EP1069275A2 - Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung - Google Patents
Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1069275A2 EP1069275A2 EP00114880A EP00114880A EP1069275A2 EP 1069275 A2 EP1069275 A2 EP 1069275A2 EP 00114880 A EP00114880 A EP 00114880A EP 00114880 A EP00114880 A EP 00114880A EP 1069275 A2 EP1069275 A2 EP 1069275A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- sun protection
- protection system
- sun
- input variables
- sensor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 230000037072 sun protection Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 84
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001932 seasonal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 206010054197 Gait deviation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009429 electrical wiring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005294 ferromagnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011835 investigation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N mercury Chemical compound [Hg] QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052753 mercury Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000037230 mobility Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009993 protective function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009420 retrofitting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B9/00—Screening or protective devices for wall or similar openings, with or without operating or securing mechanisms; Closures of similar construction
- E06B9/56—Operating, guiding or securing devices or arrangements for roll-type closures; Spring drums; Tape drums; Counterweighting arrangements therefor
- E06B9/68—Operating devices or mechanisms, e.g. with electric drive
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04F—FINISHING WORK ON BUILDINGS, e.g. STAIRS, FLOORS
- E04F10/00—Sunshades, e.g. Florentine blinds or jalousies; Outside screens; Awnings or baldachins
- E04F10/02—Sunshades, e.g. Florentine blinds or jalousies; Outside screens; Awnings or baldachins of flexible canopy materials, e.g. canvas ; Baldachins
- E04F10/06—Sunshades, e.g. Florentine blinds or jalousies; Outside screens; Awnings or baldachins of flexible canopy materials, e.g. canvas ; Baldachins comprising a roller-blind with means for holding the end away from a building
- E04F10/0644—Sunshades, e.g. Florentine blinds or jalousies; Outside screens; Awnings or baldachins of flexible canopy materials, e.g. canvas ; Baldachins comprising a roller-blind with means for holding the end away from a building with mechanisms for unrolling or balancing the blind
- E04F10/0659—Control systems therefor
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B9/00—Screening or protective devices for wall or similar openings, with or without operating or securing mechanisms; Closures of similar construction
- E06B9/24—Screens or other constructions affording protection against light, especially against sunshine; Similar screens for privacy or appearance; Slat blinds
- E06B9/26—Lamellar or like blinds, e.g. venetian blinds
- E06B9/28—Lamellar or like blinds, e.g. venetian blinds with horizontal lamellae, e.g. non-liftable
- E06B9/30—Lamellar or like blinds, e.g. venetian blinds with horizontal lamellae, e.g. non-liftable liftable
- E06B9/32—Operating, guiding, or securing devices therefor
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B9/00—Screening or protective devices for wall or similar openings, with or without operating or securing mechanisms; Closures of similar construction
- E06B9/56—Operating, guiding or securing devices or arrangements for roll-type closures; Spring drums; Tape drums; Counterweighting arrangements therefor
- E06B9/68—Operating devices or mechanisms, e.g. with electric drive
- E06B2009/6809—Control
- E06B2009/6818—Control using sensors
Definitions
- the invention relates to a sun protection system a sun protection curtain and at least one drive that the setting of the sun protection curtain via a control depending on several input variables adapts the environmental conditions.
- the object of the present invention is a To create a sun protection system that is dependent on the position of the sun Tracking enabled and more reliable than before known systems works.
- a sun protection system of the type described above Control the setting of the curtain using one in one Memory stored basic programming as a function at least of the input variables time, sun intensity and direction undertakes, the input variables, sun intensity and cardinal direction and, if necessary, others input variables relating to the environmental properties for the installation position of the sun protection system can be determined individually are.
- the sun protection system according to the invention offers the advantage that the sun-dependent tracking of the setting no longer determined by a control circuit prone to failure but as a function of the input variables time and direction is determined so that disturbances can hardly be expected are.
- The is used for tracking the system depending on the position of the sun Input variable time, for example by a clock or a radio clock is determined.
- a radio clock is preferable because it has less gait deviations and the attitude performs independently on summer and winter time.
- the Correction of summer and winter time is in the control made by programming the changeover days to the Adjust sun position correction to the changed time.
- the month and day are also preferred recorded as an input variable for the seasonal changes the solar path.
- the input variable direction i.e. Alignment of the Sun protection system
- the setting of the sun protection system can be optimized using this input variable be because at any time in connection with the input variable the side angle of incidence of the sun on the system is known.
- the input of the sky direction input variable can either done with the help of an electronic compass or the geographic orientation data can be obtained from Assembly for the sun protection system individually in one Memory can be stored.
- the concept according to the invention is suitable for all types of sun protection systems to ensure optimal at all times Heat protection and hiding direct sunlight to enable, but also for one to ensure the best possible light in the interior of the room.
- the sun protection system as an awning carried out depends on the input variables an adjustment of the extension length and / or the inclination of the Blind, while next to an apprenticeship as venetian blind the control of the extension length, especially the adjustment the slat inclination especially with regard to the tracking depending on the position of the sun.
- the sun protection systems can be designed as indoor or outdoor systems.
- the geographic data can be used when installing the sun protection system can be entered and saved, whereby a particularly precise determination of the location with the help a so-called GPS receiver is possible. It is also conceivable to integrate such a GPS receiver into the system, however, since the determination of the geographical location The transmission of data is only to be carried out once from a mobile GPS receiver or a factory Prefer preference for cost reasons.
- input variables can have protective functions for example the system when the wind is too strong, when it rains or being able to drive in, or they can be targeted used to vary the curtain setting be, for example, at low temperatures Increase direct sunlight into the room, to save heating costs.
- the sun protection system is ready for operation pre-assembled with all sensors and the pre-programmed Control is provided and a supply connection to a common household electricity network.
- the Supply connection can in addition to the power supply Connection lines to the hand switches must be assigned.
- the sensors for detecting the environmental properties reproducing input variables are preferably located within of a housing and are via suitable channels or conductors connected to the environment. Through this measure, the Largely sensors against dirt or damage protected and the effort for electrical wiring, otherwise when assembling the sun protection system must be made decreases.
- the automatic Setting is overriding. Because the basic programming always only for a certain application can be optimized, for example for jobs in close to window surfaces, and also the feeling of Users can be very different, should be manual on this Adjustability cannot be waived. Also for complete darkening of the room, for example for picture presentations, manual intervention is essential. However, it is also conceivable to differentiate certain Optimized basic programming in the uses Save the control so that a preset can already be set Adaptation of the sun protection system to the actual use of the room to be shadowed.
- the basic programming through manual intervention changeable with the help of an adaptively learnable control is.
- the adaptively learnable control extends the adaptation in Automatic operation to meet user requirements.
- the adaptively learnable The control does not detect a manual intervention only the desired setting but also the input variables, that existed at the time of the manual intervention to have. Takes place with essentially the same input variables repeated manual intervention, the control can when these input variables are recognized in the future the repeated manual setting automatically drive off. Also a gradual convergence of the Basic programming to the different manual setting with increasing number of repetitions of the manual Readjustment is conceivable.
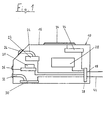
- FIG. 1 shows a sensor system 10 for determining active input variables for controlling a sun protection system 12 (see 2), which is connected to a controller 14 (see FIG. 2 and 3) are transmitted, which are defined when reached Switching values travel commands to the drives 17 (see FIG. 3) transmitted to the sun protection system 12 and thus an automatic Setting the sun protection system 12 allows.
- the sensor system 10 shown in FIG. 1 is in a separate one Housing 16 housed that with the help of connecting lines 18 is coupled to the controller 14.
- the sensors 10 at least the input variables time / date, Sun intensity and cardinal direction of the sun protection system determine an automatic control of the sun protection system 12 depending on the position of the sun can.
- the Radio receiver 20 is of course with a suitable one Antenna (not shown) designed to be safe Data reception regardless of location within the transmission range ensures. Determining the day of the week and the summer time correction can be programmed in the Control 14 can be realized.
- the sensor system 10 can also have a clock that has the required input variables provides.
- a clock that has the required input variables provides.
- gear deviations occur over the years or even one due to power outages complete adjustment comes that manual again Intervention in places of the time is necessary.
- the input variable sun intensity is determined with the help of a sun sensor 22, which acts as a photo resistor, Photodiode or solar cell is formed.
- the sun sensor 22 is immediate in the illustrated embodiment on the circuit board of the evaluation system inside the sensor housing 16 arranged and with a light guide 24 connected to a lens 26 seated on the outer wall of the housing.
- the photosensitive element it is also conceivable for the photosensitive element to assemble itself on the outside of the housing and the Connection to the board using electrical cables to manufacture.
- the sun sensor supplies the controller 14 with a Information about whether the sun protection system 14 or the window surface to be shaded by her at all Is exposed to sunlight or whether for example extension of the sun protection system due to cloudiness is necessary at all.
- the sun sensor 22 also from an opposite facade, for example Capture reflected sunlight and extend the Effect sun protection system at a time of the day the control actually assumes that the affected Facade is in shadow.
- a direction sensor 28 is provided which automatically after assembly recognizes the orientation of the sun protection system 12, what with the separately executed in Fig. 1 housing 16 of the sensors 10 of course presupposes that this is located in a precisely defined position to the sun protection system.
- the direction sensor 28 can in its execution as an electronic compass two or three axes of the final magnetic field measure and from the individual components of the magnetic field calculate the absolute direction. For the most For applications, the measurement of the two horizontal components is sufficient because the sun protection system and thus the Direction sensor 28 during assembly using a spirit level be aligned exactly. It is important to ensure, that ferromagnetic components of the sun protection system, such as e.g.
- the drive motors 17 the earth's magnetic field to be measured do not bother. During faults within the sensor system 10 The drive motors should be able to be compensated computationally 17 remain switched off during measurements, so as not to falsify the measurement result.
- the electronic Compass 28 can be used, for example, as a flux gate sensor or be designed as a magnetoresistive sensor.
- the sensor system 10 offers the possibility of using of a wind sensor 30 the input variable wind speed to detect and thus a hazard to the strong wind System caused by mechanical overload caused by starting to avoid retracting the system.
- cup cross anemometer is used as a wind sensor usable, but only the horizontal components of the wind up to a deviation of about 15 ° from the horizontal. At the wind speed becomes the input variable specified too low, with pure opening or Falling cups of this kind cannot be used at all Record wind movement.
- cup cross animometers are required relatively much space.
- Wind sensor 30 used a pressure sensor inside of the housing 16 is arranged and via a hose connection 32 communicates with the environment. Further Sensors with the aid of which an air flow can be detected thermal probes can be used as a measure of wind speed, where the airflow is electrically heated Sensor cools down so that with constant heating power the temperature or at constant temperature the Heating power is a measure of the flow velocity, or a strain gauge circuit that bends the airflow exposed certain body as a measure of the flow velocity recorded with the help of two strain gauge elements and evaluates with a bridge circuit.
- the wind sensor 30 instead of the hose connection 32, the wind sensor 30 again be mounted on the surface of the housing 16.
- the wind sensor 22 has all wind directions via a sensor head (not shown), which is either a has a large detection area or self-aligning is trained. Depending on the geometry of the sensor head different coverage areas can be covered where the deviations from measured to actual wind speed e.g. less than 5%. This may be related to known investigations with total pressure probes, especially shielded probe heads, e.g. Kiel probes as Geometry template come into question.
- the sensor head can be attached to a movable wing be attached, modeled on a simple Prandtl tube can be.
- the wing must be freely rotatable ensure according to the attacking wind and the Connection from the receiving tube to the sensor must be flexible, so as not to restrict the mobility of the wing.
- a completely different principle for determining the input variable Wind speed can be immediate deformation, Vibrations or accelerations on parts of the Determine the sun protection system as a measure of the wind speed can apply.
- deformations caused by wind can be determined with the help of strain gauge circuits. These will preferably on a heavily loaded component of the sun protection system attached, for example to awnings an awning support tube in the area of the arm holder or on the arm profiles.
- the strain gauge circuit is according to the determining deformation as a quarter, half or full bridge formed, the changes in resistance occurring in the measuring strips a measure of the deformation and thus for the attacking wind load.
- the sensor system 10 shown in FIG. 1 also has via a rain sensor 34, the precipitation or moisture can record and especially for those sensitive to moisture Sun protection systems, e.g. Awnings, retracting the Plant can initiate.
- Sun protection systems e.g. Awnings
- the sensor system 10 also has a temperature sensor 36, whose signal as a further input variable for the control 14 can be used.
- the microcontroller 38 is on a two-wire or three-wire bus line 44 connected to the controller 14.
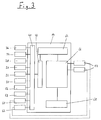
- Fig. 2 shows a schematic cross section of a Venetian blind Venetian blind 12, in the upper rail 46 a sensor system 10 corresponding to the sensor system shown in Fig. 1 without housing and a controller 14 are integrated.
- the lens 26, the temperature sensor 36 and the opening of the with the Wind sensor 30 connected hose line 32 are on the Outside of an aperture 48 provided the upper part covers a shaft 50 in which the external blind 12 is mounted.
- the venetian blind 12 has a slatted curtain 52, the individual lamellae 54 in Fig. 2 in the retracted Position as a package are shown gathered.
- the Venetian blind 12 has two motors 17 (see FIG.
- the functional diagram shown in Fig. 3 shows the Controller 14 for the motors 17 of the venetian blind 12 in FIG. 2 with the intended for determining relevant input variables Sensors.
- Sensors In addition to the temperature sensor already described 36, rain sensor 34, direction sensor 28, radio receiver 20, sun sensor 22 and wind sensor 30 are to be determined other input variables the already mentioned manual Hand switches 56, 58 for the extension length and the Angle adjustment of the curtain 52 shown.
- the hand switches can also run in the form of a remote control his.
- Further input variables represent the with the help of a Encoder 60 detected actual extension length and that with the help of a Another encoder 62 detected the actual angular position of the curtain 52.
- the two sensors 60, 62 can for example provided in the form of rotary angle sensors on the motors 17 his.
- the mentioned measured or set input variables are connected to the multiplexer 40 and this one Analog / digital converter 42 passed on to the incoming Converts sensor signals serially.
- To converter 42 is followed by a sensor signal adaptation 64, for example Characteristic curves linearized or signal impulses in converts a continuous size.
- a sensor signal adaptation 64 for example Characteristic curves linearized or signal impulses in converts a continuous size.
- sequence programs are stored, which in Dependence on the output signal of the sensor signal adaptation 64 generate the output variables for controlling the motors 17.
- the control programs are still from the content of a Memory 68 affects in which information about the longitude and latitude of the location of the exhibition Sun protection system 12 are stored, because only the exact geographical indication an exact determination of the position of the sun relative to the sun protection system 12 is possible. However, even without this information, using a Preset a good approximation for many locations possible.
- the controller 14 is constructed so that the with the hand switches 56, 58 manually entered values for the extension length or the angle setting with priority over the according to the measured input variables based on the Basic programming determined setting are treated. Will be a manual setting for a certain time not corrected, the controller 14 resembles a predefined one Period of several hours the setting independently again on the theoretical ideal course.
- the transitions are sigmoid in order to be as inconspicuous as possible To enable resetting.
- the sigmoid-shaped Transitions are realized via Bézier curves, which guarantee that the feedback curve is always only a turning point owns.
- the time of day input variables determined by the radio clock 20 and date are used to track the setting angle of the slats 54 to the height of the sun, the date information Compensate for seasonal changes in the solar path can.
- Special calculation formulas are used for tracking stored in the control 14, the azimuth and elevation angles the solar radiation.
- In connection with the input variable sky direction determined by the compass 28 can be calculated whether the sun at all can shine directly on the system and what relative position takes them to the facility.
- These calculations can be by the information stored in the memory 68 about the geographical location of the system 12 further specify, the data also from one to the System integrated GPS receiver can be provided can.
- the geographic data at Assembly of the system stored in the memory 68 for example by transmission from a mobile GPS receiver, immediate entry of the geographic data or the alternatively, entering the geographic location approximately characteristic information, e.g. Postcodes or license plate.
- the other input variables sun intensity, wind speed, Rain and temperature are treated so that at Exceeding or falling below certain threshold values
- the system 14 is brought in by the controller 14. If necessary, these threshold values can be dependent from the actual extension state determined by the sensors 60, 62 the system 12 can be varied.
- control 4 is a modified embodiment of the control 14, which enables an adaptive learning ability.
- a further memory module 70 is provided for this purpose, in which manual interventions are carried out together with the Input variables available at the time of the intervention can be saved.
- the adaptive Learning ability allows individual adaptation of the Control 14 to the user habits so that this after a short time no longer manually in the automatic Sequence of control 14 must intervene.
- a reset of the controller 14 to the original state is by entering a special switching signal via the Manual switch possible, whereby the learned data is deleted and the controller then at least again initially works according to the basic programming.
- the sensors 10, control 14 and motors 17 of the sun protection system 12 only need a conventional supply Household electricity network without additional components or even control lines, as they have been implemented in the past Systems can be found. With the connection to the power grid the system is ready for operation only the data for the geographical location and / or the alignment of the system can be stored have to.
- a controller 14 also for automatic control of others Sun protection systems, e.g. from awnings.
- the controller can select the type of sun protection system to be controlled 14 output signals for only one motor, for two motors (see embodiment) or generate more motors.
- the basic programming of the sun protection system be adapted, with adapted programming the use of one and the same unit from sensors 10 and Control 14 for different types of sun protection systems can be used.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Blinds (AREA)
- Building Awnings And Sunshades (AREA)
- Transmission And Conversion Of Sensor Element Output (AREA)
- Train Traffic Observation, Control, And Security (AREA)
- Operating, Guiding And Securing Of Roll- Type Closing Members (AREA)
- Power-Operated Mechanisms For Wings (AREA)
- Wind Motors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Fig. 1
- ein schematisches Schaubild einer Sensorik zur Ermittlung relevanter Eingangsgrößen für die Steuerung von Sonnenschutzanlagen;
- Fig. 2
- einen Schnitt einer Sonnenschutzanlage mit integrierter Sensorik;
- Fig. 3
- ein Funktionsschaubild einer mit der Sensorik gemäß Fig. 1 oder 2 verknüpften Steuerung;
- Fig. 4
- ein Funktionsschaubild einer mit der Sensorik gemäß Fig. 1 oder Fig. 2 verknüpften adaptiv lernfähigen Steuerung.
Claims (11)
- Sonnenschutzanlage mit einem Sonnenschutzbehang (52) und wenigstens einem Antrieb (17), der über eine Steuerung (14) die Einstellung des Sonnenschutzbehangs (52) in Abhängigkeit von mehreren Eingangsgrößen selbständig an den Lichteinfall anpaßt, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Steuerung (14) die Einstellung des Behangs (52) anhand wenigstens einer in einem Speicher (66) hinterlegten Grundprogrammierung als Funktion wenigstens der Eingangsgrößen Zeit, Sonnenintensität und Himmelsrichtung vornimmt, wobei die Eingangsgrößen Zeit, Sonnenintensität und Himmelsrichtung für die Einbaulage der Sonnenschutzanlage individuell erfaßbar sind.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß eine Uhr oder eine Funkuhr (20) mit Antenne zur Erfassung der Eingangsgröße Zeit mit der Steuerung (14) gekoppelt ist, wobei die Eingangsgröße Zeit vorzugsweise die Eingangsgrößen Tageszeit und Datum umfaßt.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß ein Fotoelement, eine Solarzelle oder sonstiges lichtempfindliches Element als Sensor (22) zur Erfassung der Eingangsgröße Sonnenintensität mit der Steuerung (14) gekoppelt ist.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß ein elektronischer Kompaß (28) zur Erfassung der Eingangsgröße Himmelsrichtung mit der Steuerung (14) gekoppelt oder diese Eingangsgröße als bei der Montage einzugebender Wert in einem Speicher (68) hinterlegt ist.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Steuerung mit einem Windgeber (30), Regengeber (34), Temperaturgeber (36) und/oder Luftfeuchtigkeitsgeber gekoppelt ist, die weitere die Behangstellung beeinflussende Eingangsgrößen erfassen, wobei vorzugsweise auch Sensoren (60, 62) zur Erfassung der Ist-Stellung des Behangs (52) als weitere Eingangsgröße der Steuerung (14) vorgesehen sind.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die geographischen Koordinaten des Ausstellungsortes der Sonnenschutzanlage (12) als weitere Eingangsgröße für die Steuerung (14) der Behangeinstellung dienen, wobei die geographischen Koordinaten werksseitig oder durch Eingabe bei der Montage abgespeichert sind oder durch einen integrierten GPS-Empfänger erfaßbar sind.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß sie betriebsfertig vormontiert mit allen Sensoren (20, 22, 28, 30, 34, 36) versehen ist und einen Versorgungsanschluß an ein übliches Haushalts-Stromnetz aufweist.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Sensoren (22, 32, 34, 36) zur Erfassung der die Umgebungseigenschaften wiedergebenden Eingangsgrößen innerhalb eines Gehäuses (16) sitzen und über geeignete Kanäle (32) oder Leiter (24) mit der Umgebung verbunden sind.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß eine manuelle Eingriffsmöglichkeit (56, 58) vorgesehen ist, die der automatischen Einstellung übergeordnet ist, wobei vorzugsweise die Grundprogrammierung durch manuelle Eingriffe mit Hilfe einer adaptiv lernfähigen Steuerung (66, 70) veränderbar und wiederherstellbar ist.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach Anspruch 9, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Rückkehr von einer manuell eingegebenen Einstellung in eine entsprechend der Grundprogrammierung vorzunehmende Einstellung nach einer bestimmten Zeitverzögerung anhand einer vorgegebenen Versteilcharakteristik erfolgt.
- Sonnenschutzanlage nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß sie ein Raffstore (12) ist, bei welchem die Einstellung durch Änderung der Ausgangsgrößen Ausfahrlänge und Lamellenneigung der Behanglamellen (54) in Abhängigkeit von den Eingangsgrößen variierbar ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19932731A DE19932731A1 (de) | 1999-07-14 | 1999-07-14 | Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung |
| DE19932731 | 1999-07-14 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1069275A2 true EP1069275A2 (de) | 2001-01-17 |
| EP1069275A3 EP1069275A3 (de) | 2003-01-22 |
Family
ID=7914629
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00114832A Expired - Lifetime EP1069257B1 (de) | 1999-07-14 | 2000-07-11 | Sonnenschutzanlage mit Sensorsteuerung |
| EP00114880A Withdrawn EP1069275A3 (de) | 1999-07-14 | 2000-07-12 | Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00114832A Expired - Lifetime EP1069257B1 (de) | 1999-07-14 | 2000-07-11 | Sonnenschutzanlage mit Sensorsteuerung |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (2) | EP1069257B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE278081T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE19932731A1 (de) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1816308A2 (de) | 2006-02-03 | 2007-08-08 | Roma Rolladensysteme GmbH | Vorrichtung zum Verschatten von Gebäudeöffnungen mit einem Sensor |
| WO2009049827A1 (fr) * | 2007-10-19 | 2009-04-23 | Somfy Sas | Installation de protection solaire equipee d'un capteur de vent |
| US7950827B2 (en) * | 2003-03-24 | 2011-05-31 | Lutron Electronics Co., Inc. | Electrically controllable window treatment system to control sun glare in a space |
| EP1659256A3 (de) * | 2004-11-22 | 2012-04-04 | Carefree / Scott Fetzer Company | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Einziehen einer Abdeckung |
| FR2999304A1 (fr) * | 2012-12-11 | 2014-06-13 | Somfy Sas | Procede de fonctionnement d'un dispositif domotique pour la mise en œuvre d'une periode d'inhibition de la detection de crepuscule |
| FR3013859A1 (fr) * | 2013-11-22 | 2015-05-29 | Somfy Sas | Procede de commande d'une installation exposee aux intemperies, et installation domotique associee |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU778068B2 (en) | 2000-01-31 | 2004-11-11 | Turnils A.B. | Awning assembly and control system |
| DE10202830A1 (de) * | 2002-01-24 | 2003-08-14 | Colt Internat Holdings Ag Baar | Vorrichtung zum Verstellen von Lichttechnikelementen |
| DE10204469B4 (de) * | 2002-02-05 | 2004-02-12 | Warema Renkhoff Gmbh | Sonnenschutzanlage mit integriertem Regensensor |
| CA2528368C (en) | 2004-11-29 | 2011-03-29 | Dometic Corporation | Wind sensing awning control having arm-mounted sensor |
| FR2884607B1 (fr) | 2005-04-13 | 2007-07-13 | Somfy Sas | Capteur domotique autonome et installation comprenant un tel capteur |
| DE102007029622A1 (de) * | 2007-06-26 | 2009-01-08 | Weinor Dieter Weiermann Gmbh & Co. | Sonnenschutzanlage |
| ITTV20080004A1 (it) | 2008-01-10 | 2009-07-11 | Nice Spa | Azionamento per avvolgibili con protezione contro vento eccessivo |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE755183R (fr) * | 1969-08-28 | 1971-02-01 | Hueppe Justin | Dispositif de controle pour installation pare-soleil actionnee par un moteur |
| GB1573104A (en) * | 1977-04-28 | 1980-08-13 | Colt Ltd W | Control system for external louvres on a building |
| DE2800968A1 (de) * | 1978-01-11 | 1979-07-12 | Trietex Antriebstechnik Gmbh | Anordnung zur steuerung von sonnenschutzeinrichtungen mit vertikalen lamellen |
| DE3304962C2 (de) * | 1983-02-12 | 1986-04-10 | Willi 4292 Rhede Rademacher | Verdunkelungsvorrichtung |
| DE3640241A1 (de) * | 1986-11-25 | 1988-05-26 | Ind Elektronik Und Feinmechani | Sonnenschutzverfahren und -vorrichtung |
| DE4032221A1 (de) * | 1990-10-11 | 1992-04-16 | Warema Renkhoff Gmbh & Co Kg | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum steuern von raffstores |
| DE4106033A1 (de) * | 1991-02-27 | 1992-09-03 | Warema Renkhoff Gmbh & Co Kg | Steuervorrichtung fuer sonnenschutzanlagen |
| DE4201971A1 (de) * | 1992-01-22 | 1993-08-05 | Wilhelm Rademacher | Verdunkelungsvorrichtung |
| DE9306368U1 (de) * | 1993-04-27 | 1993-07-08 | Rademacher, Wilhelm, 4292 Rhede | Verdunkelungsvorrichtung mit einer Markise, einer Außenjalousie o.dgl. |
| DE4315406C1 (de) * | 1993-05-08 | 1994-11-10 | Wilhelm Dipl Ing Brabender | Vorrichtung zur automatischen Steuerung von Antrieben für insbesondere Rolläden, Jalousien o. dgl. |
| US5663621A (en) * | 1996-01-24 | 1997-09-02 | Popat; Pradeep P. | Autonomous, low-cost, automatic window covering system for daylighting applications |
| DE19630496A1 (de) * | 1996-07-29 | 1998-02-12 | Selve Ernst Gmbh Co Kg | Vorrichtung zur Erfassung von Meßwerten, zur Realisierung von Motorsteuerungen elektromotorischer Antriebe für auf- und abwickelbare Behänge |
| EP1082502B1 (de) * | 1998-05-28 | 2005-02-02 | Hermann-Frank Müller | Markise mit flexiblen solarmodulen |
| DE20000682U1 (de) * | 2000-01-17 | 2000-03-30 | Helmut Beyers GmbH, 41066 Mönchengladbach | Vorrichtung zur Steuerung der Bewegung einer Beschattungseinrichtung |
-
1999
- 1999-07-14 DE DE19932731A patent/DE19932731A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2000
- 2000-07-11 AT AT00114832T patent/ATE278081T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-07-11 EP EP00114832A patent/EP1069257B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-07-11 DE DE50007964T patent/DE50007964D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-07-12 EP EP00114880A patent/EP1069275A3/de not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7950827B2 (en) * | 2003-03-24 | 2011-05-31 | Lutron Electronics Co., Inc. | Electrically controllable window treatment system to control sun glare in a space |
| EP1659256A3 (de) * | 2004-11-22 | 2012-04-04 | Carefree / Scott Fetzer Company | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Einziehen einer Abdeckung |
| EP1816308A2 (de) | 2006-02-03 | 2007-08-08 | Roma Rolladensysteme GmbH | Vorrichtung zum Verschatten von Gebäudeöffnungen mit einem Sensor |
| EP1816308A3 (de) * | 2006-02-03 | 2009-01-28 | Roma Rolladensysteme GmbH | Vorrichtung zum Verschatten von Gebäudeöffnungen mit einem Sensor |
| WO2009049827A1 (fr) * | 2007-10-19 | 2009-04-23 | Somfy Sas | Installation de protection solaire equipee d'un capteur de vent |
| FR2922585A1 (fr) * | 2007-10-19 | 2009-04-24 | Somfy Sas | Installation de protection solaire equipee d'un capteur de vent |
| US8261608B2 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2012-09-11 | Somfy Sas | Solar protection installation equipped with a wind sensor |
| FR2999304A1 (fr) * | 2012-12-11 | 2014-06-13 | Somfy Sas | Procede de fonctionnement d'un dispositif domotique pour la mise en œuvre d'une periode d'inhibition de la detection de crepuscule |
| FR3013859A1 (fr) * | 2013-11-22 | 2015-05-29 | Somfy Sas | Procede de commande d'une installation exposee aux intemperies, et installation domotique associee |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1069257A2 (de) | 2001-01-17 |
| EP1069257A3 (de) | 2003-05-02 |
| EP1069257B1 (de) | 2004-09-29 |
| EP1069275A3 (de) | 2003-01-22 |
| ATE278081T1 (de) | 2004-10-15 |
| DE19932731A1 (de) | 2001-03-22 |
| DE50007964D1 (de) | 2004-11-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1069275A2 (de) | Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung | |
| EP1077378A1 (de) | Windmesser für Sonnenschutzanlage | |
| US5142133A (en) | Apparatus for the control of venetian blinds including photodetector means for detecting the angle of incidence of sun light | |
| EP1069277B1 (de) | Sonnenschutzanlage mit automatischer Behangsteuerung und manueller Eingriffsmöglichkeit | |
| EP1333150B1 (de) | Motorisierte Fensterabdeckung und Verfahren zur Überwachung der Position einer motorisierten Fensterabdeckung | |
| EP1904712B1 (de) | Steuervorrichtung für jalousien an hochbauten | |
| EP0552459B1 (de) | Sicherungsvorrichtung für Rolltore und dergleichen | |
| US20060000558A1 (en) | Solar-Powered, Low-Voltage, Automatic, Motorized Exterior Window Shading Device | |
| US7454990B2 (en) | Variably controlled accelerated weathering test apparatus | |
| DE4106033A1 (de) | Steuervorrichtung fuer sonnenschutzanlagen | |
| DE4407342C2 (de) | Verdunkelungsvorrichtung mit einer Markise, einer Außenjalousie o. dgl. | |
| DE102013219040B4 (de) | Tür oder Fenster | |
| US3965348A (en) | Method of and apparatus for detecting light and controlling jalousies and the like | |
| DE102013016763A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Feststellen der Ausrichtung einer Wetterstation eines Gebäudeautomationssystems | |
| DE29924615U1 (de) | Sonnenschutzanlage mit sich dem Lichteinfall anpassender Behangeinstellung | |
| DE102012024110B4 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Messung von Solarstrahlung | |
| DE29923046U1 (de) | Sensor für eine Verdunkelungsvorrichtung und Verdunkelungsanlage | |
| BE1026474B1 (nl) | Een adaptief zonweringsysteem | |
| DE19840418C2 (de) | Sonnenschutzvorrichtung | |
| EP1538880B1 (de) | Messvorrichtung mit mehreren Sensoren zum Erfassen des Aussenlichts | |
| JP4216130B2 (ja) | 太陽追尾型センサ、及び電動ブラインドの制御装置 | |
| DE102009013752B4 (de) | Photovoltaische Vorrichtung | |
| DE9320324U1 (de) | Bedachung | |
| DE102011054697B4 (de) | Lamellenfenster mit einem elektromotorischen antrieb | |
| DE20007442U1 (de) | Blendschutzregler |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20030723 |