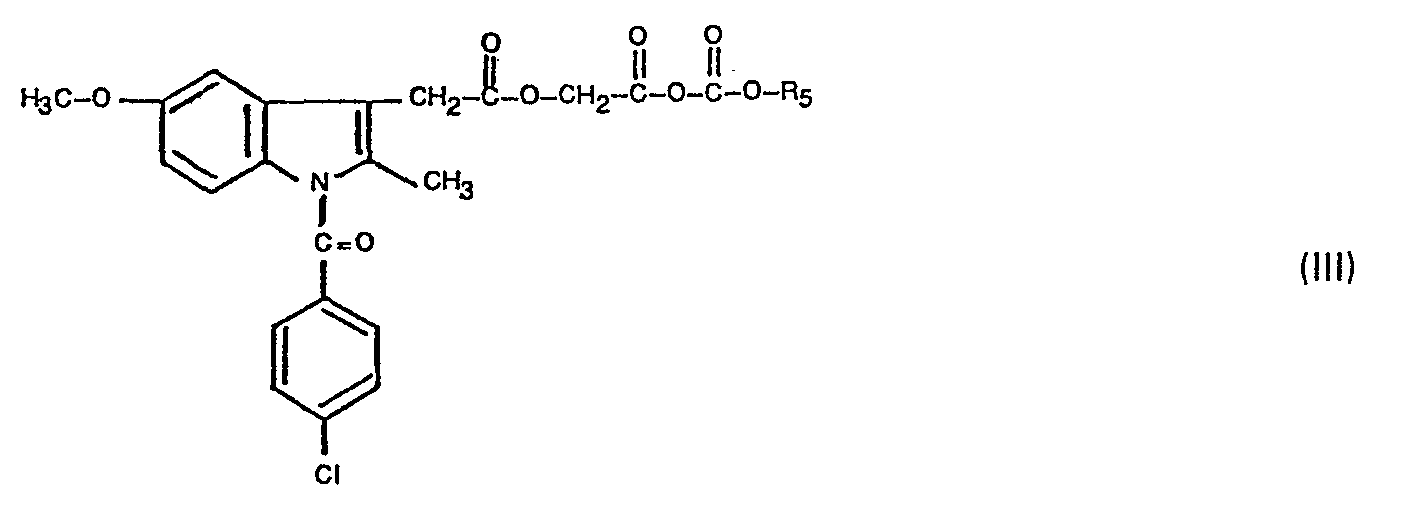EP0000741B1 - Indolacetoxyacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimittel - Google Patents
Indolacetoxyacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimittel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0000741B1 EP0000741B1 EP78100523A EP78100523A EP0000741B1 EP 0000741 B1 EP0000741 B1 EP 0000741B1 EP 78100523 A EP78100523 A EP 78100523A EP 78100523 A EP78100523 A EP 78100523A EP 0000741 B1 EP0000741 B1 EP 0000741B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- ace
- carbon atoms
- general formula
- group
- compounds
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 12
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title claims description 4
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 title claims description 3
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 title 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 29
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 22
- 150000003862 amino acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 18
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 11
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 9
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 claims description 5
- OLFABMKTCYHTND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[[2-[2-(1h-indol-2-yl)acetyl]oxyacetyl]amino]acetic acid Chemical class C1=CC=C2NC(CC(=O)OCC(=O)NCC(=O)O)=CC2=C1 OLFABMKTCYHTND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000003282 alkyl amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004414 alkyl thio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000002490 anilino group Chemical group [H]N(*)C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000440 benzylamino group Chemical group [H]N(*)C([H])([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 3
- AOGYCOYQMAVAFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorocarbonic acid Chemical class OC(Cl)=O AOGYCOYQMAVAFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004466 alkoxycarbonylamino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000006482 condensation reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 claims 1
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 95
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 18
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 14
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ether Substances CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- -1 indolacetoxyacetylamino Chemical group 0.000 description 11
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 11
- ANSUDRATXSJBLY-VKHMYHEASA-N methyl (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CO ANSUDRATXSJBLY-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 8
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 7
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Indomethacin Natural products CC1=C(CC(O)=O)C2=CC(OC)=CC=C2N1C(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229960000905 indomethacin Drugs 0.000 description 6
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000003110 anti-inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 150000003354 serine derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 5
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 4
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N (2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropansäure Chemical compound OC[C@H](N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-methionine Chemical compound CSCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 206010030113 Oedema Diseases 0.000 description 3
- FSXRLASFHBWESK-HOTGVXAUSA-N Phe-Tyr Chemical compound C([C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C=CC(O)=CC=1)C(O)=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 FSXRLASFHBWESK-HOTGVXAUSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 3
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Serine Natural products OCC(N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Trifluoroacetate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- IIDNACBMUWTYIV-VIFPVBQESA-N benzyl (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound OC[C@H](N)C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 IIDNACBMUWTYIV-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 3
- PFKFTWBEEFSNDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonyldiimidazole Chemical compound C1=CN=CN1C(=O)N1C=CN=C1 PFKFTWBEEFSNDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 3
- FSXRLASFHBWESK-UHFFFAOYSA-N dipeptide phenylalanyl-tyrosine Natural products C=1C=C(O)C=CC=1CC(C(O)=O)NC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 FSXRLASFHBWESK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- GKCXXDSWWDWUHS-BYPYZUCNSA-N ethyl (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)[C@@H](N)CO GKCXXDSWWDWUHS-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 3
- IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen chloride Substances Cl.Cl IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910000041 hydrogen chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229930182817 methionine Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 150000004702 methyl esters Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229960005190 phenylalanine Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BXRMEWOQUXOLDH-LURJTMIESA-N L-Histidine methyl ester Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 BXRMEWOQUXOLDH-LURJTMIESA-N 0.000 description 2
- COLNVLDHVKWLRT-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-phenylalanine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 COLNVLDHVKWLRT-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N L-tryptophane Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 2
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-tyrosine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 2
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tryptophan Natural products C1=CC=C2C(CC(N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FZNCGRZWXLXZSZ-CIQUZCHMSA-N Voglibose Chemical compound OCC(CO)N[C@H]1C[C@](O)(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O FZNCGRZWXLXZSZ-CIQUZCHMSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000008044 alkali metal hydroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000008052 alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000004649 carbonic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- FZFAMSAMCHXGEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloro formate Chemical compound ClOC=O FZFAMSAMCHXGEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013312 flour Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexamethylphosphoric triamide Chemical compound CN(C)P(=O)(N(C)C)N(C)C GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000015110 jellies Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920005610 lignin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N monobenzene Natural products C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002674 ointment Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- COLNVLDHVKWLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylalanine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 COLNVLDHVKWLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011435 rock Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229960001153 serine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- LPXPTNMVRIOKMN-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium nitrite Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]N=O LPXPTNMVRIOKMN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 2
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyrosine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N (2s)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid;(2s)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O.NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHOAKXBXYSJBGX-YFKPBYRVSA-N (2s)-3-hydroxy-2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]propanoic acid Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(O)=O FHOAKXBXYSJBGX-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ADFXKUOMJKEIND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dicyclohexylurea Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC(=O)NC1CCCCC1 ADFXKUOMJKEIND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LHJGJYXLEPZJPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4,5-trichlorophenol Chemical compound OC1=CC(Cl)=C(Cl)C=C1Cl LHJGJYXLEPZJPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-ylamino)-N-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound C1C(CC2=CC=CC=C12)NC1=NC=C(C=N1)C(=O)NCCC(N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2)=O VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical class NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MLXDUYUQINCFFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-acetyloxyacetic acid Chemical compound CC(=O)OCC(O)=O MLXDUYUQINCFFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-{[3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol Chemical compound OCC1OC(CO)(OC2OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C1O CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 244000105624 Arachis hypogaea Species 0.000 description 1
- 0 COC(C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(C(CCNC(OC)=O)N*)=O)=O)=O Chemical compound COC(C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(C(CCNC(OC)=O)N*)=O)=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 235000019739 Dicalciumphosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylamine Chemical class CNC ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004097 EU approved flavor enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glutamic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N L-alanine Chemical compound C[C@H](N)C(O)=O QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZGUNAGUHMKGQNY-ZETCQYMHSA-N L-alpha-phenylglycine zwitterion Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)C1=CC=CC=C1 ZGUNAGUHMKGQNY-ZETCQYMHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-O Methylammonium ion Chemical compound [NH3+]C BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 235000019483 Peanut oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001620634 Roger Species 0.000 description 1
- DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium laurylsulphate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfurous acid Chemical compound OS(O)=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DWAYENIPKPKKMV-ILKKLZGPSA-N [(2s)-3-(1h-imidazol-3-ium-4-yl)-1-methoxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]azanium;dichloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 DWAYENIPKPKKMV-ILKKLZGPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000004279 alanine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000008055 alkyl aryl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940024606 amino acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229940121363 anti-inflammatory agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002260 anti-inflammatory agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940124599 anti-inflammatory drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000005228 aryl sulfonate group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- BVCTWRNVKLXEQC-HNNXBMFYSA-N benzyl (2s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate Chemical class C([C@H](N)C(=O)OCC=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 BVCTWRNVKLXEQC-HNNXBMFYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VNBZYMVEHPBBJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl 2-amino-2-phenylacetate Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1C(N)C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 VNBZYMVEHPBBJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NRDQFWXVTPZZAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl carbonochloridate Chemical compound CCCCOC(Cl)=O NRDQFWXVTPZZAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001506 calcium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001718 carbodiimides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012876 carrier material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001805 chlorine compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001860 citric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012024 dehydrating agents Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008121 dextrose Substances 0.000 description 1
- NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K dicalcium phosphate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940038472 dicalcium phosphate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910000390 dicalcium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007865 diluting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 235000019264 food flavour enhancer Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013922 glutamic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004220 glutamic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002306 glutamic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002410 histidine derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrazine monohydrate Substances O.NN IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- WWODPCYJOLNYCQ-JGAZGGJJSA-N methyl (2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]propanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoate hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.NCC(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)OC)CC1=CC=CC=C1 WWODPCYJOLNYCQ-JGAZGGJJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SWVMLNPDTIFDDY-FVGYRXGTSA-N methyl (2s)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoate;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 SWVMLNPDTIFDDY-FVGYRXGTSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SANNKFASHWONFD-LURJTMIESA-N methyl (2s)-3-hydroxy-2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]propanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C SANNKFASHWONFD-LURJTMIESA-N 0.000 description 1
- MGJXBDMLVWIYOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylazanide Chemical compound [NH-]C MGJXBDMLVWIYOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013336 milk Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008267 milk Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004080 milk Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000012452 mother liquor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003472 neutralizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000312 peanut oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001592 potato starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006340 racemization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000376 reactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- FSYKKLYZXJSNPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N sarcosine Chemical class C[NH2+]CC([O-])=O FSYKKLYZXJSNPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008159 sesame oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011803 sesame oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001509 sodium citrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K sodium citrate Chemical compound O.O.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 235000011121 sodium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium hydroxide Substances [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000019333 sodium laurylsulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000010288 sodium nitrite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000001273 sulfonato group Chemical class [O-]S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 150000003467 sulfuric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000006188 syrup Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000020357 syrup Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000012222 talc Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003892 tartrate salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229960002898 threonine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000015112 vegetable and seed oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008158 vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K5/00—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K5/04—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof containing only normal peptide links
- C07K5/08—Tripeptides
- C07K5/0815—Tripeptides with the first amino acid being basic
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with one carbocyclic ring
- C07D209/04—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles
- C07D209/10—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D209/18—Radicals substituted by carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
- C07D209/26—Radicals substituted by carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals with an acyl radical attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D209/28—1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-indolyl-3-acetic acid, substituted in position 5 by an oxygen or nitrogen atom; Esters thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K5/00—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K5/04—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof containing only normal peptide links
- C07K5/06—Dipeptides
- C07K5/06008—Dipeptides with the first amino acid being neutral
- C07K5/06078—Dipeptides with the first amino acid being neutral and aromatic or cycloaliphatic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K5/00—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K5/04—Peptides containing up to four amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof containing only normal peptide links
- C07K5/08—Tripeptides
- C07K5/0802—Tripeptides with the first amino acid being neutral
- C07K5/0804—Tripeptides with the first amino acid being neutral and aliphatic
- C07K5/0806—Tripeptides with the first amino acid being neutral and aliphatic the side chain containing 0 or 1 carbon atoms, i.e. Gly, Ala
Definitions
- the present invention relates to new indolacetoxyacetylamino acid derivatives, processes for their preparation and their use in medicaments, in particular in anti-inflammatories and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- physiologically compatible addition salts can be formed with organic and inorganic bases.
- salts are preferably sodium salts, potassium, magnesium, ammonium, methylammonium, dimethylammonium salts or the 2-hydroxy, ethyl ammonium salt.
- addition salts which are physiologically compatible can also be formed with acids.
- salts are halides, preferably chlorides, sulfates, citrates, tartrates, maleinates and sulfonates.
- the compounds of general formula (I) according to the invention have a more advantageous activity than the indomethacinserine derivatives of DOS 2 413 125 known from the prior art, as can be seen from the following table.
- the active substances were administered orally to rats half an hour before the kaolin application (dose: see columns 2 and 4).
- dose see columns 2 and 4
- the inhibition was determined 4 hours after the edema challenge to control groups (see columns 3 and 5).
- the serine derivative according to the invention was compared with the known serine derivative of indomethacin by determining DE 50 in each case. This shows that the serine derivative according to the invention has a DE 50 of 2.14 mg / kg body weight in rats after oral administration and a DE 50 of 2.17 mg / kg body weight in subcutaneous administration. The corresponding DE so values of the serine derivative of indomethacin were in any case over 100 mg / kg body weight.
- reaction sequence of variant a) can be represented by the following formula:
- chloroformic acid esters of the general formula (11) which can be used as starting compounds are known and the ACE-OH used as starting compound is also known (DOS 2 234 651).
- the mixed anhydrides of the general formula (111) formed as an intermediate are new, but cannot be identified, since - like the majority of the mixed anhydrides known in the literature - they decompose during processing (cf.Houben-Weyl, Methods of Organic Chemistry, 4th edition, volume 15/2, page 17, 3rd paragraph).
- diluents inert organic solvents are suitable as diluents, in particular those which are polar aprotic. Examples include: tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethylformamide, hexamethylphosphoric triamide.
- the reaction is conveniently carried out in the presence of acid binders.
- acid binders All customary agents which are able to bind the hydrogen chloride released can be used as the acid binder. These preferably include alkali metal hydroxides and carbonates or organic bases such as pyridine and triethylamine.
- reaction temperatures are expediently below 0 ° C., since otherwise racemizations occur; they can be varied within a certain range.
- temperatures between 0 to -25 ° C, preferably between -10 and -20 ° C.
- the reaction is usually carried out at normal pressure.
- the reaction time is between 6 and 24 hours, preferably 14 to 20 hours.
- Working up is preferably carried out by evaporation in vacuo, taking up in one of the customary organic solvents, neutral washing, optionally cleaning on silica gel and recrystallization.
- reaction scheme If an activated ester of the general formula (V) is used for the reaction instead of a mixed anhydride of ACE-OH, the reaction of variant b) can be represented by the following reaction scheme:
- the compounds of the general formula (V) used as reactants are not yet known, but can be prepared in a manner known per se by reacting 1 mol of ACE-OH and 1 mol of the correspondingly substituted phenol in a polar aprotic organic solvent, e.g. Tetrahydrofuran, in the presence of 1 mole of a carbodiimide, e.g. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide or carbonyldiimidazole can be obtained in about 1 1/2 hour reaction time at room temperature.
- a polar aprotic organic solvent e.g. Tetrahydrofuran
- Process (V) (I) according to the invention is advantageously carried out in the presence of diluents.
- diluents are the organic solvents known for this reaction, preferably dimethylformamide, dioxane, pyridine or their mixtures with water.
- addition salts of (IV) are used for reactions, the process is advantageously carried out in the presence of acid binders.
- acid binders include: alkali metal hydroxides, carbonates or strong organic amines, preferably triethylamine.
- the reaction temperatures can be varied within a certain range. Normally one works at 15 to 25 ° C, since the reaction times are disproportionately longer at lower temperatures, but the formation of racemates is promoted at higher temperatures. A certain racemate formation cannot be ruled out even in the reaction at room temperature.
- the process is usually carried out at normal pressure.
- 1 mol of the amino acid derivative (IV) is preferably used per mole of the activated ester (V).
- Working up is expediently carried out by diluting the mixture with water, taking it up in a suitable organic solvent, neutralizing, evaporating and recrystallizing from suitable solvents.
- the serine derivatives of the general formula (VI) used as starting compounds are known.
- the reaction is preferably carried out in the presence of diluents.
- Polar aprotic organic solvents can be used as diluents. Examples include tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, dimethylformamide, hexamethylphosphoric triamide.
- the reaction according to the invention is preferably carried out in the presence of a dehydrating agent.
- a dehydrating agent examples include dicyclohexylcarbodiimide or carbonyldiimidazole in the presence of catalytic amounts of a basic catalyst, preferably sodium hydride.
- reaction temperatures can be varied over a wide range; Usually one works between 10 and 40 ° C, preferably between 15 and 25 ° C.
- ACE-OH 1 mol of the ACE-OH is first reacted with 1 mol of carbonyldiimidazole and 1 mol of the amino acid derivative is only added after CO 2 evolution has ended.
- Working up is carried out in a conventional manner, preferably by evaporation in vacuo, taking up in a suitable solvent and cleaning on silica gel.
- the amino protective group R 6 is cleaved off according to the methods known from the literature in peptide chemistry.
- the new active ingredients can be converted in a known manner into the customary formulations, such as tablets, capsules, dragées, pills, granules, aerosols, syrups, emulsions, suspensions, solutions, ointments, gels, creams, jellies, using inert, non-toxic, pharmaceutically suitable Carriers or solvents.
- the therapeutically active compound should be present in a concentration of about 0.5 to 90% by weight of the total mixture, i.e. in amounts sufficient to achieve the dosage range indicated.
- the formulations are prepared, for example, by stretching the active ingredients with solvents and / or carriers, optionally using emulsifiers and / or dispersants, e.g. if water is used as the diluent, organic solvents can optionally be used as auxiliary solvents.
- the application takes place in the usual way, preferably orally or parenterally, locally, intramuscularly or intravenously.
- tablets in addition to the carrier substances mentioned, can also contain additives such as sodium citrate, calcium carbonate and dicalcium phosphate, together with various additives such as starch, preferably potato starch, gelatin and the like.
- Lubricants such as magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate and talc can also be used for tableting.
- the active ingredients can be mixed with various flavor enhancers or colorants in addition to the auxiliaries mentioned.
- solutions of the active ingredients can be used using suitable liquid carrier materials.
- the dosage is about 10 up to 200, especially 30 to 80 mg per dose.
- the compound is formed in a known manner by adding trifluoroacetic acid to the compound from Example 15.
- Example 15 analogous to Example 15 from 10.15 g ACE-OH and 5.7 g Boc-Serinethylester.
- a suspension of 0.005 mol of phenylalanyl tyrosine methyl ester trifluoroacetate in 15 ml of absolute dimethylformamide is initially mixed with stirring at 0 ° C. with 0.005 mol of triethylamine and after 10 minutes with 0.005 mol of ACE-2,4,5-trichlorophenyl ester. After stirring for 2 hours, lastly at room temperature, 150 ml of water are added to the reaction mixture, the mixture is extracted three times with ethyl acetate and the organic phase is extracted three times with nHCl solution. The solution is then washed neutral with water, dried over Na 2 S0 4 and evaporated. After recrystallization from acetone / petroleum ether, 84% of theory of N-ACE-phenylalanyl tyrosine methyl ester of mp 131 to 132 ° C. is obtained.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft neue Indolacetoxyacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung in Arzneimitteln, insbesondere in Entzündungshemmern und Antirheumatika.
-
- m und n für die Ziffern 0 oder 1 stehen,
- X für eine -HN- oder ―OCH2-Gruppe steht,
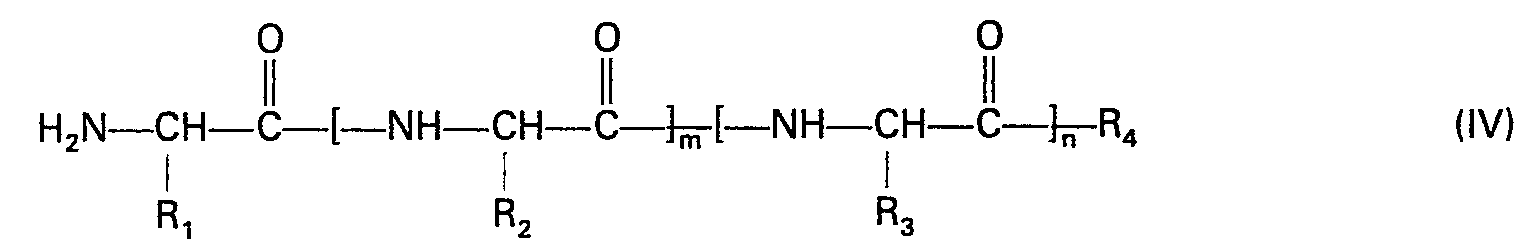
- R1, R2 und R3 gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für Wasserstoff, eine gegebenenfalls durch Hydroxy, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen, Alkylthio mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen oder durch Phenalkyloxycarbonylamino mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylteil, substituiertes Alkyl mit 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen, oder für eine Phenyl- oder Phenalkylgruppe mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylteil, wobei die Phenylringe gegebenenfalls durch Trifluormethyl, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen, Hydroxy oder Halogen substituiert sind oder für eine Heterocyclusmethylgruppe mit 5 bis 6 Ringgliedern, in welcher 1 oder 2 Glieder durch Stickstoff ersetzt sein können und an welche gegebenenfalls ein Benzolring annelliert ist, stehen oder für den Fall, daß m und n jeweils 0 bedeuten R1 zusätzlich für eine Aminogruppe, eine Alkoxycarbonylaminogruppe oder eine Phenalkoxycarbonylaminogruppe mit jeweils 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkoxyteil steht,
- R4 für Hydroxy, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen, Phenalkoxy mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkoxyteil, Amino, Alkylamino mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylteil, Benzylamino oder Phenylamino steht,
- Es wurde gefunden, daß man die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (1), in welcher X, m, n und R, bis R4 die oben angeführte Bedeutung haben, erhält, wenn man
- a) [1-(4-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolyl)acetoxyessigsäure (nachfolgend als ACE-OH bezeichnet) mit Chlorameisensäureestern der allgemeinen Formel
- R5 für eine Alkylgruppe mit 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen steht,
zu gemischten Anhydriden der allgemeinen Formel (III)- R5 die oben angegebene Bedeutung hat,
umsetzt und diese mit Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (IV)- m, n und R, bis R4 die in Anspruch 1 angeführte Bedeutung haben, zur Reaktion bringt, oder
- b) die Verbindung ACE-OH mit einem entsprechend substituierten Phenol zu einem aktivierten Ester der allgemeinen Formel
- Y für 2 bis 5 Halogenatome oder 1 bis 2 Nitrogruppen steht,
kondensiert und mit Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (IV) umsetzt oder - c) für den Fall, daß Hydroxylgruppen enthaltende Aminosäurederivate esterartig verknüpft werden sollen, die Verbindung ACE-OH mit Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (VI)
- R4 die oben angeführte Bedeutung hat und
- R6 für eine in der Peptidchemie übliche Aminoschutzgruppe steht,
- Für den Fall, daß die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) eine freie Säuregruppe enthalten (R4 = OH), können mit organischen und anorganischen Basen physiologisch verträgliche Additionssalze gebildet werden.
- Als Beispiele solcher Salze seien vorzugsweise genannt Natriumsalze-, Kalium-, Magnesium-, Ammonium-, Methylammonium-, Dimethylammoniumsalze oder auch das 2-Hydroxye,thyl- ammoniumsalz.
- Für den Fall, daß die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) eine freie Aminogruppe aufweisen, können ebenfalls mit Säuren physiologisch verträgliche Additionssalze gebildet werden.
- Als Beispiele solcher Salze seien genannt Halogenide, vorzugsweise Chloride, Sulfate, Citrate, Tartrate, Maleinate und Sulfonate.
- Überraschenderweise zeigen die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) eine vorteilhaftere Wirksamkeit als die aus dem Stand der Technik bekannten Indometacinserinderivate der DOS 2 413 125, wie aus der folgenden Tabelle hervorgeht.
- In dieser Tabelle werden die erfindungsgemäßen Aminosäurederivate den entsprechenden Aminosäurederivaten des Indometacins gegenübergestellt. Als pharmakologisches Testmodell zur Bestimmung der entzündungshemmenden Wirkung wurde das Kaolinödem an der Rattenpfote (vgl. KEMPER et al, Z. ges. exp. Med. 131 (1959), 407) verwendet. Hierbei zeigte es sich, daß die erfindungsgemäßen Aminosäurederivate überraschenderweise eine deutlich stärkere Wirkung zeigen als die aus dem Stand der Technik bekannten Aminosäurederivate des Indometacins (vgl. DT-OS 2 413 125).
-
- Weiterhin wurde das erfindungsgemäße Serinderivat mit dem bekannten Serinderivat des Indometacins verglichen, indem jeweils die DE50 ermittelt wurde. Hierbei zeigt sich, daß das erfindungsgemäße Serinderivat bei Ratten nach oraler Applikation eine DE50 von 2,14 mg/kg Körpergewicht und bei subkutaner Applikation eine DE50 von 2,17 mg/kg Körpergewicht besitzen. Die entsprechenden DEso - Werte des Serinderivates von Indometacin lagen in jedem Fall über 100 mg/kg Körpergewicht.
- Es wurden eine weitere Anzahl von Aminosäurederivaten des Indometacins, die bisher noch nicht bekannt waren, hergestellt und in dem obengenannten Testmodell zur Bestimmung der Entzündungshemmung geprüft. Hierbei zeigte sich, daß diese Derivate nach oraler Verabreichung von 50 bzw. 100 mg-Dosen nur eine sehr geringe oder keine entzünungshemmende Wirkung besitzen, wie aus der folgenden Aufstellung ersichtlich ist.
- Glutaminsäurederivat (178-180°C; 100 mg-kg; 3,5%);
- Glutaminsäuredibenzylesterderivat (143-144°C; 50 mg/kg; 6,6%);
- Tyrosinbenzylesterderivat (124-126°C; 100 mg/kg; 0,0%);
- Phenylglycinbenzylesterderivat (148-151 °C; 100 mg/kg; 0,0%);
- Tryptophenbenzylesterderivat (164-165°C; 100 mg/kg; 0,0%);
- Histidinderivat (230°C/Zers.; 50 mg/kg; 10,6%);
- N-Methylglycinderivat (165-166°C; 100 mg/kg; 21%);
- Histindinbenzylesterderivat (218-219°C; 100 mg/kg; 0,0%);
- (in Klammern die Angaben für Schmelzpunkt, Menge der oral verabreichten Substanz und Ödemhemmung in %).
- Demgegenüber zeigen die erfindungsgemäßen Aminosäurederivate überraschenderweise eine deutlich bessere entzündungshemmende Wirkung, wie aus der folgenden Aufstellung ersichtlich ist.
- N-ACE-Phenylalanyltyrosinmethylester (Beispiel 19; 12,5 mg/kg; 52,8%);
- N-ACE-Glycylalanylphenylalanylmethylester (Beispiel 20; 50 mg/kg; 42%);
- N-ACE-Phenylalanin DE50 (Beispiel 7; 5,1 mg/kg);
- N-ACE-Methionin (Beipiel 3; 25 mg/kg; 49,7%);
- N-ACE-O-Methylserin DE50 (Beispiel 10; 27,9 mg/kg);
- N-ACE-Serinmethylester DE50 (Beispiel 1; 19,7 mg/kg);
- O-ACE-Serinethylester (Beispiel 18; 12,5 mg/kg; 49,7%);
- O-ACE-Serinmethylester (Beispiel 16; 25 mg/kg; 51,1%).
- Diese Testergebnisse zeigen eindeutig die überraschend vorteilhafte Wirkung der erfindungsgemäßen Aminosäurederivate. Bei Kenntnis des Standes der Technik konnte nicht erwartet werden, daß die Einführung eines Aminosäureesters in die ACE-Verbindung einen so sprunghaften Wirkungsanstieg verursacht. Man hätte vielmehr erwarten müssen, daß die Wirkung der erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen mit der Wirkung der entsprechenden Indometacin-Aminosäurederivate vergleichbar wäre.
-
- Die als Ausgangsverbindungen verwendbaren Chlorameisensäureester der allgemeinen Formel (11) sind bekannt und die als Ausgangsverbindung verwendete ACE-OH ist ebenfalls bekannt (DOS 2 234 651).
- Die als Zwischenprodukt gebildeten gemischten Anhydride der allgemeinen Formel (111) sind neu, können aber nicht indentifiziert werden, da sie sich - wie auch der überwiegende Teil der literatur- bekannten gemischten Anhydride - bei der Aufarbeitung zersetzen (vgl. Houben-Weyl, Methoden der Organischen Chemie, 4. Auflage, Band 15/2, Seite 17, 3. Absatz).
- Die als Ausgangsverbindungen verwendbaren Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (IV) sind weitgehend literaturbekannt oder können nach bekannten Methoden hergestellt werden (vgl. u.a. Houben-Weyl, Methoden der organischen Chemie, 4. Auflage, Band 15/1 und 2).
- Die Reaktion erfolgt zweckmäßig in Gegenwart von Verdünnungsmitteln. Als Verdünnungsmittel kommen inerte organische Lösungsmittel in Frage, insbesondere solche, die polar aprotisch sind. Beispielhaft seien genannt: Tetrahydrofuran, Dioxan, Dimethylformamid, Hexamethylphosphorsäuretriamid.
- Die Reaktion erfolgt zweckmäßig in Gegenwart von Säurebindern. Als Säurebinder können alle üblichen Mittel verwendet werden, welche den freiwerdenden Chlorwasserstoff zu binden vermögen. Hierzu gehören vorzugsweise Alkalihydroxide und -carbonate oder organische Basen wie Pyridin und Triethylamin.
- Die Reaktionstemperaturen liegen zweckmäßigerweise unterhalb von 0°C, da andernfalls Racemisierungen auftreten; sie können in einem gewissen Bereich variiert werden.
- Im allgemeinen arbeitet man bei Temperaturen zwischen 0 bis -25°C, vorzugsweise zwischen -10 und -20°C.
- Die Umsetzung erfolgt üblicherweise bei Normaldruck.
- Bei der Durchführung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens setzt man vorzugsweise auf 1 Mol ACE-OH, 1 Mol Chlorameisensäureester, 1 Mol des Aminosäurederivates sowie 1 Mol des Säurebinders ein.
- Die Reaktionszeit liegt zwischen 6 und 24 Stunden, vorzugsweise bei 14 bis 20 Stunden.
- Die Aufarbeitung erfolgt vorzugsweise durch Eindampfen im Vakuum, Aufnehmen in eins der üblichen organischen Lösungsmittel, Neutralwaschen, gegebenenfalls Reinigen an Kieselgel und Rekristallisation.
-
- Die als Reaktionspartner verwendeten Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (V) sind bisher nicht bekannt, können aber in an sich bekannter Weise durch Umsetzung von 1 Mol ACE-OH und 1 Mol des entsprechend substituierten Phenols in einem polar aprotischen organischen Lösungsmittel, wie z.B. Tetrahydrofuran, in Gegenwart von 1 Mol eines Carbodiimids, wie z.B. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid oder Carbonyldiimidazol in etwa 1 1/2-stündiger Reaktionszeit bei Raumtemperatur erhalten werden.
- Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren (V) (I) erfolgt zweckmäßig in Gegenwart von Verdünnungsmitteln. Als Verdünnungsmittel kommen die für diese Reaktion literatur-bekannten organischen Lösungsmittel, vorzugsweise Dimethylformamid, Dioxan, Pyridin oder deren Gemische mit Wasser in Frage.
- Soweit Additionssalze von (IV) zu Reaktionen verwendet werden, erfolgt das Verfahren zweckmäßig in Gegenwart von Säurebindern. Beispielhaft seien genannt: Alkalihydroxide, -carbonate oder starke organische Amine, vorzugsweise Triethylamin.
- Die Reaktionstemperaturen können in einem gewissen Bereich variiert werden. Normalerweise arbeitet man bei 15 bis 25°C, da bei niedrigeren Temperaturen die Reaktionszeiten unverhältnismäßig verlängert werden, bei höheren Temperaturen jedoch die Racematbildung gefördert wird. Eine gewisse Racematbildung ist auch bei der Reaktion bei Raumtemperatur nicht auszuschließen./
- Das Verfahren wird üblicherweise bei Normaldruck durchgeführt.
- Bei der Durchführung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens wird vorzugsweise pro Mol des aktivierten Esters (V) 1 Mol des Aminosäurederivates (IV) eingesetzt. Die Aufarbeitung erfolgt zweckmäßigerweise durch Verdünnen des Ansatzes mit Wasser, Aufnehmen in einem geeigneten organischen Lösungsmittel, Neutralisieren, Eindampfen und Rekristallisieren aus geeigneten Lösungsmitteln.
-
- Die als Ausgangsverbindungen verwendeten Serinderivate der allgemeinen Formel (VI) sind bekannt. Die Reaktion erfolgt vorzugsweise in Gegenwart von Verdünnungsmitteln. Als Verdünnungsmittel können polar aprotische organische Lösungsmittel verwendet werden. Beispielhaft seien genannt Tetrahydrofuran, Dioxan, Dimethylformamid, Hexamethylphosphorsäuretriamid.
- Die erfindungsgemäße Reaktion erfolgt vorzugsweise in Gegenwart eines wasserentziehenden Mittels. Beispielhaft seien genannt Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid oder Carbonyldiimidazol in Gegenwart katalytischer Mengen eines basischen Katalysators, vorzugsweise Natriumhydrid.
- Die Reaktionstemperaturen können in größerer Breite variiert werden; üblicherweise arbeitet man zwischen 10 und 40°C, vorzugsweise zwischen 15 und 25°C.
- Zweckmäßigerweise bringt man zunächst 1 Mol der ACE-OH mit 1 Mol Carbonyldiimidazol zur Reaktion und fügt 1 Mol des Aminosäurederivates erst nach beendeter CO2-Entwicklung hinzu. Die Aufarbeitung erfolgt in üblicher Weise, vorzugsweise durch Eindampfen im Vakuum, Aufnehmen in ein geeignetes Lösungsmittel und Reinigen an Kieselgel. Die Abspaltung der Aminoschutzgruppe R6 erfolgt nach den in der Peptidchemie üblichen literaturbekannten Methoden.
- Als neue Wirkstoffe seien beispielhaft genannt:
- N―ACE-Serinmethylester;
- N-ACE-Serin;
- N-ACE-Methionin;
- N-ACE-Tyrosin;
- N-ACE-Tryptophan;
- N-ACE-DL-Threonin;
- N-ACE-Phenylalanin;
- N-ACE-Serin-N'-methylamid;
- N-ACE-Histidinmethylester;
- N-ACE-Serinbenzylester;
- O-ACE-Serinmethylester;
- O-ACE-Serinethylester;
- N-ACE-Phenylalanyltyrosinmethylester;
- N-ACE-Glycylalanylphenylalaninmethylester;
- N-a-ACE-N-y-benzyloxycarbonyldiaminobutyrylphenylalanylphenylalaninmethylester.
-
- Die neuen Wirkstoffe können in bekannter Weise in die üblichen Formulierungen überführt werden wie Tabletten, Kapseln, Dragees, Pillen, Granulate, Aerosole, Sirupe, Emulsionen, Suspensionen, Lösungen, Salben, Gele, Cremes, Gallerten, unter Verwendung inerter, nichttoxischer, pharmazeutisch geeigneter Trägerstoffe oder Lösungsmittel. Hierbei soll die therapeutisch wirksame Verbindung jeweils in einer Konzentration von etwa 0,5 bis 90 Gew.-% der Gesamtmischung vorhanden sein, d.h. in Mengen, die ausreichend sind, um den angegebenen Dosierungsspielraum zu erreichen.
- Die Formulierungen werden beispielsweise hergestellt durch Verstrecken der Wirkstoffe mit Lösungsmitteln und/oder Trägerstoffen, gegebenenfalls unter Verwendung von Emulgiermitteln und/ oder Dispergiermitteln, wobei z.B. im Falle der Benutzung von Wasser als Verdünnungsmittel gegebenenfalls organische Lösungsmittel als Hilfslösungsmittel verwendet werden können.
- Als Hilfsstoffe seien beispielhaft aufgeführt:
- Wasser, nichttoxische organische Lösungsmittel wie Paraffine (z.B. Erdölfraktionen), pflanzliche Ole (z.B. Erdnuß-/Sesamöl), Alkohole (z.B. Ethylalkohol, Glycerin), Glykole (z.B. Propylenglykol, Polyethylenglykol); feste Trägerstoffe wie z.B. natürliche Gesteinsmehle (z.B. Kaoline, Tonerden, Talkum, Kreide), synthetische Gesteinsmehle (z.B. hochdisperse Kieselsäure, Silikate), Zucker (z.B. Roh-, Milch- und Traubenzucker); Emulgiermittel wie nichtionogene und anionische Emulgatoren (z.B. Polyoxyethylen-Fettsäureester, Polyoxyethylen-Fettalkohol-Ether, Alkylsulfonate und Arylsulfonate), Dispergiermittel (z.B. Lignin, Sulfitablaugen, Methylcellulose, Stärke und Polyvinylpyrrolidon) und Gleitmittel (z.B. Magnesiumstearat, Talkum, Stearinsäure und Natrimlaurylsulfat).
- Die Applikation erfolt in üblicher Weise, vorzugsweise oral oder parenteral, lokal, intramuskulär oder intravenös.
- Im Falle der oralen Anwendung können Tabletten, selbstverständlich außer den genannten Trägerstoffen auch Zusätze wie Natriumcitrat, Calciumcarbonat und Dicalciumphosphat, zusammen mit verschiedenen Zuschlagstoffen wie Stärke, vorzugsweise Kartoffelstärke, Gelatine und dergleichen enthalten.
- Weiterhin können Gleitmittel wie Magnesiumstearat, Natriumlaurylsulfat und Talkum zum Tablettieren mitverwendet werden. Im Falle wäßriger Suspensionen und/oder Elixiere, die für orale Anwendungen gedacht sind, können die Wirkstoffe außer mit den genannten Hilfsstoffen mit verschiedenen Geschmacksaufbesserern oder Farbstoffen versetzt werden.
- Für den Fall der parenteralen Anwendung können Lösungen der Wirkstoffe unter Verwendung geeigneter flüssiger Trägermaterialien eingesetzt werden.
- Für den Fall der lokalen Anwendung kommen vorzugsweise Lösungen, Emulsionen, Salben, Gele, Cremes, Aerosole oder Gallerten mit geeigneten vorgenannten Hilfsstoffen in Betracht.
- Im allgemeinen hat es sich als vorteilhaft erwiesen, bei oraler Applikation Mengen von etwa 1 bis 100 mg, insbesondere 10 bis 40 mg pro Dosis bei 2- bis 3-maliger täglicher Verabreichung zur Erzielung wirksamer Ergebnisse einzusetzen, bei rektaler Applikation beträgt die Dosierung etwa 10 bis 200, insbesondere 30 bis 80 mg pro Dosis.
-
-
-
- In gleicher Weise können hergestellt werden:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- [α]20 D = +7,3 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- [α]20 D = +4,9 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [a]ö =-4,6 (c=0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [α]20 D = +61,8 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [α]20 D= 0 (c=0,5%: Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [α]20 D = +3,2 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- Fp. 132 bis 134°C, Ausbeute 2,3 g = 80,4% der Theorie.
- Es handelt sich um ein Zwischenprodukt für die Herstellung der folgenden Verbindungen.
-
- Nach mehrstündigem Rühren und Stehen bei Raumtemperatur wird der Ansatz mit Wasser verdünnt und mehrfach mit Ethylenchlorid extrahiert. Die Ethylenchloridlösung wird mit nHCI ausgeschüttelt und mit Wasser neutralgewaschen. Die organische Phase wird anschließend über Na2S04 getrocknet, filtriert und eingedampft. Der Rückstand wird in Chloroform/Methanol (9:1) an Kieselgel gereinigt.
- Fp. 119°C, Ausbeute 3,7 g = 34% der Theorie.
- [α]20 D = +3,5 (c = 3,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- Fp. 158 bis 159°C, Ausbeute 67% der Theorie.
- [α]20 D = 10,9 (c=0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- In dieser Lösung wird eine Lösung von 2,25 g (0,01 Mol) N-Bac-Serinmethylester in 10 ml Tetrahydrofuran in Gegenwart katalytischer Mengen von Natriumhydrid hinzugefügt und 7 Stunden bei 35°C gerührt. Anschließend wird die Lösung bei 3 Torr eingedampft, der Rückstand wird in Ethylacetat aufgenommen und an Kieselgel gereinigt. Die Verbindung ist ein Öl. Ausbeute 5,1 g (=82% der Theorie).
-
- Fp. 69 bis 70°C, Ausbeute 65% der Theorie.
- [α]20 D = +0,8 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- Fp. 99 bis 100°C, Ausbeute 6,2 g (Rohprodukt).
-
- Fp. 56 bis 58°C, Ausbeute 77% der Theorie.
- [α]20 D =-2,4 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [α]20 D = -5,2 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
-
- [α]20 D = -7,2 (c = 0,5; Dimethylformamid).
-
- 53 g (0,12 Mol) N-α-Formyl-N-γ-benzyloxycarbonyldiaminobutyrylphenylalaninmethylester werden bei 40°C in 400 ml Methanol gelöst und mit 10 g (ca. 0,16 Mol) 80 %igem Hydrazinhydrat versetzt. Nach 24-stündigem Stehen bei Raumtemperatur wird der ausgefallene Niederschlag abgesaugt, die Mutterlauge auf 50 ml eingeengt und erneut zur Kristallisation gebracht.
- Fp. 205 bis 207°C (aus wäßrigem Dimethylformamid);
- Ausbeute 50 g = 94% der Theorie;
- [α]20 D = 11,5 (c = 2; Dimethylformamid).
- Für C22H27N5O5
- 88,3 g (0,2 Mol) der vorstehend unter a) beschriebenen Verbindungen werden unter Erwärmen in 1000 ml Dimethylformamid gelöst und mit 20 ml Eisessig und 400 ml nHCI vermischt. Nach Abkühlen auf -10°C werden zunächst langsam 14,4 g (0,208 Mol) Natriumnitrit in 60 ml Wasser und anschließend eine vorgekühlte Lösung von 35,8 g (0,02 Mol) L-Phenylalaninmethylesterhydrochlorid, gelöst in 200 ml Dimethylformamid, hinzugefügt. Die Reaktionslösung wird mit etwa 54 g Triethylamin neutralgestellt und 24 Stunden im Kühlschrank aufbewahrt. Nach Aufschlämmen mit doppelter Menge Wasser wird der ausgefallene Niederschlag abfiltriert, mit n Salzsäure und Wasser gewaschen, getrocknet und aus Methanol rekristallisiert.
- Fp. 179 bis 181°C, Ausbeute 106 g = 92% der Theorie;
- [α]20 D =-22,5 (c = 2; Dimethylformamid).
- Für C32H36N407
- 52 g (0.0885 Mol) der vorstehend unter b) beschriebenen Verbindung werden in 150 ml Methanol und 35 ml n methanolischer HCI suspendiert und 20 Stunden bei Raumtemperatur gerührt. Die nunmehr klare Lösung wird eingedampft und der Rückstand aus Methanol/Ether rekristallisiert.
- Fp. 220 bis 222°C, Ausbeute 29 g (= 54% der Theorie).
- [α]20 D = +1,65 (c = 2; Dimethylformamid).
- Für C31H37CIN4O6. 1/2 H20
-
- Fp. 224 bis 227°C (aus Dioxan/Ether 2:1); Ausbeute 69% der Theorie.
- [α]20 D =-20,6 (c=0,5; Dimethylformamid).
- Für C52H52CIN5O11
sowie ihre gegebenenfalls mit Säuren und Basen gebildeten physiologisch verträglichen Salze.
umsetzt und anschließend den · Rest R6 in bekannter Weise abspaltet und gegebenenfalls die so erhaltenen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) mit Säuren und Basen in die physiologisch verträglichen Salze verwandelt.
Claims (3)
sowie ihre gegenbenenfalls mit Säuren und Basen gebildeten physiologisch verträglichen Salze.
zu gemischten Anhydriden der allgemeinen Formel (III)
umsetzt und diese mit Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (IV)
kondensiert und mit Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (IV) umsetzt oder
umsetzt und anschließend den Rest R6 bekannter Weise abspaltet und gegebenenfalls die so erhaltenen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) mit säuren und Basen in die physiologisch verträglichen Salze verwandelt.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19772735537 DE2735537A1 (de) | 1977-08-06 | 1977-08-06 | Indolacetoxyacetylaminosaeurederivate, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und ihre verwendung als arzneimittel |
| DE2735537 | 1977-08-06 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0000741A2 EP0000741A2 (de) | 1979-02-21 |
| EP0000741A3 EP0000741A3 (en) | 1979-03-07 |
| EP0000741B1 true EP0000741B1 (de) | 1981-07-22 |
Family
ID=6015810
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP78100523A Expired EP0000741B1 (de) | 1977-08-06 | 1978-07-27 | Indolacetoxyacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimittel |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0000741B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS5430160A (de) |
| DE (2) | DE2735537A1 (de) |
| IT (1) | IT7826537A0 (de) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3034005C2 (de) * | 1980-09-10 | 1982-12-09 | A. Nattermann & Cie GmbH, 5000 Köln | Indolessigsäure-Derivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und sie enthaltende pharmazeutische Zubereitungen |
| DE3206885A1 (de) * | 1982-02-26 | 1983-09-15 | Troponwerke GmbH & Co KG, 5000 Köln | Indolderivate, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und ihre verwendung als arzneimittel |
| DE3206887A1 (de) * | 1982-02-26 | 1983-09-15 | Troponwerke GmbH & Co KG, 5000 Köln | Verfahren zur herstellung von 1-(4-chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolacetoxyessigsaeure |
| JPS59204172A (ja) * | 1983-04-28 | 1984-11-19 | Kowa Co | アセメタシンの製造法 |
| JPH0417306Y2 (de) * | 1984-12-26 | 1992-04-17 | ||
| ATE115564T1 (de) * | 1988-07-05 | 1994-12-15 | Zeria Pharm Co Ltd | Indolessigsäure-derivate, verfahren zur herstellung sowie arzneimittel, die diese als aktive mittel enthalten. |
| US6762182B1 (en) | 1999-01-07 | 2004-07-13 | Vanderbilt University | Converting cox inhibition compounds that are not COX-2 selective inhibitors to derivatives that are COX-2 selective inhibitors |
| US6207700B1 (en) | 1999-01-07 | 2001-03-27 | Vanderbilt University | Amide derivatives for antiangiogenic and/or antitumorigenic use |
| US6306890B1 (en) | 1999-08-30 | 2001-10-23 | Vanderbilt University | Esters derived from indolealkanols and novel amides derived from indolealkylamides that are selective COX-2 inhibitors |
| CA2562783A1 (en) | 2004-04-26 | 2005-12-01 | Vanderbilt University | Indoleacetic acid and indenacetic acid derivatives as therapeutic agents with reduced gastrointestinal toxicity |
| EP1604656A1 (de) | 2004-06-09 | 2005-12-14 | Schwarz Pharma Ag | Neue Verwendung von Peptidverbindungen zur Behandlung von amyotropher Lateralsklerose (ALS) |
| CA2657691A1 (en) | 2006-06-19 | 2007-12-27 | Vanderbilt University | Methods and compositions for diagnostic and therapeutic targeting of cox-2 |
| WO2013059245A1 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2013-04-25 | Vanderbilt University | Indomethacin analogs for the treatment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2234651C3 (de) * | 1972-07-14 | 1978-11-09 | Troponwerke Gmbh & Co Kg, 5000 Koeln | Eckige Klammer auf l-(p-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indol] -acetoxj essigsaure, ihre Salze mit Basen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie pharmakologische Zubereitungen |
| DE2413125C2 (de) * | 1974-03-15 | 1983-06-30 | Schering Ag, 1000 Berlin Und 4619 Bergkamen | Indolylacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und diese Verbindungen enthaltende Arzneipräparate |
-
1977
- 1977-08-06 DE DE19772735537 patent/DE2735537A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1978
- 1978-07-27 EP EP78100523A patent/EP0000741B1/de not_active Expired
- 1978-07-27 DE DE7878100523T patent/DE2860858D1/de not_active Expired
- 1978-08-04 IT IT7826537A patent/IT7826537A0/it unknown
- 1978-08-04 JP JP9469878A patent/JPS5430160A/ja active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE2735537A1 (de) | 1979-02-22 |
| IT7826537A0 (it) | 1978-08-04 |
| EP0000741A2 (de) | 1979-02-21 |
| EP0000741A3 (en) | 1979-03-07 |
| DE2860858D1 (en) | 1981-10-29 |
| JPS5430160A (en) | 1979-03-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2366070C2 (de) | ||
| EP0104342B1 (de) | Triphenylimidazolyloxyalkansäuren und ihre Derivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende pharmazeutische Präparate | |
| EP0000741B1 (de) | Indolacetoxyacetylaminosäurederivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimittel | |
| EP0242851A1 (de) | N-(2'-Aminophenyl)-benzamid-Derivate, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung bei der Bekämpfung neoplastischer Erkrankungen | |
| EP0089637A2 (de) | Neue Derivate bicyclischer Aminosäuren, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, diese enthaltende Mittel und deren Verwendung sowie neue bicyclische Aminosäuren als Zwischenstufen und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung | |
| EP0115039B1 (de) | Substituierte Phenylsulfonyloxybenzimidazolcarbaminate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung als Arzneimittel | |
| DE2901170C2 (de) | ||
| DE3232672A1 (de) | (omega)-(4-(pyrid-2'-yl)-piperazin-1-yl)-alkylcarbonylanilide, verfahren und zwischenprodukte zu ihrer herstellung und die ersteren enthaltende arzneimittel | |
| EP0116360A1 (de) | 1-Phenyl-2-aminocarbonylindol-Verbindungen sowie Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese Verbindungen enthaltende Arzneimittel | |
| DE2727670A1 (de) | Neue dipeptide, verfahren zur ihrer herstellung und pharmazeutische praeparate enthaltende solche dipeptide | |
| EP0148431A1 (de) | Neue Benzimidazole, ihre Herstellung und diese Verbindungen enthaltende Arzneimittel | |
| EP0018360B1 (de) | N-(5-Methoxybentofuran-2-ylcarbonyl)-N'-benzylpiperazin und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| EP0665228A1 (de) | Neue 3-Phenylsulfonyl-3,7-diazabicyclo(3,3,1)nonan-Verbindungen enthaltende Arzneimittel | |
| EP0271099A2 (de) | Substituierte Aminopropionsäureamide, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, diese enthaltende Mittel und ihre Verwendung sowie die bei der Herstellung anfallenden neuen Zwischenprodukte | |
| EP0044266B1 (de) | Neue substituierte 3,5-Diamino-1,2,4-oxadiazole und 3,5-Diamino-1,2,4-thiadiazole, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und sie enthaltende pharmazeutische Präparate | |
| EP0083729B1 (de) | Substituierte 1-Benzoyl-2-phenylimino-imidazolidine, deren Säureadditionssalze, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und diese enthaltende Arzneimittel | |
| EP0124479B1 (de) | Iminosulfonamide und Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, die pharmazeutische Präparate solche Verbindungen enthalten, sowie die Verbindungen zur Verwendung | |
| EP0088252B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von 1-(4-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolacetoxyessigsäure | |
| DE3426720A1 (de) | Benzthiazepinon- und benzthiazocinon-derivate, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung, diese enthaltende mittel und ihre verwendung, sowie zwischenprodukte bei ihrer herstellung | |
| DE1445873A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Benzodiazepin-Derivaten | |
| DE3704404A1 (de) | Abietamidderivate | |
| DE2608238A1 (de) | Substituierte phenylguanidine und verfahren zu ihrer herstellung | |
| DE2200648A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von monosubstituierten 1-Carbamoyl-2-benzimidazolyl-carbamaten | |
| EP0371342A1 (de) | 2-Halogensubstituierte N-Indolylethyl-sulfonsäureamide, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimitteln | |
| DE1933388C (de) | l-(2-Acyl- 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisochinolin-7sulfonyl)-harnstoffe |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19810630 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19810731 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19810930 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19810930 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19810930 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 2860858 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19811029 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19820731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19830127 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19830201 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19830331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19830401 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19881117 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |