EP2954086B1 - Ôle à revêtement znalmg à microstructure particulière et procédé de réalisation correspondant - Google Patents
Ôle à revêtement znalmg à microstructure particulière et procédé de réalisation correspondant Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2954086B1 EP2954086B1 EP13762578.6A EP13762578A EP2954086B1 EP 2954086 B1 EP2954086 B1 EP 2954086B1 EP 13762578 A EP13762578 A EP 13762578A EP 2954086 B1 EP2954086 B1 EP 2954086B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- coating
- metal sheet
- content
- sheet according
- less
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C18/00—Alloys based on zinc
- C22C18/04—Alloys based on zinc with aluminium as the next major constituent
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/04—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor characterised by the coating material
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/04—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor characterised by the coating material
- C23C2/06—Zinc or cadmium or alloys based thereon
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/04—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor characterised by the coating material
- C23C2/12—Aluminium or alloys based thereon
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/26—After-treatment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/26—After-treatment
- C23C2/28—Thermal after-treatment, e.g. treatment in oil bath
- C23C2/29—Cooling or quenching
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/34—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor characterised by the shape of the material to be treated
- C23C2/36—Elongated material
- C23C2/40—Plates; Strips
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C28/00—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C28/00—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D
- C23C28/02—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D only coatings only including layers of metallic material
- C23C28/021—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D only coatings only including layers of metallic material including at least one metal alloy layer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C28/00—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D
- C23C28/02—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D only coatings only including layers of metallic material
- C23C28/023—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D only coatings only including layers of metallic material only coatings of metal elements only
- C23C28/025—Coating for obtaining at least two superposed coatings either by methods not provided for in a single one of groups C23C2/00 - C23C26/00 or by combinations of methods provided for in subclasses C23C and C25C or C25D only coatings only including layers of metallic material only coatings of metal elements only with at least one zinc-based layer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C30/00—Coating with metallic material characterised only by the composition of the metallic material, i.e. not characterised by the coating process
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C30/00—Coating with metallic material characterised only by the composition of the metallic material, i.e. not characterised by the coating process
- C23C30/005—Coating with metallic material characterised only by the composition of the metallic material, i.e. not characterised by the coating process on hard metal substrates
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12493—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.]
- Y10T428/12535—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.] with additional, spatially distinct nonmetal component
- Y10T428/12556—Organic component
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12493—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.]
- Y10T428/12771—Transition metal-base component
- Y10T428/12785—Group IIB metal-base component
- Y10T428/12792—Zn-base component
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12493—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.]
- Y10T428/12771—Transition metal-base component
- Y10T428/12785—Group IIB metal-base component
- Y10T428/12792—Zn-base component
- Y10T428/12799—Next to Fe-base component [e.g., galvanized]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12493—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.]
- Y10T428/12771—Transition metal-base component
- Y10T428/12861—Group VIII or IB metal-base component
- Y10T428/12951—Fe-base component
- Y10T428/12972—Containing 0.01-1.7% carbon [i.e., steel]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12493—Composite; i.e., plural, adjacent, spatially distinct metal components [e.g., layers, joint, etc.]
- Y10T428/12771—Transition metal-base component
- Y10T428/12861—Group VIII or IB metal-base component
- Y10T428/12951—Fe-base component
- Y10T428/12972—Containing 0.01-1.7% carbon [i.e., steel]
- Y10T428/12979—Containing more than 10% nonferrous elements [e.g., high alloy, stainless]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12993—Surface feature [e.g., rough, mirror]
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a sheet comprising a substrate of which at least one face is coated with a metal coating comprising Al and Mg, the remainder of the metal coating being Zn, unavoidable impurities and possibly one or more additional elements. chosen from Si, Sb, Pb, Ti, Ca, Mn, Sn, La, Ce, Cr, Ni or Bi, the content by weight of each additional element in the metal coating being less than 0.3%.
- Galvanized metal coatings consisting essentially of zinc and 0.1 to 0.4% by weight of aluminum are traditionally used for their good protection against corrosion.
- Such metal coatings will generally be referred to herein as zinc-aluminum-magnesium or ZnAIMg coatings.
- These sheets are for example intended for the automotive field, household appliances or construction.
- An object of the invention is to provide a coated sheet whose corrosion resistance, when it is painted, is increased.
- the first object of the invention is a sheet according to claim 1.
- the sheet may also comprise the features of claims 2 to 12, taken alone or in combination.
- the invention also relates to a method according to claim 13.
- the method may also include the features of claims 14 and 15, taken alone or in combination.
- Sheet 1 of the figure 1 comprises a substrate 3 of steel covered on each of its two faces 5 by a metal coating 7, itself covered by a film of paint 9, 11.
- the coatings 7 present on the two faces 5 are similar and only one will be described in detail later. As a variant (not shown), only one of the faces 5 has a coating 7.
- the coating 7 generally has a thickness less than or equal to 25 microns and aims to protect the substrate 3 against corrosion.
- the coating 7 comprises zinc, aluminum and magnesium.
- the weight content of aluminum t Al of the metal coating 7 is between 3.6 and 3.8%.
- the weight content of magnesium t Mg of the metal coating 7 is between 2.7 and 3.3%.
- the magnesium t Mg content is between 2.9 and 3.1%.
- the mass ratio AI / (AI + Mg) is greater than or equal to 0.45, or even greater than or equal to 0.50, or even greater than or equal to 0.55.
- the coating 7 has a particular microstructure with a lamellar matrix 13 of ternary eutectic Zn / Al / MgZn 2 .
- the lamellar matrix 13 forms grains separated by seals 19.
- the ternary eutectic constitutes the entire microstructure of the coating.
- the interlamellar distance of the lamellar matrix 13 can vary quite strongly within its grains, especially in the vicinity of the structures possibly encompassed by this matrix, structures which will now be described.
- the surface and cross-sectional microstructure may comprise Zn dendrites and Zn / MgZn 2 binary eutectic flowers in small amounts. which are not too detrimental to the improvement of the delamination resistance obtained according to the invention.
- the cumulative surface area of Zn dendrites on the outer surface 21 in the raw state is less than 5.0%, even 3.0%, even 2.0%, or even 1.0%, and ideally zero and the cumulated surface content of Zn / MgZn 2 binary eutectic flowers 17 on the outer surface 21 in the raw state is less than 15.0%, even 10.0% or even 5.0%, or even 3%, 0% and ideally zero.
- the microstructure may also comprise binary eutectic dendrites Zn / Al or islands of MgZn 2 , in very small quantities because these structures greatly deteriorate the delamination resistance of the coated sheets according to the invention.
- the cumulative surface content of Zn / Al binary eutectic dendrites on the outer surface 21 in the raw state is less than 1.0% and the cumulative surface area of MgZn 2 islands on the surface in the raw state is less than 1.0% and these accumulated contents are preferably zero.
- the respective cumulative cross-sectional contents of Zn / Al binary eutectic dendrites and MgZn 2 islands are preferably zero.
- the microstructure will consist of a lamellar matrix 13 of ternary eutectic and possibly Zn dendrites, Zn / MgZn 2 binary eutectic flowers 17, binary eutectic dendrites Zn / Al and of islands of MgZn2.
- the microstructure may also comprise small amounts of other structures included in the lamellar matrix 13 of ternary eutectic.
- the cumulative surface contents for each structure are for example measured by taking at least 30 views with an X1000 magnification of the outer surface 21 in the raw state (that is to say without polishing but optionally degreased by organic solvent) thanks to a scanning electron microscope.
- the contours of the structure whose content is to be measured are extracted, and then, for example, using the AnalySIS Docu 5.0 software from Olympus Soft Imaging Solutions GmbH, the occupancy rate of the outer surface 21 by the structure in question.
- the occupancy rate thus calculated is the cumulative surface content of the structure in question.
- the paint films 9 and 11 are for example based on polymers. These polymers may be polyesters or halogenated derivatives of vinyl polymers such as plastisols, PVDF, etc.
- the films 9 and 11 typically have thicknesses of between 1 and 200 ⁇ m. To produce the sheet 1, one can for example proceed as follows.
- the installation used may comprise a single line or, for example, two different lines for producing respectively the metal coatings and the painting.
- two different lines may be located on the same site or on separate sites. In the remainder of the description, for example, a variant in which two distinct lines are used is considered.
- a substrate 3 is used, for example obtained by hot rolling and then cold rolling.
- the substrate 3 is in the form of a strip which is scrolled in a bath to deposit the coatings 7 by hot quenching.
- the bath is a molten zinc bath containing magnesium and aluminum.
- the bath may also contain up to 0.3% by weight of additional optional elements such as Si, Sb, Pb, Ti, Ca, Mn, Sn, La, Ce, Cr, Ni or Bi.
- the bath may finally contain residual elements from the ingots or resulting from the passage of the substrate 3 in the bath, such as iron at a content of up to 0.5% by weight and generally between 0.1 and 0.4% by weight.
- the bath has a temperature Tb of between 360 ° C and 480 ° C, preferably between 420 ° C and 460 ° C.
- the substrate 3 has an immersion temperature Ti such that: 2 , 34 ⁇ t al + 0 , 665 ⁇ t mg - 10 , 1 ⁇ 10 - 6 ⁇ exp - 10584 / Ti where Ti is expressed in degrees Kelvin.
- Such an immersion temperature Ti makes it possible to obtain the abovementioned microstructure with little or no structures included in the lamellar matrix 13.
- this temperature Ti is determined on site from a measurement made a few meters upstream of the bath by a pyrometric technique then application of a thermal model to calculate the temperature Ti.
- the cooling conditions of the substrate 3 are modified upstream of the bath.
- This cooling can be provided by blowing inert cooling gas on both sides 5 of the substrate 3 by means of cooling boxes, the pressure of the gas can be regulated. It is also possible to play on the speed of travel of the substrate 3 in the cooling zone or on the temperature of the substrate 3 at the entrance of this zone, for example.
- the substrate 3 is for example spun by means of nozzles throwing a gas on either side of the substrate 3.
- the coatings 7 are then allowed to cool in a controlled manner to solidify.
- a brushing may be performed to remove the coating 7 deposited on a face 5 so that only one of the faces 5 of the sheet 1 will be finally coated with a coating 7.
- Controlled cooling of the or each coating 7 is provided at a rate preferably greater than or equal to 15 ° C / s between the onset of solidification (i.e., when the coating 7 falls just below the liquidus temperature). ) and the end of solidification (that is to say when the coating 7 reaches the temperature of the solidus). More preferably, the cooling rate of the or each coating 7 between the onset of solidification and the end of solidification is greater than or equal to 20 ° C / s.
- the band thus treated can then be subjected to a so-called skin-pass step which allows the harden and give it a roughness facilitating its subsequent shaping.
- the band may optionally be wound before being sent to a prelacing line.
- the outer surfaces 21 of the coatings 7 are optionally subjected to a degreasing step and possibly to a surface treatment step to increase the adhesion of the paint and the corrosion resistance.
- the possible steps of degreasing and surface treatment may include other sub-stages of rinsing, drying ...
- the painting can then be performed for example by depositing two layers of successive paints, namely a primer layer and a layer of finish which is generally the case for making the upper film 9, or by deposition of a single layer of paint, which is generally the case for making the lower film 11.
- a primer layer and a layer of finish which is generally the case for making the upper film 9
- deposition of a single layer of paint which is generally the case for making the lower film 11.
- Other numbers of layers can be used in certain variants .
- the deposition of the paint layers is provided for example by roller coaters.
- Each deposit of a paint layer is generally followed by a step of cooking in an oven.
- the sheet 1 thus obtained can again be wound before being cut, possibly shaped and assembled with other sheets 1 or other elements by users.
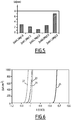
- a sample of sheet 1 according to the invention was prepared and samples of sheets not corresponding to the invention by varying the immersion temperature Ti, t Al and t Mg samples. The corresponding microstructures were analyzed to determine the existing structures and their cumulative surface contents. Microstructure of the coating - cumulative surface contents Trial t Al (%) t Mg (%) Ti (K) Ternary Eutectic (%) Dendrites of Zn (%) Binary Eutectic Flowers Zn / MgZn2 (%) Zn / AI binary eutectic dendrites (%) Islets of MgZn2 (%) * 1 3.7 3.0 753 100 0 0 0 0 2 3.7 3.0 713 95 0 0 5 0 3 * 3.7 3.3 753 100 0 0 0 0 4 3.7 3.3 713 80 0 15 0 5 * according to the invention
- a sample of sheet metal 1 according to the invention and sheets not corresponding to the invention were subjected to delamination tests to measure their resistance to paint corrosion.
- the coatings of the sheets tested had thicknesses of 8 ⁇ m.
- composition of the coatings 7 of the sheets 1 according to the invention had an Al content of 3.7% and an Mg content of 3.0%. As indicated under the abscissa axis on the figure 5 , Other coating compositions tested had t Al values of 0.3%, 1.5%, 6.0% and 11.0% and t Mg 1.0%, 1.5%, 3, 0 and 3.0%.
- test plates were phosphated, covered with a layer of cataphoresis and scratched to the substrate with a blade 1 mm wide.
- the delamination widths are optimal for the sheet according to the invention.
- Curve 23 corresponds to a composition comprising 3.7% by weight of Al and 3.0% by weight of Mg, the remainder being Zn. This curve is therefore representative of the lamellar matrix 13.
- the figure 6 shows that the risk of corrosive coupling of the lamellar matrix 13 is greater with structures containing Al (curve 25), Mg (curve 27) and Zn (curve 29).
- the sheets 1 according to the invention are not necessarily marketed in painted form ("prepainted" sheets) and / or they may be coated with at least one layer of oil.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Coating With Molten Metal (AREA)
- Other Surface Treatments For Metallic Materials (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Electroplating Methods And Accessories (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Aiming, Guidance, Guns With A Light Source, Armor, Camouflage, And Targets (AREA)
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RS20170249A RS55768B1 (sr) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | Lim sa znalmg prevlakom koja ima određenu mikrostrukturu, i odgovarajući postupak proizvodnje |
| SI201330594A SI2954086T1 (sl) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | Pločevina s prevleko ZnAlMg s posebno mikrostrukturo in ustrezen izdelovalni postopek |
| PL13762578T PL2954086T3 (pl) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | Blacha z powłoką ZnAlMg o określonej mikrostrukturze i odpowiedni sposób wytwarzania |
| HRP20170460TT HRP20170460T1 (hr) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | METALNI LIM SA ZnAlMg PREMAZOM KOJI IMA POSEBNU MIKROSTRUKTURU, TE ODGOVARAJUĆI POSTUPAK PROIZVODNJE |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR2013050250 | 2013-02-06 | ||
| PCT/IB2013/055575 WO2014122507A1 (fr) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | TÔLE À REVÊTEMENT ZnAlMG À MICROSTRUCTURE PARTICULIÈRE ET PROCÉDÉ DE RÉALISATION CORRESPONDANT |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2954086A1 EP2954086A1 (fr) | 2015-12-16 |
| EP2954086B1 true EP2954086B1 (fr) | 2017-01-11 |
Family
ID=47882388
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13762578.6A Active EP2954086B1 (fr) | 2013-02-06 | 2013-07-08 | Ôle à revêtement znalmg à microstructure particulière et procédé de réalisation correspondant |
Country Status (21)
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7257955B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-08 | 2023-04-14 | コロラド・スクール・オブ・マインズ | 低い液相線温度を有する改変された溶融亜鉛めっき被膜、その製造方法及び使用方法 |
| AU2017392662A1 (en) * | 2017-01-16 | 2019-08-15 | Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation | Plated steel material |
| MX2020005734A (es) | 2017-12-28 | 2020-08-13 | Nippon Steel Corp | Lamina de acero enchapada a base de zn fundido con resistencia a la corrosion superior despues de ser recubierta. |
| CN108913965B (zh) * | 2018-07-31 | 2021-02-26 | 中研智能装备有限公司 | 一种钢结构用ZnAlTiSiB防腐涂层及其制备方法 |
| KR102142766B1 (ko) | 2018-08-31 | 2020-08-07 | 주식회사 포스코 | 내식성 및 가공성이 우수한 용융도금강판 및 이의 제조방법 |
| PH12023551049A1 (en) * | 2020-10-21 | 2023-11-20 | Nippon Steel Corp | Coated steel product |
| WO2022107837A1 (ja) * | 2020-11-18 | 2022-05-27 | 日本製鉄株式会社 | めっき鋼材 |
| AU2021381168B2 (en) * | 2020-11-18 | 2024-07-18 | Nippon Steel Corporation | Plated steel material |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3505043A (en) * | 1969-01-08 | 1970-04-07 | Inland Steel Co | Al-mg-zn alloy coated ferrous metal sheet |
| NZ331311A (en) * | 1996-12-13 | 2000-08-25 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | Hot-dip Zn-Al-Mg plated steel sheet and method of production |
| US6465114B1 (en) * | 1999-05-24 | 2002-10-15 | Nippon Steel Corporation | -Zn coated steel material, ZN coated steel sheet and painted steel sheet excellent in corrosion resistance, and method of producing the same |
| JP2001295015A (ja) * | 2000-02-09 | 2001-10-26 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 高Al含有溶融Zn−Al−Mg系めっき鋼板 |
| JP4555492B2 (ja) * | 2000-03-16 | 2010-09-29 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 耐眩性に優れた溶融亜鉛−アルミニウム合金めっき鋼板 |
| JP2002241962A (ja) * | 2001-02-13 | 2002-08-28 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | 溶融Zn−Al−Mg合金めっき鋼板とその製造方法 |
| JP3580261B2 (ja) * | 2001-03-23 | 2004-10-20 | 住友金属工業株式会社 | 溶融Zn−Al−Mgめっき鋼板およびその製造方法 |
| JP3732141B2 (ja) * | 2001-11-09 | 2006-01-05 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 加工後の耐食性に優れた溶融亜鉛−Al系合金めっき鋼板及びその製造方法 |
| JP3779941B2 (ja) * | 2002-01-09 | 2006-05-31 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 塗装後耐食性と塗装鮮映性に優れた亜鉛めっき鋼板 |
| JP2004360056A (ja) * | 2003-06-09 | 2004-12-24 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 黒色化溶融Zn−Al−Mg系合金めっき鋼板及びその製造方法 |
| RU2417273C2 (ru) * | 2006-03-20 | 2011-04-27 | Ниппон Стил Корпорейшн | Стальной материал с высокой коррозионной стойкостью, получаемый с помощью горячего цинкования методом погружения |
| EP2119804A1 (fr) * | 2008-05-14 | 2009-11-18 | ArcelorMittal France | Procédé de fabrication d'une bande métallique revêtue présentant un aspect amélioré |
| JP2011157579A (ja) * | 2010-01-29 | 2011-08-18 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 粗面化溶融Zn−Al−Mg合金めっき鋼板およびその製造方法、ならびに溶融Zn−Al−Mg合金めっき鋼板と熱可塑性樹脂成形体とが接合された複合体およびその製造方法 |
| KR20120075235A (ko) * | 2010-12-28 | 2012-07-06 | 주식회사 포스코 | 고내식 용융아연합금 도금강판과 그 제조방법 |
| JP5901389B2 (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2016-04-06 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 溶融Al、Mg含有Znめっき鋼板 |
| JP5097305B1 (ja) * | 2012-04-25 | 2012-12-12 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 黒色めっき鋼板 |
-
2013
- 2013-07-08 LT LTEP13762578.6T patent/LT2954086T/lt unknown
- 2013-07-08 HR HRP20170460TT patent/HRP20170460T1/hr unknown
- 2013-07-08 DK DK13762578.6T patent/DK2954086T3/en active
- 2013-07-08 US US14/766,344 patent/US9598757B2/en active Active
- 2013-07-08 CA CA2900085A patent/CA2900085C/en active Active
- 2013-07-08 JP JP2015556580A patent/JP6185084B2/ja active Active
- 2013-07-08 PT PT137625786T patent/PT2954086T/pt unknown
- 2013-07-08 MX MX2015010064A patent/MX360981B/es active IP Right Grant
- 2013-07-08 KR KR1020157021987A patent/KR102070480B1/ko active Active
- 2013-07-08 EP EP13762578.6A patent/EP2954086B1/fr active Active
- 2013-07-08 MA MA38321A patent/MA38321B1/fr unknown
- 2013-07-08 PL PL13762578T patent/PL2954086T3/pl unknown
- 2013-07-08 ES ES13762578.6T patent/ES2620112T3/es active Active
- 2013-07-08 SI SI201330594A patent/SI2954086T1/sl unknown
- 2013-07-08 CN CN201380072424.2A patent/CN105247094B/zh active Active
- 2013-07-08 WO PCT/IB2013/055575 patent/WO2014122507A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2013-07-08 RU RU2015137791A patent/RU2636215C2/ru active
- 2013-07-08 HU HUE13762578A patent/HUE032189T2/hu unknown
- 2013-07-08 UA UAA201508554A patent/UA114231C2/uk unknown
- 2013-07-08 RS RS20170249A patent/RS55768B1/sr unknown
- 2013-07-08 BR BR112015018780-3A patent/BR112015018780B1/pt active IP Right Grant
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| SI2954086T1 (sl) | 2017-05-31 |
| ES2620112T3 (es) | 2017-06-27 |
| RU2636215C2 (ru) | 2017-11-21 |
| MX2015010064A (es) | 2016-04-27 |
| HRP20170460T1 (hr) | 2017-05-19 |
| BR112015018780A2 (pt) | 2017-07-18 |
| UA114231C2 (uk) | 2017-05-10 |
| CN105247094A (zh) | 2016-01-13 |
| EP2954086A1 (fr) | 2015-12-16 |
| CA2900085C (en) | 2020-10-13 |
| HUE032189T2 (hu) | 2017-09-28 |
| US20150368778A1 (en) | 2015-12-24 |
| US9598757B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 |
| KR102070480B1 (ko) | 2020-01-29 |
| PT2954086T (pt) | 2017-04-11 |
| LT2954086T (lt) | 2017-03-27 |
| MX360981B (es) | 2018-11-22 |
| CA2900085A1 (en) | 2014-08-14 |
| RS55768B1 (sr) | 2017-07-31 |
| MA38321B1 (fr) | 2016-09-30 |
| CN105247094B (zh) | 2018-03-06 |
| BR112015018780B1 (pt) | 2021-04-27 |
| WO2014122507A1 (fr) | 2014-08-14 |
| PL2954086T3 (pl) | 2017-07-31 |
| MA38321A1 (fr) | 2016-02-29 |
| RU2015137791A (ru) | 2017-03-13 |
| JP6185084B2 (ja) | 2017-08-23 |
| DK2954086T3 (en) | 2017-03-27 |
| KR20160004997A (ko) | 2016-01-13 |
| JP2016514202A (ja) | 2016-05-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2954086B1 (fr) | Ôle à revêtement znalmg à microstructure particulière et procédé de réalisation correspondant | |
| EP2430207B1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'une bande métallique revêtue présentant un aspect amélioré | |
| EP2297372B1 (fr) | Procede de fabrication d'une bande metallique revetue presentant un aspect ameliore | |
| EP2689045B1 (fr) | Tôle d'acier laminée à chaud et procédé de fabrication associé | |
| CA2892007C (fr) | Procede de realisation d'une tole a revetement znal avec un essorage optimise, tole, piece et vehicule correspondants | |
| EP3149217B1 (fr) | Tôle d'acier munie d'un revêtement à protection cathodique sacrificielle comprenant du lanthane | |
| CA2926564C (fr) | Tole a revetement znalmg a flexibilite amelioree et procede de realisation correspondant | |
| EP2839049B1 (fr) | Tôle d'acier munie d'un revêtement à protection cathodique sacrificielle, procédé de fabrication d'une pièce par mise en oeuvre d'une telle tôle et pièce ainsi obtenue | |
| EP3102348B1 (fr) | Procédé de réalisation de pièces à faible ondulation à partir d'une tôle électrozinguée, pièce et véhicule correspondants | |
| EP2841615B1 (fr) | Procédé de réalisation d'une tôle à revêtements znalmg huilés et tôle correspondante | |
| WO2012080581A1 (fr) | Tôle d'acier comprenant un revêtement multicouche | |
| EP3084031B1 (fr) | Procédé de réalisation d'une tôle à revêtement znalmg avec un essorage optimisé et tôle correspondante | |
| EP2841613B1 (fr) | PROCÉDÉS DE RÉALISATION D'UNE TÔLE PRÉLAQUÉE À REVÊTEMENTS ZnAlMg ET TÔLE CORRESPONDANTE | |
| WO2013160870A1 (fr) | PROCÉDÉ DE RÉALISATION D'UNE TÔLE À REVÊTEMENTS ZnAlMg COMPRENANT L'APPLICATION D'UNE SOLUTION ACIDE DE TRAITEMENT DE SURFACE ET D'UN ADHÉSIF, TÔLE ET ASSEMBLAGE CORRESPONDANTS | |
| EP2103706A1 (fr) | Alliage de revêtement obtenu par projection de poudre |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20150806 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20160811 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 861354 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20170115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: FRENCH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: ARNOLD AND SIEDSMA AG, CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602013016497 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: TUEP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: RO Ref legal event code: EPE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 Effective date: 20170321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Ref document number: 2954086 Country of ref document: PT Date of ref document: 20170411 Kind code of ref document: T Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20170404 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: EE Ref legal event code: FG4A Ref document number: E013551 Country of ref document: EE Effective date: 20170405 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: T1PR Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NO Ref legal event code: T2 Effective date: 20170111 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2620112 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20170627 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SK Ref legal event code: T3 Ref document number: E 23828 Country of ref document: SK |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20170400961 Country of ref document: GR Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HU Ref legal event code: AG4A Ref document number: E032189 Country of ref document: HU |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602013016497 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170111 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20171012 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170111 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: UEP Ref document number: 861354 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20170111 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20190626 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170111 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20200703 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20210707 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20220704 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230427 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20230704 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Payment date: 20230621 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Payment date: 20240619 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20240626 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20240625 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240619 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240619 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240802 Year of fee payment: 12 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240801 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240620 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Payment date: 20240701 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Payment date: 20240724 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Payment date: 20250625 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20250620 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20250625 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Payment date: 20250630 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: NO Payment date: 20250623 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20250620 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Payment date: 20250630 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20250624 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: LV Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Payment date: 20250625 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20250620 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20170460 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20250630 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Payment date: 20250627 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20250623 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20250627 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: SK Payment date: 20250625 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20250623 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Payment date: 20250627 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20250619 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Payment date: 20250714 Year of fee payment: 13 |