JP6671256B2 - 配線基板及びその製造方法 - Google Patents
配線基板及びその製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6671256B2 JP6671256B2 JP2016136291A JP2016136291A JP6671256B2 JP 6671256 B2 JP6671256 B2 JP 6671256B2 JP 2016136291 A JP2016136291 A JP 2016136291A JP 2016136291 A JP2016136291 A JP 2016136291A JP 6671256 B2 JP6671256 B2 JP 6671256B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- wiring
- electronic component
- insulating film
- electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 17
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 claims description 76
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 56
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 40
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 339
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 34
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 34
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 16
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 14
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000012779 reinforcing material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 5
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003985 ceramic capacitor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- -1 azole compound Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonium persulfate Chemical compound [NH4+].[NH4+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O ROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920006231 aramid fiber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- XLJMAIOERFSOGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M cyanate Chemical compound [O-]C#N XLJMAIOERFSOGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 238000007772 electroless plating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 2
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000009719 polyimide resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 description 2
- KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-pyrrole Natural products C=1C=CNC=1 KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LCPVQAHEFVXVKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,4-difluorophenoxy)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1OC1=CC=C(F)C=C1F LCPVQAHEFVXVKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001870 ammonium persulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011889 copper foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003949 imides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001151 other effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002335 preservative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- CHQMHPLRPQMAMX-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium persulfate Substances [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O CHQMHPLRPQMAMX-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002335 surface treatment layer Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K1/00—Printed circuits
- H05K1/18—Printed circuits structurally associated with non-printed electric components
- H05K1/182—Printed circuits structurally associated with non-printed electric components associated with components mounted in the printed circuit board, e.g. insert mounted components [IMC]
- H05K1/185—Components encapsulated in the insulating substrate of the printed circuit or incorporated in internal layers of a multilayer circuit
- H05K1/186—Components encapsulated in the insulating substrate of the printed circuit or incorporated in internal layers of a multilayer circuit manufactured by mounting on or connecting to patterned circuits before or during embedding
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/48—Manufacture or treatment of parts, e.g. containers, prior to assembly of the devices, using processes not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326
- H01L21/4814—Conductive parts
- H01L21/4846—Leads on or in insulating or insulated substrates, e.g. metallisation
- H01L21/4853—Connection or disconnection of other leads to or from a metallisation, e.g. pins, wires, bumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/48—Manufacture or treatment of parts, e.g. containers, prior to assembly of the devices, using processes not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326
- H01L21/4814—Conductive parts
- H01L21/4846—Leads on or in insulating or insulated substrates, e.g. metallisation
- H01L21/4857—Multilayer substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/48—Manufacture or treatment of parts, e.g. containers, prior to assembly of the devices, using processes not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326
- H01L21/4814—Conductive parts
- H01L21/4846—Leads on or in insulating or insulated substrates, e.g. metallisation
- H01L21/486—Via connections through the substrate with or without pins
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/683—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L21/6835—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
- H01L23/3121—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3157—Partial encapsulation or coating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5386—Geometry or layout of the interconnection structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5389—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates the chips being integrally enclosed by the interconnect and support structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0657—Stacked arrangements of devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K1/00—Printed circuits
- H05K1/02—Details
- H05K1/11—Printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K1/111—Pads for surface mounting, e.g. lay-out
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K1/00—Printed circuits
- H05K1/02—Details
- H05K1/11—Printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K1/115—Via connections; Lands around holes or via connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/40—Forming printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K3/4007—Surface contacts, e.g. bumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/40—Forming printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K3/42—Plated through-holes or plated via connections
- H05K3/423—Plated through-holes or plated via connections characterised by electroplating method
- H05K3/424—Plated through-holes or plated via connections characterised by electroplating method by direct electroplating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/46—Manufacturing multilayer circuits
- H05K3/4644—Manufacturing multilayer circuits by building the multilayer layer by layer, i.e. build-up multilayer circuits
- H05K3/4682—Manufacture of core-less build-up multilayer circuits on a temporary carrier or on a metal foil
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68345—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used as a support during the manufacture of self supporting substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/13101—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of less than 400°C
- H01L2224/13111—Tin [Sn] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/13101—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of less than 400°C
- H01L2224/13116—Lead [Pb] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16227—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16237—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bonding area disposed in a recess of the surface of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/29001—Core members of the layer connector
- H01L2224/29099—Material
- H01L2224/2919—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a polymer, e.g. polyester, phenolic based polymer, epoxy
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06513—Bump or bump-like direct electrical connections between devices, e.g. flip-chip connection, solder bumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06517—Bump or bump-like direct electrical connections from device to substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06541—Conductive via connections through the device, e.g. vertical interconnects, through silicon via [TSV]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06548—Conductive via connections through the substrate, container, or encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06582—Housing for the assembly, e.g. chip scale package [CSP]
- H01L2225/06586—Housing with external bump or bump-like connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/498—Leads, i.e. metallisations or lead-frames on insulating substrates, e.g. chip carriers
- H01L23/49811—Additional leads joined to the metallisation on the insulating substrate, e.g. pins, bumps, wires, flat leads
- H01L23/49816—Spherical bumps on the substrate for external connection, e.g. ball grid arrays [BGA]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5383—Multilayer substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5384—Conductive vias through the substrate with or without pins, e.g. buried coaxial conductors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
- H01L2924/143—Digital devices
- H01L2924/1434—Memory
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19041—Component type being a capacitor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/191—Disposition
- H01L2924/19101—Disposition of discrete passive components
- H01L2924/19102—Disposition of discrete passive components in a stacked assembly with the semiconductor or solid state device
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/38—Effects and problems related to the device integration
- H01L2924/386—Wire effects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10007—Types of components
- H05K2201/10015—Non-printed capacitor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10431—Details of mounted components
- H05K2201/10507—Involving several components
- H05K2201/10515—Stacked components
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10613—Details of electrical connections of non-printed components, e.g. special leads
- H05K2201/10621—Components characterised by their electrical contacts
- H05K2201/10636—Leadless chip, e.g. chip capacitor or resistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10613—Details of electrical connections of non-printed components, e.g. special leads
- H05K2201/10621—Components characterised by their electrical contacts
- H05K2201/10734—Ball grid array [BGA]; Bump grid array
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10613—Details of electrical connections of non-printed components, e.g. special leads
- H05K2201/10954—Other details of electrical connections
- H05K2201/10977—Encapsulated connections
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Production Of Multi-Layered Print Wiring Board (AREA)
- Printing Elements For Providing Electric Connections Between Printed Circuits (AREA)
Description
[第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板の構造]
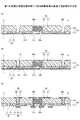
まず、第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板の構造について説明する。図1は、第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板を例示する図であり、図1(a)は断面図、図1(b)は図1(a)のA部周辺の部分拡大平面図である。但し、図1(b)において、第1配線層10、絶縁層20、及びソルダーレジスト層60の図示を省略している。
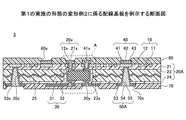
次に、第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板の製造方法について説明する。図2〜図5は、第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板の製造工程を例示する図である。本実施の形態では、支持体上に複数の配線基板となる部分を作製し支持体を除去後個片化して各配線基板とする工程の例を示すが、支持体上に1個ずつ配線基板を作製し支持体を除去する工程としてもよい。
第1の実施の形態の変形例1では、接続用配線12に貫通孔12xを形成しない例を示す。なお、第1の実施の形態の変形例1において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
第1の実施の形態の変形例2では、電子部品30を内蔵する絶縁層の構造が異なる例を示す。なお、第1の実施の形態の変形例2において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
配線基板の応用例1では、第1の実施の形態に係る配線基板に半導体チップが搭載(フリップチップ実装)された半導体パッケージの例を示す。なお、配線基板の応用例1において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
配線基板の応用例2では、配線基板の応用例1の電子部品30に代えて電子部品200を内蔵した半導体パッケージの例を示す。なお、配線基板の応用例2において、既に説明した実施の形態と同一構成部についての説明は省略する場合がある。
4、5 半導体パッケージ
10 第1配線層
11 微細配線
12 接続用配線
12x、14x、21x、41x、53x 貫通孔
20、20A 絶縁層
20x、20y、20z ビアホール
21 第1絶縁膜
22、23 第2絶縁膜
23x 電子部品収容部
24 第3絶縁膜
25 補強材
30、200 電子部品
31 本体
32 電極
40 第2配線層
41、51、53 第1層
42、52、54 第2層
43、55 第3層
50、50A 第3配線層
60、70 ソルダーレジスト層
60x、70x 開口部
100 半導体チップ
110 電極パッド
120 バンプ
130 アンダーフィル樹脂
140 外部接続端子
210、230、250 半導体チップ
220、240、260 貫通電極
270、280 接合部
400 支持体
408 キャリア付き金属箔
409 厚箔
410、530 薄箔
Claims (11)
- 絶縁層と、
前記絶縁層に内蔵された電子部品と、
前記絶縁層に形成され、前記絶縁層の一方の面側に開口し、前記電子部品の電極を露出するビアホールと、
前記絶縁層に埋め込まれ、一方の面が前記絶縁層の一方の面から露出する第1配線層と、
前記第1配線層の一方の面に形成された配線パターン、及び前記配線パターンから前記ビアホール内に延在して前記電子部品の電極と直接接続されたビア配線、を含む第2配線層と、を有し、
前記絶縁層は、前記第1配線層を埋め込む第1絶縁膜、及び前記電子部品を内蔵する第2絶縁膜が積層された構造であり、
前記第1絶縁膜は、全ての前記第1配線層の側面及び他方の面、並びに前記ビア配線の側面の一部を被覆し、
前記電子部品の電極は、前記ビア配線と接する面が前記第2絶縁膜から露出し、側面が前記第2絶縁膜に被覆され、
前記ビア配線が前記配線パターンと一体である配線基板。 - 前記ビアホールは、前記電子部品の電極上に位置する前記第1配線層、及び前記第1配線層と前記電子部品の電極との間に位置する前記絶縁層を貫通して前記電子部品の電極の一方の面を露出する請求項1に記載の配線基板。
- 前記第2配線層は、
前記第1配線層の一方の面に直接形成され、前記ビアホールと連通する貫通孔を備えた第1層と、
前記第1層上に形成され、前記第1層上から延在して前記貫通孔及び前記ビアホールの内壁に沿って形成され、更に前記ビアホール内に露出する前記電子部品の電極を被覆する第2層と、
前記第2層上に形成され、前記第2層上から延在して前記第2層が形成された前記貫通孔内及び前記ビアホール内を充填する第3層と、を有する請求項1又は2に記載の配線基板。 - 前記絶縁層の一方の面には前記配線パターンを被覆するソルダーレジスト層が形成され、
前記ソルダーレジスト層は、前記配線パターンを選択的に露出する開口部を備え、
前記開口部内に露出する前記配線パターンは、半導体チップ接続用のパッドである請求項1乃至3の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。 - 前記配線パターンは、前記ビア配線と接続された配線と、前記ビア配線と接続されていない配線と、を含み、
前記ビア配線と接続された配線と、前記ビア配線と接続されていない配線とは同一高さである請求項1乃至4の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。 - 前記絶縁層に形成され、前記絶縁層の他方の面側に開口し、前記電子部品の電極を露出する第2ビアホールと、
前記絶縁層の他方の面に形成された配線パターン、及び前記配線パターンから前記第2ビアホール内に延在して前記電子部品の電極と直接接続されたビア配線、を含む第3配線層と、を有する請求項1乃至5の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。 - 前記第1絶縁膜と前記第2絶縁膜との境界は、前記電子部品の電極の前記ビア配線と接する面と面一である請求項1乃至6の何れか一項に記載の配線基板。
- 最外層が金属箔である支持体を準備し、前記金属箔上に一方の面が前記金属箔と接する第1配線層を形成する工程と、
前記金属箔上に、前記第1配線層の側面及び他方の面を被覆する第1絶縁膜を形成する工程と、
前記第1絶縁膜上に、電子部品を搭載する工程と、
前記第1絶縁膜上に、前記電子部品を被覆する第2絶縁膜を形成する工程と、
前記金属箔を除く前記支持体を除去する工程と、
前記金属箔及び前記第1絶縁膜を貫通すると共に前記電子部品の電極を露出するビアホールを形成する工程と、
前記金属箔上及び前記ビアホール内に金属層を形成後、前記金属箔及び前記金属層をパターニングし、前記金属箔及び前記金属層を備えた配線パターン、及び前記配線パターンから前記ビアホール内に延在して前記電子部品の電極と直接接続されたビア配線、を含む第2配線層を形成する工程と、を有し、
前記第1絶縁膜は、全ての前記第1配線層の側面及び他方の面、並びに前記ビア配線の側面の一部を被覆し、
前記電子部品の電極は、前記ビア配線と接する面が前記第2絶縁膜から露出し、側面が前記第2絶縁膜に被覆され、
前記第2配線層を形成する工程において、前記ビア配線を前記配線パターンと一体に形成する配線基板の製造方法。 - 前記第2配線層を形成する工程は、
前記金属箔の全面、前記ビアホールの内壁面、及び前記ビアホール内に露出する前記電子部品の電極を連続的に被覆するシード層を形成する工程と、
前記シード層を給電層に利用した電解めっき法により、前記シード層上に選択的に電解めっき層を形成する工程と、
前記電解めっき層に覆われていない部分の前記シード層及び前記金属箔をエッチングにより除去する工程と、を有する請求項8に記載の配線基板の製造方法。 - 前記第1配線層を形成する工程では、前記第1配線層の、前記電子部品の電極が配置される予定の領域に、貫通孔を形成しておき、
前記ビアホールを形成する工程では、前記貫通孔に対応する位置の前記金属箔及び前記第1絶縁膜にレーザを照射し、前記電子部品の電極を露出する前記ビアホールを形成する請求項8又は9に記載の配線基板の製造方法。 - 前記第1絶縁膜と前記第2絶縁膜との境界は、前記電子部品の電極の前記ビア配線と接する面と面一となる請求項8乃至10の何れか一項に記載の配線基板の製造方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016136291A JP6671256B2 (ja) | 2016-07-08 | 2016-07-08 | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
| US15/635,590 US10080292B2 (en) | 2016-07-08 | 2017-06-28 | Wiring board |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016136291A JP6671256B2 (ja) | 2016-07-08 | 2016-07-08 | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018006712A JP2018006712A (ja) | 2018-01-11 |
| JP2018006712A5 JP2018006712A5 (ja) | 2019-03-28 |
| JP6671256B2 true JP6671256B2 (ja) | 2020-03-25 |
Family
ID=60911425
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016136291A Active JP6671256B2 (ja) | 2016-07-08 | 2016-07-08 | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10080292B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6671256B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020071473A1 (ja) * | 2018-10-04 | 2020-04-09 | 株式会社村田製作所 | 積層体及びその製造方法 |
| US11296030B2 (en) * | 2019-04-29 | 2022-04-05 | Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. | Embedded component package structure and manufacturing method thereof |
| KR20220086924A (ko) * | 2020-12-17 | 2022-06-24 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 인쇄회로기판 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8225503B2 (en) * | 2008-02-11 | 2012-07-24 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Method for manufacturing board with built-in electronic elements |
| US8024858B2 (en) * | 2008-02-14 | 2011-09-27 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing printed wiring board with built-in electronic component |
| JP5693977B2 (ja) | 2011-01-11 | 2015-04-01 | 新光電気工業株式会社 | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
| JP2013084692A (ja) | 2011-10-06 | 2013-05-09 | Ibiden Co Ltd | 配線板及びその製造方法 |
| JP2015226013A (ja) * | 2014-05-29 | 2015-12-14 | イビデン株式会社 | プリント配線板およびその製造方法 |
| JP2016066705A (ja) * | 2014-09-25 | 2016-04-28 | イビデン株式会社 | プリント配線板およびその製造方法 |
-
2016
- 2016-07-08 JP JP2016136291A patent/JP6671256B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-06-28 US US15/635,590 patent/US10080292B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018006712A (ja) | 2018-01-11 |
| US10080292B2 (en) | 2018-09-18 |
| US20180014407A1 (en) | 2018-01-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6752553B2 (ja) | 配線基板 | |
| KR102220757B1 (ko) | 배선 기판 및 배선 기판의 제조 방법 | |
| JP3813402B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4334005B2 (ja) | 配線基板の製造方法及び電子部品実装構造体の製造方法 | |
| US9078384B2 (en) | Wiring substrate and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP5886617B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法、半導体パッケージ | |
| JP6584939B2 (ja) | 配線基板、半導体パッケージ、半導体装置、配線基板の製造方法及び半導体パッケージの製造方法 | |
| JP6375159B2 (ja) | 配線基板、半導体パッケージ | |
| US11152293B2 (en) | Wiring board having two insulating films and hole penetrating therethrough | |
| JP6594264B2 (ja) | 配線基板及び半導体装置、並びにそれらの製造方法 | |
| US9334576B2 (en) | Wiring substrate and method of manufacturing wiring substrate | |
| JP6550260B2 (ja) | 配線基板及び配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP6566879B2 (ja) | 電子部品内蔵基板 | |
| US10779406B2 (en) | Wiring substrate | |
| JP6761064B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP7202785B2 (ja) | 配線基板及び配線基板の製造方法 | |
| KR20150004749A (ko) | 배선 기판 및 그 제조 방법, 반도체 패키지 | |
| JP2019149438A (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP6341714B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP6671256B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP7253946B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法、半導体パッケージ | |
| US20190013263A1 (en) | Wiring board and semiconductor package | |
| US20230109322A1 (en) | Wiring board | |
| JP2022173930A (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190214 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190214 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20191108 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191119 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200110 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200218 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200303 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6671256 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |