WO2011105568A1 - 学習・記憶障害および運動障害などを伴う中枢神経変性疾患を改善する乾燥植物組織および植物組織抽出物ならびにこれらを含有する医薬品および食品 - Google Patents
学習・記憶障害および運動障害などを伴う中枢神経変性疾患を改善する乾燥植物組織および植物組織抽出物ならびにこれらを含有する医薬品および食品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011105568A1 WO2011105568A1 PCT/JP2011/054358 JP2011054358W WO2011105568A1 WO 2011105568 A1 WO2011105568 A1 WO 2011105568A1 JP 2011054358 W JP2011054358 W JP 2011054358W WO 2011105568 A1 WO2011105568 A1 WO 2011105568A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- plant tissue
- extract
- weight
- nobiletin
- disease
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K36/00—Medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicines
- A61K36/18—Magnoliophyta (angiosperms)
- A61K36/185—Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons)
- A61K36/75—Rutaceae (Rue family)
- A61K36/752—Citrus, e.g. lime, orange or lemon
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; PREPARATION OR TREATMENT THEREOF
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
- A23L33/105—Plant extracts, their artificial duplicates or their derivatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/335—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin
- A61K31/35—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/352—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. methantheline
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7042—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings
- A61K31/7048—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. leucoglucosan, hesperidin, erythromycin, nystatin, digitoxin or digoxin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/14—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abnormal movements, e.g. chorea, dyskinesia
- A61P25/16—Anti-Parkinson drugs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a dried plant tissue and a plant tissue extract that improve central neurodegenerative diseases associated with learning / memory disorders and movement disorders.
- the present invention also relates to pharmaceuticals and foods containing the dried plant tissue or plant tissue extract.
- Non-Patent Document 1 N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor function, which is important for learning / memory Neurodegeneration due to polymerization and accumulation of amyloid ⁇ peptide is considered (see Non-Patent Document 1).
- NMDA N-methyl-D-aspartate
- memory In general, memory consists of three processes: memory acquisition, retention, and recall, and the mechanisms of these three processes are considered different. It is understood that learning and memory impairment, which is a core symptom of Alzheimer's disease, is particularly markedly impaired in memory retention and recall processes.
- the formula (I) See Patent Document 1 or Non-Patent Document 1 or 2), and nobiletin is also known to have a neurite outgrowth action on nerve cells (Patent Document 1). 2).
- Nobiletin is contained in the skin of various citrus plants, but is usually contained in a very small amount.
- Chen which is one of the herbal medicines derived from the peels of citrus plants, usually exhibits a gastric action, expectorant action, antitussive action, etc., and it is considered that nobiletin is not involved in these actions.
- Parkinson's disease one of the central neurodegenerative diseases, is characterized by four major motor signs such as tremor, slow movement, muscle rigidity, and postural reflex disorder, and the dopaminergic nervous system degenerates due to some factor. This is because of motor dysfunction.
- dopamine replacement therapy is currently performed. Many drugs that increase the transcriptional activity of the enzyme in the dopamine biosynthetic pathway, that is, the expression level of its mRNA, are known, but few drugs that increase the production of dopamine itself are known.
- a dried citrus plant tissue exhibiting a dopamine synthesis ability promoting action and a dopamine secretion promoting action and an extract thereof are not known.
- the present inventors have found a dried citrus plant tissue and a plant tissue extract that have a remarkable effect of improving central nervous degenerative diseases.
- the present inventors have found dried plant tissues and plant tissue extracts of citrus fruits that can be applied as a fundamental therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease among central neurodegenerative diseases.
- the inventors have further discovered dried citrus plant tissues and plant tissue extracts that enhance not only memory recall but also memory acquisition and retention in memory impairment, a core symptom of Alzheimer's disease.
- the present invention includes the following embodiments: (1) Dry plant tissue of citrus peel for improving central neurodegenerative diseases, containing 0.4% by weight or more of nobiletin with respect to 100% by weight of dry plant tissue; (2) Dry plant tissue of citrus leaves for improving central neurodegenerative diseases, containing 0.3% by weight or more of nobiletin with respect to 100% by weight of dry plant tissue; (3) The dry plant tissue according to any one of (1) and (2), wherein the weight ratio of nobiletin / nariltin is 1.0 or more; (4) The dried plant tissue according to any one of (1) and (2), wherein the central neurodegenerative disease is Alzheimer's disease and / or Parkinson's disease; (5) Improvement of central neurodegenerative diseases is increased cAMP response element (CRE) -dependent transcriptional activity, memory acquisition, retention and enhanced recall ability, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) transcriptional activity, TH expression level The dried plant tissue according to any one of (1) and (2), which is brought about by an increase, promotion of dopamine synthesis ability, or promotion
- Citrus plant tissue extract for improving central neurodegenerative diseases containing 0.6% by weight or more of nobiletin with respect to 100% by weight of plant tissue extract; (7) The plant tissue extract according to (6), wherein the content weight ratio of nobiletin / nariltin is 2.0 or more; (8) The plant tissue extract according to (6) obtained by water extraction from the dried plant tissue according to any of (1) or (2), preferably 60 to 100 ° C water extraction; (9) The plant tissue extract according to (6), wherein the central neurodegenerative disease is Alzheimer's disease and / or Parkinson's disease; (10) Improvement of central neurodegenerative diseases may increase CRE-dependent transcriptional activity, acquire memory, enhance retention and recall ability, promote TH transcriptional activity, increase TH expression, promote dopamine synthesis, or dopamine secretion The plant tissue extract according to (6), which is caused by the promotion of
- 10% to 100% by weight of the dry plant tissue according to (1) or (2) or 10% to 90% by weight of the plant tissue extract according to (6) is effective with respect to 100% by weight of the pharmaceutical product A drug for treating Alzheimer's disease as an ingredient
- 10% to 100% by weight of the dry plant tissue according to (1) or (2) or 10% to 90% by weight of the plant tissue extract according to (6) is effective with respect to 100% by weight of the pharmaceutical product A drug for treating Parkinson's disease as an ingredient
- a therapeutic drug for treating a central neurodegenerative disease preferably comprising an extract obtained by water extraction at 60 to 100 ° C.
- the content of nobiletin is 0.3 to 2.0% by weight with respect to 100% by weight of the dry plant tissue, and the content weight ratio of nobiletin / nariltin is 1.0 to 23.0.
- Dry plant tissue of (24) The dried plant tissue according to (4), which is obtained by heating and drying citrus plant tissue at 50 to 100 ° C. for 1 to 3 hours, and the yield is 20 to 50%; (25) The content of nobiletin is 0.6 to 3.0% by weight with respect to 100% by weight of the plant tissue extract, and the content weight ratio of nobiletin / nariltin is 2.0 to 14.0.
- Plant tissue extracts as described; (26) The pharmaceutical according to (19), which is in the form of a fine granule, tea, decoction, capsule, tablet, granule, jelly, powder, liquid, syrup or extract preparation.
- the citrus dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention show a significant central neurodegenerative disease improving effect as compared with the conventional citrus dried plant tissue.
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention also have the effect of activating PKA / ERK / CREB signaling and improving learning / memory impairment, which is one of the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention particularly show the effect of acquiring, maintaining and recalling memory among the learning / memory impairment improving effects.
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention further have a strong phosphorylation promoting effect and a PKA / ERK signal transduction promoting effect as compared with nobiletin alone having the same amount of nobiletin contained therein.
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention exhibit an improvement effect on Parkinson's disease by CRE transcription activity and TH transcription activity, TH expression level increasing action, dopamine synthesis ability promoting action or dopamine secretion promoting action. .
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention further has a central neurodegenerative disease ameliorating effect exceeding that predicted from its nobiletin-containing concentration, in particular, an effect of increasing CRE-dependent transcriptional activity, memory acquisition, retention and recall ability.
- a central neurodegenerative disease ameliorating effect exceeding that predicted from its nobiletin-containing concentration in particular, an effect of increasing CRE-dependent transcriptional activity, memory acquisition, retention and recall ability.
- the effect of promoting TH transcriptional activity and the effect of increasing the TH expression level the effect of promoting dopamine biosynthesis and the effect of promoting dopamine secretion are shown. These effects are considered to be due to a synergistic effect of nobiletin and other components contained in the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract.
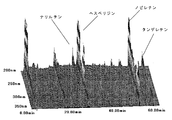
- FIG. 1A shows a three-dimensional chromatogram of flavonoids contained in the skin of the present invention.
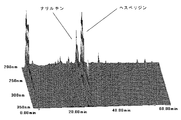
- FIG. 1B shows a three-dimensional chromatogram of flavonoids contained in a conventional skin.
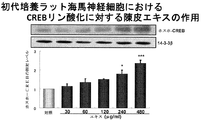
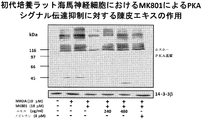
- FIG. 2A shows CREB phosphorylation promoting activity of a skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
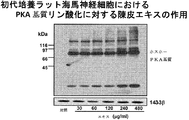
- FIG. 2B shows the PKA substrate phosphorylation promoting activity of the skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
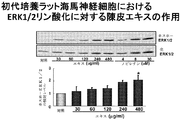
- FIG. 2C shows the ERK1 / 2 phosphorylation promoting activity of the skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 2D shows the PKA signal transduction promoting effect of the skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 2E shows the ERK signal transduction promoting effect of the skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 1A shows CREB phosphorylation promoting activity of a skin extract in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 2B shows the PKA substrate phosphorylation promoting activity of the skin extract in hippocampal
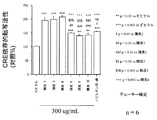
- FIG. 2F shows the CRE-dependent transcriptional activity of extracts from the present skin 1 and conventional skin 7 and nobiletin in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 2G shows the CRE-dependent transcriptional activity of extracts from the skin 2-4 of the present invention and the conventional skin 8-10 and nobiletin in hippocampal neurons.
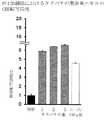
- FIG. 3A shows the effect of improving the learning / memory impairment of crustacean extract, that is, the effect of acquiring, retaining, and recalling memory.
- FIG. 3B shows the effect of nobiletin on MK801-induced learning / memory impairment.
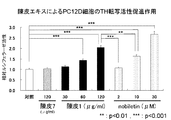
- FIG. 4A shows the TH transcriptional activity promoting effect of the skin extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 4B shows the effect of increasing the TH expression level of the crust extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 4C shows the effect of increasing the dopamine content of the skin extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 5A shows CRE transcriptional activity of Tachibana peel extract in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 5B shows the improvement effect of learning impairment of Tachibana peel extract.
- Two-way ANOVA including post Bonferroni test for all pairs of learning-promoting effects. Numerical values in the figure show mean ⁇ standard error; n 5 for all tests. ** p ⁇ 0.01 compared to control ( ⁇ ), *** p ⁇ 0.001, ### p ⁇ 0.01 compared to MK-801 ( ⁇ ), ⁇ p ⁇ 0.05.
- FIG. 5C shows the effect of improving the memory impairment of Tachibana peel extract.
- One-way ANOVA including post Tukey test for all pairs of memory improvement effects.
- FIG. 5D shows CRE transcriptional activity of Tachibana peel extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 5E shows TH transcriptional activity of Tachibana peel extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 5F shows the GCH I expression level increasing effect of Tachibana bark extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 6A shows CRE transcriptional activity of the extract derived from the leaf of Tachibana in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 6B shows CRE transcriptional activity of Tachibana leaf-derived extract in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 7A shows the CRE transcriptional activity of the extract derived from citrus pericarp in hippocampal neurons.
- FIG. 7B shows the CRE transcriptional activity of the extract derived from the citrus pericarp in PC12D cells.
- FIG. 7C shows the TH transcriptional activity of the extract derived from the citrus pericarp in PC12D cells.
- the citrus fruits used in the present invention are: Citrus tachibana, C. nipponokoreana, Hanayu, Shikitsu, Pheasant, Daidai, Mediterranean Mandarin, Dancy Tangerine, Obenimikan, Kobenimikan, Nucleus Kishu, Fukurimuta, Ponkan, Hirakishu, Sankitsu, Cleopatra, Koji, Giri Mikan, Ichan Lemon, Unshu Mikan (Citrus unshiu Markovich), Citrus reticulata Blanco (Rutaceae), Sikhwasa, Yuzu, Bungtan, Hyuganatsu, Ponkan, Natsumikan, Bunyo Among plants selected from the group consisting of those having a high nobiletin content, preferably Citrus reticulata Blanco (Rutaceae), Japanese tachibana (Citrus tachibana), Kourai tachibana (C. nip ponokoreana) or Gi
- the yield of the citrus peel or leaf is 20 to 50% in the case of the peel and 20 to 50% in the case of the leaf. It means a substance dried under such conditions.
- the heating and drying conditions include a temperature of 50 to 100 ° C. for 1 to 3 hours, and a temperature of 60 ° C. for 2 hours.
- Preferred dry plant tissues of the present invention are Chen, Tachibana and Tachibana leaves.
- Tachibana peel refers to the mature pericarp of Japanese Tachibana or Tachibana, particularly Tachibana.
- the leaf means a leaf of Tachibana such as Japanese Tachibana or Kourai Tachibana.
- the plant tissue extract of the present invention is an extract from the above-mentioned dry plant tissue, preferably an extract obtained by water extraction.
- the preferred water extraction herein is extraction with water at 60-100 ° C.
- components contained in the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention include flavonoids such as nobiletin, nariltin, tangeretin, and hesperidin.
- flavonoids such as nobiletin, nariltin, tangeretin, and hesperidin.
- the activity of the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention is remarkable as compared with the medicinal effect of nobiletin alone due to the synergistic effect due to the content and content ratio of the components contained therein.
- the dry plant tissue of the present invention comprises 0.3 or 0.4% by weight or more, preferably 0.3 to 2.0% by weight, more preferably 0.4 to 2.0% by weight of nobiletin based on the total weight. 0.7% by weight or less, preferably 0.4% by weight or less of nariltin, 0.1 to 0.8% by weight of tangeretin and 0.4 to 12% by weight of hesperidin.
- the dry plant tissue of the present invention also has a nobiletin / nariltin content weight ratio of 1.0 or more, preferably 1.5 to 23.0, more preferably 2.0 to 15.0, still more preferably 5.0 to 15.0.
- the dry plant tissue of the present invention can be derived from any plant as long as the proportion of each component contained in the dry tissue is within the above range, that is, the drug effect of the present invention, that is, the central neurodegenerative disease improving effect (anti Alzheimer's disease activity, anti-Parkinson disease activity, etc., learning / memory impairment improvement effect, phosphorylation promotion effect and PKA / ERK signaling promotion effect, CRE transcription activity and TH transcription activity, TH expression level increase effect, dopamine synthesis ability promotion effect Or show dopamine secretion promoting action.
- the drug effect of the present invention that is, the central neurodegenerative disease improving effect (anti Alzheimer's disease activity, anti-Parkinson disease activity, etc., learning / memory impairment improvement effect, phosphorylation promotion effect and PKA / ERK signaling promotion effect, CRE transcription activity and TH transcription activity, TH expression level increase effect, dopamine synthesis ability promotion effect Or show dopamine secretion promoting action.
- the plant tissue extract of the present invention is 0.6 to 2.0% by weight or more, preferably 0.6 to 3.0% by weight of nobiletin, 0.7% by weight or less, preferably 0. Contains no more than 4% by weight nariltin, 0.1-1.0% by weight tangeretin and 1.8-6.0% by weight hesperidin.
- the plant tissue extract of the present invention also has a nobiletin / nariltin content weight ratio of 2.0 or more, preferably 2.0 to 14.0, more preferably 2.5 to 10.0.
- the plant tissue extract of the present invention can be derived from any plant as long as the ratio of each component contained therein is within the above-mentioned range.
- central neurodegenerative disease includes Alzheimer's disease, particularly learning / memory impairment, and Parkinson's disease.
- Examples of the anti-Alzheimer's disease activity and / or anti-Parkinson's disease activity of the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention include improvement of learning / memory impairment related to the onset mechanism of central neurodegenerative diseases or promotion of dopamine synthesis. .
- the dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract of the present invention may exhibit different activities depending on the type of plant tissue.
- the skin or skin extract may exhibit a dopamine content increasing activity
- the tachibana skin or citrus skin extract may exhibit a dopamine secretion promoting activity.
- learning / memory failure is a failure that reduces the following three abilities in the memory process: memory acquisition (encoding), retention (retention), and recall (recall) abilities.
- acquisition refers to capturing information into memory
- retention refers to storing captured information
- recalling refers to recalling stored information.
- therapeutic agents for central neurodegenerative diseases include anti-Alzheimer's disease agents and / or anti-Parkinson's disease agents, that is, pharmaceuticals having anti-Alzheimer's disease activity and / or anti-Parkinson disease activity.
- the term “pharmaceutical” means a substance for diagnosis, treatment or prevention of diseases in humans and animals, and includes pharmaceuticals including herbal medicines, such as herbal medicines and herbal medicines.
- a preferred pharmaceutical is an oral dosage form, more preferably a fine granule, tea, decoction, capsule, tablet, granule, jelly, powder, liquid, syrup or extract.
- the term “herbal medicine” is a general term for substances used for improving the constitution of a subject without purifying active ingredients from naturally occurring products having medicinal effects, and includes one or more herbal ingredients.
- the term “Chinese medicine” means a medicine prescribed on the basis of Chinese medicine theory.
- the term “food” refers to so-called health foods and health functional foods such as foods for specified health use and functional nutritional foods that are distinguished by the presence or absence of permission from the authorities and the purpose and function of the food. Including. Preferred foods herein are fine granules, jelly sauce, peel, jam or tea, more preferably fine granules or tea.
- the blending amount of each component in the pharmaceutical and food in the present specification can be appropriately adjusted according to the intended purpose of use, sex, symptoms, etc., for example, 10 to 100% by weight of the dried plant tissue of the present invention or plant 10-90% by weight of tissue extract and 0-90% by weight of other carriers or additives.
- the daily intake amount of the dried plant tissue or plant tissue extract of the present invention per adult is preferably 3 to 50 g or 1 to 20 g, and more preferably 5 to 30 g or 2 to 10 g.
- compositions herein include those commonly used in the art, such as pharmaceutically or food hygienically acceptable herbal ingredients, ascorbic acid, aspartame, apple flavor, orange flavor, carrageenan. , Caramel, carnauba wax, carmellose, carmellose calcium, reduced maltose liquid sugar, reduced maltose starch syrup, hydrous silicon dioxide, xylitol, citric acid, trisodium citrate, granulated sugar, light anhydrous silicic acid, gelling agent (FG-2266, Nitta Gelatin Co., Ltd.), synthetic aluminum silicate, hydroxypropyl starch, crystalline cellulose, beeswax, titanium oxide, salt, sucrose fatty acid ester, magnesium stearate, cellulose, talc, dextrin, corn starch, lactose, honey, hydro Xylpropylmethylcellulose, fine silicon dioxide, pullulan, pectin, maltose, magnesium aluminate metasilicate,
- the pharmacologically or food hygienically acceptable herbal medicine components in this specification include those commonly used in the art.
- Chen 1 to 6, Tachibana 1 to 6, Tachibana leaves 1 to 3 and Obenimikan 1 are the dry plant tissue of the present invention, and Chen 7 to 12 are conventional.
- the plant tissue of the same degree can be obtained from Kotaro Hanpo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. from the viewpoint of the samples and the components used in the following examples.
- Example 1 Production of dried plant tissue
- the peels and leaves collected from various citrus fruits were shade-dried, sun-dried or heat-dried to obtain dried bodies of the peel, tachibana peels, tachibana leaves, and the fruit of periwinkle.
- Heat drying is carried out until the yield (ratio of mass after drying / mass before drying) is 20-50% for Chen and Tachibana peels, 20-50% for Tachibana leaves, and 20-50% for Prunus pericarp. Specifically, it was dried by heating at a temperature of 60 ° C. for 2 hours.
- Example 2 Production of plant tissue extract 400 mL of pure water was added to about 10 g of the cut skin, tachibana bark, leaves of tachibana or persimmon bark obtained in Example 1 and heated (tachibana bark) For 6), 1000 mL of pure water was added to about 20 g of the minced and heated. After the mixture boiled, it was extracted at 100 ° C. for 1 hour. Subsequently, it filtered through gauze (2 sheets), and the filtrate was freeze-dried to obtain a plant tissue extract. The production results of the plant tissue extract are shown in Table 1 below.
- Example 3 Analysis of contained components The contained components of the dried plant tissues and plant tissue extracts obtained in Examples 1 and 2 were measured as follows. Below, the analysis method about a crust and a crust extract is shown.
- a standard solution used for quantification of nobiletin and tangeretin was prepared as follows. Nobiletin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was dried with a desiccator (silica gel) for 24 hours or more. About 5 mg of dried nobiletin was dissolved in a methanol / water mixture (7: 3) to make 100 mL, and used as a nobiletin standard solution. Further, tangeretin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was dried with a desiccator (silica gel) for 24 hours or more. About 3 mg of dry tangeretin was dissolved in a methanol / water mixture (7: 3) to make 100 mL, and used as a tangeretin standard solution.
- a standard solution used for quantification of hesperidin and nariltin was prepared as follows. Hesperidin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was dried with a desiccator (silica gel) for 24 hours or more. About 10 mg of dry hesperidin was dissolved in 50% methanol to make 50 mL, and used as a hesperidin standard solution. Also, Nariltin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was dried with a desiccator (silica gel) for 24 hours or more. About 10 mg of dry narilutin was dissolved in 50% methanol to make 500 mL, which was used as a narilutin standard solution.
- a skin sample solution As a skin sample solution, 30 mL of methanol was added to about 0.1 g of skin powder. The mixture was irradiated with ultrasonic waves for 20 minutes (UT-305HS, Sharp Corporation), extracted, and then centrifuged (KUBOTA KN-70, Kubota Corporation) to collect the supernatant. 20 mL of methanol was added to the residue, and extraction was performed by irradiating with ultrasonic waves for 20 minutes, followed by centrifugation. This was combined with the collected supernatant to obtain a skin sample solution.
- the peel extract As a sample solution of the peel extract, about 0.1 g of the peel extract was placed in a 50 mL stoppered centrifugal sedimentation tube, and 50 mL of a methanol / water mixture (1: 1) was added thereto. The mixture was extracted with ultrasonic waves (UT-305HS, Sharp Corporation) and then centrifuged (KUBOTA KN-70, Kubota Corporation). Then, it filtered and it was set as the sample solution of the crust extract.
- ultrasonic waves UT-305HS, Sharp Corporation
- KUBOTA KN-70 centrifuged
- FIGS. 1A and 1B show three-dimensional chromatograms of flavonoids contained in the skin of the present invention and the conventional skin, respectively.
- each component may vary depending on the sampling location and timing of the citrus plants used.
- the blue peel of tachibana has some nobiletin content of about 1.60% by weight, but about 1.1% by weight of yellow peel.
- Test Example 1 The general test procedure used in Test Example 1 below is as follows. (Culture of rat fetal primary hippocampal neurons) Pregnant Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were bred by feeding and watering in a 12-hour light / dark cycle. The uterus was aseptically removed from the rat (E18) on day 18 of gestation by a midline abdominal incision under deep ether anesthesia. Under a stereomicroscope, remove the fetal hippocampus in ice-cold phosphate buffered saline (PBS), disperse the tissue with papain enzyme (SUMILON), and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 4 minutes. Removed.
- PBS ice-cold phosphate buffered saline
- SUMILON ice-cold phosphate buffered saline
- the cell pellet was dispersed in a dispersion liquid (SUMILON), and then the removal liquid (SUMILON) was added to the cells sufficiently dispersed by pipetting, followed by centrifugation at 900 rpm for 5 minutes, and then the supernatant was removed. .
- the pellet is suspended using Neurobasal Medium (Neurobasal Medium 500 mL / Phenol Red-free, 50 x B27 Supplement 10 ml, 0.5 mM L-glutamine, 0.005% penicillin-streptomycin) and added with poly-L-lysine. Seeded on coated dishes or plates. One day after the culture, the medium was changed, and then half of the medium was changed every 3 to 4 days.
- Neurobasal Medium Neurobasal Medium 500 mL / Phenol Red-free, 50 x B27 Supplement 10 ml, 0.5 mM L-glutamine, 0.005% penicillin-streptomycin
- the medium was cultured in a medium containing 10 ⁇ M AraC at 37 ° C. in a 5% CO 2 incubator for 14 days.
- Neurobasal Medium containing 10 ⁇ M AraC was used as a test medium for drug treatment experiments.
- Rat fetal primary hippocampal neurons were seeded at 1 ⁇ 10 6 cells / dish in a 35 mm dish, cultured in a growth medium for 14 days in a 5% CO 2 incubator, and then treated with the drug for 10 minutes. Each cell was treated with drugs and then washed with ice-cold PBS.
- Cell lysate (1 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, 10 mM NaF, 10 nM caliculin, 320 nM okadaic acid, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM p-APMSF, 10 ⁇ g / mL pepstatin A, 10 ⁇ g / mL Antipine, 10 ⁇ g / mL leupeptin, 10 ⁇ g / mL chymostatin, 10 ⁇ g / mL phosphoramidon, 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Thereafter, it was immediately boiled at 95 ° C. for 5 minutes to denature the protein, and then the DNA was sonicated to prepare a sample for SDS-PAGE.
- the PVDF membrane is placed in a stripping buffer (62.5 mm Tris-HCl, 2% SDS, 100 mm mM ⁇ -mercaptoethanol, pH 7.4) pre-warmed to 50 ° C and incubated for 30 minutes at 50 ° C. Was removed and washed with TBST. Thereafter, the internal standard protein was detected by reprobing.
- a stripping buffer (62.5 mm Tris-HCl, 2% SDS, 100 mm mM ⁇ -mercaptoethanol, pH 7.4) pre-warmed to 50 ° C and incubated for 30 minutes at 50 ° C. Was removed and washed with TBST. Thereafter, the internal standard protein was detected by reprobing.
- 7.2 g of the skin extract from the skin 1 was weighed and placed in a 50 ml centrifuge tube, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added thereto to make 30 mL. Then, it was sonicated for 30 minutes and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was collected and used as a skin extract.
- DMSO dimethyl sulfoxide
- Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 phosphorylation-promoting effect of skin extract in primary cultured hippocampal neurons About the effect of various concentrations of skin extract or nobiletin on ERK1 / 2 phosphorylation Blotting was used (contains nobiletin 1 ⁇ M in 60 ⁇ g / ml of skin extract). E18 rat hippocampal neurons grown at a density of 1 ⁇ 10 6 cells / 35-mm plastic dish were cultured for 14 days. Cells were treated for 10 minutes with crushed extract (30, 60, 120, 240 and 480 ⁇ g / ml) or nobiletin (4, 8 and 30 ⁇ M).
- crushed extract (30, 60, 120, 240 and 480 ⁇ g / ml) or nobiletin (4, 8 and 30 ⁇ M).
- rat hippocampal neurons were primarily cultured and then a reporter gene assay was performed.
- Hippocampal neurons were seeded in a 48-well plate at 8 ⁇ 10 4 cells / well and cultured in Neurobasal medium for 10-14 days.
- Reporter plasmid (0.1 ⁇ g / well) and Renilla pRG-TK plasmid (0.01 ⁇ g / well) were transfected by lipofection and cultured for 16 hours. It was diluted with Neurobasal medium without AraC (containing B-27 Supplement, L-glutamine, penicillin-streptomycin) and treated with a crust extract at a concentration of 300 ⁇ g / ml for 8 hours.
- the skin extract was a 150 mg / ml DMSO solution as a stock solution, dispensed, and stored at -20 ° C.
- Transcriptional activity was measured using Promega's Dual-Luciferase (registered trademark) Reporter Assay System. Hippocampal neurons were solubilized with Passive Lysis Buffer (Promega), then mixed with Luciferase Assay Regent II (Promega) and Stop & Glo (registered trademark) Reagent (Promega), and the fluorescence value was measured with a luminometer.
- the reporter gene assay and RT-PCR results were evaluated using one-way ANOVA (Tukey). The significance level was tested at 5% on both sides, and p ⁇ 0.05 was considered significant.
- the concentration of nobiletin in the skin extract used in this test example is 2.5 ⁇ M, and its CRE-dependent transcriptional activity is 1 / 12th that of 30 ⁇ M nobiletin. More than 30 ⁇ M nobiletin. That is, it was found that in the multi-component system of the skin extract of the present invention, the presence of components other than nobiletin significantly and synergistically increases the CRE-dependent transcription promoting activity of nobiletin than the activity expected from nobiletin alone. In addition, the skin extract of the present invention showed a CRE-dependent transcriptional activity stronger than that of conventional skin extracts, so it showed an action to improve learning and memory impairment and more effectively improved the recognition function of Alzheimer's disease. It has been shown.
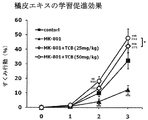
- mice were divided into 4 groups, each with a skin extract of 1.48 g / kg or 3.69 g / kg (nobiletin content: 10 mg / kg or 25 mg / kg, respectively), and 2 groups with physiological saline for 7 consecutive days Orally. On the 7th day, 90 minutes after administration of these, MK801 (0.08 mg / kg) or physiological saline was administered subcutaneously. Thirty minutes later, a fear conditioning learning test was conducted. In the horror learning test, mice were placed in a transparent box and allowed to explore freely for 2 minutes, followed by 0.7 mA, 2 s electrical stimulation.
- Comparative Test 1 Examination of learning / memory impairment improving effect of nobiletin
- Comparative Example 1-1 a comparative test was conducted by replacing oral administration of crust extract with intraperitoneal administration of nobiletin (10, 50 mg / kg). It was. The results are shown in FIG. 3B.
- the freezing action was significantly reduced by the treatment with MK801.
- the administration of the crustacean extract showed an improvement effect on the reduction in a dose-dependent manner in both the learning trial and the confirmation trial. It was.
- the mice administered with the skin extract of the present invention received the MK801 treatment, and the learning / memory function was hindered and easily forgotten.
- the ratio was about 1.5 times that of the control mouse and about 4.4 times that of the MK801-treated mouse skin extract-untreated mouse (FIG. 3A).
- Such a result was not recognized by administration of nobiletin (Comparative Test 1, FIG. 3B). That is, it has been found that the skin extract of the present invention has an effect of acquiring memory and enhancing retention ability, which is not recognized by administration of nobiletin alone.
- Test Example 4 The general test procedure used in Test Example 4 below is as follows. (PC12D cell culture) Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (9.5 g) was dissolved in MilliQ water (800 mL), and glucose (3.5 g) was added thereto to make 1 L with MilliQ water. 830 mL of the product sterilized by autoclave was taken, and 17 mL of 10% aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and 16.5 mL of 3% L-glutamine aqueous solution were added. Next, equine serum (HS) to 10% and fetal calf serum (FCS) to 5% were prepared as growth media and cultured in a 5% CO 2 incubator at 37 ° C. . The test medium used was hDMEM containing 2% HS and 1% FCS.
- DMEM Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium
- PC12D cells were seeded on a 48-well plate at 8 ⁇ 10 4 cells / well and cultured in a growth medium for 24 hours, followed by lipofection with 0.1 ⁇ g / well of pRTH plasmid and 0.01 ⁇ g / well of Renilla pRG-TK plasmid.
- the medium was replaced with a test medium in which the compound was dissolved 19 hours after transfection. After incubation for 24 hours, the medium was aspirated and collected with Passive Lysis Buffer. Firefly shiitake and Renilla luciferase were measured with a luminometer using Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega).
- PC12D cells were seeded at 0.67 ⁇ 10 6 cells / dish in a 35 mm dish, cultured in a growth medium for 2 days in a 5% CO 2 incubator, and then treated with the drug for 24 hours. Each cell was treated and then washed with ice-cold PBS.
- Cell lysate (1 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, 10 mM NaF, 10 nM caliculin, 320 nM okadaic acid, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM p-APMSF, 10 ⁇ g / mL pepstatin A, 10 ⁇ g / mL Antipine, 10 ⁇ g / mL leupeptin, 10 ⁇ g / mL chymostatin, 10 ⁇ g / mL phosphoramidon, 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Thereafter, the mixture was immediately boiled at 95 ° C. for 5 minutes to denature the protein, and then the DNA was sonicated and the centrifuged supernatant was prepared as a sample for SDS-PAGE.
- TBST containing 5% skim milk (10 mm Tris-HCl, 100 mm mM NaCl) , 0.05% Tween-20, pH 7.4; hereinafter referred to as blocking buffer) for 1 hour at room temperature. Samples were then washed with TBST and incubated overnight at 4 ° C. with primary antibody diluted 1000-fold with blocking buffer. Further, the sample was washed with TBST, incubated with an HRP-labeled IgG antibody diluted 2000 times with a blocking buffer at room temperature for 1 hour, and washed with TBST.
- the ECL method was used to detect antibody-positive bands.
- the antibody was peeled off using a stripping buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, SDS 2% SDS, 100 mM mM ⁇ -mercaptoethanol, pH 7.4), the blot was washed with TBST, and the internal standard protein was detected.
- PC12D cells were seeded at 1.0 ⁇ 10 6 cells / dish in a 35 mm dish and cultured in a 5% CO 2 incubator on a growth medium for 24 hours, and then the cell culture solution supplemented with skin 1 and skin 7 was further added for 24 hours. Cultured.
- a low K + buffer 140 mM NaCl, 4.7 mM KCl, 1.2 mM KH 2 PO 4 , 2.5 mM CaCl 2 , 1.2 mM MgSO 4 , 11 mM glucose and 15 mM HEPES-Tris, pH 7 heated to 37 ° C.
- the cells were washed in .4), a perchloric acid solution was added so that the final concentration was 0.4 N, and the cells were disrupted with ultrasonic waves for 1 minute.
- the obtained solution was centrifuged, and dopamine was separated and quantified by high performance liquid chromatography using an electrochemical detector.
- the skin 1 extract of the present invention increased the dopamine content at both 24 and 48 hours treatment compared to the control and conventional skin 7 extract.
- the skin extract of the present invention increases the TH transcriptional activity, TH expression level and dopamine content in PC12D cells in a concentration-dependent manner, and its action is unexpected and exceptional compared to nobiletin at an equal concentration. It was powerful. That is, it was revealed that the skin extract of the present invention exhibits a dopamine synthesis promoting activity more markedly than nobiletin. Since the activity is not recognized in the conventional extract derived from dermis, it is considered that the dermis extract of the present invention exhibited a dopamine synthesis promoting activity due to a synergistic effect of a high content of nobiletin and other components other than nobiletin. As described above, the skin extract of the present invention is expected to have a medicinal effect as a therapeutic agent for Parkinson's disease.
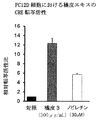
- Test Example 5 CRE Transcriptional Activity of Tachibana Skin Extract in Hippocampal Nerve Cells Using the extract extracted from Tachibana Skin 3 obtained in Example 2 by the method described herein, CRE transcriptional activity in hippocampal neurons is controlled And compared with nobiletin.
- the test procedure was the same as in Test Example 2. The result is shown in FIG. 5A.
- the Tachibana peel 3 extract 300 ⁇ g / mL used in this test example contained about 9.4 ⁇ M nobiletin.
- the extract of Tachibana peel 3 showed significant CRE transcriptional activity in hippocampal neurons compared to control and nobiletin. From this, the tachibana peel extract of the present invention is expected to have a medicinal effect as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.
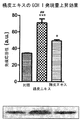
- Tachibana peel extract learning / memory impairment improving effect (in vivo test) Using the extract extracted from Tachibana bark 6 obtained in Example 2 by the method described in this specification, the effect of the Tachibana bark extract of the present invention on learning / memory impairment was examined. The test procedure was the same as in Test Example 3. The results are shown in FIGS. 5B and 5C. Tachibana peel extract 1.87 g / kg or 3.73 g / kg (nobiletin content: 25 mg / kg or 50 mg / kg, respectively) was orally administered to each group continuously for 7 days. As shown in FIG. 5B and FIG. 5C, in addition to significantly improving learning / memory impairment by chronic administration of the tachibana peel extract of the present invention, it is possible to enhance the ability to acquire and retain memory that is not observed with nobiletin. It became clear.
- the tachibana peel extract of the present invention is expected to have a medicinal effect as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.
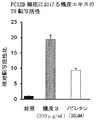
- Test Example 8 TH transcription activity of Tachibana peel extract in PC12D cells Using the extract extracted from Tachibana peel 3 obtained in Example 2 by the method described in this specification, the TH transcription activity in PC12D cells was compared with control and nobiletin. And compared. The test procedure was the same as in Test Example 4-1. The result is shown in FIG. 5E. As shown in FIG. 5E, Tachibana peel 3 extract showed significant TH transcriptional activity in PC12D cells compared to control and nobiletin.
- GTP cyclohydrolase I (GCH I) level-increasing action of Tachibana bark extract in PC12D cells
- GPC I level-increasing action was examined in PC12D cells.
- GCH I is a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of the coenzyme tetrahydrobiopterin (BH 4 ) essential for TH.
- PC12D cells were treated with Tachibana peel extract, Chen peel extract and DMSO (control) at a concentration of 120 ⁇ g / mL for 48 hours, washed with PBS, and cell lysate (1 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, 10 mM HEPES, 10 mM NaF) , 1 mM p-APMSF, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 10 nM calyculin, 320 ⁇ M okadaic acid, 10 ⁇ g / mL pepstatin, 10 ⁇ g / mL antipine, 10 ⁇ g / mL leupeptin, 10 ⁇ g / mL chymostatin, 10 ⁇ g / mL phosphoramidon, 240 pM cypermethrin).
- the Tachibana peel extract 120 ⁇ g / mL used in this test example contained about 3.76 ⁇ M nobiletin, and the cuticle extract 120 ⁇ g / mL contained about 2.02 ⁇ M nobiletin.
- Tachibana peel extract and Chen peel extract significantly increased the expression level of GCH I compared to the control.
- Tachibana peel extract significantly increased the expression level of GCH I compared to Chen peel extract.
- Coenzyme BH4 which is essential for the expression of TH activity, increases the amount of TH protein, increases the TH enzyme activity, and promotes dopamine synthesis when the intracellular BH4 content is higher than the amount indicated by the Michaelis constant. .
- the Tachibana peel extract of the present invention significantly increases the expression level of GCH I, and therefore increases the amount of GCH I, which is the rate-determining enzyme of coenzyme BH4 synthesis that is essential for the expression of TH activity.
- GCH I is the rate-determining enzyme of coenzyme BH4 synthesis that is essential for the expression of TH activity.
- TH activity is increased, and as a result, production and secretion of dopamine are presumed to be promoted, and a medicinal effect as a Parkinson's disease therapeutic agent is expected.
- Test Example 12 CRE Transcriptional Activity of Citrus Citrus Skin Extract in Hippocampal Nerve Cells Using the extract extracted from Citrus mandarin 1 obtained in Example 2 by the method described herein, CRE transcriptional activity in hippocampal neurons is controlled And compared with nobiletin. The test procedure was the same as in Test Example 2. The results are shown in FIG. 7A. In addition, 100 ⁇ g / mL of the extract derived from 1 pericarp used in this test example contained about 3.4 ⁇ M nobiletin, and about 10.1 ⁇ M nobiletin in 300 ⁇ g / mL. As shown in FIG. 7A, the extract derived from the citrus pericarp showed significant CRE transcriptional activity in hippocampal neurons as compared to the control and nobiletin.
- the extract derived from the fruit peel of the present invention shows a remarkable CRE transcriptional activity exceeding the activity predicted from the content of nobiletin, and is expected to be effective as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease.
- Fine granules A A total of 200 to 200 g in proportions of 3.0 g of leather, 3.0 g of touki, 3.0 g of butterfly, 3.0 g of cucumber, 4.0 g of peanuts, 4.0 g of bakuryo, 2.0 g of psycho, 1.5 g of licorice and 5.0 g of hanger Herbal medicine was blended to 800 kg and extracted (extracted can) with water 2000-8000 L at 60-100 ° C for 30-180 minutes. After filtration (centrifugation) at a rotational speed of 1000 to 5000 rpm, solid-liquid separation was performed, followed by concentration to a concentration of about 10 to 40% under reduced pressure of 8 kPa or less (coil rotation type concentrator).
- the concentrated solution was spray-dried (spray dryer) at a rotational speed of 10000-20000 rpm, a supply temperature of 130-180 ° C, and an exhaust temperature of 60-120 ° C to obtain an extract formulation (Yokukansanka-Chanka summer extract). .
- a total amount of 50-400 kg is obtained at a ratio of 2.9 g of an additive consisting of magnesium stearate, corn starch, lactose, pullulan and magnesium aluminate metasilicate to 6.1 g of the obtained yokukansan kachu semi-summer extract.
- the resulting fine granule A 9.0 g contains 6.1 g of Yokukansan Kashide semi-summer extract containing 3.0 g of skin and other herbal medicines. Take 2 to 3 times a day.
- additive consisting of magnesium stearate, corn starch, lactose, pullulan and magnesium aluminate metasilicate
- the resulting fine granule B 6.0 g contains 3.7 ⁇ g Kumisoto extract containing 3.0 tachibana peel and other herbal medicines.
- the fine granule B 6.0 g per day Take 2 to 3 times.
- Chotosan extract obtained in a ratio of 1.52 g of additive consisting of hydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate and corn starch in a total amount of 50-400 kg, 4 rpm for 20 minutes Mix (container rotating type mixer), mold at roll pressure of 490-2500 Pa, adjust particle size (dry granulator), classify particles between sieves 30-50 (cassette screen), fine granules C was obtained.
- the obtained fine granule C 6.0 g contains 4.48 g Chotosan extract containing 2.4 g Chen and other herbal medicines.
- the fine granule C 6.0 g 3 times a day for adults Take in divided doses.
- the ratio of 9.2 g of additive consisting of hydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate and corn starch to 10 g of the crude or powdered raw material of cinnamon bark is blended in a total amount of 50 to 400 kg, and the number of rotations Mix at 4 rpm for 20 minutes (container rotation type mixer), mold at roll pressure 490-2500 Pa, adjust size (dry granulator), and classify particles between sieves 30-42 (cassette screen) As a result, a fine granule D was obtained.
- the resulting fine granule D (19.2 g) contains 10 g of crusted or tachibana peel, and as a guideline, the fine granule D (19.2 to 38.4 g) should be taken 2 to 3 times a day for adults.
- Decoction 10-30 g of decoction or tachibana peel was decocted with 200-600 mL of 20 times the amount of water at 100 ° C. for 1 hour, and the water was halved, followed by filtration to obtain a decoction.
- the resulting decoction (100-300 mL) contains 10-30 g of decoction or tachibana peel.
- 100-300 mL of decoction is taken in three divided doses per day for adults.
- the resulting fine granule E 9.0 g contains 7.2 g of cinnamon extract or citrus peel extract equivalent to 20 g of cinnamon or tachibana peel. Take 3 divided doses.
- the 13 capsules obtained (470 to 480 mg / piece) contain 3.6 kg of crust or extract of tachibana, equivalent to 10 g of crust or tachibana, and 13 to 26 capsules as a guide. Take 2 to 3 times a day for adults.
- Coated tablets 50 kg of peel or tachibana peel was extracted (extracted can) with 500 to 2000 L of water at 60 to 100 ° C for 30 to 180 minutes. After filtration (centrifugation) at a rotational speed of 1000 to 2500 rpm, solid-liquid separation was performed, and the solution was concentrated to a concentration of about 10 to 40% under reduced pressure of 8 kPa or less (coil rotation type concentrator). The concentrate was spray-dried (spray dryer) at a rotational speed of 10000 to 20000 rpm, an air supply temperature of 130 to 180 ° C., and an exhaust temperature of 60 to 120 ° C. to obtain an extract of crust or tachibana peel.
- 10 g of the resulting extract is blended in a ratio of 9.1 g of an additive consisting of maltose, lactose, magnesium aluminate metasilicate and magnesium stearate in a total amount in the range of 50 to 400 kg, with a rotation speed of 4 rpm, Mix for 20 minutes (container rotation type mixer), tablet at a rotation speed of 20-55 rpm, primary compression 0.6 mm or more, secondary compression 0.4 mm or more (high-speed rotary tableting machine), 1 tablet 350 mg I got a tablet.
- an additive consisting of maltose, lactose, magnesium aluminate metasilicate and magnesium stearate in a total amount in the range of 50 to 400 kg, with a rotation speed of 4 rpm, Mix for 20 minutes (container rotation type mixer), tablet at a rotation speed of 20-55 rpm, primary compression 0.6 mm or more, secondary compression 0.4 mm or more (high-speed rotary tableting machine), 1 tablet 350 mg
- the obtained 20 coated tablets contain 3.6 g of peel or tachibana peel equivalent to 10 g of peel or tachibana, and as a guideline, 20 to 40 coated tablets 2-3 times a day for adults Take in divided doses.
- Fine granule F 50 kg of peel or tachibana peel was extracted (extraction can) at 500 to 2000 L of water at 60 to 100 ° C. for 30 to 180 minutes. After filtration (centrifugation) at a rotational speed of 1000 to 2500 rpm, solid-liquid separation was performed, and the solution was concentrated to a concentration of about 10 to 40% under reduced pressure of 8 kPa or less (coil rotation type concentrator). The concentrate was spray-dried (spray dryer) at a rotational speed of 10000 to 20000 rpm, an air supply temperature of 130 to 180 ° C., and an exhaust temperature of 60 to 120 ° C. to obtain an extract of crust or tachibana peel.
- 10 g of the resulting extract is blended in a ratio of 15 g of an additive consisting of corn starch, maltose, hydrous silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate in a total amount in the range of 50 to 400 kg, rotating at 4 rpm, 20 Mix for a minute (container rotation type mixer), mold at roll pressure of 490-2500 Pa, adjust the size (dry granulator), classify particles between sieves 30-42 (cassette screen), fine particles Agent F was obtained.
- the obtained fine granule F 4.5 g contains 1.8 g of the skin extract or tachibana peel equivalent to 5 g of crust or tachibana skin, and as a guideline, the fine granule F 4.5 ⁇ 9.0 g per day for adults Take 2 to 3 times.
- 10 g of the resulting extract is blended in a ratio of 40 g of an additive consisting of calcium carmellose, hydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium aluminate metasilicate and magnesium stearate in a total amount of 50 to 400 kg and rotated.
- an additive consisting of calcium carmellose, hydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium aluminate metasilicate and magnesium stearate in a total amount of 50 to 400 kg and rotated.
- Mix at several 4 rpm for 20 minutes (container rotating type mixer), mold at roll pressure 490-2500 Pa, adjust particle size (dry granulator), and classify particles between sieves 12-42 (cassette screen) ) To obtain granules.
- the obtained granule (18 g) contains 3.6 ⁇ g of peel or citrus peel extract equivalent to 10 g of cinnamon or tachibana peel.
- 18 to 36 g of granule (2 to 3 times a day for adults) Take in divided doses.
- 10 g of the resulting extract is added in a ratio of 40 g of additives consisting of carrageenan, locust bean gum, reduced maltose liquid sugar, xylitol, apple fragrance, lecithin and citric acid in a total amount of 10-30 kg
- the mixture was mixed at a rotational speed of 50 to 150 rpm (mixing stirrer), and an equal amount of hot water of 80 ° C. or higher was added with stirring and cooled to 15 ° C. or lower to obtain a jelly agent.
- the obtained jelly preparation (18 g) contains 3.6 g of cinnamon extract or tachibana peel extract equivalent to 10 g of peel or tachibana peel.
- 18 to 36 g of jelly preparation is used 2-3 times per day Take in divided doses.
- the resulting extract (3.6 g) is blended at a ratio of 0.9 g of additive consisting of finely divided silicon dioxide and sucrose fatty acid ester in a total amount of 50 to 400 kg and mixed for 20 minutes at 4 rpm.
- Rotating mixer molded at a roll pressure of 490-2500 Pa, sized (dry granulator), classified between sieves 30-42 (cassette screen) to obtain fine granules.
- the obtained 4.5g of fine grain contains 3.6g of Chen or Tachibana bark extract equivalent to 10g of Chen or Tachibana, and as a guideline, take 4.5g of fine per day for adults.
- Ratio of 15.9 g of additive consisting of lecithin, reduced maltose starch syrup, aspartame, ascorbic acid, trisodium citrate, gelling agent (FG-2266, Nitta Gelatin Co., Ltd.) and orange flavor to 10 g of the obtained extract Then, the total amount was blended in the range of 50 to 400 kg, and mixed at a rotational speed of 4 rpm for 20 minutes (container rotating type mixer) to obtain a jelly base.
- gelling agent FG-2266, Nitta Gelatin Co., Ltd.
- the resulting jelly base of 9.3 g contains 3.6 g of cinnamon extract or citrus peel extract equivalent to 10 g of crust or tachibana, and as a guideline, ingest 9.3 to 18.6 g of jelly per day for adults .
- the dried plant tissue or plant tissue extract of the present invention is useful as a pharmaceutical or food for improving central neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, and is also used as a component of a promising fundamental therapeutic agent for the disease Is possible.
- the dried plant tissue or plant tissue extract of the present invention is particularly useful for memory acquisition, retention and enhanced recall ability.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Natural Medicines & Medicinal Plants (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Alternative & Traditional Medicine (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| HK13105841.5A HK1178792B (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2011-02-25 | Dried plant tissue and plant tissue extract for ameliorating central nervous system degenerative diseases accompanied by learning/memory disorders, movement disorders and the like, and pharmaceutical agent and food or beverage each comprising the dried plant tissue and the plant tissue extract |
| JP2012501889A JP5503726B2 (ja) | 2010-02-26 | 2011-02-25 | 学習・記憶障害および運動障害などを伴う中枢神経変性疾患を改善する乾燥植物組織および植物組織抽出物ならびにこれらを含有する医薬品および食品 |
| CN201180011122.5A CN102883716B (zh) | 2010-02-26 | 2011-02-25 | 改善伴有学习/记忆障碍和运动障碍等的中枢神经变性疾病的干燥植物组织和植物组织提取物以及含有它们的药品和食品 |
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010042819 | 2010-02-26 | ||
| JP2010-042819 | 2010-02-26 | ||
| JP2010-126717 | 2010-06-02 | ||
| JP2010126717 | 2010-06-02 | ||
| JP2010-270578 | 2010-12-03 | ||
| JP2010270578 | 2010-12-03 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011105568A1 true WO2011105568A1 (ja) | 2011-09-01 |
Family
ID=44506965
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/054358 Ceased WO2011105568A1 (ja) | 2010-02-26 | 2011-02-25 | 学習・記憶障害および運動障害などを伴う中枢神経変性疾患を改善する乾燥植物組織および植物組織抽出物ならびにこれらを含有する医薬品および食品 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP5503726B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102883716B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2011105568A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013191236A1 (ja) * | 2012-06-21 | 2013-12-27 | 小太郎漢方製薬株式会社 | 中枢神経変性疾患の改善および/または治療用組成物 |
| JP2014230509A (ja) * | 2013-05-29 | 2014-12-11 | 要 有持 | 生産方法、加工方法、加工品及び茶 |
| JP2015053939A (ja) * | 2013-09-10 | 2015-03-23 | 久子 松野 | みかんの果皮の加工食品 |
| WO2015199118A1 (ja) * | 2014-06-26 | 2015-12-30 | 日本ゼオン株式会社 | 培養細胞内のerkまたはaktのリン酸化亢進方法、細胞の培養方法、およびリン酸化亢進剤 |
| WO2016075960A1 (ja) * | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-19 | 株式会社沖縄リサーチセンター | 排尿障害を予防又は改善させる医薬組成物、排尿障害関連受容体に関する拮抗剤又はその医薬組成物又は拮抗剤を用いた排尿障害を予防又は改善させる方法 |
| WO2017208868A1 (ja) * | 2016-06-01 | 2017-12-07 | 株式会社三協ホールディングス | 医薬組成物および食品 |
| WO2019102602A1 (ja) * | 2017-11-27 | 2019-05-31 | 康 大泉 | スクリーニング方法 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103479743B (zh) * | 2013-01-28 | 2015-07-08 | 钱昌美 | 治疗老年痴呆的药物组合物及其制备方法 |
| JP2016056149A (ja) * | 2014-09-11 | 2016-04-21 | 日油株式会社 | 皮膚化粧料 |
| JP6898628B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-15 | 2021-07-07 | 国立大学法人広島大学 | 神経変性疾患治療剤 |
| CN107648349A (zh) * | 2017-10-30 | 2018-02-02 | 江西中医药大学 | 代代花在制备改善睡眠障碍或改善记忆力减退或治疗阿尔茨海默病药物或保健食品中的应用 |
| KR101894491B1 (ko) * | 2018-04-30 | 2018-09-04 | 주식회사 뉴트라팜텍 | 지각 초임계 추출물을 유효성분으로 함유하는 기억력 또는 인지 기능 개선용 조성물 |
| CN112402409A (zh) * | 2020-12-11 | 2021-02-26 | 江汉大学 | 橘皮素在制备抑制β分泌酶活性药物中的应用 |
| CN115886258B (zh) * | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-05 | 上海交大昂立股份有限公司 | 一种改善生理性记忆力衰减的复合益生菌组合物 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002053152A1 (en) * | 2001-01-08 | 2002-07-11 | Imperial College Of Science, Technology & Medicine | Composition containing flavonoids for treatment brain disorders |
| JP2008127325A (ja) * | 2006-11-20 | 2008-06-05 | Tokyoto Koreisha Kenkyu Fukushi Shinko Zaidan | リン酸化mbp産生促進剤 |
-
2011
- 2011-02-25 JP JP2012501889A patent/JP5503726B2/ja active Active
- 2011-02-25 CN CN201180011122.5A patent/CN102883716B/zh active Active
- 2011-02-25 WO PCT/JP2011/054358 patent/WO2011105568A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2014
- 2014-03-14 JP JP2014052426A patent/JP5906267B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002053152A1 (en) * | 2001-01-08 | 2002-07-11 | Imperial College Of Science, Technology & Medicine | Composition containing flavonoids for treatment brain disorders |
| JP2008127325A (ja) * | 2006-11-20 | 2008-06-05 | Tokyoto Koreisha Kenkyu Fukushi Shinko Zaidan | リン酸化mbp産生促進剤 |
Non-Patent Citations (9)
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013191236A1 (ja) * | 2012-06-21 | 2013-12-27 | 小太郎漢方製薬株式会社 | 中枢神経変性疾患の改善および/または治療用組成物 |
| JPWO2013191236A1 (ja) * | 2012-06-21 | 2016-05-26 | 小太郎漢方製薬株式会社 | 中枢神経変性疾患の改善および/または治療用組成物 |
| JP2014230509A (ja) * | 2013-05-29 | 2014-12-11 | 要 有持 | 生産方法、加工方法、加工品及び茶 |
| JP2015053939A (ja) * | 2013-09-10 | 2015-03-23 | 久子 松野 | みかんの果皮の加工食品 |
| WO2015199118A1 (ja) * | 2014-06-26 | 2015-12-30 | 日本ゼオン株式会社 | 培養細胞内のerkまたはaktのリン酸化亢進方法、細胞の培養方法、およびリン酸化亢進剤 |
| JP2016146819A (ja) * | 2014-06-26 | 2016-08-18 | 日本ゼオン株式会社 | 培養細胞内のerkまたはaktのリン酸化亢進方法、および細胞の培養方法 |
| JPWO2015199118A1 (ja) * | 2014-06-26 | 2017-04-20 | 日本ゼオン株式会社 | 培養細胞内のerkまたはaktのリン酸化亢進方法、細胞の培養方法、およびリン酸化亢進剤 |
| WO2016075960A1 (ja) * | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-19 | 株式会社沖縄リサーチセンター | 排尿障害を予防又は改善させる医薬組成物、排尿障害関連受容体に関する拮抗剤又はその医薬組成物又は拮抗剤を用いた排尿障害を予防又は改善させる方法 |
| WO2017208868A1 (ja) * | 2016-06-01 | 2017-12-07 | 株式会社三協ホールディングス | 医薬組成物および食品 |
| JP2017214330A (ja) * | 2016-06-01 | 2017-12-07 | 株式会社三協ホールディングス | 医薬組成物および食品 |
| EP3466436A4 (en) * | 2016-06-01 | 2020-01-01 | Sankyo Holdings Co., Ltd. | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION AND FOOD |
| WO2019102602A1 (ja) * | 2017-11-27 | 2019-05-31 | 康 大泉 | スクリーニング方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102883716A (zh) | 2013-01-16 |
| JPWO2011105568A1 (ja) | 2013-06-20 |
| JP5503726B2 (ja) | 2014-05-28 |
| CN102883716B (zh) | 2014-05-07 |
| JP5906267B2 (ja) | 2016-04-20 |
| HK1178792A1 (zh) | 2013-09-19 |
| JP2014111664A (ja) | 2014-06-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5503726B2 (ja) | 学習・記憶障害および運動障害などを伴う中枢神経変性疾患を改善する乾燥植物組織および植物組織抽出物ならびにこれらを含有する医薬品および食品 | |
| Mondal et al. | Central-stimulating and analgesic activity of the ethanolic extract of Alternanthera sessilis in mice | |
| JP6033863B2 (ja) | 中枢神経変性疾患の改善および/または治療用組成物 | |
| CN112294821B (zh) | 5-甲基四氢叶酸的用途及其组合物 | |
| US20040247715A1 (en) | Water soluble extract from plant of solanum genus and the preparation process thereof, and pharmaceutical composition containing the water soluble extract | |
| US20210128664A1 (en) | Agent for Activating Astrocyte Glucose Metabolism | |
| JPWO2015076286A1 (ja) | エフェドリンアルカロイド除去麻黄エキスと、その製法及び用途 | |
| EP4643864A2 (en) | Novel association of gastrodia elata, citicoline, l-acetylcarnitine, vitamin b and vitamin d | |
| KR102041847B1 (ko) | 물푸레나무 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는 우울증 및 불안장애의 예방, 개선 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| JP7642212B2 (ja) | 神経機能調節用組成物 | |
| CN102151306B (zh) | 一种从荔枝果肉中提取的活性组合物及其制备方法和应用 | |
| Dimpfel et al. | Zynamite®(Mangifera indica Leaf Extract) and Caffeine Act in a Synergistic Manner on Electrophysiological Parameters of Rat Central Nervous System | |
| Nafiu et al. | Ameliorative effect of Lecaniodiscus cupanioides (Sapindaceae) aqueous root extract in loperamide-induced constipated rats | |
| KR20110095765A (ko) | 현삼 추출물을 포함하는 항알레르기 조성물 | |
| WO2011090265A2 (ko) | 신코닌을 유효성분으로 포함하는 비만, 이상지방혈증, 지방간 또는 인슐린 저항성 증후군의 예방 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| US20060269621A1 (en) | Novel therapeutic extracts and molecules for degenerative conditions | |
| Iqbal et al. | Phytochemistry, Laxative, Prokinetic and Spasmolytic Verification of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal Using In-Vitro, In-Vivo and In-Silico Approaches | |
| EP4667007A2 (en) | Novel association of gastrodia elata and vitamin b | |
| JP2018177748A (ja) | アストロサイトのグルコース代謝活性化剤 | |
| Susiloningrum et al. | Optimization of Solvent Variations from Fruit Skin Extracts Breadfruit Artocarpus Altilis (Parkinsom Ex FA, Zom) Fosberg on Analgetic Activity In Vivo | |
| KR20250012174A (ko) | 신경 보호 효과를 갖는 약제학적 조성물 및 그 치료제 | |
| JPWO2005082391A1 (ja) | ヒトβ3アドレナリン受容体アゴニスト剤 | |
| KR20250023032A (ko) | 포도근 추출물을 포함하는 천포창 개선 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| CN114605242A (zh) | 间苯三酚类化合物的制备方法与药物、保健产品和食品 | |
| CN121154749A (en) | Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating depression and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201180011122.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11747524 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2012501889 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11747524 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |