EP2803827B2 - Metallisches Hohlventil - Google Patents
Metallisches Hohlventil Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2803827B2 EP2803827B2 EP14152509.7A EP14152509A EP2803827B2 EP 2803827 B2 EP2803827 B2 EP 2803827B2 EP 14152509 A EP14152509 A EP 14152509A EP 2803827 B2 EP2803827 B2 EP 2803827B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cavity
- valve
- hollow valve
- hollow
- internal combustion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01L—CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F01L3/00—Lift-valve, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having at least a component of their opening and closing motion perpendicular to the closing faces; Parts or accessories thereof
- F01L3/20—Shapes or constructions of valve members, not provided for in preceding subgroups of this group
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01L—CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F01L3/00—Lift-valve, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having at least a component of their opening and closing motion perpendicular to the closing faces; Parts or accessories thereof
- F01L3/12—Cooling of valves
- F01L3/14—Cooling of valves by means of a liquid or solid coolant, e.g. sodium, in a closed chamber in a valve
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a metallic hollow valve of an internal combustion engine with a tubular shaft and a valve plate connected thereto according to the preamble of claim 1.
- From the DE 10 2010 051 871 A1 discloses a method for producing metal hollow valves for the gas exchange of an internal combustion engine, the cavities of the hollow parts forming the valve being connected to one another and these cavities being produced at least partially by electrochemical metal removal.
- the valve stem is first drilled through lengthwise, with the cavity in the valve head then being produced as an expansion bore transverse to the longitudinal axis of the valve stem.
- the production of hollow valves should be simplified by means of the method described and at the same time their quality should be able to be improved.
- a method for producing a metallic hollow valve of an internal combustion engine in which a bore is made in a blank designed as a forging pear. A subsequent valve head is then at least partially hollowed out by electrochemical removal, with the cavity produced in this way then being filled by means of a supporting fluid and the hollow valve being closed.
- the hollow valve can be manufactured comparatively inexpensively.
- metallic hollow valves are lighter than full valves and offer improved heat dissipation when filled with a cooling medium such as sodium.
- a hollow valve which offers particularly good heat dissipation, leads to a shift in the knock limit and thus to particularly advantageous operation.
- Knocking is the uncontrolled ignition of the fuel-air mixture due to excessive temperature and pressure. This leads to shocks in the internal combustion engine with high mechanical and thermal loads, which ultimately have a negative impact on service life and efficiency.
- the knock limit can be raised, higher compression in the cylinder is possible, which leads to a significant increase in efficiency in the combustion process and thus to higher performance with lower fuel consumption.
- the present invention is therefore concerned with the problem of specifying an improved embodiment for a metallic hollow valve of the generic type, which allows an increased knock limit.
- the present invention is based on the general idea of raising the knock limit in an internal combustion engine by designing the valves (gas exchange valves) used in this internal combustion engine as very thin-walled hollow valves and thereby cooling them particularly effectively.
- the metallic hollow valve according to the invention has, in a known manner, a tubular shaft and a valve head connected thereto.
- the shaft has an outside diameter of between 5.0 and 6.0 mm and an inside diameter of between 3.0 and 4.6 mm, as a result of which the wall thickness of the shaft can be significantly reduced in comparison to conventional hollow valves.
- a cavity is also provided in the valve head, with the walls surrounding it having a thickness of between 1.0 and at most 2.0 mm, thereby also enabling high heat transfer and excellent cooling of the hollow valve.
- the cavity in the valve head is produced by electrochemical removal, with the cavity being essentially round, ellipsoidal or conical is trained. Electrochemical removal offers the possibility of creating the largest possible cavity in the valve head without great mechanical effort and without the use of complicated tools.
- the electrochemical removal represents a process that can be controlled extremely precisely, so that the metallic hollow valves according to the invention can be produced with consistently high quality.
- the shank can also be expanded by electrochemical removal, in which case it is usually drilled first.
- a surface roughness R Z of an inner wall of the cavity is expediently >10 ⁇ m, in particular R Z >16 ⁇ m. Due to the comparatively large surface roughness on the inner wall of the cavity in the valve head, an enlarged heat transfer surface is available, which has a positive effect on heat exchange and thus also on the cooling of the hollow valves according to the invention.
- the surface roughness of an inner wall in the shaft of the hollow valve is designed in the same way.
- the hollow valve is made of X45CrSi9-3, X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, NiCr20TiAl, or NCF 3015 (Ni 30%, Cr 15%) steel.
- Such high-alloy steels allow the filigree design of the hollow valve according to the invention and also have a comparatively high wear resistance.
- such high-alloy steels usually have high corrosion resistance and in particular also high resistance to aggressive chemicals such as oils or combustion exhaust gases, so that they are particularly suitable for use in such metallic hollow valves in internal combustion engines.
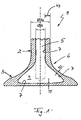
- the only figure 1 shows a cross section through a metallic hollow valve according to the invention.
- a metallic hollow valve 1 according to the invention of an internal combustion engine (otherwise not shown) has a tubular shaft 2 and a valve head 3 connected thereto.
- the shaft 2 and the valve head 3 are usually designed in one piece.
- it is filigree, i.e. it is equipped with comparatively thin wall thicknesses b 1 , b 2 and b 3 , the wall thickness b 1 being in the area of a valve head base facing a combustion chamber (not shown).
- the wall thickness b 2 is measured in the area of a valve throat 6 .
- the wall thickness b 3 refers to the thickness of the wall in the area of the shaft 2.
- the thin wall thicknesses b 1 , b 2 and b 3 not only improve the cooling of the metallic hollow valve 1, but also increase the knock limit of the internal combustion engine , whereby an uncontrolled ignition of a gasoline-air mixture with the associated high mechanical and thermal loads can be avoided, or at least greatly reduced.
- the thin walls increase the knock limit.
- the metal hollow valve 1 according to the invention has an outside diameter d a of between 5 and 6 mm in the area of its shaft 2 .
- An inner diameter d i in the area of the shaft 2 is between 3.0 and 4.6 mm, so that the wall thickness b 3 is between approximately 0.7 and 1.5 mm.
- the wall thickness b 3 can also be between about 0.5 and 1.5 mm due to tolerances, with the inner diameter d i preferably being 4.6 mm if the outer diameter d a is 6 mm.
- a cavity 4 is provided in the valve head 3, which together with a cavity 5 arranged in the shaft 2 forms a receiving space for a coolant, for example sodium.
- a wall surrounding the cavity 4 has a thickness b 1 of between 1 and 2 mm in the area of the valve head base, as well as in the area of a valve throat 6, so that the thickness b 2 of the wall is also approximately 1 to 2 mm in this area.
- the surface roughness R Z of an inner wall 7 of the cavity 4 and of the cavity 5 is greater than 10 ⁇ m, in particular greater than 16 ⁇ m is.
- the increased surface roughness R Z increases the area available for heat exchange and thus improves heat transfer.
- the hollow valve 1 can be made of a high-alloy steel, such as X45CrSi9-3, X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, NiCr20TiAl or NCF3015 steel.
- a high-alloy steel such as X45CrSi9-3, X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, NiCr20TiAl or NCF3015 steel.
- Such high-alloy steels allow the filigree design of the metallic hollow valve 1 according to the invention and are also resistant to aggressive chemical media such as oils or combustion gases. In addition, they have a high wear and corrosion resistance and thus have a long service life.
- the cavity 5 in the stem 2 is usually drilled, whereas the cavity 4 in the valve head 3 is produced by means of electrochemical machining.
- the cavity 4 can, for example, be round, conical or ellipsoidal. Such an electrochemical Removal enables the cavity 4 and thus also the walls surrounding it to be produced in a simple manner on the one hand and highly accurately on the other.
- this can be cooled significantly better and thereby indirectly raise the knock limit of the internal combustion engine, which not only increases the service life of the internal combustion engine but also leads to higher performance with lower fuel consumption at the same time.
- the filigree design also saves weight, which has a positive effect on the fuel consumption of the internal combustion engine.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Lift Valve (AREA)
- Combustion Methods Of Internal-Combustion Engines (AREA)
- Cylinder Crankcases Of Internal Combustion Engines (AREA)
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft ein metallisches Hohlventil einer Brennkraftmaschine mit einem rohrförmigen Schaft und einem daran angebundenen Ventilteller gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1.
- Die zunehmenden thermischen Belastungen in Verbrennungsmotoren, insbesondere in PKW-Motoren, erfordern es zunehmend, auch Bestandteile derselben, wie beispielsweise die Gaswechselventile, kurz auch Ventile genannt, zu kühlen. Hierfür werden sogenannten Hohlventile mit einem innenliegenden Kühlmedium verwendet.
- Aus der
EP 2 541 000 A1 ist ein Verfahren zur Herstellung von metallischen Hohlventilen bekannt, bei welchem mittels entsprechender Stempel das Ventil sukzessive verformt, insbesondere dessen Schaft verjüngt wird. - Aus der
DE 10 2010 051 871 A1 ist ein Verfahren zur Herstellung von metallischen Hohlventilen für den Gasaustausch einer Brennkraftmaschine bekannt, wobei die Hohlräume der das Ventil bildenden Hohlteile miteinander verbunden sind und wobei diese Hohlräume wenigstens teilweise durch elektrochemische Metallabtragung hergestellt sind. Hierzu wird zunächst der Ventilschaft der Länge nach durchgebohrt, wobei anschließend der Hohlraum im Ventilkopf als Erweiterungsbohrung quer zur Längsachse des Ventilschafts erzeugt wird. Mittels des beschriebenen Verfahrens soll insbesondere die Herstellung von Hohlventilen vereinfacht und zugleich deren Qualität verbessert werden können. - Aus der
DE 10 2012 209 187 A1 ist wiederum ein Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils einer Brennkraftmaschine bekannt, bei dem in einen als Schmiedebirne ausgebildeten Rohling eine Bohrung eingebracht wird. Ein späterer Ventilkopf wird anschließend durch elektrochemisches Abtragen zumindest teilweise ausgehöhlt, wobei anschließend der derart hergestellte Hohlraum mittels eines Stützfluides befüllt und das Hohlventil geschlossen wird. Hierdurch kann das Hohlventil vergleichsweise kostengünstig hergestellt werden. - Aus der
DE 10 2011 077 198 A1 ist wiederum ein Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils einer Brennkraftmaschine mit einem in einen Ventilschaft übergehenden Ventilkopf bekannt, bei welchem in den Ventilkopf eine Bohrung eingebracht wird und dieser anschließend durch elektrochemisches Abtragen zumindest teilweise ausgehöhlt wird. Auch hierdurch soll prinzipiell die Herstellung derartiger metallischer Hohlventile verbessert werden. - Aus der
EP 2 357 326 A1 ist ein gattungsgemäßes metallisches Hohlventil einer Brennkraftmaschine mit einem rohrförmigen Schaft mit einem Hohlraum und einem daran angebundenen Ventilkopf bekannt. - Generell gilt für metallische Hohlventile, dass diese leichter sind als Vollventile und bei Füllung mit einem Kühlmedium, wie beispielsweise Natrium, eine verbesserte Wärmeabfuhr bieten. Bei Ottomotoren führt ein Hohlventil, das eine besonders gute Wärmeableitung bietet, zu einer Verschiebung der Klopfgrenze und damit zu einem besonders vorteilhaften Betrieb. Das Klopfen bezeichnet das unkontrollierte Zünden des Benzin-Luft-Gemisches aufgrund zu hoher Temperatur und Druck. Dies führt zu Schlägen in der Brennkraftmaschine mit hohen mechanischen und thermischen Belastungen, welche schlussendlich die Lebensdauer und den Wirkungsgrad negativ beeinträchtigen. Kann die Klopfgrenze jedoch angehoben werden, wird eine höhere Verdichtung im Zylinder möglich, die zu einer deutlichen Effizienzsteigerung im Verbrennungsprozess und damit zu einer höheren Leistung bei geringerem Kraftstoffverbrauch führt.
- Die vorliegende Erfindung beschäftigt sich daher mit dem Problem, für ein metallisches Hohlventil der gattungsgemäßen Art eine verbesserte Ausführungsform anzugeben, die eine erhöhte Klopfgrenze ermöglicht.
- Dieses Problem wird erfindungsgemäß durch den Gegenstand des unabhängigen Anspruchs 1 gelöst. Vorteilhafte Ausführungsformen sind Gegenstand der abhängigen Ansprüche.
- Die vorliegende Erfindung beruht auf dem allgemeinen Gedanken, die Klopfgrenze in einer Brennkraftmaschine anzuheben, indem die in dieser Brennkraftmaschine eingesetzten Ventile (Gaswechselventile) als sehr dünnwandige Hohlventile ausgebildet werden und dadurch besonders effektiv zu kühlen sind. Das erfindungsgemäße metallische Hohlventil weist hierzu in bekannter Weise einen rohrförmigen Schaft sowie einen daran angebundenen Ventilkopf auf. Der Schaft besitzt erfindungsgemäß einen Außendurchmesser zwischen 5,0 und 6,0 mm sowie einen Innendurchmesser zwischen 3,0 und 4,6 mm, wodurch eine Wandstärke des Schaftes im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Hohlventilen deutlich reduziert werden kann. Im Ventilkopf ist zusätzlich ein Hohlraum vorgesehen, wobei die diesen umgebenden Wände eine Dicke zwischen 1,0 und maximal 2,0 mm aufweist und dadurch ebenfalls eine hohe Wärmeübertragung und eine exzellente Kühlung des Hohlventils ermöglicht. Durch die vergleichsweise filigrane Ausbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Hohlventils kann insbesondere eine effektive Kühlung an der planen und dem Brennraum zugewandten Ventilkopfunterseite erreicht werden, welche dazu beiträgt, die Klopfgrenze zu verschieben, das heißt anzuheben, und dadurch die mechanischen und thermischen Belastungen der Brennkraftmaschine, hervorgerufen durch das Klopfen, zu senken. In dem erfindungsgemäßen filigranen Ventil kann darüber hinaus eine höhere Verdichtung im Zylinder erzielt werden, die zu einer deutlichen Effizienzsteigerung im Verbrennungsprozess und damit zu einer höheren Leistung bei gleichzeitig geringerem Kraftstoffverbrauch führt. Dabei ist der Hohlraum im Ventilkopf durch elektrochemisches Abtragen hergestellt, wobei der Hohlraum im Wesentlichen rund, ellipsoidisch oder kegelförmig ausgebildet ist. Das elektrochemische Abtragen bietet dabei die Möglichkeit, ohne großen mechanischen Aufwand und ohne Einsatz komplizierter Werkzeuge einen möglichst großen Hohlraum im Ventilkopf zu schaffen. Das elektrochemische Abtragen stellt dabei einen äußerst genau kontrollierbaren Prozess dar, sodass die erfindungsgemäßen metallischen Hohlventile mit gleichbleibend hoher Qualität hergestellt werden können. Der Schaft kann dabei ebenfalls durch elektrochemisches Abtragen erweitert werden, wobei dieser üblicherweise zunächst gebohrt wird.
- Zweckmäßig beträgt eine Oberflächenrauheit RZ einer Innenwand des Hohlraums > 10 µm, insbesondere RZ > 16 µm. Durch die vergleichsweise große Oberflächenrauheit an der Innenwand des Hohlraums im Ventilkopf steht eine vergrößerte Wärmeübertragungsfläche zur Verfügung, die einen Wärmetausch positiv beeinflusst und damit auch die Kühlung der erfindungsgemäßen Hohlventile. In gleicher Weise ist auch die Oberflächenrauheit einer Innenwand im Schaft des Hohlventils gestaltet.
- Bei einer weiteren vorteilhaften Ausführungsform der erfindungsgemäßen Lösung ist das Hohlventil aus X45CrSi9-3, aus X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, aus NiCr20TiAl, oder aus NCF 3015 (Ni 30%, Cr 15%) Stahl hergestellt. Derartige hochlegierte Stähle erlauben erst die filigrane Ausbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Hohlventils und weisen darüber hinaus einen vergleichsweise hohen Verschleißwiderstand auf. Derartige hochlegierte Stähle besitzen darüber hinaus üblicherweise eine hohe Korrosionsbeständigkeit und insbesondere auch eine hohe Beständigkeit gegen aggressive Chemikalien, wie beispielsweise Öle oder Verbrennungsabgase, sodass sie besonders geeignet für den Einsatz bei derartigen metallischen Hohlventile in Brennkraftmaschinen sind.
- Weitere wichtige Merkmale und Vorteile der Erfindung ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen, aus der Zeichnung und aus der zugehörigen Figurenbeschreibung anhand der Zeichnung.
- Es versteht sich, dass die vorstehend genannten und die nachstehend noch zu erläuternden Merkmale nicht nur in der jeweils angegebenen Kombination, sondern auch in anderen Kombinationen oder in Alleinstellung verwendbar sind, ohne den Rahmen der vorliegenden Erfindung zu verlassen.
- Ein bevorzugtes Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung ist in der Zeichnung dargestellt und wird in der nachfolgenden Beschreibung näher erläutert.
- Die einzige
Figur 1 zeigt einen Querschnitt durch ein erfindungsgemäßes metallisches Hohlventil. - Entsprechend der
Figur 1 , weist ein erfindungsgemäßes metallisches Hohlventil 1 einer im Übrigen nicht gezeigten Brennkraftmaschine einen rohrförmigen Schaft 2 sowie einen daran angebundenen Ventilkopf 3 auf. Der Schaft 2 und der Ventilkopf 3 sind dabei üblicherweise einstückig ausgebildet. Um nun eine möglichst effiziente Kühlung des metallischen Hohlventils 1 erreichen zu können, ist dieses filigran, das heißt mit vergleichsweise dünnen Wandstärken b1, b2 und b3 ausgestattet, wobei die Wandstärke b1 im Bereich eines einem nicht gezeigten Brennraum zugewandten Ventilkopfbodens ist, wogegen die Wandstärke b2 im Bereich einer Ventilkehle 6 gemessen wird. Die Wandstärke b3 bezieht sich auf die Dicke der Wand im Bereich des Schafts 2. Durch die dünnen Wandstärken b1, b2 und b3 wird jedoch nicht nur eine verbesserte Kühlung des metallischen Hohlventils 1 erreicht, sondern auch eine Erhöhung der Klopfgrenze der Brennkraftmaschine, wodurch ein unkontrolliertes Zünden eines Benzin-Luft-Gemisches mit den damit verbundenen hohen mechanischen und thermischen Belastungen vermieden, zumindest aber stark reduziert werden kann. Die dünnen Wandstärken bewirken dabei die Erhöhung der Klopfgrenze. Um dies zu erreichen, weist das erfindungsgemäße metallische Hohlventil 1 im Bereich seines Schaftes 2 einen Außendurchmesser da auf, der zwischen 5 und 6 mm liegt. Ein Innendurchmesser di liegt im Bereich des Schaftes 2 zwischen 3,0 und 4,6 mm, sodass die Wandstärke b3 zwischen circa 0,7 und 1,5 mm liegt. Selbstverständlich kann die Wandstärke b3 toleranzbedingt auch zwischen ca. 0,5 und 1,5mm liegen, wobei vorzugsweise der Innendurchmesser di bei 4,6 mm liegt, sofern der Außendurchmesser da bei 6 mm liegt. Im Ventilkopf 3 ist dabei ein Hohlraum 4 vorgesehen, der zusammen mit einem im Schaft 2 angeordneten Hohlraum 5 einen Aufnahmeraum für ein Kühlmittel, beispielsweise Natrium, bildet. Eine den Hohlraum 4 umgebende Wand weist dabei im Bereich des Ventilkopfbodens eine Dicke b1 zwischen 1 und 2 mm auf, ebenso wie im Bereich einer Ventilkehle 6, sodass auch in diesem Bereich die Dicke b2 der Wand circa 1 bis 2 mm beträgt. - Um die Wärmeübertragung zwischen dem im Hohlraum 4 und 5 angeordneten Kühlmittel und dem metallischen Hohlventil 1 weiter verbessern zu können, kann vorgesehen sein, dass eine Oberflächenrauheit RZ einer Innenwand 7 des Hohlraums 4 und des Hohlraums 5 größer als 10 µm, insbesondere größer als 16 µm ist. Durch die erhöhte Oberflächenrauheit RZ wird die für den Wärmetausch zur Verfügung stehende Fläche vergrößert und dadurch die Wärmeübertragung verbessert.
- Generell kann das Hohlventil 1 aus einem hochlegierten Stahl, wie beispielsweise X45CrSi9-3, aus X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, aus NiCr20TiAl oder aus NCF3015 Stahl hergestellt sein. Derartige hochlegierte Stähle ermöglichen die filigrane Ausbildung des erfindungsgemäßen metallischen Hohlventils 1 und sind darüber hinaus beständig gegen aggressive chemische Medien, wie beispielsweise Öle oder Verbrennungsabgase. Zudem besitzen sie einen hohen Verschleiß- und Korrosionswiderstand und besitzen dadurch eine hohe Lebensdauer.
- Der Hohlraum 5 im Schaft 2 wird üblicherweise gebohrt, wogegen der Hohlraum 4 im Ventilkopf 3 mittels elektrochemischen Abtragens hergestellt wird. Der Hohlraum 4 kann beispielsweise rund, kegelförmig oder aber auch ellipsoidisch ausgebildet sein. Ein derartiges elektrochemisches Abtragen ermöglicht eine einerseits einfache und andererseits höchst genaue Herstellung des Hohlraums 4 und damit auch diesen umgebenden Wände.
- Mit dem erfindungsgemäßen metallischen Hohlventil 1 lässt sich dieses deutlich besser kühlen und dadurch indirekt die Klopfgrenze der Brennkraftmaschine anheben, was nicht nur die Lebensdauer der Brennkraftmaschine erhöht, sondern auch zu einer höheren Leistung bei gleichzeitig geringerem Kraftstoffverbrauch führt. Durch die filigrane Ausführung wird zudem Gewicht eingespart, was sich positiv auf einen Kraftstoffverbrauch der Brennkraftmaschine auswirkt.
Claims (4)
- Metallisches Hohlventil (1) einer Brennkraftmaschine, mit einem rohrförmigen Schaft (2) mit einem Hohlraum (5) und einem daran angebundenen Ventilkopf (3), wobei- der Schaft (2) einen Außendurchmesser 5,0 mm < da < 6,0 mm und einen Innendurchmesser 3,0 mm < di < 4,6 mm aufweist,- im Ventilkopf (3) ein Hohlraum (4) vorgesehen ist,- eine den Hohlraum (4) umgebende Wand eine Dicke 1,0 mm < b1,2 < 2,0 mm aufweist,dadurch gekennzeichnet,dass der Hohlraum (4) im Ventilkopf (3) durch elektrochemisches Abtragen hergestellt ist, unddass eine Oberflächenrauheit RZ einer Innenwand (7) der Hohlräume (4,5) größer als 10 µm, insbesondere größer als 16 µm, ist.
- Hohlventil nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass eine den Hohlraum (5) umgebende Wand eine Dicke 0,7 mm < b3 < 1,5 mm aufweist. - Hohlventil nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche,
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass das Hohlventil (1) aus X45CrSi9-3, aus X50CrMnNiNbN21-9, aus NiCr20TiAl oder aus NCF 3015 Stahl hergestellt ist. - Hohlventil nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3,
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass der Hohlraum (4) im Wesentlichen rund, ellipsoidisch oder kegelförmig ausgebildet ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102013203443.1A DE102013203443A1 (de) | 2013-02-28 | 2013-02-28 | Metallisches Hohlventil |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2803827A1 EP2803827A1 (de) | 2014-11-19 |
| EP2803827B1 EP2803827B1 (de) | 2015-11-18 |
| EP2803827B2 true EP2803827B2 (de) | 2023-01-04 |
Family
ID=50002556
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14152509.7A Not-in-force EP2803827B2 (de) | 2013-02-28 | 2014-01-24 | Metallisches Hohlventil |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2803827B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2014169696A (de) |
| KR (1) | KR20140108150A (de) |
| CN (1) | CN104018904B (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102013203443A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014225618A1 (de) * | 2014-12-11 | 2016-06-16 | Mahle International Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Hohlventils |
| DE102016200739A1 (de) * | 2016-01-20 | 2017-07-20 | Mahle International Gmbh | Metallisches Hohlventil für eine Brennkraftmaschine eines Nutzkraftfahrzeugs |
| DE102017202585A1 (de) * | 2016-02-17 | 2017-08-17 | Mahle International Gmbh | Brennkraftmaschine mit zumindest einem Zylinder und mit zumindest zwei Hohlkopfventilen |
| WO2017194091A1 (de) | 2016-05-09 | 2017-11-16 | Mahle International Gmbh | Gaswechselventil |
| DE102020202739A1 (de) | 2020-03-04 | 2021-09-09 | Mahle International Gmbh | Gesintertes Lagerbuchsenmaterial, Gleitlager, Brennkraftmaschine und elektrische Maschine |
| DE102020202738A1 (de) | 2020-03-04 | 2021-09-09 | Mahle International Gmbh | Gleitlager, Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Gleitlagers, Brennkraftmaschine mit Gleitlager sowie elektrische Maschine mit Gleitlager |
| DE102022206387A1 (de) * | 2022-06-24 | 2024-01-04 | Mahle International Gmbh | Wasserstoffverbrennungsmotor sowie Personenkraftfahrzeug und Nutzfahrzeug |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2627259A (en) * | 1942-06-24 | 1953-02-03 | Gen Motors Corp | Valve |
| DE1213457B (de) * | 1964-10-06 | 1966-03-31 | Teves Thompson & Co G M B H | Waermebehandlungsverfahren zur Herstellung von geschweissten, natriumgefuellten Ventilkegeln |
| JPS56121803A (en) * | 1980-02-27 | 1981-09-24 | Hitachi Ltd | Manufacture of nozzle blade |
| JPH03264714A (ja) * | 1990-03-14 | 1991-11-26 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 中空ポペットバルブ |
| US5413073A (en) * | 1993-04-01 | 1995-05-09 | Eaton Corporation | Ultra light engine valve |
| DE19746235A1 (de) * | 1996-11-02 | 1998-05-07 | Volkswagen Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Tellerventiles |
| EP0911493A3 (de) * | 1997-10-21 | 2000-04-12 | Eaton Corporation | Verbesserte Spitzengestaltung in einem ultraleichten Brennkraftmaschinenventil |
| DE19804053A1 (de) * | 1998-02-03 | 1999-08-05 | Mwp Mahle J Wizemann Pleuco Gm | Leichtbauventil |
| JP4264284B2 (ja) * | 2003-04-09 | 2009-05-13 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | サイジングプレス用金型 |
| US7104762B2 (en) * | 2004-01-06 | 2006-09-12 | General Electric Company | Reduced weight control stage for a high temperature steam turbine |
| DE102005005041A1 (de) * | 2005-02-03 | 2006-08-10 | Märkisches Werk GmbH | Ventil zur Steuerung des Gasaustauschs, insbesondere bei Verbrennungsmotoren |
| DE102005013088B4 (de) * | 2005-03-18 | 2006-12-28 | Man B & W Diesel Ag | Gaswechselventil mit Korrosionsschutzschicht |
| US20090081073A1 (en) | 2007-06-07 | 2009-03-26 | Celso Antonio Barbosa | Alloys with high corrosion resistance for engine valve applications |
| JP2009013935A (ja) * | 2007-07-06 | 2009-01-22 | Toyota Motor Corp | 内燃機関用中空バルブ |
| CN101169054A (zh) * | 2007-10-16 | 2008-04-30 | 韩鸿滨 | 轻质气门 |
| JP4390291B1 (ja) * | 2008-09-18 | 2009-12-24 | 株式会社 吉村カンパニー | 中空エンジンバルブの弁傘部の製造方法及び中空エンジンバルブ |
| EP2357326B1 (de) * | 2008-10-10 | 2015-07-08 | Nittan Valve Co., Ltd. | Hohles tellerventil und herstellungsverfahren dafür |
| JP5297402B2 (ja) | 2010-02-26 | 2013-09-25 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 金属ナトリウム封入エンジンバルブの製造方法 |
| DE102010051871A1 (de) | 2010-11-22 | 2012-05-24 | Märkisches Werk GmbH | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Ventilen für den Gasaustausch und nach einem derartigen Verfahren hergestellte Ventile |
| DE102011077198A1 (de) | 2011-06-08 | 2012-12-13 | Mahle International Gmbh | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils mit verbesserter Kühlung |
| DE102012209187A1 (de) | 2011-06-08 | 2012-12-13 | Mahle International Gmbh | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils mit verbesserter Kühlung |
| CN202360166U (zh) * | 2011-07-29 | 2012-08-01 | 马勒技术投资(中国)有限公司 | 带与外部相通油道的气门 |
-
2013
- 2013-02-28 DE DE102013203443.1A patent/DE102013203443A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2014
- 2014-01-24 EP EP14152509.7A patent/EP2803827B2/de not_active Not-in-force
- 2014-02-17 CN CN201410053267.7A patent/CN104018904B/zh not_active Ceased
- 2014-02-20 JP JP2014030232A patent/JP2014169696A/ja active Pending
- 2014-02-27 KR KR1020140023156A patent/KR20140108150A/ko not_active Withdrawn
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104018904B (zh) | 2017-10-24 |
| EP2803827A1 (de) | 2014-11-19 |
| KR20140108150A (ko) | 2014-09-05 |
| CN104018904A (zh) | 2014-09-03 |
| EP2803827B1 (de) | 2015-11-18 |
| JP2014169696A (ja) | 2014-09-18 |
| DE102013203443A1 (de) | 2014-08-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2803827B2 (de) | Metallisches Hohlventil | |
| DE112012005045B4 (de) | Vorkammervorrichtung für einen Verbrennungsmotor | |
| DE69403843T2 (de) | Ultraleichtes Ventil für Brennkraftmaschine | |
| EP2049315B1 (de) | Auswerferstift für eine werkzeugform sowie verfahren zum herstellen eines solchen auswerferstifts | |
| DE102019115844A1 (de) | Zylinderkopfanordnung mit einem hybriden Ventilsitz-Einsatz | |
| EP3582910B1 (de) | Verfahren zum querkeilwalzen von tellerventilen | |
| DE112015003874B4 (de) | Hohles Motorventil und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| EP2038078A1 (de) | Kühlkanalkolben für eine brennkraftmaschine und verfahren zu seiner herstellung | |
| DE102016116046A1 (de) | Kolben mit niedriger Bauhöhe | |
| DE102008037747A1 (de) | Bimetallventil | |
| DE102010051871A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Ventilen für den Gasaustausch und nach einem derartigen Verfahren hergestellte Ventile | |
| DE102011077198A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils mit verbesserter Kühlung | |
| DE102013210900A1 (de) | Gaswechselventil einer Brennkraftmaschine | |
| DE102012209187A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines metallischen Hohlventils mit verbesserter Kühlung | |
| DE102012111521A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Zylinderkurbelgehäuses | |
| DE102016201619A1 (de) | Kolben einer Brennkraftmaschine | |
| EP2950031B1 (de) | Abgaswärmetauscher aus duplexstahl | |
| DE102013002097A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines kühlbaren Werkzeugteils für ein Formwerkzeug zum Warmumformen und/oder Presshärten, sowie hiermit hergestelltes Formwerkzeug | |
| DE102016014769A1 (de) | Ventil für eine Verbrennungskraftmaschine eines Kraftwagens | |
| DE102010052579A1 (de) | Kolben für eine Brennkraftmaschine und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| EP3199770A1 (de) | Metallisches hohlventil für eine brennkraftmaschine eines nutzkraftfahrzeugs | |
| DE102014222416A1 (de) | Kolben für eine Brennkraftmaschine | |
| DE102012215541A1 (de) | Kolben | |
| DE102010029052A1 (de) | Kraftstoffverteiler und dessen Verwendung | |
| DE102013016358A1 (de) | Hubkolben-Verbrennungskraftmaschine für einen Kraftwagen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140124 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| R17P | Request for examination filed (corrected) |
Effective date: 20150210 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20150408 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20150825 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 761698 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20151215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502014000187 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20160218 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160218 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160318 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160318 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160219 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160131 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 502014000187 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160124 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: FEDERAL-MOGUL VALVETRAIN GMBH Effective date: 20160804 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160124 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20180130 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20140124 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20180129 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151118 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20190124 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190124 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 761698 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20190124 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190124 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20230104 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 502014000187 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240119 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20240527 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502014000187 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20250801 |