JP4954515B2 - Method for manufacturing display device - Google Patents
Method for manufacturing display device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4954515B2 JP4954515B2 JP2005257447A JP2005257447A JP4954515B2 JP 4954515 B2 JP4954515 B2 JP 4954515B2 JP 2005257447 A JP2005257447 A JP 2005257447A JP 2005257447 A JP2005257447 A JP 2005257447A JP 4954515 B2 JP4954515 B2 JP 4954515B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- insulating film
- film
- sheet material
- substrate
- display device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 102
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 85
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 342
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 294
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 249
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 206
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 56
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 56
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 43
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 40
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 33
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000002216 antistatic agent Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000005001 laminate film Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 206010040844 Skin exfoliation Diseases 0.000 description 64
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 48
- 230000032258 transport Effects 0.000 description 23
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 22
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 20
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 19
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 19
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 17
- -1 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 15
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 12
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 11
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 9
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 9
- 229910000476 molybdenum oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-benzoxazole Chemical class C1=CC=C2OC=NC2=C1 BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 8
- KPUWHANPEXNPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N disiloxane Chemical class [SiH3]O[SiH3] KPUWHANPEXNPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 8
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 7
- UMIVXZPTRXBADB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzocyclobutene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CCC2=C1 UMIVXZPTRXBADB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 238000007646 gravure printing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 6
- PQQKPALAQIIWST-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxomolybdenum Chemical compound [Mo]=O PQQKPALAQIIWST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 6
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 6
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc oxide Inorganic materials [Zn]=O XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000012943 hotmelt Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 5
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 239000005060 rubber Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910001925 ruthenium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910001935 vanadium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229920003227 poly(N-vinyl carbazole) Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- WOCIAKWEIIZHES-UHFFFAOYSA-N ruthenium(iv) oxide Chemical compound O=[Ru]=O WOCIAKWEIIZHES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000007779 soft material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920002803 thermoplastic polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 4
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004831 Hot glue Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004640 Melamine resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000877 Melamine resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 3
- BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Vinyl chloride Chemical compound ClC=C BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XHCLAFWTIXFWPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[V+5].[V+5] Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[V+5].[V+5] XHCLAFWTIXFWPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920001519 homopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 description 3
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010955 niobium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920003986 novolac Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920000052 poly(p-xylylene) Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 230000002940 repellent Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 3
- YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc indium(3+) oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O--].[Zn++].[In+3] YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011787 zinc oxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline Chemical compound C=12C=CC3=C(C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=C(C)N=C3C2=NC(C)=CC=1C1=CC=CC=C1 STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UOCMXZLNHQBBOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenol zinc Chemical compound [Zn].Oc1ccccc1-c1nc2ccccc2o1.Oc1ccccc1-c1nc2ccccc2o1 UOCMXZLNHQBBOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZVFQEOPUXVPSLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-4-phenyl-5-(4-phenylphenyl)-1,2,4-triazole Chemical compound C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=C1C(N1C=2C=CC=CC=2)=NN=C1C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=C1 ZVFQEOPUXVPSLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DHDHJYNTEFLIHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=NC2=C1C=CC1=C(C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=CN=C21 DHDHJYNTEFLIHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylhydroxytoluene Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910004261 CaF 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 241000284156 Clerodendrum quadriloculare Species 0.000 description 2
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001609 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 2
- XTXRWKRVRITETP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Vinyl acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OC=C XTXRWKRVRITETP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- UFVXQDWNSAGPHN-UHFFFAOYSA-K bis[(2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxy]-(4-phenylphenoxy)alumane Chemical compound [Al+3].C1=CC=C([O-])C2=NC(C)=CC=C21.C1=CC=C([O-])C2=NC(C)=CC=C21.C1=CC([O-])=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 UFVXQDWNSAGPHN-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000005038 ethylene vinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011049 filling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910003437 indium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002736 metal compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[4-(n-naphthalen-1-ylanilino)phenyl]phenyl]-n-phenylnaphthalen-1-amine Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC=1)C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)C=C1 IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGLKJKCYBOYXKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N nonaoxidotritungsten Chemical compound O=[W]1(=O)O[W](=O)(=O)O[W](=O)(=O)O1 QGLKJKCYBOYXKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000962 organic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- IEQIEDJGQAUEQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phthalocyanine Chemical compound N1C(N=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C(N=C3C4=CC=CC=C4C(=N4)N3)=N2)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1N=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C4=N1 IEQIEDJGQAUEQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Substances [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001200 poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000123 polythiophene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920002620 polyvinyl fluoride Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010944 silver (metal) Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- OFIYHXOOOISSDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegallium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ga] OFIYHXOOOISSDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001930 tungsten oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- POILWHVDKZOXJZ-ARJAWSKDSA-M (z)-4-oxopent-2-en-2-olate Chemical compound C\C([O-])=C\C(C)=O POILWHVDKZOXJZ-ARJAWSKDSA-M 0.000 description 1
- IYZMXHQDXZKNCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-n,1-n-diphenyl-4-n,4-n-bis[4-(n-phenylanilino)phenyl]benzene-1,4-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 IYZMXHQDXZKNCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VFMUXPQZKOKPOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octaethyl-21,23-dihydroporphyrin platinum Chemical compound [Pt].CCc1c(CC)c2cc3[nH]c(cc4nc(cc5[nH]c(cc1n2)c(CC)c5CC)c(CC)c4CC)c(CC)c3CC VFMUXPQZKOKPOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SNTWKPAKVQFCCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dihydro-1h-triazole Chemical compound N1NC=CN1 SNTWKPAKVQFCCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OEPOKWHJYJXUGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carbaldehyde Chemical compound O=CC1=CSC(C=2C=C(OCC=3C=CC=CC=3)C=CC=2)=N1 OEPOKWHJYJXUGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FQJQNLKWTRGIEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-5-[3-[5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole Chemical compound C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=C1C1=NN=C(C=2C=C(C=CC=2)C=2OC(=NN=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)C(C)(C)C)O1 FQJQNLKWTRGIEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GEQBRULPNIVQPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[3,5-bis(1-phenylbenzimidazol-2-yl)phenyl]-1-phenylbenzimidazole Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N1C2=CC=CC=C2N=C1C1=CC(C=2N(C3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=CC(C=2N(C3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 GEQBRULPNIVQPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- POXIZPBFFUKMEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyanoethenylideneazanide Chemical class [N-]=C=[C+]C#N POXIZPBFFUKMEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWXGSYPUMWKTBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-carbazol-9-yl-n,n-bis(4-carbazol-9-ylphenyl)aniline Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C2N1C1=CC=C(N(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N2C3=CC=CC=C3C3=CC=CC=C32)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N2C3=CC=CC=C3C3=CC=CC=C32)C=C1 AWXGSYPUMWKTBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004860 4-ethylphenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C([H])C([H])=C1*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- DIVZFUBWFAOMCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-n-(3-methylphenyl)-1-n,1-n-bis[4-(n-(3-methylphenyl)anilino)phenyl]-4-n-phenylbenzene-1,4-diamine Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=C(C)C=CC=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=C(C)C=CC=2)=C1 DIVZFUBWFAOMCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001148 Al-Li alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920008347 Cellulose acetate propionate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical compound CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 101000837344 Homo sapiens T-cell leukemia translocation-altered gene protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229910018068 Li 2 O Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl methacrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)=C VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910017911 MgIn Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052779 Neodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004677 Nylon Substances 0.000 description 1
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004962 Polyamide-imide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004820 Pressure-sensitive adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- NRCMAYZCPIVABH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Quinacridone Chemical class N1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=C1C=C1C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3NC1=C2 NRCMAYZCPIVABH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910007991 Si-N Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002808 Si–O–Si Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910006294 Si—N Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 102100028692 T-cell leukemia translocation-altered gene protein Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229910003087 TiOx Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002433 Vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- DDRUQPGRDYOZHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Eu].c1ccc2c(c1)ccc1ccccc21 Chemical compound [Eu].c1ccc2c(c1)ccc1ccccc21 DDRUQPGRDYOZHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CUJRVFIICFDLGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetylacetonate Chemical compound CC(=O)[CH-]C(C)=O CUJRVFIICFDLGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001893 acrylonitrile styrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004220 aggregation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001508 alkali metal halide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000008045 alkali metal halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910000272 alkali metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005376 alkyl siloxane group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000005407 aluminoborosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002280 amphoteric surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001491 aromatic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N barium atom Chemical compound [Ba] DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WZJYKHNJTSNBHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzo[h]quinoline Chemical group C1=CN=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC2=C1 WZJYKHNJTSNBHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052790 beryllium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ATBAMAFKBVZNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N beryllium atom Chemical compound [Be] ATBAMAFKBVZNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004305 biphenyl Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- QDWJUBJKEHXSMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N boranylidynenickel Chemical compound [Ni]#B QDWJUBJKEHXSMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005388 borosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N but-3-enoic acid;ethene Chemical compound C=C.OC(=O)CC=C DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XZCJVWCMJYNSQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl pbd Chemical compound C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=C1C1=NN=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)O1 XZCJVWCMJYNSQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 239000003093 cationic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002301 cellulose acetate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006217 cellulose acetate butyrate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012461 cellulose resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004696 coordination complex Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001893 coumarin derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000018044 dehydration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004049 embossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007850 fluorescent dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical group [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- RBTKNAXYKSUFRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N heliogen blue Chemical compound [Cu].[N-]1C2=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1N=C([N-]1)C3=CC=CC=C3C1=NC([N-]1)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1N=C([N-]1)C3=CC=CC=C3C1=N2 RBTKNAXYKSUFRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002460 imidazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PJXISJQVUVHSOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium(iii) oxide Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[In+3].[In+3] PJXISJQVUVHSOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940079865 intestinal antiinfectives imidazole derivative Drugs 0.000 description 1
- UEEXRMUCXBPYOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium;2-phenylpyridine Chemical compound [Ir].C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=N1.C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=N1.C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=N1 UEEXRMUCXBPYOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004898 kneading Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000040 m-tolyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C(=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel Substances [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N niobium atom Chemical compound [Nb] GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001778 nylon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000010943 off-gassing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004866 oxadiazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium Substances [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920003055 poly(ester-imide) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000172 poly(styrenesulfonic acid) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002037 poly(vinyl butyral) polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002312 polyamide-imide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000767 polyaniline Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000306 polymethylpentene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011116 polymethylpentene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005672 polyolefin resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001709 polysilazane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940005642 polystyrene sulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- SCUZVMOVTVSBLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N prop-2-enenitrile;styrene Chemical compound C=CC#N.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 SCUZVMOVTVSBLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001453 quaternary ammonium group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002943 quinolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012827 research and development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- YYMBJDOZVAITBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N rubrene Chemical class C1=CC=CC=C1C(C1=C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C2=CC=CC=C2C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 YYMBJDOZVAITBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N stilbene Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003051 synthetic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005061 synthetic rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940042055 systemic antimycotics triazole derivative Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012815 thermoplastic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002397 thermoplastic olefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N tin dioxide Chemical compound O=[Sn]=O XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001887 tin oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HLLICFJUWSZHRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tioxidazole Chemical compound CCCOC1=CC=C2N=C(NC(=O)OC)SC2=C1 HLLICFJUWSZHRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012780 transparent material Substances 0.000 description 1
- TVIVIEFSHFOWTE-UHFFFAOYSA-K tri(quinolin-8-yloxy)alumane Chemical compound [Al+3].C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1.C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1.C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1 TVIVIEFSHFOWTE-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- JOHWNGGYGAVMGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N trifluorochlorine Chemical compound FCl(F)F JOHWNGGYGAVMGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- GWDUZCIBPDVBJM-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc;2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3h-1,3-benzothiazole-2-carboxylate Chemical compound [Zn+2].OC1=CC=CC=C1C1(C([O-])=O)SC2=CC=CC=C2N1.OC1=CC=CC=C1C1(C([O-])=O)SC2=CC=CC=C2N1 GWDUZCIBPDVBJM-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- QEPMORHSGFRDLW-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc;2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3h-1,3-benzoxazole-2-carboxylate Chemical compound [Zn+2].OC1=CC=CC=C1C1(C([O-])=O)OC2=CC=CC=C2N1.OC1=CC=CC=C1C1(C([O-])=O)OC2=CC=CC=C2N1 QEPMORHSGFRDLW-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y02B20/342—
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Description
本発明は、表示装置およびその作製方法並びにその製造装置に関し、特に折り曲げることが可能な可撓性基板上に設けられた表示装置およびその作製方法並びにその製造装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a display device, a manufacturing method thereof, and a manufacturing apparatus thereof, and more particularly to a display device provided on a foldable flexible substrate, a manufacturing method thereof, and a manufacturing apparatus thereof.
近年、発光素子を用いた表示装置の研究、開発が盛んに行われている。発光素子を用いた表示装置は、液晶を用いた表示装置等のようにバックライトを必要とせず、さらに高視野角で表示することが可能となるといった利点を有している。また、最近では、表示装置そのものを折り曲げることが可能なフィルム状の表示装置が注目を集めている。 In recent years, research and development of display devices using light-emitting elements have been actively conducted. A display device using a light emitting element does not require a backlight unlike a display device using liquid crystal, and has an advantage that a display can be performed with a high viewing angle. Recently, a film-like display device that can be bent is attracting attention.
フィルム状の表示装置を作製する方法としては、大きく分けて2通りの方法がある。1つは、あらかじめプラスチック等の可撓性(フレキシブル性)を有する基板を用意して、その基板上に配線や画素電極等の回路のパターンを金属材料や絶縁物材料を用いて直接形成していく方法がある。もう1つの方法は、あらかじめガラス等の剛性を有する基板上に配線や画素電極等の回路のパターンを金属材料や絶縁物材料を用いて形成し、その後剛性を有する基板のみを研削・研磨することによって薄膜化したり、剛性を有する基板と可撓性を有する基板を置き換えたりする方法がある。 As a method for manufacturing a film-like display device, there are roughly two methods. First, a flexible substrate such as plastic is prepared in advance, and a circuit pattern such as a wiring or a pixel electrode is directly formed on the substrate using a metal material or an insulating material. There are ways to go. Another method is to form a circuit pattern such as wiring and pixel electrodes on a rigid substrate such as glass in advance using a metal material or an insulating material, and then grind and polish only the rigid substrate. There is a method in which a thin film is formed or a rigid substrate and a flexible substrate are replaced.
しかしながら、プラスチック等の可撓性を有する基板上に直接金属材料や絶縁物材料を形成することによって、フィルム状の表示装置を作製する場合、基板の耐熱性等に伴い作製条件が制限される。つまり、可撓性基板の耐熱性や強度等の種々の耐性を考慮して表示装置の作製を行わなければならない。例えば、表示装置の画素や駆動回路等を薄膜トランジスタ(TFT)を用いて形成する場合には、熱処理等の条件が制限され、半導体膜の結晶化を十分行うことができないため、特性の高いTFTを得ることができない。 However, in the case where a film-like display device is manufactured by directly forming a metal material or an insulating material on a flexible substrate such as plastic, manufacturing conditions are limited due to heat resistance of the substrate. That is, the display device must be manufactured in consideration of various resistances such as heat resistance and strength of the flexible substrate. For example, when a pixel of a display device, a driver circuit, or the like is formed using a thin film transistor (TFT), conditions for heat treatment and the like are limited, and a semiconductor film cannot be sufficiently crystallized. Can't get.
一方、ガラス基板等の剛性を有する基板上に表示装置を形成し、その後表示装置を剛性を有する基板から剥離して可撓性基板に移し替えることによってフィルム状の表示装置を作製する場合、剥離の際に表示装置に加わる応力による配線等の断線の問題や、表示装置の大きさが基板(ここではガラス基板)の大きさに依存するため大型の表示装置の作製が困難となる問題がある。 On the other hand, when a display device is formed on a rigid substrate such as a glass substrate, and then the display device is peeled off from the rigid substrate and transferred to a flexible substrate, a film-like display device is manufactured. There is a problem of disconnection of wiring or the like due to stress applied to the display device, and a problem that makes it difficult to manufacture a large display device because the size of the display device depends on the size of the substrate (here, a glass substrate). .
本発明は、上記問題を鑑み、フィルム状表示装置を効率よく生産し、また大型のフィルム状の表示装置の形成が可能となる作製方法およびフィルム状の表示装置を作製するための装置並びにフィルム状表示装置の提供を課題とする。 In view of the above problems, the present invention can efficiently produce a film-like display device, and a production method capable of forming a large-sized film-like display device, an apparatus for producing a film-like display device, and a film-like device It is an object to provide a display device.
本発明の表示装置の製造装置は、表示装置を構成する素子形成部が設けられた基板を搬送する搬送手段と、素子形成部の一方の面を第1のシート材に接着させて、基板から素子形成部を剥離する第1の剥離手段と、素子形成部の他方の面を第2のシート材に接着させて、第1のシート材から素子形成部を剥離する第2の剥離手段と、素子形成部に画素部を形成する加工手段と、加工された素子形成部を第2のシート材と第3のシート材で挟み込み封止する封止手段とを有することを特徴としている。 The display device manufacturing apparatus according to the present invention includes a transport unit that transports a substrate on which an element forming unit constituting the display device is provided, and one surface of the element forming unit is bonded to the first sheet material, A first peeling means for peeling the element forming portion; a second peeling means for peeling the element forming portion from the first sheet material by bonding the other surface of the element forming portion to the second sheet material; It is characterized by having processing means for forming a pixel portion in the element formation portion and sealing means for sandwiching and sealing the processed element formation portion between the second sheet material and the third sheet material.
また、本発明の表示装置の製造装置の他の構成として、表示装置を構成する素子形成部が設けられた基板を搬送する搬送手段と、第1のシート材が巻きつけられた第1の供給用ロールと、素子形成部の一方の面を第1のシート材に接着させて、基板から素子形成部を剥離する第1の剥離手段と、第2のシート材が巻きつけられた第2の供給用ロールと、素子形成部の他方の面を第2のシート材に接着させて、第1のシート材から素子形成部を剥離する第2の剥離手段と、素子形成部に画素部を形成する加工手段と、第3のシート材が巻きつけられた第3の供給用ロールと、加工された素子形成部を第2のシート材と第3のシート材で挟み込み封止する封止手段と、封止されて形成された表示装置を巻き取る回収用ロールとを有することを特徴としている。また、本発明では、上記構成において、加工された素子形成部を第2のシート材と第3のシート材で封止する方法として、第3のシート材を加熱溶融状態で押し出しながら供給して封止することができる。 Further, as another configuration of the display device manufacturing apparatus of the present invention, a transport means for transporting a substrate provided with an element forming portion constituting the display device, and a first supply in which a first sheet material is wound. A first peeling means for bonding one surface of the roll and the element forming portion to the first sheet material, and peeling the element forming portion from the substrate; and a second wound around the second sheet material The supply roll, the second surface of the element forming portion are bonded to the second sheet material, the second peeling means for peeling the element forming portion from the first sheet material, and the pixel portion is formed in the element forming portion Processing means, a third supply roll around which the third sheet material is wound, and a sealing means for sandwiching and sealing the processed element forming portion between the second sheet material and the third sheet material And a recovery roll for winding up the sealed display device It is. In the present invention, in the above configuration, as a method of sealing the processed element forming portion with the second sheet material and the third sheet material, the third sheet material is supplied while being extruded in a heated and melted state. It can be sealed.
また、本発明の表示装置の製造装置は、上記構成において、複数の異なる基板上に設けられた表示装置を構成する素子形成部をつなげ合わせて表示装置を形成する場合にも適用することができる。この場合は、基板上に設けられた素子形成部を剥離する前に、制御手段により精確に複数の基板の配列を調整する。また基板を配列させる際に、基板同士を接合させてもよい。 The display device manufacturing apparatus of the present invention can also be applied to the case where, in the above configuration, the display device is formed by connecting element forming portions constituting the display device provided on a plurality of different substrates. . In this case, the arrangement of the plurality of substrates is accurately adjusted by the control means before the element forming portion provided on the substrate is peeled off. Further, when arranging the substrates, the substrates may be bonded to each other.
上記構成において、加工手段は、画素部を形成する手段である。ここでいう画素部とは、配線や電極等の導電膜、層間絶縁膜や保護膜等の絶縁膜、EL素子等の発光層または液晶等の画素部を構成するものであればどのようなものでも含まれる。また、画素領域の周辺に設けられた駆動回路部等と画素部とを接続する配線等の導電膜や配線を覆う絶縁膜等も加工手段により形成することができる。また、加工手段としては、液滴吐出法やスクリーン印刷法またはグラビア印刷法等の各種印刷法や大気圧プラズマ装置を用いることができる。液滴吐出法とは、導電物や絶縁物等の材料を含んだ組成物の液滴(ドットともいう)を選択的に吐出(噴射)して任意の場所にパターンを形成する方法であり、その方式によってはインクジェット法とも呼ばれている。また、封止手段は、少なくとも対向して設けられた2つのローラーを有することを特徴としている。 In the above configuration, the processing means is means for forming a pixel portion. As used herein, the pixel portion may be anything that constitutes a pixel portion such as a conductive film such as a wiring or an electrode, an insulating film such as an interlayer insulating film or a protective film, a light emitting layer such as an EL element, or a liquid crystal. But included. In addition, a conductive film such as a wiring connecting the driver circuit portion and the like provided in the periphery of the pixel region and the pixel portion, an insulating film covering the wiring, and the like can be formed by the processing means. As processing means, various printing methods such as a droplet discharge method, a screen printing method or a gravure printing method, or an atmospheric pressure plasma apparatus can be used. The droplet discharge method is a method of selectively discharging (jetting) droplets (also referred to as dots) of a composition containing a material such as a conductor or an insulator to form a pattern at an arbitrary place. Depending on the method, it is also called an inkjet method. Moreover, the sealing means has at least two rollers provided to face each other.
本発明の表示装置の作製方法は、基板上に剥離層を形成し、剥離層上に表示装置の一部を構成する素子形成部を形成し、素子形成部に開口部を形成して剥離層を露出させ、開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、剥離層を除去し、素子形成部の一方の面を第1のシート材に接着させて、基板から素子形成部を剥離し、素子形成部の他方の面を第2のシート材に接着させて、第1のシート材から素子形成部を剥離し、加工手段を用いて素子形成部に画素部を形成し、素子形成部の一方の面を第3のシート材に接着させて封止することを特徴としている。つまり、剛性を有する基板上にあらかじめ熱処理等が必要な表示装置を構成する素子形成部の一部を形成し、その後剥離して可撓性基板上に設けた後に表示装置を構成する残りの部分を形成する。 In the method for manufacturing a display device of the present invention, a release layer is formed over a substrate, an element formation portion that forms part of the display device is formed over the release layer, and an opening is formed in the element formation portion. Is exposed, an etching agent is introduced into the opening, the peeling layer is removed, one surface of the element forming portion is adhered to the first sheet material, and the element forming portion is peeled off from the substrate. The other surface of the element is adhered to the second sheet material, the element forming portion is peeled from the first sheet material, the pixel portion is formed in the element forming portion using the processing means, and one surface of the element forming portion is formed. Is bonded to a third sheet material and sealed. In other words, a part of an element forming portion that constitutes a display device that requires heat treatment or the like is formed on a rigid substrate in advance, and then the remaining portion that constitutes the display device after being peeled and provided on a flexible substrate Form.
また、本発明の表示装置の作製方法の異なる構成として、基板上に剥離層を形成し、剥離層上に下地絶縁膜と、下地絶縁膜上に形成されたチャネル領域とソースまたはドレイン領域を含む半導体膜と、半導体膜のチャネル領域の上方にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成されたゲート電極と、ゲート電極を覆って形成された層間絶縁膜と、層間絶縁膜上に形成された半導体膜のソースまたはドレイン領域と電気的に接続するソースまたはドレイン電極および配線と、ソースまたはドレイン電極の一方と電気的に接続した画素電極と、画素電極の端部を覆って形成された絶縁膜とから構成される素子形成部を形成し、絶縁膜、層間絶縁膜、ゲート絶縁膜および下地絶縁膜に剥離層に達する開口部を形成して剥離層を露出させ、開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、剥離層を除去し、素子形成部の一方の面に第1のシート材を接着させて、基板から前記素子形成部を剥離し、素子形成部の他方の面に第2のシート材を接着させて、第1のシート材から素子形成部を剥離し、加工手段を用いて画素電極上に発光層および対向電極を形成し、対向電極上に保護膜を形成し、保護膜の表面に第3のシート材を接着させて封止することを特徴としている。 In addition, as a different structure of the method for manufacturing the display device of the present invention, a separation layer is formed over a substrate, a base insulating film is formed over the separation layer, and a channel region and a source or drain region formed over the base insulating film are included. A semiconductor film; a gate electrode formed above the channel region of the semiconductor film via a gate insulating film; an interlayer insulating film formed to cover the gate electrode; and a source of the semiconductor film formed on the interlayer insulating film Or a source or drain electrode and wiring electrically connected to the drain region, a pixel electrode electrically connected to one of the source or drain electrode, and an insulating film formed so as to cover an end of the pixel electrode. An element forming portion is formed, an opening reaching the peeling layer is formed in the insulating film, the interlayer insulating film, the gate insulating film, and the base insulating film to expose the peeling layer, and an etching agent is introduced into the opening. Then, the peeling layer is removed, the first sheet material is adhered to one surface of the element forming portion, the element forming portion is peeled from the substrate, and the second sheet material is peeled from the other surface of the element forming portion. The element forming portion is peeled off from the first sheet material, the light emitting layer and the counter electrode are formed on the pixel electrode using the processing means, the protective film is formed on the counter electrode, and the surface of the protective film And a third sheet material is adhered and sealed.
また、本発明は上記構成において、剥離処理を行う前に基板上設けられた剥離層上に下地絶縁膜と、下地絶縁膜上に形成されたチャネル領域とソースまたはドレイン領域を含む半導体膜と、ゲート絶縁膜とからなる構造を形成して、その後剥離層を除去して剥離を行い、可撓性基板に移し替えた後に、残りの構造を形成してフィルム状表示装置を作製してもよい。他にも、剥離処理を行う前に基板上設けられた剥離層上に下地絶縁膜と、下地絶縁膜上に形成されたチャネル領域とソースまたはドレイン領域を含む半導体膜と、ゲート絶縁膜と、半導体膜のチャネル領域の上方にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成されたゲート電極と、ゲート電極を覆って形成された層間絶縁膜とからなる構造を形成して、その後剥離層を除去し、層間絶縁膜に半導体膜のソースまたはドレイン領域に達する開口部を形成して剥離を行い、可撓性基板に移し替えた後に、残りの構造を形成してフィルム状表示装置を作製してもよい。 Further, in the above structure according to the present invention, the base insulating film is formed over the peeling layer provided over the substrate before performing the peeling treatment, and the semiconductor film including the channel region and the source or drain region formed over the base insulating film; A structure comprising a gate insulating film may be formed, and then the release layer may be removed and peeled off. After transferring to a flexible substrate, the remaining structure may be formed to produce a film display device. . In addition, a base insulating film on a separation layer provided over the substrate before the separation treatment, a semiconductor film including a channel region and a source or drain region formed on the base insulating film, a gate insulating film, A structure comprising a gate electrode formed over the channel region of the semiconductor film via a gate insulating film and an interlayer insulating film formed so as to cover the gate electrode is formed, and then the release layer is removed and the interlayer insulating film is removed. An opening reaching the source or drain region of the semiconductor film may be formed in the film, and the film may be peeled off and transferred to a flexible substrate, and then the remaining structure may be formed to manufacture a film display device.
また、本発明の表示装置の作製方法は、複数の基板上に剥離層を形成し、剥離層上に表示装置の一部を構成する素子形成部を形成し、素子形成部に開口部を形成して剥離層を露出させ、開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、剥離層を除去し、素子形成部がそれぞれ設けられた複数の基板を配列させ、複数の基板上にそれぞれ設けられた素子形成部の一方の面を第1のシート材に接着させて、複数の基板から素子形成部を剥離し、素子形成部の他方の面を第2のシート材に接着させて、第1のシート材から素子形成部を剥離し、加工手段を用いて素子形成部に画素部を形成し、素子形成部の一方の面を第3のシート材に接着させて封止することを特徴としている。上記構成において、複数の基板上にそれぞれ形成される素子形成部のうち、素子形成部の構造は異なっている場合にも適用することができる。この場合、機能が異なる素子形成部の構造を組み合わせて一つの表示装置を形成することができる。 In the display device manufacturing method of the present invention, a separation layer is formed over a plurality of substrates, an element formation portion that forms part of the display device is formed over the separation layer, and an opening is formed in the element formation portion. Then, the release layer is exposed, an etching agent is introduced into the opening, the release layer is removed, a plurality of substrates each provided with an element formation portion are arranged, and an element formed on each of the plurality of substrates is formed. The first sheet material is bonded to the first sheet material, the element forming portion is peeled from the plurality of substrates, and the other surface of the element forming portion is bonded to the second sheet material. The element forming portion is peeled off, a pixel portion is formed in the element forming portion using a processing means, and one surface of the element forming portion is bonded to a third sheet material and sealed. In the above structure, the present invention can also be applied to a case where the structure of the element forming portions among the element forming portions formed on the plurality of substrates is different. In this case, one display device can be formed by combining structures of element formation portions having different functions.
また、上記構成において、加工手段は、画素部を形成する手段である。画素部とは配線や電極等の導電膜、層間絶縁膜や保護膜等の絶縁膜、EL素子等の発光層または液晶等の画素部を構成するものであればどのようなものでも含まれる。また、画素領域の周辺に設けられた駆動回路部等と画素部とを接続する配線等の導電膜や配線を覆う絶縁膜等も加工手段により形成することができる。加工手段としては、液滴吐出法またはスクリーン印刷法やグラビア印刷法等の各種印刷法や大気圧プラズマ装置を用いることができる。 In the above configuration, the processing means is means for forming a pixel portion. The pixel portion includes any conductive layer such as a wiring or an electrode, an insulating film such as an interlayer insulating film or a protective film, a light emitting layer such as an EL element, or a pixel portion such as a liquid crystal. In addition, a conductive film such as a wiring connecting the driver circuit portion and the like provided in the periphery of the pixel region and the pixel portion, an insulating film covering the wiring, and the like can be formed by the processing means. As the processing means, a droplet discharge method, various printing methods such as a screen printing method and a gravure printing method, and an atmospheric pressure plasma apparatus can be used.
本発明の表示装置の製造装置を用いることによって、可撓性基板上に設けられた表示装置を低コストで効率良く作製することができる。また、本発明の作製方法を用いることにより、特性の高い薄膜トランジスタを有する表示装置を得ることができる。 By using the display device manufacturing apparatus of the present invention, a display device provided over a flexible substrate can be efficiently manufactured at low cost. In addition, by using the manufacturing method of the present invention, a display device including a thin film transistor with high characteristics can be obtained.
本発明の実施の形態について、図面を用いて以下に説明する。但し、本発明は以下の説明に限定されず、本発明の趣旨及びその範囲から逸脱することなくその形態及び詳細を様々に変更し得ることは当業者であれば容易に理解される。従って、本発明は以下に示す実施の形態の記載内容に限定して解釈されるものではない。なお、以下に説明する本発明の構成において、同じものを指す符号は異なる図面間で共通して用いる。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the following description, and it is easily understood by those skilled in the art that modes and details can be variously changed without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Therefore, the present invention should not be construed as being limited to the description of the embodiments below. Note that in the structures of the present invention described below, the same reference numerals are used in common in different drawings.
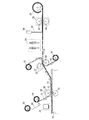
本発明は、あらかじめガラス等の剛性を有する基板上に表示装置の少なくとも一部を形成し、その後基板を剥離して可撓性基板上に設けた後に、表示装置の残りの部分を形成することによって表示装置を作製する。その模式図を図1に示す。なお、図1において、図1(A)は表示装置の作製工程を示しており、図1(B)は、各工程における表示装置を構成する模式図を示している。 In the present invention, at least a part of a display device is formed in advance on a substrate having rigidity such as glass, and then the substrate is peeled and provided on a flexible substrate, and then the remaining portion of the display device is formed. Thus, a display device is manufactured. The schematic diagram is shown in FIG. 1A illustrates a manufacturing process of a display device, and FIG. 1B illustrates a schematic diagram of a display device in each process.
本発明が提案する表示装置の製造装置は、図1(A)に示すように、表示装置を構成する素子形成部102(以下素子形成部102と記す)が設けられた基板101を搬送する搬送手段100と、少なくとも一方の面に粘着層を有する第1のシート材103と、表示装置を封止する第2のシート材104および第3のシート材106とを有している。さらに、基板101の位置を制御する制御手段111、基板101から素子形成部102を剥離する第1の剥離手段112、第1のシート材103から素子形成部102を剥離する第2の剥離手段113、素子形成部102に導電膜と絶縁膜の一方または両方を形成する加工手段114、素子形成部102を封止する封止手段115等の構成が設けられている。なお、これらの構成は、全て設けてもよいし、いくつかの構成を組み合わせて設けてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 1A, a display device manufacturing apparatus proposed by the present invention transports a
図1に示す装置では、まず素子形成部102が設けられた基板101が搬送手段100によって搬送される。この際、制御手段111によって基板の位置が調整される。また、複数の基板上にそれぞれ形成された素子形成部をつなぎ合わせて1つの表示装置を形成する場合には、制御手段111により複数の基板の位置を調整する。なお、この場合、基板同士を貼り合わせてもよい。
In the apparatus shown in FIG. 1, first, the
制御手段111(基板の位置の調整に使用される)は、CCD(charge coupled device)カメラ等を用いることができる。複数の基板を精度よく並べることによって、複数の基板に設けられた表示装置を構成する素子形成部をつなぎ合わせて大型の表示装置の作製が可能となる。なお、複数の基板をつなぎ合わせて表示装置を形成する場合には、画素部に表示を行う際につなぎ合わせた境目を目立たないようにする必要がある。本発明では、境目に画素と画素の隙間を配置するように形成したり、つなげ合わせた後に配線や電極あるいは発光層や液晶等を形成したりすることにより境目が目立つのを防止することが可能となる。 As the control unit 111 (used for adjusting the position of the substrate), a CCD (charge coupled device) camera or the like can be used. By arranging a plurality of substrates with high precision, a large display device can be manufactured by connecting element forming portions constituting a display device provided on the plurality of substrates. Note that in the case where a display device is formed by connecting a plurality of substrates, it is necessary to make the boundary between the connected portions inconspicuous when performing display on the pixel portion. In the present invention, it is possible to prevent the boundary from being noticeable by forming the gap between the pixels at the boundary, or by forming the wiring, the electrode, the light emitting layer, the liquid crystal, or the like after the connection. It becomes.
続いて、第1の剥離手段112によって、基板101上に設けられた素子形成部102を第1のシート材103に接着させて基板101から剥離する。そして、剥離した素子形成部102は第1のシート材に接着したまま次の工程に流れていく。それと同時に基板101は回収され、再利用される。
Subsequently, the
次に、第1のシート材103に接着した薄膜である素子形成部102を、第2の剥離手段113によって第2のシート材104に接着させて第1のシート材103から剥離する。そして、素子形成部102は第2のシート材104に接着されて次の工程に流れていく。
Next, the
次に、第2のシート材104に接着した素子形成部102の表面に、加工手段114によって配線、発光層、電極等を形成する。加工手段114としては、素子形成部102に直接形成できる手段を用いることが好ましく、例えば液滴吐出法やスクリーン印刷やグラビア印刷等の各種印刷法を用いることができる。液滴吐出法や印刷法を用いて素子形成部102に配線、発光層、電極等を直接形成することによって、材料の利用効率および作業効率を向上させることができる。
Next, wiring, a light emitting layer, an electrode, and the like are formed by the processing means 114 on the surface of the
続いて、封止手段115によって、加工手段114により加工された素子形成部105の表面に第3のシート材106を接着させて、素子形成部105を第2のシート材104と第3のシート材106によって封止する。
Subsequently, the
以上の工程によって、表示装置を作製することができる。なお、第2のシート材および第3のシート材に可撓性を有するフィルム状のシート材を用いることによって、フィルム状の表示装置を作製することができる。本発明の表示装置の作製方法および作製装置は、液晶表示装置や発光素子を用いた表示装置をはじめとしてどのような表示装置にも利用することができる。また、アクティブマトリクス型の表示装置でもパッシブマトリクス型の表示装置でも適用することが可能である。 Through the above process, a display device can be manufactured. Note that a film-like display device can be manufactured by using a flexible film-like sheet material for the second sheet material and the third sheet material. The manufacturing method and the manufacturing apparatus of the display device of the present invention can be used for any display device including a liquid crystal display device and a display device using a light emitting element. Further, the present invention can be applied to either an active matrix display device or a passive matrix display device.
以下に、本発明のより具体的な構成に関して図面を用いて説明を行う。 Hereinafter, a more specific configuration of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(実施の形態1)
本実施の形態1では、図1に示した表示装置の製造装置のより具体的な構成について図面を参照して説明する。
(Embodiment 1)
In the first embodiment, a more specific configuration of the display device manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. 1 will be described with reference to the drawings.
本実施の形態1で示す装置は、図2に示すように、表示装置の一部を構成する素子形成部12(以下素子形成部12と記す)が設けられた基板11を搬送する搬送手段10と、基板11の位置を調整する制御手段21と、第1のシート材13が巻き付けられた第1の供給用ロール14と、基板11から素子形成部12を第1のシート材13に接着させて剥離するローラー26を備えた第1の剥離手段22と、第2のシート材16が巻き付けられた第2の供給用ロール17と、第1のシート材13から素子形成部12を第2のシート材16に接着させて剥離するローラー27、28を備えた第2の剥離手段23と、第1のシート材13を回収する回収用ロール15と、素子形成部12に画素部を形成する加工手段24と、第3のシート材18を供給する第3の供給用ロール19と、加工手段によって加工された素子形成部を第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18により封止する封止手段25と、封止された素子形成部12を巻き取る回収用ロール20とを有する。以下に全体の流れについて説明する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the apparatus shown in the first embodiment is a transfer means 10 for transferring a
まず、搬送手段10によって基板11上に設けられた素子形成部12が搬送される。搬送されてきた素子形成部12は、制御手段21によって基板の位置が調整される。そして、ローラー26の方向に流れていく。基板の位置の精度がそれほど厳密に求められない場合は、位置制御手段21は設けなくともよい。なお、複数の基板に形成された素子形成部をつなげ合わせて表示装置を形成する場合には、制御手段21によって位置を調整して基板同士を接合する。
First, the
次に、第1の供給用ロール14から供給された第1のシート材13がローラー26を備えた第1の剥離手段22によって、基板11上に設けられた素子形成部12に接着し、基板11から素子形成部12を剥離する。その後、剥離された素子形成部12は、第1のシート材13に接着されてローラー27の方向に流れていく。また、第2の供給用ロール17から供給される第2のシート材16がローラー28の方向に流れていく。
Next, the
そして、ローラー27、28を備えた第2の剥離手段23によって、第1のシート材13に接着されて搬送されてきた素子形成部12の表面に第2のシート材16が接着し、第1のシート材13から素子形成部12を剥離する。なお、第2の剥離手段23は、第1のシート材13に接着された素子形成部12を第2のシート材16に接着する際に、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行う。その後、剥離された素子形成部12は、第2のシート材16に接着されて加工手段24の方向に流れていく。
Then, the
加工手段24では、第2の剥離手段23から流れてきた素子形成部12に、画素部を形成する。加工手段は、導電膜、絶縁膜、有機EL素子等の発光層または液晶等の画素部を構成するものであればどのようなものでも形成することができる。加工手段24としては、導電体や絶縁体や半導体等を含んだ組成物を吐出(噴射)してパターンを直接形成する液滴吐出法やスクリーン印刷やグラビア印刷等の印刷法、大気圧プラズマ装置等を用いることができる。その後、画素部が形成された素子形成部は、封止手段25の方向に流れていく。また、第3の供給用ロール19から供給される第3のシート材18がローラー30の方向に流れていく。
In the processing means 24, a pixel portion is formed in the
封止手段25では、第3のシート材18に、第2のシート材に接着されて搬送されてきた素子形成部の表面を接着させて挟み込むと共に、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行う。その後、挟み込まれた(封止された)素子形成部は、回収用ロール20の方向に流れていき、回収用ロール20に巻き付いていく。
In the sealing means 25, the surface of the element forming portion that has been transported while being bonded to the second sheet material is bonded to the
上述したように、図2で示した装置において、第1のシート材13は、第1の供給用ロール14から供給され、第1の剥離手段22が含むローラー26、ローラー27の順に流れて、回収用ロール15に回収される。また、第1の供給用ロール14とローラー26とローラー27は同じ方向に回転する。第2のシート材16は第2の供給用ロール17から供給され、第2の剥離手段23が含むローラー28、封止手段25が含むローラー29の順に流れて回収用ロール20に回収される。また、第2の供給用ロール17とローラー28とローラー29は同じ方向に回転する。第3のシート材18は第3の供給用ロール19から供給され、封止手段25が含むローラー30を流れた後に回収用ロール20に回収される。また、第3の供給用ロール19とローラー30は同じ方向に回転する。
As described above, in the apparatus shown in FIG. 2, the
搬送手段10は、素子形成部12が設けられた基板11を搬送するものであり、図2ではローラー31を具備し、当該ローラー31が回転することで、基板11が搬送される。なお、搬送手段10は基板11を搬送できるものならどのような構成でもよく、例えばベルトコンベア、複数のローラーまたはロボットアーム等を用いることができる。ロボットアームは、基板11をそのまま搬送したり、基板11が設けられたステージを搬送したりする。また、搬送手段10は、第1のシート材13が移動する速度に合わせて、所定の速度で基板11を搬送する。
The transport means 10 transports the
第1の供給用ロール14、第2の供給用ロール17、第3の供給用ロール19にはそれぞれ、第1のシート材13、第2のシート材16、第3のシート材18が巻き付けられている。第1の供給用ロール14を所定の速度で回転することによって、第2の剥離手段が含むローラー27に向かって第1のシート材13を所定の速度で流し、第2の供給用ロール17および第3の供給用ロール19をそれぞれ所定の速度で回転することによって、封止手段25に向かって第2のシート材16、第3のシート材18をそれぞれ所定の速度で流す。なお、第1の供給用ロール14、第2の供給用ロール17、第3の供給用ロール19は、円柱状であり、樹脂材料、金属材料またはゴム材料等からなる。
A
第1のシート材13は、可撓性のフィルムからなっており、少なくとも一方の面に粘着剤を有する面が設けてある。具体的には、ポリエステル等の基材として用いるベースフィルム上に粘着剤が設けてある。粘着剤としては、アクリル樹脂等を含んだ樹脂材料または合成ゴム材料からなる材料を用いることができる。また、第1のシート材13には粘着力が弱いフィルム(粘着力が、好ましくは0.01N〜1.0N、より好ましくは0.05N〜0.5N)を用いるのが好ましい。これは、基板上に設けられた素子形成部を第1のシート材に接着した後に、第2のシート材を素子形成部に接着して、第1のシート材を素子形成部から剥離するためである。させるためである。接着剤の厚さは、1μm〜100μm、好ましくは1μm〜30μmにすることができる。また、ベースフィルムとしては、ポリエステル等のフィルムを用いて10μm〜1mmで形成すると加工時に扱いやすくなるため好ましい。
The 1st sheet |
粘着層の表面がセパレーター32で保護されている場合は、使用する時に図2に示すようにセパレーター回収ロール33を設け、使用時にセパレーター32を除去すればよい。また、基材として用いたベースフィルム上に帯電防止処理が施されたものを用いることもできる。セパレーターはポリエステル等のフィルムや紙等からなるが、ポリエチレンテレフタレート等のフィルムで形成されている場合は、加工時に紙粉などが生じないため好ましい。
When the surface of the adhesive layer is protected by the
第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18は、可撓性のフィルムからなっており、例えばラミネートフィルムや繊維質な材料からなる紙などを利用することができる。ラミネートフィルムは、ラミネート処理等の封止に用いることができるフィルム全般を指し、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリエステル、ビニル、ポリフッ化ビニル、塩化ビニル、メタクリル酸メチル、ナイロン、ポリカーボネート等の材料からなり、その表面にエンボス加工等の加工処理が施されていてもよい。
The
また、本実施の形態では、ホットメルト接着剤を用いて素子形成部の封止を行うのが好ましい。ホットメルト接着材は、水や溶剤を含まず、室温では固体で不揮発性の熱可塑性材料からなり、溶融状態で塗布し冷却することにより物と物を接着する化学物質である。また、接着時間が短く、無公害、安全で衛生的、省エネルギーであり、低コストであるといった利点を有する。 Moreover, in this Embodiment, it is preferable to seal an element formation part using a hot-melt-adhesive. A hot-melt adhesive is a chemical substance that does not contain water or a solvent, is made of a solid and non-volatile thermoplastic material at room temperature, and adheres to an object by being applied and cooled in a molten state. In addition, the bonding time is short, pollution-free, safe and hygienic, energy saving, and low cost.
ホットメルト接着剤は常温で固体であるため、あらかじめフィルム状、繊維状に加工したもの、またはポリエステル等のベースフィルム上にあらかじめ接着層を形成してフィルム状にしたものを用いることができる。ここでは、ポリエチレンテレフタレートからなるベースフィルム上にホットメルトフィルムを形成したシート材を用いる。ホットメルトフィルムは、ベースフィルムよりも軟化点の低い樹脂からなっており、加熱することによってホットメルトフィルムのみが溶融してゴム状になり接着し、冷却すると硬化する。また、ホットメルトフィルムとして、例えばエチレン・酢酸ビニル共重合体(EVA)、ポリエステル、ポリアミド、熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリオレフィン等を主成分としたフィルムを用いることができる。 Since the hot-melt adhesive is solid at room temperature, it can be used in the form of a film or fiber, or a film obtained by forming an adhesive layer in advance on a base film such as polyester. Here, a sheet material in which a hot melt film is formed on a base film made of polyethylene terephthalate is used. The hot melt film is made of a resin having a softening point lower than that of the base film. When heated, only the hot melt film is melted to form a rubber-like adhesive and is cured when cooled. Further, as the hot melt film, for example, a film mainly composed of ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), polyester, polyamide, thermoplastic elastomer, polyolefin or the like can be used.
また、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18の一方または両方は、一方の面に接着面を有していてもよい。接着面は、熱硬化樹脂性樹脂、紫外線硬化樹脂、エポキシ樹脂系接着剤、光硬化型接着剤、湿気硬化型接着剤、樹脂添加剤等の接着剤を塗布したものを用いることができる。
One or both of the
また、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18の一方または両方は、透光性を有していてもよい。また、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18の一方または両方に、保護膜として炭素を主成分とする薄膜(ダイヤモンドライクカーボン膜)や、インジウム錫酸化物(ITO)等の導電性材料によりコーティングしてもよい。また、他にも、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18として、静電気等を防止する帯電防止対策を施したフィルム(以下、帯電防止フィルムと記す)を用いることもできる。帯電防止フィルムとしては、帯電防止可能な材料を樹脂中に分散させたフィルム、及び帯電防止可能な材料が貼り付けられたフィルム等が挙げられる。帯電防止可能な材料が設けられたフィルムは、片面に帯電防止可能な材料を設けたフィルムであってもよいし、両面に帯電防止可能な材料を設けたフィルムであってもよい。さらに、片面に帯電防止可能な材料が設けられたフィルムは、帯電防止可能な材料が設けられた面をフィルムの内側になるように層に貼り付けてもよいし、フィルムの外側になるように貼り付けてもよい。なお、帯電防止可能な材料はフィルムの全面、あるいは一部に設けてあればよい。ここでの帯電防止可能な材料としては、金属、インジウムと錫の酸化物(ITO)、両性界面活性剤や陽イオン性界面活性剤や非イオン性界面活性剤等の界面活性剤を用いることができる。また、他にも帯電防止材料として、側鎖にカルボキシル基および4級アンモニウム塩基をもつ架橋性共重合体高分子を含む樹脂材料等を用いることができる。これらの材料をフィルムに貼り付けたり、練り込んだり、塗布したりすることによって帯電防止フィルムとすることができる。帯電防止フィルムで封止を行うことによって、商品として取り扱う際に、外部からの静電気等によって素子形成部に悪影響が及ぶことを抑制することができる。
In addition, one or both of the
制御手段21は、搬送されてくる基板11の位置を制御するものであり、図2ではCCDカメラを用いることによって、基板11を配列させる。また、複数の基板の位置を精確に制御して配列させることにより、複数の基板をつなぎ合わせた表示装置を作製することができる。このとき、制御手段21によって、複数の基板の位置を精確に制御して基板同士を接合する。なお、つなぎ合わせた境目が画素部に形成される場合には、境目が目立たないようにする必要がある。本実施の形態では、制御手段21において精確に複数の基板を並べてつなぎ合わせ、且つ加工手段24において、つなぎ合わせた後に配線、電極または発光層を形成することができるため、境目をより目立たなくすることが可能となる。なお、基板を精確に配列させる必要がない場合には、制御手段21は設けなくともよい。
The control means 21 controls the position of the
第1の剥離手段22は、少なくともローラー26を備え、素子形成部12の一方の面を、第1のシート材13の一方の面に接着させて、基板11から素子形成部12を剥離する。ローラー26が回転することによって、素子形成部12が第1のシート材13に接着し、基板11から素子形成部12が剥離される。従って、ローラー26は、素子形成部12が設けられた側の基板11と対向するように設けられる。また、ローラー26は円柱状であり、樹脂材料、金属材料またはゴム材料等からなり、好ましくは柔らかい材料からなる。
The first peeling means 22 includes at least a
第2の剥離手段23は、少なくとも対向するローラー27、28を備え、第1のシート材13に接着した素子形成部12を、第2のシート材16の一方の面に接着させて、第1のシート材13から素子形成部12を剥離する。このとき、第2の供給用ロール17からローラー28に向かって流れる第2のシート材16に、素子形成部を接着させると共に、ローラー27とローラー28の間を通過する際に、ローラー27とローラー28の一方または両方を用いて、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行う。
The second peeling means 23 includes at
この処理を行うことによって、第1のシート材13に接着された素子形成部12が第2のシート材16に接着する。加熱処理の方法としては、熱エネルギーを加えることができればどのような方法でもよく、例えばオーブン、電熱線のヒータ、オイル等の温度媒体、ホットスタンプ、サーマルヘッド、レーザー光、赤外線フラッシュ、熱ペン等を適宜選択して用いることができる。また、ローラー27とローラー28は円柱状であり、樹脂材料、金属材料またはゴム材料等からなり、好ましくは柔らかい材料からなる。
By performing this process, the
加工手段24は、第2のシート材16に接着した素子形成部12の表面に画素部を形成する。具体的には、配線、電極等の導電膜、絶縁膜、発光層、液晶等の表示装置の画素を完成させるために必要なものを形成する。加工手段としては、導電体や絶縁体等を含んだ組成物を吐出(噴射)してパターンを直接形成する液滴吐出法や、原版に材料を載せてパターンを転写するスクリーン印刷やグラビア印刷法等の印刷法を用いることができる。本実施の形態では、液滴吐出法を用いる場合を示している。例えば、あらかじめ基板11に半導体膜、ゲート電極、配線および画素電極等を形成した場合には、加工手段24を用いて液滴を選択的に吐出して発光層や対向電極等を形成する。また、他にも基板11に半導体層のみを形成し、その後加工手段24を用いてゲート電極、配線、画素電極、発光層または対向電極等を形成してもよく、実施者が適宜選択して行うことができる。
The processing means 24 forms a pixel portion on the surface of the
また、本実施の形態では、基板11から第1の剥離手段22により剥離した素子形成部12をさらに第2の剥離手段により剥離を行っているため、加工手段24に流れてくる素子形成部の表面は、基板11上に形成された素子形成部の表面と同じとなる。このように、剥離を2回行うことによって加工手段24によって素子形成部に発光層等を形成する際に効率よく行うことができる。
Further, in the present embodiment, since the
封止手段25は、加工手段24によって加工された素子形成部が流れてくると、当該素子形成部の表面に第3のシート材18を接着させると共に、素子形成部を第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18により封止する。また、封止手段25は、互いに対向して設けられたローラー29とローラー30を有する。そして、第3の供給ロール19からローラー30に向かって流れる第3のシート材18に、素子形成部の他方の面を接着させると共に、ローラー29とローラー30の間を通過する際に、ローラー29とローラー30を用いて、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行う。この処理を行うことによって、素子形成部は、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18によって封止される。
When the element forming portion processed by the processing means 24 flows, the sealing means 25 adheres the
封止手段25を構成するローラー29、30の一方または両方は、加熱手段を有する。加熱手段は、例えば、オーブン、電熱線のヒータ、オイル等の温媒、ホットスタンプ、サーマルヘッド、レーザー光、赤外線フラッシュ、熱ペン等を用いることができる。また、ローラー29とローラー30は、ローラー28と第2の供給用ロール17と第3の供給用ロール19の回転する速度に合わせて、所定の速度で回転する。また、ローラー29とローラー30は円柱状であり、樹脂材料、金属材料またはゴム材料等からなり、好ましくは柔らかい材料からなる。
One or both of the
回収用ロール20は、第2のシート材16と第3のシート材18により封止された素子形成部を巻き取ることで回収するロールである。回収用ロール20は、ローラー29とローラー30の回転する速度に合わせて、所定の速度で回転する。また、回収用ロール20は、円柱状であり、樹脂材料、金属材料またはゴム材料等からなり、好ましくは柔らかい材料からなる。
The
このように、図2に示した装置によると、第1〜第3の供給用ロール14、15、21、ローラー26、31、27、28、29、30および回収用ロール20が回転することで、基板11上に設けられた素子形成部12を連続的に剥離・封止・回収することができる。従って、図2で示した装置は、量産性が高く、製造効率を向上させることができる。
Thus, according to the apparatus shown in FIG. 2, the first to third supply rolls 14, 15, 21, the
次に、上記とは異なるフィルム状表示装置の製造装置の形態について図3を用いて説明する。 Next, the form of the manufacturing apparatus of the film-like display apparatus different from the above will be described with reference to FIG.
図3に示す装置は、素子形成部12が設けられた基板11を搬送する搬送手段10と、基板11の位置を調整する制御手段21と、第1のシート材13が巻き付けられた第1の供給用ロール14と、基板11から素子形成部12を第1のシート材13に接着させて剥離するローラー26を備えた第1の剥離手段22と、第2のシート材16が巻き付けられた第2の供給用ロール17と、第1のシート材13から素子形成部12を第2のシート材16に接着させて剥離する第2の剥離手段23と、第1のシート材13を回収する回収用ロール15と、素子形成部12に画素部を形成する加工手段24と、第2のシート材16が接着した面と反対側の素子形成部12の面に樹脂55を加熱溶融状態で押し出して、第2のシート材16と樹脂55により素子形成部を封止する封止手段25と、封止された素子形成部12を巻き取る回収用ロール20とを有する。図3に示す構成は、図2に示す構成に、第3の供給用ロール19と第3のシート材18がダイ54と樹脂55に置き換わった構成となっている。
The apparatus shown in FIG. 3 includes a
図3に示す装置では、基板11上に設けられた素子形成部12を第1のシート材13で剥離し、第1のシート材に接着した素子形成部12を第2のシート材16に接着させ、第2のシート材16に接着した素子形成部12が加工手段24によって加工され、封止手段25に向かって流れるところまでは、図1と同様に行うことができる。その後、図3では、第2のシート材16に接着した素子形成部の他方の面(第2のシート材が接着した面と反対側の面)にダイ54から加熱溶融状態で押し出された樹脂55が供給される。続いて、圧着ローラー56と冷却ローラー57との間に導入された第2のシート材16と樹脂55を、圧着ローラー56と冷却ローラー57で加圧しながら冷却することによって、素子形成部の他方の面に樹脂55を接着させると共に、第2のシート材16と樹脂55により素子形成部12を封止する。最後に、封止された素子形成部12は、回収用のロール20の方向に流れていき、回収用ロール20に巻き取られて回収される。
In the apparatus shown in FIG. 3, the
図3に示すラミネート装置の構成において、樹脂55には、熱可塑性樹脂を用いればよい。樹脂55に用いる熱可塑性樹脂は、軟化点の低いものが好ましい。例えば、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリメチルペンテン等のポリオレフィン系樹脂、塩化ビニル、酢酸ビニル、塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル共重合体、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体、塩化ビニリデン、ポリビニルブチラール、ポリビニルアルコール等のビニル系共重合体、アクリル系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、セルロース、セルロースアセテート、セルロースアセテートブチレート、セルロースアセテートプロピオネート、エチルセルロース等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリスチレン、アクリロニトリル−スチレン共重合体等のスチレン系樹脂等が挙げられる。なお、樹脂55は、ダイ54からの単層で押し出したものでもよいし、2層以上を共押し出ししたものでもよい。なお、第1のシート材13または第2のシート材16は、上記で示したいずれかの材料を用いることができる。
In the configuration of the laminating apparatus illustrated in FIG. 3, a thermoplastic resin may be used as the
このように、図3に示した装置によると、搬送手段10、第1、第2の供給用ロール14、17、ローラー26、ローラー27、28、圧着ローラー56、冷却ローラー57および回収用ロール20が回転することで、基板11上に設けられた素子形成部12を連続的に剥離・封止・回収することができる。従って、図3で示した装置は、量産性が高く、製造効率を向上させることができる。
Thus, according to the apparatus shown in FIG. 3, the conveying
次に、上記とは異なるフィルム状表示装置の製造装置の形態について図4を用いて説明する。 Next, the form of the manufacturing apparatus of a film-like display apparatus different from the above will be described with reference to FIG.
カセット41は、基板供給用のカセットであり、素子形成部12が複数設けられた基板11がセットされる。カセット42は、基板回収用のカセットであり、素子形成部12が剥離された後の基板11が回収される。カセット41とカセット42の間には、搬送手段として複数のローラー43〜45が設けられており、当該ローラー43〜45が回転することで、基板11が搬送される。
The
その後、上述したように、素子形成部12の剥離と封止が行われ、続いて、封止された素子形成部12は、切断手段46により切断される。切断手段46は、ダイシング装置、スクライビング装置、レーザー照射装置(CO2レーザー照射装置等)等を用いたものである。上記の工程を経て、封止された素子形成部12が完成する。
Thereafter, as described above, the
本実施の形態において、剥離された基板11は再利用することができる。そのため、ガラス基板より原価の高い石英基板を用いた場合でも低コスト化を達成することができる。石英基板を用いた場合は、基板に伴う作製工程の条件がガラス基板に比べて緩和されるため、より特性の高い表示装置を形成することができる。なお、基板を再利用する場合、剥離の工程において基板に傷が生成されないように制御するのが望ましい。しかし、傷が生成された場合であっても、有機樹脂や無機樹脂膜を塗布法や液滴吐出法によって形成したり、研削、研磨したりすることによって平坦化処理を行えばよい。
In the present embodiment, the peeled
以上のように、本実施の形態で示した装置を用いることによって、効率良く可撓性を有する表示装置を製造することができる。 As described above, by using the device described in this embodiment, a flexible display device can be manufactured efficiently.
(実施の形態2)
次に、表示装置の作製方法の具体例に関して図面を用いて説明を行う。
(Embodiment 2)
Next, a specific example of a method for manufacturing a display device will be described with reference to drawings.
本実施の形態では、ガラス等の耐熱性を有する基板上にあらかじめ表示装置の一部を形成し、その後基板上に形成された表示装置の一部を剥離して可撓性を有する基板上に設け、表示装置の残りの部分を形成する場合に関して示す。 In this embodiment mode, a part of a display device is formed in advance on a heat-resistant substrate such as glass, and then the part of the display device formed on the substrate is peeled off to be on a flexible substrate. A case of providing and forming the remaining part of the display device will be described.
一般的に、表示装置の概略図は図5(A)に示すように、ガラス基板等の基板200上に複数の画素部からなる画素領域402と、画素部を駆動するための駆動回路403、404が設けられている。また、この他にも画素部を制御する回路が基板200上または電気的に接続されて外部に設けられている。
In general, as shown in FIG. 5A, a schematic diagram of a display device includes a
本実施の形態では、基板200上に表示装置を完成させるのではなく、基板200上に表示装置の構成の一部を形成した後に、一旦、形成した表示装置の構成の一部を可撓性を有する基板上に設ける。そして、続けて残りの表示装置を構成する部分を改めて形成する。具体的な作製工程について、図6、図7を用いて以下に説明する。
In this embodiment, instead of completing the display device over the
まず、図6(A)に示すように基板200上に、剥離層201、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203、半導体膜204、ゲート絶縁膜205、ゲート電極206、層間絶縁膜207、ソースまたはドレイン電極208、209、画素電極210、配線211、隔壁212を設ける。なお、図6に示す断面図は、図5(B)のA−B間の断面に対応している。以下に、図6(A)の構造に関して詳しく説明を行う。
First, as shown in FIG. 6A, a
基板200としては、例えばバリウムホウケイ酸ガラスや、アルミノホウケイ酸ガラスなどのガラス基板、石英基板、セラミック基板等を用いることができる。また、ステンレスを含む金属基板または半導体基板の表面に絶縁膜を形成したものを用いても良い。基板200の表面を、CMP法などの研磨により平坦化しておいても良い。
As the
基板200上に設ける剥離層201としては、タングステン(W)、モリブデン(Mo)、ニオブ(Nb)またはチタン(Ti)等を含んだ金属膜やシリコン(Si)等の半導体膜で形成する。本実施の形態では、剥離層201としてWを含んだ金属膜を用いる。なお、Wの形成方法はCVD法、スパッタ法または電子ビーム等によって形成することができ、ここではスパッタ法を用いて形成する。また、剥離層201として金属膜(例えばW)上に金属酸化物(例えばWOx)を形成した膜を用いてもよい。他にも金属膜と金属酸化膜の組み合わせとして、MoとMoOx、NbとNbOxまたはTiとTiOx(X=2〜3)等を用いることができる。
The
なお、図6では、基板200上に直に剥離層201を形成しているが、基板200と剥離層201の間に下地膜を形成してもよい。下地膜は、酸化珪素(SiOx)、窒化珪素(SiNx)、酸化窒化珪素(SiOxNy)(x>y)、窒化酸化珪素(SiNxOy)(x>y)等の酸素または窒素を有する絶縁膜の単層構造、またはこれらの積層構造を用いることができる。特に、基板からの汚染が懸念される場合には、基板200と剥離層201間に下地膜を形成するのが好ましい。
In FIG. 6, the
基板200上に剥離層201を形成した後に、剥離層201上に絶縁膜を形成する。絶縁膜は、単層構造または積層構造で形成することができ、図6では、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203からなる積層構造で形成する。絶縁膜としては、例えば第1の絶縁膜202として酸化珪素膜、第2の絶縁膜203として酸化窒化珪素膜を用いる。また、他にも第1の絶縁膜として酸化珪素、第2の絶縁膜として窒化酸化珪素膜、第3の絶縁膜として酸化窒化珪素膜からなる3層の積層構造で形成してもよい。
After the
次に、第2の絶縁膜203上に薄膜トランジスタを形成する。薄膜トランジスタは、少なくとも所望の形状にパターニングされた半導体膜204、ゲート絶縁膜205を介して形成されたゲート電極206、層間絶縁膜207、半導体膜204と電気的に接続したソースまたはドレイン電極208、209から構成されている。
Next, a thin film transistor is formed over the second
半導体膜204は、非晶質半導体、非晶質状態と結晶状態とが混在したSAS、非晶質半導体中に0.5nm〜20nmの結晶粒を観察することができる微結晶半導体、及び結晶性半導体から選ばれたいずれの状態を有してもよい。また成膜処理温度に耐えうる基板、例えば石英基板を使用するならば、当該基板へCVD法等により結晶性半導体膜を形成してもよい。
The
本実施の形態では、非晶質半導体膜を形成し、加熱処理により結晶化された結晶性半導体膜を形成する。加熱処理とは、加熱炉、レーザー照射、もしくはレーザー光の代わりにランプから発する光の照射(ランプアニール)、またはそれらを組み合わせて用いることができる。 In this embodiment, an amorphous semiconductor film is formed and a crystalline semiconductor film crystallized by heat treatment is formed. The heat treatment can be performed using a heating furnace, laser irradiation, irradiation of light emitted from a lamp instead of laser light (lamp annealing), or a combination thereof.
また、ゲート絶縁膜205は、半導体膜204を覆うように形成されている。ゲート絶縁膜205には、例えば酸化珪素、窒化珪素または窒化酸化珪素等を用いて単層または複数の膜を積層させて形成することができる。また成膜方法は、プラズマCVD法、スパッタ法などを用いることができる。
The
ゲート電極206は、ゲート絶縁膜205上に形成する。ゲート電極206としては、例えば、Ta、W、Ti、Mo、Al、Cu、Cr、Ndから選ばれた元素、または前記元素を主成分とする合金材料若しくは化合物材料で形成することができる。また、リン等の不純物元素をドーピングした多結晶珪素膜に代表される半導体膜を用いてもよい。また、AgPdCu合金を用いてもよい。さらに、その組み合わせも適宜選択すればよい。またゲート電極206は単層構造としてもよいし複数の層からなる積層構造としてもよい。
The
次に、ゲート電極またはレジストを形成しパターニングしたものをマスクとして用い、半導体膜204にn型またはp型の導電性を付与する不純物を選択的に添加する。半導体膜204は、チャネル形成領域および不純物領域(ソース領域、ドレイン領域、GOLD領域、LDD領域を含む)を有し、添加される不純物元素の導電型によりnチャネル型TFT、またはpチャネル型TFTを選択的に形成することができる。また、ゲート電極206の側壁にサイドウォールを形成してもよい。
Next, an impurity imparting n-type or p-type conductivity is selectively added to the
次に、層間絶縁膜207を形成する。層間絶縁膜207としては、無機絶縁膜や有機絶縁膜を用いることができる。無機絶縁膜としては、CVD法により形成された酸化シリコン膜や酸化窒化珪素、またはSOG(Spin On Glass)法により塗布された酸化シリコン膜などを用いることができ、有機絶縁膜としてはポリイミド、ポリアミド、BCB(ベンゾシクロブテン)、アクリルまたはポジ型感光性有機樹脂、ネガ型感光性有機樹脂等の膜を用いることができる。また、アクリル膜と酸化窒化シリコン膜の積層構造を用いても良い。
Next, an
また、層間絶縁膜として、シロキサン樹脂を用いることができる。シロキサン樹脂とは、Si−O−Si結合を含む樹脂に相当する。シロキサンは、シリコン(Si)と酸素(O)との結合で骨格構造が構成される。置換基として、少なくとも水素を含む有機基(例えばアルキル基、芳香族炭化水素)が用いられる。置換基として、フルオロ基を用いてもよい。または置換基として、少なくとも水素を含む有機基と、フルオロ基とを用いてもよい。 A siloxane resin can be used as the interlayer insulating film. A siloxane resin corresponds to a resin including a Si—O—Si bond. Siloxane has a skeleton structure formed of a bond of silicon (Si) and oxygen (O). As a substituent, an organic group containing at least hydrogen (for example, an alkyl group or an aromatic hydrocarbon) is used. A fluoro group may be used as a substituent. Alternatively, an organic group containing at least hydrogen and a fluoro group may be used as a substituent.
シロキサン樹脂は、その構造により、例えば、シリカガラス、アルキルシロキサンポリマー、アルキルシルセスキオキサンポリマー、水素化シルセスキオキサンポリマー、水素化アルキルシルセスキオキサンポリマーなどに分類することができる。また、Si−N結合を有するポリマー(ポリシラザン)を含む材料で層間絶縁膜を形成してもよい。 Siloxane resins can be classified according to their structure into, for example, silica glass, alkylsiloxane polymers, alkylsilsesquioxane polymers, hydrogenated silsesquioxane polymers, hydrogenated alkylsilsesquioxane polymers, and the like. Alternatively, the interlayer insulating film may be formed using a material containing a polymer (polysilazane) having a Si—N bond.
上記の材料を用いることで、膜厚を薄くしても十分な絶縁性および平坦性を有する層間絶縁膜を得ることができる。また、上記の材料は耐熱性が高いため、多層配線におけるリフロー処理にも耐えうる層間絶縁膜を得ることができる。さらに、吸湿性が低いため、脱水量の少ない層間絶縁膜を形成することができる。 By using the above material, an interlayer insulating film having sufficient insulation and flatness can be obtained even when the film thickness is reduced. In addition, since the above material has high heat resistance, an interlayer insulating film that can withstand reflow processing in a multilayer wiring can be obtained. Further, since the hygroscopic property is low, an interlayer insulating film with a small amount of dehydration can be formed.
次いで、層間絶縁膜207をエッチングし、半導体膜204のソースおよびドレイン領域に達するコンタクトホールを形成する。続いて、各ソースおよびドレイン領域とそれぞれ電気的に接続するソースまたはドレイン電極208、209および配線211を形成する。ソースまたはドレイン電極208、209、配線211としては、Al、Ni、C、W、Mo、Ti、Pt、Cu、Ta、Au、Mnから選ばれた一種の元素または該元素を複数含む合金からなる単層または積層構造を用いることができる。例えば、Ti膜とAlとTiを含む合金膜との積層膜をパターニングして形成することができる。もちろん、2層構造に限らず、単層構造でも良いし、3層以上の積層構造にしても良い。
Next, the
次に、層間絶縁膜207上に画素電極210を形成する。画素電極210はソースまたはドレイン電極208と電気的に接続するように形成する。なお、図6では、ソースまたはドレイン電極208を形成した後に画素電極210を形成しているが、画素電極210を先に形成した後にソースまたはドレイン電極208を形成してもよい。
Next, the
画素電極210を陽極として用いる場合には、仕事関数の大きい材料を用いることが好ましい。例えば、ITO(インジウムスズ酸化物)膜、IZO(インジウム亜鉛酸化物)膜、窒化チタン膜、クロム膜、タングステン膜、Zn膜、Pt膜等の単層の膜の他、窒化チタン膜とアルミニウムを主成分とする膜との積層、窒化チタン膜とアルミニウムを主成分とする膜と窒化チタン膜との3層構造等を用いることができる。なお、積層構造とすると、配線としての抵抗も低く、良好なオーミックコンタクトがとれ、さらに陽極として機能させることができる。
When the
一方、画素電極210を陰極として用いる場合には、仕事関数の小さい材料を用いることが好ましい。例えばAl、Ag、Li、Ca、またはこれらの合金MgAg、MgIn、Al−Li、CaF2、またはCaNを用いることができる。なお、画素電極210に光を透過させたい場合には、画素電極210として、膜厚を薄くした金属薄膜と、透明導電膜(ITO(インジウム錫酸化物)、酸化インジウム酸化亜鉛合金(In2O3―ZnO)、酸化亜鉛(ZnO)等)との積層を用いるのがよい。
On the other hand, when the
次に、ソースまたはドレイン電極208、209、配線211および画素電極210の端部を覆うように絶縁膜を選択的に形成し隔壁212(以下、絶縁膜212とも記す)を設ける。隔壁212としては、アクリル、ポリイミド等の有機材料、酸化珪素、酸窒化珪素、シロキサン樹脂等の材料等を用いることができる。好ましくは、後に画素電極210を覆って形成する発光層が段切れしないように、曲率半径が連続的に変化する形状に形成するとよい。
Next, an insulating film is selectively formed so as to cover the end portions of the source or drain
以上の工程により、図6(A)に示す構成を形成することができる。 Through the above steps, the structure illustrated in FIG. 6A can be formed.
次に、薄膜トランジスタや配線の形成部を避けて、エッチング剤を導入する開口部213を選択的に形成する(図6(B))。開口部213は絶縁膜212、層間絶縁膜207、ゲート絶縁膜205、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203を除去して剥離層201が露出するように形成する。
Next, an
続いて、開口部213へエッチング剤を導入し、剥離層201を除去する。本実施の形態では、剥離層とエッチング剤を化学的に反応させて、剥離層201の除去を行う。剥離層201は完全に除去してもよいが、ここでは、剥離層201を完全には除去せずに、画素電極210の下方に位置する剥離層を少なくとも一部分残す(図6(C))。剥離層をどのくらい残すかは、剥離層とエッチング剤の反応を考慮して、エッチング流量と反応時間を設定することによって制御することができる。剥離層201を残すことによって、剥離層201を除去した後も基板200から表示装置を構成する素子形成部215(以下素子形成部215と記す)が完全には離れずばらばらになるのを防止することができる。
Subsequently, an etchant is introduced into the
エッチング剤としては、剥離層と反応しやすいフッ化ハロゲン(ハロゲン間化合物)を含む気体または液体を使用することができる。例えば、剥離層201としてW膜を用いた場合には、Wとよく反応する三フッ化塩素ガス(ClF3)を用いることが好ましい。また、エッチング剤としては、この他にもCF4、SF6、NF3、F2等を用いてもよく、実施者が適宜選択すればよい。
As the etchant, a gas or liquid containing halogen fluoride (interhalogen compound) that easily reacts with the release layer can be used. For example, when a W film is used as the
また、開口部213の形成はレーザー光を照射することによって行うことができる。また、レーザー光を照射して開口部を形成した後に、エッチング剤を用いて剥離層を除去せず、剥離することも可能である。これは、レーザー光の照射によって剥離層が部分的に除去されているためである。
The
次に、基板200の反対側から第1のシート材214を絶縁膜212に接着させて、基板200から剥離層201を介して基板200上に設けられた素子形成部215を剥離する(図6(D))。第1のシート材214は、可撓性のフィルムからなっており、少なくとも素子形成部215と接する面に粘着剤が設けてある。例えば、ポリエステル等からなるベースフィルム上にアクリル樹脂等を含んだ粘着力が弱い粘着剤が設けてあるフィルムを用いることができる。
Next, the
次に、素子形成部215の第1のシート材214が接着している面と反対側の面を第2のシート材216に接着させて、第1のシート材214から素子形成部215を剥離する(図7(A))。
Next, the surface of the
続いて、画素電極210上に発光層217を選択的に形成する(図7(B))。発光層217は、液滴吐出法を用いて選択的に形成してもよいし、スクリーン印刷やグラビア印刷法を用いて形成してもよい。本実施の形態では、液滴吐出法を用いることによって選択的に発光層217を形成する。また、カラー表示可能な表示装置を形成する場合には、R、G、Bの3色を発光する発光層をそれぞれ選択的に形成する。このように、液滴吐出法や印刷法を用いて発光層を形成することによって、無駄な材料を減らすことができるためコストを削減することが可能となる。
Subsequently, a
また、強度等で問題がある場合には、発光層217を形成する前に開口部213に絶縁膜等を形成してもよい。この場合も、液滴吐出法を用いて選択的に絶縁膜を形成することができる。
In the case where there is a problem with strength or the like, an insulating film or the like may be formed in the
また、発光素子から発せられる光は、基板側に光が出射する上面出射と、その反対に光が出射する下面出射、一対の電極を透明材料、又は光を透過できる厚さで形成することで基板側とその反対の両方に光が出射する両面出射とがあり、いずれを適用してもよい。また、発光層217は、単層型、積層型、また層の界面がない混合型のいずれでもよい。さらに、発光層217は、シングレット材料、トリプレット材料、又はそれらを組み合わせた材料のいずれを用いてもよい。また、低分子材料、高分子材料及び中分子材料を含む有機材料、電子注入性に優れる酸化モリブデン等に代表される無機材料、有機材料と無機材料の複合材料のいずれを用いてもよい。
In addition, the light emitted from the light emitting element is formed by forming the upper surface emission from which light is emitted to the substrate side, the lower surface emission from which light is emitted, and a pair of electrodes with a transparent material or a thickness capable of transmitting light. There are two-sided emission in which light is emitted on both the substrate side and the opposite side, and either may be applied. The
その後、対向電極218を形成する(図7(B))。対向電極218も液滴吐出法を用いて導電体を含む組成物を吐出して選択的に形成することができる。また、対向電極218の材料としては、陽極として用いるか陰極として用いるかによって上記画素電極210の材料で示した材料のいずれかを用いることができる。また、対向電極218は全面に形成してもよく、この場合は、開口部213により対向電極に段切れ等が生じないようにあらかじめ開口部213に絶縁膜を充填しておくことが好ましい。絶縁膜としては、ポリイミド、ポリアミド、BCB(ベンゾシクロブテン)、アクリル、フェノール等の樹脂材料を用いることができる。
After that, the
続いて、第2のシート材216に接着している面とは反対側の素子形成部215の面に第3のシート材220を接着させると共に、素子形成部215を第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220により封止する(図7(C))。そうすると、素子形成部215は第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220により封止された状態となる。なお、発光層の耐水性等が懸念される場合には、封止を行う前に保護膜219を形成しておいてもよい。保護膜219は、発光層を外部の空気や水分と接触させないために形成する。そのため、保護膜219としては、エポキシ樹脂、アクリル樹脂、フェノール樹脂、ノボラック樹脂、アクリル樹脂、メラミン樹脂、ウレタン樹脂等の樹脂材料や撥液性の材料としてフッ素原子が含まれた樹脂や炭化水素のみで構成された樹脂等を用いることができる。より詳しくは、分子内にフッ素原子を含有するモノマーを含む樹脂、或いは全て炭素と水素原子のみから構成されるモノマーを含む樹脂が挙げられる。他にも、ベンゾシクロブテン、パリレン、フレア、透過性を有するポリイミドなどの有機材料、シロキサン樹脂等の重合によってできた化合物材料、水溶性ホモポリマーと水溶性共重合体を含む組成物等を用いることができる。他にも、無機材料で形成してもよい。
Subsequently, the
また、第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220は、可撓性のフィルムからなっており、例えばラミネートフィルムで形成することができる。具体的に、ここではポリエステル等のベースフィルム上にホットメルトフィルムが形成されたものを利用することができる。第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220を素子形成部215に接着するときに、加圧処理または加熱処理の一方または両方を行うことによって、短時間で接着することができる。また、第3のシート材の表面に対向電極を設けておくことによって、素子形成部215を封止する際に対向電極を併せて形成することができる。
Moreover, the
なお、本実施の形態において、剥離された基板200は再利用することができる。その結果、基板を用いた表示装置の作製において、同じ基板を繰り返して用いることが可能となるため、ガラス基板より原価の高い石英基板を用いた場合でも低コスト化を達成することができる。なお、基板を再利用する場合、剥離の工程において基板に傷が生成されないように制御するのが望ましい。しかし、傷が生成された場合であっても、有機樹脂や無機樹脂膜を塗布法や液滴吐出法によって形成したり、研削、研磨したりすることによって平坦化処理を行えばよい。
Note that in this embodiment mode, the peeled
以上の工程により、フィルム状表示装置が完成する。なお、本実施の形態では、電解発光層を用いた有機EL表示装置に関して例を示したが、これに限られず液晶表示装置や他の発光素子を用いる表示装置にも同じように適用することができる。液晶表示装置に上記工程を適用した場合について、図22に示す。まず、上述したように、剛性を有する基板上に液晶表示装置の一部を構成する素子形成部230を形成し、その後素子形成部230の一方の面に第1のシート材214を接着させて素子形成部230を基板から剥離する。なお、ここでは、基板上に素子形成部を形成する際に画素電極を覆うように配向膜271を形成しておく。次に、素子形成部230の他方の面に第2のシート材216を接着させて素子形成部230を第1のシート材214から剥離する(図22(A))。その後、加工手段によって、素子形成部230に液晶層および対向電極を形成する(図22(B))。なお、液晶層は、公知の方法を用いて形成すればよく、例えば滴下注入法等によって形成する。続いて、素子形成部230上に形成された液晶層219および対向電極229上に第3のシート材220を接着させて、第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220で封止することによって、液晶表示装置を形成することができる(図22(C))。液晶表示装置は、配向膜271、272の間に形成されており、液晶表示装置の上下に偏光板を設けることによって表示することができる。
The film display device is completed through the above steps. Note that in this embodiment mode, an example of an organic EL display device using an electroluminescent layer is shown; however, the present invention is not limited to this, and the present invention can be similarly applied to a display device using a liquid crystal display device or another light emitting element. it can. FIG. 22 shows the case where the above process is applied to a liquid crystal display device. First, as described above, the
また、本実施の形態を用いて作製したフィルム状表示装置は画素と画素の間に開口部213が形成されているため、完成したフィルム状表示装置を折り曲げ安くなっている。つまり、開口部213を設けることによって、折り曲げた際に画素にかかる圧力が減少するという利点を有している。なお、開口部213に曲がりやすい物質を充填することによっても同様の効果が得られる。曲がりやすい物質としては、ポリエチレン、酢酸ビニル、エチレン酢酸ビニル、ポリスチレン、ポリウレタン、ポリプロピレン、ポリフッ化ビニル、塩化ビニル、ポリエステル、ポリアミドまたはポリイミド等の有機材料を用いることができる。
In addition, since a film-like display device manufactured using this embodiment has an
なお、本実施の形態では、トップゲートの薄膜トランジスタに関して具体例を挙げて説明を行ったが、ボトムゲートの薄膜トランジスタを用いてもよい。また、アクティブマトリクス型に関して例を示したが、パッシブマトリクス型の構成を用いてもよい。また、画素領域に関して説明を行ったが、画素部を駆動するための駆動回路も同様に基板に形成し、画素領域と同時に剥離を行って可撓性基板上に設けてもよい。画素領域と駆動回路を接続するための配線は剥離前に形成しておいてもよいし、剥離後に可撓性基板に設けた後に加工手段を用いて形成してもよい。他にも駆動回路や画素領域を制御する回路等を別の基板に形成し、基板から剥離して可撓性基板にそれぞれ設けた後に、これらを電気的に接続する配線を形成してもよい。この場合、基板ごとによって、それぞれの構成を作り分けることができるため、効率的に表示装置を形成することができる。 Note that in this embodiment mode, a top gate thin film transistor is described using a specific example; however, a bottom gate thin film transistor may be used. Further, although an example has been shown regarding the active matrix type, a passive matrix type configuration may be used. Although the pixel region has been described, a driver circuit for driving the pixel portion may be formed over the substrate in the same manner, and may be peeled off at the same time as the pixel region and provided over the flexible substrate. Wiring for connecting the pixel region and the driver circuit may be formed before peeling, or may be formed using a processing means after being provided on the flexible substrate after peeling. In addition, a driver circuit, a circuit for controlling a pixel region, and the like may be formed over another substrate, separated from the substrate, provided on the flexible substrate, and then a wiring for electrically connecting them may be formed. . In this case, since each structure can be made for each substrate, a display device can be formed efficiently.
なお、本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせて行うことができる。 Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態3)
本実施の形態では、実施の形態2に示した表示装置の作製方法とは異なる形態に関して図面を用いて説明する。具体的には、実施の形態2とは異なる2通りの作製方法に関してそれぞれ図8、9と図10、11を用いて説明する。なお、上記実施の形態で示した図面と同じものを表す箇所は同様の符号を用いて示す。
(Embodiment 3)
In this embodiment, a mode different from the method for manufacturing the display device described in Embodiment 2 will be described with reference to drawings. Specifically, two kinds of manufacturing methods different from those in Embodiment Mode 2 will be described with reference to FIGS. Note that parts that are the same as those shown in the above embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals.
図8、図9に示す例では、はじめに基板200上に、剥離層201、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203、半導体膜204、ゲート絶縁膜205等の表示装置を構成する一部を設けて基板200から剥離を行う。その後剥離したものを可撓性基板に移し替え、ゲート電極、層間絶縁膜、ソースまたはドレイン電極、配線、画素電極、発光層、対向電極等の表示装置を構成する残りの部分を形成する。以下に具体的な作製方法に関して説明する。なお、本実施の形態において特に示さない限り、用いる材料については上記実施の形態2で示したものと同じ材料を用いるものとする。
In the example shown in FIGS. 8 and 9, first, a display device including a
まず、基板200上に剥離層201、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203、半導体膜204およびゲート絶縁膜205を形成し、その後にエッチング剤を導入する開口部231を形成する(図8(A))。開口部231は、半導体膜や後に形成される配線や電極を避け、後に形成される画素部と画素部の間に形成する。
First, a
続いて、エッチング剤を導入して剥離層201を除去する。剥離層201を完全に除去してもよいが、ここでは基板200から表示装置を構成する素子形成部232(以下素子形成部232と記す)が剥がれてしまわないように、剥離層201を完全には除去せずに一部を残しておく(図8(B))。
Subsequently, the
次に、第1のシート材214を素子形成部232の表面のゲート絶縁膜205に接着させて、基板200上に一部の剥離層を介して接続されている素子形成部232を基板200から剥離する(図8(C))。
Next, the
続いて、第2のシート材216を素子形成部232の第1のシート材214が接着している面と反対側の面に接着させて、薄膜である素子形成部232を第1のシート材214から剥離する(図8(D))。このように、2回の剥離を行うことによって、基板200を可撓性を有する基板に置き換えることができる。なお、2回の剥離のうち、1回目の剥離に用いる第1のシート材は素子形成部232に接着した後に再度剥がすため、粘着力が弱いものを用いるのが好ましい。
Subsequently, the
その後、第2のシート材216上に設けられた素子形成部232に、ゲート電極233、層間絶縁膜234、ソースまたはドレイン電極235、236、配線237、画素電極238、発光層217、対向電極218を形成していく(図9(A)〜(D))。
After that, the
図9(A)では、液滴吐出法によって選択的にゲート電極233を形成する。ゲート電極としては、Ag、Au、Cu、Pd等の金属、金属化合物を1つまたは複数有する導電性材料を用いる。なお、分散剤により凝集を抑え、溶液に分散させることができるならば、Cr、Mo、Ti、Ta、W、Al等の金属、金属化合物を1つまたは複数有する導電材料を用いることも可能である。また、液滴吐出法による導電材料の吐出を複数回行うことで、複数の導電膜が積層されたゲート電極を形成することも可能である。但し、ノズル孔吐出する組成物は、比抵抗値を考慮して、Au、Ag、Cuのいずれかの材料を溶媒に溶解または分散させたものを用いることが好適であり、より好適には低抵抗なAg、Cuを用いるとよい。但し、Ag、Cuを用いる場合には、不純物対策のため、合わせてバリア膜を設けるとよい。バリア膜としては、窒化珪素膜やニッケルボロン(NiB)を用いることができる。
In FIG. 9A, the
次に、ゲート電極233を覆って層間絶縁膜234を形成する(図9(B))。ここでは、液滴吐出法を用いて絶縁体を溶媒に溶解または分散させたものを吐出して選択的に層間絶縁膜234を形成する。そして、選択的に形成した層間絶縁膜234をマスクとして用いることによってゲート絶縁膜205をエッチングして、半導体膜204に形成されたソースまたはドレイン領域に達するコンタクトホールを形成する。
Next, an
吐出する絶縁体としては、エポキシ樹脂、アクリル樹脂、フェノール樹脂、ノボラック樹脂、アクリル樹脂、メラミン樹脂、ウレタン樹脂等の樹脂材料を用いることができる。なお、これらの樹脂材料を用いる場合、その粘度は、溶媒を用いて溶解又は分散することで調整するとよい。また、撥液性の材料としてフッ素原子が含まれた樹脂や炭化水素のみで構成された樹脂等を用いることができる。より詳しくは、分子内にフッ素原子を含有するモノマーを含む樹脂、或いは全て炭素と水素原子のみから構成されるモノマーを含む樹脂が挙げられる。他にも、ベンゾシクロブテン、パリレン、フレア、透過性を有するポリイミドなどの有機材料、シロキサン樹脂等の重合によってできた化合物材料、水溶性ホモポリマーと水溶性共重合体を含む組成物等を用いることができる。有機材料を用いると、その平坦性が優れているため、後に導電体を成膜した際にも、段差部で膜厚が極端に薄くなったり、断線が起こったりすることがなく、好適である。但し、有機材料は、脱ガス発生の防止のため、下層と上層に珪素を含む無機材料で薄膜を形成するとよい。 As the insulator to be discharged, a resin material such as an epoxy resin, an acrylic resin, a phenol resin, a novolac resin, an acrylic resin, a melamine resin, or a urethane resin can be used. In addition, when using these resin materials, the viscosity is good to adjust by melt | dissolving or disperse | distributing using a solvent. Further, as the liquid repellent material, a resin containing a fluorine atom, a resin composed only of hydrocarbon, or the like can be used. More specifically, a resin containing a monomer containing a fluorine atom in the molecule, or a resin containing a monomer composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms can be given. In addition, organic materials such as benzocyclobutene, parylene, flare, permeable polyimide, compound materials made by polymerization of siloxane resins, compositions containing water-soluble homopolymers and water-soluble copolymers, etc. are used. be able to. When an organic material is used, the flatness thereof is excellent, and therefore, even when a conductor is formed later, the film thickness is not extremely reduced at the stepped portion, and disconnection does not occur. . However, the organic material may be formed as a thin film of an inorganic material containing silicon in the lower layer and the upper layer in order to prevent outgassing.
次に、半導体膜204のソースまたはドレイン領域と電気的に接続されるソースまたはドレイン電極235、346、配線237、画素電極238を形成する(図9(C))。ここでは、これらの電極または配線を液滴吐出法によって選択的に形成する。ソースまたはドレイン電極235、236や配線237としては、上記ゲート電極233で示した材料のいずれかを用いて形成することができる。
Next, source or drain
その後、隔壁(土手)として機能する絶縁膜239を形成し、発光層217、対向電極218を形成して(図9(D))、その後、図7(C)のように第2のシート材と第3のシート材で封止する。絶縁膜239も液滴吐出法を用いることによって選択的に形成することができる。また絶縁膜239の材料は、上記絶縁膜234で示した材料のいずれかを用いることができる。また、対向電極218は全面に形成してもよい。
After that, an insulating
このように、液滴吐出法を用いて電極や配線や絶縁膜を形成することによって、材料の利用効率を向上させ、低コストで作製することが可能となる。なお、ここでは、ゲート電極、絶縁膜、配線、画素電極等を液滴吐出法で形成したが、他にもスクリーン印刷法やグラビア印刷法等の各種印刷法や大気圧プラズマ装置を用いることによって形成してもよい。 In this manner, by forming an electrode, a wiring, or an insulating film by using a droplet discharge method, it is possible to improve the utilization efficiency of the material and to manufacture at a low cost. Here, the gate electrode, the insulating film, the wiring, the pixel electrode, and the like are formed by a droplet discharge method, but by using various printing methods such as a screen printing method and a gravure printing method and an atmospheric pressure plasma apparatus. It may be formed.
次に、図8、9で示した具体例とは異なる作製方法に関して図10、11を用いて説明する。 Next, a manufacturing method different from the specific example shown in FIGS. 8 and 9 will be described with reference to FIGS.
図10に示す例では、はじめに基板200上に、剥離層201、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203、半導体膜204、ゲート絶縁膜205、ゲート電極206、層間絶縁膜207等を設けて基板200から剥離を行う。その後剥離したものを可撓性基板に移し替え、ソースまたはドレイン電極、配線、画素電極、発光層、対向電極等を形成する。以下に具体的な作製方法に関して説明する。
In the example shown in FIG. 10, first, a
まず、基板200上に、剥離層201、第1の絶縁膜202、第2の絶縁膜203、半導体膜204およびゲート絶縁膜205、ゲート電極206、層間絶縁膜207を形成する(図10(A))。
First, the
その後、エッチング剤を導入する開口部241および半導体層204のソース領域またはドレイン領域に達するコンタクトホール242を同時に形成する。開口部241は、半導体膜や後に形成される配線や電極を避けた部分に形成するのが好ましい。
After that, an
続いて、エッチング剤を導入して剥離層201を除去する。剥離層201を完全に除去してもよいが、ここでは基板200から表示装置を構成する素子形成部243(以下素子形成部243と記す)が剥がれてしまわないように、剥離層201を完全には除去せずに一部を残しておく(図10(B))。
Subsequently, the
次に、第1のシート材214を素子形成部243の一方の面(層間絶縁膜207表面)に接着させて、素子形成部243を基板200から剥離する(図10(C))。
Next, the
続いて、第2のシート材216を素子形成部243の第1のシート材214が接着している面と反対側の面に接着させて、薄膜素子形成部243を第1のシート材214から剥離する(図10(D))。このように、2回の剥離を行うことによって、基板200を可撓性を有する基板に置き換えることができる。なお、2回の剥離のうち、1回目の剥離に用いる第1のシート材は素子形成部232に接着した後に再度剥がすため、粘着力が弱いものを用いるのが好ましい。
Subsequently, the
その後、図11(A)〜(C)に示すように、ソースまたはドレイン電極235、236、配線237、画素電極238、発光層217、対向電極218を形成し、その後、第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220とで封止することによってフィルム状の表示装置を完成することができる。なお、発光層217を形成する前に、開口部241に絶縁膜等を形成し、画素領域の全面に発光層を形成してもよい。
Thereafter, as shown in FIGS. 11A to 11C, source or drain
以上のように、剥離を行う前に基板上に表示装置の一部を形成する際にどの部分の構成を作製するかに関して2つの具体例を挙げて説明を行ったが、これに限られず剥離する前にどのような構成を設けもよい。 As described above, two specific examples have been described as to which part of the display device is to be formed when part of the display device is formed on the substrate before peeling, but the present invention is not limited to this. Any configuration may be provided before the operation.
なお、本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせて行うことができる。 Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態4)
本実施の形態では、別の基板にそれぞれ設けた表示装置をつなぎ合わせて一つの表示装置を形成する場合について説明する。具体的には、複数の基板にそれぞれ表示装置を構成する一部を設けた後に基板を配置して、その後複数の基板に設けられた表示装置を構成する一部を基板から剥離して残りの表示装置の部分を形成することによって一つの表示装置を作製する。以下に図面を用いて説明する。なお、上記実施の形態で示した図面と同じものを表す箇所は同様の符号を用いて示す。
(Embodiment 4)
In this embodiment, the case where one display device is formed by connecting display devices provided over different substrates is described. Specifically, after a part of each of the plurality of substrates constituting the display device is provided, the substrate is arranged, and then a part of the display device provided on the plurality of substrates is peeled off from the substrate and the rest One display device is manufactured by forming a portion of the display device. This will be described below with reference to the drawings. Note that parts that are the same as those shown in the above embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals.
はじめに、図12(A)に示すように、2つの異なる基板300a、300bにそれぞれ設けられた画素領域351a、351bをつなぎ合わせる場合の画素領域の構成について、図13、図14に示す。
First, as illustrated in FIG. 12A, FIGS. 13 and 14 illustrate a configuration of a pixel region in a case where
まず、上記実施の形態で示したように、図6(C)と同様の構成をそれぞれ基板300a、300b上に設ける(図13(A))。なお、図12(B)のA−B間の断面図が図13(A)のA−B間に対応している。
First, as shown in the above embodiment mode, the same structure as that in FIG. 6C is provided over the
続いて、CCDカメラ等の制御手段を用いて、基板300aと基板300bを配置させて、基板300aと基板300bを接着剤356でつなぎ合わせる(図13(B))。ここで接着剤356は基板300a、300bにのみ接着し、基板300a、300bに設けられた表示装置を構成する素子形成部215a、215b(以下素子形成部215a、215bと記す)には接着しないようにする。この時、基板300aと基板300bとの間に間隔(以下接続間隔355と記す)が生じる。接続間隔355が後に形成される表示装置の画素と画素の間に位置するように基板300a上と基板300b上に形成する素子形成部の位置を調整する。なお、基板300a、300bが固定されてずれる恐れがない場合には、接着剤を用いずに配置させてもよい。また、基板の端部を削ってつなぎ合わせてもよい。基板300aと基板300bの接続の関係上、接続間隔355は、基板300aにおける画素電極間または基板300bにおける画素電極間より大きくなるように設けてもよいが、なるべく基板300aにおける画素電極間または基板300bにおける画素電極間と同じくなるように設けることが好ましい。
Subsequently, using a control means such as a CCD camera, the
その後、基板300aおよび基板300b上に設けられた素子形成部215a、215bの表面に第1のシート材214を接着させて、素子形成部215a、215bを基板300a、300bから剥離する(図13(C))。
Thereafter, the
続いて、素子形成部215a、215bの第1のシート材214に接着した面と反対側の面に、第2のシート材216を接着させて、第1のシート材214に接着した素子形成部215a、215bを剥離する(図13(D))。
Subsequently, the element forming portion bonded to the
その後、上記実施の形態で示したように、発光層217および対向電極218を形成する(図14(A))。また、この時、開口部213および接続間隔355に絶縁膜等を選択的に形成してもよい。このように、開口部213および接続間隔355に同じ物質を充填することによって、異なる基板を接続した際に生じる境目を目立たなくすることができる。
After that, as described in the above embodiment mode, the light-emitting
次に、発光層217および対向電極218を形成した素子形成部を第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220を用いて封止することによって、フィルム状表示装置が完成する(図14(B))。なお、上述したように、第3のシート材を接着させる前に、対向電極218上に保護膜219を形成することが好ましい。この際開口部213と接続間隔355に何も形成されていない場合には、開口部213と接続間隔355に保護膜を充填するように形成する。
Next, the element forming portion in which the
一般的に、複数の表示装置をつなげ合わせることによって一つの表示装置を形成する場合には、つなげ合わせる基板間に間隔(境目)が生じるため画像を表示する際にその境目が欠陥として目立つという問題がある。しかし、本実施の形態においては、接続間隔355を画素と画素の間(ここでは開口部213)と同じ幅になるように制御してつなぎ合わせることによって境目を目立たなくすることができる。さらに、異なる2つの基板300a、300bを貼り合わせた後に、基板から基板上に形成された表示装置の一部を剥離し、新たに可撓性基板上に設け、当該可撓性基板を共通の基板として設けるため、より境目を目立たなくすることが可能となる。
In general, when a single display device is formed by connecting a plurality of display devices, a gap (border) is generated between the substrates to be connected, and the boundary is conspicuous as a defect when displaying an image. There is. However, in this embodiment, the boundary can be made inconspicuous by controlling and connecting the
このように、2つの基板に別途設けた表示装置をつなげ合わせて1つの表示装置を形成することによって、大型のフィルム状表示装置を形成することが可能となる。 In this manner, a large film display device can be formed by connecting one display device separately provided on two substrates to form one display device.
なお、ここでは、基板上に隔壁まで形成した後に剥離する例(図6、7に対応)を示したが、図8〜図11に示した構成にも同じように適用することが可能である。 Here, an example (corresponding to FIGS. 6 and 7) in which a partition wall is formed on a substrate and then peeled is shown, but the present invention can be similarly applied to the configurations shown in FIGS. .
次に、図15に示すように別の基板450a〜450dにそれぞれ設けられた画素領域451a〜451dをつなぎ合わせる場合の画素領域の構成について、図16、図17に示す。なお、ここでは、画素領域451bと画素領域451dの接続部分に関して具体的に説明する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 15, FIGS. 16 and 17 illustrate a configuration of a pixel region in a case where
まず、上記実施の形態で示したように、図10(B)と同様の構成を基板450a〜450b上に設ける(図16(A))。その後、CCDカメラ等の制御手段を用いて、基板450a〜450dを精確に配置させ、それぞれ隣り合った基板を接着剤456でつなぎ合わせる(図16(B))。ここで接着剤456は基板450a〜450dにのみ接着し、基板450a〜450b上に設けられた表示装置を構成する素子形成部243a〜243dには接着しないようにする。
First, as shown in the above embodiment mode, a structure similar to that in FIG. 10B is provided over the
次に、基板450a〜450d上に設けられた素子形成部243a〜243dの表面に第1のシート材214を接着させて、素子形成部243a〜243dを基板450a〜450dから剥離する(図16(C))。
Next, the
続いて、素子形成部243a〜243dの第1のシート材214に接着した面と反対側の面に、第2のシート材216を接着させて、第1のシート材214に接着した素子形成部243a〜243dを剥離する(図16(D))。
Subsequently, the element forming portion bonded to the
次に、第2のシート材216上に設けられた素子形成部243a〜243dに、加工手段を用いてソースまたはドレイン電極、配線、画素電極、発光層、対向電極等を形成していく。
Next, a source or drain electrode, a wiring, a pixel electrode, a light emitting layer, a counter electrode, and the like are formed on the element formation portions 243a to 243d provided on the
まず、それぞれの基板をつなげ合わせた際に隣り合う素子形成部243a〜243d間に形成された接続間隔455に絶縁物を形成する(図17(A))。ここでは、液滴吐出法を用いて接続間隔455に選択的に絶縁体を含む組成物を吐出して絶縁膜457を形成する。吐出する絶縁体としては、エポキシ樹脂、アクリル樹脂、フェノール樹脂、ノボラック樹脂、アクリル樹脂、メラミン樹脂、ウレタン樹脂等の樹脂材料を用いることができる。なお、これらの樹脂材料を用いる場合、その粘度は、溶媒を用いて溶解又は分散することで調整するとよい。また、撥液性の材料としてフッ素原子が含まれた樹脂や炭化水素のみで構成された樹脂等を用いることができる。より詳しくは、分子内にフッ素原子を含有するモノマーを含む樹脂、或いは全て炭素と水素原子のみから構成されるモノマーを含む樹脂が挙げられる。他にも、ベンゾシクロブテン、パリレン、フレア、透過性を有するポリイミドなどの有機材料、シロキサン樹脂等の重合によってできた化合物材料、水溶性ホモポリマーと水溶性共重合体を含む組成物等を用いることができる。有機材料を用いると、その平坦性が優れているため、後に導電体を成膜した際にも、段差部で膜厚が極端に薄くなったり、断線が起こったりすることがなく、好適である。
First, an insulator is formed in the
次に、ソースまたはドレイン電極235、236、配線237および画素電極238を形成する(図17(B))。この場合、ソースまたはドレイン電極235、236、配線237および画素電極238は絶縁膜457上に形成される。そのため、層間絶縁膜207と絶縁膜457にわずかな凹凸の段差がある場合には、絶縁膜457上に形成されるソースまたはドレイン電極235、236、配線237および画素電極238も同様に凹部または凸部の段差を有する。
Next, source or drain
図16、17では、異なる基板の端部にそれぞれ形成された素子形成部に共通して画素電極が形成される。そのため、複数の表示装置をつなげ合わせた場合であっても、境目を目立たなくすることができる。 In FIGS. 16 and 17, pixel electrodes are formed in common in element formation portions formed at the end portions of different substrates. Therefore, even when a plurality of display devices are connected, the boundary can be made inconspicuous.
その後、上記実施の形態で示したように、隔壁(土手)239、発光層217および対向電極218を形成し(図17(C))、第2のシート材216と第3のシート材220で封止することによって、フィルム状表示装置が完成する(図17(D))。
After that, as shown in the above embodiment mode, a partition wall (bank) 239, a
また、画素部451aと451bまたは451cと451dの接続部に関しては、上述した方法を用いて接続することができる。
In addition, connection portions of the
なお、本実施の形態では、画素領域を貼り合わせて作製する方法について示したが、画素領域を貼り合わせる場合に限定されず、画素領域と駆動回路または画素領域を制御する回路(制御回路)を形成する場合にも適用することができる。つまり、画素領域と駆動回路または制御回路を別々の基板にあらかじめ形成しておき、それぞれ基板から剥離して共通の可撓性を有する基板上に形成することができる。この場合、画素領域と駆動回路または制御回路とを接続する配線も可撓性を有する基板上に設けた後に形成することができる。 Note that although a method for manufacturing a pixel region by bonding is described in this embodiment mode, the present invention is not limited to the case where the pixel region is bonded, and a circuit (control circuit) that controls the pixel region and the driver circuit or the pixel region is provided. The present invention can also be applied when forming. In other words, the pixel region and the driver circuit or the control circuit can be formed over different substrates in advance, and can be formed on a substrate having common flexibility by being peeled from the substrate. In this case, a wiring for connecting the pixel region to the driver circuit or the control circuit can be formed after being provided over the flexible substrate.
以上のように、本実施の形態を用いることによって、複数の基板をつなげ合わせることが可能となり、大型のフィルム状表示装置が作製できる。 As described above, by using this embodiment mode, a plurality of substrates can be connected to each other, and a large film display device can be manufactured.
なお、本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせて行うことができる。 Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態5)
本実施の形態では、発光素子の構成について図18を用いて説明する。
(Embodiment 5)
In this embodiment, the structure of the light-emitting element is described with reference to FIGS.
図18に示す発光素子は、基板500上に形成された第1の電極501と、第1の電極501上に形成された電界発光層502と、電界発光層502上に形成された第2の電極503とを有する。なお実際には、基板500と第1の電極501の間には、各種の層または半導体素子などが設けられている。
18 includes a
本実施の形態では、第1の電極501が陽極、第2の電極が陰極の場合について説明するが、第1の電極501が陰極、第2の電極が陽極であっても良い。
In this embodiment, the case where the
電界発光層502は単数または複数の層で構成されている。複数の層で構成されている場合、これらの層は、キャリア輸送特性の観点から正孔注入層、正孔輸送層、発光層、電子輸送層、電子注入層などに分類することができる。なお各層の境目は必ずしも明確である必要はなく、互いの層を構成している材料が一部混合し、界面が不明瞭になっている場合もある。各層には、有機系の材料、無機系の材料を用いることが可能である。有機系の材料として、高分子系、中分子系、低分子系のいずれの材料も用いることが可能である。なお中分子系の材料とは、構造単位の繰返しの数(重合度)が2から20程度の低重合体に相当する。
The
正孔注入層と正孔輸送層との区別は必ずしも厳密なものではなく、これらは正孔輸送性(正孔移動度)が特に重要な特性である意味において同じである。便宜上正孔注入層は陽極に接する側の層であり、正孔注入層に接する層を正孔輸送層と呼んで区別する。電子輸送層、電子注入層についても同様であり、陰極に接する層を電子注入層と呼び、電子注入層に接する層を電子輸送層と呼んでいる。発光層は電子輸送層を兼ねる場合もあり、発光性電子輸送層とも呼ばれる。図18では、第1〜第5の層504〜508を電界発光層502が有している場合を例示している。第1〜第5の層504〜508は、第1の電極501から第2の電極503に向かって順に積層されている。
The distinction between a hole injection layer and a hole transport layer is not necessarily strict, and these are the same in the sense that hole transportability (hole mobility) is a particularly important characteristic. For convenience, the hole injection layer is a layer in contact with the anode, and the layer in contact with the hole injection layer is referred to as a hole transport layer to be distinguished. The same applies to the electron transport layer and the electron injection layer. The layer in contact with the cathode is called an electron injection layer, and the layer in contact with the electron injection layer is called an electron transport layer. The light emitting layer may also serve as an electron transport layer, and is also referred to as a light emitting electron transport layer. FIG. 18 illustrates the case where the
第1の層504は、正孔注入層として機能するため、正孔輸送性を有し、なおかつイオン化ポテンシャルが比較的小さく、正孔注入性が高い材料を用いるのが望ましい。大別すると金属酸化物、低分子系有機化合物、および高分子系有機化合物に分けられる。金属酸化物であれば、例えば、酸化バナジウム、酸化モリブデン、酸化ルテニウム、酸化アルミニウムなど用いることができる。低分子系有機化合物あれば、例えば、m−MTDATAに代表されるスターバースト型アミン、銅フタロシアニン(略称:Cu−Pc)に代表される金属フタロシアニン、フタロシアニン(略称:H2−Pc)、2,3−ジオキシエチレンチオフェン誘導体などを用いることができる。低分子系有機化合物と上記金属酸化物とを共蒸着させた膜であっても良い。高分子系有機化合物であれば、例えば、ポリアニリン(略称:PAni)、ポリビニルカルバゾール(略称:PVK)、ポリチオフェン誘導体などの高分子を用いることができる。ポリチオフェン誘導体の一つであるポリエチレンジオキシチオフェン(略称:PEDOT)にポリスチレンスルホン酸(略称:PSS)をドープしたものを用いても良い。また、ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体と、TCQn、FeCl3、C60またはF4TCNQのいずれか一または複数の材料とを併せて用いても良い。
Since the
第2の層505は、正孔輸送層として機能するため、正孔輸送性が高く、結晶性の低い公知の材料を用いることが望ましい。具体的には芳香族アミン系(すなわち、ベンゼン環−窒素の結合を有するもの)の化合物が好適であり、例えば、4,4−ビス[N−(3−メチルフェニル)−N−フェニルアミノ]ビフェニル(TPD)や、その誘導体である4,4’−ビス[N−(1−ナフチル)−N−フェニル−アミノ]ビフェニル(α−NPD)などがある。4,4’,4’’−トリス(N,N−ジフェニルアミノ)トリフェニルアミン(TDATA)や、MTDATAなどのスターバースト型芳香族アミン化合物も用いることができる。また4,4’,4’’−トリス(N−カルバゾリル)トリフェニルアミン(略称:TCTA)を用いても良い。また高分子材料としては、良好な正孔輸送性を示すポリ(ビニルカルバゾール)(略称:PVK)などを用いることができる。
Since the
第3の層506は発光層として機能するため、イオン化ポテンシャルが大きく、かつバンドギャップの大きな材料を用いるのが望ましい。具体的には、例えば、トリス(8−キノリノラト)アルミニウム(Alq3)、トリス(4−メチル−8−キノリノラト)アルミニウム(Almq3)、ビス(10−ヒドロキシベンゾ[η]−キノリナト)ベリリウム(BeBq2)、ビス(2−メチル−8−キノリノラト)−(4−ヒドロキシ−ビフェニリル)−アルミニウム(BAlq)、ビス[2−(2−ヒドロキシフェニル)−ベンゾオキサゾラト]亜鉛(Zn(BOX)2)、ビス[2−(2−ヒドロキシフェニル)−ベンゾチアゾラト]亜鉛(Zn(BTZ)2)などの金属錯体を用いることができる。また、各種蛍光色素(クマリン誘導体、キナクリドン誘導体、ルブレン、ジシアノメチレン誘導体、1−ピロン誘導体、スチルベン誘導体、各種縮合芳香族化合物など)も用いることができる。白金オクタエチルポルフィリン錯体、トリス(フェニルピリジン)イリジウム錯体、トリス(ベンジリデンアセトナート)フェナントレンユーロピウム錯体などの燐光材料も用いることができる。
Since the
また、第3の層506に用いるホスト材料としては、上述した例に代表されるホール輸送材料や電子輸送材料を用いることができる。また、4,4’−N,N’−ジカルバゾリルビフェニル(略称:CBP)などのバイポーラ性の材料も用いることができる。
As the host material used for the
第4の層507は電子輸送層として機能するため、電子輸送性の高い材料を用いることが望ましい。具体的には、Alq3に代表されるような、キノリン骨格またはベンゾキノリン骨格を有する金属錯体やその混合配位子錯体などを用いることができる。具体的には、Alq3、Almq3、BeBq2、BAlq、Zn(BOX)2、Zn(BTZ)2などの金属錯体が挙げられる。さらに、金属錯体以外にも、2−(4−ビフェニリル)−5−(4−tert−ブチルフェニル)−1,3,4−オキサジアゾール(PBD)、1,3−ビス[5−(p−tert−ブチルフェニル)−1,3,4−オキサジアゾール−2−イル]ベンゼン(OXD−7)などのオキサジアゾール誘導体、3−(4−tert−ブチルフェニル)−4−フェニル−5−(4−ビフェニリル)−1,2,4−トリアゾール(TAZ)、3−(4−tert−ブチルフェニル)−4−(4−エチルフェニル)−5−(4−ビフェニリル)−1,2,4−トリアゾール(p−EtTAZ)などのトリアゾール誘導体、TPBIのようなイミダゾール誘導体、バソフェナントロリン(BPhen)、バソキュプロイン(BCP)などのフェナントロリン誘導体を用いることができる。
Since the
第5の層508は電子注入層として機能するため、電子注入性の高い材料を用いるのが望ましい。具体的には、LiF、CsFなどのアルカリ金属ハロゲン化物や、CaF2のようなアルカリ土類ハロゲン化物、Li2Oなどのアルカリ金属酸化物のような絶縁体の超薄膜がよく用いられる。また、リチウムアセチルアセトネート(略称:Li(acac)や8−キノリノラト−リチウム(略称:Liq)などのアルカリ金属錯体も有効である。また、モリブデン酸化物(MoOx)やバナジウム酸化物(VOx)、ルテニウム酸化物(RuOx)、タングステン酸化物(WOx)等(x>0)の金属酸化物またはベンゾオキサゾール誘導体と、アルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、または遷移金属のいずれか一または複数の材料とを含むようにしても良い。また酸化チタンを用いていても良い。
Since the
上記構成を有する発光素子において、第1の電極501と第2の電極503の間に電圧を印加し、電界発光層502に順方向バイアスの電流を供給することで、第3の層506から光を発生させ、該光を第1の電極501側から、または第2の電極503側から取り出すことができる。なお、電界発光層502は、必ずしもこれら第1〜第5の層を全て有している必要はない。本発明では、少なくとも発光層として機能する第3の層506を有していれば良い。また必ずしも第3の層506からのみ発光が得られるわけではなく、第1〜第5の層に用いられる材料の組み合わせによっては、第3の層506以外の層から発光が得られる場合もある。また、第3の層506と第4の層507の間に正孔ブロック層を設けても良い。
In the light-emitting element having the above structure, light is applied from the
なお色によっては、燐光材料の方が蛍光材料よりも、駆動電圧を低くすることができ、信頼性も高い場合がある。そこで、三原色(R、G、B)の各色に対応する発光素子を用いて、フルカラーの表示を行なう場合は、蛍光材料を用いた発光素子と、燐光材料を用いた発光素子とを組み合わせて、各色の発光素子における劣化の度合いを揃えるようにしても良い。 Note that depending on the color, the phosphorescent material can have a lower driving voltage and higher reliability than the fluorescent material. Therefore, when performing full color display using light emitting elements corresponding to the three primary colors (R, G, B), a combination of a light emitting element using a fluorescent material and a light emitting element using a phosphorescent material, You may make it arrange | equalize the degree of deterioration in the light emitting element of each color.
図18では、第1の電極501が陽極、第2の電極503が陰極である場合について示しているが、第1の電極501が陰極、第2の電極503が陽極である場合、第1〜第5の層504〜508は逆に積層される。具体的には、第1の電極501上に第5の層508、第4の層507、第3の層506、第2の層505、第1の層504が順に積層される。
FIG. 18 illustrates the case where the
なお電界発光層502のうち、第2の電極503に最も近い層(本実施の形態では第5の層508)に、エッチングされにくい材料を用いることで、電界発光層502上に第2の電極503をスパッタ法で形成する際に、第2の電極503に最も近い層に与えられるスパッタダメージを軽減させることができる。エッチングされにくい材料とは、例えばモリブデン酸化物(MoOx)やバナジウム酸化物(VOx)、ルテニウム酸化物(RuOx)、タングステン酸化物(WOx)等(x>0)の金属酸化物、またはベンゾオキサゾール誘導体、金属薄膜を用いることができる。これらは蒸着法によって形成されることが好ましい。
Note that a material that is difficult to be etched is used for the layer closest to the
例えば、第1の電極が陰極、第2の電極が陽極の場合、前記電界発光層のうち最も陽極に近い、ホール注入性またはホール輸送性を有する層として、上述したエッチングされにくい材料を用いる。具体的に、ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体を用いる場合は、当該ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体と、TCQn、FeCl3、C60またはF4TCNQのいずれか一または複数の材料とを含む層を、最も陽極に近くなるように形成する。 For example, in the case where the first electrode is a cathode and the second electrode is an anode, the above-described material that is not easily etched is used as the layer having hole injecting property or hole transporting property that is closest to the anode among the electroluminescent layers. Specifically, when a benzoxazole derivative is used, a layer including the benzoxazole derivative and any one or more materials of TCQn, FeCl 3 , C 60, or F 4 TCNQ is positioned closest to the anode. Form.
また例えば、第1の電極が陽極、第2の電極が陰極の場合、前記電界発光層のうち最も陰極に近い、電子注入性または電子輸送性を有する層として、上述したエッチングされにくい材料を用いる。具体的に、モリブデン酸化物を用いる場合は、当該モリブデン酸化物と、アルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、または遷移金属のいずれか一または複数の材料とを含む層を、最も陰極に近くなるように形成する。またベンゾオキサゾール誘導体を用いる場合は、当該ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体と、アルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、または遷移金属のいずれか一または複数の材料とを含む層を、最も陰極に近くなるように形成する。なお、金属酸化物とベンゾオキサゾール誘導体を共に用いていても良い。 In addition, for example, when the first electrode is an anode and the second electrode is a cathode, the above-described material that is not etched easily is used as the layer having the electron injecting property or the electron transporting property closest to the cathode among the electroluminescent layers. . Specifically, in the case of using molybdenum oxide, a layer containing the molybdenum oxide and one or more materials of alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, or transition metal is closest to the cathode. Form. In the case of using a benzoxazole derivative, a layer including the benzoxazole derivative and one or more materials of an alkali metal, an alkaline earth metal, or a transition metal is formed so as to be closest to the cathode. Note that a metal oxide and a benzoxazole derivative may be used together.
上記構成により、第2の電極として、スパッタ法で形成した透明導電膜、例えばインジウム錫酸化物(ITO)や珪素を含有したインジウム錫酸化物(ITSO)、酸化インジウムに2〜20atomic%の酸化亜鉛(ZnO)を混合したIZO(Indium Zinc Oxide)等を用いても、電界発光層が有する有機物を含む層への、スパッタダメージを抑えることができ、第2の電極を形成するための物質の選択性が広がる。 With the above structure, as the second electrode, a transparent conductive film formed by sputtering, for example, indium tin oxide (ITO), indium tin oxide containing silicon (ITSO), indium oxide with 2 to 20 atomic% of zinc oxide Even when IZO (Indium Zinc Oxide) mixed with (ZnO) or the like is used, sputter damage to a layer containing an organic substance included in the electroluminescent layer can be suppressed, and selection of a material for forming the second electrode Sex spreads.
なお、本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせることができる。 Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態6)
表示機能を有する本発明の表示装置の画素部の回路について、図19を用いて説明する。図19(A)は、画素の等価回路図を示したものであり、該画素は、信号線6114、電源線6115、6117、走査線6116の各配線で囲まれた領域に、画素6101に対するビデオ信号の入力を制御するTFT6110、発光素子6113の両電極間に流れる電流値を制御するTFT6111、該TFT6111のゲート・ソース間電圧を保持する容量素子6112を有する。なお、図19(B)では、容量素子6112を図示したが、TFT6111のゲート容量や他の寄生容量で賄うことが可能な場合には、設けなくてもよい。
(Embodiment 6)
A circuit of a pixel portion of the display device of the present invention having a display function will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 19A shows an equivalent circuit diagram of a pixel. The pixel is a video signal for the pixel 6101 in an area surrounded by
図19(B)は、図19(A)に示した画素に、TFT6118と走査線6119を新たに設けた構成の画素回路である。TFT6118の配置により、強制的に発光素子6113に電流が流れない状態を作ることができるため、全ての画素に対する信号の書き込みを待つことなく、書き込み期間の開始と同時または直後に点灯期間を開始することができる。従って、デューティ比が向上して、動画の表示は特に良好に行うことができる。
FIG. 19B illustrates a pixel circuit in which a
図19(C)は、図19(B)に示した画素6101のTFT6111を削除して、新たにTFT6125、6126と、配線6127を設けた画素回路である。本構成では、TFT6125のゲート電極を一定の電位に保持した配線6127に接続することにより、このゲート電極の電位を固定し、なおかつ飽和領域で動作させる。また、TFT6125と直列に接続させ、線形領域で動作するTFT6126のゲート電極には、TFT6110を介して、画素の点灯または非点灯の情報を伝えるビデオ信号を入力する。線形領域で動作するTFT6126のソース・ドレイン間電圧の値は小さいため、TFT6126のゲート・ソース間電圧のわずかな変動は、発光素子6113に流れる電流値には影響をおよぼさない。従って、発光素子6113に流れる電流値は、飽和領域で動作するTFT6125により決定される。なお、TFT6125のチャネル長L1、チャネル幅W1、TFT6126のチャネル長L2、チャネル幅W2は、L1/W1:L2/W2=5〜6000:1を満たすように設定するとよい。また、両TFTは同じ導電型を有していると作製工程上好ましい。さらに、TFT6125には、エンハンスメント型だけでなく、ディプリーション型のTFTを用いてもよい。
FIG. 19C illustrates a pixel circuit in which the
表示装置に多階調の画像を表示するときの駆動方法として、アナログのビデオ信号を用いるアナログ駆動とデジタルのビデオ信号を用いるデジタル駆動が挙げられる。両方式の違いは、発光素子の発光、非発光のそれぞれの状態において該発光素子を制御する方法にある。前者のアナログ駆動は、発光素子に流れる電流を制御して階調を制御する。また後者のデジタル駆動は、発光素子がオン状態(輝度がほぼ100%である状態)と、オフ状態(輝度がほぼ0%である状態)の2つの状態のみによって階調表現する。デジタル駆動は、オンとオフの2つの状態だけを用いると、2階調しか表示できないため、別の方式と組み合わせて多階調の画像を表示する駆動方法があり、例えば面積階調方式や時間階調方式が挙げられる。 As a driving method for displaying a multi-tone image on a display device, there are analog driving using an analog video signal and digital driving using a digital video signal. The difference between the two methods lies in the method of controlling the light emitting element in each of the light emitting and non-light emitting states of the light emitting element. In the former analog drive, gradation is controlled by controlling the current flowing through the light emitting element. In the latter digital drive, gradation is expressed only by two states, that is, a light emitting element is in an on state (a luminance is almost 100%) and an off state (a luminance is almost 0%). Since only two gradations can be displayed using only two states, on and off, there is a driving method for displaying a multi-gradation image in combination with another method, for example, an area gradation method or time A gradation method is mentioned.
但し、デジタルのビデオ信号を用いる場合、そのビデオ信号が電圧を用いているのか、電流を用いているのかで異なる。つまり、発光素子の発光時において、画素に入力されるビデオ信号は、定電圧のものと、定電流のものがある。ビデオ信号が定電圧のものには、発光素子に印加される電圧が一定のものと、発光素子に流れる電流が一定のものとがある。またビデオ信号が定電流のものには、発光素子に印加される電圧が一定のものと、発光素子に流れる電流が一定のものとがある。この発光素子に印加される電圧が一定のものは定電圧駆動であり、発光素子に流れる電流が一定のものは定電流駆動である。定電流駆動は、発光素子の抵抗変化によらず、一定の電流が流れる。 However, when a digital video signal is used, it differs depending on whether the video signal uses voltage or current. That is, when the light emitting element emits light, a video signal input to the pixel includes a constant voltage signal and a constant current signal. A video signal having a constant voltage includes a constant voltage applied to the light emitting element and a constant current flowing through the light emitting element. In addition, a video signal having a constant current includes a constant voltage applied to the light emitting element and a constant current flowing in the light emitting element. A constant voltage applied to the light emitting element is constant voltage driving, and a constant current flowing through the light emitting element is constant current driving. In constant current driving, a constant current flows regardless of the resistance change of the light emitting element.
本発明の表示装置は、液晶パネル及び発光素子を用いたパネルを問わず、アナログ駆動またはデジタル駆動のいずれを使用してもよく、また、デジタル駆動において面積階調方式や時間階調方式のいずれを適用してもよい。他にも、本実施の形態で挙げなかった他の駆動方法を適用してもよい。また、定電圧駆動、定電流駆動のどちらを用いてもよい。 The display device of the present invention may use either analog driving or digital driving regardless of whether it is a liquid crystal panel or a panel using a light-emitting element. May be applied. In addition, other driving methods not mentioned in this embodiment may be applied. Further, either constant voltage driving or constant current driving may be used.
なお、表示装置はアクティブマトリクス型またはパッシブマトリクス型のどちらを用いても構わない。ただし、アクティブマトリクス型を適用した場合には、発光素子は電流駆動型の素子であるため、画素内のトランジスタのバラツキが少ない場合にアナログ駆動を用いることが好適である。 Note that the display device may be either an active matrix type or a passive matrix type. However, when the active matrix type is applied, the light-emitting element is a current-driven element, and thus it is preferable to use analog driving when there is little variation in transistors in the pixel.
なお、本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせることができる。 Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態7)
本実施の形態では、上記実施の形態で示したフィルム状表示装置の用途に関して説明する。本発明の作製方法または製造装置によって作製されたフィルム状表示装置は、様々な電子機器の表示部に用いることができる。その一例を図20に示す。
(Embodiment 7)
In this embodiment mode, applications of the film display device described in the above embodiment mode will be described. The film display device manufactured by the manufacturing method or manufacturing apparatus of the present invention can be used for display portions of various electronic devices. An example is shown in FIG.
図20(A)はディスプレイであり、本体4101、支持台4102、表示部4103を含む。表示部4103は可撓性基板を用いて形成されており、軽量で薄型のディスプレイを実現できる。また、表示部4103を湾曲させることも可能であり、支持台4102から取り外して壁に掛けることも可能である。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4103の加工に用いることによって、ディスプレイを作製することができる。
FIG. 20A illustrates a display, which includes a
図20(B)は巻き取り可能な大型ディスプレイであり、本体4201、表示部4202を含む。本体4201および表示部4202は可撓性基板を用いて形成されているため、ディスプレイを折り畳んだり、巻き取ったりして持ち運ぶことが可能である。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4202の加工に用いることによって、軽量、薄型の大型のディスプレイを作製することができる。
FIG. 20B illustrates a large display that can be wound, which includes a
図20(C)は、シート型のコンピュータであり、本体4401、表示部4402、キーボード4403、タッチパッド4404、外部接続ポート4405、電源プラグ4406等を含んでいる。表示部4402は可撓性基板を用いて形成されており、軽量で薄型のコンピュータを実現できる。また、電源プラグ4406の部分に収納スペースを設けることによって表示部2402を巻き取って収納することが可能である。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4402に用いることによって、コンピュータを作製することができる。
FIG. 20C illustrates a sheet-type computer including a
図20(D)は、20〜80インチの大型の表示部を有する表示装置であり、筐体4300、操作部であるキーボード部4301、表示部4302、スピーカー部4303等を含む。また、表示部4302は可撓性基板を用いて形成されており、キーボード部4301を取り外して筐体4300を折り畳んだり巻き取ったりして持ち運ぶことが可能である。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4302に用いることによって大型の表示装置を作製することができる。
FIG. 20D illustrates a display device having a large display portion of 20 to 80 inches, which includes a
図20(E)は電子ブックであり、本体4501、表示部4502、操作キー4503等を含む。またモデムが本体4501に内蔵されていても良い。表示部4502は可撓性基板を用いて形成されており、折り曲げることができる。さらに、表示部4502は文字等の静止画像はもちろん動画も表示することが可能となっている。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4502に用いることによって電子ブックを作製することができる。
FIG. 20E illustrates an electronic book which includes a
図20(F)はICカードであり、本体4601、表示部4602、接続端子4603等を含む。表示部4602は可撓性基板を用いて軽量、薄型のシート状になっているため、カードの表面に張り付けて形成することができる。また、ICカードを非接触でデータの受信が行える場合に外部から取得した情報を表示部4602に表示することが可能となっている。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を表示部4602に用いることによってICカードを作製することができる。
FIG. 20F illustrates an IC card, which includes a
また、本発明のフィルム状表示装置は、様々な物品に張り付けることによって情報を表示することができる。その具体例を図21に示す。 In addition, the film-like display device of the present invention can display information by sticking to various articles. A specific example is shown in FIG.
図21(A)は、カメラ4707、センサ4703、ライト4704、車輪4705及びフロントガラス4706等を含むバスであり、4705は運転手である。フロントガラス4706に表示部A4700、表示部B4701を有しており、必要な情報を表示している。また、車体の側面に表示部C4702を有しており、ポスター等として情報を表示することができる。表示部A4700、表示部B4701、表示部C4702は可撓性基板を用いて軽量、薄型のシート状になっているため、フロントガラス4706や車体の側面に張り付けることができる。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を用いて表示部A4700、表示部B4701、表示部C4702を作製することができる。 FIG. 21A shows a bus including a camera 4707, a sensor 4703, lights 4704, wheels 4705, a windshield 4706, and the like, and 4705 is a driver. The windshield 4706 has a display portion A4700 and a display portion B4701, and displays necessary information. Further, a display portion C4702 is provided on the side surface of the vehicle body, and information can be displayed as a poster or the like. Since the display portion A 4700, the display portion B 4701, and the display portion C 4702 are light and thin sheets using a flexible substrate, they can be attached to the windshield 4706 or the side surface of the vehicle body. The display portion A 4700, the display portion B 4701, and the display portion C 4702 can be manufactured using the manufacturing method or manufacturing apparatus described in the above embodiment modes.
図21(B)では、表示部を自動車の運転席周辺に搭載した例を示している。ダッシュボード4806には音響再生装置、具体的にはカーオーディオや、カーナビゲーションが設けられている。カーオーディオの本体4804は、表示部A4800、表示部B4801、操作ボタン4805を含む。またフロントガラス4803にも表示部C4802が設けられている。各表示装置は可撓性基板を用いて軽量、薄型のシート状になっているため、各部位に張り付けて情報を表示することができる。上記実施の形態で示した作製方法または製造装置を用いて各表示装置を作製することができる。 FIG. 21B shows an example in which the display unit is mounted around the driver's seat of an automobile. The dashboard 4806 is provided with a sound reproducing device, specifically car audio and car navigation. A car audio main body 4804 includes a display portion A 4800, a display portion B 4801, and operation buttons 4805. A display portion C4802 is also provided on the windshield 4803. Since each display device is a lightweight and thin sheet using a flexible substrate, information can be displayed by being attached to each part. Each display device can be manufactured using the manufacturing method or manufacturing apparatus described in the above embodiment modes.
なお、ここでは乗物の例を示したが、本発明を用いて作製されたフィルム状表示装置は、他にも、鉄道の駅や空港などにおける情報表示盤や、街頭における広告表示盤等の情報を表示する場所であれば至る所に用いることが可能である。以上の様に、本発明の適用範囲は極めて広く、あらゆる分野の電子機器や情報表示手段に用いることが可能である。なお、本実施の形態は上記実施の形態と自由に組み合わせて行うことができる。 In addition, although the example of the vehicle was shown here, the film-like display device manufactured by using the present invention can also be used for information such as information display boards at railway stations and airports, advertisement display boards on streets, etc. It can be used everywhere as long as it is a place to display. As described above, the application range of the present invention is extremely wide and can be used for electronic devices and information display means in various fields. Note that this embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
Claims (14)
前記剥離層上に下地絶縁膜と、前記下地絶縁膜上に形成されたチャネル領域、ソース領域およびドレイン領域を含む半導体膜と、前記半導体膜の前記チャネル領域の上方にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成されたゲート電極と、前記ゲート電極を覆って形成された層間絶縁膜と、前記層間絶縁膜上に形成され且つ前記半導体膜の前記ソース領域または前記ドレイン領域と電気的に接続するソース電極またはドレイン電極と、前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極の一方と電気的に接続する画素電極と、前記画素電極の端部を覆って形成された絶縁膜と、を有する素子形成部を形成し、
前記絶縁膜、前記層間絶縁膜、前記ゲート絶縁膜および前記下地絶縁膜に前記剥離層に達する開口部を形成して前記剥離層を露出させ、
前記開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、前記剥離層を除去し、
第1のローラーを用いて、前記素子形成部の一方の面に第1のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記基板から前記素子形成部を剥離し、
第2のローラーを用いて、前記素子形成部の他方の面に第2のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記第1のシート材から前記素子形成部を剥離し、
前記第1のシート材の剥離後、加工手段を用いて前記画素電極上に発光層および対向電極を形成し、
前記対向電極上に保護膜を形成し、
第3のローラーを用いて、前記保護膜の表面に第3のシート材を接着させて封止し、
前記第1、第2、及び第3のローラーを回転させることにより、前記第1のローラーを用いた剥離から前記第3のローラーを用いた封止まで連続的に行うことを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 Forming a release layer on the substrate,
A base insulating film on the release layer, a semiconductor film including a channel region, a source region, and a drain region formed on the base insulating film, and a gate insulating film formed above the channel region of the semiconductor film A gate electrode, an interlayer insulating film formed over the gate electrode, and a source electrode or drain formed on the interlayer insulating film and electrically connected to the source region or the drain region of the semiconductor film Forming an element forming portion having an electrode, a pixel electrode electrically connected to one of the source electrode or the drain electrode, and an insulating film formed to cover an end of the pixel electrode;
Forming an opening reaching the peeling layer in the insulating film, the interlayer insulating film, the gate insulating film, and the base insulating film to expose the peeling layer;
Introducing an etchant into the opening to remove the release layer;
Using the first roller, the first sheet material is adhered to one surface of the element forming portion, and the element forming portion is peeled from the substrate,
Using the second roller, the second sheet material is adhered to the other surface of the element forming portion, and the element forming portion is peeled off from the first sheet material,
After peeling off the first sheet material, a light emitting layer and a counter electrode are formed on the pixel electrode using processing means,
Forming a protective film on the counter electrode;
Using a third roller, the third sheet material is adhered and sealed to the surface of the protective film,
By rotating the first, second, and third rollers, the display device performs continuously from peeling using the first roller to sealing using the third roller. Manufacturing method.
前記剥離層上に下地絶縁膜を介してチャネル領域、ソース領域およびドレイン領域を含む半導体膜を形成し、
前記半導体膜を覆ってゲート絶縁膜を形成し、
前記ゲート絶縁膜および前記下地絶縁膜に前記剥離層に達する開口部を形成して、前記剥離層を露出させ、
前記開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、前記剥離層を除去し、
第1のローラーを用いて、前記ゲート絶縁膜に第1のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記基板から前記下地絶縁膜、前記半導体膜および前記ゲート絶縁膜を剥離し、
第2のローラーを用いて、前記下地絶縁膜に第2のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記第1のシート材から前記下地絶縁膜、前記半導体膜および前記ゲート絶縁膜を剥離し、
前記第1のシート材の剥離後、加工手段を用いて、前記半導体膜の前記チャネル領域上に配置するように前記ゲート絶縁膜上にゲート電極を形成し、
前記ゲート電極を覆って、層間絶縁膜を形成し、
前記層間絶縁膜上に、前記半導体膜の前記ソース領域または前記ドレイン領域と電気的に接続するソース電極またはドレイン電極を形成し、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極の一方と電気的に接続する画素電極を形成し、
前記画素電極の端部を覆って絶縁膜を形成し、
前記画素電極上に発光層および対向電極を形成し、
前記対向電極上に保護膜を形成し、
第3のローラーを用いて、前記保護膜の表面に第3のシート材を接着させて封止し、
前記第1、第2、及び第3のローラーを回転させることにより、前記第1のローラーを用いた剥離から前記第3のローラーを用いた封止まで連続的に行うことを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 Forming a release layer on the substrate,
A semiconductor film including a channel region, a source region, and a drain region is formed over the peeling layer through a base insulating film,
Forming a gate insulating film covering the semiconductor film;
Forming an opening reaching the release layer in the gate insulating film and the base insulating film to expose the release layer;
Introducing an etchant into the opening to remove the release layer;
Using the first roller, the first sheet material is adhered to the gate insulating film, and the base insulating film, the semiconductor film and the gate insulating film are peeled from the substrate,
Using a second roller, the second sheet material is adhered to the base insulating film, and the base insulating film, the semiconductor film, and the gate insulating film are peeled from the first sheet material,
After peeling off the first sheet material, a processing means is used to form a gate electrode on the gate insulating film so as to be disposed on the channel region of the semiconductor film,
Covering the gate electrode, forming an interlayer insulating film,
Forming a source electrode or a drain electrode electrically connected to the source region or the drain region of the semiconductor film on the interlayer insulating film;
Forming a pixel electrode electrically connected to one of the source electrode or the drain electrode;
Covering the end of the pixel electrode to form an insulating film;
Forming a light emitting layer and a counter electrode on the pixel electrode;
Forming a protective film on the counter electrode;
Using a third roller, the third sheet material is adhered and sealed to the surface of the protective film,
By rotating the first, second, and third rollers, the display device performs continuously from peeling using the first roller to sealing using the third roller. Manufacturing method.
前記剥離層上に下地絶縁膜を介してチャネル領域、ソース領域およびドレイン領域を含む半導体膜を形成し、
前記半導体膜の前記チャネル領域の上方にゲート絶縁膜を介してゲート電極を形成し、
前記ゲート電極を覆って層間絶縁膜を形成し、
前記層間絶縁膜、前記ゲート絶縁膜および前記下地絶縁膜に前記剥離層に達する開口部を形成して前記剥離層を露出させ、
前記開口部にエッチング剤を導入して、前記剥離層を除去し、
前記層間絶縁膜および前記ゲート絶縁膜に前記半導体膜の前記ソース領域または前記ドレイン領域に達する開口部を形成し、
第1のローラーを用いて、前記層間絶縁膜に第1のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記基板から前記下地絶縁膜、前記半導体膜、前記ゲート絶縁膜、前記ゲート電極および前記層間絶縁膜を剥離し、
第2のローラーを用いて、前記下地絶縁膜に第2のシート材を接着させ、かつ、前記第1のシート材から前記下地絶縁膜、前記半導体膜、前記ゲート絶縁膜、前記ゲート電極および前記層間絶縁膜を剥離し、
前記第1のシート材の剥離後、加工手段を用いて、前記層間絶縁膜上に、前記半導体膜の前記ソース領域または前記ドレイン領域と電気的に接続するソース電極またはドレイン電極を形成し、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極の一方と電気的に接続する画素電極を形成し、
前記画素電極の端部を覆って絶縁膜を形成し、
前記画素電極上に発光層および対向電極を形成し、
前記対向電極上に保護膜を形成し、
第3のローラーを用いて、前記保護膜の表面に第3のシート材を接着させて封止し、
前記第1、第2、及び第3のローラーを回転させることにより、前記第1のローラーを用いた剥離から前記第3のローラーを用いた封止まで連続的に行うことを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 Forming a release layer on the substrate,
A semiconductor film including a channel region, a source region, and a drain region is formed over the peeling layer through a base insulating film,
Forming a gate electrode over the channel region of the semiconductor film via a gate insulating film;
Forming an interlayer insulating film covering the gate electrode;
Forming an opening reaching the peeling layer in the interlayer insulating film, the gate insulating film and the base insulating film to expose the peeling layer;
Introducing an etchant into the opening to remove the release layer;
Forming an opening reaching the source region or the drain region of the semiconductor film in the interlayer insulating film and the gate insulating film;
Using a first roller, the first sheet material is adhered to the interlayer insulating film, and the base insulating film, the semiconductor film, the gate insulating film, the gate electrode, and the interlayer insulating film are bonded from the substrate. Exfoliate,
Using a second roller, a second sheet material is bonded to the base insulating film, and the base insulating film, the semiconductor film, the gate insulating film, the gate electrode, and the gate electrode are formed from the first sheet material. Strip the interlayer insulation film,
After peeling off the first sheet material, using a processing means, a source electrode or a drain electrode that is electrically connected to the source region or the drain region of the semiconductor film is formed on the interlayer insulating film,
Forming a pixel electrode electrically connected to one of the source electrode or the drain electrode;
Covering the end of the pixel electrode to form an insulating film;
Forming a light emitting layer and a counter electrode on the pixel electrode;
Forming a protective film on the counter electrode;
Using a third roller, the third sheet material is adhered and sealed to the surface of the protective film,
By rotating the first, second, and third rollers, the display device performs continuously from peeling using the first roller to sealing using the third roller. Manufacturing method.
前記半導体膜は、非晶質半導体膜、非晶質状態と結晶状態が混在した膜、微結晶半導体膜、又は結晶性半導体膜のいずれかであることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 3,
The method for manufacturing a display device is characterized in that the semiconductor film is any one of an amorphous semiconductor film, a film in which an amorphous state and a crystalline state are mixed, a microcrystalline semiconductor film, or a crystalline semiconductor film.
前記基板は、ガラス基板、石英基板、セラミック基板、金属基板、又は半導体基板の表面に絶縁膜を形成した基板のいずれかであることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 4,
The method for manufacturing a display device, wherein the substrate is any one of a glass substrate, a quartz substrate, a ceramic substrate, a metal substrate, and a substrate in which an insulating film is formed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate.
前記加工手段は液滴吐出法またはスクリーン印刷法が用いられることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 5,
A manufacturing method of a display device, wherein the processing means uses a droplet discharge method or a screen printing method.
前記第2のシート材にラミネートフィルム又は繊維質な材料からなる紙を用いることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 6,
A method for manufacturing a display device, wherein a laminate film or a paper made of a fibrous material is used for the second sheet material.
前記第3のシート材にラミネートフィルム又は繊維質な材料からなる紙を用いることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 7,
A manufacturing method of a display device, wherein a laminate film or paper made of a fibrous material is used for the third sheet material.
前記第2のシート材及び前記第3のシート材のいずれか一方又は両方に炭素を主成分とする薄膜又は導電性材料がコーティングされた膜が設けられていることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 8,
One or both of the second sheet material and the third sheet material are provided with a thin film containing carbon as a main component or a film coated with a conductive material. Method.
前記第2のシート材及び前記第3のシート材のいずれか一方又は両方に帯電防止フィルムを用いることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 6,
A method for manufacturing a display device, wherein an antistatic film is used for one or both of the second sheet material and the third sheet material.
前記帯電防止フィルムは、その片面又は両面に帯電防止可能な材料が設けられたフィルムであることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In claim 10,
The method for manufacturing a display device, wherein the antistatic film is a film provided with an antistatic material on one side or both sides thereof.
前記帯電防止フィルムは、帯電防止可能な材料を樹脂中に分散させたフィルムであることを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In claim 10,
The method for manufacturing a display device, wherein the antistatic film is a film in which an antistatic material is dispersed in a resin.
前記第2のローラーを用いて、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行うことを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 to 12,
A method for manufacturing a display device, wherein one or both of pressure treatment and heat treatment is performed using the second roller.
前記第3のローラーを用いて、加圧処理と加熱処理の一方または両方を行うことを特徴とする表示装置の作製方法。 In any one of Claims 1 thru / or Claim 13,
A method for manufacturing a display device, wherein one or both of pressure treatment and heat treatment is performed using the third roller.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005257447A JP4954515B2 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2005-09-06 | Method for manufacturing display device |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004264580 | 2004-09-10 | ||
| JP2004264580 | 2004-09-10 | ||
| JP2005257447A JP4954515B2 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2005-09-06 | Method for manufacturing display device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006108077A JP2006108077A (en) | 2006-04-20 |
| JP2006108077A5 JP2006108077A5 (en) | 2008-10-16 |
| JP4954515B2 true JP4954515B2 (en) | 2012-06-20 |
Family
ID=36377513
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005257447A Expired - Fee Related JP4954515B2 (en) | 2004-09-10 | 2005-09-06 | Method for manufacturing display device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4954515B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7968382B2 (en) * | 2007-02-02 | 2011-06-28 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| WO2008129819A1 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2008-10-30 | Nikon Corporation | Display element manufacturing method, display element manufacturing apparatus and display element |
| KR101004849B1 (en) | 2008-09-02 | 2010-12-28 | 삼성전기주식회사 | Fabrication method of thin film device |
| KR20100027526A (en) * | 2008-09-02 | 2010-03-11 | 삼성전기주식회사 | Fabrication method of thin film device |
| JP2010153813A (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2010-07-08 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Light-emitting device, method of manufacturing the same, and portable telephone |
| WO2011135780A1 (en) * | 2010-04-27 | 2011-11-03 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | Light-emitting device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP6314836B2 (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2018-04-25 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus of organic electroluminescence panel |
| WO2014098183A1 (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Organic electroluminescent panel, and production method and production apparatus therefor |
| WO2014129519A1 (en) | 2013-02-20 | 2014-08-28 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Peeling method, semiconductor device, and peeling apparatus |
| KR101462586B1 (en) * | 2014-05-22 | 2014-11-19 | 주식회사 코엠에스 | Semiconducter Substrate Protect Film Auto Peeler |
| US9676175B2 (en) * | 2014-06-20 | 2017-06-13 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Peeling apparatus |
| TWI738641B (en) * | 2015-03-20 | 2021-09-11 | 日商味之素股份有限公司 | Manufacturing method of package |
| JP7105543B2 (en) | 2017-05-26 | 2022-07-25 | エルジー ディスプレイ カンパニー リミテッド | organic display element |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02220392A (en) * | 1989-02-22 | 1990-09-03 | Teijin Ltd | Field light-emitting module |
| JPH05313151A (en) * | 1992-05-08 | 1993-11-26 | Idemitsu Kosan Co Ltd | Production of liquid crystal element |
| JP2004140380A (en) * | 1996-08-27 | 2004-05-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method of transferring thin film device and method of manufacturing device |
| JP4748859B2 (en) * | 2000-01-17 | 2011-08-17 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Method for manufacturing light emitting device |
| JP4765170B2 (en) * | 2001-01-24 | 2011-09-07 | ソニー株式会社 | Manufacturing method of display device |
| JP4244120B2 (en) * | 2001-06-20 | 2009-03-25 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2003142666A (en) * | 2001-07-24 | 2003-05-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | Transfer method for element, method for manufacturing element, integrated circuit, circuit board, electrooptic device, ic card and electronic apparatus |
| KR100944886B1 (en) * | 2001-10-30 | 2010-03-03 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device |
| JP2004047691A (en) * | 2002-07-11 | 2004-02-12 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, electrooptic device and electronic apparatus |
-
2005
- 2005-09-06 JP JP2005257447A patent/JP4954515B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006108077A (en) | 2006-04-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4954515B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing display device | |
| US8040469B2 (en) | Display device, method for manufacturing the same and apparatus for manufacturing the same | |
| JP6403914B1 (en) | EL display device | |
| JP5078246B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| CN100585868C (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP4049330B2 (en) | Electroluminescent display device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2001272923A (en) | Production method of display device | |
| EP1659647A1 (en) | Organic electroluminescence device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR20090033861A (en) | Light emitting device and electronic appliance | |
| JP4934920B2 (en) | Display panel and display device using the same | |
| JP4689249B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing display device | |
| JP5352599B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2014179636A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2017037312A (en) | Display device and portable information terminal | |
| JP2015207779A (en) | semiconductor device | |
| JP2013118401A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2013153178A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2011086962A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080829 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080829 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110512 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110517 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110715 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110830 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111020 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111213 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120131 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120313 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120314 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4954515 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150323 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150323 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |