EP0807710B1 - Procédé et dispositif pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un media liquide ou pâteux sur une bande de matériau en mouvement,en particulier une bande de papier ou de carton - Google Patents
Procédé et dispositif pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un media liquide ou pâteux sur une bande de matériau en mouvement,en particulier une bande de papier ou de carton Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0807710B1 EP0807710B1 EP97105849A EP97105849A EP0807710B1 EP 0807710 B1 EP0807710 B1 EP 0807710B1 EP 97105849 A EP97105849 A EP 97105849A EP 97105849 A EP97105849 A EP 97105849A EP 0807710 B1 EP0807710 B1 EP 0807710B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- supporting beam
- bearing
- supporting
- length
- rods
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21H—PULP COMPOSITIONS; PREPARATION THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES D21C OR D21D; IMPREGNATING OR COATING OF PAPER; TREATMENT OF FINISHED PAPER NOT COVERED BY CLASS B31 OR SUBCLASS D21G; PAPER NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D21H23/00—Processes or apparatus for adding material to the pulp or to the paper
- D21H23/02—Processes or apparatus for adding material to the pulp or to the paper characterised by the manner in which substances are added
- D21H23/22—Addition to the formed paper
- D21H23/32—Addition to the formed paper by contacting paper with an excess of material, e.g. from a reservoir or in a manner necessitating removal of applied excess material from the paper
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C11/00—Component parts, details or accessories not specifically provided for in groups B05C1/00 - B05C9/00
- B05C11/02—Apparatus for spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to a surface ; Controlling means therefor; Control of the thickness of a coating by spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to the coated surface
- B05C11/04—Apparatus for spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to a surface ; Controlling means therefor; Control of the thickness of a coating by spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to the coated surface with blades
- B05C11/041—Apparatus for spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to a surface ; Controlling means therefor; Control of the thickness of a coating by spreading or distributing liquids or other fluent materials already applied to the coated surface with blades characterised by means for positioning, loading, or deforming the blades
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for direct or indirect application of a liquid or pasty medium a running material web, in particular made of paper or Carton, according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the invention relates to a method for direct or indirect application of a liquid or pasty Medium on a running material web, in particular from Paper or cardboard.
- Such devices and methods are diverse Design known.
- Known devices include Commissioned works resting on a supporting beam and either for the direct or indirect application of a liquid or pasty coating medium on a running material web or for final dosing of a previously applied onto the material web Coating medium are designed.
- the Application of the coating medium via a pressure chamber with a Doctor element, a free jet nozzle or a comparable other known application device.
- the coating medium is applied directly to the e.g. from a counter roller opposite the support beam supported running material web applied, while at indirect application of the coating medium, e.g. on a applicator roller opposite the support beam and then from the surface of which is transferred to the material web.
- the second case that is to say with an order unit for final dosing a doctor blade or a comparable other known Doctor element provided to the already on the material web applied coating slip to the desired application quantity fine dosing.
- the two bearings are in two each at the front ends of the support beam, i.e.
- this type of device does not only have that Disadvantage of problematic supporting beam deflections and comparatively low natural frequencies, too undesirable resonances, e.g. with vibration frequencies of Base of the device or the hall floor in which the Device is set up, lead, but requires about it a very large, massive and therefore heavy and costly pivoting device.
- the invention is therefore based on the technical problem to create a generic device that the above avoids mentioned problems of the prior art and the a simple and effective way to adapt the Device to changing operating conditions, in particular a change of the string or Blade angle and the contact pressure of the final metering device, enables.
- a respective storage location of the device comprises two spaced apart bearing rods, each with one end articulated at articulation points of the support beam and with its other end articulated on at least one foundation are fixed.
- the support beam thus comprises a total of two Bearing rod pairs, i.e. one bearing rod pair per Depository.
- at least one support rod is included one end articulated to the support beam and with its other end articulated to the foundation.
- at least one of the aforementioned rods adjustable in length. It should be noted that under a length adjustment of one of the two bearing rods one Bearing position of course a synchronous adjustment of the corresponding bearing rod of the two bearing rods on the other Bearing point is to be understood to tilt the support beam to avoid and to evenly adjust the To ensure the supporting beam.
- the hinge point or the Joint axis of the at least one support rod is to be reached a certain desired support beam movement preferably spaced from the hinge points of the two bearing rods or differs from the joint axes of these two bearing rods.
- a suitable arrangement of the articulation points or hinge axes of the two bearing rods can Hinge point or the hinge axis of the at least a support rod, however, with the hinge point or Joint axis of one of the two bearing rods coincide.
- bars are any Understand transmission links with two pivot points.
- the inventive design form either the two spaced apart bearing rods together with the Support beam or one of the two bearing rods together with the at least one support rod and the support beam at the side Examination of the application work, a kind of quadrilateral joint, the Support beam as a connecting link between the bearing bars or between a storage stick per storage location and serves the support rod.
- At least one of the mentioned bars the as a simple lever or adjustable in length can be designed, this stabilizes itself movable structure. That from the bearing rods, the support beam and the at least one support rod
- the overall construction is therefore rigid, if not at least one of the rods is adjusted.
- the two bearing rod pairs together with the at least one support rod a kind of tripod.
- joints for the rods can also be suitable flexible or serve elastic components or hinges.
- the device according to the invention allows the application mechanism of the device to be adapted to changing operating conditions in a simple and effective manner, in particular it enables the strike angle (or blade angle if a doctor blade is used as a final metering device) and the contact pressure of the final metering device to be changed easily ongoing operation as well as at standstill. Not only this adjustment of the end metering device, but also a movement of the entire support beam into an operating, standby or service or maintenance position can be done universally by only one. Functional component, namely the length-adjustable rods. This saves complex and expensive additional individual adjusting devices and therefore allows a simplified and less expensive overall construction.
- one of the two bearing rods and the at least one support rod, which together with one of the bearing rods takes on a substantial part in the adjustment of the supporting beam and the components associated with the supporting beam is an essentially rotary or combined one rotatory-translational movement of the support beam around an axis or on a short movement path near the axis of the lowest moment of inertia of the support beam, the adjustment movements can be carried out very quickly and with little effort.
- the device according to the invention Due to its specific design, the device according to the invention, with a suitable choice of the respective rod lengths and positions and the arrangement of the articulation points of the support beam, also opens up the possibility of setting a largely arbitrary blade angle of the final metering device without the blade lifting off the counter roller during the adjustment process, the contact pressure changes unintentionally or there is an impermissible deflection of the blade. This ensures a regular coating profile and contributes to the creation of a high quality end product. It should be noted that the position of the point of contact between the blade tip of a doctor blade used as a final metering device and the counter roller, ie the applicator roller, changes slightly when the blade angle is adjusted due to the special design of the device according to the invention.
- the device can be easily adapted to different roller diameters and to any blade wear.
- the device according to the invention is also suitable for various types of final metering devices, for example for doctor bars (for example PC-Rollflex®), scraper bars, or when using doctor blades for both so-called stiff-blade and bent-blade operation. In this way, the device can adapt flexibly to any larger blade angle changes or deviations.
- the device according to the invention is therefore basically suitable for processing a wide variety of material web types.
- the hinge points of the support beam the two bearing rods essentially match. This Configuration is particularly convenient to the one previously described desired movement of the support beam to adjust the Blade angle and the contact pressure to realize.
- the Bearing rods and / or the at least one support rod further than length-adjustable actuators designed.
- Actuators can be suitable, for example mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electromagnetic actuators and the like, and more Act combinations of these.
- Another advantageous embodiment of the invention provides that the length-adjustable actuators are dependent and / or are adjustable independently of one another. To this Way can be by a suitable, coordinated Movement of one or more of these actuators Desired movement of the support beam and directly on it or indirectly attached components, especially the Final metering device, such as a doctor blade and the like, relative to one of the support beams opposite counter roller are executed.
- the device according to the invention further at least one Control and / or control and / or regulating device for controlled adjustment of the length-adjustable rods or actuators.
- a Control device advantageously includes one automatic control loop based on measured values for example the blade angle, the contact pressure, the Cross profile or other properties of the counter roll applied liquid or pasty medium especially the Final dosing device, i.e. the blade angle and if necessary, the contact pressure of the doctor blade suitable adjustment of the length-adjustable actuators and thus readjusted by moving the supporting beam. This permits the fastest possible adaptation of the commissioned work the device to changed conditions and avoids also longer downtimes.
- Control and / or control and / or regulating device can further include components that also include a manual, automatic or remote-controlled actuation of the actuators allow. It also enables a central one if required Control or regulation and control-related linkage of the length-adjustable actuators with other components the device.
- the at least one articulated Supported support rod related to the longitudinal direction of the supporting beam in Bar center is arranged.
- the at least one articulated Supported support bar related to the longitudinal direction of the supporting beam may also be arranged asymmetrically to the center of the supporting beam.
- the two can be hinged Bearing rods and movable structures shaped the supporting beam stabilized particularly easily and the distance of the support beam over its entire length relative to opposite counter roll to a constant value being held.
- the at least one articulated support rod at least one bearing point is provided. Using it is therefore only a support rod also an arrangement asymmetrical to the center of the supporting beam. This also allows a very stable and rigid fixation of the Beam and an exact positioning relative to opposite counter roller. Furthermore, the support rod in this position due to its proximity to the side Beam ends also easily accessible and easy to maintain.
- the device according to the invention there is a doctor blade as a particularly advantageous final metering device exposed.
- the device according to the invention not only different doctor blade designs, such as stiff blade and bent blade driving style, but also various others Final metering devices such as doctor blades or the like successfully used.
- the Bearing points of the supporting beam in the longitudinal direction of the beam in each case a distance to its two front ends inside the longitudinal beam extension are arranged.
- This arrangement the bearing points of the support beam decreased at the same Cross sections and wall thicknesses the deflection of the support beam compared to conventional designs.
- the natural frequency of Support beam higher than with conventional configurations. This results in a larger distance between the natural frequency of the Support beam from the vibration frequencies e.g. of Machine foundations and the hall floor on which the Applicator is at rest so that a resonance oscillation in the supporting beam is reliably prevented. Due to the higher natural frequency there is also greater flexibility in terms of constructive design of the supporting beam.
- the two bearing points of the supporting beam in the longitudinal direction of the beam arranged symmetrically to the center of the beam.
- the two Bearing in a further favorable embodiment of the Invention in the longitudinal direction of the bar also asymmetrical Bar center can be arranged.
- the distances between the bearing points and the front Bar ends each 15% to 30% of the bar length.
- At a preferred embodiment with symmetrical to the center of the bar arranged bearings is the distance between Bearing point and end of the beam with regard to one as little beam deflection as possible in a length range, which is about 22% to 25% of the beam length.
- a further advantageous embodiment of the invention exists in the support beam with a known Deflection compensation device.
- a deflection compensation device can be one on a thermal, pneumatic or hydraulic Equalization based configuration, but also about one on another balancing principle, such as one magnetic, inductive or mechanical compensation based Configuration.
- a thermal, pneumatic or hydraulic Equalization based configuration can be one on a thermal, pneumatic or hydraulic Equalization based configuration, but also about one on another balancing principle, such as one magnetic, inductive or mechanical compensation based Configuration.
- the wall thicknesses of the supporting beam can also be reduced Deflection compensation device compared to one conventional construction can be dimensioned smaller because the support beam with the smaller wall thicknesses in can compensate for its deflection.
- the solution according to the invention can therefore also be used Realize cheaper.
- the cross-sectional shape of the The supporting beam can vary depending on the structural conditions triangular, polygonal, round or in any other suitable way to get voted.
- the object underlying the invention is further solved by an inventive method for direct or indirect application of a liquid or pasty medium a running material web, in particular made of paper or Carton, by means of a device according to claim 1, wherein the Method comprising the features of claim 16.
- one according to the invention comprises Process step an independent and / or dependent controlled length adjustment of at least one of the bearing rods of the device per bearing or that at least one support rod to Bell angle between the final metering device and the Opposing roller and / or a device Contact pressure of the final metering device on this counter roller adjust and / or the support beam in an operating, Move intermediate or maintenance position.
- the different rods can also be executed sequentially.
- a single rod length adjustment (always with the bearing rods related to a respective bearing point of the support beam) therefore perform several functions, i.e. the aforementioned Adjustment of the line or blade angle of the Enddosier gifted, the change in contact pressure Final dosing device or moving the support beam into a Operating, intermediate or maintenance position. Additionally offers the method according to the invention which is already related advantages described with the device according to the invention.
- Another advantageous process step of The method according to the invention provides for movement of the support beam on a predetermined trajectory by means of each other independent and / or dependent controlled Length adjustment of the two bearing rods of a respective one Bearing point of the supporting beam.
- this Adjustment can be quite different, the length of the at least one support rod, it is adjustable in length or not, kept constant.
- Embodiment of the method according to the invention Method step provided in which the support beam by means of independent and / or dependent controlled Length adjustment of at least one of the two bearing rods per Bearing point and the at least one support rod on one predetermined trajectory is moved.
- the Freedom of movement of the support beam can be expanded.
- the path curve can be influenced so that it shrinks to almost a point, i.e. the support beam essentially rotates.
- An adjustment of both two bearing rods as well as the at least one support rod also encompassed by this process step.
- the respective Adjustment movements can be in the same direction and / or in opposite directions his.
- the inventive method provides that the support beam a predetermined trajectory by means of independent and / or dependent controlled length adjustment of at least one of the two bearing rods per bearing position and at least one a support rod is moved.
- the support beam can advantageously also by means of an independent and / or dependent one controlled length adjustment of the two bearing rods per Bearing point are moved on a predetermined trajectory.
- the movement of the support beam automatically regulated by means of suitable control devices is, the regulation depending on a desired Coating weight and / or wear of the Final metering device and / or the counter roller takes place.
- This again allows the fastest possible adjustment of the Application of the device to changed conditions and avoids longer downtimes.
- This also enables Measure if necessary a central control and control engineering linkage of the movement of the Length-adjustable actuators with a supporting beam other components of the device.
- the one provided according to the invention has proven particularly useful computer-aided regulation of the movement of the supporting beam.
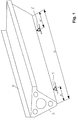
- FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective Representation of a first general embodiment of a Device according to the invention for direct or indirect Apply a liquid or pasty medium to a running material web, in particular made of paper or cardboard refer to.
- the one not shown in this figure Counter roll (which is basically both a one running material support roller for a direct Application of a coating medium as well as around an application roller
- Execution of an indirect application of the coating medium opposite device comprises one Beam 2, consisting of an outer tube with a closed polygonal cross-section, i.e. in the present case an im essential triangular cross section. In principle, however, any other suitable one Cross section usable.
- Inside the outer tube is a Inner tube arranged with a closed circular cross section and connected in one piece to the outer tube.
- the support beam 2 is only clean on two in FIG. 1 schematically indicated bearings S stored, of which the one (the left in Figure 1) as a fixed bearing and the others (the right one in FIG. 1) are designed as floating bearings is.
- the bearing points S are symmetrical in the present case arranged to the middle of the supporting beam and are from the front Ends of the support beam 2 each by an equal distance A, A 'indented towards the center.
- the ratio of the distance A, A 'between bearing S and the neighboring one end of the beam to the total length L of the support beam 2 is in the range of 15% to 30%. With a view to there has been as little beam deflection as possible Range of about 22% to 25% is particularly suitable proven.
- Arrangement of the bearing points S can be the distance A of one Bearing position to the adjacent end of the beam end different be selected as the distance A 'to the second bearing point the adjacent front end of the beam.
- Liquid e.g. Water
- the flowing through Liquids in the individual chambers in their temperature are variable that they are the thermal Deflection compensation.
- a mechanical one Deflection compensation device using Pressure hoses are used, as they are already from the DE-C-39 25 517 is known.
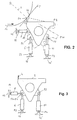
- Fig. 2 shows a schematic side view of others Details of the invention shown in Fig. 1 Device in the area of a depository S.
- a respective bearing S Device two spaced-apart bearing rods 6 and 8, which have different lengths in the present case and each with one end articulated to each other spaced articulation points P1, P5 of the support beam 2 and with their other end in different points P2 and P6 articulated on a foundation 12 of the device are, the pivot point P5 of the lever 8 slightly above the upper pivot point P1 of the Bearing rod 6 lies.
- the device therefore has two Bearing rod pairs, each consisting of a bearing rod 6 and 8 are formed. Since the design and arrangement of the Bearing bars 6, 8 are the same for each bearing S, are in the following description only the bearing rods one individual depository S can be considered.
- the bearing rod 6 runs essentially starting from the left side of the supporting beam vertically downward, while the bearing rod 8 of the left side of the supporting beam is essentially horizontal to the left and approximately at right angles to that Bearing rod 6 extends.
- the bearing rod 8 is the present case designed as a simple lever 8 of constant length.
- One starting from the right side of the supporting beam and in the extending substantially parallel to the bearing lever 6 individual support rod 10 is articulated at its upper end one spaced from the pivot point P1 of the bearing rod 6 Joint point P3 on the right side of the support beam 2 and with its lower end articulated to the foundation at point P4 12 of the device or another foundation 12 'fixed.
- the support rod 10 is related to the longitudinal direction of the supporting beam thus asymmetrical to the center of the supporting beam in the area of one individual bearing S arranged.
- top view of the support beam 2 forms the Support rod 10 together with the at the two bearings S provided bearing rod pairs 6, 8 a kind of tripod.
- the lower pivot point P4 of the support rod 10 is compared to the lower pivot point P2 of the bearing rod 6 slightly arranged lower.
- the bearing rod 6 and the support rod 10 are in the present embodiment as length-adjustable actuators in the form of hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 designed. Basically, however, that is also Use of other suitable mechanical, pneumatic, electrical, electromagnetic actuators and the like more, as well as combinations of them.
- This self-moving structure is created by the laterally on the support beam 2 attacking lever 8 stabilized, so that from the hydraulic cylinders 6, 10, the support beam 2 and the overall construction formed by the lever 8 is rigid in itself, if no length adjustment of at least one of the Hydraulic cylinder 6, 10 takes place.
- Hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 of the device In an operating position PB, which is shown in FIG Solid thick lines are illustrated Hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 of the device on each different defined lengths extended. This Length presetting can of course depend on the used cylinders and their arrangement from case to case vary considerably.
- the at the pivot points P1, P3 of the Support beam 2 attacking upper hinge points P1, P3 the Hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 are in this position in the essentially on the same horizontal plane and the Longitudinal axes of the hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 run as above already mentioned, approximately parallel to each other.
- this Configuration is the lever 8 in the illustration according to FIG.
- doctor blade 4 is given in the operating position PB Counter roll diameter with a defined contact pressure and a defined blade angle ⁇ on that of the device opposite counter roller 14 (the direction of rotation of the Counter roll 14 is indicated by an arrow).
- the Point of contact B1 between doctor blade 4 and counter roller 14 is in an ideal working position a straight line G through the center of the roller 14 and the Blade tip of the doctor blade 4.
- the blade angle ⁇ i.e.
- the Angle between one at the point of contact B1 to the counter roll 14 applied tangent T and the doctor blade 4, is in the Operating position PB is usually around 40 °, but it is strong depending on the type of doctor blade used and the Doctor blade attachment and the liquid to be processed or pasty medium or the material web in the case a direct order.
- the Blade angle ⁇ usually around 20-45 ° and in the bent blade style approximately up to 20 °. The settings mentioned however, they should only be understood as rough reference values.
- the Contact pressure of the doctor blade 4 against the counter roller 14 increased a combined, i.e. here also one interdependent, adjusting movement of the two Hydraulic cylinders 6, 10, the right hydraulic cylinder 10 slightly up and the left hydraulic cylinder 6 slightly is shut down.
- the device according to the invention can be as in the previously explained blade angle adjustment the point of contact B1 between the blade tip of the doctor blade 4 and the Change counter roller 14.
- a length adjustment of one the hydraulic cylinder 6, 10 for changing the blade angle ⁇ and / or the contact pressure should be sufficient.
- the contact pressure is reduced in the opposite way.
- the support beam 2 To start from the operating position PB the support beam 2 an intermediate position in a maintenance or It is generally the case to transfer the standby position to PW sufficient to retract the right hydraulic cylinder 10, i.e. the length between the two hinge points P3 and P4 shorten.
- the support beam 2 then moves from the above operating position at a predetermined Path curve in the in Fig. 2 by a dash-dotted line Line indicated maintenance position PW. If necessary the left one can of course do this at the same time Hydraulic cylinder 6 adjusted and a combined Actuating movement are carried out.
- the device according to the invention comprises one in the Computer-aided control and not shown drawings Control device for controlled adjustment of the length-adjustable hydraulic cylinder 6, 10.
- This device has an automatic control loop, which due to Measured values of, for example, the blade angle ⁇ , the Contact pressure of the doctor blade 4 on the roller 12, the Cross profile or other properties of the counter roll 14 applied liquid or pasty medium Blade angle ⁇ and / or the contact pressure of the doctor blade 4 by suitable length adjustment of the hydraulic cylinders 6, 10 and thus readjusted by a movement of the support beam 2.
- the control and regulating device also comprises Components that are also manual or remote controlled Actuating the actuators, for example via a control panel Central computer or the like, allow to the support beam 2 for example from the operating position PB in the Move maintenance position PW and vice versa.
- This Components are not in the drawing for the sake of simplicity shown.
- FIG. 3 shows a side view comparable to FIG. 2 a highly schematic representation of a second Embodiment of the device according to the invention.
- the variant provided at each storage location S is also a variant Bearing rod 8, the only in the embodiment of FIG. 2 is designed as a simple lever of constant length, designed to be adjustable in length.
- the bearing rod 8 is also thus articulated at one end to the supporting beam 2 connected that the hinge axis P5 this this Bearing bar 8 with the hinge axis of the left hinge point P1 of the support beam 2 and thus also with the support beam side Pivot point P1 of the bearing rod 6 matches. With his the other end is the length-adjustable bearing rod 8 in turn at point P6 articulated on one side of the foundation 12 fixed.
- this device corresponds to essentially that shown in Fig. 2, so that more Explanations are not required.
- the 3 has the support beam 2 due to the additional length adjustability of the bearing rod 8 a Another degree of freedom, so that if necessary, a still more differentiated movement of the support beam 2 and this attached doctor blade 4 is executable.
- the invention is not based on the above Embodiments, which are only examples, limited. Rather, the device and the inventive method depending on the application differ significantly from these variants. So in one device according to the invention different or different than the rod types described above are used, where always have a kinematic gear link under a "rod" two articulation points can be understood.
- the articulated storage the bearing rods, the at least one support rod and the Support beam 2 can also be used via other suitable flexible or elastic components or hinges. Can also both for a specific position of the device, for example the operating position, predetermined rod or Lever lengths as well as those with a length adjustment occurring changes in length of the respective rods or levers be different from each other. Furthermore, more than a support rod 10 may be provided.
- the attachment one support rod per bearing S possible.
- the single ones Bars may also be other than those discussed above and in suitable arrangements to each other shown in the figures accept. So it is conceivable that the bearing rod 6 and the support rod 10 in one as in FIGS. 2 and 3 cross the view shown in an X shape. Further can adjust the positioning speeds of the individual rods differ from each other.
- an indirect application of a liquid or pasty Medium are the device according to the invention and the The inventive method also for direct Application of said medium is suitable.
Landscapes
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Paper (AREA)
Claims (20)
- Procédé pour le transfert de signaux d'une sortie d'un premier circuit vers une entrée d'un second circuit, les circuits étant alimentés par une première et une seconde tension de fonctionnement et par un premier et un second potentiel de masse et des différences de potentiels variables pouvant se présenter entre les potentiels des masses, caractérisé en ce qu'un courant contrôlé par le signal à transférer circule de la sortie du premier circuit vers un point du circuit alimenté par un autre potentiel et contrôle un autre courant, partant du point du circuit, qui est amené à l'entrée du second circuit, et en ce que l'autre potentiel est choisi de telle sorte que lorsque des différences de potentiels se présentent, il existe chaque fois une tension permettant la circulation du courant et de l'autre courant entre la sortie du premier circuit et l'autre potentiel d'une part, et entre l'autre potentiel et l'entrée du second circuit d'autre part.
- Circuit pour le transfert de signaux d'une sortie d'un premier circuit vers une entrée d'un second circuit, les circuits étant alimentés par une première et une seconde tension de fonctionnement et par un premier et un second potentiel de masse et des différences de potentiels variables pouvant se présenter entre les potentiels des masses, caractérisé en ce que la sortie du premier circuit est pourvue d'une source de courant contrôlable (9, 13 ; 9', 13') dont le courant circule en direction d'un point du circuit alimenté par un autre potentiel et contrôle une autre source de courant (12, 15 ; 12', 15') raccordée au point du circuit (11, 11') dont le courant circule en direction de l'entrée de l'autre circuit, et en ce que l'autre potentiel est choisi de telle sorte que lorsque des différences de potentiels se présentent, il existe chaque fois une tension permettant le courant et l'autre courant entre la sortie du premier circuit et l'autre potentiel d'une part, et entre l'autre potentiel et l'entrée du second circuit d'autre part.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que l'autre potentiel (GND3) est inférieur à la première tension de fonctionnement d'au moins la somme de la tension émetteur-collecteur d'un transistor (9) constituant au moins partiellement la source de courant, son émetteur étant alimenté par la première tension de fonctionnement, et de la tension base-émetteur d'un transistor (12) constituant au moins partiellement l'autre source de courant, et est inférieur à la seconde tension de fonctionnement d'au moins la somme de la tension collecteur-émetteur du transistor (12) constituant l'autre source de courant, et de la tension base-émetteur d'un transistor (16) relié à l'entrée du second circuit.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que l'autre potentiel (GND3) est supérieur au premier potentiel de masse d'au moins la somme de la tension émetteur-collecteur d'un transistor (9') constituant au moins partiellement la source de courant, son émetteur étant alimenté par le premier potentiel de masse, et de la tension base-émetteur d'un transistor (12') constituant au moins partiellement l'autre source de courant, et est supérieur au second potentiel de masse d'au moins la somme de la tension collecteur-émetteur du transistor (12') constituant l'autre source de courant, et de la tension base-émetteur d'un transistor (16') relié à l'entrée du second circuit.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que les tensions de fonctionnement sont positives par rapport aux potentiels des masses, en ce que la source de courant du premier circuit comporte un transistor pnp (9) et est alimentée par la première tension de fonctionnement, en ce que l'entrée du second circuit comporte une résistance (14) alimentée par la seconde tension de fonctionnement, et en ce que l'autre potentiel correspond essentiellement au potentiel de masse le plus négatif.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que les tensions de fonctionnement sont positives par rapport aux potentiels des masses, en ce que la source de courant du premier circuit comporte un transistor npn (9') et est alimentée par le premier potentiel de masse, en ce que l'entrée du second circuit comporte une résistance (14') alimentée par le second potentiel de masse, et en ce que l'autre potentiel correspond essentiellement à la tension de fonctionnement la plus positive.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que les tensions de fonctionnement sont négatives par rapport aux potentiels des masses, en ce que la source de courant du premier circuit comporte un transistor npn et est alimentée par la première tension de fonctionnement, en ce que l'entrée du second circuit comporte une résistance alimentée par la seconde tension de fonctionnement, et en ce que l'autre potentiel correspond essentiellement au potentiel de masse le plus positif.
- Circuit selon la revendication 2, caractérisé dispositif de dosage terminal (4) et le rouleau conjugué (14) opposé au dispositif et/ou d'une pression d'application du dispositif de dosage terminal (4) contre ce rouleau conjugué (14) et/ou à déplacer la poutre porteuse (2) dans une position de fonctionnement, intermédiaire ou d'entretien.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de dosage terminal est une lame de racloir (4) ou similaire.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 9, caractérisé en ce que les deux points d'appui (S) de la poutre porteuse (2) sont disposés dans la direction longitudinale de la poutre porteuse de manière symétrique par rapport au centre de la poutre porteuse.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 9, caractérisé en ce que les deux points d'appui (S) de la poutre porteuse (2) sont disposés dans la direction longitudinale de la poutre porteuse de manière asymétrique par rapport au centre de la poutre porteuse.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 10 ou 11, caractérisé en ce que les distances (A, A') des points d'appui (S) par rapport aux extrémités de la poutre porteuse du côté frontal représentent respectivement 15% à 30% de la longueur (L) de la poutre porteuse.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 10, caractérisé en ce que les distances (A, A') des points d'appui (S) par rapport aux extrémités de la poutre porteuse du côté frontal se trouvent respectivement dans une gamme de longueur qui représente approximativement 22 à 25% de la longueur (L) de la poutre porteuse.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 13, caractérisé en ce que la poutre porteuse (2) est pourvue d'un dispositif d'équilibrage en flexion.
- Procédé pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un milieu liquide ou pâteux sur une bande de matériau en mouvement, en particulier en papier ou en carton, au moyen d'un dispositif selon la revendication 1,
comprenant l'étape consistant à
ajuster le réglage longitudinal d'au moins l'une des barres d'appui (6, 8) du dispositif, contrôlé de manière indépendante et/ou dépendante l'une de l'autre, par point d'appui (S) ou de l'au moins une barre de support (10), d'un angle d'enduction (α) entre le dispositif de dosage terminal (4) et le rouleau conjugué (14) opposé au dispositif et/ou d'une pression d'application du dispositif de dosage terminal (4) contre ce rouleau conjugué (14) et/ou à déplacer la poutre porteuse (2) dans une position de fonctionnement, intermédiaire ou d'entretien. - Procédé selon la revendication 15, caractérisé par le déplacement de la poutre porteuse (2) suivant une trajectoire prédéterminée au moyen d'un réglage longitudinal des deux barres d'appui (6, 8) contrôlé de manière indépendante et/ou dépendante l'une de l'autre, par point d'appui (S).
- Procédé selon la revendication 16, caractérisé par le déplacement de la poutre porteuse (2) suivant une trajectoire prédéterminée au moyen d'un réglage longitudinal d'au moins l'une des deux barres d'appui (6, 8) contrôlé de manière indépendante et/ou dépendante, par point d'appui (S), et de l'au moins une barre de support (10).
- Procédé selon la revendication 16, caractérisé par le déplacement de la poutre porteuse (2) et la modification de l'angle d'enduction (α) seulement par réglage longitudinal contrôlé de la barre d'appui (6), de sorte que le dispositif de dosage terminal (4) suive essentiellement exactement le contour du rouleau conjugué (12) lors du mouvement de la poutre porteuse (2) et de la modification de l'angle d'enduction (α).
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 16 à 18, caractérisé par le réglage automatique du mouvement de la poutre porteuse (2), le réglage s'effectuant en fonction d'un poids d'enduction souhaité et/ou d'une usure du dispositif de dosage terminal (4) et/ou du rouleau conjugué (14).
- Procédé selon la revendication 19, caractérisé en ce que le réglage est assisté par ordinateur.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19619250 | 1996-05-13 | ||
| DE19619250A DE19619250A1 (de) | 1996-05-13 | 1996-05-13 | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum direkten oder indirekten Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Mediums auf eine laufende Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Karton |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0807710A1 EP0807710A1 (fr) | 1997-11-19 |
| EP0807710B1 true EP0807710B1 (fr) | 2001-10-17 |
Family
ID=7794189
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97105849A Expired - Lifetime EP0807710B1 (fr) | 1996-05-13 | 1997-04-09 | Procédé et dispositif pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un media liquide ou pâteux sur une bande de matériau en mouvement,en particulier une bande de papier ou de carton |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5958513A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0807710B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPH1052663A (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE207158T1 (fr) |
| BR (1) | BR9700639A (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19619250A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19722456A1 (de) * | 1997-05-28 | 1998-12-03 | Voith Sulzer Papiermasch Gmbh | Einrichtung zum Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Mediums auf eine laufende Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Pappe |
| DE19743520B4 (de) * | 1997-10-01 | 2005-12-08 | Voith Paper Patent Gmbh | Rakeleinrichtung für eine Vorrichtung zum Auftragen eines flüssigen bis pastösen Mediums auf einen sich vorbeibewegenden Untergrund |
| DE19748684A1 (de) * | 1997-11-04 | 1999-05-06 | Voith Sulzer Papiertech Patent | Vorrichtung zum Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Mediums auf eine Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Karton |
| DE19812929A1 (de) * | 1998-03-24 | 1999-09-30 | Voith Sulzer Papiertech Patent | Vorrichtung zum Egalisieren oder/und Dosieren einer auf einen Untergrund aufgebrachten Schicht eines flüssigen oder pastösen Auftragsmediums |
| DE19926091A1 (de) * | 1999-06-08 | 2000-12-14 | Voith Sulzer Papiertech Patent | Vorrichtung zum direkten oder indirekten Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Auftragsmediums auf eine Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Karton, Verfahren zur Inbetriebnahme einer derartigen Vorrichtung |
| AU2003298931A1 (en) * | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-30 | Stora Enso North America Corp. | Doctor apparatus |
| DE102004005079A1 (de) * | 2004-02-02 | 2005-08-18 | Voith Paper Patent Gmbh | Auftragsvorrichtung |
| ES2311416B1 (es) * | 2007-07-24 | 2009-12-03 | Jose Joaquin Amonarriz Azcolain | Doctor para la industria papelera. |
| DE102009002027A1 (de) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur Egalisierung |
| EP2883999B1 (fr) * | 2013-12-11 | 2016-04-20 | Garcia Xabier Echeverria | Racle pour une machine à papier |
| CN104069992B (zh) * | 2014-07-04 | 2016-11-02 | 深圳市泰仁恩科技有限公司 | 一种涂布刮刀的组装结构 |
| DE102017109549B4 (de) * | 2017-05-04 | 2021-07-29 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Streicheinrichtung zur Behandlung einer Faserstoffbahn |
| WO2023222299A1 (fr) * | 2022-05-19 | 2023-11-23 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Dispositif, utilisation et procédé de dosage ou de nivellement et procédé de dosage ou de mise à niveau |
| CN117900093B (zh) * | 2024-03-18 | 2024-05-24 | 洛阳沃虹石化设备有限公司 | 一种油气分离膜刮膜机及其换刀方法 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3245378A (en) * | 1962-05-14 | 1966-04-12 | Kimberly Clark Co | Doctor blade holders for a papermaking machine |
| DE3311999A1 (de) * | 1983-04-02 | 1984-10-11 | J.M. Voith Gmbh, 7920 Heidenheim | Streicheinrichtung zur beschichtung laufender warenbahnen |
| DE3825816A1 (de) * | 1988-07-29 | 1990-02-01 | Jagenberg Ag | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen beschichten einer um eine gegenwalze gefuehrten materialbahn |
| FI100311B (fi) * | 1988-09-23 | 1997-11-14 | Voith Gmbh J M | Päällystyskoneiston kiillotuslaite |
| FI886062A (fi) * | 1988-12-30 | 1990-07-01 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Vinkelkompensationsanordning foer schaberblad. |
| FI90634C (fi) * | 1989-01-17 | 1994-03-10 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Sivelylaite ja menetelmä materiaalirainan sivelemiseksi |
| DE3908386A1 (de) * | 1989-03-15 | 1990-09-27 | Jagenberg Ag | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum beschichten von materialbahnen, insbesondere von papier- oder kartonbahnen |
| FI91367C (fi) * | 1990-12-13 | 1994-06-27 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Taipumakompensoitu teräpalkki |
| DE4130118C2 (de) * | 1991-09-11 | 1995-04-20 | Jagenberg Ag | Vorrichtung zum Beschichten einer um eine Gegenwalze geführten Materialbahn, insbesondere einer Papier- oder Kartonbahn |
| FI91903C (fi) * | 1992-03-19 | 1994-08-25 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Pidin päällystyssauvan kehtoa tai päällystysterää varten |
| FI93884C (fi) * | 1992-04-10 | 1995-06-12 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Applikointipalkki liimapuristimessa |
| DE4230241C2 (de) * | 1992-09-10 | 1994-07-14 | Voith Gmbh J M | Auftragswerk zur Beschichtung von Bahnen aus Papier oder Karton |
| FI93665C (fi) * | 1992-11-13 | 1995-05-10 | Valmet Paper Machinery Inc | Menetelmä ja laitteisto paperirainan päällystämiseksi |
| BR9307832A (pt) * | 1993-12-11 | 1995-12-05 | Voith Gmbh J M | Um conjunto de montagem para uma estação de pintar papel de contra-rolo único |
-
1996
- 1996-05-13 DE DE19619250A patent/DE19619250A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-04-09 AT AT97105849T patent/ATE207158T1/de active
- 1997-04-09 EP EP97105849A patent/EP0807710B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-04-09 DE DE59704923T patent/DE59704923D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-04-30 BR BR9700639A patent/BR9700639A/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1997-05-12 US US08/854,694 patent/US5958513A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-05-13 JP JP9121868A patent/JPH1052663A/ja active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE59704923D1 (de) | 2001-11-22 |
| DE19619250A1 (de) | 1997-11-20 |
| JPH1052663A (ja) | 1998-02-24 |
| US5958513A (en) | 1999-09-28 |
| EP0807710A1 (fr) | 1997-11-19 |
| ATE207158T1 (de) | 2001-11-15 |
| BR9700639A (pt) | 1998-09-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0807710B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un media liquide ou pâteux sur une bande de matériau en mouvement,en particulier une bande de papier ou de carton | |
| DE102004045651B4 (de) | Flügel, insbesondere Tragflügel eines Flugzeugs, mit veränderbarem Profil | |
| EP0701022B1 (fr) | Appareil d'enduction pour déposer directement ou indirectement un matériau fluide ou pâteux sur une bande en mouvement | |
| EP2905108B1 (fr) | Châssis d'une machine | |
| DE2632302B2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Herstellen von Schaumstoffblöcken mit rechteckigem Querschnitt | |
| DE4432177A1 (de) | Auftragswerk zum direkten oder indirekten Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Mediums auf eine laufende Materialbahn | |
| CH680653A5 (fr) | ||
| DD153404A5 (de) | Gleisstopfmaschine | |
| EP1637450B1 (fr) | Aile, en particulier aile d'aéronef, avec profil variable | |
| AT522456B1 (de) | Stopfaggregat zum Unterstopfen von Schwellen eines Gleises | |
| DE19832064C2 (de) | Kalander für Bahnen aus Papier oder ähnlichem Material | |
| EP0781884A1 (fr) | Appareil d'enduction pour déposer directement ou indirectement un matériau fluide ou pâteux sur une bande en mouvement | |
| EP0807711A2 (fr) | Dispositif pour l'application directe ou indirecte d'un matériau fluide ou pâteux sur une bande en défilement | |
| DE69620464T2 (de) | Klingenhalterung | |
| DE3018851C2 (de) | Ortbetonschalung für Tunnels | |
| DE102020112767B3 (de) | Behälterbefüllmaschine mit einer Hubeinheit sowie eine Hubeinheit für eine Behälterbefüllmaschine | |
| EP1186703B1 (fr) | Dispositif de raclage | |
| DE2638964C3 (de) | Sägegatter | |
| DE19983788C2 (de) | Biegsamer Balken für eine Papier- oder Kartonmaschine | |
| DE10392825B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Steuerung von Schwingungen eines Rakelbalkens einer Beschichtungsstation | |
| DE2744990C3 (de) | Kalander zur Druckbehandlung von Bahnen | |
| CH676369A5 (fr) | ||
| DE3841859C2 (fr) | ||
| CH667478A5 (en) | Jig control - has adjustment to deflection roller angle to keep fabric edge straight during winding and unwinding | |
| DE19620261A1 (de) | Auftragwerk zum direkten oder indirekten Auftragen eines flüssigen oder pastösen Mediums auf eine laufende Materialbahn |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FI FR IT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19980519 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VOITH SULZER PAPIERTECHNIK PATENT GMBH |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19991213 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VOITH PAPER PATENT GMBH |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FI FR IT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRE;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED.SCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20011017 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20011017 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 207158 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 20011115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59704923 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20011122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020430 |
|
| EN | Fr: translation not filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20110414 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20110421 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20110414 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20110414 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: EUG |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 207158 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120409 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120409 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59704923 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20121101 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120410 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121101 |