JP6649890B2 - バックコンバータのためのモノリシックに集積されたトランジスタ - Google Patents
バックコンバータのためのモノリシックに集積されたトランジスタ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6649890B2 JP6649890B2 JP2016549475A JP2016549475A JP6649890B2 JP 6649890 B2 JP6649890 B2 JP 6649890B2 JP 2016549475 A JP2016549475 A JP 2016549475A JP 2016549475 A JP2016549475 A JP 2016549475A JP 6649890 B2 JP6649890 B2 JP 6649890B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- side transistor
- substrate
- integrated circuit
- source
- transistor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/08—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind
- H01L27/085—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind including field-effect components only
- H01L27/088—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind including field-effect components only the components being field-effect transistors with insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
- H01L21/761—PN junctions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823493—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the wells or tubs, e.g. twin tubs, high energy well implants, buried implanted layers for lateral isolation [BILLI]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0642—Isolation within the component, i.e. internal isolation
- H01L29/0649—Dielectric regions, e.g. SiO2 regions, air gaps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1025—Channel region of field-effect devices
- H01L29/1029—Channel region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors
- H01L29/1033—Channel region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate, e.g. characterised by the length, the width, the geometric contour or the doping structure
- H01L29/1041—Channel region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate, e.g. characterised by the length, the width, the geometric contour or the doping structure with a non-uniform doping structure in the channel region surface
- H01L29/1045—Channel region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate, e.g. characterised by the length, the width, the geometric contour or the doping structure with a non-uniform doping structure in the channel region surface the doping structure being parallel to the channel length, e.g. DMOS like
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/107—Substrate region of field-effect devices
- H01L29/1075—Substrate region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors
- H01L29/1079—Substrate region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/1087—Substrate region of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate characterised by the contact structure of the substrate region, e.g. for controlling or preventing bipolar effect
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/4175—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices for lateral devices where the connection to the source or drain region is done through at least one part of the semiconductor substrate thickness, e.g. with connecting sink or with via-hole
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7816—Lateral DMOS transistors, i.e. LDMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7833—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate with lightly doped drain or source extension, e.g. LDD MOSFET's; DDD MOSFET's
- H01L29/7835—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate with lightly doped drain or source extension, e.g. LDD MOSFET's; DDD MOSFET's with asymmetrical source and drain regions, e.g. lateral high-voltage MISFETs with drain offset region, extended drain MISFETs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/265—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation
- H01L21/26506—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in group IV semiconductors
- H01L21/26533—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in group IV semiconductors of electrically inactive species in silicon to make buried insulating layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/12—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body
- H01L27/1203—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body the substrate comprising an insulating body on a semiconductor body, e.g. SOI
- H01L27/1207—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body the substrate comprising an insulating body on a semiconductor body, e.g. SOI combined with devices in contact with the semiconductor body, i.e. bulk/SOI hybrid circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/402—Field plates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1588—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load comprising at least one synchronous rectifier element
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B70/00—Technologies for an efficient end-user side electric power management and consumption
- Y02B70/10—Technologies improving the efficiency by using switched-mode power supplies [SMPS], i.e. efficient power electronics conversion e.g. power factor correction or reduction of losses in power supplies or efficient standby modes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
- Rectifiers (AREA)
- Dc-Dc Converters (AREA)
Description
Claims (14)
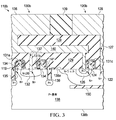
- 集積回路であって、
第1の面と前記第1の面と対向する第1の面とを有する基板と、
横方向拡散された金属酸化物半導体(LDMOS)トランジスタを含むハイサイドトランジスタと、
前記基板の第1の面に沿ったドレインと、前記基板の第2の面に沿ったソースと、前記基板の第1の面と第2の面との間の垂直区分に沿ったチャネル領域とを含むローサイドトランジスタと、
前記ハイサイドトランジスタと前記ローサイドトランジスタのソースとの間に位置するnドープされたウェルと、
前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインと前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースとをスイッチノードで結合する金属層と、
を含む、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインが前記基板の第1の面に沿ったLDD領域を含む、集積回路。 - 請求項2に記載の集積回路であって、
前記基板の第1の面から前記基板の中に延在して前記LDD領域と前記nドープされたウェルとの間に介在するフィールドプレートを更に含む、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記LDMOSトランジスタが、前記nドープされたウェル内のpドープされた領域と、前記pドープされた領域内のnドープされたソース領域とを含む、集積回路。 - 請求項4に記載の集積回路であって、
前記pドープされた領域と前記nドープされたウェルと前記基板とが、前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースと前記ローサイドトランジスタのソースとの間にp−n−p構造を形成する、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記nドープされたウェルと前記基板の第2の面との間に分離層を更に含む、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記金属層を前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインに接続する第1のビアと、
前記金属層を前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースに接続する第2のビアと、
を更に含む、集積回路。 - バックコンバータであって、
集積回路であって、
第1の面と前記第1の面と対向する第1の面とを有する基板と、
横方向拡散された金属酸化物半導体(LDMOS)トランジスタを含むハイサイドトランジスタと、
前記基板の第1の面に沿ったドレインと、前記基板の第2の面に沿ったソースと、前記基板の第1の面と第2の面との間の垂直区分に沿ったチャネル領域とを含むローサイドトランジスタと、
前記ハイサイドトランジスタと前記ローサイドトランジスタのソースとの間に位置するnドープされたウェルと、
前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインと前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースとをスイッチノードで結合する金属層と、
を含む、
前記集積回路を含む、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項8に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインが前記基板の第1の面に沿ったLDD領域を含む、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項9に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記集積回路が、前記基板の第1の面から前記基板の中に延在して前記LDD領域と前記nドープされたウェルとの間に介在するフィールドプレートを更に含む、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項8に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記LDMOSトランジスタが、前記nドープされたウェル内のpドープされた領域と、前記pドープされた領域内のnドープされたソース領域とを含む、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項11に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記pドープされた領域と前記nドープされたウェルと前記基板とが、前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースと前記ローサイドトランジスタのソースとの間にp−n−p構造を形成する、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項8に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記集積回路が、前記nドープされたウェルと前記基板の第2の面との間に分離層を更に含む、バックコンバータ。 - 請求項8に記載のバックコンバータであって、
前記集積回路が、前記金属層を前記ローサイドトランジスタのドレインに接続する第1のビアと、前記金属層を前記ハイサイドトランジスタのソースに接続する第2のビアとを更に含む、バックコンバータ。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201461933717P | 2014-01-30 | 2014-01-30 | |
| US61/933,717 | 2014-01-30 | ||
| US14/608,391 US9646965B2 (en) | 2014-01-30 | 2015-01-29 | Monolithically integrated transistors for a buck converter using source down MOSFET |
| US14/608,391 | 2015-01-29 | ||
| PCT/US2015/013989 WO2015117038A1 (en) | 2014-01-30 | 2015-01-30 | Monolithic ally integrated transistors for a buck converter |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017510062A JP2017510062A (ja) | 2017-04-06 |
| JP2017510062A5 JP2017510062A5 (ja) | 2018-03-08 |
| JP6649890B2 true JP6649890B2 (ja) | 2020-02-19 |
Family
ID=53679763
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016549475A Active JP6649890B2 (ja) | 2014-01-30 | 2015-01-30 | バックコンバータのためのモノリシックに集積されたトランジスタ |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9646965B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3127154A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6649890B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106104802B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015117038A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6326858B2 (ja) * | 2014-02-24 | 2018-05-23 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| EP3144974B1 (en) * | 2015-09-18 | 2022-01-26 | Ampleon Netherlands B.V. | Semiconductor device |
| CN105552075B (zh) * | 2016-01-22 | 2018-06-22 | 成都芯源系统有限公司 | 一种减少系统环路寄生电感的半导体器件 |
| US10319712B2 (en) | 2016-11-10 | 2019-06-11 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Integrated transistor and protection diode and fabrication method |
| US10581426B1 (en) | 2019-03-11 | 2020-03-03 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Source down power FET with integrated temperature sensor |
Family Cites Families (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4023062B2 (ja) * | 2000-03-03 | 2007-12-19 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US7074659B2 (en) | 2003-11-13 | 2006-07-11 | Volterra Semiconductor Corporation | Method of fabricating a lateral double-diffused MOSFET (LDMOS) transistor |
| JP4212551B2 (ja) * | 2003-12-18 | 2009-01-21 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体集積回路装置 |
| US7566931B2 (en) | 2005-04-18 | 2009-07-28 | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Monolithically-integrated buck converter |
| US7235845B2 (en) * | 2005-08-12 | 2007-06-26 | Ciclon Semiconductor Device Corp. | Power LDMOS transistor |
| US7768064B2 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2010-08-03 | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Structure and method for improving shielded gate field effect transistors |
| US7554154B2 (en) * | 2006-07-28 | 2009-06-30 | Alpha Omega Semiconductor, Ltd. | Bottom source LDMOSFET structure and method |
| CN101378075B (zh) * | 2007-08-31 | 2012-10-31 | 谭健 | Ldmos及集成ldmos与cmos的半导体器件 |
| US8026549B2 (en) * | 2008-10-31 | 2011-09-27 | United Microelectronics Corp. | LDMOS with N-type isolation ring and method of fabricating the same |
| US8168490B2 (en) * | 2008-12-23 | 2012-05-01 | Intersil Americas, Inc. | Co-packaging approach for power converters based on planar devices, structure and method |
| US20100171543A1 (en) * | 2009-01-08 | 2010-07-08 | Ciclon Semiconductor Device Corp. | Packaged power switching device |
| JP2011049394A (ja) * | 2009-08-27 | 2011-03-10 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US8362555B2 (en) | 2009-11-24 | 2013-01-29 | Intersil Americas Inc. | Voltage converter and systems including same |
| US20110210956A1 (en) * | 2010-02-26 | 2011-09-01 | Dev Alok Girdhar | Current sensor for a semiconductor device and system |
| JP5584090B2 (ja) | 2010-10-22 | 2014-09-03 | トランスフォーム・ジャパン株式会社 | Dc−dcコンバータ |
| JP5605241B2 (ja) * | 2011-01-27 | 2014-10-15 | 富士通セミコンダクター株式会社 | Mosトランジスタおよび半導体集積回路装置の製造方法 |
| JP2012238741A (ja) * | 2011-05-12 | 2012-12-06 | Panasonic Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP5692379B2 (ja) * | 2011-06-30 | 2015-04-01 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2013168487A (ja) * | 2012-02-15 | 2013-08-29 | Renesas Electronics Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法および半導体装置 |
| US20130270636A1 (en) * | 2012-04-17 | 2013-10-17 | Broadcom Corporation | Transistor Having An Isolated Body For High Voltage Operation |
| CN103545363B (zh) * | 2012-07-09 | 2016-04-13 | 上海华虹宏力半导体制造有限公司 | P型ldmos器件及其制造方法 |
| US8674440B2 (en) * | 2012-07-31 | 2014-03-18 | Io Semiconductor Inc. | Power device integration on a common substrate |
| KR101957529B1 (ko) * | 2013-06-28 | 2019-03-13 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
-
2015
- 2015-01-29 US US14/608,391 patent/US9646965B2/en active Active
- 2015-01-30 WO PCT/US2015/013989 patent/WO2015117038A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-01-30 JP JP2016549475A patent/JP6649890B2/ja active Active
- 2015-01-30 EP EP15742923.4A patent/EP3127154A4/en active Pending
- 2015-01-30 CN CN201580012800.8A patent/CN106104802B/zh active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3127154A4 (en) | 2018-01-17 |
| CN106104802B (zh) | 2019-07-23 |
| JP2017510062A (ja) | 2017-04-06 |
| EP3127154A1 (en) | 2017-02-08 |
| US20150214222A1 (en) | 2015-07-30 |
| US9646965B2 (en) | 2017-05-09 |
| WO2015117038A1 (en) | 2015-08-06 |
| CN106104802A (zh) | 2016-11-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5612268B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びdc−dcコンバータ | |
| US9818686B2 (en) | Semiconductor modules and methods of forming the same | |
| JP6649890B2 (ja) | バックコンバータのためのモノリシックに集積されたトランジスタ | |
| JP2020074562A (ja) | フェライトビーズを有するスイッチング回路 | |
| EP3097584B1 (en) | Integrated high side gate driver structure and circuit for driving high side power transistors | |
| JP4602465B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2002368121A (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| JP2015509665A (ja) | 半導体パワーモジュール及びデバイス | |
| US9257907B2 (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit and method for operating the same | |
| US9418984B2 (en) | Normally off power electronic component | |
| US20190259830A1 (en) | Ldmos transistors with breakdown voltage clamps | |
| JPWO2015001926A1 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US10573713B2 (en) | High voltage junction terminating structure of high voltage integrated circuit | |
| JP2012124207A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US7423325B2 (en) | Lateral field-effect-controllable semiconductor component for RF applications | |
| TWI533435B (zh) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2022046240A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2008199037A (ja) | 電力用半導体装置および電源回路 | |
| TWI577020B (zh) | 高壓金氧半導體電晶體元件 | |
| JP2014116631A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2011009767A (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20160801 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180123 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180123 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190226 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20190524 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190724 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20191225 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200117 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6649890 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |