and the chain 82 into the space portion formed by the groove portion 14 and the chain 82. Therefore, a stopper 34 for preventing the previously inserted upper key material 30 (key material 30C) from dropping or jumping out from the carry-out port 40b side of the groove portion 14 is provided at the other end of the groove portion 14 on the carry-out port 40b side. Is provided.
- the upper key material 30 is composed of three, but the present invention is not limited to this.
- a taper portion 32 that is inclined from the lower surface portion toward the upper outside is provided at the end of the key material 30 ⁇ / b> A on the carry-in port 40 a side.
- the tapered portion 32 functions as a guide portion for ensuring a wide entrance of the chain 82 and smoothly transporting the chain 82 into the reflow apparatus main body 40.
- the end portion 30a of the upper key material 30 (key material 30A) on the carry-in port 40a side is a distance X2 from the end portion 20a on the carry-in port 40a side of the lower key material 20 (key material 20A). It is provided at a position shifted to the downstream side of the transport path H1. This is because, when the end portion 20a of the key material 20A and the end portion 30a of the key material 30A are set at the same position, the entrance between the key material 20A and the key material 30A becomes narrow, so the carry-in port 40a.
- the upper key material 30 is inserted into the space formed between the upper part of the chain 82 and the groove 14 of the transport rail 10 from the carry-in entrance 40a side. Since the upper key member 30 is divided into a plurality of pieces, these are sequentially inserted into the space portion. Since the stop portion 34 is provided on the carry-out port 40 b side of the groove portion 14, the upper key material 30 is pushed in until the previously inserted upper key material 30 is stopped by the stop portion 34. In this way, the transport device 80 can be configured.
- the upper key member 30 is movably disposed in the groove portion 14 via the gaps A1 and A2, even when the chain 82 vibrates during running, Since the key member 30 can absorb the vibration in the vertical direction of the chain 82, the chain 82 can be driven stably. Further, even when the upper key material 30 and the chain 82 are expanded by the material, the upper key material 30 can absorb the expansion in the range of the gaps A1 and A2, so that the chain 82 can be run stably. . As a result, the situation where the operation of the chain 82 stops can be avoided.
- the technical scope of the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and includes those in which various modifications are made to the above-described embodiment without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
- the guide portion may be formed in a convex shape instead of the groove. .
- the key material may be provided with a concave portion so as to engage with the convex portion.
- this invention is applicable also to a flow type soldering apparatus and the similar conveying apparatus.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Electric Connection Of Electric Components To Printed Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
De façon à stabiliser le fonctionnement d'une chaîne transportant une carte à circuit, la présente invention présente un rail de transport (10) qui transporte une carte à circuit imprimé à l'intérieur d'un tunnel de dispositif de refusion, forme un canal (12) dans un rail inférieur (10A) du rail de transport (10), et forme une partie de canal (14) dans un rail supérieur (10B). Un matériau de clavette (20) de partie inférieure est inséré dans le canal (12) et soutient la partie inférieure d'une chaîne (82) ; un matériau de clavette (30) de partie supérieure est placé et maintenu sur la surface supérieure des bagues (82c) de la chaîne (82) par son propre poids, disposé de telle sorte qu'un mouvement est possible par l'intermédiaire des espaces (A1, A2) dans le canal (14), et soutient la partie supérieure de la chaîne (82). De plus, selon la présente invention, lorsqu'il y a une vibration durant le fonctionnement de la chaîne, par exemple, la vibration verticale de la chaîne (82) est absorbée par le matériau de clavette (30) de partie supérieure, et un fonctionnement stable de la chaîne est assuré.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201180055615.9A CN103221171B (zh) | 2010-11-19 | 2011-11-16 | 输送装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010-258596 | 2010-11-19 | ||
| JP2010258596A JP5299409B2 (ja) | 2010-11-19 | 2010-11-19 | 搬送装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012067155A1 true WO2012067155A1 (fr) | 2012-05-24 |
Family
ID=46084078
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/076426 WO2012067155A1 (fr) | 2010-11-19 | 2011-11-16 | Dispositif de transport |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5299409B2 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN103221171B (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2012067155A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102745457A (zh) * | 2012-07-05 | 2012-10-24 | 无锡金洋铝业有限公司 | 一种异型双t型轨道 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61200654U (fr) * | 1985-06-07 | 1986-12-16 | ||
| JPH01118091A (ja) * | 1987-10-30 | 1989-05-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 加熱炉用搬送装置 |
| JPH03216268A (ja) * | 1990-01-22 | 1991-09-24 | Toyo Radiator Co Ltd | 熱交換器ろう付け用ハンガ |
| JPH0486609U (fr) * | 1990-11-30 | 1992-07-28 | ||
| JPH04344869A (ja) * | 1991-05-17 | 1992-12-01 | Denkoo:Kk | 熱処理装置 |
| JPH0645747A (ja) * | 1992-07-23 | 1994-02-18 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | リフロー装置 |
| JP2003179342A (ja) * | 2001-12-10 | 2003-06-27 | Senju Metal Ind Co Ltd | リフロー炉 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61200654A (ja) * | 1985-02-28 | 1986-09-05 | Futaba Corp | 螢光表示装置 |
| JPH01133668A (ja) * | 1987-11-20 | 1989-05-25 | Kenji Kondo | プリント基板の保持搬送方法およびその装置 |
| JPH0486609A (ja) * | 1990-07-27 | 1992-03-19 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 光コネクタ |
| JP4401537B2 (ja) * | 2000-05-26 | 2010-01-20 | 千住金属工業株式会社 | リフロー炉 |
| JP2002037431A (ja) * | 2000-07-27 | 2002-02-06 | Nec Saitama Ltd | 板状物体の搬送機構及びリフロー装置 |
| JP4559656B2 (ja) * | 2001-04-03 | 2010-10-13 | 株式会社タムラ製作所 | 搬送装置および加熱装置 |
| TWI289033B (en) * | 2002-11-25 | 2007-10-21 | Senju Metal Industry Co | Solder reflow oven |
| CN100522444C (zh) * | 2003-12-26 | 2009-08-05 | 株式会社田村制作所 | 焊锡连接装置 |
| TW200524496A (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2005-07-16 | Senju Metal Industry | Reflow furnace |
-
2010
- 2010-11-19 JP JP2010258596A patent/JP5299409B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-11-16 CN CN201180055615.9A patent/CN103221171B/zh active Active
- 2011-11-16 WO PCT/JP2011/076426 patent/WO2012067155A1/fr active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61200654U (fr) * | 1985-06-07 | 1986-12-16 | ||
| JPH01118091A (ja) * | 1987-10-30 | 1989-05-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 加熱炉用搬送装置 |
| JPH03216268A (ja) * | 1990-01-22 | 1991-09-24 | Toyo Radiator Co Ltd | 熱交換器ろう付け用ハンガ |
| JPH0486609U (fr) * | 1990-11-30 | 1992-07-28 | ||
| JPH04344869A (ja) * | 1991-05-17 | 1992-12-01 | Denkoo:Kk | 熱処理装置 |
| JPH0645747A (ja) * | 1992-07-23 | 1994-02-18 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | リフロー装置 |
| JP2003179342A (ja) * | 2001-12-10 | 2003-06-27 | Senju Metal Ind Co Ltd | リフロー炉 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5299409B2 (ja) | 2013-09-25 |
| CN103221171B (zh) | 2015-04-15 |
| CN103221171A (zh) | 2013-07-24 |
| JP2012106273A (ja) | 2012-06-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5463129B2 (ja) | リフロー装置 | |
| JP4993015B2 (ja) | 搬送装置の給油装置 | |
| KR20070021817A (ko) | 솔더링 장치 및 솔더링 방법 | |
| JP5218097B2 (ja) | 自動はんだ付け装置及び搬送装置 | |
| WO2012067155A1 (fr) | Dispositif de transport | |
| JP2012106273A5 (fr) | ||
| US11235407B2 (en) | Soldering apparatus and method of fixing gasket to the soldering apparatus | |
| KR101922902B1 (ko) | 회로기판 처짐방지구조를 포함하는 리플로우 납땜장치 | |
| JP5264079B2 (ja) | 加熱装置 | |
| JPWO2009154225A1 (ja) | 自動はんだ付け装置 | |
| JP6133631B2 (ja) | リフロー装置 | |
| JP2024106042A (ja) | 搬送加熱装置 | |
| JP2003179342A (ja) | リフロー炉 | |
| JP2014110331A (ja) | 反り防止治具および基板の製造方法 | |
| JP3813027B2 (ja) | はんだ付け装置 | |
| JPH032375Y2 (fr) | ||
| JP2003031940A (ja) | リフロー半田装置 | |
| JP4229580B2 (ja) | リフロー半田付け装置 | |
| KR200255705Y1 (ko) | 납땜 장치용 인쇄회로기판 이송 장치 | |
| JP2009009972A (ja) | リフロー半田付け装置 | |
| JP2005265202A (ja) | 加熱装置 | |
| JP2022071912A (ja) | グリス供給ユニット及び搬送加熱装置 | |
| JP2008226980A (ja) | リフロー装置 | |
| JP4477868B2 (ja) | はんだ付け装置 | |
| JP2013004789A (ja) | リフロー装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11841707 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE2 | Request for preliminary examination filed before expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11841707 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |