WO2010134345A1 - 血液凝固時間延長剤 - Google Patents
血液凝固時間延長剤 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010134345A1 WO2010134345A1 PCT/JP2010/003401 JP2010003401W WO2010134345A1 WO 2010134345 A1 WO2010134345 A1 WO 2010134345A1 JP 2010003401 W JP2010003401 W JP 2010003401W WO 2010134345 A1 WO2010134345 A1 WO 2010134345A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- blood coagulation
- alkyl group
- amino group
- measurement
- time
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CCCCC(N*)OC Chemical compound CCCCC(N*)OC 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/86—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving blood coagulating time or factors, or their receptors
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/13—Amines
- A61K31/155—Amidines (), e.g. guanidine (H2N—C(=NH)—NH2), isourea (N=C(OH)—NH2), isothiourea (—N=C(SH)—NH2)
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P7/00—Drugs for disorders of the blood or the extracellular fluid
- A61P7/02—Antithrombotic agents; Anticoagulants; Platelet aggregation inhibitors
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C279/00—Derivatives of guanidine, i.e. compounds containing the group, the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C279/02—Guanidine; Salts, complexes or addition compounds thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C279/00—Derivatives of guanidine, i.e. compounds containing the group, the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C279/04—Derivatives of guanidine, i.e. compounds containing the group, the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton
- C07C279/14—Derivatives of guanidine, i.e. compounds containing the group, the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton being further substituted by carboxyl groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C281/00—Derivatives of carbonic acid containing functional groups covered by groups C07C269/00 - C07C279/00 in which at least one nitrogen atom of these functional groups is further bound to another nitrogen atom not being part of a nitro or nitroso group
- C07C281/16—Compounds containing any of the groups, e.g. aminoguanidine
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q1/00—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions
- C12Q1/56—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions involving blood clotting factors, e.g. involving thrombin, thromboplastin, fibrinogen
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N2333/00—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature
- G01N2333/435—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature from animals; from humans
- G01N2333/745—Assays involving non-enzymic blood coagulation factors
Definitions
- the present invention is a blood coagulation ability measurement reagent typified by a fibrinogen measurement reagent, that is, a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent and / or a blood coagulation time extending agent used for a specimen dilution liquid for blood coagulation ability measurement, and the same.
- the present invention relates to a reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability.
- the mechanism of blood coagulation is generally roughly divided into two systems.
- One is an endogenous system that starts with contact activation of blood coagulation factor XII with a foreign substance, and finally generates thrombin through a multistage reaction, and the other is blood coagulation by blood coagulation factor VII and tissue thromboplastin.
- It is an extrinsic system that begins with the activation of factor X and also generates thrombin (FIG. 1).
- coagulation finally occurs as fibrinogen is converted into fibrin by the action of the generated thrombin.
- There are several blood coagulation ability tests using a blood coagulation activator in order to clarify the presence or absence of abnormalities in these blood coagulation mechanisms and the causes of the abnormalities, and they are widely used in clinical examinations.
- Blood coagulation activators and blood coagulation tests using the same are as follows. 1) Blood coagulation test using thrombin Fibrinogen measurement, ATIII measurement, thrombin time measurement 2) Blood coagulation test using tissue thromboplastin Prothrombin time measurement, II, V, VII and X factor activity measurements using prothrombin time , Complex factor measurement (thrombotest, hepaplastin test, etc.) 3) Examination of blood coagulation ability using phospholipids Activity measurement of partial thromboplastin time measurement, activated partial thromboplastin time measurement, activated partial thromboplastin time measurement, activity of VIII, IX, XI, factor XII, prekallikrein, and high molecular weight kininogen , Snake venom time measurement, factor X quantification using snake venom time measurement, lupus anticoagulant (LA) measurement using diluted snake venom time measurement, protein C activity measurement, thromboplastin production test Any of the above 1) to 3) tests In this method, the time
- the methods for detecting coagulation in the blood coagulation test can be broadly divided into mechanical detection methods and optical detection methods.
- the dynamic detection method is a method of monitoring a magnetic substance or the like put in a reaction solution by a magnetic force or the like and detecting that the viscosity becomes high due to solidification and the movement of the magnetic substance becomes slow.
- the optical detection method is a method for detecting the white turbidity of the reaction solution due to coagulation as a change amount of transmitted light or scattered light, and is most widely used because it is relatively simple. These are now generally detected by automated equipment. An example of the intensity change curve of the scattered light obtained by the scattered light detection method is shown in FIG.
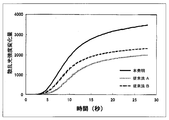
- point A indicates the point at which coagulation is induced by mixing a reagent containing a blood coagulation activator, and then fibrin precipitation starts through a multi-stage reaction. Change appears. When fibrinogen is consumed one after another and almost depleted in the reaction solution, the change in scattered light intensity disappears, the curve becomes flat like point C, and coagulation is completed. Based on such an intensity change curve of scattered light, the coagulation time is calculated by a known calculation parameter (Patent Document 1). Here, if the maximum value of the intensity change amount of the scattered light is ⁇ H, it is obvious that the larger ⁇ H makes the coagulation detection more sensitive and more accurate detection possible.
- the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability used has such a characteristic that the optical change amount is greatly displayed.
- the change from point A to point C occurs in a very short time, the coagulation time cannot be measured with high accuracy. Therefore, a substance that extends the coagulation time is usually added to adjust the coagulation time to a desired length.
- Patent Document 2 exemplifies alkali metal or alkaline earth metal halide salts including sodium chloride
- Patent Document 3 exemplifies sodium propionate.
- such a conventional blood coagulation time prolonging agent has a problem in that it has a large negative effect of reducing ⁇ H depending on the addition amount at the same time.
- Patent Documents 4 and 5 In order to solve the problems of these conventional methods, methods using a reagent added with a polymer substance such as polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, and polymer polysaccharide have been proposed (Patent Documents 4 and 5).
- JP-A-8-15263 Japanese Patent No. 2994557 Japanese Patent No. 3330685 Japanese Patent No. 3074611 Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 5-60763
- an object of the present invention is to provide a reagent having a composition that extends the blood coagulation time to a desired time and enhances the optical change. This can contribute to improving the accuracy of the blood coagulation test.
- the present inventor has searched for a blood coagulation time extending agent that enhances optical changes using various compounds.
- a guanidine compound having a specific structure or a salt thereof is used. It has the effect of enhancing optical changes during coagulation, and it has been found that blood coagulation ability can be measured accurately and with high sensitivity if it is used as an additive for a blood coagulation ability measurement reagent, and the present invention has been completed.
- R 1 represents a hydrogen atom, an amino group, or an alkyl group which may have a substituent
- a blood coagulation time extending agent comprising a guanidine compound or an acid addition salt thereof as an active ingredient To do.
- the present invention provides a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent or a specimen dilution liquid for measuring blood coagulation ability, characterized by containing the above-mentioned blood coagulation time extending agent.
- the present invention provides a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent for fibrinogen measurement or a specimen diluent for fibrinogen measurement, characterized in that it contains the above-mentioned blood coagulation time extending agent and the blood coagulation activator is thrombin. To do.
- the present invention provides the following formula (1) for prolonging blood coagulation time.
- R 1 represents a hydrogen atom, an amino group or an alkyl group which may have a substituent
- a guanidine compound represented by the above or an acid addition salt thereof is used with a blood coagulation activator.
- the guanidine compound or the acid addition salt thereof is used together with a specimen diluent for measuring blood coagulation ability.
- the present invention also provides a plasma sample with the following formula (1): (In the formula, R 1 represents a hydrogen atom, an amino group, or an alkyl group which may have a substituent)
- the guanidine compound represented by It provides a way to In one embodiment, the guanidine compound or an acid addition salt thereof is added together with a specimen diluent for measuring blood coagulation ability. In another embodiment, the guanidine compound or acid addition salt thereof is added with a blood coagulation activator.
- the present invention provides a step of preparing a reaction solution containing a plasma sample, a blood coagulation activator, and the guanidine compound or an acid addition salt thereof; and a step of measuring the coagulation time of the reaction solution.
- a method for measuring blood coagulation ability is provided.
- the present invention also compares the measured value of the clotting time using the plasma sample with the measured value obtained by measuring the clotting time in the same manner using a diluted standard solution instead of the plasma sample.
- a method for determining the fibrinogen concentration in a plasma sample is provided.
- blood coagulation ability such as fibrinogen measurement, PT, and APTT can be accurately measured.
- the mechanism of blood coagulation in clinical examination is shown schematically.
- An example of a scattered light intensity change curve obtained by the scattered light detection method when measuring blood coagulation ability is shown.
- the relationship between the addition amount of each compound and the coagulation time is shown.
- the relationship between the coagulation time and the maximum amount of change in scattered light intensity when the coagulation time is adjusted by adding each compound is shown.
- the scattered light intensity change curve by the conventional method reagent and this invention reagent is shown.
- the blood coagulation time prolonging agent of the present invention comprises a compound represented by the formula (1) or a salt thereof as an active ingredient.
- R 1 represents a hydrogen atom, an amino group, or an alkyl group that may have a substituent.
- the alkyl group an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is preferable, and an alkyl group having 2 to 5 carbon atoms is particularly preferable.
- the group that can be substituted with the alkyl group include a carboxyl group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, and an amino group, and it is preferable that both the carboxyl group and the amino group, or both the alkoxycarbonyl group and the amino group are substituted.
- the compound represented by the formula (1) examples include guanidine, aminoguanidine, arginine, and arginine alkyl ester.
- aminoguanidine is a compound that has a large optical change enhancement effect and enables accurate measurement.
- the acid addition salt of the compound of the formula (1) include hydrochloride, sulfate, nitrate, phosphate, sulfamate and the like.
- the blood coagulation time prolonging agent of the present invention not only prolongs the blood coagulation time but also has an action of enhancing the turbidity change of the reaction solution in measuring blood coagulation ability. This indicates that the formation state of the fibrin network, which is the final product of blood coagulation, becomes stronger. Therefore, the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention can be used for an optical detection method for directly detecting a change in turbidity, a mechanical detection method for monitoring the formation state of a fibrin network with a magnetic substance, and the like. It is preferred to use.
- the optical detection method includes a scattered light amount detection method and a transmitted light amount detection method, and is preferably used for the scattered light amount detection method.
- the blood coagulation ability test to which the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention can be applied is based on the fact that fibrinogen is finally converted into fibrin from the initiation of coagulation by mixing a reagent containing a blood coagulation activator or the like with a patient sample. What is necessary is just to measure the time until precipitation.
- Examples include fibrinogen measurement, ATIII measurement, thrombin time measurement, prothrombin time measurement, II, V, VII, factor X activity measurement using prothrombin time, complex factor measurement (thrombotest, hepaplastin test, etc.), partial thromboplastin Time measurement, activated partial thromboplastin time measurement, activated partial thromboplastin time measurement using VIII, IX, XI, factor XII, prekallikrein, macromolecular kininogen activity measurement, snake venom time measurement, snake venom time measurement using factor X Quantification, lupus anticoagulant (LA) measurement using dilution snake venom time measurement, protein C activity measurement, thromboplastin production test, and other detection of abnormal coagulation.
- fibrinogen measurement ATIII measurement, thrombin time measurement, prothrombin time measurement, II, V, VII, factor X activity measurement using prothrombin time, complex factor measurement (thrombotest, hepaplastin test, etc.
- a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent for example, a thrombin-containing reagent in fibrinogen measurement
- the sample is appropriately diluted with a sample diluent as necessary.
- the blood coagulation time prolonging agent of the present invention may be contained in the measurement system, and may be contained in a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent or in a specimen diluent. That is, the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention may be contained in a thrombin-containing reagent or in a specimen dilution solution, for example, in fibrinogen measurement.
- the blood coagulation activator-containing reagent only needs to be used for the blood coagulation ability test.
- Examples include a thrombin-containing reagent, a tissue thromboplastin-containing reagent, a phospholipid-containing reagent, and the like.
- the specimen dilution solution may be any one that is used for the blood coagulation ability test.
- MES MES
- Bis-Tris ADA
- PIPES ACES
- MOPSO BES
- MOPS MOPS
- TES HEPES
- DIPSO DIPSO
- TAPSO POPSO
- HEPPSO EPPS
- Tricine Tricine
- Bicine Tricine
- TAPS CHES and other good buffers
- citrate buffers Liquid, phosphate buffer, acetate buffer, imidazole buffer, barbital buffer, physiological saline, water and the like.
- the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention is preferably contained in the reaction solution so that a coagulation time that can be accurately measured in a blood coagulation test is obtained.
- the reaction solution is such that a clotting time of 5 to 50 seconds, preferably 7 to 20 seconds, more preferably 9 to 15 seconds is obtained. It is preferable to contain in.
- the concentration in the reaction solution for fibrinogen measurement that is, the concentration in the mixed solution of the specimen, the specimen diluent, and the thrombin-containing reagent is 10 to 500 mM, preferably 20 to 200 mM. More preferably, it is 30 to 120 mM.
- the concentration in the sample diluent is 10 to 900 mM, preferably 30 to 400 mM, more preferably 50 to 200 mM.
- prothrombin time measurement when normal plasma (activity of about 100%) is measured, the reaction solution is allowed to have a clotting time of 9 to 60 seconds, preferably 9 to 30 seconds, and more preferably 10 to 16 seconds. It is preferable to contain.
- the activated partial thromboplastin time measurement when normal plasma is measured, it is contained in the reaction solution so that a clotting time of 15 to 80 seconds, preferably 15 to 60 seconds, and more preferably 20 to 50 seconds can be obtained.
- Other blood coagulation ability tests may be included in the reaction solution so that a coagulation time suitable for the measurement method can be obtained.
- known polymer polysaccharides and synthetic polymers are included in the blood coagulation ability measurement reagent including the specimen diluent and the blood coagulation activator-containing reagent used for the blood coagulation ability test. Can be contained.
- polymer polysaccharide examples include dextran, dextran 70, dextran 70, dextran 200000, dextran 500000, and the like. These high molecular polysaccharides can be used alone or in combination of two or more. The amount of these polymeric polysaccharides added is preferably 0.01 to 10 W / V%, more preferably 0.1 to 5 W / V%, in the blood coagulation ability measuring reagent.
- the synthetic polymers include polyvinyl alcohols such as polyvinyl alcohol 500, polyvinyl alcohol 1500, and polyvinyl alcohol 2000, polyethylene glycol 1500, polyethylene glycol 2000, polyethylene glycol 4000, polyethylene glycol 6000, polyethylene glycol 8000, polyethylene glycol 20000, and the like. And polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. These synthetic polymers can be used alone or in combination of two or more. The addition amount of these synthetic polymers is not particularly limited, but the concentration in the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability is preferably 0.01 to 10 W / V%, more preferably 0.1 to 5 W / V. %.
- the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability may contain a buffer, calcium ion, an antagonist of an anticoagulant, etc. in addition to the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention.
- a buffer having a buffer capacity in the range of pH 4 to 9 is appropriately selected and used.
- good buffers such as MES, Bis-Tris, ADA, PIPES, ACES, MOPSO, BES, MOPS, TES, HEPES, DIPSO, TAPSO, POPSO, HEPPSO, EPPS, Tricine, Bicine, TAPS, CHES, citric acid,
- concentration in the blood coagulation ability measuring reagent is preferably 1 to 1000 mM, more preferably 5 to 500 mM.
- water-soluble calcium compounds such as calcium chloride, calcium lactate, calcium gluconate, calcium glucuronate, calcium tartrate are used. These calcium compounds can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the amount of calcium compound used is not particularly limited as long as it can support the coagulation reaction, but the concentration in the blood coagulation ability measurement reagent is preferably 5 mM to 100 mM, more preferably 10 mM to 50 mM. is there.
- protamine As an antagonist of the anticoagulant, protamine, polybrene (hexadimethrine bromide), or the like is used. These anticoagulant antagonists can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the amount of the anticoagulant antagonist used is not particularly limited as long as it is sufficient to neutralize the anticoagulant contained in the sample plasma, such as heparin, but the concentration in the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability is 10%.
- -5 to 10 -2 W / V% is preferable, and more preferably 5 ⁇ 10 -4 to 5 ⁇ 10 -3 W / V%.
- the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability may be a liquid product, a frozen product or a dried product, and the dried product is dissolved by adding purified water or a buffer solution.
- An appropriate preservative may be added to the reagent for measuring blood coagulation ability.
- the preservative one or a combination of two or more of ciprofloxacin, propionic acid, sodium benzoate, sodium azide, and procrine 300 can be selected and used.
- concentration described above describes the concentration in the solution product, but the dried product describes the concentration when dissolved in water or a buffer solution at the time of use.
- the standard solution is diluted 5 times, 10 times, and 20 times with the sample diluent (dilution ratio can be adjusted as appropriate).
- 2 volumes of each diluted standard solution is heated at 37 ° C. for 3 minutes, 1 volume of thrombin reagent previously heated to 37 ° C. is added, and the coagulation time is measured.
- the measured values of each diluted standard solution are plotted on a graph.
- a plasma sample is diluted 10-fold with a sample diluent (dilution ratio can be adjusted as appropriate), the diluted sample is measured in the same manner, and the concentration can be obtained from the graph based on the obtained clotting time. it can.
- Example 1 Confirmation of prolongation of clotting time
- thrombin time method When measuring the fibrinogen concentration in a plasma sample by the thrombin time method, generally add thrombin to plasma and measure the clotting time. Determine the concentration.
- 90 ⁇ L of a sample diluent is added to and mixed with 10 ⁇ L of sample plasma, 50 ⁇ L of a thrombin-containing reagent is added as a blood coagulation activator-containing reagent, and the clotting time is measured.
- HEPES buffer solution pH 7.5
- aminoguanidine hydrochloride was added to HEPES buffer (pH 7.5) as a blood coagulation time prolonging agent, the coagulation time was prolonged depending on the addition concentration as in the case of sodium chloride and sodium bromide, which are conventional methods (Fig. 3 shows the results). That is, it can be seen that the present invention has a coagulation time extending action equivalent to that of the conventional method.
- Example 2 Normal commercial plasma was measured in the same manner as in Example 1 using a sample diluent (HEPES buffer pH 7.5) in which the addition concentration of the blood coagulation time extender was adjusted so that the same degree of coagulation time was obtained.
- Table 1 shows a comparison result of ⁇ H of the scattered light intensity change maximum value of the conventional method and the present invention and the simultaneous reproducibility of the measurement.
- the blood coagulation time extending agent of the present invention that is, arginine hydrochloride, arginine methyl ester, guanidine hydrochloride, guanidine phosphate, guanidine sulfamate, aminoguanidine hydrochloride dramatically improves ⁇ H. It can also be seen that the measurement accuracy (simultaneous reproducibility, etc.) is also improved. Further, it was found that aminoguanidine hydrochloride is particularly excellent in improving the measurement accuracy (simultaneous reproducibility, etc.).
- Example 3 Sample diluent containing sodium chloride as a blood coagulation time extender is added to conventional method A and conventional method A, and further contains polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 20000) (hereinafter referred to as PEG 20000) as a light intensity change amount enhancer.
- PEG 20000 polyethylene glycol
- HEPES buffer pH 7.5
- the concentration of addition was set to 0.1%.
Abstract
Description
1)トロンビンを使用した血液凝固能検査
フィブリノゲン測定、ATIII測定、トロンビン時間測定
2)組織トロンボプラスチンを使用した血液凝固能検査
プロトロンビン時間測定、プロトロンビン時間を用いたII、V、VII、X因子の活性測定、複合因子測定(トロンボテスト・ヘパプラスチンテスト等)
3)リン脂質を使用した血液凝固能検査
部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定、活性化部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定、活性化部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定を用いたVIII、IX、XI、XII因子、プレカリクレイン、高分子キニノゲンの活性測定、蛇毒時間測定、蛇毒時間測定を用いたX因子の定量、希釈蛇毒時間測定を用いたループスアンチコアグラント(LA)測定、プロテインC活性測定、トロンボプラスチン生成試験
上記1)~3)のいずれの検査においても、患者検体に血液凝固活性化剤等を含む試薬を混合することによる凝固の惹起から最終的にフィブリノゲンがフィブリンに転化し析出するまでの時間を測定する。
従って本発明の課題は、血液凝固時間を所望の時間に延長し、かつ光学的変化を増強させるような組成の試薬を提供することにある。このことによって、血液凝固能検査の正確性向上に寄与することができる。
一実施形態において、上記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩は、血液凝固活性化剤とともに使用される。別の実施形態において、上記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩は、血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液とともに使用される。
一実施形態において、上記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩は、血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液とともに添加される。別の実施形態において、上記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩は、血液凝固活性化剤とともに添加される。
また一態様において、本発明は、当該血漿検体を用いた凝固時間の測定値と、当該血漿検体の代わりに希釈標準液を用いて同様に凝固時間を測定して得られた測定値とを比較することによる、血漿検体中のフィブリノゲン濃度を求める方法を提供するものである。
上記血液凝固活性化剤含有試薬は、上記血液凝固能検査に使用されるものであればよい。例えば、トロンビン含有試薬、組織トロンボプラスチン含有試薬、リン脂質含有試薬等が挙げられる。また、上記検体希釈液は、上記血液凝固能検査に使用されるものであればよい。例えば、MES、Bis-Tris、ADA、PIPES、ACES、MOPSO、BES、MOPS、TES、HEPES、DIPSO、TAPSO、POPSO、HEPPSO、EPPS、Tricine、Bicine、TAPS、CHESなどのグッド緩衝液、クエン酸緩衝液、リン酸緩衝液、酢酸緩衝液、イミダゾール緩衝液、バルビタール緩衝液、生理食塩液、水等を挙げることができる。
プロトロンビン時間測定の場合、正常血漿(活性約100%)を測定したとき、9~60秒、好ましくは9~30秒、さらに好ましくは10~16秒の凝固時間が得られるように反応液中に含有させることが好ましい。活性化部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定においては正常血漿を測定したとき、15~80秒、好ましくは15~60秒、さらに好ましくは20~50秒の凝固時間が得られるように反応液中に含有させることが好ましい。その他の血液凝固能検査に関しても、測定方法に適した凝固時間が得られるように反応液中に含有させればよい。
合成高分子類の具体例としては、ポリビニルアルコール500、ポリビニルアルコール1500、ポリビニルアルコール2000等のポリビニルアルコール、ポリエチレングリコール1500、ポリエチレングリコール2000、ポリエチレングリコール4000、ポリエチレングリコール6000、ポリエチレングリコール8000、ポリエチレングリコール20000等のポリエチレングリコール及びポリビニルピロリドン等を挙げることができる。これら合成高分子類は1種もしくは2種以上を組み合わせて用いることができる。これら合成高分子類の添加量は、特に限定されないが、前記血液凝固能測定試薬中の濃度が0.01~10W/V%であることが好適で、より好ましくは0.1~5W/V%である。
また前記血液凝固能測定試薬には適当な防腐剤を添加してもよい。防腐剤としては、シプロフロキサシン、プロピオン酸、安息香酸ナトリウム、アジ化ナトリウム、プロクリン300等の中から1種もしくは2種以上を組み合わせて選択し用いることができる。また、必要に応じて塩化ナトリウム等の塩や、アミノ酸、糖等の一般的な安定化剤等を含ませてもよい。
上記に記載の濃度は、溶液品中の濃度を記載しているが、乾燥品等は使用時に水又は緩衝液等で溶解したときの濃度を記載している。
(1)凝固時間延長作用の確認
トロンビン時間法で血漿検体中のフィブリノゲン濃度を測定する場合、一般的にトロンビンを血漿に添加して凝固時間を測定し、フィブリノゲン濃度既知の標準液による検量線から濃度を求める。手順としては、検体血漿10μLに対して90μLの検体希釈液を添加・混合した後、血液凝固活性化剤含有試薬として50μLのトロンビン含有試薬を添加し、凝固時間を測定する。
散乱光強度変化量の極大値をΔHとして算出し、凝固時間との関係を図4に示した。凝固時間が延長するのに伴い、従来法である塩化ナトリウム及び臭化ナトリウムではΔHが著しく低下するのに対し、本発明ではΔHは大きいまま維持された。すなわち、同程度の凝固時間で比較すると、従来法に比べ本発明のほうが散乱光強度の変化量が増大し、凝固時間をより正確に測定できることが分かる。
同程度の凝固時間が得られるように、血液凝固時間延長剤の添加濃度を調節した検体希釈液(HEPES緩衝液 pH7.5)を用いて、実施例1と同様に正常市販血漿を測定した。従来法と本発明の散乱光強度変化量極大値のΔHと、測定の同時再現性の比較結果を、表1に示した。従来法と比較して、本発明の血液凝固時間延長剤、すなわちアルギニン塩酸塩、アルギニンメチルエステル、グアニジン塩酸塩、グアニジンリン酸塩、グアニジンスルファミン酸塩、アミノグアニジン塩酸塩がΔHを飛躍的に向上させ、さらに測定の精度(同時再現性等)についても向上させていることがわかる。また、測定の精度(同時再現性等)向上効果については、アミノグアニジン塩酸塩が特に優れていることが判明した。
血液凝固時間延長剤として塩化ナトリウムを含む検体希釈液を従来法A、従来法Aに、更に光強度変化量増強剤としてポリエチレングリコール(分子量20000)(以下、PEG20000という)を含有させた検体希釈液を従来法Bとし、血液凝固時間延長剤と光強度変化量増強剤を兼ねたアミノグアニジン塩酸塩(本発明)を採用した検体希釈液と比較した。なお、いずれの場合も緩衝液としてはHEPES緩衝液(pH7.5)を用いた。また、従来法Bでは、PEG20000の添加量が多いと粘性が高まり、分取精度が低下するおそれがあることから、添加濃度は0.1%とした。それぞれの検体希釈液を使用して、実施例1と同様に市販正常血漿の凝固時間を測定した結果、図5に示すような散乱光の強度変化曲線を得た。また、凝固時間とΔHを表2に示した。PEG20000を添加した従来法Bでは、添加しなかった従来法Aに比べ、散乱光強度の変化量が大きくなったが、本発明の採用により散乱光強度変化量はさらに飛躍的に向上し、凝固時間をより正確に測定できることが分かる。
Claims (21)
- フィブリノゲン測定用血液凝固時間延長剤である請求項1記載の血液凝固時間延長剤。
- R1が、水素原子、アミノ基、アルキル基、カルボキシル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基、又はアルコキシカルボニル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基である請求項1又は2記載の血液凝固時間延長剤。
- 請求項1~3のいずれか1項記載の血液凝固時間延長剤を含有することを特徴とする血液凝固活性化剤含有試薬。
- 血液凝固活性化剤がトロンビンであるフィブリノゲン測定用の請求項4記載の血液凝固活性化剤含有試薬。
- 請求項1~3のいずれか1項記載の血液凝固時間延長剤を含有することを特徴とする血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液。
- フィブリノゲン測定用検体希釈液である請求項6記載の血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液。
- フィブリノゲン測定において血液凝固時間を延長させるための、請求項8記載の使用。
- R1が、水素原子、アミノ基、アルキル基、カルボキシル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基、又はアルコキシカルボニル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基である、請求項8又は9記載の使用。
- 血液凝固活性化剤とともに使用される、請求項8~10のいずれか1項記載の使用。
- 血液凝固活性化剤がトロンビンである請求項11記載の使用。
- 血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液とともに使用される、請求項8~10のいずれか1項記載の使用。
- 検体希釈液がフィブリノゲン測定用検体希釈液である請求項13記載の使用。
- R1が、水素原子、アミノ基、アルキル基、カルボキシル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基、又はアルコキシカルボニル基とアミノ基が置換したアルキル基である、請求項15記載の方法。
- 前記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩が血液凝固能測定用検体希釈液とともに添加される、請求項15記載の方法。
- 前記検体希釈液がフィブリノゲン測定用検体希釈液である請求項17記載の方法。
- 前記グアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩が血液凝固活性化剤とともに添加される、請求項15記載の方法。
- 血液凝固活性化剤がトロンビン含有試薬である請求項19記載の方法。
- 下記工程を含む血液凝固能測定方法:
血漿検体と、血液凝固活性化剤と、請求項15記載のグアニジン化合物又はその酸付加塩とを含有する反応液を調製する工程;及び
反応液の凝固時間を測定する工程。
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA2762611A CA2762611C (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
| KR1020187004669A KR101882408B1 (ko) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | 혈액응고시간 연장제 |
| JP2011514341A JPWO2010134345A1 (ja) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | 血液凝固時間延長剤 |
| CN2010800220995A CN102428372A (zh) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | 凝血时间延长剂 |
| EP10777581.9A EP2434290B1 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
| US13/321,732 US20120064553A1 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
| US14/153,739 US20140127727A1 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2014-01-13 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
| US14/658,911 US9733262B2 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2015-03-16 | Method for measuring blood coagulation |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009-121834 | 2009-05-20 | ||
| JP2009121834 | 2009-05-20 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/321,732 A-371-Of-International US20120064553A1 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
| US14/153,739 Division US20140127727A1 (en) | 2009-05-20 | 2014-01-13 | Blood coagulation time prolonging agent |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010134345A1 true WO2010134345A1 (ja) | 2010-11-25 |
Family
ID=43126036
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2010/003401 WO2010134345A1 (ja) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-05-20 | 血液凝固時間延長剤 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US20120064553A1 (ja) |
| EP (2) | EP3018481B1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JPWO2010134345A1 (ja) |
| KR (2) | KR101882408B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102428372A (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2762611C (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010134345A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012181033A (ja) * | 2011-02-28 | 2012-09-20 | Sysmex Corp | ループスアンチコアグラント検出用試薬キット及びループスアンチコアグラントの存否を判定する方法 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MX2016003182A (es) | 2013-09-11 | 2017-03-31 | Arsia Therapeutics Inc | Formulaciones de proteínas líquidas que contienen líquidos iónicos. |
| MX2017004306A (es) | 2014-10-01 | 2017-12-20 | Eagle Biologics Inc | Formulaciones de polisacáridos y ácido nucleico que contienen agentes de reducción de viscosidad. |
| CN105372424A (zh) * | 2015-11-12 | 2016-03-02 | 武汉景川诊断技术股份有限公司 | 肝促凝血活酶试验测定试剂盒及其制备方法 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2994557B2 (ja) * | 1994-09-02 | 1999-12-27 | 株式会社アズウェル | フィブリノゲン測定方法およびその測定試薬 |
| JP2003344418A (ja) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-12-03 | F Hoffmann La Roche Ag | 血液凝固試験のためのコントロール物質および較正物質 |
| JP2004191367A (ja) * | 2002-11-28 | 2004-07-08 | Sysmex Corp | トロンビン試薬及び検査試薬キット |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3180824B2 (ja) | 1991-08-30 | 2001-06-25 | シスメックス株式会社 | 血液凝固試薬 |
| JP3074611B2 (ja) | 1991-08-30 | 2000-08-07 | シスメックス株式会社 | 血液凝固測定方法 |
| US5358853A (en) | 1992-08-03 | 1994-10-25 | Akzo Av | Liquid thromboplastin reagent |
| JPH0815263A (ja) | 1994-06-24 | 1996-01-19 | Shimadzu Corp | 血液凝固分析装置 |
| DE19549118C2 (de) * | 1995-12-29 | 2000-07-13 | Thomas W Stief | Hämostaseaktivierungs-Inhibitor und Verfahren zum Hemmen der Hämostaseaktivierung in Blut oder anderen biologischen Flüssigkeiten |
| TW499412B (en) * | 1996-11-26 | 2002-08-21 | Dimensional Pharm Inc | Aminoguanidines and alkoxyguanidines as protease inhibitors |
| AU751412B2 (en) * | 1997-11-26 | 2002-08-15 | 3-Dimensional Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Heteroaryl aminoguanidines and alkoxyguanidines and their use as protease inhibitors |
| CN1504580A (zh) * | 2002-11-28 | 2004-06-16 | 希森美康株式会社 | 凝血酶试剂以及检查试剂套装 |
| DE10362199B4 (de) * | 2003-06-04 | 2009-09-10 | Stief, Thomas, Dr.med. | Nachweisverfahren für Fibrinogen |
| EP1672369A1 (de) | 2004-12-16 | 2006-06-21 | Roche Diagnostics GmbH | Verfahren zur Bestimmung von Blutkoagulationsparametern, insbesondere in Durchflussmesssystemen |
-
2010
- 2010-05-20 EP EP15196430.1A patent/EP3018481B1/en active Active
- 2010-05-20 KR KR1020187004669A patent/KR101882408B1/ko active Search and Examination
- 2010-05-20 CN CN2010800220995A patent/CN102428372A/zh active Pending
- 2010-05-20 WO PCT/JP2010/003401 patent/WO2010134345A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2010-05-20 KR KR1020117027191A patent/KR20120024610A/ko active Search and Examination
- 2010-05-20 US US13/321,732 patent/US20120064553A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2010-05-20 EP EP10777581.9A patent/EP2434290B1/en active Active
- 2010-05-20 JP JP2011514341A patent/JPWO2010134345A1/ja active Pending
- 2010-05-20 CA CA2762611A patent/CA2762611C/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-01-13 US US14/153,739 patent/US20140127727A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-10-06 JP JP2014205566A patent/JP5840273B2/ja active Active
-
2015
- 2015-03-16 US US14/658,911 patent/US9733262B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2994557B2 (ja) * | 1994-09-02 | 1999-12-27 | 株式会社アズウェル | フィブリノゲン測定方法およびその測定試薬 |
| JP2003344418A (ja) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-12-03 | F Hoffmann La Roche Ag | 血液凝固試験のためのコントロール物質および較正物質 |
| JP2004191367A (ja) * | 2002-11-28 | 2004-07-08 | Sysmex Corp | トロンビン試薬及び検査試薬キット |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012181033A (ja) * | 2011-02-28 | 2012-09-20 | Sysmex Corp | ループスアンチコアグラント検出用試薬キット及びループスアンチコアグラントの存否を判定する方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2434290B1 (en) | 2016-02-10 |
| JP5840273B2 (ja) | 2016-01-06 |
| JP2015042652A (ja) | 2015-03-05 |
| EP3018481A1 (en) | 2016-05-11 |
| KR20120024610A (ko) | 2012-03-14 |
| JPWO2010134345A1 (ja) | 2012-11-08 |
| KR20180019781A (ko) | 2018-02-26 |
| CA2762611C (en) | 2017-03-28 |
| KR101882408B1 (ko) | 2018-07-27 |
| CA2762611A1 (en) | 2010-11-25 |
| US20120064553A1 (en) | 2012-03-15 |
| EP2434290A4 (en) | 2013-01-30 |
| US20140127727A1 (en) | 2014-05-08 |
| US20150185236A1 (en) | 2015-07-02 |
| US9733262B2 (en) | 2017-08-15 |
| EP2434290A1 (en) | 2012-03-28 |
| EP3018481B1 (en) | 2018-02-21 |
| CN102428372A (zh) | 2012-04-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5169786A (en) | Method of determining levels of extrinsic and intrinsic clotting factors and protein c | |
| CN102066947B (zh) | 凝血时间延长原因的判定方法 | |
| JP5911345B2 (ja) | 凝固時間測定用試薬、凝固時間測定用試薬キットおよび凝固時間の測定方法 | |
| JP5840273B2 (ja) | 血液凝固時間延長剤 | |
| CN104076156A (zh) | 活化部分凝血活酶时间测定法和活化部分凝血活酶时间测定用试剂盒 | |
| CN109884326B (zh) | 血小板聚集功能检测试剂盒 | |
| WO1994007145A1 (fr) | Procede de determination de l'activite du facteur de coagulation sanguine xiii et trousse de reactifs appropries | |
| JP2008145278A (ja) | ガストリン放出ペプチド前駆体の免疫学的測定方法 | |
| KR101979865B1 (ko) | 루프스 안티코아귤란트의 검출방법 | |
| JP6058726B2 (ja) | 血液凝固反応における血液凝固時間延長剤 | |
| RU2669796C1 (ru) | Способ определения функционального фибриногена | |
| JP2011069718A (ja) | 血液凝固反応における血液凝固時間延長剤 | |
| JP7473282B1 (ja) | 凝固第xii因子欠乏血液検体の血液凝固時間短縮剤 | |
| JP2014197019A (ja) | 血液凝固反応における血液凝固時間延長剤 | |
| JP2013145238A (ja) | 血液凝固反応における血液凝固時間延長剤 | |
| JP7473283B1 (ja) | 活性化部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定のための試薬、及びループスアンチコアグラント陽性血液検体又はヘパリン含有血液検体の血液凝固時間調節剤 | |
| JP6174367B2 (ja) | トロンビン含有試薬及び測定方法 | |
| CN115219486B (zh) | 一种肝素和低分子肝素抗Xa活性的检测试剂盒及其非疾病诊断检测方法 | |
| WO2024080372A1 (ja) | 凝固第viii、ix又はxi因子欠乏血液検体の血液凝固時間調節剤、及び活性化部分トロンボプラスチン時間測定のための試薬 | |
| JP6278454B2 (ja) | 生体試料中の直接トロンビン阻害薬の測定試薬及び測定方法 | |
| Laffan et al. | 18 Laboratory control of anticoagulant, thrombolytic, and antiplatelet therapy | |
| CN116026761A (zh) | 抗Xa发色底物法测定试剂盒 | |
| CN103649758B (zh) | 狼疮抗凝物的检测方法 | |
| JP2004301612A (ja) | 補体価測定用試薬及びそれを用いた補体価測定値の安定化方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201080022099.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10777581 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2011514341 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117027191 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2010777581 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2762611 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |