WO2009144905A1 - 検査機能を有する折畳機 - Google Patents
検査機能を有する折畳機 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2009144905A1 WO2009144905A1 PCT/JP2009/002277 JP2009002277W WO2009144905A1 WO 2009144905 A1 WO2009144905 A1 WO 2009144905A1 JP 2009002277 W JP2009002277 W JP 2009002277W WO 2009144905 A1 WO2009144905 A1 WO 2009144905A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- conveyor
- sheet
- article
- folding
- inspection
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06F—LAUNDERING, DRYING, IRONING, PRESSING OR FOLDING TEXTILE ARTICLES
- D06F89/00—Apparatus for folding textile articles with or without stapling
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/88—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination
- G01N21/89—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination in moving material, e.g. running paper or textiles
- G01N21/892—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination in moving material, e.g. running paper or textiles characterised by the flaw, defect or object feature examined
- G01N21/898—Irregularities in textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. textiles, wood
- G01N21/8983—Irregularities in textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. textiles, wood for testing textile webs, i.e. woven material
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a folding machine having an inspection function in continuous processing of a sheet-like article, and more particularly to a folding machine having a double-sided inspection function such as dirt, tearing, and shape defect for a sheet-like article.
- Patent Document 1 A defect inspection apparatus for a piece of cloth to be inspected is proposed (Patent Document 1).
- the applicant also includes a conveyor device, a workpiece detector that detects a conveyance speed of the cloth piece, an illumination device, an input unit that images the inspection target portion of the cloth piece in a line shape, and a linear image pickup from the input unit.
- a storage unit that stores data as two-dimensional image data, a defect information storage unit that stores defect information of a piece of cloth, and a defect in the two-dimensional image data stored in the storage unit based on the input detection setting information
- a processing unit that transmits the defect information to the defect information storage unit, a plurality of cloth folding means disposed in the conveyor device, and a discharge that discharges the cloth piece to a predetermined location according to the number of folds And a folding unit having a means for transmitting the defect information to the folding unit, and the folding unit has different folding information according to the defect information from the processing unit. Eject the piece of cloth by number And it recommended the cloth inspection apparatus according to claim (patent document 2).
- the applicant is a defective cloth detection device that detects a defective portion of the stretch cloth with a camera while the spread cloth is being conveyed by the conveyer, and is conveyed to the conveyer face-up.
- the camera includes a camera that detects a defective portion on the upper surface side of the back-facing fabric that is transported through the back transport portion.
- Patent Document 3 A featured defect cloth detection device is proposed (Patent Document 3).
- Patent Document 4 As an inspection plate for inspecting defects on the surface of a sheet-like article, an inspection plate composed of a white inspection plate and a black inspection plate has been proposed (Patent Document 4).
- the sheet-like article is often placed on the conveyance surface so that the surface (front surface) used by the user becomes the lower surface during conveyance.
- the surface of the sheet-like article needs to abut on the iron surface side.
- an inspection apparatus that inspects only the surface of the sheet-like article cannot inspect the surface on the side actually used by the user. Compared to the surface that can be visually inspected by workers, the need for backside inspection is high.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a folding machine having a sheet-like article inspection function.
- the first invention is a folding machine including a folding mechanism for folding a sheet-like article conveyed by a plurality of conveyors, the longest first conveyor receiving the sheet-like article from a previous step, and the first A second conveyor that moves the sheet-like article downward in cooperation with the first conveyor, a third conveyor that continues between the second conveyor and the inspection plate, an imaging unit, and an illumination unit, And a back side inspection mechanism for inspecting a sheet-like article passing through the inspection plate from the back side, wherein the back side inspection mechanism is disposed below the first conveyor.
- a front side inspection mechanism for inspecting the sheet-like article from the front side is arranged above the first conveyor.
- a third invention is characterized in that, in the first or second invention, the first conveyor is provided with a sensor for measuring the length of the sheet-like article.
- 4th invention is a folding machine provided with the conveyor mechanism which consists of a some conveyor which conveys a sheet-like article, the folding mechanism which folds the sheet-like article conveyed by a conveyor mechanism, and a main body, The folding machine is characterized in that a back side inspection mechanism for inspecting a sheet-like article from the back side is disposed below the longest conveyor protruding from the main body.
- the conveyor mechanism includes an upper conveyor group and a lower conveyor group that are continuous with an inspection plate interposed therebetween, and the imaging unit and the illumination unit included in the back side inspection mechanism include the inspection unit. It is arranged to face the plate.
- the sixth invention is characterized in that in the fourth or fifth invention, the sheet-like article is further provided with a front side inspection mechanism for inspecting the sheet-like article from the front side.
- a seventh invention is characterized in that, in any one of the fourth to sixth inventions, the longest conveyor protruding from the main body is a conveyor arranged at an angle to receive a sheet-like article from the previous process. To do.
- An eighth invention is characterized in that, in any one of the fourth to seventh inventions, a sensor for measuring a length of a sheet-like article is provided on the longest conveyor protruding from the main body. .
- a ninth invention is characterized in that, in any one of the first to eighth inventions, the imaging section is constituted by one or two cameras. According to a tenth aspect, in any one of the first to ninth aspects, the inspection plate has a dark color area and a light color area.
- the present invention it is possible to provide a space-saving folding machine having an inspection function for sheet-like articles. Moreover, since the folding machine of the present invention has a simple structure, cost and maintenance are good.
- FIG. 3 is a plan view of a main part of a surface imaging unit according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 3 is a side view of the main part of the surface imaging unit according to the first embodiment.
- It is side surface sectional drawing (a), (b) for demonstrating the action
- FIG. It is side surface sectional drawing (c), (d) for demonstrating the action
- a folding machine of the best mode for carrying out the present invention includes a conveyor mechanism composed of a plurality of conveyors that convey sheet-like articles, a folding mechanism that folds sheet-like articles conveyed by the conveyor mechanism, and sheet-like articles.
- An inspection mechanism front side inspection mechanism
- An inspection mechanism back side inspection mechanism
- the conveyor mechanism is, for example, a first conveyor (21) that receives a sheet-like article from a previous process, and a first conveyor that sends the sheet-like article downward from the terminal end of the first conveyor in cooperation with the first conveyor.
- the first conveyor is provided with a sensor for measuring the length of the sheet-like article.
- a sensor is provided on the first conveyor which is the longest conveyor in the conveyor mechanism. Since the measurement of the length of the sheet-like article needs to be completed before the movable folding claw is operated, at least one of the conveyor mechanisms needs to be provided with a conveyor equivalent to or more than the sheet-like article. This is because the distance from the sensor to the movable folding claw needs to be at least the length of the sheet-like article minus the folding margin. For example, when the sheet-like article is folded in four, the folding margin is 1 ⁇ 4 of the total length, and thus the distance is at least 3/4 of the total length of the sheet-like article.
- the present invention since it is necessary to provide a conveyor having a length equal to or longer than that of the sheet-like article, the total length of the folding machine becomes longer as the sheet-like article becomes longer.
- the back side inspection mechanism in an empty space generated by the length of the first conveyor.
- the back side inspection mechanism is arranged between the longest conveyor and the floor surface under a long conveyor protruding from the main body.
- the present invention is characterized by effectively utilizing the structural problem that the conveyor becomes longer according to the length of the sheet-like article, and can be implemented with appropriate modifications within the scope of using this technical idea. Is possible.
- the present invention is suitable for a sheet-like article having a long side of 1 m or more, still more suitable for a sheet-like article having a long side of 2 m or more, and further suitable for a sheet-like article having a long side of 3 m or more.
- the merit from another viewpoint of arranging the back side inspection mechanism below the long conveyor is that the distance between the imaging unit and the sheet-like article can be secured.
- the distance between the imaging unit and the sheet-like article needs to be a certain value or more. This distance can be shortened to some extent by increasing the number of cameras constituting the imaging unit.
- increasing the number of cameras increases the cost of the apparatus, complicates adjustment and control, and reduces maintainability.
- the present invention provides a structure that can realize space saving even if the number of cameras is not three or four or more.
- the folding mechanism is composed of a sword for turning a sheet-shaped article into a gap between a pair of conveyors, folding the sheet-shaped article, a rotating plate-shaped claw, and the like.
- the folding mechanism is optimally configured according to the number of folding sheets.
- Patent Document 2 discloses a folding mechanism that folds a piece of cloth 32 times.
- the front side inspection mechanism and the back side inspection mechanism of the present invention have the same configuration and have the following features.
- Work detector that detects the moving speed of the article 4) Receives a signal from the work detector, sends an imaging start signal to the color camera, continuously receives the electrical signal of the line-shaped image captured by the color camera, Input unit for transfer to processing unit 5)
- Mask processing is performed on image data, and defect position information and defect type information (tear, black stain, non-black stain) detected in comparison with the defect level are transferred to the defect information storage unit.
- Processing unit 6 Storage unit for storing a two-dimensional RGB image obtained from line-shaped image data transferred from the processing unit 7) Defect information for storing defect position information and defect type information received from the processing unit Storage unit 8) Output unit that outputs a classification signal based on defect position information and defect type information stored in the defect information storage unit 9) Illumination controller unit that illuminates the area to be inspected in a line and increases or decreases the light quantity 10) Defect Display unit for displaying information stored in information storage unit and two-dimensional RGB image 11) Rejector for sorting sheet-like article in response to sorting signal
- the front side inspection mechanism and the back side inspection mechanism have the following functions.
- Image Data Capture Function A sheet-like article being conveyed by the conveying device can be stored in the storage means as a two-dimensional RGB image.
- the image data has a format in which a flowing inspection object is taken in two dimensions, and includes not only a defective portion but also noise such as a flaw and a ground. By adjusting the image data as it is instead of the input electric signal, it is not necessary to repeatedly flow the sheet-like article sample.
- Light intensity adjustment function This is a function that automatically adjusts the input light intensity to a certain level by increasing or decreasing the light intensity based on the image data captured from the image sensor.
- (III) Basic mask function The presence or absence of a defect is determined based on the captured image data. The region to be inspected is determined by performing mask processing on the image data. Since mask processing is applied to the image data, it is also possible to perform curved mask processing at a fixed distance along the edge of the detected sheet-like article. Also, it is designated from the center position of the sheet-like article. It is also possible to perform a width mask.
- Color mask function It has a color mask function for masking patterns such as logos and patterns attached to sheet-like articles.
- a color range based on a value obtained by digitizing the designated color with a predetermined algorithm is provided, and it is determined that an object belonging to the color range is a pattern, and mask processing is performed. This is performed by digitizing hues that have regularity in change even during pattern judgment and color loss, but may be combined with saturation and lightness.
- the specific procedure is as follows. i) Capture an RGB image of a sheet-like article. ii) Specify the part to be masked and capture the color. iii) Replace the captured color with a color space such as HSV, and digitize the hue.
- the hue is converted to a frequency (for example, 0 to 360 degrees), so that a color is specified with a threshold before and after the specified frequency (for example, in the case of red, the center is 0 degree). ).
- Color mask processing is performed based on the color range calculated based on the set value. With the above procedure, it is possible to accurately mask a pattern such as a logo / pattern.
- V Pattern-related information storage function The present invention is applied to a model business in which used sheet-like articles are regularly conveyed from a specific user. Therefore, by storing information related to the pattern of a sheet-like article that has been subjected to mask processing in the past, it is possible to minimize misunderstandings in color mask processing.
- a technique for storing a pattern signal in advance is disclosed, but as the number of patterns increases, the number of comparison objects increases, and a pattern for each direction is prepared in case the sheet-like article is placed in a different direction. Since it is necessary to prepare and matching with these data, there is a problem that the processing speed is lowered, which is not preferable. In order to obtain a constant processing speed without impairing the convenience of the operator, it is effective to store the relationship between the pattern and the area. Thus, if an abnormal value belonging to a specific color range and a specific area range is detected, it can be determined that the pattern is a pattern. Note that not only the area but also the aspect ratio, shape, position information, and the like may be used.
- (VI) Defect type information emphasis function Both tear information and dirt information are detected as noise on the image data of the workpiece, but it is difficult to accurately determine these types.
- the defect type information can be emphasized by passing the work on the inspection plate having a plurality of color regions and utilizing the characteristics of the three primary colors of light. That is, as shown in FIG. 4, three image lines of RGB are associated with the color region of the inspection plate, and each image data of RGB imaged is synthesized to obtain synthesized image data in which defect type information is emphasized. be able to. Even when the imaging unit is an area type color camera, the same effect can be obtained by appropriately setting the color components to be extracted at a predetermined position.
- the number of folds is increased so as not to take up space, and that non-black dirt is discharged with fewer folds so that it can be easily re-inspected by humans. .
- the number of different folds is discharged by associating the hue range with the defect type information. For example, since the tear is captured as a color close to cyan, if a color close to cyan is detected, it is determined that the tear is broken and the sheet is discharged with a predetermined number of folds. Similarly, non-black and black (or a color close to black) can be discharged with different fold numbers.
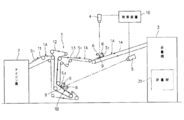
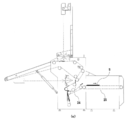
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a folding machine 3 having an ironing machine 2 in the previous process and an inspection mechanism of the present embodiment.
- the ironing machine 2 is a machine that automatically irons the spread fabric S.
- the cloth S ironed by the ironing machine 2 is transferred onto the belt conveyor 21 of the folding machine 3 in a stretched state (see FIG. 5A).
- the surface of the cloth S conveyed on the belt conveyor 21 is inspected by the surface imaging unit 4. As shown in FIG.
- the surface imaging unit 41 of this embodiment includes two line-type color cameras arranged on the same line, and lines the inspection target region of the cloth S in a direction orthogonal to the transport direction. Image.
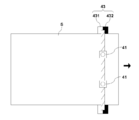
- the inspection target area of the cloth S is illuminated by the light source 42, and an inspection plate 43 is disposed below the inspection target area.
- the cloth S passes over the inspection plate 43. Since the cloth S is wide (for example, about 3 m), the surface imaging unit 41 captures 1 ⁇ 2 of the width of the cloth S with each camera.
- the surface imaging unit 4 may be constituted by a single color camera or may be constituted by an area type camera.
- the inspection plate 43 includes a white area 431 and a black area 432.
- the reason why the inspection plate 43 is composed of a light color area and a dark color area is to facilitate identification of defects.
- the torn image appears bright in the white area 431 and appears dark in the black area 432.
- the defect type information can be emphasized by associating three RGB lines and the color area of the inspection plate and synthesizing the captured RGB image data.
- the reflection in the white region 431 and the black region 432 changes in different manners between non-black stain and black stain. For example, yellow non-black stains appear darker in blue line image data than yellow non-black stains when they are combined with green line image data and red line image data.
- the tear is captured darkly only on the black region 432 (red line), it is captured as a color close to cyan in the composite image data.
- the black stain remains as it is after being synthesized. In this case, it can be said that a hue pattern in a certain range from a color close to cyan has a high probability of being broken.
- the length and movement speed of the cloth S are measured by the work detection sensor 45 and a conveyor speed detector (not shown).
- the imaging of the fabric S is performed by the imaging units 41 and 51 after the calculated time (see FIG. 5B).
- Various mask processes are performed on the image data from the imaging units 41 and 51, and defect determination work is performed. When it is determined that there is a defect by the defect determination work, a defect flag is recorded.
- the cloth S determined to be defective is sorted, and for example, the number of folds is changed and discharged to a different stacker.
- a belt conveyor 22 is disposed at the rear end of the belt conveyor 21.
- the cloth S sandwiched between the belt conveyor 21 and the belt conveyor 22 is conveyed in the direction of the belt conveyor 23.
- An inspection plate 53 having the same configuration as that of the inspection plate 43 is disposed between the belt conveyor 22 and the belt conveyor 23.
- the position of the inspection plate 53 is an inspection target region, and the inspection target region is illuminated by a light source 52 provided to face the inspection plate 53.
- the back surface imaging unit 51 images the inspection target part of the cloth S in a line shape from the gap between the light sources 51 arranged with a gap above and below.
- the back imaging unit 51 has the same configuration as the front imaging unit 41, and the light source 52 has the same configuration as the light source 42. Based on the image data imaged by the back surface imaging unit 51, the back surface inspection is performed by the same procedure as the front surface inspection.
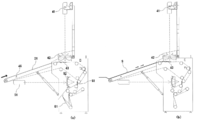
- the cloth S that has passed through the end of the belt conveyor 23 hangs down.
- the movable folding claw 61 is in a position that substantially contacts the conveyor 24.
- 1/4 of the cloth S hangs down and is in a state suitable for four-folding the movable folding claw 61 moves to the contact member 62 side, and the movable folding claw 61 and the contact member 62 sandwich the cloth S. (See FIG. 6C). Accordingly, the cloth S hangs down between the belt conveyor 24 and the movable folding claw 61 by the rotation of the belt conveyor 23.
- the inspection mechanism provided in the folding machine of the present embodiment is not limited to the above combination.
- a metal detector meter reading device
- the conveyance conveyor 25 may be provided with metal.
- a detector meter reading device
- the folding machine of the present embodiment having the above configuration, it is possible to reduce the installation space of a machine in a factory such as a laundry. Further, since the increase in the number of belt conveyors and the number of axes necessary for providing the double-sided inspection function can be minimized, the cost and maintenance are excellent.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Investigating Materials By The Use Of Optical Means Adapted For Particular Applications (AREA)
Abstract
課題:シート状物品の検査機能を有した折畳機の提供。 解決手段:シート状物品を搬送する複数のコンベアからなるコンベア機構と、コンベア機構により搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構と、本体と、を備える折畳機であって、撮像部および照明部を有し、シート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構を、本体から突出した最も長いコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とし、好ましくは、シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構をさらに備えることを特徴とする折畳機。
Description
本発明は、シート状物品の連続加工における検査機能を有する折畳機に関し、特に、シート状物品について、汚れ、破れ、形状不良等の両面検査機能を有する折畳機に関する。
従来、布片を水洗、乾燥、アイロン掛けをした後、折り畳むためにベルト上に広げて移動する布片の表面検査をするのに布片面に光を当て、布片面からの反射光をカメラ等で捕らえて、カメラ等が捕えた映像の光の強弱(欠陥部は反射光が弱くなる)を電気信号に変え、該電気信号を処理することによって、布片面の破損や汚れ等の欠陥を自動的に検査する布片面の欠陥検査装置が提言されている(特許文献1)。
また、出願人は、コンベア装置と、布片の搬送速度を検出するワーク検出器と、照明装置と、布片の検査対象部位をライン状に撮像する入力部と、入力部からのライン状撮像データを2次元画像データとして記憶する記憶部と、布片の欠陥情報を記憶する欠陥情報記憶部と、入力された検出設定情報に基づき前記記憶部の記憶する2次元画像データの欠陥を判定し、欠陥を検出した場合には欠陥情報を欠陥情報記憶部に送信する処理部と、コンベア装置に配設された複数の布折り手段および折数に応じて布片を所定の箇所に排出する排出手段を有する折り畳み部と、を備えた布片検査装置であって、前記処理部は、前記折り畳み部に欠陥情報を送信し、前記折り畳み部は、前記処理部からの欠陥情報に応じて異なる折数で布片を排出することを特徴とする布片検査装置を提言している(特許文献2)。
また、出願人は、展張布類を搬送コンベアで搬送中に該展張布類の欠陥部をカメラで検出するようにした欠陥布類検出装置であって、前記搬送コンベアに、表向きに搬送される展張布類を裏向きに反転させて搬送する裏向き搬送部を設けるとともに、該裏向き搬送部を搬送される裏向き展張布類の上面側の欠陥部を検出するカメラを備えた、ことを特徴とする欠陥布類検出装置を提言している(特許文献3)。
シート状物品面の欠陥を検査する検査板としては、白色検査板と黒色検査板からなる検査板が提言されている(特許文献4)。
ところで、シート状物品は搬送時に、ユーザーが使用する側の面(表面)が下面となるように、搬送面に載置されることが多い。これは、例えば、上面に配置された押圧板と、その下方に配置されたアイロン面を有するチェストロール機等においては、アイロン面の側にシート状物品の表面が当接する必要があるからである。この場合、シート状物品の表面のみを検査する検査装置では、実際にユーザーが使用する側の面を検査することができないことになる。作業員による目視検査ができる表面に比べ、裏面検査のニーズは高い。
また、シーツ等のシート状物品においては、汚れが片面にしか現れない(透過しない)ものがあり、例えば、表面のみを検査する検査装置においては、裏面の汚れを検出することができなかった。
他方、図2に記載される特許文献3に係る欠陥布類検出装置は、折畳機とは別途に設置されるため、多大なスペースを必要とした。また、折畳機とは別途に複数のコンベアを設ける必要があるため、コスト性およびメンテナンス性に劣るという課題もある。
他方、図2に記載される特許文献3に係る欠陥布類検出装置は、折畳機とは別途に設置されるため、多大なスペースを必要とした。また、折畳機とは別途に複数のコンベアを設ける必要があるため、コスト性およびメンテナンス性に劣るという課題もある。
上記課題を解決するために、本発明は、シート状物品の検査機能を有した折畳機を提供することを目的とする。
シート状物品を裏側から検査するためには、コンベアを増やす必要があるが、設置のためのスペースが増え、構造が複雑になるという課題が生じる。特に、シート状物品が大型である場合(例えば、長辺が3mの布類の場合)、検査機構に設ける撮像部をシート状物品と距離をおいて配置する必要が生じる。そのため、裏側から検査する検査機構を設けながら、省スペースを実現することは困難であった。
また、この問題は、シート状物品を表側から検査する検査機構(表側検査機構)と、裏側から検査する検査機構(裏側検査機構)を設ける場合に一層顕著となる。
発明者鋭意工夫の上、上述した検査機構を有しながら、省スペースで構造がシンプルな折畳機を創作した。
また、この問題は、シート状物品を表側から検査する検査機構(表側検査機構)と、裏側から検査する検査機構(裏側検査機構)を設ける場合に一層顕著となる。
発明者鋭意工夫の上、上述した検査機構を有しながら、省スペースで構造がシンプルな折畳機を創作した。
すなわち、第1の発明は、複数のコンベアにより搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構を備える折畳機であって、前工程からシート状物品を受け取る最も長い第1のコンベアと、前記第1のコンベアと協働してシート状物品を下方に移送する第2のコンベアと、前記第2のコンベアと検査板を挟んで連続する第3のコンベアと、撮像部および照明部を有し、前記検査板を通過するシート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構と、を備え、前記裏側検査機構を、第1のコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とする折畳機である。
第2の発明は、第1の発明において、シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構を、第1のコンベアの上方に配置したことを特徴とする。
第3の発明は、第1または2の発明において、前記第1のコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする。
第4の発明は、シート状物品を搬送する複数のコンベアからなるコンベア機構と、コンベア機構により搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構と、本体と、を備える折畳機であって、撮像部および照明部を有し、シート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構を、本体から突出した最も長いコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とする折畳機である。
第5の発明は、第4の発明において、前記コンベア機構は、検査板を挟んで連続する上方コンベア群と下方コンベア群とを含み、前記裏側検査機構の有する撮像部および照明部は、前記検査板と対向して配置されることを特徴とする。
第6の発明は、第4または5の発明において、シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構をさらに備えることを特徴とする。
第7の発明は、第4ないし6のいずれかの発明において、前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアは、前工程からシート状物品を受け取るために傾斜して配置されたコンベアであることを特徴とする。
第8の発明は、第4ないし7のいずれかの発明において、前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする。
第9の発明は、第1ないし8のいずれかの発明において、前記撮像部は、1台または2台のカメラにより構成されることを特徴とする。
第10の発明は、第1ないし9のいずれかの発明において、前記検査板は、暗色領域と明色領域とを有することを特徴とする。
第2の発明は、第1の発明において、シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構を、第1のコンベアの上方に配置したことを特徴とする。
第3の発明は、第1または2の発明において、前記第1のコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする。
第4の発明は、シート状物品を搬送する複数のコンベアからなるコンベア機構と、コンベア機構により搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構と、本体と、を備える折畳機であって、撮像部および照明部を有し、シート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構を、本体から突出した最も長いコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とする折畳機である。
第5の発明は、第4の発明において、前記コンベア機構は、検査板を挟んで連続する上方コンベア群と下方コンベア群とを含み、前記裏側検査機構の有する撮像部および照明部は、前記検査板と対向して配置されることを特徴とする。
第6の発明は、第4または5の発明において、シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構をさらに備えることを特徴とする。
第7の発明は、第4ないし6のいずれかの発明において、前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアは、前工程からシート状物品を受け取るために傾斜して配置されたコンベアであることを特徴とする。
第8の発明は、第4ないし7のいずれかの発明において、前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする。
第9の発明は、第1ないし8のいずれかの発明において、前記撮像部は、1台または2台のカメラにより構成されることを特徴とする。
第10の発明は、第1ないし9のいずれかの発明において、前記検査板は、暗色領域と明色領域とを有することを特徴とする。
本発明によれば、シート状物品の検査機能を有する省スペース型折畳機を提供することが可能となる。また、本発明の折畳機は、構造がシンプルなため、コスト性およびメンテナンス性も良好である。
本発明を実施するための最良の形態の折畳機は、シート状物品を搬送する複数のコンベアからなるコンベア機構と、コンベア機構により搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構と、シート状物品の表面を検査するための検査機構(表側検査機構)と、シート状物品の裏面を検査するための検査機構(裏側検査機構)と備える。
《コンベア機構》
上記コンベア機構は、例えば、前工程からシート状物品を受け取る第1のコンベア(21)と、第1のコンベアと協働して第1のコンベアの終端部から下方にシート状物品を送出する第2のコンベア(22)と、第2のコンベアと検査板を介して接続される第3のコンベア(23)と、第3のコンベア(23)の下方に並設された第4のコンベア(24)と、次工程へシート状物品を受け渡す第5のコンベア(25)とから構成される。
第1のコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられている。シート状物品を折り畳むためには、シート状物品の長さを正確に測定する必要があるため、上記コンベア機構の中で最も長いコンベアである第1のコンベアにセンサを設けている。
シート状物品の長さの測定は、可動折爪が作動する前に終了している必要があるため、上記コンベア機構中には少なくとも1つはシート状物品と同等以上のコンベアを設ける必要がある。これは、上記センサを通過してから可動折爪に至るまでの距離が、少なくとも、シート状物品の長さから折りしろを引いた長さである必要があるからである。例えば、シート状物品を4つ折りにする場合、折りしろは全長の1/4となるから、上記の距離は少なくともシート状物品の全長の3/4となる。このように、シート状物品と同等以上の長さのコンベアを設ける必要があることから、シート状物品が長くなるのに伴い折畳機の全長も長くなる。
最良の形態の本発明では、上記第1のコンベアの長さにより生じる空きスペースに上記裏側検査機構を配置することにより、省スペース化を図ることを可能としている。すなわち、本体から突出した長いコンベアの下方に、別の言い方をすれば、最長のコンベアと床面の間に、上記裏側検査機構を配置することを特徴としている。
本発明は、コンベアがシート状物品の長さに応じて長くなるという構造上の問題を有効利用することに特徴を有し、この技術思想を利用する範囲内で適宜変形して実施することが可能である。例えば、検査機構として金属探知機(検針器)を代替的に、或いは付加的に設けることも本発明の範囲に含まれる。
本発明は、長辺が1m以上のシート状物品に好適であり、長辺が2m以上のシート状物品になお好適であり、長辺が3m以上のシート状物品にさらに好適である。
上記コンベア機構は、例えば、前工程からシート状物品を受け取る第1のコンベア(21)と、第1のコンベアと協働して第1のコンベアの終端部から下方にシート状物品を送出する第2のコンベア(22)と、第2のコンベアと検査板を介して接続される第3のコンベア(23)と、第3のコンベア(23)の下方に並設された第4のコンベア(24)と、次工程へシート状物品を受け渡す第5のコンベア(25)とから構成される。
第1のコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられている。シート状物品を折り畳むためには、シート状物品の長さを正確に測定する必要があるため、上記コンベア機構の中で最も長いコンベアである第1のコンベアにセンサを設けている。
シート状物品の長さの測定は、可動折爪が作動する前に終了している必要があるため、上記コンベア機構中には少なくとも1つはシート状物品と同等以上のコンベアを設ける必要がある。これは、上記センサを通過してから可動折爪に至るまでの距離が、少なくとも、シート状物品の長さから折りしろを引いた長さである必要があるからである。例えば、シート状物品を4つ折りにする場合、折りしろは全長の1/4となるから、上記の距離は少なくともシート状物品の全長の3/4となる。このように、シート状物品と同等以上の長さのコンベアを設ける必要があることから、シート状物品が長くなるのに伴い折畳機の全長も長くなる。
最良の形態の本発明では、上記第1のコンベアの長さにより生じる空きスペースに上記裏側検査機構を配置することにより、省スペース化を図ることを可能としている。すなわち、本体から突出した長いコンベアの下方に、別の言い方をすれば、最長のコンベアと床面の間に、上記裏側検査機構を配置することを特徴としている。
本発明は、コンベアがシート状物品の長さに応じて長くなるという構造上の問題を有効利用することに特徴を有し、この技術思想を利用する範囲内で適宜変形して実施することが可能である。例えば、検査機構として金属探知機(検針器)を代替的に、或いは付加的に設けることも本発明の範囲に含まれる。
本発明は、長辺が1m以上のシート状物品に好適であり、長辺が2m以上のシート状物品になお好適であり、長辺が3m以上のシート状物品にさらに好適である。
上記の長いコンベアの下方に上記裏側検査機構を配置することの別の観点からのメリットは、撮像部とシート状物品の距離を確保できることである。シート状物品を幅方向にライン状に撮像する場合、シート状物品の幅が大きくなると、撮像部とシート状物品の距離を一定以上にする必要がある。この距離は、撮像部を構成するカメラの台数を増やすことにより、ある程度は短くすることができる。しかし、カメラの台数を増やすことは、装置のコストを高めることとなり、調整や制御も複雑となり、メンテナンス性も下がる。この点、本発明は、カメラの台数を3~4台以上としなくとも、省スペース化を実現することができる構造を提供するものである。
《折畳機構》
折畳機構は、一対のコンベアの間隙にシート状物品を投入し、シート状物品を折り畳むためのソードや回動する板状の折爪などにより構成される。折畳機構は、シート状物品の折り畳み数に応じて最適に構成される。例えば、特許文献2には、布片を32折りする折畳機構が開示される。
折畳機構は、一対のコンベアの間隙にシート状物品を投入し、シート状物品を折り畳むためのソードや回動する板状の折爪などにより構成される。折畳機構は、シート状物品の折り畳み数に応じて最適に構成される。例えば、特許文献2には、布片を32折りする折畳機構が開示される。
《検査機構》
本発明の表側検査機構と上記裏側検査機構は同様の構成であり、以下の特徴を備えている。
1)カラー映像をライン状に取り込み電気信号に変える撮像部
2)明色領域(例えば、白色領域)と暗色領域(例えば、黒色領域)とから構成される検査板
3)シート状物品およびシート状物品の移動速度を検出するワーク検出器
4)ワーク検出器より信号を受けてカラーカメラへの撮像開始信号を送り、カラーカメラで撮像されたライン状映像の電気信号を受け連続して数値化し、処理部に転送する入力部
5)画像データにマスク処理を施し、欠陥レベルと比較して検出した欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報(破れ、黒汚れ、非黒汚れ)を欠陥情報記憶部に転送する処理部
6)処理部より転送されたライン状の画像データから得られた2次元RGB画像を記憶する記憶部
7)処理部より受けた欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報を記憶する欠陥情報記憶部
8)欠陥情報記憶部の記憶する欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報にもとづいて分別信号を出力する出力部
9)ライン状に検査対象領域を照明し光量の増減をする照明コントローラ部
10)欠陥情報記憶部の記憶する情報および2次元RGB画像を表示する表示部
11)分別信号を受けてシート状物品を分別するリジェクタ
本発明の表側検査機構と上記裏側検査機構は同様の構成であり、以下の特徴を備えている。
1)カラー映像をライン状に取り込み電気信号に変える撮像部
2)明色領域(例えば、白色領域)と暗色領域(例えば、黒色領域)とから構成される検査板
3)シート状物品およびシート状物品の移動速度を検出するワーク検出器
4)ワーク検出器より信号を受けてカラーカメラへの撮像開始信号を送り、カラーカメラで撮像されたライン状映像の電気信号を受け連続して数値化し、処理部に転送する入力部
5)画像データにマスク処理を施し、欠陥レベルと比較して検出した欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報(破れ、黒汚れ、非黒汚れ)を欠陥情報記憶部に転送する処理部
6)処理部より転送されたライン状の画像データから得られた2次元RGB画像を記憶する記憶部
7)処理部より受けた欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報を記憶する欠陥情報記憶部
8)欠陥情報記憶部の記憶する欠陥位置情報、欠陥種別情報にもとづいて分別信号を出力する出力部
9)ライン状に検査対象領域を照明し光量の増減をする照明コントローラ部
10)欠陥情報記憶部の記憶する情報および2次元RGB画像を表示する表示部
11)分別信号を受けてシート状物品を分別するリジェクタ
さらに、上記表側検査機構および上記裏側検査機構は、以下の機能を有する。
(I)画像データ取込機能
搬送装置により搬送中のシート状物品を2次元RGB画像として記憶手段に記憶することができる。画像データは流れている検査対象を2次元として取り込んだ形式となっており、欠陥部だけでなく皺や地合などのノイズも同様に含まれる。画像データをそのまま入力電気信号の代わりに利用して調整を行うことで、シート状物品のサンプルを繰り返して流すことを不要としている。
(II)光量調整機能
イメージセンサーより取り込んだ画像データにもとづき光量を増減させることで行い、入力光量を一定に自動調整する機能である。光量増減により行うため電気信号ノイズを増幅しないので安定した検査を行うことができる。
(III)基本マスク機能
取り込んだ画像データにもとづき欠陥の有無を判定する。検査対象となる領域は、画像データにマスク処理を施すことによって決定される。画像データに対してマスク処理を施すため、検出したシート状物品の縁辺(エッジ)に沿って一定距離に曲線状のマスク処理を施すことも可能であるまた、シート状物品の中央位置から指定した幅のマスクを行うことも可能である。
(IV)カラーマスク機能
シート状物品に付されたロゴや柄等の模様をマスクするカラーマスク機能を有する。ロゴや柄等の模様は、洗濯による脱水により無段階に変色するため、特定の色を予め設定しておくことは難しい。そこで、指定色を所定のアルゴリズムで数値化した値を基準とした色範囲を設け、その色範囲に属するものは模様であると判定し、マスク処理を施すこととした。模様の判定、色抜け時も変化に規則性がある色相を数値化することにより行うが、彩度や明度を組み合わせてもよい。具体的な手順は、次に示すとおりである。
i)シート状物品のRGB画像を取り込む。
ii)マスクをかける部分を指定し、色を取り込む。
iii)取り込んだ色をHSV等の色空間に置き換え、色相を数値化する。例えば、HSV色空間では色相を度数(例えば、0~360度)に変換するので指定された度数より前後に閾値を持たせ色を指定する(例えば、赤系の場合0度を中心とするなど)。
iv)設定値に基づき算出した色範囲により、カラーマスク処理を行う。
以上の手順によりロゴ・柄等の模様を正確にマスクすることが可能となる。
(V)模様関連情報記憶機能
本発明は、特定のユーザから定期的に使用済みシート状物品が搬送されるモデルの事業に適用される。そのため、過去にマスク処理を施したシート状物品の模様に関する情報を記憶しておくことで、カラーマスク処理における誤判を最小限とすることができる。ここで、予めパターン模様信号を記憶しておく手法が開示されるが、模様の種類が増えると比較対象が増え、またシート状物品が異なる方向に載置された場合に備え方向毎のパターンを準備しておく必要があり、これらのデータとのマッチングを行うことにより処理速度が低下するという問題があるので好ましくない。作業者の便宜を損なわず、一定の処理速度を得るためには、模様と面積の関係を記憶しておくのが効果的である。これにより、特定の色範囲および特定の面積範囲に属する異常値が検出されれば、模様であると判定すればよいこととなる。なお、面積だけでなく、縦横比、形状、位置情報等による絞りをかけてもよい。
(VI)欠陥種別情報強調機能
破れ情報と汚れ情報は、共にワークの画像データ上にノイズとして検出されるが、これらの種別を正確に判定することは難しい。しかし、複数の色領域を有する検査板上をワークを通過させ、光の三原色の特性を利用することで、これらの欠陥種別情報を強調させることができる。すなわち、図4に示すように、RGBの3つのラインと検査板の色領域を対応させ、撮像されたRGBの各画像データを合成することにより、欠陥種別情報を強調した合成画像データを取得することができる。なお、撮像部がエリア式のカラーカメラの場合においても、所定の位置で抽出する色成分を適切に設定することで同じ効果を奏することができる。
各ライン上を汚れ等の欠陥部分が通過することにより、欠陥部分の色が変化した状態で撮像される。非黒汚れは特定色のラインにおいてより濃く変化し、また、破れは、検査板の暗色領域(例えば、黒色領域)で黒に近い暗色に変化することから、これらを合成することで、欠陥種別情報が強調された画像データを取得することができる。色の変化は、加法混色による。
以上の処理を施すことにより、従来は識別が困難であった黒汚れと破れの判定を容易に行うことが可能となった。なお、RGBラインと検査板の色の組み合わせが、上記に限定されないことは言うまでもない。
(VII)欠陥種別毎排出機能
欠陥種別情報(破れ、黒汚れ、非黒汚れ)に基づいて、折り数を変えて排出する機能を有する。例えば、破れがある場合には、場所を取らないよう折り数を多くして排出し、非黒汚れについては人による再検査が容易なように、折りを少なくして排出することが開示される。この際、色相の範囲と欠陥種別情報の関連付けをすることにより、異なる折数で排出させるのが好ましい。例えば、破れはシアンに近い色として捉えられるので、シアンに近い色が検出された場合には、破れと判断して所定の折数で排出することとなる。同様に非黒色と黒色(ないしは黒に近い色)で折り数を違えて排出することもできる。
(I)画像データ取込機能
搬送装置により搬送中のシート状物品を2次元RGB画像として記憶手段に記憶することができる。画像データは流れている検査対象を2次元として取り込んだ形式となっており、欠陥部だけでなく皺や地合などのノイズも同様に含まれる。画像データをそのまま入力電気信号の代わりに利用して調整を行うことで、シート状物品のサンプルを繰り返して流すことを不要としている。
(II)光量調整機能
イメージセンサーより取り込んだ画像データにもとづき光量を増減させることで行い、入力光量を一定に自動調整する機能である。光量増減により行うため電気信号ノイズを増幅しないので安定した検査を行うことができる。
(III)基本マスク機能
取り込んだ画像データにもとづき欠陥の有無を判定する。検査対象となる領域は、画像データにマスク処理を施すことによって決定される。画像データに対してマスク処理を施すため、検出したシート状物品の縁辺(エッジ)に沿って一定距離に曲線状のマスク処理を施すことも可能であるまた、シート状物品の中央位置から指定した幅のマスクを行うことも可能である。
(IV)カラーマスク機能
シート状物品に付されたロゴや柄等の模様をマスクするカラーマスク機能を有する。ロゴや柄等の模様は、洗濯による脱水により無段階に変色するため、特定の色を予め設定しておくことは難しい。そこで、指定色を所定のアルゴリズムで数値化した値を基準とした色範囲を設け、その色範囲に属するものは模様であると判定し、マスク処理を施すこととした。模様の判定、色抜け時も変化に規則性がある色相を数値化することにより行うが、彩度や明度を組み合わせてもよい。具体的な手順は、次に示すとおりである。
i)シート状物品のRGB画像を取り込む。
ii)マスクをかける部分を指定し、色を取り込む。
iii)取り込んだ色をHSV等の色空間に置き換え、色相を数値化する。例えば、HSV色空間では色相を度数(例えば、0~360度)に変換するので指定された度数より前後に閾値を持たせ色を指定する(例えば、赤系の場合0度を中心とするなど)。
iv)設定値に基づき算出した色範囲により、カラーマスク処理を行う。
以上の手順によりロゴ・柄等の模様を正確にマスクすることが可能となる。
(V)模様関連情報記憶機能
本発明は、特定のユーザから定期的に使用済みシート状物品が搬送されるモデルの事業に適用される。そのため、過去にマスク処理を施したシート状物品の模様に関する情報を記憶しておくことで、カラーマスク処理における誤判を最小限とすることができる。ここで、予めパターン模様信号を記憶しておく手法が開示されるが、模様の種類が増えると比較対象が増え、またシート状物品が異なる方向に載置された場合に備え方向毎のパターンを準備しておく必要があり、これらのデータとのマッチングを行うことにより処理速度が低下するという問題があるので好ましくない。作業者の便宜を損なわず、一定の処理速度を得るためには、模様と面積の関係を記憶しておくのが効果的である。これにより、特定の色範囲および特定の面積範囲に属する異常値が検出されれば、模様であると判定すればよいこととなる。なお、面積だけでなく、縦横比、形状、位置情報等による絞りをかけてもよい。
(VI)欠陥種別情報強調機能
破れ情報と汚れ情報は、共にワークの画像データ上にノイズとして検出されるが、これらの種別を正確に判定することは難しい。しかし、複数の色領域を有する検査板上をワークを通過させ、光の三原色の特性を利用することで、これらの欠陥種別情報を強調させることができる。すなわち、図4に示すように、RGBの3つのラインと検査板の色領域を対応させ、撮像されたRGBの各画像データを合成することにより、欠陥種別情報を強調した合成画像データを取得することができる。なお、撮像部がエリア式のカラーカメラの場合においても、所定の位置で抽出する色成分を適切に設定することで同じ効果を奏することができる。
各ライン上を汚れ等の欠陥部分が通過することにより、欠陥部分の色が変化した状態で撮像される。非黒汚れは特定色のラインにおいてより濃く変化し、また、破れは、検査板の暗色領域(例えば、黒色領域)で黒に近い暗色に変化することから、これらを合成することで、欠陥種別情報が強調された画像データを取得することができる。色の変化は、加法混色による。
以上の処理を施すことにより、従来は識別が困難であった黒汚れと破れの判定を容易に行うことが可能となった。なお、RGBラインと検査板の色の組み合わせが、上記に限定されないことは言うまでもない。
(VII)欠陥種別毎排出機能
欠陥種別情報(破れ、黒汚れ、非黒汚れ)に基づいて、折り数を変えて排出する機能を有する。例えば、破れがある場合には、場所を取らないよう折り数を多くして排出し、非黒汚れについては人による再検査が容易なように、折りを少なくして排出することが開示される。この際、色相の範囲と欠陥種別情報の関連付けをすることにより、異なる折数で排出させるのが好ましい。例えば、破れはシアンに近い色として捉えられるので、シアンに近い色が検出された場合には、破れと判断して所定の折数で排出することとなる。同様に非黒色と黒色(ないしは黒に近い色)で折り数を違えて排出することもできる。
本発明の詳細を実施例で説明する。が、本発明は実施例によって何ら限定されるものではない。
実施例1は、シーツやベッドカバー等の比較的大面積の布類の汚れ、破れ、形状不良等の欠陥検査をすることができる、折畳機に関する。
図1は、前工程のアイロン機2および本実施例の検査機構を有する折畳機3の構成図である。
アイロン機2は、展張された布類Sを自動アイロンがけする機械である。アイロン機2によりアイロンがけされた布類Sは、展張された状態で折畳機3のベルトコンベア21上に移送される(図5(a)参照)。ベルトコンベア21上を搬送される布類Sは、表面撮像部4により表面検査がされる。本実施例の表面撮像部41は、図3に示すように、同一ライン上に配置された2台のライン式カラーカメラを備え、搬送方向と直交する方向に布類Sの検査対象領域をライン状に撮像する。布類Sの検査対象領域は、光源42により照らされており、検査対象領域の下方には検査板43が配置される。布類Sは検査板43の上を通過する。表面撮像部41は、布類Sが広幅(例えば3m程度)であるため、布類Sの幅の1/2をそれぞれのカメラにより撮像している。なお、表面撮像部4を1台のカラーカメラにより構成してもよく、またエリア式のカメラにより構成してもよい。
図1は、前工程のアイロン機2および本実施例の検査機構を有する折畳機3の構成図である。
アイロン機2は、展張された布類Sを自動アイロンがけする機械である。アイロン機2によりアイロンがけされた布類Sは、展張された状態で折畳機3のベルトコンベア21上に移送される(図5(a)参照)。ベルトコンベア21上を搬送される布類Sは、表面撮像部4により表面検査がされる。本実施例の表面撮像部41は、図3に示すように、同一ライン上に配置された2台のライン式カラーカメラを備え、搬送方向と直交する方向に布類Sの検査対象領域をライン状に撮像する。布類Sの検査対象領域は、光源42により照らされており、検査対象領域の下方には検査板43が配置される。布類Sは検査板43の上を通過する。表面撮像部41は、布類Sが広幅(例えば3m程度)であるため、布類Sの幅の1/2をそれぞれのカメラにより撮像している。なお、表面撮像部4を1台のカラーカメラにより構成してもよく、またエリア式のカメラにより構成してもよい。
検査板43は、白色領域431と、黒色領域432とから構成される。検査板43を明色領域と暗色領域とから構成するのは、欠陥を識別しやすくするためである。布類に破れがある場合、破れは白色領域431では明るく写り、黒色領域432では暗く写る。
また、図4に示すように、RGBの3つのラインと検査板の色領域を対応させ、撮像されたRGBの各画像データを合成することにより、欠陥種別情報を強調することができる。この場合、非黒汚れと黒汚れでは、白色領域431と黒色領域432における写りが異なる態様で変化する。例えば、黄色系の非黒汚れは、青ライン画像データでは黄色系の非黒汚れはより濃く変化し、これと緑ライン画像データおよび赤ライン画像データを合成すると、より濃い黄色系の汚れとして捉えることができる。また、破れは、黒領域432上(赤ライン)でのみ暗く捉えられることから、合成画像データでは、シアンに近い色として捉えられることとなる。黒汚れは、合成してもそのままである。この場合、シアンに近い色から一定の範囲にある色相の模様は、破れである蓋然性が高いと言える。
また、図4に示すように、RGBの3つのラインと検査板の色領域を対応させ、撮像されたRGBの各画像データを合成することにより、欠陥種別情報を強調することができる。この場合、非黒汚れと黒汚れでは、白色領域431と黒色領域432における写りが異なる態様で変化する。例えば、黄色系の非黒汚れは、青ライン画像データでは黄色系の非黒汚れはより濃く変化し、これと緑ライン画像データおよび赤ライン画像データを合成すると、より濃い黄色系の汚れとして捉えることができる。また、破れは、黒領域432上(赤ライン)でのみ暗く捉えられることから、合成画像データでは、シアンに近い色として捉えられることとなる。黒汚れは、合成してもそのままである。この場合、シアンに近い色から一定の範囲にある色相の模様は、破れである蓋然性が高いと言える。
ワーク検知センサ45および図示しないコンベア速度検出器により布類Sの長さと移動速度が計測される。布類Sの先端がワーク検知センサ45を通過後、計算された時間の後に撮像部41,51により布類Sの撮像が行われる(図5(b)参照)。撮像部41,51からの画像データに各種マスク処理を施し、欠陥判定作業が行われる。欠陥判定作業により、欠陥ありとされた場合には欠陥フラグが記録される。欠陥ありと判定された布類Sは分別され、例えば、折り数を変えて異なるスタッカに排出される。
ベルトコンベア21の後端部には、ベルトコンベア22が配置されている。ベルトコンベア21とベルトコンベア22に挟まれた布類Sは、ベルトコンベア23の方向へ搬送される。ベルトコンベア22とベルトコンベア23との間に、検査板43と同一構成の検査板53が配置されている。検査板53の位置が検査対象領域であり、検査対象領域は検査板53と対向して設けられた光源52により照らされている。そして、上下に間隙を設けて配置された光源51の間隙から、裏面撮像部51により布類Sの検査対象部位がライン状に撮像される。裏面撮像部51は表面撮像部41と同一構成であり、光源52は光源42と同一構成である。
裏面撮像部51により撮像された画像データに基づき、表面検査と同様の手順により、裏面検査が行われる。
裏面撮像部51により撮像された画像データに基づき、表面検査と同様の手順により、裏面検査が行われる。
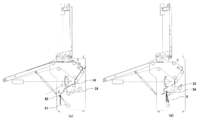
ベルトコンベア23の終端部を通過した布類Sは、下方に垂れ下がった状態とされる。この際、可動折爪61はコンベア24にほぼ当接する位置にある。そして、布類Sの1/4が垂れ下がり、4つ折りに適した状態になると、可動折爪61が当接部材62側へ移動し、可動折爪61と当接部材62が布類Sを挟んだ状態となる(図6(c)参照)。これにより、ベルトコンベア23の回転により、ベルトコンベア24と可動折爪61の間に布類Sが垂れ下がるようになる。可動折爪61とベルトコンベア24との間に、布類Sの1/4が垂れ下がり、4つ折りに適した状態になると、可動折爪61がベルトコンベア24に当接する位置に移動し、ベルトコンベア23とベルトコンベア24との間隙に布類Sが投入される(図6(d)参照)。4つ折りされた布類Sは、ベルトコンベア25により次工程へ搬送される(図7参照)。
なお、本実施例の折畳機に設ける検査機構は、上記の組み合わせに限定されず、例えば、表側検査機構の代わりに金属探知機(検針器)を設けてもよいし、搬送コンベア25に金属探知機(検針器)を付加的に設けてもよい。
以上の構成を有する本実施例の折畳機によれば、ランドリー等の工場における機械の設置スペースを削減することができる。また、両面検査機能を設けるために必要なベルトコンベアおよびその軸数の増加を最小限にできるため、コスト性およびメンテナンス性にも優れる。
2 アイロン機
3 折畳機
21~25 搬送コンベア
32 本体(筐体)
41 表面撮像部
42 光源(表面検査用)
43 検査板
44 支持柱
45 ワーク検知センサ
51 裏面撮像部
52 光源(裏面検査用)
53 検査板
61 可動折爪
62 当接部材
431 白色領域
432 黒色領域
411 青ライン画像データ
412 緑ライン画像データ
413 赤ライン画像データ
3 折畳機
21~25 搬送コンベア
32 本体(筐体)
41 表面撮像部
42 光源(表面検査用)
43 検査板
44 支持柱
45 ワーク検知センサ
51 裏面撮像部
52 光源(裏面検査用)
53 検査板
61 可動折爪
62 当接部材
431 白色領域
432 黒色領域
411 青ライン画像データ
412 緑ライン画像データ
413 赤ライン画像データ
Claims (10)
- 複数のコンベアにより搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構を備える折畳機であって、
前工程からシート状物品を受け取る最も長い第1のコンベアと、
前記第1のコンベアと協働してシート状物品を下方に移送する第2のコンベアと、
前記第2のコンベアと検査板を挟んで連続する第3のコンベアと、
撮像部および照明部を有し、前記検査板を通過するシート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構と、を備え、
前記裏側検査機構を、第1のコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とする折畳機。 - シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構を、第1のコンベアの上方に配置したことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の折畳機。
- 前記第1のコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の折畳機。
- シート状物品を搬送する複数のコンベアからなるコンベア機構と、コンベア機構により搬送されるシート状物品を折り畳む折畳機構と、本体と、を備える折畳機であって、
撮像部および照明部を有し、シート状物品を裏側から検査する裏側検査機構を、本体から突出した最も長いコンベアの下方に配置したことを特徴とする折畳機。 - 前記コンベア機構は、検査板を挟んで連続する上方コンベア群と下方コンベア群とを含み、
前記裏側検査機構の有する撮像部および照明部は、前記検査板と対向して配置されることを特徴とする請求項4に記載の折畳機。 - シート状物品を表側から検査する表側検査機構をさらに備えることを特徴とする請求項4また5に記載の折畳機。
- 前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアは、前工程からシート状物品を受け取るために傾斜して配置されたコンベアであることを特徴とする請求項4ないし6のいずれか一項に記載の折畳機。
- 前記本体から突出した最も長いコンベアには、シート状物品の長さを測定するためのセンサが設けられていることを特徴とする請求項4ないし7のいずれか一項に記載の折畳機。
- 前記撮像部は、1台または2台のカメラにより構成されることを特徴とする請求項1ないし8のいずれか一項に記載の折畳機。
- 前記検査板は、暗色領域と明色領域とを有することを特徴とする請求項1ないし9のいずれか一項に記載の折畳機。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008-140306 | 2008-05-29 | ||
| JP2008140306A JP5248919B2 (ja) | 2008-05-29 | 2008-05-29 | 検査機能を有する折畳機 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2009144905A1 true WO2009144905A1 (ja) | 2009-12-03 |
Family
ID=41376795
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/002277 WO2009144905A1 (ja) | 2008-05-29 | 2009-05-22 | 検査機能を有する折畳機 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5248919B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2009144905A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3075896A1 (de) * | 2015-04-01 | 2016-10-05 | Herbert Kannegiesser GmbH | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum nachbehandeln von wäschestücken |
| EP3093385A1 (de) * | 2015-05-13 | 2016-11-16 | Herbert Kannegiesser GmbH | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum nachbehandeln von wäschestücken |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4792521B2 (ja) * | 2009-12-15 | 2011-10-12 | 株式会社アイ.エス.テイ | 布製品識別装置および布製品把持システム |
| JP5881278B2 (ja) * | 2010-05-20 | 2016-03-09 | 株式会社プレックス | 布片検査装置および検査方法 |
| JP5952136B2 (ja) * | 2012-08-29 | 2016-07-13 | 倉敷紡績株式会社 | 布片の縁部の自動検出方法とその装置、および、該装置を有する布片展開送り装置 |
| JP6048872B2 (ja) * | 2012-09-04 | 2016-12-21 | 株式会社プレックス | 布片検査方法および布片検査装置 |
| JP6108535B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-27 | 2017-04-05 | 株式会社プレックス | 布類検査装置 |
| JP6133161B2 (ja) * | 2013-07-27 | 2017-05-24 | 株式会社プレックス | 布類捌き装置 |
| JP7185500B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-14 | 2022-12-07 | 東都フォルダー工業株式会社 | シート材の画像処理装置 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0633368A (ja) * | 1992-07-14 | 1994-02-08 | Gunze Ltd | 生地の検反方法およびその装置 |
| JP2000329701A (ja) * | 1999-02-12 | 2000-11-30 | Pouya Firouzu | シート状物品面の欠陥を検査する方法及び検査板 |
| JP3813121B2 (ja) * | 2002-11-29 | 2006-08-23 | 株式会社プレックス | 布片検査装置 |
-
2008
- 2008-05-29 JP JP2008140306A patent/JP5248919B2/ja active Active
-
2009
- 2009-05-22 WO PCT/JP2009/002277 patent/WO2009144905A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0633368A (ja) * | 1992-07-14 | 1994-02-08 | Gunze Ltd | 生地の検反方法およびその装置 |
| JP2000329701A (ja) * | 1999-02-12 | 2000-11-30 | Pouya Firouzu | シート状物品面の欠陥を検査する方法及び検査板 |
| JP3813121B2 (ja) * | 2002-11-29 | 2006-08-23 | 株式会社プレックス | 布片検査装置 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3075896A1 (de) * | 2015-04-01 | 2016-10-05 | Herbert Kannegiesser GmbH | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum nachbehandeln von wäschestücken |
| EP3093385A1 (de) * | 2015-05-13 | 2016-11-16 | Herbert Kannegiesser GmbH | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum nachbehandeln von wäschestücken |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5248919B2 (ja) | 2013-07-31 |
| JP2009285109A (ja) | 2009-12-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5248919B2 (ja) | 検査機能を有する折畳機 | |
| JP4440281B2 (ja) | シート状物品の検査方法および装置 | |
| EP2573550B1 (en) | Cloth inspection device and inspection method | |
| JP6120405B2 (ja) | 布類検査装置 | |
| JP4973332B2 (ja) | 海苔の外観検査装置 | |
| JP2011079564A (ja) | 包装不良検査方法及び装置 | |
| WO2017207115A1 (en) | Surface inspection system and inspection method | |
| WO1998001746A1 (en) | Visual inspection apparatus | |
| JP3813121B2 (ja) | 布片検査装置 | |
| JP2004257929A (ja) | 転写箔欠点検査装置 | |
| JP2010099235A (ja) | 検査装置付き折畳機 | |
| JP2008128822A (ja) | 透光性を有するシート材の外観検査装置および方法 | |
| JPH06129996A (ja) | 織布の検反装置 | |
| JP2018124127A (ja) | シート検査装置 | |
| JP5818948B2 (ja) | 布片検査装置 | |
| JPH08117499A (ja) | 布片欠陥検出装置 | |
| JP4355479B2 (ja) | 欠陥布片検出装置における欠陥レベル情報設定方法 | |
| JPH08276100A (ja) | 布片欠陥検出装置 | |
| JP4174305B2 (ja) | 欠陥布類検出装置 | |
| JPH0710720Y2 (ja) | 布片欠陥検査装置 | |
| JPH095258A (ja) | シート状面の欠陥を検査する方法および装置 | |
| WO2021166729A1 (ja) | 複合シートの製造方法及び製造装置 | |
| JP3634300B2 (ja) | 布類の重ね折り装置 | |
| JP6216591B2 (ja) | シート材の外観検査装置 | |
| JPH08299700A (ja) | 布片欠陥検出装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09754414 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 09754414 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |