JP6252569B2 - ハイブリッド車両 - Google Patents
ハイブリッド車両 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6252569B2 JP6252569B2 JP2015178322A JP2015178322A JP6252569B2 JP 6252569 B2 JP6252569 B2 JP 6252569B2 JP 2015178322 A JP2015178322 A JP 2015178322A JP 2015178322 A JP2015178322 A JP 2015178322A JP 6252569 B2 JP6252569 B2 JP 6252569B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- engine
- motor generator
- short
- phase
- ecu
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W20/00—Control systems specially adapted for hybrid vehicles
- B60W20/50—Control strategies for responding to system failures, e.g. for fault diagnosis, failsafe operation or limp mode
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/22—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs
- B60K6/36—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the transmission gearings
- B60K6/365—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the transmission gearings with the gears having orbital motion
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/42—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by the architecture of the hybrid electric vehicle
- B60K6/44—Series-parallel type
- B60K6/445—Differential gearing distribution type
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W10/00—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function
- B60W10/04—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of propulsion units
- B60W10/06—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of propulsion units including control of combustion engines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W10/00—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function
- B60W10/04—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of propulsion units
- B60W10/08—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of propulsion units including control of electric propulsion units, e.g. motors or generators
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W10/00—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function
- B60W10/10—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of change-speed gearings
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W10/00—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function
- B60W10/10—Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function including control of change-speed gearings
- B60W10/11—Stepped gearings
- B60W10/115—Stepped gearings with planetary gears
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/02—Ensuring safety in case of control system failures, e.g. by diagnosing, circumventing or fixing failures
- B60W50/0205—Diagnosing or detecting failures; Failure detection models
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/02—Ensuring safety in case of control system failures, e.g. by diagnosing, circumventing or fixing failures
- B60W50/029—Adapting to failures or work around with other constraints, e.g. circumvention by avoiding use of failed parts
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H3/00—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion
- F16H3/44—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion
- F16H3/72—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion with a secondary drive, e.g. regulating motor, in order to vary speed continuously
- F16H3/727—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion with a secondary drive, e.g. regulating motor, in order to vary speed continuously with at least two dynamo electric machines for creating an electric power path inside the gearing, e.g. using generator and motor for a variable power torque path
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/22—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs
- B60K6/26—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the motors or the generators
- B60K2006/268—Electric drive motor starts the engine, i.e. used as starter motor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/22—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs
- B60K6/38—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the driveline clutches
- B60K2006/381—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the driveline clutches characterized by driveline brakes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/22—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs
- B60K6/38—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the driveline clutches
- B60K6/383—One-way clutches or freewheel devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/22—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs
- B60K6/38—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs characterised by apparatus, components or means specially adapted for HEVs characterised by the driveline clutches
- B60K6/387—Actuated clutches, i.e. clutches engaged or disengaged by electric, hydraulic or mechanical actuating means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K6/00—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00
- B60K6/20—Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems comprising electric motors and internal combustion engines ; Control systems therefor, i.e. systems controlling two or more prime movers, or controlling one of these prime movers and any of the transmission, drive or drive units Informative references: mechanical gearings with secondary electric drive F16H3/72; arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine H02K7/00; machines comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts H02K51/00; dynamo-electric machines not otherwise provided for in H02K see H02K99/00 the prime-movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines, e.g. HEVs
- B60K6/50—Architecture of the driveline characterised by arrangement or kind of transmission units
- B60K6/54—Transmission for changing ratio
- B60K6/547—Transmission for changing ratio the transmission being a stepped gearing
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W20/00—Control systems specially adapted for hybrid vehicles
- B60W20/30—Control strategies involving selection of transmission gear ratio
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2510/00—Input parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2510/06—Combustion engines, Gas turbines
- B60W2510/0638—Engine speed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2510/00—Input parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2510/08—Electric propulsion units
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2510/00—Input parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2510/08—Electric propulsion units
- B60W2510/081—Speed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2710/00—Output or target parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2710/06—Combustion engines, Gas turbines
- B60W2710/0666—Engine torque
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2710/00—Output or target parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2710/08—Electric propulsion units
- B60W2710/081—Speed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2710/00—Output or target parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2710/08—Electric propulsion units
- B60W2710/083—Torque
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2710/00—Output or target parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2710/10—Change speed gearings
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2710/00—Output or target parameters relating to a particular sub-units
- B60W2710/10—Change speed gearings
- B60W2710/1005—Transmission ratio engaged
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60Y—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO ASPECTS CROSS-CUTTING VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
- B60Y2200/00—Type of vehicle
- B60Y2200/90—Vehicles comprising electric prime movers
- B60Y2200/92—Hybrid vehicles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60Y—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO ASPECTS CROSS-CUTTING VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
- B60Y2306/00—Other features of vehicle sub-units
- B60Y2306/13—Failsafe arrangements
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H3/00—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion
- F16H3/44—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion
- F16H2003/445—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion without permanent connection between the input and the set of orbital gears
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2200/00—Transmissions for multiple ratios
- F16H2200/003—Transmissions for multiple ratios characterised by the number of forward speeds
- F16H2200/0043—Transmissions for multiple ratios characterised by the number of forward speeds the gear ratios comprising four forward speeds
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2200/00—Transmissions for multiple ratios
- F16H2200/20—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion
- F16H2200/2002—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the number of sets of orbital gears
- F16H2200/2007—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the number of sets of orbital gears with two sets of orbital gears
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2200/00—Transmissions for multiple ratios
- F16H2200/20—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion
- F16H2200/203—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the engaging friction means not of the freewheel type, e.g. friction clutches or brakes
- F16H2200/2041—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the engaging friction means not of the freewheel type, e.g. friction clutches or brakes with four engaging means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2200/00—Transmissions for multiple ratios
- F16H2200/20—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion
- F16H2200/203—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the engaging friction means not of the freewheel type, e.g. friction clutches or brakes
- F16H2200/2066—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion characterised by the engaging friction means not of the freewheel type, e.g. friction clutches or brakes using one freewheel mechanism
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2200/00—Transmissions for multiple ratios
- F16H2200/20—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion
- F16H2200/2079—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion using freewheel type mechanisms, e.g. freewheel clutches
- F16H2200/2082—Transmissions using gears with orbital motion using freewheel type mechanisms, e.g. freewheel clutches one freewheel mechanisms
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H3/00—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion
- F16H3/44—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion with variable gear ratio or for reversing rotary motion using gears having orbital motion
- F16H3/62—Gearings having three or more central gears
- F16H3/66—Gearings having three or more central gears composed of a number of gear trains without drive passing from one train to another
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S903/00—Hybrid electric vehicles, HEVS
- Y10S903/902—Prime movers comprising electrical and internal combustion motors
- Y10S903/903—Prime movers comprising electrical and internal combustion motors having energy storing means, e.g. battery, capacitor
- Y10S903/93—Conjoint control of different elements
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S903/00—Hybrid electric vehicles, HEVS
- Y10S903/902—Prime movers comprising electrical and internal combustion motors
- Y10S903/903—Prime movers comprising electrical and internal combustion motors having energy storing means, e.g. battery, capacitor
- Y10S903/945—Characterized by control of gearing, e.g. control of transmission ratio
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
Description
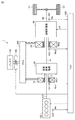
図1は、本実施の形態に係るハイブリッド車両の全体構成を概略的に示すブロック図である。図1を参照して、車両1は、エンジン100と、モータジェネレータ10,20と、遊星歯車機構30と、自動変速機40と、車輪50と、バッテリ150と、システムメインリレー(SMR:System Main Relay)160と、電力制御ユニット(PCU:Power Control Unit)200と、電子制御ユニット(ECU:Electronic Control Unit)300とを備える。
図4は、車両1の電気システムの構成を概略的に示すブロック図である。図1および図4を参照して、PCU200は、コンデンサC1と、コンバータ210と、コンデンサC2と、インバータ221,222と、電圧センサ230と、電流センサ241,242とを含む。ECU300は、HV−ECU310と、MG−ECU320とを含む。
このような車両1において、走行中に、モータジェネレータ10を駆動するインバータ221にてスイッチング素子が導通状態のままとなってしまう短絡故障が発生する場合がある。
インバータ221の三相短絡制御を実行すると、車両1の退避走行に伴いモータジェネレータ10が回転駆動されたときの逆起電力(電磁気的な作用)によって、モータジェネレータ10の回転を止める方向に引きずりトルクが生ずる。
Claims (2)
- エンジンと、
三相交流モータを含む第1の回転電機と、
駆動軸に動力を出力可能に構成された第2の回転電機と、
前記第1の回転電機が連結されたサンギヤ、前記第2の回転電機が連結されたリングギヤ、および前記エンジンが連結されたキャリアを含む遊星歯車機構と、
各々が上アームおよび下アームを有する三相の駆動アームを含み、前記第1の回転電機を駆動可能に構成されたインバータと、
複数の変速段を有し、前記第2の回転電機と前記駆動軸との間に連結された変速機と、
前記インバータおよび前記変速機を制御する制御装置とを備え、
前記制御装置は、前記エンジンが停止している場合に、
前記三相の駆動アームのうちの1つの相において前記上アームおよび前記下アームの一方に短絡故障が発生すると、前記短絡故障が生じていない相における前記上アームおよび前記下アームのうち、前記短絡故障が生じたアームと同じ側のアームを短絡させる三相短絡制御を実行し、
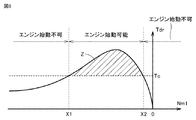
前記第1の回転電機の回転速度が、前記三相短絡制御により生じるトルクによって前記エンジンを始動可能な範囲にないときには、
前記第1の回転電機の回転速度が前記範囲内になるように前記変速機の変速制御を実行する、ハイブリッド車両。 - 前記制御装置は、前記変速制御において、
前記複数の変速段のうちの2以上の変速段の各々について、当該変速段に切替えたときに予測される前記第1の回転電機の回転速度の予測値を算出し、
前記予測値が前記範囲内にある変速段のうち、より低速側の変速段を選択する、請求項1に記載のハイブリッド車両。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015178322A JP6252569B2 (ja) | 2015-09-10 | 2015-09-10 | ハイブリッド車両 |
| US15/252,600 US9873424B2 (en) | 2015-09-10 | 2016-08-31 | Hybrid vehicle |
| CN201610809547.5A CN107031613B (zh) | 2015-09-10 | 2016-09-08 | 混合动力车辆 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015178322A JP6252569B2 (ja) | 2015-09-10 | 2015-09-10 | ハイブリッド車両 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017052422A JP2017052422A (ja) | 2017-03-16 |
| JP6252569B2 true JP6252569B2 (ja) | 2017-12-27 |
Family
ID=58257050
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015178322A Active JP6252569B2 (ja) | 2015-09-10 | 2015-09-10 | ハイブリッド車両 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9873424B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6252569B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN107031613B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3131198B1 (en) * | 2015-08-10 | 2022-06-08 | Goodrich Actuation Systems Limited | Control strategy of a dual lane fault tolerant permanent magnet motor to reduce drag torque under fault condition |
| JP6631571B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-17 | 2020-01-15 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ハイブリッド自動車 |
| JP6959817B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-29 | 2021-11-05 | 日立建機株式会社 | 作業車両 |
| JP6982770B2 (ja) * | 2018-02-23 | 2021-12-17 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | モータ制御装置 |
| CN109263633B (zh) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-04-24 | 吉林大学 | 一种行星混联式汽车能量管理控制方法 |
| CN109278561B (zh) * | 2018-11-22 | 2021-10-12 | 科力远混合动力技术有限公司 | 双电机功率分流式混合动力汽车电机故障处理控制方法 |
| CN109649153B (zh) * | 2019-01-15 | 2023-08-18 | 无锡商业职业技术学院 | 一种插电式单、双级双行星排混合动力车辆的传动系统 |
| CN109795307B (zh) * | 2019-02-20 | 2022-04-08 | 奇瑞汽车股份有限公司 | 混合动力耦合系统及混合动力汽车 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4032639B2 (ja) * | 2000-11-30 | 2008-01-16 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両の回生制御装置 |
| JP2007008201A (ja) * | 2005-06-28 | 2007-01-18 | Toyota Motor Corp | 自動車およびこれに搭載された内燃機関の始動方法 |
| JP4784478B2 (ja) * | 2006-04-20 | 2011-10-05 | 株式会社デンソー | 多相回転電機の制御装置 |
| CN101667808B (zh) * | 2006-04-20 | 2012-10-17 | 株式会社电装 | 多相旋转电机的控制系统 |
| JP4449942B2 (ja) * | 2006-06-19 | 2010-04-14 | 株式会社デンソー | ハイブリッド電気自動車の制御装置 |
| JP5075034B2 (ja) * | 2008-07-02 | 2012-11-14 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ハイブリッド車両の退避走行制御装置 |
| JP5120202B2 (ja) * | 2008-10-27 | 2013-01-16 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用動力伝達装置の制御装置 |
| JP4968698B2 (ja) * | 2008-12-26 | 2012-07-04 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 電動機の制御装置 |
| JP5397432B2 (ja) * | 2011-08-22 | 2014-01-22 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 回転電機の駆動システム |
| JP5845827B2 (ja) * | 2011-11-07 | 2016-01-20 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ハイブリッド車両 |
| CN103042926B (zh) * | 2012-12-04 | 2016-09-28 | 联合汽车电子有限公司 | 新能源汽车的拖车保护方法及实现电路 |
| US9088231B2 (en) * | 2013-06-07 | 2015-07-21 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | System and method for implementing a remedial electrical short |
| JP2014241690A (ja) * | 2013-06-12 | 2014-12-25 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両 |
| US9156357B2 (en) * | 2013-09-11 | 2015-10-13 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Controller for an electric motor, and a method thereof |
| JP5929940B2 (ja) * | 2014-02-06 | 2016-06-08 | 株式会社デンソー | ハイブリッド車両 |
-
2015
- 2015-09-10 JP JP2015178322A patent/JP6252569B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-08-31 US US15/252,600 patent/US9873424B2/en active Active
- 2016-09-08 CN CN201610809547.5A patent/CN107031613B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20170072946A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 |
| CN107031613B (zh) | 2018-10-16 |
| US9873424B2 (en) | 2018-01-23 |
| JP2017052422A (ja) | 2017-03-16 |
| CN107031613A (zh) | 2017-08-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6252569B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6330782B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| US9300233B2 (en) | Vehicle including rotating electric machine, inverter, and electronic control unit; and control method for the same | |
| JP4747968B2 (ja) | モータ駆動装置 | |
| WO2009101729A1 (ja) | モータ駆動装置およびハイブリッド駆動装置ならびにモータ駆動装置の制御方法 | |
| JP6426584B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6365502B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6252574B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6252573B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6354723B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6330834B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6330837B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2010200582A (ja) | 車両 | |
| JP6344345B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP6264354B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2018176970A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両及びその制御方法 | |
| JP2010178556A (ja) | モータ駆動システム | |
| JP6398924B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2017047846A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2008022640A (ja) | 車両駆動装置、車両駆動装置の制御方法、車両駆動装置の制御方法をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラム、およびそのプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 | |
| JP6455379B2 (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2017039404A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2017114209A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2017056851A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 | |
| JP2017061186A (ja) | ハイブリッド車両 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170303 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20171019 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20171031 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20171113 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6252569 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |