EP0476264B1 - Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen - Google Patents
Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0476264B1 EP0476264B1 EP91112203A EP91112203A EP0476264B1 EP 0476264 B1 EP0476264 B1 EP 0476264B1 EP 91112203 A EP91112203 A EP 91112203A EP 91112203 A EP91112203 A EP 91112203A EP 0476264 B1 EP0476264 B1 EP 0476264B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- pallet
- stacking
- platform
- sensing element
- sheets
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000011111 cardboard Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000011087 paperboard Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000123 paper Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000881 depressing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000994 depressogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H31/00—Pile receivers
- B65H31/32—Auxiliary devices for receiving articles during removal of a completed pile
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2301/00—Handling processes for sheets or webs
- B65H2301/40—Type of handling process
- B65H2301/42—Piling, depiling, handling piles
- B65H2301/422—Handling piles, sets or stacks of articles
- B65H2301/4225—Handling piles, sets or stacks of articles in or on special supports
- B65H2301/42256—Pallets; Skids; Platforms with feet, i.e. handled together with the stack
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2701/00—Handled material; Storage means
- B65H2701/10—Handled articles or webs
- B65H2701/17—Nature of material
- B65H2701/176—Cardboard
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S414/00—Material or article handling
- Y10S414/10—Associated with forming or dispersing groups of intersupporting articles, e.g. stacking patterns
- Y10S414/106—Associated with forming or dispersing groups of intersupporting articles, e.g. stacking patterns including means for supplying pallet or separator to group
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for stacking sheets, in particular sheets of paper or cardboard, on a pallet according to the preamble of patent claim 1.
- Generic stacking devices are used in the processing of paper or cardboard to store sheets which, for. B. were produced with a cross cutting machine, continuously stacked on pallets. In order to keep the drop height of the sheets constant when laying them down, the pallets lie on a lifting and lowering storage platform that is continuously lowered in accordance with the height of the stack.
- a generic stacking device in which the sheets are stacked during a pallet change on an auxiliary stacking platform that can be moved into the area of the storage platform in order to be able to carry out the stack change without loss, that is to say without removing sheets, at full working speed .
- the storage platform can be lowered to remove the finished stack and pick up a new empty pallet.
- the new pallet is then moved up with the storage platform to below the auxiliary stacking platform, and the intermediate stack is transferred to the new pallet by moving out the auxiliary stacking platform.
- the invention has for its object to be able to determine the pallet height in a generic stacking device so that a problem-free transfer of the intermediate stack from the auxiliary stacking platform to the new pallet is possible.
- the entire pallet surface is scanned when determining the pallet height.
- the sensing element can depress depressing elevations, which are therefore not registered.
- the feeler element is advantageously arranged fixed in the area of the pallet feed to the storage platform. The pallet height can thus be determined when a new pallet is transported to the storage platform.
- Claim 4 contains an advantageous arrangement for measuring the vertical deflection of the probe element to determine the maximum deflection.
- the adjustable contact pressure according to claim 5 enables the adjustment of the pallet height determination to disturbing and non-disturbing elevations.
- the probe element is expediently connected to a double-acting piston-cylinder unit, so that the contact pressure can be increased or decreased.
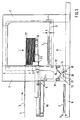
- Fig. 1 shows a stacking device according to the invention in side view transverse to the direction of the sheets.
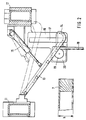
- FIG. 2 shows the device for determining the pallet height in an enlarged detail from FIG. 1.
- the frame of the stacking device has four stands 1, 2, between which there is a lifting and lowering storage platform 3.
- the depositing platform 3 can be raised up to the conveying plane 4 of the scalloped sheets 5 and lowered down to the floor, where it is aligned with an infeed conveyor 6 for empty pallets 7 which leads through the space between the stands 1.
- the feed conveyor 6 as well as the top of the platform 3 funding, z. B. roles with which the pallets 7 can be transported for a pallet change in the running direction of the sheets 5.
- auxiliary stacking platform 8 In the uprights 1 there is a lifting and lowering auxiliary stacking platform 8 which can be moved horizontally into the area of the storage platform 3 by means of a drive 9. The sheets 5 are stacked on the auxiliary stacking platform 8, while full stacks are removed and new pallets 7 are transported into the stacking area. When stacking on a pallet 7, which lies on the storage platform 3, the auxiliary stacking platform 8 is located outside the stacking area (on the left in FIG. 1). As far as the stacking device is known and z. B. described in DE-PS 37 39 194.
- a device for determining the pallet height is arranged between the two upright stands 1 and is shown enlarged in FIG. 2.
- two cross members 11, 12 are fastened at the same height over the working width.
- Two lateral pivoting levers 13 pointing in the direction of sheet travel are articulated on the front crossmember 11, between the free ends of which a runner 14 extending over the working width is fastened.
- the length of the pivot lever 13 and its position is chosen so that the runner 14 can be lowered to close to the floor (up to a distance of approximately 80 mm) and raised to a position above the maximum height of a pallet 7 and thus onto the surfaces the continuous pallets 7 can be placed.
- the downward pressure in the piston-cylinder unit 15 can be adjusted by means of a fine control valve.
- a side plate 16 on one side on the crossmember 12 with a vertical guide 17 for a vertical rack 18 connected to the runner 14 attached, which meshes with the pinion 19 of an angle encoder 20 attached to the side plate 16.
- the angular encoder 20 thus registers the vertical deflection of the runner 14 when passing through a pallet 7.
- the contact pressure which depends on the weight of the runner 14, is set by means of the piston-cylinder unit 15 in such a way that non-disturbing elevations, such as protective papers lying on top, which are folded up, are depressed and are therefore not registered.
- Disturbing surveys such as protruding nails, on the other hand, lead to a deflection and are registered.
- the stored maximum height h of the pallet 7 then serves to control the approach of the storage platform 3 with the pallet 7 lying on it from below to the auxiliary stacking platform 8. So that the supply of sheets 5 does not have to be interrupted when changing stacks, an intermediate stack 22 is formed on the auxiliary stack platform 8 until a full stack has been removed and a new pallet 7 has been moved under the auxiliary platform 8 carrying the intermediate stack 22. During the intermediate stacking, the auxiliary platform 8 moves continuously downward in order to keep the surface of the intermediate stack 22 approximately at the level of the feed plane 4. Since the intermediate stack 22 is placed on the advancing new pallet 7 by pulling out the auxiliary stack platform 8, it is It is necessary to position the new pallet 7 exactly below the auxiliary stacking platform 8 to a small safety distance (approx. 10 mm).
- the movement of a new pallet 7 against the underside of the auxiliary stacking platform 8 is controlled in such a way that an inductive proximity switch 23 arranged on the underside of the supporting structure of the slide 8 registers the approach of the storage platform 3 as a reference point if the pallet 7 is still a sufficiently large distance from the auxiliary stacking platform 8 has.
- This known distance is then further reduced by lowering the auxiliary stacking platform 8 and lifting the storage platform 3 until the distance of the surface of the storage platform 3 from the auxiliary stacking platform 8 is only the measured height of the pallet plus 10 mm safety distance.
- These further approaches are controlled via two angle encoders, one of which measures the vertical movement of the auxiliary stacking platform 8, the other the vertical movement of the storage platform 3.
- the feeler element (runner 14) is arranged horizontally in a stationary manner.
- the palette is moved relative to the probe element to scan the entire pallet surface. It is also possible to arrange the probe element so that it can be moved horizontally, so that it can be moved over the entire surface of a stationary pallet. So z. B. a movable between the stands 1, 2 feel the palette 7 resting on the storage platform 3. Then it has to Push element can be moved from the storage area into a position not disturbing the stacking.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Pile Receivers (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Forming Counted Batches (AREA)
- Discharge By Other Means (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen, insbesondere Papier- oder Kartonbögen, auf eine Palette gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs 1.
- Bei der Verarbeitung von Papier oder Karton werden gattungsgemäße Stapelvorrichtungen eingesetzt, um Bögen, die z. B. mit einer Querschneidemaschine hergestellt wurden, kontinuierlich auf Paletten zu stapeln. Um die Fallhöhe der Bögen beim Ablegen konstant zu halten, liegen die Paletten auf einer heb- und senkbaren Ablageplattform, die entsprechend dem Höhenzuwachs des Stapels kontinuierlich abgesenkt wird.
- Aus der DE-PS 37 39 194 ist eine gattungsgemäße Stapelvorrichtung bekannt, bei der die Bögen während eines Palettenwechsels auf einer in den Bereich der Ablageplattform einfahrbaren Hilfsstapelplattform zwischengestapelt werden, um den Stapelwechsel verlustlos, also ohne Ausschleusen von Bögen, bei voller Arbeitsgeschwindigkeit durchführen zu können. Während auf der Hilfsstapelplattform gestapelt wird, kann die Ablageplattform abgesenkt werden, um den fertigen Stapel abzutransportieren und eine neue leere Palette aufzunehmen. Die neue Palette wird anschließend mit der Ablageplattform bis unterhalb der Hilfsstapelplattform hochbewegt, und der Zwischenstapel wird durch Herausfahren der Hilfsstapelplattform auf die neue Palette übergeben.
- Um die Fallhöhe des Zwischenstapels bei der Übergabe auf eine neue Palette möglichst gering zu halten, ist es erforderlich, diese vor dem Herausfahren der Hilfsstapelplattform mit möglichst geringem Abstand unterhalb der Hilfsstapelplattform exakt zu positionieren. Beim Positionieren muß die Höhe der Palette berücksichtigt werden, daher ist es aus der Praxis bekannt, mittels Fotozellen die Höhe der jeweiligen neuen Palette zu messen.
- Diese Meßmethode hat sich jedoch bei Verwendung bestimmter Paletten als unzulänglich gezeigt. Die Fotozellen sprechen einerseits auf die Übergabe des Zwischenstapels auf die neue Palette nicht störende Erhebungen wie auf der Palette aufliegendes, hochstehendes Schutzpapier an, andererseits werden zu Störungen führende Erhebungen, wie hervorstehende Nägel, häufig nicht registriert.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, bei einer gattungsgemäßen Stapelvorrichtung die Palettenhöhe so bestimmen zu können, daß eine problemlose Übergabe des Zwischenstapels von der Hilfsstapelplattform auf die neue Palette möglich ist.
- Diese Aufgabe wird mit den kennzeichnenden Merkmalen des Patentanspruchs 1 gelöst.
- Nach der Erfindung wird bei der Bestimmung der Palettenhöhe die gesamte Palettenoberfläche abgetastet. Dabei kann das Tastelement nicht störende Erhebungen niederdrücken, die somit nicht registriert werden.
- Die Unteransprüche enthalten bevorzugte, da besonders vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung:
- Während die an seitlichen Schwenkhebeln befestigte Kufe nach Anspruch 2 eine konstruktiv vorteilhafte Ausgestaltung eines Tastelements enthält, ist nach Anspruch 2 das Tastelement vorteilhaft ortsfest im Bereich der Palettenzuführung zur Ablageplattform angeordnet. Somit läßt sich die Palettenhöhe beim Transport einer neuen Palette zu der Ablageplattform bestimmen.
- Patentanspruch 4 enthält eine vorteilhafte Anordnung zur Messung der vertikalen Auslenkung des Tastelements, um die maximale Auslenkung zu bestimmen.
- Der einstellbare Auflagedruck nach Anspruch 5 ermöglicht die Anpassung der Palettenhöhenbestimmung auf störende und nicht störende Erhebungen. Zweckmäßigerweise ist dazu das Tastelement mit einer doppelt wirkenden Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit verbunden, so daß sich der Auflagedruck vergrößern oder verkleinern läßt.
- Die Zeichnungen dienen zur Erläuterung der Erfindung anhand eines vereinfacht dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiels.
- Fig. 1 zeigt eine Stapelvorrichtung nach der Erfindung in Seitenansicht quer zur Laufrichtung der Bögen.
- Fig. 2 zeigt in einem vergrößerten Ausschnitt von Fig. 1 die Einrichtung zur Bestimmung der Palettenhöhe.
- Das Gestell der Abstapelvorrichtung weist vier Ständer 1, 2 auf, zwischen denen sich eine heb- und senkbare Ablageplattform 3 befindet. Die Ablegeplattform 3 ist bis in die Förderebene 4 der geschuppt zugeförderten Bogen 5 anhebbar und bis auf den Boden absenkbar, wo sie mit einem einlaufseitig angeordneten, durch den Zwischenraum zwischen den Ständern 1 führenden Zuförderer 6 für leere Paletten 7 fluchtet. Der Zuförderer 6 weist ebenso wie die Oberseite der Plattform 3 Fördermittel auf, z. B. Rollen, mit denen die Paletten 7 für einen Palettenwechsel in Laufrichtung der Bögen 5 transportiert werden können.
- In den einlaufseitigen Ständern 1 ist eine heb- und senkbare Hilfsstapelplattform 8 gelagert, die mittels eines Antriebs 9 horizontal in den Bereich der Ablageplattform 3 bewegt werden kann. Auf die Hilfsstapelplattform 8 werden die Bögen 5 zwischengestapelt, während volle Stapel abtransportiert und neue Paletten 7 in den Abstapelbereich transportiert werden. Beim Stapeln auf eine Palette 7, die auf der Ablageplattform 3 liegt, befindet sich die Hilfsstapelplattform 8 außerhalb des Stapelbereichs (in Fig. 1 links). Soweit ist die Abstapelvorrichtung bekannt und z. B. in der DE-PS 37 39 194 beschrieben.
- Zwischen den beiden einlaufseitigen Ständern 1 ist eine Einrichtung zur Bestimmung der Palettenhöhe angeordnet, die in Fig. 2 vergrößert dargestellt ist. Unterhalb der Führung 10 der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 und oberhalb des Palettenzuförderers 6 sind über die Arbeitsbreite zwei Quertraversen 11, 12 in gleicher Höhe befestigt. An der vorderen Quertraverse 11 sind zwei seitliche, in Bogenlaufrichtung weisende Schwenkhebel 13 angelenkt, zwischen deren freien Enden eine sich über die Arbeitsbreite erstreckende Kufe 14 befestigt ist. Die Länge der Schwenkhebel 13 und ihre Position ist so gewählt, daß die Kufe 14 bis nahe an den Boden (bis auf ca. 80 mm Abstand) absenkbar und bis in eine Position oberhalb der maximalen Höhe einer Palette 7 anhebbar ist und somit auf die Oberflächen der durchlaufenden Paletten 7 aufgelegt werden kann. Zum Anheben und Absenken der Kufe 14 dienen zwei seitliche, an der hinteren Ouertraverse 12 angelenkte doppelt wirkende Kolben-Zylinder-Einheiten 15, die jeweils an den Schwenkhebeln 13 angreifen. Zur Einstellung des Auflagedrucks der Kufe 14 auf den Paletten 7 ist der nach unten wirkende Druck in der Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit 15 mittels eines Feinregelventils einstellbar. Außerhalb der Arbeitsbreite ist an einer Seite an der Traverse 12 ein Seitenschild 16 mit einer senkrechten Führung 17 für eine mit der Kufe 14 verbundene, senkrechte Zahnstange 18 befestigt, die mit dem Ritzel 19 eines am Seitenschild 16 befestigten Winkelcodierers 20 kämmt. Der Winkelcodierer 20 registriert so die vertikale Auslenkung der Kufe 14 beim Durchlauf einer Palette 7.
- Beim Zufördern der leeren Paletten 7 zu der Ablageplattform 3 wird deren maximale Höhe h beim Durchlauf zwischen den beiden Ständern 1 gemessen und abgespeichert. Eine vor der Kufe 14 angeordnete Lichtschranke 21, die auf die Vorderkante einer Palette 7 anspricht, löst die Absenkung der Kufe 14 aus der oberen Ruheposition aus. Dazu wird der nach oben wirkende Druck in der Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit 15 vermindert, so daß die Kufe 14 aufgrund ihres Eigengewichtes absinkt und sich auf die Palettenoberfläche auflegt. Die Kufe 14 tastet die Oberfläche der Palette 7 beim Durchlauf ab, wobei der Winkelcodierer 20 jeweils die vertikale Auslenkung registriert. Der maximale Wert wird als Höhe h der Palette 7 abgespeichert. Der vom Gewicht der Kufe 14 abhängige Auflagedruck wird mittels der Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit 15 so eingestellt, daß nicht störende Erhebungen wie aufliegende Schutzpapiere, die aufgefaltet hochstehen, niedergedrückt und somit nicht registriert werden. Störende Erhebungen wie hervorstehende Nägel führen dagegen zu einer Auslenkung und werden registriert.
- Die abgespeicherte maximale Höhe h der Palette 7 dient anschließend dazu, die Annäherung der Ablageplattform 3 mit der aufliegenden Palette 7 von unten an die Hilfstapelplattform 8 zu steuern. Damit die Zufuhr von Bögen 5 bei einem Stapelwechsel nicht unterbrochen werden muß, wird auf der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 ein Zwischenstapel 22 gebildet, bis ein voller Stapel abtransportiert und eine neue Palette 7 unter die den Zwischenstapel 22 tragenden Hilfsplattform 8 bewegt wurde. Während des Zwischenstapelns bewegt sich die Hilfsplattform 8 kontinuierlich nach unten, um die Oberfläche des Zwischenstapels 22 etwa in Höhe der Zuförderebene 4 zu halten. Da der Zwischenstapel 22 auf die heranbewegte neue Palette 7 durch Herausziehen der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 abgelegt wird, ist es erforderlich, die neue Palette 7 bis auf einen geringen Sicherheitsabstand (ca. 10 mm) exakt unter der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 zu positionieren. Feste Erhebungen wie hervorstehende Nägel auf der Palettenoberfläche, würden zu Kollisionen mit der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 führen, falls sie nicht beim Anheben der Palette 7 berücksichtigt würden. Die Übergabe des Zwischenstapels 22 auf die Palette 8 nicht störende Erhebungen, wie aufgefaltete Schutzpapiere, dürfen dagegen nicht berücksichtigt werden, da andernfalls der Zwischenstapel 22 mit einer zu großen Fallhöhe auf die Palette 7 übergeben wird. Diese Anforderungen werden durch die vorstehend beschriebene Bestimmung der Palettenhöhe erfüllt.
- Die Bewegung einer neuen Palette 7 gegen die Unterseite der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 wird so gesteuert, daß ein an der Unterseite der Tragkonstruktion des Schlittens 8 angeordneter induktiver Näherungsschalter 23 als Referenzpunkt die Annäherung der Ablageplattform 3 registriert, wenn die Palette 7 noch ausreichend großen Abstand von der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 hat. Dieser bekannte Abstand wird dann durch Absenken der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 und Anheben der Ablageplattform 3 weiter vermindert bis der Abstand der Oberfläche der Ablageplattform 3 von der Hilfsstapelplattform 8 nur noch die gemessene Höhe der Palette plus 10 mm Sicherheitsabstand beträgt. Die Steuerung dieser weiteren Annäherungen erfolgt über zwei Winkelcodierer, von denen einer die vertikale Bewegung der Hilfsstapelplattform 8, der andere die vertikale Bewegung der Ablageplattform 3 mißt.
- Im vorliegenden Ausführungsbeispiel ist das Tastelement (Kufe 14) horizontal ortsfest angeordnet. Zur Abtastung der gesamten Palettenoberfläche wird die Palette relativ zum Tastelement bewegt. Ebenso ist es möglich, das Tastelement horizontal verfahrbar anzuordnen, so daß es über die gesamte Oberfläche einer stillstehenden Palette bewegt werden kann. So kann z. B. ein zwischen den Ständern 1, 2 bewegbares Tastelement die auf der Ablageplattform 3 aufliegenden Paletten 7 abtasten. Dann muß das Tastelement aus dem Ablagebereich in eine das Stapeln nicht störende Position bewegbar sein.
Claims (5)
- Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen, insbesondere Papier- oder Kartonbögen, auf eine Palette- mit einer heb- und senkbaren Ablageplattform (3), auf der die Palette (7) beim Stapeln aufliegt, und- mit einer in den Bereich der lageplattform (3) einfahrbaren Hilfstapelplattform (8) zum Zwischenstapeln der Bögen (5) während eines Palettenwechselsgekennzeichnet durch eine Einrichtung zur Bestimmung der Palettenhöhe mit einem vertikal beweglichen, auf die Palettenoberfläche auflegbaren und über die gesamte Palettenoberfläche bewegbaren Tastelement (14) und mit Mitteln zur Bestimmung der maximalen Auslenkung des Tastelements nach oben bei der Bewegung über die Palettenoberfläche.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Tastelement eine sich über die Arbeitsbreite erstreckende Kufe (14) ist, die am freien Ende von zwei seitlichen Schwenkhebeln (13) befestigt ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Tastelement (14) horizontal ortsfest neben der Ablageplattform (3) im Bereich der Palettenzuführung angeordnet ist und die Paletten (7) beim Transport zur Ablageplattform (3) abtastet.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Messung der Auslenkung des Tastelements (14) mittels einer am Tastelement senkrecht befestigten Zahnstange (18) erfolgt, die mit einem vertikal feststehenden Ritzel (19) kämmt, an dem ein Winkelkodierer (20) angeschlossen ist.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Tastelement (14) mit einstellbarem Druck auf der Palettenoberfläche aufliegt.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT9191112203T ATE104642T1 (de) | 1990-09-21 | 1991-07-20 | Vorrichtung zum stapeln von boegen. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4029919A DE4029919C1 (de) | 1990-09-21 | 1990-09-21 | |
| DE4029919 | 1990-09-21 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0476264A1 EP0476264A1 (de) | 1992-03-25 |
| EP0476264B1 true EP0476264B1 (de) | 1994-04-20 |
Family
ID=6414690
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP91112203A Expired - Lifetime EP0476264B1 (de) | 1990-09-21 | 1991-07-20 | Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5240369A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0476264B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE104642T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE4029919C1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2056529T3 (de) |
| FI (1) | FI914437A (de) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4125450C2 (de) * | 1991-08-01 | 1995-08-10 | Kodak Ag | Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung der Dicke von Papierblättern |
| DE4217816C2 (de) * | 1992-05-29 | 1995-01-26 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Einrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Auslage flächiger Druckprodukte |
| DE19642479A1 (de) | 1996-10-15 | 1998-04-16 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Einrichtung zur Führung vertikal verfahrbarer Bogenstapelträger |
| DE59901625D1 (de) * | 1998-02-25 | 2002-07-11 | Jagenberg Papiertech Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum stapeln von bögen |
| DE10045883A1 (de) * | 2000-09-14 | 2002-03-28 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Ausleger für eine flechige Bedruckstoffe verarbeitende Maschine |
| DE102007022908A1 (de) * | 2007-05-14 | 2008-11-20 | Krones Ag | Verfahren zum Be- und Entladen einer Palette und entsprechender Palettierer |
| GB0801889D0 (en) * | 2008-02-01 | 2008-03-12 | Meadwestvaco Packaging Systems | Twin packaging line and metering system |
| EP4389662A1 (de) * | 2022-12-21 | 2024-06-26 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Vorrichtung zum stapeln und/oder zuführen von blättern für einen drucker |
| CN116198898B (zh) * | 2023-04-20 | 2023-07-25 | 巴斯夫一体化基地(广东)有限公司 | 用于存储货物的仓库 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH504670A (de) * | 1969-08-12 | 1971-03-15 | Bjuro Vzaimozamenyaemosti V Me | Einrichtung zum Prüfen der Abmessungen von bewegten Werkstücken |
| DE2410775C2 (de) * | 1974-03-07 | 1982-09-30 | Enzinger-Union-Werke Ag, 6800 Mannheim | Förderbahnabschnitt für einzeln hintereinander ankommende Stückgüter |
| GB1581544A (en) * | 1976-06-29 | 1980-12-17 | Masson Scott Thrissell Eng Ltd | Sheet stacking apparatus |
| DE2758291C3 (de) * | 1977-12-27 | 1980-07-10 | Jagenberg-Werke Ag, 4000 Duesseldorf | Stapelwechselvorrichtung |
| IT1137511B (it) * | 1981-03-26 | 1986-09-10 | Ezio Curti | Dispositivo per impilare automaticamente e senza interruzione piastre di supporto per circuiti stampati,alimentate in modo continuo da un trasportatore |
| US4512701A (en) * | 1982-12-22 | 1985-04-23 | Olin Corporation | Pallet height sensing mechanism |
| DE3535113A1 (de) * | 1985-10-02 | 1987-04-23 | Jagenberg Ag | Bogenableger |
| DE3739194A1 (de) * | 1987-11-19 | 1989-06-01 | Jagenberg Ag | Vorrichtung zum abstapeln von boegen |
-
1990
- 1990-09-21 DE DE4029919A patent/DE4029919C1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1991
- 1991-07-20 ES ES91112203T patent/ES2056529T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-07-20 EP EP91112203A patent/EP0476264B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-07-20 AT AT9191112203T patent/ATE104642T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-07-20 DE DE59101435T patent/DE59101435D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-09-20 FI FI914437A patent/FI914437A/fi unknown
- 1991-09-20 US US07/762,844 patent/US5240369A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FI914437A0 (fi) | 1991-09-20 |
| ATE104642T1 (de) | 1994-05-15 |
| US5240369A (en) | 1993-08-31 |
| DE59101435D1 (de) | 1994-05-26 |
| DE4029919C1 (de) | 1992-04-02 |
| ES2056529T3 (es) | 1994-10-01 |
| EP0476264A1 (de) | 1992-03-25 |
| FI914437A (fi) | 1992-03-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE3730126C2 (de) | ||
| DE3718601C2 (de) | ||
| DE3621297C2 (de) | ||
| EP1724078A2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Abschieben mindestens eines Teilstapels mit mindestens einem plattenförmigen Werkstück von einem Reststapel | |
| EP0560112A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Zuführen von Zwischenlagen zu einem Stapel | |
| EP0476264B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen | |
| EP0316568B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Abstapeln von Bögen | |
| DE69015431T3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Papierzuführen/Stapeln für eine Bogendruckmaschine. | |
| CH638149A5 (de) | Staustation in einer faltschachtelpackmaschine. | |
| DE4131014A1 (de) | Bogenanleger | |
| DE19711406C1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen, insbesondere von geschuppt zugeförderten Papier- oder Kartonbögen auf Paletten | |
| EP0161513B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Paletten mit auf diesen abgesetzten Gegenständen, vorzugsweise Grosssäcken | |
| DE1531086A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Transport einzelner Tafeln von einem Stapel zu einer Verarbeitungsmaschine | |
| DE19807855C1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Stapeln von Bögen | |
| EP0896945B1 (de) | Einrichtung und Verfahren zum Stapeln von Stapelschichten aus Papier | |
| DE4101038A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum stapeln von boegen auf paletten | |
| AT506539A1 (de) | Fírdervorrichtung mit einem aufnahmemittel für eine trennlage | |
| CH658639A5 (de) | Verfahren und anordnung zum selbsttaetigen foerdern von bogen von einer druckerpresse zu einer bogenbindevorrichtung. | |
| DE2856295A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum anlegen von flachen gegenstaenden wie kartons o.dgl. fuer maschinen zum bearbeiten solcher gegenstaende | |
| DE19839923C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Abnahme von Folien von einem Folienstapel in einer Stapelstation und zur Ablage der abgenommenen Folien in einer Zusammenlegestation | |
| DE4403701C1 (de) | Stapel-Einrichtung | |
| CH678518A5 (en) | Sorting device for wood planks - has hooked support arm vertically movable on horizontally displaceable support and discharge station | |
| AT395311B (de) | Gabelstapelgeraet fuer aufteil- und sortieranlagen bei aufteilsaegemaschinen | |
| DE2038219C3 (de) | Automatischer Stapelanleger | |
| DE1810954A1 (de) | Maschine zum Stapeln von keramischen Platten,insbesondere Wand- und Fussbodenfliesen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB IT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19920212 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19930922 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB IT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19940420 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 104642 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19940515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19940420 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59101435 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19940526 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19940720 |
|
| EN | Fr: translation not filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19940916 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2056529 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19990614 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000720 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20000720 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050720 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20100726 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20100723 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59101435 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59101435 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20120110 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20110721 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20110721 |