EP2501632B1 - Führungsanordnung mit einem transportorgan - Google Patents
Führungsanordnung mit einem transportorgan Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2501632B1 EP2501632B1 EP10779451.3A EP10779451A EP2501632B1 EP 2501632 B1 EP2501632 B1 EP 2501632B1 EP 10779451 A EP10779451 A EP 10779451A EP 2501632 B1 EP2501632 B1 EP 2501632B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- guide
- elements
- guide rail
- arrangement according
- running surface
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 38
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 38
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 38
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 27
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 27
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 23
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002430 Fibre-reinforced plastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011151 fibre-reinforced plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007373 indentation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 241000446313 Lamella Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010038743 Restlessness Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004809 Teflon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006362 Teflon® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003032 molecular docking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G17/00—Conveyors having an endless traction element, e.g. a chain, transmitting movement to a continuous or substantially-continuous load-carrying surface or to a series of individual load-carriers; Endless-chain conveyors in which the chains form the load-carrying surface
- B65G17/20—Conveyors having an endless traction element, e.g. a chain, transmitting movement to a continuous or substantially-continuous load-carrying surface or to a series of individual load-carriers; Endless-chain conveyors in which the chains form the load-carrying surface comprising load-carriers suspended from overhead traction chains
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G17/00—Conveyors having an endless traction element, e.g. a chain, transmitting movement to a continuous or substantially-continuous load-carrying surface or to a series of individual load-carriers; Endless-chain conveyors in which the chains form the load-carrying surface
- B65G17/30—Details; Auxiliary devices
- B65G17/32—Individual load-carriers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G21/00—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors
- B65G21/16—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors for conveyors having endless load-carriers movable in curved paths
- B65G21/18—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors for conveyors having endless load-carriers movable in curved paths in three-dimensionally curved paths
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G23/00—Driving gear for endless conveyors; Belt- or chain-tensioning arrangements
- B65G23/02—Belt- or chain-engaging elements
- B65G23/14—Endless driving elements extending parallel to belt or chain
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H29/00—Delivering or advancing articles from machines; Advancing articles to or into piles
- B65H29/003—Delivering or advancing articles from machines; Advancing articles to or into piles by grippers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2405/00—Parts for holding the handled material
- B65H2405/50—Gripping means
- B65H2405/55—Rail guided gripping means running in closed loop, e.g. without permanent interconnecting means
- B65H2405/552—Rail guided gripping means running in closed loop, e.g. without permanent interconnecting means with permanent interconnection and determined spacing between the grippers
- B65H2405/5521—Rail guided gripping means running in closed loop, e.g. without permanent interconnecting means with permanent interconnection and determined spacing between the grippers details of interconnection, e.g. chain, link
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H29/00—Delivering or advancing articles from machines; Advancing articles to or into piles
Definitions
- the invention relates to a guide arrangement for guiding the movement of a product for conveying products according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the DE 2 347 459 discloses such a guide arrangement.
- Conveying devices with a conveyor chain guided by means of a suitable guide arrangement along a preferably endlessly circulating conveying path are used for transporting printed products between individual processing stations, such as inserting machines, addressing devices, gluing machines, etc.
- the printed products are usually held by grippers or clamps mounted on the chain links and, if appropriate, released from the grippers at the processing stations.
- the conveyor chain is usually driven endlessly circumferentially along the conveying path defined by the guide arrangement.
- the conveyor line usually has straight and arcuate sections, wherein the arcuate sections may be arranged within a horizontal plane, a vertical plane or an obliquely upwardly or downwardly extending plane.
- the guide arrangement must also have rectilinear and arc-shaped guide elements, by means of which the arcs of the conveying path are determined.
- the conveyor line can extend over a length of 100 m or more and thereby pass through an entire production space in the horizontal and vertical directions. Therefore, the guiding arrangement serving to define the conveying path can not be manufactured in one piece, but must be composed of individual guide elements interconnected by means of suitable connecting arrangements. Corresponding guide arrangements are, for example, in the WO 99/33731 . EP 1 029 815 A1 . WO 99/33722 . WO 99/33732 . WO 99/33730 described. When mounting the known guide arrangements, the individual guide elements are usually combined on the end surface side and connected by means of engaging in the side walls of the guide elements clamping devices, which in turn od via connecting elements in the form of bolts. Like. Connected to each other, firmly connected.
- the present invention seeks to provide a guide assembly for guiding the movement of a designed for conveying printed products conveyor chain, which is easy to install while ensuring low-noise and low-wear operation, and to provide a conveyor with such a guide arrangement.
- the invention aims to remedy this situation.
- the invention as characterized in the claims, the object is to propose a guide arrangement, which is able to overcome the disadvantages of belonging to the prior art arrangements.
- the object of the invention is also to provide a guide arrangement, which can be operated without further including with belonging to the prior art transport organs.
- the inventive guide arrangement is therefore designed according to the task not only for a special tailored transport organ. Another task The invention is to ensure a low-noise and wear-minimized operation.
- connecting elements are positively fixed to the transversely, in particular approximately perpendicularly, the conveyor track extending end faces of the individual guide elements, which can then be connected in the correct position by positive engagement with each other.
- the determination of the connecting elements on the guide elements can be made at the factory, so that the components consisting of guide element and connecting elements can be prefabricated by resorting to standard components, such as linearly extending guide elements, arcuate guide elements and connecting elements. In this case, a smooth transition from guide element to connecting element can be ensured in the factory pre-assembly.
- the prefabricated assemblies in the area facing each other surface side, d.
- the positive engagement of mutually facing end-face contact surfaces of the fasteners fixed to the guide elements can be achieved if a contact surface has at least one projection and the other contact surface at least one positive fit receiving the projection complementary thereto formed recess and / or recess.
- the connecting elements usually have a substantially flat boundary surface facing the guide element and a contact surface extending approximately parallel to this flat boundary surface, wherein a projection of the contact surface extends approximately along the conveying path into that of the guide element facing boundary surface extends opposite, while the recess extends in the direction of the guide element facing the boundary surface.
- each contact surface has at least one projection and at least one recess such that a positive connection can be effected in the region of two mutually facing uniform contact surfaces .
- projection and recess of the contact surface are preferably mirror-symmetrical with respect to a straight line running perpendicular to the conveyor line.
- a projection in a sectional plane running perpendicular to the conveying direction has a cross-sectional area tapering in the direction of the adjacent contact surface or depression wherein the recess intended to receive the projection may also have a correspondingly tapering cross-sectional area.
- At least one projection and the complementary recess to have a cross-sectional surface which counteracts a rotational movement about a rotation axis extending parallel to the conveying direction in a sectional plane extending perpendicularly to the conveying direction, ie. H. if this cross-sectional area deviates from a circular disk or ring shape.
- An improvement in the mounting accuracy can be achieved if at least one contact surface has two, three or more projections which are positively received in the mounted state in correspondingly complementary recesses or recesses of the other contact surface.
- connection arrangement serving for coupling the connecting elements in the region of the contact surfaces , Preferably accessible from the outside, mounting arrangement, with which the positive connection of the connecting elements can be secured.
- Such a fastening arrangement can be realized in a particularly simple manner in the form of a fastening bolt extending in parallel to the conveying path, passing through a connecting element and inserted in a thread which is preferably inserted into the adjacent connecting element, such as a threaded nut accessible from the outside, in particular a screw bolt.
- a fastening bolt is received in a groove-shaped recess formed in an outer boundary surface of the guide element and extending along the conveying path, in which the bolt head is accessible, for example, for an Allen wrench is.
- the threaded nut can be secured against rotation in a corresponding receptacle in one of the connecting elements.
- the fastening bolts are inserted into corresponding recesses in the connecting elements, wherein the locking of the fastening bolts in the corresponding recesses of the connecting elements by means of a snap connection can be made. Thereafter, the locking element is pushed onto outside of the connecting elements exposed areas of the fastening bolts, so as to secure the positive connection of the connecting elements.
- the fastening arrangement just described is carried out on the model of a chain lock, wherein all components, including the locking element, can be recessed in an outer boundary surface of the fastening elements, so as to avoid projecting parts of the guide assembly.
- the fastening bolts can first be connected to one another via the locking element formed, for example, in the manner of a U-bracket, and then inserted into the receptacles of the connecting elements. This can be advantageous in difficult installation conditions.
- At least one projection has an angular cross-section in a sectional plane running perpendicular to the conveying path, wherein the then existing legs of the projection can enclose a right angle with each other, so as to provide a particularly high transverse rigidity in mutually perpendicular directions.
- the guide elements of the guide arrangement serve not only the leadership of the conveying member along the conveying path, but also the protection of the conveying member from contamination and mechanical loads.
- the guide elements and the connecting elements delimit a guide channel extending along the conveying path and designed to receive the conveying member and open on one side.
- Guide elements and connecting elements are designed in this embodiment of the invention in a direction perpendicular to the conveying section cutting plane substantially C-shaped, wherein the continuously along the conveying path extending opening of the guide channel serves to the passage of defined on the conveying member functional means, such as brackets or grippers to capture printed products.
- a guide assembly for guiding the movement of a designed for conveying printed products conveying member, which consists of a number of transport organs, along a preferably endless circulating conveyor line with a plurality of a Provided along the conveying path, designed for receiving the conveyor chain and open on one side guide channel limiting guide elements, which is characterized essentially in that four or more with four or more arranged on individual chain links of the transport member guide means, esp.
- each guide element within the guide channel co-operating guide surfaces are arranged, which extend along the conveying path.
- a separate guide surface is provided for each guide means so as to help avoid the tilting of the transport member with respect to the guide arrangement particularly reliable.
- the correspondingly executed guide elements with the aid of the above-described connecting elements can be positively connected to each other, so that the particularly tamper-proof guide of the transport member can be provided while avoiding excessive installation work.
- a second guide surface of the guide elements of a pivoting movement of the transport member cooperating with a second guide means of the transport member with respect to a parallel to the conveyor line and parallel to a first guide surface a pivot axis extending therefrom in a first pivoting direction counteracts, transversely, in particular approximately perpendicular, to the first guide surface in a first pivoting direction.
- the first and the second guide surface are preferably arranged at a right angle to each other enclosing planes, so that for corresponding guide means of the transport member support surfaces in two transverse, in particular approximately perpendicular, mutually extending support directions are provided.
- a further improvement in the anti-tilting of the guide arrangement can be achieved if a third guide surface extending approximately parallel to the second guide surface cooperatively counteracts a third guide device of the conveyor member with a pivoting movement relative to the pivot axis in the first pivoting direction.
- the third guide surface for providing a play-free guidance of the transport member is expediently spaced in a direction perpendicular thereto from the second guide surface, that the transport member with the voltage applied to the second guide surface second guide means and the third guide surface adjacent third guide means play-free with respect to a is guided perpendicular to the second and / or third guide surface extending direction between these guide surfaces.
- a play-free and at the same time frictionless guidance can be carried out using guide means in the form of rotatable with respect to predetermined roller axes guide rollers.
- the second guide roller may be spaced from the third guide roller in a direction perpendicular to the first guide surface direction.
- a particularly precise guidance of the transport member along the conveying path can be achieved if a fourth guide surface cooperates with a fourth guide device of the transport member abutting the pivoting movement of the transport member with respect to the pivot axis in a second opposite direction of the first pivoting direction Counteracts pivoting direction and transverse, in particular approximately perpendicular, to the second guide surface and preferably runs approximately parallel to the first guide surface. This completely counteracts any pivoting or tilting of the transport member with respect to a pivoting or tilting axis extending parallel to the conveying path.
- the fourth guide surface is spaced in a direction perpendicular thereto in such a direction from the first guide surface, that the transport member with the voltage applied to the fourth guide surface fourth guide means and the the first guide surface adjacent first guide means is guided without play with respect to a direction perpendicular to the first and / or fourth guide surface extending direction.
- the arrangement of the guide surfaces just described is particularly useful in the region of rectilinear sections of the guide track, because in this area with the four guide surfaces described a play-free and secured against tilting guidance of the transport member can be done. Care must be taken in the region of arcuate sections of the conveying path that the tracking error occurring in the bow regions of the transport member or the guide elements arranged on the transport member does not lead to excessive wear. In this context, it is expedient if the guide means of the transport organ with minor Game are guided between guide surfaces of the guide arrangement.
- Such a guide can be ensured if in the guide channel a with a distance approximately parallel to the first and preferably coplanar to the fourth guide surface extending fifth guide surface, a distance approximately parallel to the second and preferably approximately coplanar to the third guide surface extending sixth guide surface, a distance is provided approximately parallel to the third and preferably approximately coplanar with the second guide surface extending seventh guide surface and / or a distance approximately parallel to the fourth and preferably approximately coplanar to the first guide surface extending eighth guide surface.
- a first guide roller of the transport member between the first and the fifth guide surface, a second guide roller of the transport member between the second and the sixth guide surface, a third guide roller of the transport member between the third and the seventh guide surface and a fourth guide roller of the transport member between the fourth and the eighth guide surface may be arranged, wherein all guide rollers may be arranged with slight play between the guide surfaces, so as to minimize a wear caused by tracking error.
- the guide surfaces of the guide elements guide surfaces of the connecting elements are assigned, in which pass over the guide surfaces of the guide elements.
- These guide surfaces of the connecting elements are formed according to the invention by releasably fixable in recesses of the connecting elements adapter elements.
- the adapter elements can simultaneously form projections of the connecting elements, which contribute to the positive connection of the connecting elements.
- At least one guide surface is formed by a releasably fixed to a support portion of a guide element tread element. From an assembly point of view, it has proven to be expedient in this context if the carrier area is formed in the form of a section extending along the conveying path and in a section plane T-shaped extending perpendicularly thereto and the tread element is in the form of a C-shaped bridge which can be pushed onto the T-shaped web. Profile is formed.
- an adapter element fixed to a connecting element can fulfill a dual function if it forms a stop after mounting of the connecting element on the guide element after assembly of the tread element on the support area a displacement of the tread element along the conveyor line counteracting stop, wherein the pushed onto the web tread element a can overlap along the conveyor line over a portion of the length of the connecting element extending ridge-shaped carrier lug.
- the guide elements of the guide arrangement have a preferably on the extending in the conveying direction opening of the guide channel side of the guide surfaces having guide channel arranged drive channel arranged which may be open in the direction of the guide channel, so that formed between the guide channel and drive channel along the conveying path extending open recess is, by which, for example, a drive element ensures the movement.
- the guide channel and the drive channel can be delimited by mutually aligned and approximately mutually parallel side walls, which are connected on their side facing away from the opening of the guide channel side via a connecting wall.
- the connecting channel defining the conveying channel on its side facing away from the opening of the guide channel may have at least one drive opening extending along the conveying path and designed to introduce a drive element, such as a drive chain, into the drive channel.
- a device for conveying printed products has a guide arrangement according to the invention and a transport element which can be moved along the guide arrangement and is designed to convey printed products.
- the transport member may be received in a guide channel of the guide assembly.
- the chain links of the conveying member of a corresponding conveying device are usually driven endlessly circumferentially along a conveying path.
- these must be articulated generally coupled to each other about two axes independently pivotable.
- the conveyor line may have a length of 100 m or more. Accordingly complex is the assembly of the guide rail assemblies and the chain links, over the entire conveyor organ length, the articulated connection between the individual chain links must be ensured.
- the bearing housing consists of two bearing housing parts which engage over a spherical bearing body, so as to form a ball joint.
- the idea is taken up again to divide the bearing bodies in equatorial planes.
- conveyor chains that in addition to the formation of a functional arrangement rigidly coupled to each other chain links along the conveyor track successively mountable chain links to form a hinge assembly are coupled together.
- two functional arrangements which can be successively mounted along the conveying path can be articulated to one another to form a joint arrangement.
- conveyor chain sections can be prefabricated with a number of joint arrangements and / or functional arrangements and threaded into a guide rail arrangement which is also composed of prefabricated assemblies according to the invention.
- conveyor chain sections and guide elements having assemblies can be prefabricated.
- Adjacent chain links Transportorgans can then be rigidly connected together to form a functional arrangement of an endless revolving conveyor member. Overall, this results in a significant simplification of assembly, because the time required to ensure the reliability of the conveyor organ articulated connections already during the assembly of the conveying member, respectively. the transport organs are produced at the production site and during assembly at the installation site only rigid connections between individual chain links must be formed.
- the connecting regions of the individual functional members may have transversely to the conveying direction extending hook-shaped projections which engage in the positive connection.
- the connection region of one of the functional members may overlap the connection region of the other functional member in the conveying direction so as to establish a secure connection.
- the connecting member may be particularly simple in the form of a recess in one of the functional members and screwed into a recorded in the other functional member threaded bolts have, the bolt expediently rests at least indirectly on a functional member with a arranged on the thread opposite side bolt head.
- the individual functional members of a functional assembly can therefore be initially positioned by the positive engagement in the connecting region and then locked in this position with the connecting member. It has been found that the assembly of the conveying devices can be carried out particularly easily when the bolt axis of the bolt transversely, esp. Vertically, extends to the conveying direction, because this arrangement provides extra space for mounting options, in particular mounting holes, in guide rail assemblies can.
- Such slot-shaped openings extending in the conveying direction of the guide rail arrangement are already required within guide rail arrangements for the functional devices required for transporting the printed products, such as grippers or clamps, which extend from the transport element in a direction extending transversely to the conveying direction and are freely accessible outside the guide rails have to be.
- the first functional member has a coupling region designed for coupling the transport member to a drive device and the second functional element, ie chain link, has a guide device designed to guide the transport member along a guide rail arrangement.
- the second functional element ie chain link
- an improvement in the operational reliability of conveyor chains is achieved because conventional drive devices in the guide device on the conveyor chains attack, such as.
- the guide means of the guide devices are subject by the simultaneous drive function increased wear.
- the conventional drive of transport organs in the region of the guide devices requires engagement of the conveyor in the region of the guide rails or guide rail arrangement and in many cases also the wrapping of a drive element by the transport member.
- the chain drive can be realized completely independent of the guiding function and the conveying function for the printed products.
- a further functional optimization is achieved, which is still supported by the arrangement of the coupling region in the drive channel of the guide arrangement and the arrangement of the guide device in the guide channel.
- the coupling region for the drive device to that for coupling the functional device, if necessary. is arranged on a connecting device, serving bolt head opposite side of the functional assembly, so that at below the transport organ hanging functional devices, such as grippers, slats, etc., the drive means above the transport member can be arranged and with the projecting in this position upwards from the transport member Coupling areas cooperates.
- the coupling region can be realized in a structurally particularly simple manner if it is embodied in a comb-like manner with comb teeth extending transversely, in particular approximately perpendicular, to the conveying direction. In the spaces between these comb teeth, the chain pins of a drive chain can intervene for the purpose of driving the transport member. It is also no wrap of a drive wheel by transport institution required. Rather, the drive of the transport member can also take place along a rectilinear section of the conveyor line. For this purpose, however, it is expedient if the transport member is supported on the side opposite the conveyor on and / or in a guide rail arrangement.
- the guide device of the second functional member expediently at least one, preferably two, three or more with respect to corresponding roller axes rotatably mounted guide rollers, each of which preferably rests against a guide surface of the guide assembly and / or disposed between two guide surfaces of the guide assembly.
- the desired separation of functions between the drive function on the one hand and the guide function on the other hand can be brought about particularly effectively if all the guide rollers are arranged on the side of the coupling section of the coupling device for coupling the drive device, so that outside the guide roller is arranged on the side of the coupling device used for coupling a functional device, such as a gripper Guide rollers can be accessed freely on the docking area.
- the guide rollers can also be arranged along the conveying direction offset from each other on the second functional member, it has proven to be expedient in terms of a compact design of conveying devices when two guide rollers with respect to a common, transverse, esp. Perpendicular to the conveying path or conveying direction extending first roller axis are rotatably mounted, wherein two further guide rollers with respect to a transversely, esp. About perpendicular to the plane formed by the conveying direction and the first roller axis plane common second roller shaft are rotatably mounted.
- the guide rollers can be arranged on the sides of a square, along the side bisecting the roller axes.
- the roller axes are expediently each approximately parallel to two, three or more guide surfaces of the guide arrangement.
- the guide device has at least four guide rollers, wherein two guide rollers are rotatably mounted with respect to a common roller axis and the two Roller axes are arranged perpendicular to each other extending in a plane.
- certain cam guides are pivotable about two transversely, esp. About perpendicular, mutually extending pivot axes against each other.
- the chain links of the joint arrangement can be connected to one another via a ball joint arrangement having a spherical segment and a spherical shell segment.
- the spherical segment and the spherical shell segment are attached to an insertion region of one of the chain links and accommodated together with the insertion region in a receiving region of the other chain link of the joint arrangement.
- the reception area can also be between be used for the rotatable storage of guide rollers used guide pin.
- the ball segment and the spherical shell segment can be penetrated by a receiving region of the other chain link passing through connecting bolts.
- the insertion region of the one chain link of the joint arrangement carrying the ball segment and the ball shell segment is first inserted into the receiving region of the other chain link, and then the connecting bolt is guided through an opening passing through the ball segment, the ball shell segment and the receiving region
- Make connection between the chain links, in which the ball segment with respect to the receiving portion having chain links can be fixed by means of the bolt, while the spherical shell segment can be pivoted together with the insertion of the corresponding chain link to the ball segment, so a pivoting of the insertion region having chain link with respect to allow the receiving area having chain link.
- the ball segment is formed of a metallic material, wherein the spherical shell segment may be formed from a plastic with a low coefficient of friction, such as a polyamide and / or a Teflon-containing plastic, wherein it is expedient in the sense of a particularly simple production, when the insertion region is such a positive and / or material fit with the insertion, that the insertion is rotatably mounted together with the spherical shell segment with respect to the spherical segment.
- the insertion region can be formed, for example, by molding the spherical segment region with a preferably fiber-reinforced plastic.
- the spherical shell segment can be formed by prefabricated partial shells, which are placed around the spherical segment, wherein centering pins and corresponding centering openings can be provided on mutually facing end faces of the partial shells.
- the insertion area can be in the form of a circular disc segment of a circular disc revolving around the pin axis, whereby also the pin axis facing boundary surface of the receiving area can be designed as a circular disk shell segment.
- Insertable conveyor chains can be made particularly simple while avoiding an excessive number of different components and a corresponding storage, if a chain link of the hinge assembly is designed as a first functional member of the functional assembly and / or the other chain link of the joint assembly as a second functional member of the functional arrangement.
- connection of the individual chain links of the joint arrangement can be carried out safely and reliably while avoiding influencing the coupling of the drive device to the transport member in this embodiment, when the insertion region extending transversely to the functional members of the functional assembly interconnecting bolts and preferably approximately along the conveying direction Has approach of the first functional member.
- the circular disk segment-shaped insertion region can be arranged in a plane spanned by the conveying direction and the bolt axis to ensure sufficient rigidity under load by the loads attached thereto and usually below it.
- the receiving area may be penetrated by at least one roller axis, wherein the connecting pin axis extends approximately parallel, preferably approximately colinear, to the second roller axis, while the first roller axis is arranged in the plane of the circular disk segment-shaped insertion region.
- the insertion region is arranged between the guide pins of the second functional element, on which the guide rollers rotatably mounted with respect to the first roller axle and / or the second roller axle are mounted.
- An insertable transport member can be provided by successive hinge assemblies and functional arrangements, if in each case a first functional member between two second functional members arranged and on the one hand hingedly connected to one of the first functional members and the other rigidly connected to the other of the first functional members.
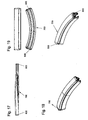
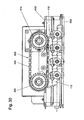
- guide rail assembly 600 includes substantially rectilinear along the conveyor line extending guide rail elements 700 and generally designated 800 connecting elements.
- the straightness shown here is not absolute, nor is it predetermined over the entire conveyor line. It can easily be followed by a straight stretch curvy passages that extend in the plane or in the room. In principle, there may also be twisted conveyor sections.
- the guide rail elements 700 form individual channel sections, which are connected to one another on the opposite end faces of the guide rail elements 700.
- a releasable connection is provided here, which offers the best possible flexibility.
- the guide rail elements 700 each front side connecting elements 800, which are described in more detail in the following figures.
- connecting elements 800th consist of one on the end faces of the guide rail elements 700 facing away from each other flanges, which engage via counter-equal increased and recessed contact surfaces form-fitting manner.
- Such a connecting element is in the Figures 3-5 shown closer.
- the connection between the two flanges is done via a screw, for better understanding is recommended, at the same time the FIGS. 6 and 7 to draw on, from which the opposite form-fitting contact surfaces are particularly well visible.
- Fig. 2 is a longitudinal view of two assembled guide rail elements 700 with the inclusion of the two flanges 910, 920, which are struck each end face. The frictional connection between the two adjacent flanges 910, 920 is then made by a screw 900, which will be discussed in more detail below.
- Fig. 3 shows the connecting element in a three-dimensional view, which is helpful for understanding the structural design. From this figure it can be seen that a projection 930 formed on a contact surface engages in a recess 940 provided on the opposite contact surface of the connected flange.
- the projection 930 has a three-dimensional vertical guide which is widened with a horizontal projecting nose.
- the yoke surface of the flange has two further centering means 931 and 941, which also behave as described above, ie they also exercise a guiding and centering function.
- Both the projection 930, 941 and the recesses 940, 931 have on all sides a tapered contour, whereby the assembly is simplified and at the same time an optimal centering function is achieved.
- the respective connecting element 910 or 920 is connected to the respective guide rail element 700 by screw 950, and this preferably by means of countersunk screws, which do not affect the abutment surface for the axial positioning.
- FIG. 4 shows the front part of the flange 910 according FIG. 3 ,
- the internal passages correspond essentially to the channel-shaped design of each guide rail element (see Fig. 1 and 10 ) over its entire length, ie connecting element 910 and 920 and guide rail element 700 have the same bushings why the following description of the flange can also be transferred to the guide rail element 700.
- the guide arrangement 600 has a guide channel 620 and a drive channel 610.
- the guide channel 620 has on its side facing away from the drive channel 610 a slot-shaped opening 630, through the functional means 350 of the drive chain 10 (see also Fig. 16 ) can be led out of the guide channel 620.
- Fig. 4 are within the flange 910, 920 the guide channel 620 limiting adapter elements 850 releasably inserted. Through these adapter elements 850, a smooth transition between the running surfaces of the flange 910, 920 and the subsequent guide rail elements 700 is ensured. This is accomplished by the fact that tread portions 852 of the adapter elements 850, which are chamfered in opposite directions or tapered in the conveying direction F, reach 850, as can be seen from FIG Fig. 5 evident.
- FIG. 6 and 7 show the structure of the connecting elements 800, which frictionally connect the flanges 910, 920 and the guide rail elements 700 firmly connected to these flanges to a guide rail arrangement 600.
- two 960 screws are used (see Fig. 7 ), which act on both sides of the flanges to be connected in the vertical direction.
- the upper and lower sides of the shaft screw 960 with two Brids 961, 962 in operative connection, wherein the screwing done from above, therefore, the lower Bride 962 a thread for tightening the shaft cover 960 on.
- the two bridges 961, 962 each have a dovetail profile 963, which also detect dovetail portions of the flanges and which act in opposite directions.
- Fig. 8 shows a profile of a guide rail element 700 of an inventive guide rail assembly 600 d.
- the guide rail member 700 defines the guide channel 620 and the drive channel 630.
- the guide channel 620 has a substantially square cross-section, wherein at the corners of the guide channel 620 each two support portions 702 to 709 for tread elements 750 (see FIG. Fig. 15 ) are provided.
- the carrier regions 702 to 709 are designed essentially in the form of T-profiles extending along the conveying path, so that the tread elements 750 of the in Fig. 15 shown type with substantially C-shaped profiles can be releasably pushed onto it.
- a recess 720 extending along the conveying path is provided, into which screw bolts serving for fastening the connecting elements 800 to the guide rail elements 700 are screwed.
- the screw bolts simultaneously stabilize the position of the carrier regions 702 to 709.
- the spatial proximity between the recesses 720 serving to receive the screw bolts and the carrier regions 702 to 709 ensures a particularly precise alignment of the carrier regions 702 to 709 with respect to carrier regions of adjacent connecting elements 800.
- outwardly open channels 740 are arranged. Within these channels can be received externally accessible and extending with its bolt axis in the conveying direction bolts that are used to Attachment of the guide rail elements 700 to each other via the flanges 910, 920. What the fasteners 800 and their attachment is to the description of 6 and 7 directed
- the connecting element according to Fig. 3-7 in conjunction with the guide rail element according to Fig. 8-10 it is merely necessary to ensure that the axial connection between the two is ensured, ie, that the screw connections 950 between the connecting element and the guide rail element are aligned with one another.
- the recesses 720 See Fig. 8
- other possible connections between the two elements come into play, for example, if instead of an axial screw a circumferential anchorage is made, in which case also take into account that the last still the guide rail elements 700 must be connected to each other via the flanges.
- tread elements 750 may be implemented with uniform T-shaped recesses 752 having different wall thicknesses so as to ensure desired guide conditions for the guide rollers of the transport member received in the guide channel 620 FIGS. 14 and 15 is explained.
- the tread segments 852 (See also Fig. 11 ) of the adapter elements 850 are releasably secured to the main body 854 of the adapter elements 850 in order to be able to obtain the desired guidance properties in the area of the adapter elements 850 as well. It can be seen that the tread elements 852 make an acute angle ⁇ (see FIG Fig. 13a ) having in the conveying direction F including treads 853, so as to in Fig. 5 to be able to achieve recognizable opposing chamfering of the running surfaces.
- Fig. 14 shows a sectional view of a conveying device with a received in a rectilinear portion of a guide arrangement according to the invention conveyor member 10 (see also Fig. 16 ), which is the basis here Profile according to a guide rail element Fig. 8-10 equivalent.
- the guide roller 202 of the transport member rests on a tread element 750 pushed onto the carrier region 702 of the guide rail element 700.
- the guide roller 208 of the transport member abuts against a tread element 750 pushed onto the carrier region 704.
- the guide roller 204 rests against a tread element 750 pushed onto the carrier region 708 and the guide roller 206 bears against a tread element 750 pushed onto the carrier region 706.
- the wall thicknesses of the tread elements 750 are selected such that the transport element resting against them with their guide rollers 202 to 208 is guided without play in the guide channel 620 of the guide rail element 700. As a result of the spatial arrangement of the tread elements 750, a friction-friction-free guidance of the transport element in the guide rail element 700 is ensured.
- Fig. 15 shows a sectional view of a conveyor along a plane perpendicular to the conveying direction cutting plane of an arcuate portion of the guide assembly.
- corresponding tread elements 750 are also pushed onto the carrier regions 703, 705, 707 and 709.
- the wall thicknesses of the tread elements 750 are selected in the arcuate regions so that the guide rollers 202, 204, 206 and 208 are received between the carrier regions 702 and 703 or 704 and 705 or 708 and 709 or 706 and 707 with slight play.
- FIGS. 14 and 15 For a better understanding of the guide arrangement and its operation nor a transport organ is shown in three-dimensional representation.
- This transport member which will be described in more detail below, forms an advantageous embodiment.
- an application of the guide arrangement described here with the transport element shown here offers great advantages.
- a coupling of the two is therefore not an indispensable requirement.
- gripper-like functional devices 350 can be fastened to the functional members of the conveying members belonging to the conveying member 10 via connecting devices 310 and pass through the recess 630 in the conveying channel.
- the illustrated guide rail assembly 600 in addition to the illustrated application can also fulfill other functions.
- substantially flat metal sheets are provided on the underside of the chain link 200 (see FIG Fig. 24, 25 ) can be arranged.
- the guide pin 216 (see FIG Fig. 24, 25 ) are suitable.
- These sheets can also be designed so that they are flexible and material behave like a lamellar.
- the application of this product-compliant transport surface can be achieved by pivoting the entire guide rail assembly 600 through 180 ° so that the chain drive (See Fig. 30 , Pos.
- the guide rail elements can be designed to be twisted with respect to a torsion axis running parallel to the conveying direction, wherein connecting elements 800 can be arranged on both end faces of the guide rail elements 700.
- the guide rail elements 700 may be circular arc-shaped in a vertical arc axis, with those provided by the functional device 350 (See FIG Fig. 16 ) 630 (See Fig. 8 ) may face the bow axis.
- This transport member is particularly well suited to be used in conjunction with the guide member described above.
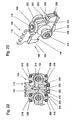
- the transport members shown in various figures comprises functional members in the form of first chain links 100 and second chain links 200.
- Each of the first chain links 100 has a comb-shaped coupling region 110 for coupling the transport member to a drive chain 530 (cf. Fig. 30 ) on.
- each of the second chain links 200 has a total of four guide rollers 202, 204, 206, 208, wherein the guide rollers 206 and 208 are rotatably mounted with respect to a first common roller axis and the guide rollers 202, 204 are rotatably mounted with respect to a second common roller axis.
- the first and second roller axes are perpendicular to each other and arranged in a plane.
- Each of the first links 100 is disposed between two second links 200.
- each of the first chain links 100 is connected rigidly with one of the second chain links 200 on the one hand to form a functional arrangement and on the other hand with the other of the second chain links 200 to form a joint arrangement.
- a screw bolt 300 is inserted, which passes through a bore in a connecting region 250 of the second chain link 200 and is screwed into a connecting region 150 of the first chain link 100.
- a blind hole 152 is formed in the first link 100, in which a threaded insert 310 is inserted, which is penetrated by the bolt 300.
- the blind hole 152 is according to Fig.
- the bolt head 302 lies on the side of the second chain link 200 facing away from the coupling region 110 with the interposition of a connecting device 310 on.
- the connecting device 310 serves for the coupling of functional devices, such as gripper or staple elements, or lamellae to the transport member.
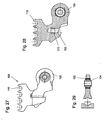
- the connecting portion 250 of the first chain link 100 has a projection 256 and a groove-shaped recess 252, into which a bulge 254 of the projection 256 protrudes, while the connecting portion 150 of the first chain link 100 complementary thereto with an engaging into the channel-shaped recess 252 Projection 152 and a projection 256 receiving indentation 156 is executed, wherein the projection 152 also has a recess 254 receiving indentation, so that by nesting the connecting portion 150 of the first chain link 100 in the connecting portion 250 of the second chain link 200 is a positive connection between the first chain link 100 and the second chain link 200, the bolts passing through the projection 256 and inserted into the blind hole 152 formed between the recess 156 and the coupling region 110 of the first chain link 100 (see FIG Fig. 22 ) can be locked.
- the projection 256 also has a nose-like engagement region 258, which
- the coupling region 110 is comb-like with comb teeth extending transversely to the conveying direction and approximately parallel to the axis of the bolt 300, a space is formed between the comb teeth into which the chain pins of the drive chain 530 (see FIG Fig. 30 ) intervene.
- the guide rollers 202, 204, 206, 208 are rotatably mounted on guide pins 212, 214, 216, 218, so that between the guide pins 212, 214, 216, 218 still space for producing a hinged connection between the first chain links 100 and second chain links 200 to Available.
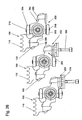
- the joint arrangement produced by the articulated connection between the first chain links 100 and the second chain links 200 will be described with reference to FIGS Fig. 14-17 explained.
- the first chain link 100 has an insertion region 120 that extends transversely to the pin axis in the conveying direction and that engages in a receiving region 220 formed between the guide pins 212, 214, 216, 218 of the first chain link 100 is included.
- the insertion region 120 is embodied in the manner of a circular disc segment, while the receiving region 220 is designed in the form of a circular disc segment, so that a guide for pivotal movement of the first chain link 100 relative to the second chain link 200 about a pivot axis formed by the second roller axis is formed by the boundary surfaces of the insertion region 120 and the receiving region 220 is.
- the articulated connection between the first chain link 100 and the second chain link 200 has a ball segment 124 received in the insertion region 120, a spherical shell segment-shaped sliding element 122 made of a plastic material having a low coefficient of sliding friction being arranged between the ball segment 124 and the outer region of the insertion region 120. Ball segment 124 and spherical shell segment 122 pass through the insertion region 120.
- the insertion region 120 accommodating the spherical segment 124 is rotatably mounted on the spherical segment 124 via the spherical shell segment 122 so that the first chain link 100 engages with the insertion region 120 after insertion of the insertion region 120 into the receiving region 220
- Axis of the connecting bolt 126 and a perpendicular thereto and parallel to the bolt 130 extending axis 128 is pivotally mounted, wherein the pivoting movement with respect to the pivot axis 128 is determined by the width of the receiving portion 220 in the direction determined by the axis of the bolt 126 direction. If necessary, this width can be increased.
- Fig. 26 shows a mounted conveying member, which consists of a number of transport organs, each consisting of a first and a second chain link, this figure is explained in more detail below.
- the first chain link 100 is shown in detail.
- the insertion region 120 of the first chain link 100 is according to FIGS. 28 and 29 by partially sheathing the ball segment 124 with a low-friction plastic material to form a spherical shell segment 122, whereby the ball segment 124 thus formed can be overmolded with a plastic, in particular a fiber-reinforced plastic, to form the insertion region 120.
- the spherical shell segment 122 is formed in one piece, may also be two or more parts.
- the connecting region 150 and the coupling region 110 can be formed at the same time, wherein also it is thought to insert the threaded insert 310 in the blind hole 152 during the injection process.
- Fig. 26 can conveyors resp. Transport organs are mounted by first joint assemblies of first chain links 100 and second chain links 200 pre-assembled, then put together in the connecting portions 150 and 250 and then locked by means of the screw 300.
- conveyor chains 500 can be conveyed along a conveying path formed by a guide rail arrangement 600, wherein the conveying member is accommodated within the guide rail 600 and guided by means of the guide rollers 202, 204, 206, 208 on corresponding running surfaces of the guide rail 600.
- the coupling regions 110 are accommodated in a drive space 610 of the guide rails 600 and mesh in drive sections of the guide rail arrangement 600 a drive chain 530 of a drive device 500, which rotates two chain wheels 510 and 520.
- For coupling the drive device 530 only a recess in a boundary surface of the drive space 610 has to be produced, through which the drive chain 530 can reach the region of the coupling regions 110.
- the invention is not limited to the embodiment explained with reference to the drawing. Rather, od also differently configured guide rail arrangements with three or less guide rollers, guide pins. Like. Intended. Furthermore, the coupling regions of the transport organs can be configured differently. Also, the gimbal connection of individual links to the formation of joint arrangements is intended.
- the sequentially arranged functional units then have means or connecting elements for a detachable, or due to adhesion-related releasable, and / or a non-detachable connection.
- the functional units can be connected to each other differently at least to form a transport member. In most cases, one will opt for a detachable connection, such as a screw connection. However, it is also possible to provide a frictional merger, which then behaves as a releasable connection when needed.
- the individual conveyor units can be firmly connected to each other by a non-detachable connection, for example via a welded connection.
- a non-detachable connection for example via a welded connection.
- installed additional units between the individual functional units and / or chain links resp. may be arranged, which fulfill a certain functionality. This functionality is broad: it can for example improve the operation of the functional units, or it can be provided aggregates, which are related to the transport of the printed products or the conveyed goods.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Framework For Endless Conveyors (AREA)
- Chain Conveyers (AREA)
- Feeding Of Articles By Means Other Than Belts Or Rollers (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH01781/09A CH702278A1 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2009-11-18 | Führungsanordnung mit einem Transportorgan. |
| PCT/CH2010/000281 WO2011060560A2 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2010-11-09 | Führungsanordnung mit einem transportorgan |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2501632A2 EP2501632A2 (de) | 2012-09-26 |
| EP2501632B1 true EP2501632B1 (de) | 2014-07-16 |
Family
ID=42062064
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10779451.3A Active EP2501632B1 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2010-11-09 | Führungsanordnung mit einem transportorgan |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8627943B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2501632B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5937010B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102596764B (ja) |
| CH (1) | CH702278A1 (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2516868T3 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011060560A2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102012103130B4 (de) * | 2012-04-12 | 2016-07-07 | Ws Beteiligungs Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Tragen und zum Befördern von Waren, ein Trägerelement dafür sowie Fördersystem mit einer Mehrzahl solcher Vorrichtungen |
| BR102014011463A2 (pt) * | 2013-05-31 | 2015-01-06 | Mueller Martini Holding Ag | Conjunto transportador para emprego de um órgão transportador |
| CN103818681A (zh) * | 2013-09-04 | 2014-05-28 | 江南嘉捷电梯股份有限公司 | 组合式滚轮导轨和包括它的输送系统 |
| EP3163725A1 (de) * | 2015-11-02 | 2017-05-03 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Maschineneinheit, teilstück und zwischenelement sowie verfahren zum verbinden und/oder lösen einer anschlussleitung |
| CH711921A1 (de) * | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-30 | Ferag Ag | Laufrollengeführtes Förderorgan und Förderanlage mit derartigen Förderorganen. |
| IT201800004175A1 (it) * | 2018-04-03 | 2019-10-03 | Guida di ritorno per la guida del ramo di ritorno di una catena di un trasportatore a catena, in particolare guida di ritorno curva. | |
| JP6853221B2 (ja) * | 2018-07-23 | 2021-03-31 | 株式会社オーイズミ | チェーンコンベア装置 |
| USD975954S1 (en) * | 2019-12-02 | 2023-01-17 | Daifuku Co., Ltd. | Rail for conveyor machine |
| JP7221321B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-09 | 2023-02-13 | 株式会社オーイズミ | チェーンコンベア装置 |
| CN113734701B (zh) * | 2021-09-23 | 2022-10-04 | 江苏泗阳协力轻工机械有限公司 | 一种输送设备 |
| DE102022103810A1 (de) | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-17 | Dematic Gmbh | Profilverbinder für Hängeförderanlage |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2201400A1 (de) * | 1972-01-13 | 1973-07-26 | Halbach & Braun | Foerderrinne fuer insbes. kettenkratzfoerderer |
| DE2347459A1 (de) * | 1973-09-20 | 1975-04-10 | Michel Baud | Haenge-foerdervorrichtung |
| JPS572389Y2 (ja) * | 1977-02-28 | 1982-01-14 | ||
| JPS6077011A (ja) * | 1983-09-30 | 1985-05-01 | Trinity Ind Corp | 搬送装置 |
| RU2027648C1 (ru) * | 1988-10-20 | 1995-01-27 | Радуцкий Григорий Аврамович | Пространственный конвейер |
| DE59206908D1 (de) * | 1991-11-06 | 1996-09-19 | Ferag Ag | Kettentrieb |
| US5400717A (en) * | 1993-09-17 | 1995-03-28 | Hoehn; Robert A. | Modular conveyor track connection |
| US5598784A (en) * | 1994-11-22 | 1997-02-04 | Jervis B. Webb Company | Extruded aluminum conveyor with track offset |
| DE19758468A1 (de) * | 1997-05-02 | 1998-11-12 | Koenig & Bauer Albert Ag | Längenvariables Führungsschienenstück |
| US5960938A (en) * | 1997-06-19 | 1999-10-05 | Tekno, Inc. | Conveyor for cantilevered loads |
| DE29722233U1 (de) * | 1997-12-17 | 1998-02-12 | PEP Fördertechnik GmbH, 33609 Bielefeld | Kreisförderer |
| RU2213687C2 (ru) | 1997-12-23 | 2003-10-10 | Фераг Аг | Транспортная система |
| CA2310405C (en) | 1997-12-23 | 2007-10-30 | Ferag Ag | Conveying apparatus and corresponding transporting means |
| ES2189270T3 (es) | 1997-12-23 | 2003-07-01 | Ferag Ag | Transportador para ser guiado por carriles y carril de guidado para conducir el transportador. |
| RU2200694C2 (ru) | 1997-12-23 | 2003-03-20 | Фераг Аг | Конвейерное устройство |
| US6269944B1 (en) * | 1999-01-29 | 2001-08-07 | Gorbel, Inc. | Channeled beam extruded of aluminum alloy for crane or conveyor |
| EP1029815B1 (de) | 1999-02-16 | 2004-04-07 | Ferag AG | Kraftübertragungs- oder Transportvorrichtung |
| FI106113B (fi) * | 1999-02-22 | 2000-11-30 | Kci Kone Cranes Int Oy | Profiilikiskoliitos |
| JP3498179B2 (ja) * | 2000-04-13 | 2004-02-16 | 山久チヱイン株式会社 | 搬送コンベヤに於けるフレーム材及びこのフレーム材を利用した走行フレーム装置 |
| EP1557387B1 (de) * | 2004-01-21 | 2007-07-11 | Müller Martini Holding AG | Transportorgan mit einer Gliederkette und Klammern |
| DE202008007100U1 (de) * | 2008-05-27 | 2009-10-08 | Psb Intralogistics Gmbh | Hängeförderanlage |
-
2009
- 2009-11-18 CH CH01781/09A patent/CH702278A1/de not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2010
- 2010-11-09 EP EP10779451.3A patent/EP2501632B1/de active Active
- 2010-11-09 WO PCT/CH2010/000281 patent/WO2011060560A2/de active Application Filing
- 2010-11-09 JP JP2012539155A patent/JP5937010B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-11-09 ES ES10779451.3T patent/ES2516868T3/es active Active
- 2010-11-09 CN CN201080052329.2A patent/CN102596764B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2012
- 2012-05-16 US US13/473,055 patent/US8627943B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20130001051A1 (en) | 2013-01-03 |
| EP2501632A2 (de) | 2012-09-26 |
| CH702278A1 (de) | 2011-05-31 |
| CN102596764B (zh) | 2017-02-15 |
| ES2516868T3 (es) | 2014-10-31 |
| US8627943B2 (en) | 2014-01-14 |
| WO2011060560A2 (de) | 2011-05-26 |
| WO2011060560A3 (de) | 2011-07-14 |
| JP2013511449A (ja) | 2013-04-04 |
| JP5937010B2 (ja) | 2016-06-22 |
| CN102596764A (zh) | 2012-07-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2501632B1 (de) | Führungsanordnung mit einem transportorgan | |
| EP2218661B1 (de) | Sortierförderer | |
| DE10321736B3 (de) | Baukastensystem für einen Förderer zum Längs-oder Querfördern von Stückgutträgern | |
| DE69109836T2 (de) | Modulartiger Förderer. | |
| EP2163495B1 (de) | Rollenförderer mit Antriebswellenbaugruppe | |
| EP0752968B1 (de) | Hängeförderanlage | |
| EP2368817B1 (de) | Führungsanordnung | |
| EP2325113B1 (de) | Transportorgan zum Fördern von Druckprodukten | |
| EP1935782A1 (de) | Befestigungsschiene zur Befestigung von Ladeeinrichtungen auf dem Ladedeck eines Flugzeugs | |
| EP0607957B1 (de) | Bausatz zur Standardisierung und Bildung eines Baukastensystems für Kettenförderer, Kettenstauförderer und/oder Zahnriemenförderer | |
| EP2876062B1 (de) | Fördereinrichtung für den Einsatz eines Transportorgans | |
| EP1925499A2 (de) | Zustiegs- und/oder Zufahrtshilfe für Fahrzeuge mit Personenbeförderung | |
| EP2314529B1 (de) | Transporteinheit mit Stauröllchenketten | |
| DE3302266C2 (de) | Weiche für eine Einschienenhängebahn | |
| DE7320344U (de) | Transportkette fur Holzbearbeitungs maschinen | |
| EP3763639B1 (de) | Transportsystem sowie behandlungsmaschine mit einem solchen transportsystem | |
| DE69204775T2 (de) | Förderrinne mit mit Zapfen versehenem Boden. | |
| DE102013107866B4 (de) | Gabellaschenkette | |
| EP2163497B1 (de) | Rollenförderer | |
| EP1249406A1 (de) | Umlenkvorrichtung für ein Fördermittel | |
| DE102006053913A1 (de) | Fördereinrichtung für Lastträger | |
| EP0367755B1 (de) | Mitnehmeranordnung | |
| CH701855A1 (de) | Fördereinrichtung mit über Flansche miteinander verbundenen Führungskanalabschnitten. | |
| EP3721100B1 (de) | Verbindungsanordnung | |
| EP0327652A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Förderrollenbahn mit Tragprofilen sowie eine Förderollenbahn hierzu |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20120416 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20130318 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20140129 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20140424 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 677473 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20140815 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010007473 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20140828 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2516868 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20141031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141017 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141016 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141117 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141016 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141116 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010007473 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20150417 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141130 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141109 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141109 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20101109 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 677473 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20151109 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20161127 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151109 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20161130 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20180731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171130 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171109 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140716 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20181025 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: EUG |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191110 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20210528 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191110 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20221124 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231121 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20231201 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20231109 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20231109 |