EP1375709B1 - Ansetzverfahren oder Anspinnen für Spinnstellen von Luftspinnmaschinen - Google Patents
Ansetzverfahren oder Anspinnen für Spinnstellen von Luftspinnmaschinen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1375709B1 EP1375709B1 EP03013347.4A EP03013347A EP1375709B1 EP 1375709 B1 EP1375709 B1 EP 1375709B1 EP 03013347 A EP03013347 A EP 03013347A EP 1375709 B1 EP1375709 B1 EP 1375709B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- spinning
- outlet side
- driven part
- piecing
- thread
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 title claims description 75
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 40
- 238000007382 vortex spinning Methods 0.000 title 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 70
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 22
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010042 air jet spinning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007670 refining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008092 positive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H1/00—Spinning or twisting machines in which the product is wound-up continuously
- D01H1/11—Spinning by false-twisting
- D01H1/115—Spinning by false-twisting using pneumatic means
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H15/00—Piecing arrangements ; Automatic end-finding, e.g. by suction and reverse package rotation; Devices for temporarily storing yarn during piecing
- D01H15/002—Piecing arrangements ; Automatic end-finding, e.g. by suction and reverse package rotation; Devices for temporarily storing yarn during piecing for false-twisting spinning machines
Definitions
- the invention is in the field of spinning technology and relates to a method according to the preamble of the first claim.
- the inventive method is used to prepare a yarn which is formed in a spinning machine or in a spinning unit of an air spinning machine from a staple fiber material, for example after a can change, after a bobbin change, after a yarn breakage or after another spinning failure.
- the method can also serve for piecing, that is, for the restart of a spinning process.
- the invention further relates to a spinning station equipped for carrying out the method according to the invention according to the preamble of the corresponding independent patent claim.
- Air-jet spinning machines are in particular a device for producing a spun yarn from a fiber structure comprising a fiber guide channel with a fiber guide surface for guiding the fibers of the fiber assembly in an inlet mouth of Garn Entryskanals, further comprising a fluid means for generating a vortex flow around the inlet mouth of Garn arrangementskanals and the inventive Measure for influencing the flow conditions in the spindle channel of a stationary spindle.
- Air-jet spinning machines for spinning staple fiber materials usually have a large number of spinning stations, wherein a yarn is spun in each spinning station from a fed longitudinal fiber structure.
- the fiber longitudinal structure is first refined, that is, the amount of fiber per unit length is reduced by delay.
- the refined fiber strand is spun by twisting into a yarn, which yarn is then peeled off and wound up.
- the fiber longitudinal structure is stretched, for example, by means of a drafting device or dissolved by means of an opening roller.
- an air-spinning method is used, that is, the yarn formation is done by air-twist distribution.
- the fibers of the fiber structure are swirled by the twist distribution with the fibers of the yarn end region and the initial region of the fiber structure is bonded to the end region of the yarn in a kind of splice.
- the spinning process is thus put back into operation.
- the initial region of the longitudinal fiber structure which is believed to have a tapered shape as a result of the tearing off, is first subjected to the main distortion, it being assumed that the said taper is stretched accordingly, thereby providing an improved attachment point.
- the piecing or piecing methods of the prior art still have a further disadvantage.
- the piecing does not always succeed, so that the proportion of failed piecing on the total number of attempted piecing operations can be relatively high.
- the object of the invention is now to provide a method for setting or piecing, which has a high probability of success of the piecing process and with the quality of Ansetzstellen, in particular the tensile strength is improved.
- the method according to the invention is based on the recognition that the chances of obtaining a successful piecing process are substantially higher if the overlapping ones are successful End portions of the yarn end and the torn fiber longitudinal structure are pressed together in the overlapping state.
- the intervening frictional forces ie, static friction forces
- This increased cohesion of the end regions has a positive effect on the subsequent course of the piecing process.
- the likelihood is reduced that the so-called " soldered-together" end regions separate before the means for imparting twist or on average, for example during the impulse distribution by means of air, and the attaching process thereby fails.
- the process reliability of the piecing or piecing process and thus also the process reliability of the air spinning machine is thereby increased.
- the piecing quality is increased with respect to tear strength.
- the piecing or the Ansetzstelle for a sufficient tear strength has compared to the remaining yarn up to 200% increased fiber mass.
- the piecing thus has a much smaller thickness. Thanks to the tensile strength, the length of the placement can be chosen shorter. The fact that both the fiber mass and the length of the piecing is reduced, the disadvantages which are associated with a piecing, are reduced overall.
- the compression of the overlapping end portions of the yarn end and the torn fiber longitudinal structure is preferably realized by the existing possibilities, i. without additional devices.
- Particularly suitable for this purpose is the clamping point of the downstream-driven part of the refinement unit (for example pair of outfeed rollers in the main drafting of the drafting system).
- the piecing process it would also be possible for the piecing process to provide a special clamping-type pressing device which compresses the yarn end and the torn fiber longitudinal structure.
- the variant has been found to roughen or taper the yarn end or its end region to be overlapped, for example with a device according to DE4240653-A1 , Also, the use of a pointed end region of the longitudinal fiber structure, eg according to US 5802831 , is possible.
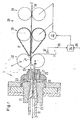
- FIG. 1 shows an exemplary embodiment of a spinning station of air-spinning machines for carrying out the inventive method.
- This spinning station is equipped for a so-called air spinning process with refinement by stretching.
- the spinning station has a means 3 for air twist distribution with a nozzle block 21 with nozzles 22 embedded therein, a spindle 23 with a yarn channel 24 and a feed block 25 with a fiber feed channel 26 and a needle 27 directed against the entrance of the yarn channel 24.
- the spinning station as a refinement unit on a drafting system 28 with, for example, three pairs of cylinders (inlet cylinder 29, central cylinder 30 with straps 31 and outlet cylinder 32 with nip 11).
- the inlet of the drafting device 28, so for example, the inlet cylinder 29 and the central cylinder 30 with straps 31 are driven by a motor 33.
- the motor 33 is controllable by a control unit 34.
- the control unit 34 uses for the control of the motor 33, a ready signal 35 and a yarn end signal 36 for determining the exact position of the end 2 of the yarn end 1 of a yarn end sensor 37, and spinning unit-own parameters.
- the fiber longitudinal formation 10 'fed in the feed direction Z enters into the refinement between the inlet cylinders 29, and becomes entangled with a usually constant draw ratio between inlet cylinders 29 and center cylinders 30 and between a central cylinders 30 and outlet cylinders 32 subjected to an optionally variable draw ratio.
- the refined fiber elongate structure 10 is drawn from the discharge cylinders 32 through the fiber supply channel 26 against the entrance of the yarn channel 24.
- Compressed air supplied by the nozzles 22 generates, in addition to the aforementioned suction effect in the region of the yarn channel entrance, a swirling flow which serves for the swirl distribution.
- the yarn 11 produced by this twist distribution is drawn off through the yarn channel 24 in withdrawal direction Z (means for yarn withdrawal).
- the motor 33 is first stopped, while the discharge cylinder 32 continue at least for a limited period.
- the supplied fiber longitudinal structure 10 ' is torn between the straps 31 and the outlet cylinders 32 and the downstream piece is conveyed away from the drafting arrangement by the outlet cylinders 32.
- the downstream piece is possibly disposed of thereon, the means for twist distribution 3 is possibly cleaned.
- the upper or lower part of the feed block 25 and the upper or lower of the discharge cylinder 32 can be lifted from their working position, such that the fiber feed channel 26 and the passage between the discharge cylinders 32 for a return and positioning of the yarn end 1 becomes accessible.
- the yarn end 1, which is unwound from the yarn package or may be an auxiliary yarn (bobbin change) is retracted or returned in such a spinning station for the resumption of the spinning process into the main delay region between center cylinders 30 and 31 and run-out cylinders 32 and hangs freely around the lower of the discharge cylinders 32, where it is monitored by the yarn end sensor 37 (in particular its end 2).
- the piecing process is carried out in a spinning station, as described in the FIG. 1 If the yarn end 1 is positioned and all the relevant parts of the spinning station are repositioned in their working position, the control unit 34, for example, by personnel or by a piecing robot, the ready signal 35 is transmitted. The control unit then starts the piecing process. That is, the twisting of the means for air twist distribution 3 and the yarn withdrawal (optionally with a predetermined staggering), so that the yarn end 1 begins to move against the twist distribution point. As soon as the yarn end sensor 37 detects the passage of the effective yarn end 2, the control unit receives the yarn end signal 36, by which the actual piecing routine is started.
- the motor 33 brings the pairs of rollers 30 and 29 within a very short time (hundredths of seconds) to a synchronized with the discharge cylinders 32 speed, so that at the time of overlap of the first fibers of the end portions of yarn end 1 and fiber elongated 10 'the rollers already in the correct speed ratio to each other rotate.
- the rolls may already have the appropriate nominal or operating speed (ie, the speed of the normal, stationary spinning process) at the beginning of the piecing or piecing process just explained. But it is also conceivable that the piecing or piecing takes place at a lower speed level. Whereupon, after piecing, all the rotating rolls of the refinement unit rise synchronously to their respective nominal or operating speed (eg on a ramp with a gearbox).
- nominal or operating speed ie, the speed of the normal, stationary spinning process
- control unit 34 For such a piecing routine, it is at most necessary for the control unit 34 to also provide data relating to the starting profile of the outlet cylinders 32, the central cylinders 30 and inlet cylinders 29, and the yarn take-off (not shown) and, if appropriate, measurement data from correspondingly arranged rotational speed sensors.
- the swirl pitch of the means 3 that is, in the present case, the speed of the air supplied from the nozzles 22 for the production of the Ansetzstelle compared to the normal spinning process changed, for example, be increased for a stronger Faserverwirbelung.
- the upstream of an air twist distribution in a spinning unit drafting system 28 may also have only two or more than three pairs of cylinders, wherein at a spinning break an inlet-side part of the cylinder pairs is stopped in front of an outlet side part of the cylinder pairs. In this case, after the spinning interruption, at least the inlet-side part of the cylinder pairs is retarded after a predetermined or determined based on sensor signals ramp.
- FIG. 1 represent the center cylinder 30 and inlet cylinder 29 the inlet side (by motor 33) drivable part of the refinement unit (here drafting system 28), while the outlet cylinder 32 represent the outlet side drivable parts.
- the position from the end of the yarn end is detected by means and transmitted to a control, which retards the startup of the inlet side driven part of the refinement unit in such a time when resuming the production of the yarn that the end portions of the torn fiber longitudinal structure and the yarn overlap over a predetermined length ,
- the length of the overlapping end regions substantially corresponds to the spinning distance d of the spinning station (see FIG. 1 ).
- the spinning distance d is defined as the distance between the mouth of the spindle 23 and the nip or clamping point 11 of the outlet cylinder 32nd
- this length of the overlapping end regions is also possible for this length of the overlapping end regions to be longer than the abovementioned spinning distance d of the spinning station.
- the end region of the yarn end 1 to be overlapped is roughened or tapered.
- the spinning station equipped for carrying out the method according to the invention has internal spinning stations its own controllable drive for the inlet-side parts of the refining agent or a correspondingly controllable transmission between these inlet-side parts of the refining means and a central drive.
- the other parts of the spinning unit to be driven can be driven by simple coupling to central drives or also by internally spinning, optionally controllable drives.
- the invention also includes a spinning station according to the invention of an air-spinning machine. This corresponds constructively to the embodiment according to FIG. 1 , why at this point to the description of FIG. 1 is referred back.
- the spinning unit according to the invention comprises a refinement unit (drafting unit) with parts which can be driven on the inlet side and outlet side, wherein at least the part which can be driven on the outlet side is equipped with at least one clamping point.
- the apparatus comprises means for air twisting, a means for yarn withdrawal, with a means for detecting the position of the end of a yarn end.
- the part of the refinement unit driven downstream can be opened in such a way that its clamping point or clamping points are exposed for a return and positioning of the yarn end.
- the outlet-side driven part consists of at least one outlet cylinder pair (32), wherein the upper or the lower cylinder of the outlet cylinder pair can be lifted (see arrow and dashed roller in FIG. 1 ).
- the means for air twist distribution (3) has an effective twist stop (27) for the yarn end.
- a mandrel 27 is shown here.
- the special feature is that the twist stop (27) is effective for the yarn end and not only for the fiber longitudinal structure. This results in very good piecing.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH10672002 | 2002-06-21 | ||
| CH10672002 | 2002-06-21 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1375709A2 EP1375709A2 (de) | 2004-01-02 |
| EP1375709A3 EP1375709A3 (de) | 2004-05-12 |
| EP1375709B1 true EP1375709B1 (de) | 2014-08-06 |
Family
ID=29716493
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03013347.4A Expired - Lifetime EP1375709B1 (de) | 2002-06-21 | 2003-06-16 | Ansetzverfahren oder Anspinnen für Spinnstellen von Luftspinnmaschinen |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6959532B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP1375709B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4718108B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN100379911C (ja) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6802353B2 (en) * | 2001-10-10 | 2004-10-12 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Apparatus for recycling waste from an absorbent article processing line |
| DE10335651B4 (de) * | 2003-07-29 | 2017-02-23 | Wilhelm Stahlecker Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Wiederherstellen eines unterbrochenen Spinnvorganges |
| US20090189319A1 (en) * | 2004-02-02 | 2009-07-30 | Kim Hak-Yong | Process of preparing continuous filament composed of nanofibers |
| EP1564317A1 (de) * | 2004-02-10 | 2005-08-17 | Maschinenfabrik Rieter Ag | Verfahren zum Erreichen einer Konstanten Ansetzermasse bei Vortex-Luftspinnverfahren |
| DE102004050968A1 (de) * | 2004-10-15 | 2006-04-20 | Wilhelm Stahlecker Gmbh | Verfahren zum Vorbereiten eines Ansetzvorganges an einer Luftdüsenspinnvorrichtung |
| CZ301752B6 (cs) * | 2005-12-20 | 2010-06-16 | Rieter Cz S.R.O. | Zpusob obnovování predení složkové príze, zejména na rotorovém doprádacím stroji pomocí spliceru a zarízení k provádení zpusobu |
| CN101294319B (zh) * | 2008-05-26 | 2010-06-02 | 东华大学 | 低落纤的喷气涡流纺装置 |
| CN101565866B (zh) * | 2009-04-17 | 2010-10-27 | 北京经纬纺机新技术有限公司 | 转杯纺纱机全自动接头控制方法及装置 |
| DE102011054302A1 (de) * | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Maschinenfabrik Rieter Ag | Garnbildungselement für eine Spinnstelle einer Luftspinnmaschine mit einem Drallstoppelement |
| CZ2013275A3 (cs) * | 2013-04-09 | 2014-10-22 | Rieter Cz S.R.O. | Způsob zahájení předení na spřádacím stroji, zejména vzduchovém dopřádacím stroji nebo rotorovém dopřádacím stroji |
| CH709756A1 (de) * | 2014-06-13 | 2015-12-15 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Spinndüse für eine Luftspinnmaschine sowie Luftspinnmaschine mit einer entsprechenden Spinndüse. |
| CH709953A1 (de) * | 2014-07-30 | 2016-02-15 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Verfahren zum Betrieb einer Luftspinnmaschine. |
| CZ306368B6 (cs) * | 2015-05-14 | 2016-12-21 | Rieter Cz S.R.O. | Způsob hromadného zapřádání příze na pracovních místech rotorového dopřádacího stroje a zařízení k jeho provádění |
| JP2017071865A (ja) * | 2015-10-06 | 2017-04-13 | 村田機械株式会社 | 紡績機 |
| DE102018007464A1 (de) * | 2018-09-21 | 2020-03-26 | Saurer Spinning Solutions Gmbh & Co. Kg | Servicewagen und Verfahren zum selbsttätigen Versorgen von Spinnstellen einer Spinnmaschine |
| CN111519286B (zh) * | 2020-04-28 | 2021-11-26 | 天津工业大学 | 一种多捻纺纱装置、多捻纺纱设备及纺纱方法 |
| CN111778601B (zh) * | 2020-06-29 | 2021-06-15 | 苏州优百纺织有限公司 | 一种断线自动接线器 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5966527A (ja) * | 1982-10-07 | 1984-04-16 | Toyoda Autom Loom Works Ltd | 結束紡績装置における糸継方法 |
| US5339614A (en) | 1991-07-11 | 1994-08-23 | Maschinenfabrik Rieter Ag | Rotating disc for separating and processing the end of yarn |
| US5524427A (en) | 1992-11-10 | 1996-06-11 | Howa Machinery, Ltd. | Method and apparatus for piecing slivers in a spinning machine by throttling in a nozzle |
| KR100296977B1 (ko) * | 1996-01-30 | 2001-11-22 | 무라타 기카이 가부시키가이샤 | 방적기의피이싱방법 |
| TW341605B (en) | 1996-05-16 | 1998-10-01 | Murada Kikai Kk | Piecing method for a spinning machine |
| JP2973961B2 (ja) * | 1997-01-13 | 1999-11-08 | 村田機械株式会社 | 紡績機のピーシング方法及びその装置 |
| ATE284987T1 (de) | 2000-11-08 | 2005-01-15 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Steuerung von spinnstellen in einer spinnmaschine |
| EP1219737B2 (de) * | 2000-12-22 | 2012-01-18 | Maschinenfabrik Rieter Ag | Verfahren zum Ansetzen eines in einer Spinnstelle gebildeten Garnes oder zum Anspinnen, sowie zur Durchführung des Verfahrens ausgerüstete Spinnstelle |
-
2003
- 2003-06-16 EP EP03013347.4A patent/EP1375709B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-06-18 US US10/464,054 patent/US6959532B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-06-20 CN CNB031438822A patent/CN100379911C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-06-23 JP JP2003178317A patent/JP4718108B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN100379911C (zh) | 2008-04-09 |
| JP2004027473A (ja) | 2004-01-29 |
| EP1375709A2 (de) | 2004-01-02 |
| US20040045270A1 (en) | 2004-03-11 |
| JP4718108B2 (ja) | 2011-07-06 |
| US6959532B2 (en) | 2005-11-01 |
| EP1375709A3 (de) | 2004-05-12 |
| CN1477247A (zh) | 2004-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1375709B1 (de) | Ansetzverfahren oder Anspinnen für Spinnstellen von Luftspinnmaschinen | |
| EP1219737B2 (de) | Verfahren zum Ansetzen eines in einer Spinnstelle gebildeten Garnes oder zum Anspinnen, sowie zur Durchführung des Verfahrens ausgerüstete Spinnstelle | |
| DE19501545C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Andrehen eines Garnes in einer Spinnmaschine | |
| EP1817448B1 (de) | Verfahren zum optimieren der produktionsleistung einer spinnmaschine | |
| WO2013143874A1 (de) | Vorspinnmaschine mit einer anordnung zur detektion und entfernung von garnfehlern | |
| DE3413894C2 (ja) | ||
| EP3276057A1 (de) | Fadenführungseinheit, offenend-spinnmaschine und verfahren zum betreiben einer spinnstelle | |
| WO1987003310A1 (en) | Process and device for rethreading a spinning device provided with a pneumatic twisting element | |
| DE3411577C2 (ja) | ||
| DE3336294A1 (de) | Verfahren zum garnansetzen beim spinnen von faserbuendelgarnen | |
| DE10335651B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Wiederherstellen eines unterbrochenen Spinnvorganges | |
| WO2006042686A1 (de) | Verfahren zum vorbereiten eines ansetzvorganges an einer luftdüsenspinnvorrichtung | |
| DE3539383C2 (ja) | ||
| DE3819858A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum erzeugen von als vorlagespulen fuer ein zwirnen dienenden spulen | |
| WO1989010990A1 (en) | Process and device for starting spinning in an open-end spinning device | |
| DE10346194B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Wiederherstellen eines unterbrochenen Spinnvorgangs | |
| EP0205962B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Anspinnen eines Garnes an einer Friktionsspinnvorrichtung | |
| DE69114951T2 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Auffangen und Vorbereiten des Fadenendes beim Wiederanspinnen in einer Offenendmaschine. | |
| CH685946A5 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum automatischen Ansetzen eines neu zu spinnenden Garnes an ein bestehendes Garnende. | |
| EP1295974B1 (de) | Luftspinnvorrichtung mit Auflöseeinrichtung | |
| WO2003018887A1 (de) | Verfahren zum handhaben einer spinnvorrichtung bei einem fadenbruch | |
| DE1710021A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Anspinnen des Garnes bei Garnbruch oder Wiederaufnahme des unterbrochenen Spinnvorganges beim Kapselspinnen von Textilgarnen | |
| EP3140233B1 (de) | Textilmaschine zur herstellung von vorgarn sowie verfahren zum starten der vorgarnherstellung an einer entsprechenden textilmaschine | |
| WO2005075721A2 (de) | Verfahren zum erreichen einer konstanten ansetzermasse bei vortex-luftspinnverfahren. | |
| DE10217243B4 (de) | Verfahren zum Anspinnen eines Fadens an einer Offenend-Spinnvorrichtung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: 7D 01H 4/48 A Ipc: 7D 01H 4/02 B |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20041105 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): CH CZ ES IT LI TR |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): CH CZ DE ES IT LI TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): CH CZ DE ES IT LI TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20071123 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20140116 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH CZ DE ES IT LI TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 50315098 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20140918 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140806 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140806 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140806 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 50315098 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20150507 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150630 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150630 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20210628 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20210610 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50315098 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220616 |