EP0945534A2 - Fournisseur positif à faible inertie pour des fils élastomères - Google Patents
Fournisseur positif à faible inertie pour des fils élastomères Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0945534A2 EP0945534A2 EP99102382A EP99102382A EP0945534A2 EP 0945534 A2 EP0945534 A2 EP 0945534A2 EP 99102382 A EP99102382 A EP 99102382A EP 99102382 A EP99102382 A EP 99102382A EP 0945534 A2 EP0945534 A2 EP 0945534A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- thread
- tension
- delivery device
- delivery
- wheel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B15/00—Details of, or auxiliary devices incorporated in, weft knitting machines, restricted to machines of this kind
- D04B15/38—Devices for supplying, feeding, or guiding threads to needles
- D04B15/48—Thread-feeding devices
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B15/00—Details of, or auxiliary devices incorporated in, weft knitting machines, restricted to machines of this kind
- D04B15/38—Devices for supplying, feeding, or guiding threads to needles
- D04B15/48—Thread-feeding devices
- D04B15/50—Thread-feeding devices for elastic threads
Definitions
- the invention relates to a positive feeder, the especially for supplying thread consumption points with abruptly fluctuating thread requirements and for elastic Threads is provided.
- Elastic threads or yarns change according to the Tension under which they stand, their length, in detail very large possible changes in length are.
- elastomer threads are in use that itself up to 7 times its length or even more let it stretch.
- the amount of thread supplied therefore depends on highly dependent on the tension under which the thread is delivered becomes. While in many cases it is sufficient if the Elastic thread tension within predetermined Boundaries are kept constant, there are a number of Use cases where it is important that in a given amount of thread in a given time interval is delivered.
- the amount of thread is, for example, by a thread length defined for a given thread tension. Is the Thread very elastic, can not be guaranteed that a certain amount of thread is delivered.
- the thread delivery device has a thread delivery wheel driven by a stepper motor on, the outer circumference of six wire brackets is defined. Regarding the thread run in front of the thread delivery wheel a thread brake is arranged. On the thread delivery wheel a thread tension sensor follows to regulate the Stepper motor and thus the amount of thread. The thread delivery device is used to supply thread with constant tension.
- a thread delivery device known for the delivery of time-varying quantities should serve elastic threads.
- the thread delivery device points a disc motor with a thread delivery wheel connected is. This is from the thread to be delivered entwined.
- Thread brake arranged to generate the Braking effect a permanent magnet or for adjustable Generation of the same contains an electromagnet.
- a thread tension sensor is connected downstream of the thread delivery wheel, that controls the disc motor.
- the thread delivery device is used to deliver elastic Threads with more or less constant tension, but not the positive delivery of specified thread quantities.
- the thread delivery device comprises two yarn feeders working independently of each other, that the thread passes through one after the other. First it is passed through a thread delivery device that pulls the thread pulls from spools of thread.
- the thread delivery wheel is from one Electric motor driven, which corresponds to that of one thread tension sensor arranged after the thread feed wheel detected thread tension is controlled. Of the Thread is thus with more or less constant tension to two thread delivery wheels in frictional engagement or rollers supplied with fixed speed are driven and thus deliver constant thread quantities. This means that thread quantities that are constant over time become one Thread consumption point at which the elastic Thread is combined with a hard thread.
- This arrangement is not for delivery variable thread quantities set up. It is also over DE-AS 1585111 a thread delivery device for feeding of threads to a knitting machine with constant Thread speed and at the same time with constant Thread tension known.
- This thread delivery device has two uniformly driven conical rollers on the are wrapped in succession by the thread. The string passes through a thread guide for each roller, which determines the diameter of the thread on the Roll on and off of this.
- By different Definition of the two drain diameters can be achieved that the thread with a small roller diameter first pulled from the bobbin and from the next roller with a larger diameter is taken over, so that the thread between the rollers is stretched a lot.
- This device and the method are especially for the processing of time-constant quantities of crimped Threads with hysteresis effect have been developed.
- Thread delivery device with which to change over time Defined quantities of elastic threads at thread consumption points have it delivered. It is also the job of Invention to provide a corresponding method.
- Thread delivery device has a tensioning device that the a defined tension coming from a bobbin communicates.
- the thread delivery device works on the input side voltage-controlled and quantity-based on the output side.
- a at least relatively constant thread tension is between the tensioning device and the positive delivery device generated.
- Voltage fluctuations caused by outside influences of the thread delivery device are generated, such as changed thread friction on thread eyelets on the way to a Thread consumption point, are controlled by the tension Section between tensioning device and positive delivery device kept away. It can be used to define a quantity Thread delivery of elastic threads independent of Friction influences take place after the thread delivery device. This is especially true when the thread demand fluctuates over time. Here the thread running conditions are speed dependent.
- the separation of the on the thread delivery device following thread travel range from the tension set Path allows a controlled and correct route Thread delivery of fluctuating quantities.
- the clamping device can be on the non-linear Force-displacement relationship, as is the case with elastic threads is found, be set up.
- Commonly elastic Threads for example elastane threads, show less in the area Forces with small changes in force large changes in elongation on. With increasing thread tension or force in the longitudinal direction of the thread, the resulting changes in length however, less and less. Does the thread have its If the maximum stretch is reached, a further increase can also be made the force to no more significant stretching of the thread to lead. If the force is removed, the thread jumps however largely returned to its original length. This property usually makes it relatively difficult to supply predetermined thread quantities.
- Thread delivery device existing tensioning device circumvents this problem by making the thread so strong stretches that a change in thread tension hardly has any influence on the thread length.
- the thread is delivered to the thread delivery wheel by a Electric motor driven according to the current thread requirement and is therefore independent of the one that arises Thread tension provides the desired amount of thread.
- a Defined thread delivery also becomes positive delivery called and thus stands in a certain contrast to Thread delivery devices, the thread with constant (lower) Deliver tension and be called negative feed.
- the thread delivery wheel is independent of a motor the tensioning device driven.
- the Tensioning device can be designed so that it is independent a high thread tension from the operation of the thread feed wheel generated.
- the tensioning device can, for example, be a type of thread brake be independent of the thread speed is working.
- this can be a friction brake be in which the thread is braked by friction elements on which he glides.
- the thread brake creates one more or less constant thread tension, can be here relatively large thread tension range are allowed, without noticeable the amount of thread delivered varies. This is a result of the tension of the thread up to its maximum limit.
- the tensioning device can also be a regulated one Thread brake, for example, depending on the Thread tension between the thread brake and the thread delivery wheel is set. This makes it possible for additional To compensate for frictional influences that occur, for example the thread delivery device can result. In addition, the Responsiveness of the device to sudden changes the delivery request improved in many cases.
- Thread brake into consideration. For example, it is possible to have a simple one Use friction brake with two brake actuators. This can move towards each other by a spring or by magnets to be excited. You can also use an electromagnet or other electrically controllable means are used, for example by the control loop can be controlled.
- the thread brakes can also be a separate clamping device Thread delivery wheel to be provided, its own Has drive motor. This second thread delivery wheel has the task of pulling the thread from a spool of thread and with defined tension in a stretched state to the the direction of movement of the thread downstream Thread delivery wheel to deliver while the upstream Thread delivery wheel is connected to a motor, which is preferably the motor works downstream thread delivery wheel preferably quantity-based. This applies accordingly to the above Design with controlled brake.
- the thread delivery device is preferably to a control unit connected or has one that the Motor of the thread delivery wheel with the desired thread delivery controls the corresponding speed.
- the data the control unit can, for example, from a sample data memory receive. With flat knitting machines it can be useful be the thread requirement from the movement of the thread guide to derive, in the simplest case with light barriers Limit switches or the like is detected. Besides, can it be appropriate to meet the need for elastic thread Measurement of the running speed of another e.g. hard thread to determine by the machine in question is to be processed. A measuring device can be used for this be provided for the thread speed with the Control unit is connected. This then enables the elastic thread, for example, strictly proportional to one otherwise to deliver thread to a thread consumption point.
- the sensor device is, for example, a measuring wheel, that the other (hard) thread is entwined and sits on the shaft of an encoder.
- the control unit can also be connected to the tensioning device connected to regulate this.
- the control unit is then with corresponding electrical Actuators of the brakes or with the engine a corresponding thread delivery wheel and a tension sensor connected, between the tensioning device and the thread delivery wheel is arranged.
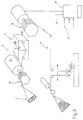
- the thread delivery device schematically illustrated in FIG. 1 is used to elastic thread 1 of a Yarn spool 2 to knitting points 3 of a flat knitting machine 4 to deliver.
- the knitting points 3 are by individual Needles 5 formed on which a thread guide 6 back and forth walking past (arrow).
- the thread guide 6 will both with the elastic thread 1 and with a hard thread 11 supplied. This is from a corresponding pulled off another spool 12.
- the delivery of the hard thread can be positive a feeder (thread delivery device), not further illustrated or by the pulling action of the needles 5 done during the knitting process.
- the delivered or The amount of thread 11 drawn off determines the stitch size.
- the amount of thread is not constant over time. In the Reversal areas of the thread guide 6 comes the thread consumption briefly completely to a standstill. In addition, the Thread consumption in the outward and return stroke at least then different, if the distance between the thread guide 6 and the supplying devices when going back and forth of the Thread guide is changed.
- the supply of the elastic thread 1 is used Thread delivery device 14, to which a tensioning device 15 and a thread delivery wheel 16 belonging to an electric motor 17 is driven.
- the thread 1 wraps around it Thread delivery wheel 16 a few times and is driven by this thus taken slip-free.
- the thread delivery wheel determines thus the amount of thread supplied to the thread guide 6.
- the thread 1 of the tensioning device 15 is almost up to its maximum value, but at least up to one Value tense, with changes in force hardly any changes in length cause.
- the tensioning device 15 has one Turning device 19 on the output of which two support pins 21, 22 are mounted eccentrically.
- the thread 1 wraps around these support pins 21, 22 at an angle, that of the rotational position of the rotary actuator 19 is dependent and thus controllable by the control unit 18.
- a thread tension sensor 24 is arranged, which here the thread tension is recorded.
- the thread tension sensor 24 supplies its measured value or its data to the control unit 18, which can be designed, for example, as a microcomputer can.
- the control unit 18 does not receive any further illustrated input device a setpoint for the Tension of the thread 1. This can be done in a manner shown in FIG illustrated memory cell 25 may be stored. Of the Setpoint is set to a value at which the thread has almost reached its yield strength.
- the control unit 18 controls the tensioning device 15 during operation of the thread delivery device 15 so that the of the thread delivery wheel 16 thread 1 pulled by the tensioning device 15 the desired one high target voltage reached. Is from the thread tension sensor 24 detected a deviation, controls the control unit 18 the tensioning device 15 accordingly after.
- the motor 17 of the yarn feed wheel 16 is actual thread consumption controlled accordingly.
- a measuring device 26 is arranged, to which a thread roll 27 and, for example, an incremental angle encoder 28 heard from the shaft 29, the thread roll 27 carried is.
- the thread roll 27 is wrapped in the hard thread 11 and turns according to its speed.
- the angle sensor 28 thus detects the thread speed and delivers corresponding signals via a Line, not shown, to an input 31 the control unit 18.
- Another input 32 of the control unit 18 is with connected to the thread tension sensor 24 and receives a Thread tension signal from this.
- Sample data or other Control data representing the amount of elastic to be delivered Mark thread will be sent to another entrance 33 supplied to the control unit 18.
- a first exit 34 of control unit 18 controls motor 17 while a second output 35 is connected to the clamping unit 15 and regulates it.
- the thread delivery device 14 described so far works as follows:
- control unit 18 receives at least information about the direction of movement of the thread guide 6. Ideally control unit 18 also receives information about the thread guide speed. This can be determined by position or speed measurement or as fixed or specified value must be made available. Out the speed of the thread guide and the direction of movement the control unit 18 determines those during the movement of the thread guide 6 resulting extension or Shortening the respective path for thread 1 and Thread 11.
- the one detected by the measuring device 26 Speed of thread 11 is a speed resulting from the change in the length of the thread travel and the thread consumption present on the needles.
- the control unit 18 is the change in length of the thread path decreasing proportion known or from the thread guide speed determinable so that from the measured value of the thread running speed the actual Thread consumption can be determined and accordingly is determined.
- the control unit determines from this value 18 the amount required on the needles 5 elastic Thread, for example, as a fixed ratio of that of the needles 5 processing amount of hard thread 11. Added to this the control unit 18 the amount of thread, which by extension or shortening the path of the thread 1, correct sign. Based on the value obtained in this way control pulses to control the motor 17 with formed a speed that the resulting yarn delivery corresponds.
- the process regulates the control unit 18 by means of the tensioning device 15 the thread tension in front of the thread feed wheel 16 to a defined value that is so high, for example, that the elastic thread 1 is almost fully stretched is and thus behaves almost like a hard thread.
- FIG. 2 Embodiment is the clamping device 15 by a Thread brake 41 formed, which works uncontrolled.
- the Thread brake 41 has, for example, two ends serving as braking elements For example.
- Disc-shaped plates 42, 43 on a Bolts 44 sit and against each other by means of a spring 45 are excited.
- the thread 1 is between the plates 42, 43 clamped and can be pulled through with friction.
- the Thread brake 41 is fixed to a thread tension value set so high that the thread 1 in the Area between the thread brake 41 and the thread delivery wheel 16 essentially regardless of its running speed is fully stretched. Accordingly, the Thread tension sensor 24 and the corresponding input 32 the control unit 18. Otherwise this embodiment is correct the thread delivery device 14 in structure and function with the thread delivery device described above (Fig. 1).
- the same reference numerals are therefore used used and referred to the above description.
- FIG. 3 A further modified embodiment of the thread delivery device can be seen from Fig. 3. The differences are in turn in the clamping device 15; Furthermore reference is made to the above description, which accordingly applies.
- the tensioning device 15 of the thread delivery device 14 3 has a yarn feed wheel 51, which on the Shaft of another drive motor 52 is seated.
- the thread delivery wheel 51 corresponds essentially to the thread delivery wheel 16 and is like this one or more times from the thread 1 entwined.
- the thread tension sensor 24 arranged with the input 32 of the control unit is connected.
- the control unit 18 gives at its output 35 corresponding control pulses.
- the advantage of this embodiment is that rapid build-up of the defined thread tension between two yarn delivery wheels 52, 16 and the decoupling of Thread tension in this distance from external influences from the thread path to the positive supplier. This can be done as needed take place without turning the thread feed wheel 16, when the thread feed wheel 52 is driven to rotate in reverse becomes.
- a thread delivery device for delivering elastic (soft) threads to a thread consumption point A control unit has a time-fluctuating thread requirement that determines or reports the current thread requirement gets. According to this need, a thread delivery wheel with a speed corresponding to the thread requirement driven. The thread passes through a tensioning device to the thread delivery wheel. The tensioning device is set so that the thread almost completely, at least but is stretched in a defined way. This makes it a firm one Assignment of the desired thread delivery quantity and speed of the thread delivery wheel possible.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Tension Adjustment In Filamentary Materials (AREA)
- Knitting Machines (AREA)
- Sewing Machines And Sewing (AREA)
- Forwarding And Storing Of Filamentary Material (AREA)
- Unwinding Of Filamentary Materials (AREA)
- Braiding, Manufacturing Of Bobbin-Net Or Lace, And Manufacturing Of Nets By Knotting (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19813351 | 1998-03-26 | ||
| DE19813351A DE19813351A1 (de) | 1998-03-26 | 1998-03-26 | Trägheitsarmer Positivfournisseur für Elastomerfäden |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0945534A2 true EP0945534A2 (fr) | 1999-09-29 |
| EP0945534A3 EP0945534A3 (fr) | 2000-11-22 |
| EP0945534B1 EP0945534B1 (fr) | 2004-09-22 |
Family
ID=7862417
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99102382A Expired - Lifetime EP0945534B1 (fr) | 1998-03-26 | 1999-02-08 | Fournisseur positif à faible inertie pour des fils élastomères |
Country Status (14)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6105398A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0945534B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP3010171B2 (fr) |
| KR (1) | KR100292422B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1154754C (fr) |
| BR (1) | BR9901117A (fr) |
| CA (1) | CA2265979C (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19813351A1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2224469T3 (fr) |
| HK (1) | HK1022934A1 (fr) |
| ID (1) | ID22332A (fr) |
| IL (1) | IL129084A (fr) |
| RU (1) | RU2150537C1 (fr) |
| UY (1) | UY25427A1 (fr) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001094247A2 (fr) * | 2000-06-08 | 2001-12-13 | Dupont-Toray Company, Ltd | Dispositif et procede d'apport de fil |
| WO2008017319A1 (fr) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-02-14 | Memminger-Iro Gmbh | Dispositif délivreur de fil à palpeur de fil novateur |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100307913B1 (ko) * | 1999-07-24 | 2001-09-24 | 차영진 | 환편기의 스판얀 장력조절장치 |
| US6202450B1 (en) * | 2000-05-24 | 2001-03-20 | Jen Fu Chen | Uniform yarn delivery method and apparatus for knitting machine |
| ITMI20020770A1 (it) * | 2002-04-10 | 2003-10-10 | Tiziano Barea | Dispositivo e metodo per alimentare un filo elastomerico ad una macchina tessile al fine di avere un manufatto di qualita' costante in ogni |
| KR100483705B1 (ko) * | 2002-09-18 | 2005-04-19 | 이성훈 | 섬유기계용 급사장치 |
| ITMI20030892A1 (it) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-01 | Riccardo Lonati | Dispositivo e procedimento di regolazione della grammatura |
| CZ300483B6 (cs) * | 2003-09-04 | 2009-05-27 | Rieter Cz A.S. | Zarízení k odvíjení lineárního textilního materiálu pri výrobe složkové príze |
| DE102004009057A1 (de) * | 2004-02-23 | 2005-09-08 | Memminger-Iro Gmbh | Elektronischer Positivfournisseur |
| ITMI20042293A1 (it) * | 2004-11-26 | 2005-02-26 | Tiziano Barea | Metodo perfezionato per alimentare un filato ad una macchina tessile atto alla sua lavorazione e macchina attuante detto metodo |
| US7540174B2 (en) * | 2005-04-19 | 2009-06-02 | Invista North America S.Ar.L. | Method and apparatus for circular knitting with elastomeric yarn that compensate for yarn package relaxation |
| ITTO20050469A1 (it) * | 2005-07-07 | 2007-01-08 | L G L Elecrtronics S P A | Dispositivo di recupero del filato per macchine tessili |
| JP4916193B2 (ja) * | 2006-03-08 | 2012-04-11 | グンゼ株式会社 | 衣類およびその編成方法 |
| CN101501261B (zh) * | 2006-09-15 | 2011-06-08 | 株式会社岛精机制作所 | 针织纱的弹性特性测定方法和针织机 |
| JP4943803B2 (ja) * | 2006-10-12 | 2012-05-30 | 株式会社島精機製作所 | 編機での張力設定方法および編機 |
| JP5969730B2 (ja) | 2009-12-28 | 2016-08-17 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品の製造装置 |
| KR101336303B1 (ko) * | 2012-01-17 | 2013-12-02 | 관 욱 김 | 연선기 관리 시스템 및 방법 |
| KR101271941B1 (ko) * | 2012-01-26 | 2013-06-07 | 이선옥 | 신축도 가변기능을 갖는 스판사 제조 장치 |
| ITTO20130017A1 (it) * | 2013-01-10 | 2014-07-11 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Gruppo di alimentazione di filato per macchine tessili. |
| CN103508266A (zh) * | 2013-09-17 | 2014-01-15 | 吴江永固纺配有限公司 | 一种采用步进式电机驱动的超喂装置 |
| CN104828645B (zh) * | 2015-03-23 | 2018-01-26 | 华东理工大学 | 纱线超喂张力控制装置及其测试方法、及张力控制系统 |
| BE1023220B1 (nl) * | 2015-07-03 | 2017-01-03 | Nv Michel Van De Wiele | Aanvoerinrichting voor aanvoeren van garens, werkwijze voor het bepalen van de spanning van garens en gebruik van controlemiddelen voor het aansturen van actuatoren voor het aanvoeren van garens |
| CN109987448B (zh) * | 2019-04-08 | 2020-11-24 | 安徽诚意电气科技有限公司 | 一种用于阻燃电缆的防拉断放卷缓冲保护装置 |
| KR102115261B1 (ko) * | 2019-07-24 | 2020-05-26 | 우정후 | 편직물 제조를 위한 원사 급사 방법 및 장치 |
| JP7460477B2 (ja) * | 2020-08-05 | 2024-04-02 | 株式会社島精機製作所 | 糸管理システム |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1585111A1 (de) * | 1965-05-18 | 1971-04-22 | Inst Textile De France | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Zufuehrung eines stark dehnbaren Fadens zu einer Web- oder Wirkmaschine |
| US4673139A (en) * | 1984-08-08 | 1987-06-16 | Gustav Memminger | Textile machinery yarn supply apparatus |
| DE3824034C1 (fr) * | 1988-07-15 | 1989-09-14 | Gustav 7290 Freudenstadt De Memminger | |
| EP0499380A1 (fr) * | 1991-02-12 | 1992-08-19 | JONES STROUD & CO LTD | Système d'alimentation en fil |
| DE4206607A1 (de) * | 1991-09-26 | 1993-04-01 | Erich Roser | Fadenliefergeraet fuer fadenverbrauchende textilmaschinen |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1574144A (fr) * | 1968-05-08 | 1969-07-11 | ||
| FR2264904B1 (fr) * | 1974-03-21 | 1977-08-19 | Inst Textile De France | |
| DE3627731C1 (de) * | 1986-08-16 | 1988-03-31 | Gustav Memminger | Fadenliefervorrichtung mit elektronischer Fadenspannungsregelung |
| DE19537215C2 (de) * | 1995-10-06 | 1999-09-02 | Memminger Iro Gmbh | Fadenliefergerät für elastische Garne |
-
1998
- 1998-03-26 DE DE19813351A patent/DE19813351A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1999
- 1999-02-08 EP EP99102382A patent/EP0945534B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-02-08 ES ES99102382T patent/ES2224469T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-02-08 DE DE59910553T patent/DE59910553D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-03-11 UY UY25427A patent/UY25427A1/es not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1999-03-17 CA CA002265979A patent/CA2265979C/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-03-22 IL IL12908499A patent/IL129084A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-03-22 ID IDP990244D patent/ID22332A/id unknown
- 1999-03-23 JP JP11077769A patent/JP3010171B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-03-24 BR BR9901117-4A patent/BR9901117A/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-03-24 US US09/275,460 patent/US6105398A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-03-25 KR KR1019990010199A patent/KR100292422B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-03-25 RU RU99106151/12A patent/RU2150537C1/ru not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-03-25 CN CNB991057465A patent/CN1154754C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2000
- 2000-03-27 HK HK00101871A patent/HK1022934A1/xx not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1585111A1 (de) * | 1965-05-18 | 1971-04-22 | Inst Textile De France | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Zufuehrung eines stark dehnbaren Fadens zu einer Web- oder Wirkmaschine |
| US4673139A (en) * | 1984-08-08 | 1987-06-16 | Gustav Memminger | Textile machinery yarn supply apparatus |
| DE3824034C1 (fr) * | 1988-07-15 | 1989-09-14 | Gustav 7290 Freudenstadt De Memminger | |
| EP0499380A1 (fr) * | 1991-02-12 | 1992-08-19 | JONES STROUD & CO LTD | Système d'alimentation en fil |
| DE4206607A1 (de) * | 1991-09-26 | 1993-04-01 | Erich Roser | Fadenliefergeraet fuer fadenverbrauchende textilmaschinen |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001094247A2 (fr) * | 2000-06-08 | 2001-12-13 | Dupont-Toray Company, Ltd | Dispositif et procede d'apport de fil |
| WO2001094247A3 (fr) * | 2000-06-08 | 2002-06-06 | Du Pont | Dispositif et procede d'apport de fil |
| WO2008017319A1 (fr) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-02-14 | Memminger-Iro Gmbh | Dispositif délivreur de fil à palpeur de fil novateur |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CA2265979A1 (fr) | 1999-09-26 |
| ID22332A (id) | 1999-09-30 |
| DE19813351A1 (de) | 1999-09-30 |
| CA2265979C (fr) | 2003-07-08 |
| ES2224469T3 (es) | 2005-03-01 |
| US6105398A (en) | 2000-08-22 |
| JPH11314840A (ja) | 1999-11-16 |
| CN1230606A (zh) | 1999-10-06 |
| EP0945534A3 (fr) | 2000-11-22 |
| RU2150537C1 (ru) | 2000-06-10 |
| KR100292422B1 (ko) | 2001-06-01 |
| EP0945534B1 (fr) | 2004-09-22 |
| KR19990078236A (ko) | 1999-10-25 |
| DE59910553D1 (de) | 2004-10-28 |
| UY25427A1 (es) | 1999-07-19 |
| HK1022934A1 (en) | 2000-08-25 |
| BR9901117A (pt) | 1999-12-14 |
| JP3010171B2 (ja) | 2000-02-14 |
| IL129084A0 (en) | 2000-02-17 |
| CN1154754C (zh) | 2004-06-23 |
| IL129084A (en) | 2002-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0945534B1 (fr) | Fournisseur positif à faible inertie pour des fils élastomères | |
| DE2736416C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Zuführen von Garn zu einer Strickmaschine | |
| DE19537215C2 (de) | Fadenliefergerät für elastische Garne | |
| DE4324412C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Einstellung der Fadenspannung | |
| DE19544202B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Einregeln einer nach einem Rechenspanner vorliegenden Fadenzugkraft in einer Textilmaschine | |
| DE3812449C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Regeln der Fadenspannung in einer Spulstelle eines Spulautomaten | |
| EP1783252A1 (fr) | Dipositif et méthode de séparation d'un faisceau de fibres de carbone | |
| DE2905713A1 (de) | Garnwickelvorrichtung | |
| EP0240799B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour régler la longueur et les mailles d'articles tricotés | |
| EP3766814B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'acheminement de câble, système d'usinage de câble et procédé d'acheminement d'un câble dans une machine d'usinage de câble | |
| DE2715988A1 (de) | Einrichtung zum steuern des bandauftrages beim schaeren | |
| EP1156143A1 (fr) | Méthode d'utilisation d'un cantre et cantre pour une machine d'enroulage | |
| DE19923802A1 (de) | Rundstrickmaschine zur Herstellung von Strickwaren mit wahlweise unterschiedlichen Eigenschaften und Verfahren zu ihrer Einstellung | |
| DE2812100C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Führen eines aus Einzelsträngen zusammengesetzten Gesamtstranges und Herstellen von gefachten Drahtspulen sowie Vorrichtung zum Durchführen des Verfahrens | |
| WO2009052846A1 (fr) | Dispositif de livraison de fil à régulateur adaptatif | |
| DE19811240A1 (de) | Fadenliefergerät mit verbessertem Fadenlauf | |
| EP0875479A1 (fr) | Procédé pour améliorer le processus de bobinage et station de bobinage pour la mise en oeuvre du procédé | |
| DE2635200C2 (de) | Fadenzuführeinrichtung | |
| WO2007045302A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de regulation de la densite de bobine d'une bobine de fil | |
| DE10032705B4 (de) | Fadenliefereinrichtung für Textilmaschinen | |
| EP1162295B1 (fr) | Méthode d'utilisation d'un cantre et cantre pour une machine d'enroulage | |
| DE102010046692B4 (de) | Dockenwickler zum Wickeln einer Warenbahn zu einer Docke | |
| DE19635373C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Ausgleichen von Fadenverbrauchs- und Fadenspannungsschwankungen bei der Zuführung von fadenförmigem Material | |
| DE1124407B (de) | Spulmaschine zur Erzeugung von Spulen mit ueber der Spulreise vorbestimmter Fadenspannung | |
| DE1585111B2 (de) | Verfahren zur Zuführung eines texturierten Fadens zu einer Textilmaschine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: SCHMODDE, HERMANN Inventor name: LEINS, EBERHARD |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20001228 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20021031 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59910553 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20041028 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20050125 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20050124 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2224469 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20050623 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060208 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20060208 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20080227 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20080423 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090901 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090208 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20180322 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20180226 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20210205 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20190209 |