JP5355915B2 - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5355915B2 JP5355915B2 JP2008072770A JP2008072770A JP5355915B2 JP 5355915 B2 JP5355915 B2 JP 5355915B2 JP 2008072770 A JP2008072770 A JP 2008072770A JP 2008072770 A JP2008072770 A JP 2008072770A JP 5355915 B2 JP5355915 B2 JP 5355915B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- layer
- photoelectric conversion
- insulating film
- interlayer insulating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 82
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 98
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 58
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 147
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 140
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 52
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 44
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 13
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegermanium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ge] JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000004873 anchoring Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 abstract description 18
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 16
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 15
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 15
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 13
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 8
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 7
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 6
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 6
- -1 tungsten nitride Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 4
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052743 krypton Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N krypton atom Chemical compound [Kr] DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052779 Neodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910020286 SiOxNy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000002679 ablation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001307 helium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052734 helium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N helium atom Chemical compound [He] SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- QEFYFXOXNSNQGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N neodymium atom Chemical compound [Nd] QEFYFXOXNSNQGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052754 neon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GKAOGPIIYCISHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N neon atom Chemical compound [Ne] GKAOGPIIYCISHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003870 refractory metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010948 rhodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- SBEQWOXEGHQIMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon Chemical compound [Si].[Si] SBEQWOXEGHQIMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001237 Raman spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ruthenium Chemical compound [Ru] KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910003902 SiCl 4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002441 X-ray diffraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- GPBUGPUPKAGMDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N azanylidynemolybdenum Chemical compound [Mo]#N GPBUGPUPKAGMDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- SLLGVCUQYRMELA-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorosilicon Chemical compound Cl[Si] SLLGVCUQYRMELA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007865 diluting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002223 garnet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- CPBQJMYROZQQJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N helium neon Chemical compound [He].[Ne] CPBQJMYROZQQJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052741 iridium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium atom Chemical compound [Ir] GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000005416 organic matter Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052762 osmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N osmium atom Chemical compound [Os] SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052703 rhodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhodium atom Chemical compound [Rh] MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010979 ruby Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001750 ruby Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N selanylidenegallium;selenium Chemical compound [Se].[Se]=[Ga].[Se]=[Ga] VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- MZLGASXMSKOWSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum nitride Chemical compound [Ta]#N MZLGASXMSKOWSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011800 void material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052724 xenon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FHNFHKCVQCLJFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N xenon atom Chemical compound [Xe] FHNFHKCVQCLJFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N yttrium atom Chemical compound [Y] VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/14—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/11—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/17—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of bump connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/14—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation
- H01L27/144—Devices controlled by radiation
- H01L27/146—Imager structures
- H01L27/14643—Photodiode arrays; MOS imagers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/02—Details
- H01L31/02002—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the device in operations
- H01L31/02005—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the device in operations for device characterised by at least one potential jump barrier or surface barrier
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/0401—Bonding areas specifically adapted for bump connectors, e.g. under bump metallisation [UBM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05575—Plural external layers
- H01L2224/0558—Plural external layers being stacked
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05599—Material
- H01L2224/056—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/05638—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/05639—Silver [Ag] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05599—Material
- H01L2224/056—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/05638—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/05644—Gold [Au] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05599—Material
- H01L2224/056—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/05638—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/05655—Nickel [Ni] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/11—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/1147—Manufacturing methods using a lift-off mask
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/812—Applying energy for connecting
- H01L2224/8121—Applying energy for connecting using a reflow oven
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/812—Applying energy for connecting
- H01L2224/8122—Applying energy for connecting with energy being in the form of electromagnetic radiation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/818—Bonding techniques
- H01L2224/81801—Soldering or alloying
- H01L2224/81815—Reflow soldering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/12—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/14—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation
- H01L27/144—Devices controlled by radiation
- H01L27/146—Imager structures
- H01L27/14601—Structural or functional details thereof
- H01L27/14618—Containers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00013—Fully indexed content
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01004—Beryllium [Be]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01007—Nitrogen [N]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0101—Neon [Ne]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01014—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01015—Phosphorus [P]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01018—Argon [Ar]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01022—Titanium [Ti]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01023—Vanadium [V]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01024—Chromium [Cr]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01027—Cobalt [Co]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01028—Nickel [Ni]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0103—Zinc [Zn]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01032—Germanium [Ge]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0104—Zirconium [Zr]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01042—Molybdenum [Mo]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01044—Ruthenium [Ru]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01045—Rhodium [Rh]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01046—Palladium [Pd]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01047—Silver [Ag]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0105—Tin [Sn]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01054—Xenon [Xe]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0106—Neodymium [Nd]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01067—Holmium [Ho]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01068—Erbium [Er]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0107—Ytterbium [Yb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01073—Tantalum [Ta]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01074—Tungsten [W]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01076—Osmium [Os]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01077—Iridium [Ir]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01078—Platinum [Pt]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/011—Groups of the periodic table
- H01L2924/01105—Rare earth metals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/014—Solder alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/049—Nitrides composed of metals from groups of the periodic table
- H01L2924/0494—4th Group
- H01L2924/04941—TiN
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/049—Nitrides composed of metals from groups of the periodic table
- H01L2924/0495—5th Group
- H01L2924/04953—TaN
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/049—Nitrides composed of metals from groups of the periodic table
- H01L2924/0504—14th Group
- H01L2924/05042—Si3N4
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/095—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00 with a principal constituent of the material being a combination of two or more materials provided in the groups H01L2924/013 - H01L2924/0715
- H01L2924/097—Glass-ceramics, e.g. devitrified glass
- H01L2924/09701—Low temperature co-fired ceramic [LTCC]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12043—Photo diode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/156—Material
- H01L2924/15786—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a non metallic, non metalloid inorganic material
- H01L2924/15787—Ceramics, e.g. crystalline carbides, nitrides or oxides
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Light Receiving Elements (AREA)
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
Description
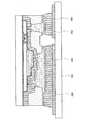
本実施の形態を、図1、図3(A)〜図3(D)、図4(A)〜図4(C)、図5(A)〜図5(C)、図6(A)〜図6(B)、図7(A)〜図7(B)、図8、図9(A)〜図9(B)、図10、図11、図12、図13、図14、図21、図22(A)〜図22(B)、図23を用いて以下に説明する。
本実施の形態では、実施の形態1により得られた光電変換素子を様々な電子機器に組み込んだ例について説明する。本形態で示す電子機器の一例として、コンピュータ、ディスプレイ、携帯電話、テレビなどが挙げられる。それらの電子機器の具体例を、図15、図16(A)〜図16(B)、図17(A)〜図17(B)、図18、図19(A)〜図19(B)に示す。
104 TFT
105 TFT
105i TFT
111 カレントミラー回路
118 回路
118i 回路
119 端子
119i 端子
120 端子
120i 端子
121 端子
121i 端子
125 層間絶縁膜
131 カレントミラー回路
134 TFT
135 TFT
144 配線
145 配線
201 基板
202 絶縁膜
205 ゲート絶縁膜
206 層間絶縁膜
211 TFT
212 島状半導体膜
213 ゲート電極
213a 下層ゲート電極
213b 上層ゲート電極
214 ゲート配線
215 ソース電極
216 ドレイン電極
221 電極
221i 電極
222 電極
223 電極
225 光電変換層
225i i型半導体層
225n n型半導体層
225p p型半導体層
227 保護膜
228 層間絶縁膜
231 電極
232 電極
235 層間絶縁膜
241 電極
242 電極
243 電極
244 電極
261 空隙
265 開口部
271 固着層
271a 層
271b 層
271c 層
281 プリント基板
282 電極
283 電極
285 導電性材料
286 導電性材料
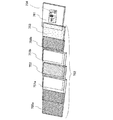
701 本体(A)
702 本体(B)
703 筐体
704 操作キー
705 音声入力部
706 音声出力部
707 回路基板
708 表示パネル(A)
709 表示パネル(B)
710 蝶番
711 透光性材料部
712 光電変換素子
721 本体
722 筐体
723 表示パネル
724 操作キー
725 音声出力部
726 音声入力部
727 光電変換素子
728 光電変換素子
731 本体
732 筐体
733 表示部
734 キーボード
735 外部接続ポート
736 ポインティングデバイス
741 筐体
742 支持台
743 表示部
751a 基板
751b 基板
752 液晶層
753 バックライト
754 光電変換素子形成領域
755a 偏光フィルタ
755b 偏光フィルタ
761 筐体
762 液晶パネル
801 リリースボタン
802 メインスイッチ
803 ファインダ窓
804 フラッシュ
805 レンズ
806 鏡胴
807 筺体
811 ファインダ接眼窓
812 モニタ
813 操作ボタン
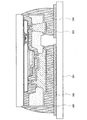
1601 基板
1602 透光性電極
1603 光電変換層
1604a 光反射性電極
1604b 光反射性電極
1605 開口部
1606 開口部
1607 開口部
1610 基板
1611 光反射性電極
1612 光電変換層
1613 透光性電極
1614 絶縁層
1615 絶縁層
1616 絶縁層
1617 外部接続端子
1618 外部接続端子
1619 透光性電極
1800 配線基板
1850 配線
1851 導電性粒子
1852 樹脂
1853 導電性材料
Claims (7)
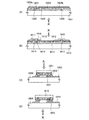
- 第1の基板上に、
光電変換層と、前記光電変換層の出力電流を増幅する、少なくとも2つの薄膜トランジスタからなる増幅回路と、
前記光電変換層及び前記増幅回路上の第1の層間絶縁膜と、
前記第1の層間絶縁膜に設けられた第1の開口部を介して前記光電変換層に電気的に接続された、前記第1の層間絶縁膜上の第1の電極と、
前記第1の層間絶縁膜及び前記第1の電極上の第2の層間絶縁膜と、
前記第2の層間絶縁膜に設けられた第2の開口部を介して前記第1の電極に電気的に接続された、前記第2の層間絶縁膜上の第2の電極と、
前記第2の電極上の、半田と合金を形成することができる金属を含む固着層と、を有し、
第2の基板上に、
第3の電極を有し、
前記固着層は、前記第1の層間絶縁膜と前記第2の層間絶縁膜の側面を覆って設けられ、
前記第3の電極は、前記半田を介して前記固着層と固着され、
前記半田は、前記固着層の前記第1の層間絶縁膜と前記第2の層間絶縁膜の側面を覆う領域に接して設けられていることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1において、
前記第1の電極は前記光電変換層の全体又は一部と重なるように設けられていることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1または請求項2において、
前記固着層は、前記第1の基板の側面の一部を覆って設けられ、
前記半田は、前記固着層の前記第1の基板の側面の一部を覆う領域に接して設けられていることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれか一において、
前記固着層は、ニッケル(Ni)、銅(Cu)、亜鉛(Zn)、パラジウム(Pd)、銀(Ag)、スズ(Sn)、白金(Pt)、金(Au)のうちの1つを少なくとも含むことを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれか一において、
前記第2の電極は、ニッケルペーストを用いて形成された電極であり、
前記固着層は、チタン層、ニッケル層、金層を順に積層した積層膜であり、
前記チタン層は、前記第1の電極と接しており、前記ニッケル層及び前記金層は、前記半田と合金を形成していることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれか一において、
前記第2の電極は、ニッケルペーストを用いて形成された電極であり、
前記固着層は、ニッケル層、金層を順に積層した積層膜であり、
前記ニッケル層は、前記第1の電極と接しており、前記ニッケル層及び前記金層は、前記半田と合金を形成していることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれか一において、
前記第2の電極上に銅ペーストを用いて形成された電極を有し、
前記銅を含む電極上に前記固着層を有し、
前記固着層は、銅を含むことを特徴とする半導体装置。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008072770A JP5355915B2 (ja) | 2007-04-18 | 2008-03-21 | 半導体装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007108795 | 2007-04-18 | ||
| JP2007108795 | 2007-04-18 | ||
| JP2008072770A JP5355915B2 (ja) | 2007-04-18 | 2008-03-21 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008288562A JP2008288562A (ja) | 2008-11-27 |
| JP2008288562A5 JP2008288562A5 (ja) | 2011-03-31 |
| JP5355915B2 true JP5355915B2 (ja) | 2013-11-27 |
Family
ID=40035104
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008072770A Expired - Fee Related JP5355915B2 (ja) | 2007-04-18 | 2008-03-21 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7679091B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5355915B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101423055B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN101290940B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9095066B2 (en) * | 2008-06-18 | 2015-07-28 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Printed board |
| US9048788B2 (en) * | 2011-05-13 | 2015-06-02 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device comprising a photoelectric conversion portion |
| US10861816B2 (en) | 2018-10-18 | 2020-12-08 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Electronic assemblies having a mesh bond material and methods of forming thereof |
| CN112649711B (zh) * | 2019-10-12 | 2022-04-15 | 成都辰显光电有限公司 | 微发光二极管的检测装置及方法 |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3347804B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-22 | 2002-11-20 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 半導体回路の作製方法 |
| JPH0767152B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-25 | 1995-07-19 | 日本電気株式会社 | イメージセンサとその駆動方法 |
| JPH1051033A (ja) | 1996-07-30 | 1998-02-20 | Showa Denko Kk | 半導体受発光素子 |
| JPH11191640A (ja) | 1997-12-26 | 1999-07-13 | Showa Denko Kk | 半導体受発光素子用の電極 |
| JPH11307756A (ja) * | 1998-02-20 | 1999-11-05 | Canon Inc | 光電変換装置および放射線読取装置 |
| US6401183B1 (en) * | 1999-04-01 | 2002-06-04 | Flash Vos, Inc. | System and method for operating system independent storage management |
| JP5110748B2 (ja) | 2000-06-06 | 2012-12-26 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 表示装置 |
| US6995753B2 (en) | 2000-06-06 | 2006-02-07 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Display device and method of manufacturing the same |
| DE10392377T5 (de) * | 2002-03-12 | 2005-05-12 | FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP. (n.d.Ges.d. Staates Delaware) | Auf Waferniveau beschichtete stiftartige Kontakthöcker aus Kupfer |
| GB0216075D0 (en) * | 2002-07-11 | 2002-08-21 | Qinetiq Ltd | Photodetector circuits |
| JP4283087B2 (ja) | 2002-10-30 | 2009-06-24 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 光電変換素子 |
| EP1523043B1 (en) * | 2003-10-06 | 2011-12-28 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Optical sensor and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP4481135B2 (ja) * | 2003-10-06 | 2010-06-16 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 半導体装置及びその作製方法 |
| CN100477240C (zh) * | 2003-10-06 | 2009-04-08 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | 半导体器件以及制造该器件的方法 |
| JP4827396B2 (ja) * | 2003-10-06 | 2011-11-30 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 半導体装置の作製方法 |
| EP1542272B1 (en) | 2003-10-06 | 2016-07-20 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same |
| US7691686B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2010-04-06 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2006032753A (ja) * | 2004-07-20 | 2006-02-02 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US7492028B2 (en) | 2005-02-18 | 2009-02-17 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Photoelectric conversion device and manufacturing method of the same, and a semiconductor device |
| JP4809715B2 (ja) * | 2005-05-20 | 2011-11-09 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 光電変換装置及びその作製方法、並びに半導体装置 |
| EP1724844A2 (en) * | 2005-05-20 | 2006-11-22 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Photoelectric conversion device, manufacturing method thereof and semiconductor device |
| JP2007081001A (ja) * | 2005-09-13 | 2007-03-29 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 電子部品 |
-
2008
- 2008-03-21 KR KR1020080026486A patent/KR101423055B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2008-03-21 JP JP2008072770A patent/JP5355915B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-03-26 CN CN2008100883432A patent/CN101290940B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-03-27 US US12/078,090 patent/US7679091B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101290940B (zh) | 2011-08-31 |
| KR101423055B1 (ko) | 2014-07-25 |
| US7679091B2 (en) | 2010-03-16 |
| US20080308851A1 (en) | 2008-12-18 |
| CN101290940A (zh) | 2008-10-22 |
| KR20080093867A (ko) | 2008-10-22 |
| JP2008288562A (ja) | 2008-11-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI444600B (zh) | 光電轉換裝置及提供該光電轉換裝置的電子裝置 | |
| TWI437214B (zh) | 光電轉換裝置及具有光電轉換裝置之電子裝置 | |
| TWI423431B (zh) | 光電轉換裝置和其製造方法 | |
| US7772667B2 (en) | Photoelectric conversion device and semiconductor device | |
| KR101227022B1 (ko) | 광전 변환 장치 및 그 제작 방법과, 반도체 장치 | |
| TWI453565B (zh) | 光電轉換裝置及具有該光電轉換裝置之電子裝置 | |
| JP5844858B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の作製方法、及び、半導体装置 | |
| KR101369863B1 (ko) | 반도체장치 및 전자기기 | |
| JP4809715B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置及びその作製方法、並びに半導体装置 | |
| US8592936B2 (en) | Photoelectric conversion device and electronic device, and method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion device | |
| KR20070106459A (ko) | 반도체 장치 | |
| JP2008270757A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP5355915B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP4532418B2 (ja) | 光センサ及びその作製方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110215 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110215 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121225 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130108 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130208 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130820 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130828 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5355915 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |