JP6783648B2 - 配線基板、半導体装置 - Google Patents
配線基板、半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6783648B2 JP6783648B2 JP2016251599A JP2016251599A JP6783648B2 JP 6783648 B2 JP6783648 B2 JP 6783648B2 JP 2016251599 A JP2016251599 A JP 2016251599A JP 2016251599 A JP2016251599 A JP 2016251599A JP 6783648 B2 JP6783648 B2 JP 6783648B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- region
- pad
- pads
- dummy
- wiring board
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/498—Leads, i.e. metallisations or lead-frames on insulating substrates, e.g. chip carriers
- H01L23/49838—Geometry or layout
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3157—Partial encapsulation or coating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/14—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bump connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/17—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of bump connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/13101—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of less than 400°C
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/14—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bump connectors
- H01L2224/141—Disposition
- H01L2224/1412—Layout
- H01L2224/1413—Square or rectangular array
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16227—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16238—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bonding area protruding from the surface of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8119—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting
- H01L2224/81193—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting wherein the bump connectors are disposed on both the semiconductor or solid-state body and another item or body to be connected to the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/81438—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/81439—Silver [Ag] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/81438—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/81444—Gold [Au] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/81463—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than 1550°C
- H01L2224/81464—Palladium [Pd] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/8338—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/83385—Shape, e.g. interlocking features
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/91—Methods for connecting semiconductor or solid state bodies including different methods provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/80 - H01L2224/90
- H01L2224/92—Specific sequence of method steps
- H01L2224/921—Connecting a surface with connectors of different types
- H01L2224/9212—Sequential connecting processes
- H01L2224/92122—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a bump connector
- H01L2224/92125—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a bump connector the second connecting process involving a layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/498—Leads, i.e. metallisations or lead-frames on insulating substrates, e.g. chip carriers
- H01L23/49866—Leads, i.e. metallisations or lead-frames on insulating substrates, e.g. chip carriers characterised by the materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/91—Methods for connecting semiconductor or solid state bodies including different methods provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/80 - H01L24/90
- H01L24/92—Specific sequence of method steps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0655—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 the devices being arranged next to each other
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/18—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof the devices being of types provided for in two or more different subgroups of the same main group of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/50—Multistep manufacturing processes of assemblies consisting of devices, each device being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 or H01L29/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
- H01L2924/143—Digital devices
- H01L2924/1431—Logic devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
- H01L2924/143—Digital devices
- H01L2924/1434—Memory
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
- H01L2924/143—Digital devices
- H01L2924/1434—Memory
- H01L2924/1435—Random access memory [RAM]
- H01L2924/1436—Dynamic random-access memory [DRAM]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Manufacturing Of Printed Wiring (AREA)
- Production Of Multi-Layered Print Wiring Board (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Description
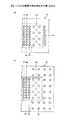
図1は、第1の実施の形態に係る半導体装置を例示する図であり、図1(a)は平面図、図1(b)は図1(a)のA−A線に沿う部分拡大断面図である。但し、図1(a)は主としてパッドの配置を示しており、図1(b)に示す構成要素の一部は図示が省略されている。
第1の実施の形態の変形例では、ダミーパッドの配置のバリエーションを示す。なお、第1の実施の形態の変形例において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
第2の実施の形態では、ダミーパッド18の配置が第1の実施の形態とは異なる形態を示す。なお、第2の実施の形態において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
10 配線基板
11 配線層
12 絶縁層
12a 絶縁層12の上面
12x ビアホール
13 パッド
13v ビア配線
14 ニッケルめっき層
15 金属層
18 ダミーパッド
21、22、23 半導体チップ
30 電極
40 バンプ
50 アンダーフィル樹脂
Claims (9)
- 絶縁層の上面において、半導体チップ接続用の外部接続端子として使用される複数のパッドが配置されたパッド配置領域が画定され、
前記パッド配置領域は、複数の前記パッドが所定密度で配置された第1領域と、複数の前記パッドが前記第1領域の所定密度よりも低密度で配置された第2領域と、を含み、
前記第2領域のみ、外部接続端子として使用されないダミーパッドが少なくとも1つ配置され、
前記ダミーパッドは、少なくとも前記第2領域の最外周に位置する前記パッドの外側、かつ前記半導体チップの外形よりも外側に位置し、
前記パッド及び前記ダミーパッドの表面には、めっき層が形成され、前記めっき層はニッケルを含む配線基板。 - 前記第2領域の最外周に位置するパッドと前記ダミーパッドとが千鳥状に配置されている請求項1に記載の配線基板。
- 前記第2領域の最外周に位置するパッドと前記ダミーパッドとの距離が、前記第2領域内で隣接する前記パッド同士の距離よりも短い請求項1又は2に記載の配線基板。
- 前記ダミーパッドのピッチが、前記第2領域内で隣接する前記パッドのピッチよりも狭い請求項1乃至3の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。
- 少なくとも前記第2領域の最外周に位置するパッドの間、及び第2領域の最外周よりも内側に位置するパッドの間にも前記ダミーパッドを配置した請求項1乃至4の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。
- 前記ダミーパッドは、前記第2領域の最外周に位置するパッドに沿った細長状のパターンに形成されている請求項1に記載の配線基板。
- 前記第2領域の最外周に位置するパッドの外側に、複数列のダミーパッドが配置されている請求項1乃至5の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。
- 前記第2領域内で隣接する前記パッドのピッチは、前記第1領域内で隣接する前記パッドのピッチよりも広い請求項1乃至7の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。
- 請求項1乃至8の何れか一項に記載の配線基板と、
前記配線基板の複数の前記パッドに接続された半導体チップと、
前記配線基板と前記半導体チップとの間に充填された樹脂と、を有し、
前記樹脂は、前記ダミーパッドを被覆している半導体装置。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016251599A JP6783648B2 (ja) | 2016-12-26 | 2016-12-26 | 配線基板、半導体装置 |
| US15/819,310 US10438883B2 (en) | 2016-12-26 | 2017-11-21 | Wiring board and semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016251599A JP6783648B2 (ja) | 2016-12-26 | 2016-12-26 | 配線基板、半導体装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018107267A JP2018107267A (ja) | 2018-07-05 |
| JP2018107267A5 JP2018107267A5 (ja) | 2019-06-27 |
| JP6783648B2 true JP6783648B2 (ja) | 2020-11-11 |
Family
ID=62625891
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016251599A Active JP6783648B2 (ja) | 2016-12-26 | 2016-12-26 | 配線基板、半導体装置 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10438883B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6783648B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7353113B2 (ja) * | 2019-09-27 | 2023-09-29 | 日本電波工業株式会社 | 電子部品及び電子部品の製造方法 |
| US12027493B2 (en) * | 2019-11-04 | 2024-07-02 | Xilinx, Inc. | Fanout integration for stacked silicon package assembly |
| JP2021093417A (ja) * | 2019-12-09 | 2021-06-17 | イビデン株式会社 | プリント配線板、及び、プリント配線板の製造方法 |
| CN112382618B (zh) * | 2020-11-09 | 2023-10-27 | 成都海光集成电路设计有限公司 | 一种封装结构及封装方法 |
| KR20230016089A (ko) | 2021-07-22 | 2023-02-01 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
| US11997842B2 (en) * | 2021-08-31 | 2024-05-28 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited | Dummy metal bonding pads for underfill application in semiconductor die packaging and methods of forming the same |
| CN114488632B (zh) * | 2022-01-27 | 2023-06-20 | 武汉天马微电子有限公司 | 一种显示面板、显示装置及其检测方法 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3596807B2 (ja) * | 2000-08-09 | 2004-12-02 | インターナショナル・ビジネス・マシーンズ・コーポレーション | プリント配線板及びその製造方法 |
| JP4580633B2 (ja) * | 2003-11-14 | 2010-11-17 | スタンレー電気株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4820683B2 (ja) * | 2006-04-28 | 2011-11-24 | 川崎マイクロエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置と半導体装置の絶縁破壊防止方法 |
| JP5595524B2 (ja) * | 2010-12-28 | 2014-09-24 | 京セラ株式会社 | 光モジュールおよび光配線基板 |
| JP2014183085A (ja) | 2013-03-18 | 2014-09-29 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | マルチチップモジュール用基板、マルチチップモジュール用多層配線基板、マルチチップモジュール及びマルチチップ多層配線モジュール |
| US9799622B2 (en) * | 2014-06-18 | 2017-10-24 | Dyi-chung Hu | High density film for IC package |
-
2016
- 2016-12-26 JP JP2016251599A patent/JP6783648B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-11-21 US US15/819,310 patent/US10438883B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018107267A (ja) | 2018-07-05 |
| US20180182701A1 (en) | 2018-06-28 |
| US10438883B2 (en) | 2019-10-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6783648B2 (ja) | 配線基板、半導体装置 | |
| US8749046B2 (en) | Wiring substrate and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US7396753B2 (en) | Semiconductor package substrate having bonding pads with plated layer thereon and process of manufacturing the same | |
| JP5018483B2 (ja) | 電子デバイスパッケージ、モジュール、および電子機器 | |
| US8610001B2 (en) | Printed wiring board and method for manufacturing printed wiring board | |
| US8790504B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing wiring substrate | |
| US20150156880A1 (en) | Printed wiring board and method for manufacturing printed wiring board | |
| JP2005109496A (ja) | プリ半田構造を形成するための半導体パッケージ基板及びプリ半田構造が形成された半導体パッケージ基板、並びにこれらの製法 | |
| US11784173B2 (en) | Semiconductor device including a circuit for transmitting a signal | |
| US20160095219A1 (en) | Printed wiring board and semiconductor device having the same | |
| US9935029B2 (en) | Printed wiring board for package-on-package | |
| KR20150047747A (ko) | 인쇄회로기판 및 그 제조방법과 이를 이용하는 반도체 패키지 | |
| JP2017118067A (ja) | 配線基板、半導体装置及び配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP2016076533A (ja) | バンプ付きプリント配線板およびその製造方法 | |
| TWI533424B (zh) | 封裝載板 | |
| JP2023528811A (ja) | パッケージ基板 | |
| JP4494249B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9373576B2 (en) | Flip chip pad geometry for an IC package substrate | |
| JP2010232616A (ja) | 半導体装置及び配線基板 | |
| JP6473002B2 (ja) | バンプ付きプリント配線板 | |
| JP2016122776A (ja) | バンプ付きプリント配線板およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2013211497A (ja) | 部品接合構造 | |
| JP2017045923A (ja) | バンプ付きプリント配線板およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2017191874A (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2013131775A (ja) | 配線基板 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190522 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190522 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20200227 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200310 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200423 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200630 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200731 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20201006 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20201022 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6783648 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |