EP2063018A2 - Temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement - Google Patents
Temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2063018A2 EP2063018A2 EP08020124A EP08020124A EP2063018A2 EP 2063018 A2 EP2063018 A2 EP 2063018A2 EP 08020124 A EP08020124 A EP 08020124A EP 08020124 A EP08020124 A EP 08020124A EP 2063018 A2 EP2063018 A2 EP 2063018A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- strands
- strand element
- silicone
- element according
- strand
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B5/00—Making ropes or cables from special materials or of particular form
- D07B5/10—Making ropes or cables from special materials or of particular form from strands of non-circular cross-section
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B21/00—Warp knitting processes for the production of fabrics or articles not dependent on the use of particular machines; Fabrics or articles defined by such processes
- D04B21/20—Warp knitting processes for the production of fabrics or articles not dependent on the use of particular machines; Fabrics or articles defined by such processes specially adapted for knitting articles of particular configuration
- D04B21/205—Elongated tubular articles of small diameter, e.g. coverings or reinforcements for cables or hoses
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04C—BRAIDING OR MANUFACTURE OF LACE, INCLUDING BOBBIN-NET OR CARBONISED LACE; BRAIDING MACHINES; BRAID; LACE
- D04C1/00—Braid or lace, e.g. pillow-lace; Processes for the manufacture thereof
- D04C1/06—Braid or lace serving particular purposes
- D04C1/12—Cords, lines, or tows
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B1/00—Constructional features of ropes or cables
- D07B1/02—Ropes built-up from fibrous or filamentary material, e.g. of vegetable origin, of animal origin, regenerated cellulose, plastics
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B1/00—Constructional features of ropes or cables
- D07B1/02—Ropes built-up from fibrous or filamentary material, e.g. of vegetable origin, of animal origin, regenerated cellulose, plastics
- D07B1/04—Ropes built-up from fibrous or filamentary material, e.g. of vegetable origin, of animal origin, regenerated cellulose, plastics with a core of fibres or filaments arranged parallel to the centre line
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B1/00—Constructional features of ropes or cables
- D07B1/22—Flat or flat-sided ropes; Sets of ropes consisting of a series of parallel ropes
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B5/00—Making ropes or cables from special materials or of particular form
- D07B5/04—Rope bands
- D07B5/045—Belts comprising additional filaments for laterally interconnected load bearing members
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/10—Rope or cable structures
- D07B2201/1004—General structure or appearance
- D07B2201/1008—Several parallel ropes
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2001—Wires or filaments
- D07B2201/2002—Wires or filaments characterised by their cross-sectional shape
- D07B2201/2003—Wires or filaments characterised by their cross-sectional shape flat
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2001—Wires or filaments
- D07B2201/2009—Wires or filaments characterised by the materials used
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2015—Strands
- D07B2201/2016—Strands characterised by their cross-sectional shape
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2015—Strands
- D07B2201/2022—Strands coreless
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2015—Strands
- D07B2201/2023—Strands with core
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2015—Strands
- D07B2201/2033—Parallel wires
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2015—Strands
- D07B2201/2036—Strands characterised by the use of different wires or filaments
- D07B2201/2037—Strands characterised by the use of different wires or filaments regarding the dimension of the wires or filaments
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2047—Cores
- D07B2201/2048—Cores characterised by their cross-sectional shape
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2047—Cores
- D07B2201/2052—Cores characterised by their structure
- D07B2201/2055—Cores characterised by their structure comprising filaments or fibers
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2047—Cores
- D07B2201/2052—Cores characterised by their structure
- D07B2201/2055—Cores characterised by their structure comprising filaments or fibers
- D07B2201/2056—Cores characterised by their structure comprising filaments or fibers arranged parallel to the axis
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2047—Cores
- D07B2201/2066—Cores characterised by the materials used
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2047—Cores
- D07B2201/2067—Cores characterised by the elongation or tension behaviour
- D07B2201/2069—Cores characterised by the elongation or tension behaviour being elastic
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2083—Jackets or coverings
- D07B2201/2088—Jackets or coverings having multiple layers
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2083—Jackets or coverings
- D07B2201/209—Jackets or coverings comprising braided structures
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2083—Jackets or coverings
- D07B2201/20903—Jackets or coverings comprising woven structures
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2201/00—Ropes or cables
- D07B2201/20—Rope or cable components
- D07B2201/2083—Jackets or coverings
- D07B2201/20907—Jackets or coverings comprising knitted structures
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2205/00—Rope or cable materials
- D07B2205/30—Inorganic materials
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2401/00—Aspects related to the problem to be solved or advantage
- D07B2401/20—Aspects related to the problem to be solved or advantage related to ropes or cables
- D07B2401/2005—Elongation or elasticity
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D07—ROPES; CABLES OTHER THAN ELECTRIC
- D07B—ROPES OR CABLES IN GENERAL
- D07B2501/00—Application field
- D07B2501/20—Application field related to ropes or cables
- D07B2501/2084—Mechanical controls, e.g. door lashes
Definitions
- the invention relates to temperature-resistant, elastic strand element, in particular in the form of a profile strip, a cord, a strand or a round cord.
- the object of the invention is therefore to provide a temperature-resistant, elastic strand element which has the increased requirements in the automotive sector, in particular a permanent elasticity in a wide temperature range.
- a temperature-resistant, elastic strand element having the features of claim 1.
- a strand element such as, for example, a profiled strip, a cord, a strand or a round cord, comprises at least one sheath and a rope-shaped core extending in the longitudinal direction of the strand element.
- the core of silicone material causes sufficient tensile and compressive force for the elastic clamping element and ensures the permanent elasticity in a temperature range of -40 ° C to 120 ° C.
- the jacket is preferably formed from one or more textile layers. These layers may be a braid, a woven fabric or a knitted fabric, wherein these layers surround the soul as completely as possible in the longitudinal direction and thus protect the soul from mechanical influences.
- a braid, woven or knitted fabric is also stable in the required temperature range of -40 ° C to 120 ° C and preferably consists of monofilament or multifilament threads of polyester fibers, viscose fibers, Cotton fibers, polyamide fibers or other, in this required temperature range resistant fibers.
- elastic strand element may additionally be provided an elastic support thread which is arranged in the textile jacket so that it surrounds the soul and exerts a radial load in the direction of the soul. In this way it is achieved that the jacket always returns in terms of its diameter after a tensile load in the starting position.
- the coat can also contain a further, non-textile layer in addition to the textile layers. This position must also be stable in the required temperature range.
- a temperature-resistant, elastic strand element consists of one or more silicone strands. These silicone strands can be individually covered by the sheath or a bundle of silicone strands is wrapped by the sheath. Such a bundle of silicone strands may be designed so that the individual silicone strands run almost parallel to each other in the longitudinal direction of the strand element or else the silicone strands are braided together like a plait.
- the individual silicone strands can be used in different cross-sectional shape, preferably round, square and / or rectangular cross-sectional shapes are used. In a strand element, the silicone strands preferably have the same cross-sectional shape and the same cross-sectional size.
- silicone strands are used with different cross-sectional shapes or cross-sectional sizes.
- the soul which consists of these silicone strands, surrounded by a coat. This allows an application of these temperature-resistant, elastic strand elements in the automotive sector. So far, silicone materials have not been used, since contained silicone oils or other ingredients contained lead to problems in painting. By the Sheath of the silicone material in the temperature-resistant, elastic strand element such problems are avoided or significantly reduced.
- the strand element has the advantage that the permanent elasticity, which consists of silicone strands soul is not affected by other influences, since the silicone material hydrophobic, UV resistant to chemicals and resistant to many aggressive media. Due to the achieved permanent elasticity of the temperature-resistant, elastic strand element, in particular the elastic properties of the silicone material, cross section optimized strand elements can be used for a wide variety of applications, resulting in a high material savings, namely material savings of 10 to 20%. This in turn allows an almost cost equal production of the strand elements in comparison to known strand elements and this with improved use properties.
- the temperature-resistant, elastic strand elements according to the invention can be used in a wide variety of fields, in particular in the automotive sector, for example for convertibles of convertibles, but also in the field of "life safety", where they serve, for example, as tensioning and / or traction means.
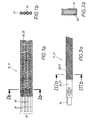
- the jacket 20 is made of a fabric 22 made of polyester.
- the fabric 22 separately covers the individual silicone strands 31, 32.
- the silicone strands 31, 32 have a round cross-section and all the same diameter.
- profile strips 11 which are drawn in their application not only in the longitudinal direction, but also on the narrow side transverse to the longitudinal direction, strands with a larger diameter can be selected for the silicone strands 31 in the edge region in comparison to the silicone strands 32 in the middle region of the profile strip eleventh In such an arrangement, in Fig. 1 is not shown, a profile tape 11 does not exhausts so fast at the edges.
- a strand element 10 in the form of a cord 12 is shown.
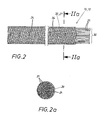
- a sheath 20 is used from a braid 21 made of polyester threads.
- the shell 30 encompassed soul 30 consists of round silicone strands 31, which are arranged in this case as a bundle in the jacket 20.
- pairs of elastic support threads 24 are provided and that runs a pair in the clockwise direction around the soul 30 and the other pair in the counterclockwise system. In this way, one obtains a uniform load of the braid 21 in the direction of the soul 30.
- the core 30 is radially loaded by these support threads 24. These support threads 24 ensure that the braid 21 returns to its original position after the tensile load.
- FIG. 3a and 3b another inventive strand element 10 is shown.
- the core 30 of this strand 13 consists of a band-shaped silicone strand 34 with a rectangular Cross-section.
- This single silicone strand 34 is surrounded by a braid 21 made of viscose threads.
- This braid 21 forms the lower layer of the shell 20 of the strand 13.
- another layer namely in this case a knitted fabric 23 made of polyester threads, arranged as the outer layer of the shell 20.
- a multi-layer jacket 20 is provided in particular when the strand element 10 has to meet different mechanical loads.
- Fig. 4a and 4b show another inventive strand element 10, here in the form of a round belt 14, which has a braid 21 made of polyamide threads as sheath 20.
- a core 30 is provided with a bundle of silicone strands 33.
- the longitudinally parallel silicone strands have a rectangular cross-section.
- the number of silicone strands 33 depends on the application, ie on the clamping force to be achieved.
- these temperature-resistant, elastic strand elements 10 are provided at the end with a connector to connect them to the corresponding objects.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Braiding, Manufacturing Of Bobbin-Net Or Lace, And Manufacturing Of Nets By Knotting (AREA)
- Woven Fabrics (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Knitting Of Fabric (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement, insbesondere in Form eines Profilbandes, einer Kordel, einer Litze oder einer Rundschnur.
- Bekannt sind elastische Schmaltextilien mit mehreren in Längsrichtung verlaufenden elastischen Gummischnüren. Derartige Schmaltextilien werden insbesondere auch im industriellen Bereich eingesetzt. Sie dienen beispielsweise dazu um eine Zugkraft auf zwei Gegenstände auszuüben, so dass diese Gegenstände eine bevorzugte Lage einnehmen können, beispielsweise die Schließstellung einer bewegbaren Tür. Für die meisten Anwendungszwecke besitzen diese bekannten elastischen Schmaltextilien eine ausreichende Dauerelastizität. Für spezielle Anwendungszwecke, wie beispielsweise im Kraftfahrzeugbereich, aber auch im Bereich der Sicherheitstechnik für Tür- und Torsysteme, wird eine höhere Dauerelastizität gefordert, insbesondere den Erhalt der Spann- und Zugkraft des elastischen Strangelements in einem weiten Temperaturbereich oder bei sonstigen Umwelteinflüssen, wie beispielsweise UV-Licht oder Feuchtigkeit. Des Weiteren wird ein Beibehalten der elastischen Eigenschaften gefordert, wenn diese elastischen Strangelemente in einem Bereich angewendet werden, wo die Atmosphäre mit aggressiven Medien angereichert sein kann. Die vorgenannten Einflüsse verändern die bekannten elastischen Strangelemente nachhaltig, insbesondere elastische Dehnfäden aus Gummi altern unter diesen vorgenannten Einflüssen und werden brüchig. Es wurde daher versucht, bei solchen elastischen Strangelementen die Gummifäden durch eine besondere Beschichtung der Mäntel oder durch einen zusätzlichen Mantel zu schützen. Für verschiedene industrielle Anwendungszwecke wurde der nachlassenden Elastizität und Spannkraft dadurch begegnet, dass ein elastisches Strangelement mit höherer Spannkraft ausgewählt wird, als dies für den Anwendungszweck notwendig wäre. Solche Strangelemente werden also überdimensioniert, was in vielen Anwendungsbereichen als nachteilig empfunden wird. Trotzdem können die vorbeschriebenen Maßnahmen die Anforderungen, die im Bereich Automotive gestellt werden, nicht befriedigend erfüllen. Es wird für diesen Anwendungszweck beispielsweise eine Dauerelastizität in einem Temperaturbereich von -40° C bis 120° C gefordert.
- Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es daher, ein temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement zur Verfügung zu stellen, das die erhöhten Anforderungen im Bereich Automotive, insbesondere eine Dauerelastizität in einem weiten Temperaturbereich, besitzt.
- Diese Aufgabe wird mit einem temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelement mit den Merkmalen des Anspruches 1 erfüllt. Ein solches Strangelement, wie beispielsweise ein Profilband, eine Kordel, eine Litze oder eine Rundschnur umfasst mindestens einen Mantel und eine in Längsrichtung des Strangelements verlaufende strangförmige Seele. Die Seele aus Silikonmaterial bewirkt eine ausreichende Zug- und Spannkraft für das elastische Spannelement und gewährleistet die Dauerelastizität in einem Temperaturbereich von -40°C bis 120°C.
- Der Mantel wird vorzugsweise aus einer oder mehreren textilen Lagen gebildet. Bei diesen Lagen kann es sich um ein Geflecht, ein Gewebe oder ein Gewirke handeln, wobei diese Lagen die Seele in Längsrichtung möglichst vollständig umgeben und so die Seele vor mechanischen Einflüssen schützen. Ein solches Geflecht, Gewebe oder Gewirke ist ebenfalls in dem geforderten Temperaturbereich von -40°C bis 120°C beständig und besteht vorzugsweise aus monofilen oder multifilen Fäden aus Polyesterfasern, Viskosefasern, Baumwollfasern, Polyamidfasern oder anderen, in diesem geforderten Temperaturbereich beständigen Fasern.
- Bei einer besonderen Ausführungsform des temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelements kann zusätzlich ein elastischer Stützfaden vorgesehen sein, der im textilen Mantel so angeordnet ist, dass er die Seele umgibt und eine radiale Belastung in Richtung der Seele ausübt. Auf diese Weise wird erzielt, dass der Mantel hinsichtlich seines Durchmessers nach einer Zugbelastung immer wieder in die Ausgangslage zurückkehrt.
- Für spezielle Anwendungszwecke kann der Mantel neben den textilen Lagen auch eine weitere, nichttextile Lage enthalten. Auch diese Lage muss ebenfalls in dem geforderten Temperaturbereich beständig sein.
- Die Seele eines solchen temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelements besteht aus einem oder mehreren Silikonsträngen. Diese Silikonstränge können einzeln vom Mantel umfasst sein oder ein Bündel an Silikonsträngen wird vom Mantel umhüllt. Ein solches Bündel an Silikonsträngen kann so ausgestaltet sein, dass die einzelnen Silikonstränge in Längsrichtung des Strangelements nahezu parallel zueinander verlaufen oder aber die Silikonstränge sind zopfartig miteinander verflochten. Die einzelnen Silikonstränge können in verschiedenen Querschnittsform eingesetzt werden, vorzugsweise werden runde, quadratische und/ oder rechteckige Querschnittsformen eingesetzt. In einem Strangelement besitzen die Silikonstränge vorzugsweise die gleiche Querschnittsform und die gleiche Querschnittsgröße.
- Bei einer besonderen Ausführungsform werden aber auch Silikonstränge mit unterschiedlichen Querschnittsformen oder Querschnittsgrößen eingesetzt. In jedem Fall wird die Seele, die aus diesen Silikonsträngen besteht, von einem Mantel umgeben. Dies ermöglicht eine Anwendung dieser temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelemente im Automobilbereich. Hier wurden bisher Silikonmaterialien nicht eingesetzt, da enthaltene Silikonöle oder andere enthaltene Bestandteile zu Problemen beim Lackieren führen. Durch die Ummantelung des Silikonmaterials in dem temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelement werden solche Probleme vermieden bzw. erheblich reduziert.
- Neben der Temperaturbeständigkeit dieses erfinderischen elastischen Strangelements in einem weiten Temperaturbereich von -40°C bis 120°C hat das Strangelement den Vorteil, dass die Dauerelastizität, der aus Silikonsträngen bestehenden Seele auch durch andere Einflüsse nicht beeinträchtigt wird, da das Silikonmaterial hydrophob, UV-beständig und gegenüber vielen aggressiven Medien chemikalienbeständig ist. Aufgrund der erzielten dauerhaften Elastizität des temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelements, insbesondere der elastischen Eigenschaften des Silikonmaterials können querschnittsoptimierte Strangelemente für die verschiedensten Anwendungszwecke eingesetzt werden, was zu einer hohen Materialeinsparung führt, nämlich zu Materialeinsparungen von 10 bis 20%. Dies wiederum ermöglicht eine nahezu kostengleiche Herstellung der Strangelemente im Vergleich zu bekannten Strangelementen und dies bei verbesserten Verwendungseigenschaften.
- Die erfindungsgemäßen temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelemente können in den verschiedensten Bereichen eingesetzt werden, insbesondere im Bereich Automotive, beispielsweise für Verdecke von Cabriolets, aber auch im Bereich "Life-Safety", wo sie beispielsweise als Spann- und/oder Zugmittel dienen.
- Die Erfindung wird nachfolgend anhand der Zeichnung in mehreren Ausführungsbeispielen dargestellt. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1a + b
- die Seitenansicht und den Querschnitt eines erfindungsgemäßen Strangelements,
- Fig. 2 + 2a
- die Seitenansicht und den Querschnitt eines weiteren erfindungsgemäßen Strangelements,
- Fig. 3a + b
- die Seitenansicht und den Querschnitt eines weiteren erfindungsgemäßen Strangelements,
- Fig. 4a + b
- die Seitenansicht und der Querschnitt eines weiteren erfindungsgemäßen Strangelements.
- In den
Fig. 1a und b ist ein temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement 10 in Form eines Profilbandes 11 gezeigt. Der Mantel 20 besteht aus einem Gewebe 22 aus Polyester. Das Gewebe 22 umhüllt separat die einzelnen Silikonstränge 31, 32. Die Silikonstränge 31, 32 haben einen runden Querschnitt und alle den gleichen Durchmesser. Bei Profilbändern 11, die bei ihrer Anwendung nicht nur in Längsrichtung, sondern auch über die Schmalseite quer zur Längsausrichtung gezogen werden, können für die Silikonstränge 31 im Randbereich Stränge mit größerem Durchmesser gewählt werden in Vergleich zu den Silikonsträngen 32 im mittleren Bereich des Profilbandes 11. Bei einer solchen Anordnung, die inFig. 1 nicht gezeigt ist, leiert ein Profilband 11 nicht so schnell an den Rändern aus. - In den
Fig. 2 und 2a ist ein Strangelement 10 in Form einer Kordel 12 dargestellt. Bei dieser Kordel 12 wird ein Mantel 20 aus einem Geflecht 21 aus Polyesterfäden eingesetzt. Die vom Mantel 20 umfasste Seele 30 besteht aus runden Silikonsträngen 31, die in diesem Fall als Bündel im Mantel 20 angeordnet sind. Im Geflecht 21 sind paarweise elastische Stützfäden 24 vorgesehen und zwar läuft das eine Paar im Uhrzeigersinn um die Seele 30 und das andere Paar im Gegenuhrzeigersystem. Auf diese Weise erhält man eine gleichmäßige Belastung des Geflechts 21 in Richtung der Seele 30. Bei einer Längsausdehnung der Kordel 12 wird durch diese Stützfäden 24 die Seele 30 radial belastet. Diese Stützfäden 24 stellen sicher, dass das Geflecht 21 nach der Zugbelastung in seine Ausgangslage zurückkehrt. - In den
Fig. 3a und 3b ist ein weiteres erfindungsgemäßes Strangelement 10 dargestellt. In diesem Fall in Form einer Litze 13. Die Seele 30 dieser Litze 13 besteht aus einem bandförmigen Silikonstrang 34 mit einem rechteckigen Querschnitt. Dieser einzelne Silikonstrang 34 wird von einem Geflecht 21 aus Viskosefäden umgeben. Dieses Geflecht 21 bildet die untere Lage des Mantels 20 der Litze 13. Darüber ist eine weitere Lage, nämlich in diesem Fall ein Gewirke 23 aus Polyesterfäden, als äußere Lage des Mantels 20 angeordnet. Ein mehrlagiger Mantel 20 wird insbesondere vorgesehen, wenn das Strangelement 10 unterschiedlichen mechanischen Belastungen genügen muss. - Die
Fig. 4a und 4b zeigen ein weiteres erfindungsgemäßes Strangelement 10, hier in Form eines Rundbandes 14, welches als Mantel 20 ein Geflecht 21 aus Polyamidfäden besitzt. In diesem Mantel 20 ist eine Seele 30 mit einem Bündel an Silikonsträngen 33 vorgesehen. In diesem Fall haben die in Längsrichtung parallel angeordneten Silikonstränge einen rechteckigen Querschnitt. Die Anzahl der Silikonstränge 33 hängt vom Anwendungsfall ab, d.h. von der zu erzielenden Spannkraft. - Für die verschiedenen Einsatzzwecke werden diese temperaturbeständigen, elastischen Strangelemente 10 endseitig mit einem Verbinder versehen, um sie mit den entsprechenden Gegenstände zu verbinden.
-
- 10
- Strangelement
- 11
- Profilband
- 12
- Kordel
- 13
- Litze
- 14
- Rundband
- 20
- Mantel
- 21
- Geflecht
- 22
- Gewebe
- 23
- Gewirke
- 24
- Stützfaden
- 30
- Seele
- 31
- Silikonstrang, rund
- 32
- Silikonstrang, rund
- 33
- Silikonstrang, rechteckig
- 34
- Silikonstrang, rechteckig + breit
Claims (13)
- Temperaturbeständiges elastisches Strangelement, insbesondere in Form eines Profilbandes (11), einer Kordel (12), einer Litze (13), einer Rundschnur (14),
umfassend mindestens einen Mantel (20), der eine in Längsrichtung des Strangelements (10) verlaufende strangförmige Seele (30) aus Silikonmaterial umgibt,
wobei das Strangelement (10) bei Temperaturen von -40°C bis 120°C beständig ist. - Strangelement nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass ein oder mehrere textile Lagen den Mantel (20) bilden, wobei die einzelnen Lagen aus einem Geflecht (21), einem Gewebe (22) oder einem Gewirk (23) bestehen und diese Lagen die Seele (30) in Längsrichtung vollständig umgeben.
- Strangelement nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Geflecht (21), das Gewebe (22) oder das Gewirke (23) aus monofilen und/oder multifilen Fäden aus Polyesterfasern, Viskosefasern, Baumwollfasern, Polyamidfasern oder anderen im Temperaturbereich von -40°C bis 120°C beständigen Fasern besteht.
- Strangelement nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Seele (30) aus einem oder mehreren Silikonsträngen (31, 32, 33, 34) besteht.
- Strangelement nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Seele (30) aus einem Bündel an parallel verlaufender einzelner Silikonstränge (31, 32, 33) besteht.
- Strangelement nach Anspruch 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Seele aus einem Bündel an parallel verlaufenden einzelnen Silikonsträngen (31, 32, 33) besteht, wobei alle Silikonstränge die gleiche Querschnittsform und die gleiche Querschnittsgröße aufweisen.
- Strangelement nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Seele aus einem Bündel miteinander verflochtener Silikonstränge besteht.
- Strangelement nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Seele aus einem Bündel miteinander verflochtener Silikonstränge besteht, wobei alle Silikonstränge die gleiche Querschnittsform und die gleiche Querschnittsgröße aufweisen.
- Strangelement nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Silikonstränge (31, 32) eine runde Querschnittsform aufweisen.
- Strangelement nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Silikonstränge (33, 34) eine rechteckige Querschnittsform aufweisen.
- Strangelement nach einem der Ansprüche 5 bis 10, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Mantel (20) mindestens einen Stützfaden (24) enthält, der sich um die Seele (30) erstreckt.
- Profilband nach einem der Ansprüche 5 bis 11, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Profilband (11) einen rechteckigen Querschnitt aufweist, wobei die Breite des Profilbandes wesentlich größer ist als die Dicke des Profilbandes und wobei die in Längsrichtung parallel verlaufenden Silikonstränge (32) im mittleren Breitenabschnitt einen kleiner Durchmesser aufweisen als die Silikonstränge (32) im Randbereich des Profilbandes (11).
- Spann- und/oder Zugmittel dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass es ein oder mehrere temperaturbeständige elastische Strangelemente (10) gemäß einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 12 enthält.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE202007016240U DE202007016240U1 (de) | 2007-11-21 | 2007-11-21 | Temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2063018A2 true EP2063018A2 (de) | 2009-05-27 |
| EP2063018A3 EP2063018A3 (de) | 2010-02-17 |
Family
ID=38973608
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08020124A Withdrawn EP2063018A3 (de) | 2007-11-21 | 2008-11-19 | Temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2063018A3 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE202007016240U1 (de) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102336824A (zh) * | 2010-07-27 | 2012-02-01 | 中国科学院植物研究所 | 与植物种子大小相关的蛋白及其编码基因与应用 |
| WO2013143965A2 (de) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Teufelberger Gesellschaft M.B.H. | Kern-mantelseil |
| WO2013143966A2 (de) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Teufelberger Gesellschaft M.B.H. | Kern-mantelseil |
| CN103726370A (zh) * | 2013-12-20 | 2014-04-16 | 苏州鑫帛泰纺织科研有限公司 | 一种三角形夹芯编织绳 |
| CN103741371A (zh) * | 2013-12-20 | 2014-04-23 | 苏州鑫帛泰纺织科研有限公司 | 一种方形编织绳 |
| CN112626706A (zh) * | 2020-12-10 | 2021-04-09 | 山东鲁普科技有限公司 | 一种用于服装行业双色环保背带绳及其制作方法 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110004528A (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2019-07-12 | 宿迁市柯信纺织品股份有限公司 | 一种应用于纺织业梳棉工序的再处理方法 |
| CN110939003A (zh) * | 2019-12-17 | 2020-03-31 | 山东鲁普科技有限公司 | 一种耐磨缓冲保护绳索及其制备方法 |
| CN112195509A (zh) * | 2020-10-21 | 2021-01-08 | 上海骐杰碳素材料有限公司 | 整体螺旋编织坩埚预制体及以其制成的涂层坩埚 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB726479A (en) * | 1953-06-10 | 1955-03-16 | Dow Corning Ltd | Improvements in or relating to elastic yarns and fabrics |
| DE2245394B1 (de) * | 1972-09-15 | 1974-03-21 | Windmoeller & Hoelscher | Schweiss- und trennvorrichtung fuer kunststoffolien |
| US3889038A (en) * | 1953-05-04 | 1975-06-10 | Sol B Wiczer | Coated filament and method of forming same |
| GB2082213A (en) * | 1980-08-16 | 1982-03-03 | Inst Textil & Faserforschung | Surgical stitching thread |
| US4642119A (en) * | 1984-07-16 | 1987-02-10 | Johnson & Johnson | Connective tissue prosthesis |
| WO2004066847A1 (en) * | 2003-01-27 | 2004-08-12 | Sergio Capurro | Sheathed elastic surgigal thread |
-
2007
- 2007-11-21 DE DE202007016240U patent/DE202007016240U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2008
- 2008-11-19 EP EP08020124A patent/EP2063018A3/de not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3889038A (en) * | 1953-05-04 | 1975-06-10 | Sol B Wiczer | Coated filament and method of forming same |
| GB726479A (en) * | 1953-06-10 | 1955-03-16 | Dow Corning Ltd | Improvements in or relating to elastic yarns and fabrics |
| DE2245394B1 (de) * | 1972-09-15 | 1974-03-21 | Windmoeller & Hoelscher | Schweiss- und trennvorrichtung fuer kunststoffolien |
| GB2082213A (en) * | 1980-08-16 | 1982-03-03 | Inst Textil & Faserforschung | Surgical stitching thread |
| US4642119A (en) * | 1984-07-16 | 1987-02-10 | Johnson & Johnson | Connective tissue prosthesis |
| WO2004066847A1 (en) * | 2003-01-27 | 2004-08-12 | Sergio Capurro | Sheathed elastic surgigal thread |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102336824A (zh) * | 2010-07-27 | 2012-02-01 | 中国科学院植物研究所 | 与植物种子大小相关的蛋白及其编码基因与应用 |
| WO2013143965A2 (de) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Teufelberger Gesellschaft M.B.H. | Kern-mantelseil |
| WO2013143966A2 (de) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Teufelberger Gesellschaft M.B.H. | Kern-mantelseil |
| US9845572B2 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2017-12-19 | Tuefelberger Fiber Rope Gmbh | Core-sheath rope |
| US9845571B2 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2017-12-19 | Teufelberger Gesellschaft M.B.H. | Core-sheath rope |
| CN103726370A (zh) * | 2013-12-20 | 2014-04-16 | 苏州鑫帛泰纺织科研有限公司 | 一种三角形夹芯编织绳 |
| CN103741371A (zh) * | 2013-12-20 | 2014-04-23 | 苏州鑫帛泰纺织科研有限公司 | 一种方形编织绳 |
| CN112626706A (zh) * | 2020-12-10 | 2021-04-09 | 山东鲁普科技有限公司 | 一种用于服装行业双色环保背带绳及其制作方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2063018A3 (de) | 2010-02-17 |
| DE202007016240U1 (de) | 2008-01-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2063018A2 (de) | Temperaturbeständiges, elastisches Strangelement | |
| EP1721039B1 (de) | Kernmantelseil | |
| EP1430176B1 (de) | Seilartiges gebilde | |
| EP1451091B1 (de) | Hebegurtschlinge | |
| DE2505568B2 (de) | Seil zur bewehrung von gegenstaenden aus elastischen oder leicht verformbaren stoffen | |
| DE19526721B4 (de) | Reifencord | |
| DE69524786T2 (de) | Endlosband und herstellungsverfahren | |
| DE202006002987U1 (de) | Elastische leitfähige Schaltextilie | |
| DE2446951A1 (de) | Treibriemen | |
| DE2911753C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Fördergurtes oder Treibriemens sowie ein nach diesem Verfahren hergestellter Treibriemen oder Fördergurt | |
| EP3222776B1 (de) | Muschelzuchtseil | |
| DE2822693A1 (de) | Seil aus metalldraehten zum verstaerken von plast- und elastartikeln und verfahren und vorrichtung zu seiner herstellung | |
| DE3917358A1 (de) | Stuetzgewebe zur abstuetzung von schuettgut | |
| DE4035814A1 (de) | Seil, insbesondere reckarmes faserseil | |
| EP2362920B1 (de) | Leitfähiges textiles flächengebilde mit dreherbindung | |
| DE102008060226B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Trägergewebes und derartiges Trägergewebe | |
| DE102011017273A1 (de) | Kletterseil | |
| DE2720071C2 (de) | Zugfestes, biegsames elektrisches Kabel | |
| EP0556452A1 (de) | Gewebter Schutzschlauch | |
| DE102006043714B4 (de) | Technische Schmaltextilie, wie Sicherheitsgurt, Spanngurt, Traggurt, Zurrgurt oder dergleichen Mittel aus gewebten textilen Filamentfäden | |
| DE202013101326U1 (de) | Mehrlitziges Stahldrahtseil mit einer mehrschäftigen Fasereinlage | |
| DE9113602U1 (de) | Drahtlitze für ein Schmuckstück | |
| DE10056913B4 (de) | Flechtlitze | |
| DE2010021A1 (en) | Rubber or plastic tube with fibre reinforce- - conductors | |
| AT213172B (de) | Drahtseil |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA MK RS |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA MK RS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20100212 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20100617 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Effective date: 20110414 |