JP6500579B2 - 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 - Google Patents
回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6500579B2 JP6500579B2 JP2015091211A JP2015091211A JP6500579B2 JP 6500579 B2 JP6500579 B2 JP 6500579B2 JP 2015091211 A JP2015091211 A JP 2015091211A JP 2015091211 A JP2015091211 A JP 2015091211A JP 6500579 B2 JP6500579 B2 JP 6500579B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- circuit
- current
- voltage
- output
- circuit device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 141
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 100
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 77
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 34
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 44
- 235000014676 Phragmites communis Nutrition 0.000 description 30
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000013139 quantization Methods 0.000 description 4
- 101000658138 Homo sapiens Thymosin beta-10 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102100034998 Thymosin beta-10 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N (2s)-2-[[4-[2-(2,4-diaminoquinazolin-6-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]-4-methylidenepentanedioic acid Chemical compound C1=CC2=NC(N)=NC(N)=C2C=C1CCC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=C)C(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100031663 Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101150082608 TPN1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010039203 Tripeptidyl-Peptidase 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100040411 Tripeptidyl-peptidase 2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- RDYMFSUJUZBWLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N endosulfan Chemical compound C12COS(=O)OCC2C2(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C1(Cl)C2(Cl)Cl RDYMFSUJUZBWLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011045 prefiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011946 reduction process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 108010039189 tripeptidyl-peptidase 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K7/00—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements
- G01K7/16—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements
- G01K7/18—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements the element being a linear resistance, e.g. platinum resistance thermometer
- G01K7/20—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements the element being a linear resistance, e.g. platinum resistance thermometer in a specially-adapted circuit, e.g. bridge circuit
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C19/00—Gyroscopes; Turn-sensitive devices using vibrating masses; Turn-sensitive devices without moving masses; Measuring angular rate using gyroscopic effects
- G01C19/56—Turn-sensitive devices using vibrating masses, e.g. vibratory angular rate sensors based on Coriolis forces
- G01C19/5776—Signal processing not specific to any of the devices covered by groups G01C19/5607 - G01C19/5719
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K1/00—Details of thermometers not specially adapted for particular types of thermometer
- G01K1/20—Compensating for effects of temperature changes other than those to be measured, e.g. changes in ambient temperature
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K7/00—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements
- G01K7/16—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements
- G01K7/22—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements the element being a non-linear resistance, e.g. thermistor
- G01K7/24—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements using resistive elements the element being a non-linear resistance, e.g. thermistor in a specially-adapted circuit, e.g. bridge circuit
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K7/00—Measuring temperature based on the use of electric or magnetic elements directly sensitive to heat ; Power supply therefor, e.g. using thermoelectric elements
- G01K7/42—Circuits effecting compensation of thermal inertia; Circuits for predicting the stationary value of a temperature
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C19/00—Gyroscopes; Turn-sensitive devices using vibrating masses; Turn-sensitive devices without moving masses; Measuring angular rate using gyroscopic effects
- G01C19/56—Turn-sensitive devices using vibrating masses, e.g. vibratory angular rate sensors based on Coriolis forces
- G01C19/5719—Turn-sensitive devices using vibrating masses, e.g. vibratory angular rate sensors based on Coriolis forces using planar vibrating masses driven in a translation vibration along an axis
- G01C19/5726—Signal processing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K13/00—Thermometers specially adapted for specific purposes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K2219/00—Thermometers with dedicated analog to digital converters
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Analogue/Digital Conversion (AREA)
- Measuring Temperature Or Quantity Of Heat (AREA)
- Gyroscopes (AREA)
- Amplifiers (AREA)
Description
まず本実施形態の手法について説明する。特許文献1や特許文献2のように、種々の温度センサー、温度検出回路が知られている。温度データを求める際には、温度依存性を有する所与の出力電圧(特許文献1等における温度依存電圧)を用いることが一般的である。そして、出力電圧の生成には、I−V変換回路を用いることが多く、当該I−V変換回路は所与の抵抗素子を有するものとなる。
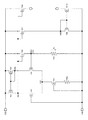
本実施形態に係る回路装置20の詳細な構成例を示す。まず回路装置20の全体構成例を説明し、その後、各部の詳細について説明する。
本実施形態に係る回路装置20の全体構成例は図1に示したとおりである。回路装置20は、第1の電流生成回路181と、第2の電流生成回路182と、電圧出力回路150と、A/D変換回路160と、処理部170を含む。
図1に示したように、本実施形態に係る回路装置20は、第1の電流IREFを生成する第1の電流生成回路181と、第2の電流IPTATを生成する第2の電流生成回路182を含む。このようにすれば、第1の電流IREFと第2の電流IPTATとを、それぞれ電流生成回路(狭義には後述するような仕事関数差を用いた回路)により生成することが可能になる。以下、図2〜図5を用いて、各電流生成回路の構成や、第1,第2の電流の温度特性について説明する。
次に、電圧出力回路150について説明する。電圧出力回路150は、第1の電流IREFに基づく第1の出力電圧VREFと、第2の電流IPTATに基づく第2の出力電圧VPTATを出力する。上述したように、第1,第2の電流がそれぞれ第1,第2の電流生成回路により生成されるのであれば、電圧出力回路150は、第1の電流生成回路181により生成された第1の電流IREFが、抵抗素子に流れたときの電圧を第1の出力電圧VREFとして出力し、第2の電流生成回路182により生成された第2の電流IPTATが、抵抗素子に流れたときの電圧を第2の出力電圧VPTATとして出力すればよい。
VREFN=VDD−IREFR2 ・・・・・(2)
VREF=IREF(R1+R2)−VDD ・・・・・(3)
また、第2の期間では第2の電流IPTATを抵抗素子に出力する。つまり第2の期間では、図7(B)に示したように、トランジスターTC2及びTC4をオンにし、TC1及びTC3をオフにすればよい。この場合、抵抗素子R1及びR2にはそれぞれ第2の電流IPTATが流れることになり、ノードNC1の電圧値VPTATP及びノードNC2の電圧値VPTATNが第2の出力電圧VPTATとしてA/D変換回路160に対して出力される。具体的なVPTATP、VPTATN、VPTATの値は上式(1)〜(3)と同様であり、下式(4)〜(6)により求めることができる。
VPTATN=VDD−IPTATR2 ・・・・・(5)
VPTAT=IPTAT(R1+R2)−VDD ・・・・・(6)
なお、電圧出力回路150に含まれる抵抗素子R1,R2は種々の手法により実現可能である。例えばR1及びR2は広く知られたポリ抵抗(ポリシリコン抵抗)により実現してもよいし、ウェル抵抗により実現してもよい。
次にA/D変換回路160の詳細について説明する。図7(A)、図7(B)に示したように、A/D変換回路160は差動型、SAR型のA/D変換回路であってもよい。なお、A/D変換回路の具体的な構成例については、種々の手法が知られており、本実施形態ではそれらを広く適用可能であるため、詳細な説明は省略する。
=(Vdiff/VDD)×29 ・・・・・(7)
上式(7)において、2VDDという電圧値はA/D変換における入力電圧範囲(フルスケールレンジ)であり、例えば図11(A)等における−VDDを最小のデジタル値(例えば−511)、+VDDを最大のデジタル値(例えば+511)として出力する場合に相当する。なお、入力電圧範囲は他の値に変更してもよい。
図12に処理部170の詳細な構成例を示す。処理部170は、除算処理部171と、摂氏変換部173と、LPF175を含んでもよい。処理部170は、例えばDSPにより実現され、当該DSPが、除算処理、摂氏変換処理、デジタルローパスフィルター処理を実行すればよい。
・・・・・(10)
よって、上式(10)を一般化すれば、第1のデジタル値をDREFとし、第2のデジタル値をDPTATとし、所与の定数をmとした場合に、処理部170は、除算処理として、(DPTAT+m)/(DREF+m)を演算する処理を行うことになる。上述したように、A/D変換のビット数やフルスケールレンジが変化すれば、mの値も変化することになる。また、図19及び下式(15)〜(20)を用いて後述するように、A/D変換回路160がシングルエンドであるとすれば、A/D変換のビット数やフルスケールレンジによらずm=0となる。つまりここでのmとは、0であってもよいし、0以外の定数であってもよい。
また、本実施形態の回路装置20は、物理量トランスデューサー18から出力される物理量に応じた検出信号に基づいて、物理量に対応する物理量データを出力する検出回路60と、物理量トランスデューサーを駆動する駆動回路30を含んでもよい。そして処理部170は、検出回路60からの物理量データに対して、温度データに基づく補正処理を行ってもよい。
以上では、図7(A)、図7(B)に示したように、電圧出力回路150は2つの入力信号で構成される差動入力信号に対応する2つの出力電圧VREFP,VREFN(VPTATP,VPTATN)をA/D変換回路160に出力するものであり、A/D変換回路160は差動型のA/D変換回路であるものとした。
また、第2の期間では第2の電流IPTATを抵抗素子に出力する。つまり第2の期間では、図19(B)に示したように、トランジスターTC2をオンにし、TC1をオフにすればよい。この場合、抵抗素子R1には第2の電流IPTATが流れることになり、ノードNC1の電圧値である第2の出力電圧VPTATがA/D変換回路160に対して出力される。VPTATの値は下式(16)により求めることができる。
この場合、A/D変換回路160でのA/D変換は、下式(17)により行われる。ビット数は差動の場合と同様に10ビットとしているが、シングルでの動作ではフルスケールレンジが差動の場合の半分(差動がシングルの倍)となるため、上式(7)に対応する例ではVDDとなる。
よって、第1のデジタル値DREF及び第2のデジタル値DPTATは下式(18)、(19)により求められる。
シングルの場合には、上式(10)の29に相当するような値は必要なく、上述したように定数mは0とすればよい。
18 物理量トランスデューサー、20 回路装置、30 駆動回路、32 増幅回路、
40 ゲイン制御回路、50 駆動信号出力回路、52 同期信号出力回路、
60 検出回路、61 増幅回路、81 同期検波回路、90 フィルター部、
100 A/D変換回路、140 制御部、142 レジスター部、
150 電圧出力回路、160 A/D変換回路、170 処理部、
171 除算処理部、173 摂氏変換部、175 LPF、
181 第1の電流生成回路、182 第2の電流生成回路、206 自動車、
207 車体、208 車体姿勢制御装置、209 車輪、500 電子機器、
510 ジャイロセンサー、520 処理部、530 メモリー、540 操作部、
550 表示部、C1,C2 コンデンサー、
R1,R2,RA1,RA2,RB1,RB2 抵抗素子、
TA1〜TA10,TB1〜TB11,TC1〜TC4 トランジスター
Claims (17)
- 第1の温度特性の第1の電流が抵抗素子に流れたときの第1の出力電圧と、前記第1の温度特性とは異なる第2の温度特性の第2の電流が前記抵抗素子に流れたときの第2の出力電圧と、を出力する電圧出力回路と、
前記第1の出力電圧をA/D変換して第1のデジタル値を出力し、前記第2の出力電圧をA/D変換して第2のデジタル値を出力するA/D変換回路と、
前記第1のデジタル値及び前記第2のデジタル値に基づくデジタル演算処理により、温度データを求める処理部と、
を含むことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1に記載の回路装置において、
前記処理部は、
前記抵抗素子の抵抗値に対する前記温度データの依存性を低減する前記デジタル演算処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1に記載の回路装置おいて、
前記処理部は、
前記抵抗素子の抵抗値の変動による前記温度データの第1の変動、及び前記抵抗素子の温度特性による前記温度データの第2の変動のうち、少なくとも一方の変動を低減する前記デジタル演算処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至3のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
前記処理部は、
前記第2のデジタル値を前記第1のデジタル値で除算する除算処理を含む前記デジタル演算処理により、前記温度データを求めることを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項4に記載の回路装置おいて、
前記第1のデジタル値をDREFとし、前記第2のデジタル値をDPTATとし、所与の定数をmとした場合に、
前記処理部は、
前記除算処理として、(DPTAT+m)/(DREF+m)を演算する処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至5のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
前記第1の電流を生成する第1の電流生成回路と、
前記第2の電流を生成する第2の電流生成回路と、
を含み、
前記電圧出力回路は、
前記第1の電流生成回路により生成された前記第1の電流が、前記抵抗素子に流れたときの電圧を前記第1の出力電圧として出力し、
前記第2の電流生成回路により生成された前記第2の電流が、前記抵抗素子に流れたときの電圧を前記第2の出力電圧として出力することを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至6のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
前記電圧出力回路は、
第1の期間においては、前記第1の電流を選択して前記抵抗素子に出力し、第2の期間においては前記第2の電流を選択して前記抵抗素子に出力する選択回路を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至7のいずれか一項の記載の回路装置において、
前記第1の電流は、温度特性がフラットな基準電流であり、
前記第2の電流は、正の温度特性又は負の温度特性の一方の温度特性を有する電流であることを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項8に記載の回路装置において、
前記第2の電流が正の温度特性を有する場合には、前記抵抗素子は正の温度特性を有する抵抗素子であり、
前記第2の電流が負の温度特性を有する場合には、前記抵抗素子は負の温度特性を有する抵抗素子であることを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項8又は9に記載の回路装置において、
前記第2の電流は、正の温度特性を有し、
前記抵抗素子は、ウェル抵抗又は拡散抵抗であることを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至10のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
前記処理部は、
前記デジタル演算処理により求められた前記温度データに対して、デジタルローパスフィルター処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項11に記載の回路装置において、
前記処理部は、
前記デジタル演算処理により求められた前記温度データに対して、カットオフ周波数が可変の前記デジタルローパスフィルター処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項12に記載の回路装置において、
前記処理部は、
起動後の第1の期間においては、前記カットオフ周波数を第1の周波数に設定し、
前記第1の期間の経過後の第2の期間においては、前記カットオフ周波数を前記第1の周波数よりも低い第2の周波数に設定することを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至13のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
前記A/D変換回路は、第1の入力信号と第2の入力信号で構成される差動入力信号が入力される差動型のA/D変換回路であり、
前記電圧出力回路は、
前記抵抗素子として第1の抵抗素子と第2の抵抗素子を有し、
前記電圧出力回路は、
前記第1の出力電圧を出力する場合は、前記第1の電流が前記第1の抵抗素子に流れたときの出力電圧を前記第1の入力信号の電圧として前記A/D変換回路に出力し、前記第1の電流が前記第2の抵抗素子に流れたときの出力電圧を前記第2の入力信号の電圧として前記A/D変換回路に出力し、
前記第2の出力電圧を出力する場合は、前記第2の電流が前記第1の抵抗素子に流れたときの出力電圧を前記第1の入力信号の電圧として前記A/D変換回路に出力し、前記第2の電流が前記第2の抵抗素子に流れたときの出力電圧を前記第2の入力信号の電圧として前記A/D変換回路に出力することを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至14のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置において、
物理量トランスデューサーから出力される物理量に応じた検出信号に基づいて、前記物理量に対応する物理量データを出力する検出回路と、
前記物理量トランスデューサーを駆動する駆動回路と、
を含み、
前記処理部は、
前記検出回路からの前記物理量データに対して、前記温度データに基づく補正処理を行うことを特徴とする回路装置。 - 請求項1乃至15のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置を含むことを特徴とする電子機器。
- 請求項1乃至15のいずれか一項に記載の回路装置を含むことを特徴とする移動体。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015091211A JP6500579B2 (ja) | 2015-04-28 | 2015-04-28 | 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
| US15/131,183 US10190918B2 (en) | 2015-04-28 | 2016-04-18 | Circuit apparatus, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| CN201610266763.XA CN106092360B (zh) | 2015-04-28 | 2016-04-26 | 电路装置、电子设备以及移动体 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015091211A JP6500579B2 (ja) | 2015-04-28 | 2015-04-28 | 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016206126A JP2016206126A (ja) | 2016-12-08 |
| JP2016206126A5 JP2016206126A5 (ja) | 2018-05-10 |
| JP6500579B2 true JP6500579B2 (ja) | 2019-04-17 |
Family
ID=57204022
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015091211A Active JP6500579B2 (ja) | 2015-04-28 | 2015-04-28 | 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10190918B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6500579B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106092360B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11152882B2 (en) * | 2015-02-13 | 2021-10-19 | Resonant Systems, Inc. | Oscillating-resonant-module controller |
| JP6586735B2 (ja) | 2015-02-20 | 2019-10-09 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 回路装置、物理量検出装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
| JP6492739B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-20 | 2019-04-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 回路装置、物理量検出装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
| FR3057370B1 (fr) * | 2016-10-11 | 2019-08-23 | Airbus Operations | Procede et systeme de commande de vol d'un aeronef. |
| JP2018165641A (ja) * | 2017-03-28 | 2018-10-25 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 故障判定回路、物理量検出装置、電子機器及び移動体 |
| CN108195477B (zh) * | 2018-02-05 | 2020-08-14 | 华大半导体有限公司 | 一种精度可调的温度传感器及测试方法 |
| JP6801684B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-29 | 2020-12-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 振動型ジャイロスコープ |
| CN111427414B (zh) * | 2019-01-10 | 2021-09-07 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | Sar-dac器件及其工作方法 |
| JP7204576B2 (ja) * | 2019-05-15 | 2023-01-16 | 株式会社東芝 | センサ |
| JP7534590B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-24 | 2024-08-15 | ミツミ電機株式会社 | 放電制御回路 |
| TWI731708B (zh) * | 2020-06-08 | 2021-06-21 | 創意電子股份有限公司 | 溫度感測裝置以及溫度感測方法 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5932942U (ja) * | 1982-08-25 | 1984-02-29 | 株式会社アドバンテスト | トランジスタ温度計 |
| JP3209091B2 (ja) * | 1996-05-30 | 2001-09-17 | 富士電機株式会社 | 絶縁ゲートバイポーラトランジスタを備えた半導体装置 |
| US6194958B1 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2001-02-27 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Filter having minimized cut-off frequency variations |
| JP2002048651A (ja) * | 2000-08-04 | 2002-02-15 | Nippon Precision Circuits Inc | 半導体温度検出方法およびその回路 |
| JP4642364B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-17 | 2011-03-02 | オリンパス株式会社 | 温度検出回路、温度検出装置、及び光電変換装置 |
| US20070237207A1 (en) * | 2004-06-09 | 2007-10-11 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Beta variation cancellation in temperature sensors |
| US7150561B1 (en) * | 2004-09-16 | 2006-12-19 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Zero temperature coefficient (TC) current source for diode measurement |
| US7573275B2 (en) * | 2005-08-31 | 2009-08-11 | Ngk Spark Plug Co., Ltd. | Temperature sensor control apparatus |
| JP2007192718A (ja) | 2006-01-20 | 2007-08-02 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 温度センサ |
| US7821320B2 (en) | 2007-02-07 | 2010-10-26 | Denso Corporation | Temperature detection circuit |
| JP4483903B2 (ja) | 2007-02-07 | 2010-06-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 温度検出回路 |
| JP5360361B2 (ja) * | 2008-07-17 | 2013-12-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 角速度検出装置用回路、角速度検出装置及び故障判定システム |
| US20100214271A1 (en) * | 2009-02-25 | 2010-08-26 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Liquid crystal device, temperature detection method, and electronic apparatus |
| JP5447805B2 (ja) * | 2009-07-09 | 2014-03-19 | 国立大学法人 宮崎大学 | 温度検出方法および温度センサ |
| JP2013205085A (ja) * | 2012-03-27 | 2013-10-07 | Renesas Electronics Corp | 半導体装置 |
| US9488529B2 (en) * | 2013-05-29 | 2016-11-08 | Intel IP Corporation | Temperature measurement system |
| US9470585B2 (en) * | 2013-05-29 | 2016-10-18 | Intel IP Corporation | Calibrated temperature measurement system |
| US9528883B2 (en) * | 2014-04-22 | 2016-12-27 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Temperature sensor circuitry with scaled voltage signal |
| US20160003683A1 (en) * | 2014-07-01 | 2016-01-07 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Remote temperature sensing |
| US9829387B2 (en) * | 2014-10-28 | 2017-11-28 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | System and method for temperature sensing |
-
2015
- 2015-04-28 JP JP2015091211A patent/JP6500579B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-04-18 US US15/131,183 patent/US10190918B2/en active Active
- 2016-04-26 CN CN201610266763.XA patent/CN106092360B/zh active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US10190918B2 (en) | 2019-01-29 |
| JP2016206126A (ja) | 2016-12-08 |
| US20160320187A1 (en) | 2016-11-03 |
| CN106092360A (zh) | 2016-11-09 |
| CN106092360B (zh) | 2019-12-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6500579B2 (ja) | 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP6277689B2 (ja) | 検出装置、センサー、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP6641712B2 (ja) | 回路装置、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP3964875B2 (ja) | 角速度センサ | |
| JP4671305B2 (ja) | 物理量センサ | |
| CN106027043B (zh) | 电路装置、电子设备以及移动体 | |
| US10704907B2 (en) | Circuit device, electronic apparatus, moving object and method of manufacturing of physical quantity detection device | |
| JP4668407B2 (ja) | 角速度センサ | |
| US10031176B2 (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity detection device, electronic apparatus, and moving object | |
| US10794776B2 (en) | Failure determination circuit, physical quantity measurement device, electronic apparatus, and vehicle | |
| JP2018007165A (ja) | 温度補償型発振回路、発振器、電子機器、移動体及び発振器の製造方法 | |
| JP2007081530A (ja) | 増幅回路及びそれを用いた物理量センサ | |
| JP7077617B2 (ja) | 回路装置、振動デバイス、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP4867385B2 (ja) | 発振回路及び物理量トランスデューサ | |
| JP5714388B2 (ja) | センサ駆動回路、及びそれを用いた物理量センサ | |
| Ouh et al. | Capacitive readout circuit for tri-axes microaccelerometer with sub-fF offset calibration | |
| US10175044B2 (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity detection device, electronic apparatus, and moving object | |
| JP2015090352A (ja) | 検出装置、センサー、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP6572585B2 (ja) | 回路装置、物理量検出装置、電子機器、移動体、回路装置の製造方法 | |
| Ko | Highly configurable capacitive interface circuit for tri‐axial MEMS microaccelerometer | |
| JP2011169672A (ja) | 物理量測定装置及び電子機器 | |
| JP2005127978A (ja) | 発振回路および角速度センサ | |
| JP2022115891A (ja) | 抵抗素子、フィルター回路、回路装置、物理量測定装置、電子機器及び移動体 | |
| JP2011171882A (ja) | スイッチトキャパシター回路を用いたハイパスフィルター及び電子機器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180322 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180322 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20180905 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20181115 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190118 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190219 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20190304 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6500579 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |