EP0945539B1 - Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung - Google Patents
Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0945539B1 EP0945539B1 EP99105825A EP99105825A EP0945539B1 EP 0945539 B1 EP0945539 B1 EP 0945539B1 EP 99105825 A EP99105825 A EP 99105825A EP 99105825 A EP99105825 A EP 99105825A EP 0945539 B1 EP0945539 B1 EP 0945539B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- roller
- compartment
- rollers
- caustic soda
- soda solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 title claims description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 title claims description 12
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 161
- 235000011121 sodium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000005470 impregnation Methods 0.000 claims description 55
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 25
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005517 mercerization Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000029087 digestion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004043 dyeing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004061 bleaching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009529 body temperature measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003518 caustics Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010924 continuous production Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005265 energy consumption Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002386 leaching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008237 rinsing water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002994 synthetic fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B7/00—Mercerising, e.g. lustring by mercerising
- D06B7/08—Mercerising, e.g. lustring by mercerising of fabrics of indefinite length
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method and a device for the continuous alkali treatment of textile products with partial differences in thickness, such as tips and embroidery made primarily from cellulosic raw materials, but also consist of synthetic material can.
- Lace is a flat textile object in the form of an ornament, the effect of which is shown through of the background by itself between the pattern shapes located openings is based.
- alkali treatments of lace and embroidery serve the fiber digestion and prepare the goods for bleaching, Dyeing and printing before. These alkali treatments are done currently discontinuous in the low concentration range. There are alkali, usually sodium hydroxide and soda, for use. Their effect can be the usual textile auxiliaries are supported.
- DE 196 35 171 C 1 describes a method for washing out of polyvinyl alcohol base fabric made of lace and embroidery described, also according to the principle of spraying and sucking works. It also becomes Improvement of the drainage effect by hanging up described with a brush. This device is for continuous lye treatment is not provided and unsuitable.
- the invention has for its object a method and to develop a device that the tips and Embroidery through an adapted alkali treatment like this be modified so that they have a very good fiber digestion have an evenly improved staining, a differentiated improved staining, a excellent printability, even using modern spray printing technology, and enable a very high degree of whiteness.
- the products should be managed continuously with lye of different concentrations and Temperature and length can be treated Width of the goods can be set in an exactly defined manner and there must be either homogeneous and inhomogeneous lye effects can be generated and there must be another Minimize alkali consumption.
- the device consists of a pre-impregnation compartment, a main impregnation compartment 1, a post-impregnation compartment 5, a stabilizing compartment 15 and one Washing section 19.
- the pre-impregnation compartment not shown consists of a usual low-tension working Wide washer and a squeegee on the End of the pre-impregnation compartment is arranged and a Has cover.
- the main impregnation compartment 1 exists from the first pair of rollers 2 and 4, which run against each other are arranged and thereby form a gusset 3.
- the main impregnation compartment 1 has a separate one Not shown drive.
- the re-impregnation compartment 5 consists of a chassis 6, which is under the roller 4 of the first pair of rollers 2, 4 and the subsequent roller 8 of the second pair of rollers 7, 8 attached and heated and is equipped with a temperature control device.
- the axes of the rollers 4 and 8 are at the same height and parallel to the axis of the roller 2.
- the roller 7 is closed the rollers 4 and 8 arranged on gap, so that the roller 7 is supported on the rollers 4 and 8.
- the roller 8 is arranged so that by means of both sides Spring pressure on the roller 10 of the following vertical crushing unit 9 is pressed.
- a spray tube 11 which is connected to the chassis 6 stands, attached.
- the post-impregnation compartment 5 as shown in FIG. 2 so that instead the roller 8 are two parallel rollers, the supporting roller 12 and the goods guide roller 13 and a Suction bar 14 are located.
- the roller 12 is also a material guide roller and at the same time the holder for the roller 7.
- the roller 13 is a material guide roller over the suction bar 14 arranged.
- the chassis 6 is through a smaller chassis 6a replaced and is located on the underside of the roller 4.
- the spray tube 11 is out of operation.
- the vertical crusher 9 of the post-impregnation compartment 5 has one separate drive.
- the stabilization compartment 15 exists of two endlessly running on the edges of the textile product Needle or clip chains with web guides and needle devices 16, the inlet field 17, the Residence zone 18, a washing section 19 and a downstream Pull-out crushing unit 20.
- the washing section 19 is located 1 at the end of the stabilization compartment 15, which also includes the entry field 17 and the dwelling zone 18.
- the inlet field 17 is adjustable in width.
- Above the washing section 19 are spray nozzles 21 at equal intervals attached across the width of the textile product.
- Each in front of the spray nozzles 21 is above the path of the textile product and across the entire width of the Stabilizing compartment 15 a partition 22 is arranged. Between the spray nozzles 21 are suction bars 23 with Sealing lips attached. Over the sealing lips of the squeegees 23 there is a sealing brush 24. Below the spray nozzle 21 and the suction bar 23 is the drip pan 25.
- the stabilizing compartment 15 with the pull-out crushing unit 20 has one drive each.
- an air tip made of 100% Cotton provided. for a modern spray printing process should be pretreated. This requires homogeneous mercerization. The top will be there boiled alkaline and submitted wet to the device. For this purpose, it should contain 270 g / l sodium hydroxide solution be mercerized. The lace and also embroidery can be pre-impregnated dry or wet and there through a content of sodium hydroxide solution 50 g / l be prepared for the subsequent process. Through a pre-impregnation They will be finished with an even finish and very low moisture level. The fleet content is max. 80%. In this case After pre-impregnation, the tip has a sodium hydroxide solution of 30 g / kg. The aspirated tip contains still 60% water.
- the fleet consists of those used for shock de-leaching rinsing water from the following compartments.
- the suction bar works at the end of the pre-impregnation with a special cover to a low Moisture level with low energy consumption too to back up.
- the tip then becomes the main impregnation compartment 1 fed and impregnated with sodium hydroxide solution.
- a gusset 3 formed and thus exerted pressure.
- this Gusset 3 is made of alkali solution using a metering pump the suds container filled. This is from the Tip picked up or flowing over an overflow back to the tub.
- the suds container there is a temperature measurement and control device that has an intended temperature the lye enables and a lye concentration measurement and control device that the backflowing Amount of alkali lye, commercially available alkali lye and water, mixed to alkali, which in turn the gusset 3 is supplied.
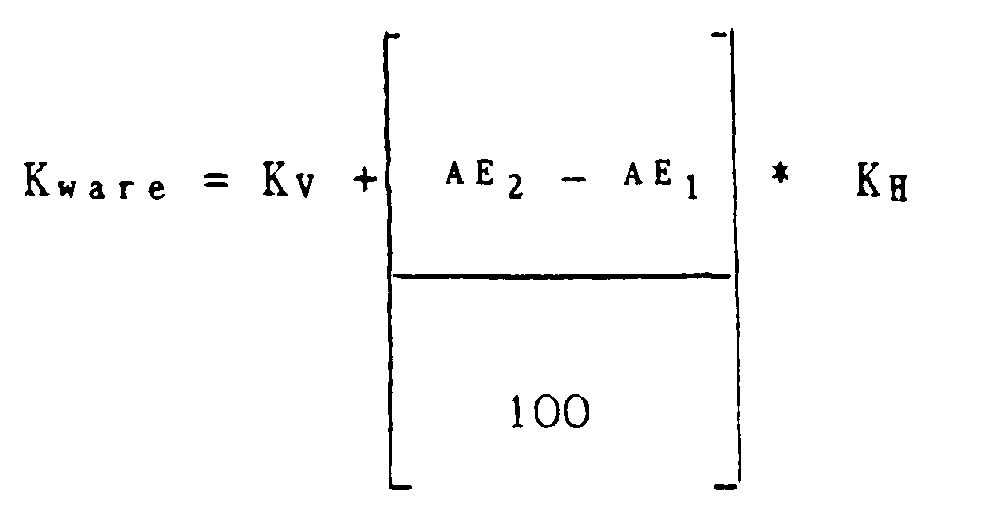
- K ware is generally up to 300 g / l sodium hydroxide solution and K H should be a maximum of 600 g / l sodium hydroxide solution.
- the tip After the main impregnation, the tip still contains 110% water at a squeezing pressure of 5 bar.
- the alkali concentration of the main impregnation must be 480 g / l sodium hydroxide solution. As soon as the tip leaves the horizontal crushing unit of the main impregnation compartment 1, it arrives at the post-impregnation compartment 5 in the bound goods run.
- the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution which corresponds to the target concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution on the tip, in the example 270 g / l, is used.
- the tip is impregnated in the chassis 6, squeezed off by the roller 7 resting on it, impregnated again by means of a spray tube 11, squeezed again by the roller 7 resting on it, impregnated again in the chassis 6, dewatered by the lower roller 10 of the vertical crushing unit 9. impregnated by spray tube 11 and finally dewatered in the vertical crushing unit 9 at 5 bar to a liquor content of 110%.
- the tip generally runs in the bound goods run.
- the squeezing pressure of either 3 - 8 bar of the main impregnation compartment 1 and the vertical crushing unit 9 can optionally also be of different heights and thus the Squeeze effect fluctuate. Since it can be assumed that in the vertical crushing unit 9 in the sense of a minimized Use of caustic solution takes place to a maximum no or only a slight excess of lye in the Chassis 6 arise, the dilution of the commercially available Sodium hydroxide solution is used and so the main impregnation is fed.
- the re-impregnation can also optionally be carried out according to FIG. 2 be carried out so that the tip first in Chassis 6a impregnated by the roller 7 lying thereon squeezed under the supporting roller 12 above the Suction bar 14 under the guide roller 13 and in the bound Goods run to the vertical crushing unit 9 is fed.
- the Tip is through the suction bar 14 to a liquor content brought by 100%.
- the extracted sodium hydroxide solution is the Chassis 6a of the re-impregnation compartment 5 is fed again.
- the excess lye is used to dilute the commercially available Sodium hydroxide solution used and so the main impregnation fed again.
- the speed of the vertical crusher 9 of the post-impregnation compartment 5 can deviate negatively or positively from the main impregnation compartment 1.
- the speed difference of the vertical crushing mechanism is 9 + 1%.
- the tip leaves the vertical crushing unit 9 and comes over a short distance on the tension chain of the Stabilization compartment 15.
- the speed of the Tension chain can be negative or positive to the main impregnation compartment 1 deviate.
- the speed difference is the tension chain + 2%.
- the tip is also open in the conical inlet field 17 brought the desired width, in the example to + 2% the starting width and then by lingering this state stabilized.
- the latitude and Length gain of the tip is thus in length and Transverse direction 2% each.
- Sodium hydroxide solution is present in the first spray tube 21 a concentration of 94 g / l, the liquor temperature is close to the cooking temperature. It will be 100% from Goods weight applied to fleet. The top leaves the compartment with 182 g / l sodium hydroxide solution.
- the vacuumed Fleet of the first squeegee 23 is in production of the caustic soda liquors for main and secondary impregnation used to dilute the strong alkali.
- the second spray tube 21 brings liquor with a sodium hydroxide content from 50 g / l.
- the liquor temperature is approx. 90 ° C. There are 200% of the weight of the goods Fleet applied.
- the tip leaves the compartment with 94 g / l sodium hydroxide solution.
- the extracted liquor is heated up and fed 50% to the first spray tube 21.
- the remaining liquor is used for pre-impregnation.
- the third spray tube 21 carries liquor with a sodium hydroxide solution from 28 g / l to.
- the liquor temperature is approx. 90 ° C. There are 200% of the weight of the water upset.
- the tip leaves the compartment at 50 g / l Caustic soda.
- the squeezed liquor is heated up and supplied to the second spray tube 21.
- the laces and embroidery are excellent Dye absorption capacity and significantly improved textile properties.
- the consumption at Sodium hydroxide solution is used consistently greatly reduced in the overall process.
- the alkaline boiled and pre-bleached embroidery can be fed to the pre-impregnation compartment analogously to Example 1 and be treated there or they will be like
- the main impregnation compartment immediately dries 1 submitted and with sodium hydroxide solution in the concentration range from 50 g / l to 300 g / l impregnated and squeezed at 5-6 bar. Because of the differences in thickness the tip enriches itself when squeezed Sodium hydroxide in the embroidery base, or in the tip itself there is only a reduced amount of sodium hydroxide solution / kg of goods. It passes through the post-impregnation compartment 5 without additional Exposure to lye. Changes in length and width the embroidery will not be done.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
Description
- Fig. 1
- Prinzipskizze einer Seitenansicht der Vorrichtung ohne Vorimprägnierabteil
- Fig. 2
- Prinzipskizze einer Seitenansicht des Haupt- und Nachimprägnierabteils mit Saugtechnik
- Kware :
- Konzentration der Natronlauge auf der Ware in g/l
- Kv
- : Konzentration der Natronlauge auf der Ware durch die Vorimprägnierung in g/l
- KH
- : Konzentration der Natronlauge im Zwickel der Hauptimprägnierung in g/l
- AE1
- : Abquetscheffekt der Ware nach der Vorimprägnierung in %
- AE2
- : Abquetscheffekt der Ware nach der Hauptimprägnierung in %
- 1
- Hauptimprägnierabteil
- 2
- Walze
- 3
- Zwickel
- 4
- Walze
- 5
- Nachimprägnierabteil
- 6
- Chassis
- 6a
- Chassis
- 7
- Walze
- 8
- Walze
- 9
- Vertikalquetschwerk
- 10
- Walze
- 11
- Spritzrohr
- 12
- Walze
- 13
- Walze
- 14
- Saugbalken
- 15
- Stabilisierungsabteil
- 16
- Warenbahnführer und Aufnadelvorrichtungen
- 17
- Einlauffeld
- 18
- Verweilzone
- 19
- Waschstrecke
- 20
- Auszugsquetschwerk
- 21
- Spritzdüsen
- 22
- Trennblech
- 23
- Saugbalken 23
- 24
- Abdichtbürste
- 25
- Auffangwanne
Claims (5)
- Verfahren zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung von textilen bahnförmigen Erzeugnissen mit partiellen Dickenunterschieden, insbesondere von Spitzen und Stickereien, wobei diese alkalisch vorbehandelt, mit Schwachlauge vorimprägniert, entwässert, die Beladungsdichte gemessen, einer Hauptimprägnierung (1) mit konzentrierter Lauge zugeführt werden, wobei die Laugezuführung über einen Zwickel (3) erfolgt und die Erzeugnisse anschließend abgequetscht, einer Verweil- und Stabilisierzone (15) in Form von Walzen oder Spannfeld zugeführt werden und eine Wiederaufbereitung der Lauge vorgenommen wird, deren Konzentration und Temperatur korrigiert wird, diese dem Zwickel (3) wieder zugeführt wird sowie die Wiederaufbereitung der Behandlungsflotten nach dem Gegenstromprinzip erfolgt,
durch gekennzeichnet, dassdem alkalisch abgekochten und vorimprägnierten textilen Erzeugnis bei der Hauptimprägnierung (1) Natronlauge, gemäß der Formel, (wobei die verschiebenen Parameter in Beschreibung erkhärt sind)
jedoch bis maximal 600 g/l im Zwickel (3) des ersten Walzenpaares (2, 4) zugeführt wird,das textile Erzeugnis vom Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) im gebundenen Warenlauf durch die Walze (4) des ersten Walzenpaares (2, 4), die gleichzeitig als Quetschwalze des Hauptimprägnierabteils (1) und als erste Warenleitwalze des Nachimprägnierabteils (5) dient, auf einer sehr kurzen Wegstrecke in das Nachimprägnierabteil (5) gelangt und darin mit einer Laugekonzentration, die der Sollkonzentration der Natronlauge auf dem textilen Erzeugnis entspricht, behandelt wird, indem dieses im Chassis (6) imprägniert, zwischen der Walze (4) des ersten Walzenpaares und Walze (7) des zweiten Walzenpaares abgequetscht, durch das Spritzrohr (11) erneut imprägniert, zwischen der Walze (7) und nachfolgender Walze (8) abgequetscht, im Chassis (6) imprägniert, zwischen der Walze (8) und der Walze (10) des Vertikalquetschwerkes (9) abgequetscht, durch das Spritzrohr (11) imprägniert und im Vertikalquetschwerk (9) auf einen niedrigen Flottengehalt entwässert wird und nach Verlassen des Nachimprägnierabteils (5) keine weitere Beaufschlagung mit Natronlauge erfolgt,das textile Erzeugnis zur Einstellung der gewünschten Länge und Breite zunächst vom Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) in das Nachimprägnierabteil (5) geführt wird, wobei Geschwindigkeitsdifferenzen zwischen dem Vertikalquetschwerk (9) und dem Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) positiv oder negativ einstellbar sind,anschließend das stabilisierte, durch das Vertikalquetschwerk (9) oder den Saugbalken (14) hoch entwässerte textile Erzeugnis der Waschstrecke (19) zugeführt und mittels Sprühen und Saugen schockentlaugiert wird. - Verfahren insbesondere nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Nachimprägnierung zunächst im Chassis (6a) erfolgt, das textile Erzeugnis durch die aufliegende Walze (7) in Verbindung mit Walze (4) abgequetscht und in Verbindung mit der Walze (12), die als Warenleitwalze dient und die Halterung der Walze (7) darstellt, nochmals abgequetscht wird und anschließend im ungebundenen Warenlauf unter der abstützenden Walze (12) dem Saugbalken (14) zugeführt und unter Walze (13), die als Warenleitwalze über den Saugbalken (14) angeordnet ist, zum Vertikalquetschwerk (9) gelangt, wobei mittels des Saugbalkens (14) ein Flottengehalt von 100 % erreicht und die abgesaugte Natronlauge dem Chassis (6a) zurückgeführt, die überschüssige Lauge der Hauptimprägnierung wieder zugeführt wird, die Geschwindigkeitsdifferenzen und die Weiterbehandlung des textilen Erzeugnisses nach Anspruch 1 erfolgt.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 öder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das abgekochte und vorgebleichte textile Erzeugnis trocken dem Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) vorgelegt, mit einer Natronlauge im Konzentrationsbereich von 50 - 300 g/l imprägniert mit 5 - 6 bar zwischen den Walzen (2 und 4) abgequetscht werden.
- Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, bestehend aus einem Vorimprägnierabteil mit einer Breitwaschmaschine, einem Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) mit einer Anordnung von Walzen (2, 4), über denen sich Spritzrohre (11) und unter denen sich Auffangbehälter (6) sowie Förderpumpen mit Rohrleitungen angeordnet sind zur Herstellung eines Kreislaufes der Behandlungsflüssigkeit von den Auffangbehältern (6) über die Spritzrohre (11) zurück zu den Auffangbehältern (6), und weiterhin bestehend aus gegeneinander laufenden einen Zwickel (3) bildenden Walzen (2, 4), dadurch gekennzeichnet, dassdem Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) mit direkter Zuführung der Lauge zum Zwickel (3) ein Nachimprägnierabteil (5) und diesem ein Stabilisierungsabteil (15) mit einer Waschstrecke (19) nachgeordnet ist,das Hauptimprägnierabteil (1) aus bekannten gegeneinanderlaufenden einen Zwickel (3) bildenden Walzen (2 und 4) besteht, wobei die Walze (4) eine Warenleitwalze des Nachimprägnierabteiles (5) ist,das Nachimprägnierabteil (5) unter den Walzen (4 und 8) ein beheizbares Chassis (6) aufweist, wobei diese Walzen (4 und 8) sich in gleicher Höhe zur Walze (2) befinden, wobei die Walze (7) auf diesen Walzen (4 und 8) abstützbar angeordnet ist und sich weiterhin die Walze (8) mit darüberliegendem Spritzrohr (11) andrückbar an die Walze (10) des nachfolgenden Vertikalquetschwerkes (9) befindet,eine Waschstrecke (19) mit Spritzdüsen (21) und ein Auszugsquetschwerk (20) am Ende des Stabilisierungsabteils (15) angeordnet ist, das auch das Einlauffeld (17) und die Verweilzone (18) umfaßt, wobei vor den Spritzdüsen (21) über die gesamte Breite des Stabilisierungsabteils (15) ein Trennblech (22) sich befindet und zwischen den Spritzdüsen (21) sich Saugbalken (23) mit Dichtlippen, über denen Abdichtbürsten (24) liegen, befinden, und unter diesen Spritzdüsen (21) eine bekannte Auffangwanne (25) angeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Nachimprägnierabteil (5) in Aussparung der Walze (8) zwei parallel angeordnete Walzen (12 und 13) mit Saugbalken (14) aufweist, wobei das Chassis (6a) sich an der Unterseite der Walze (4) unter Ausschaltung des Spritzrohres (11) befindet.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19813237A DE19813237C2 (de) | 1998-03-26 | 1998-03-26 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung |
| DE19813237 | 1998-03-26 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0945539A1 EP0945539A1 (de) | 1999-09-29 |
| EP0945539B1 true EP0945539B1 (de) | 2001-02-28 |
Family
ID=7862335
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99105825A Expired - Lifetime EP0945539B1 (de) | 1998-03-26 | 1999-03-23 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0945539B1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE19813237C2 (de) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008059469A2 (en) * | 2008-02-14 | 2008-05-22 | Hasan Eka Permana | An apparatus for mercerizing fabric goods and the method of mercerizing fabric goods using the same |
| EP3494254B1 (de) | 2016-08-04 | 2021-09-29 | PVH Corp. | Bügelfreie stoffe und kleidungsstücke sowie verfahren zur endfertigung derselben |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT305182B (de) * | 1969-03-28 | 1973-02-12 | Textilwerke Josef Otten | Mercerisiermaschine |
| DE2544494A1 (de) * | 1975-10-04 | 1977-04-07 | Kleinewefers Ind Co Gmbh | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen mercerisieren einer textilbahn |
| EP0295608B1 (de) * | 1987-06-15 | 1992-02-05 | ZITTAUER MASCHINENFABRIK GmbH | Verfahren zum Mercerisieren von textilen Stoffbahnen |
| EP0340166B1 (de) * | 1988-04-29 | 1992-06-17 | Benninger AG | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Breitstrecken einer Gewebebahn in einer Mercerisiermaschine |
| DE4213127C1 (de) * | 1992-04-21 | 1993-07-01 | Babcock Textilmaschinen Gmbh, 2105 Seevetal, De | |
| DE19635171C1 (de) * | 1996-08-30 | 1997-11-06 | Titv Greiz | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Auslösen von Stickgrund aus Polyvinylalkohol-Material |
-
1998
- 1998-03-26 DE DE19813237A patent/DE19813237C2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1999
- 1999-03-23 DE DE59900045T patent/DE59900045D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-03-23 EP EP99105825A patent/EP0945539B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE19813237C2 (de) | 2000-05-04 |
| DE19813237A1 (de) | 1999-09-30 |
| EP0945539A1 (de) | 1999-09-29 |
| DE59900045D1 (de) | 2001-04-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2713800C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Indigo-Färbung von Kettfäden aus Baumwoll-Spinngarnen | |
| EP3294939B1 (de) | Verfahren zur behandlung eines textilen substrates sowie vorrichtungen zur durchführung des verfahrens | |
| DE2622256A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur fixierung von farbstoffen und anderen chemischen substanzen auf textilien | |
| CH646477A5 (de) | Einrichtung zum impraegnieren einer bewegten fasermatte mit einer fluessigkeit. | |
| EP0945539B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Alkalibehandlung | |
| EP0320701B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur diskontinuierlichen Nassbehandlung von gestricktem oder gewirktem Textilgut | |
| DE102012007802B4 (de) | Verfahren zum Ausrüsten und Veredeln von textilen oder textilähnlichen Warenbahnen | |
| DE8013619U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen behandeln einer stoffbahn | |
| DE2840932A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen behandlung von textilmaterialien unter hohem druck | |
| DE4303920C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Entschlichten von mit wasserlöslicher Schlichte beladenem Textilgut | |
| DE69027605T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Mercerisieren | |
| EP0624677A2 (de) | Verfahren zum Säubern von kontinuierlich vorlaufendem, bahnförmigen Textilgut und Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens | |
| CH554446A (de) | Vorrichtung zur verbesserung der faserstruktur von cellulosefasern enthaltendem textilgut. | |
| DE4331275C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Behandeln von textilen Warenbahnen | |
| DE3045647C2 (de) | ||
| DE19536355C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Behandeln einer textilen Warenbahn | |
| DE2837359A1 (de) | Verfahren zum faerben von dickem, bahnfoermigem textilgut | |
| DE2722125B2 (de) | Verfahren zum Mercerisieren von Geweben oder Gewirken | |
| DE850133C (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Zellwolltransparentgeweben | |
| AT164008B (de) | Verfahren und Einrichtung zur Herstellung von Zellwolltransparentgeweben | |
| DE2049885C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Vorbehandeln einer Textilbahn | |
| AT222613B (de) | Vorrichtung zur Naßbehandlung von Fasermaterial | |
| DE3423154A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen auswaschen von bahnfoermigem textilgut | |
| DE1635103A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Behandeln von dicken,voluminoesen Textilien | |
| DE3106257A1 (de) | "verfahren zum behandeln eines textilen produkts" |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19991028 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20000221 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: HELLWICH, HARTMUT Inventor name: HELLWICH, BRIGITTE |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20010228 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20010228 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59900045 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20010405 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20010418 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20010829 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030331 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20090302 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20090327 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20090527 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20100323 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20101130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20101001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100323 |