EP0798750B1 - Résistance de limitation de courant à comportement PTC - Google Patents
Résistance de limitation de courant à comportement PTC Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0798750B1 EP0798750B1 EP97810116A EP97810116A EP0798750B1 EP 0798750 B1 EP0798750 B1 EP 0798750B1 EP 97810116 A EP97810116 A EP 97810116A EP 97810116 A EP97810116 A EP 97810116A EP 0798750 B1 EP0798750 B1 EP 0798750B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- double
- resistance body
- resistor according
- varistor
- resistance
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01C—RESISTORS
- H01C7/00—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material
- H01C7/13—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material current responsive
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01C—RESISTORS
- H01C1/00—Details
- H01C1/14—Terminals or tapping points or electrodes specially adapted for resistors; Arrangements of terminals or tapping points or electrodes on resistors
- H01C1/1406—Terminals or electrodes formed on resistive elements having positive temperature coefficient
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01C—RESISTORS
- H01C13/00—Resistors not provided for elsewhere
- H01C13/02—Structural combinations of resistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01C—RESISTORS
- H01C7/00—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material
- H01C7/02—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material having positive temperature coefficient
- H01C7/027—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material having positive temperature coefficient consisting of conducting or semi-conducting material dispersed in a non-conductive organic material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01C—RESISTORS
- H01C7/00—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material
- H01C7/10—Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material voltage responsive, i.e. varistors
- H01C7/12—Overvoltage protection resistors
Definitions
- the invention is based on an electrical resistance according to the preamble of claim 1.
- Such a Resistance detects and limits flowing in a load circuit Short circuit or overcurrents. Only then does an im interrupts Load circuit provided switch the limited current. Of the Switch can therefore be on one compared to the short circuit power low breaking capacity be designed.
- a current limiting resistor of the aforementioned type For example, in US 5,313,184 A described. Such a resistance contains two connection electrodes between them connected in parallel with a PTC behavior resistance body and a varistor are arranged. The resistance body and the varistor contact each other over the entire isolation distance between the two connection electrodes. hereby become local overvoltages in the resistor body and thus Inadmissibly high local thermal loads of the resistance body avoided.
- resistors can be connected in series.
- a Such arrangement is relatively expensive, since both between the individual resistance bodies as well as between the individual ones Varistors metal electrodes are arranged.
- the contact resistance between a metal electrode and the material of the resistor body is generally relatively high and contributes to current limiting tasks typical resistance with a total resistance of about 50 m ⁇ as much as the material of the resistor body to the total resistance.
- metal electrodes and usually as a material for the resistor body used filler-filled polymers different electrical conductivities and different thermal expansion coefficients on. This allows mechanical stresses in the Inside of the resistance arise, which its mechanical and possibly affect electrical properties can.
- the invention as defined in claim 1 is located the task is based on a current-limiting resistor To create PTC behavior, which is easier and less expensive Way can be produced and both a high rated current carrying capacity and a wide voltage range as well as a has great operational safety.
- the resistance according to the invention is the PTC behavior having resistive body designed such that it both the electrical contact to the terminal electrodes as well as to Varistor guaranteed. This will be the electrical contact saved the varistor serving metal electrodes.
- the resistance according to the invention can be extremely high cost-effective and in one for a mass production particularly suitable methods are produced.
- the varistor and the terminal electrodes holding and usually from one filled body filled polymer formed resistance body can namely extremely inexpensive in a common plastic processing method, as generated by injection molding become. By inserting the varistor in the resistance body and applying the terminal electrodes to the resistor body can then in an extremely simple manner the inventive Resistance to be completed.
- the resistor according to the invention has more than two in series switched varistors, so eliminating metal electrodes between each varistor and between PTC behavior having partial bodies of the resistance body, which as well how the varistors are connected in series.
- the cold resistance of the resistance is so much lowered and according to the rated current carrying capacity of the current limiting Resistance significantly improved according to the invention.
- a particularly high rated current carrying capacity is achieved when the Resistive body is integrally formed. The otherwise between the individual partial bodies existing low Contact resistance is then completely eliminated.
- the Resistance then manufactured in a particularly cost-effective manner become.
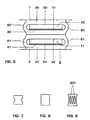
- Figures 7 to 9 show in a side view from the right formed as a contact point part of the according to the figures 1 and 2 performed resistance.
- FIG. 12 shows a diagram in which the time profile of electrical quantities which are typical in limiting a short-circuit current for the behavior of the resistor designed according to FIG. 2, such as the voltage U PTC applied to the resistor body and that guided in the resistance body Current I PTC and the varistor in the guided current I varistor .
- the varistors 40-45 are preferably formed of a doped ceramic based on a metal oxide such as ZnO or a titanate such as SrTiO 3 or BaTiO 3 , or a carbide such as SiC.
- the varistor 40 provided in the embodiments according to FIGS. 1, 2 and 10 has a breakdown voltage which is above the rated voltage of the electrical system in which the resistor is used.
- a plurality of varistors for example the varistors 40, 41, 42, 43, 44 and 45, are arranged in series in a stack. This varistor stack has a breakdown voltage which is also above the rated voltage of the current-limiting resistor-containing electrical system.
- the resistance body 3 consists of a PTC behavior exhibiting material and may be formed by a filled with an electrically conductive filler, such as conductivity black, TiC or TiB 2 , in particular thermosetting or thermosetting polymer.
- an electrically conductive filler such as conductivity black, TiC or TiB 2 , in particular thermosetting or thermosetting polymer.
- the resistance body 3 has two Contact surfaces 50, 51 and a response point 60, which over the two contact surfaces 50, 51 parallel to the varistor 40th is switched.
- the response point 60 is dimensioned such that it performs a PTC transition when a resistance-led Current exceeds a predetermined threshold.
- the contact surfaces 50 and 51 are respectively on the inner surfaces the leg of the U arranged. This ensures that the Varistor 40 without additional metal contacts via the resistor body 3 in an electrically conductive manner with the connection electrodes 1, 2 is connected.
- in the embodiment according to FIG. 2 is additionally made of metal or conductive polymer existing intermediate piece 70 is provided, which between a Contact surface of the varistor 40 and the contact surface 51 of the Resistive body 3 is arranged.
- This intermediate piece allows on the one hand the expansion of the U. on the other hand serves the intermediate piece 70 of the absorption of thermal energy from the Varistor 40. Such energy is generated when due a occurring at the contact surfaces 50, 51 overvoltage Leakage is passed through the varistor 40.
- the address 60 is located in the bent connecting part of the U.
- the point of contact can have the same cross-section as the resistance body 3 in the region of the two contact surfaces 50, 51, because by the bend of the U already a local increase the resistance is ensured.
- the Contact point in general, be designed as a material molding, which reduces the cross-section of the U in the region of its bend.
- the cross section of the resistor body should be 3 in the area of the response 60 be smaller than each the two contact surfaces between the resistor body and the two terminal electrodes 1, 2, because only the PTC junction can be relocated to the point 60 out.
- Constructive training of the point 60 are from the Figures 7, 8 and 9 can be seen and can by waist of the Cross-section of the U transverse to the plane (Fig.7) or in Direction of the legs of the U in the drawing plane (Fig.8 in In connection with FIGS. 1 and 2), by arrangement of in Direction of the ends of the U guided and essentially mutually parallel slots 601 ( Figure 9) or in achieved particularly simple way through round through holes become.
- the slotted embodiment of Point 60 is characterized by the fact that the current not only evenly distributed over the narrowed cross-section is guided, but that when executing the PTC transition the Material of the point of contact in virtually all directions can move, causing unwanted mechanical stresses in the Resistance body 3 can be avoided in a particularly strong mass.
- Resistors is next to the varistor 40 at least one another varistor connected in series with this varistor 41 provided to 45. Accordingly, the resistance body 3 more contact surfaces, for reasons of clarity only the varistor 41 at potential leading contact surfaces 52 and 53 are designated. About two of the others Contact surfaces, such. B. 52, 53, each parallel to a, like e.g. 41, the other varistors 41 to 45 are more Contact points are switched, for reasons of clarity only the address 61 is shown. Corresponding the contact point 60 are also these other contact points, as the address 61, locally decoupled from the varistors formed in the resistance body 3 and perform accordingly 60 address a PTC junction off when in resistance guided current exceeds the predetermined threshold.
- the at least two varistors 40, 41 connected in series containing embodiments of the inventive resistor are for use in load circuits with high voltages intended.
- the in Series switched 60, 61 switched off the PTC transition and thus the current flowing through the resistor becomes fast limited.
- After limiting the current to the terminal electrodes 1, 2 occurring overvoltages are by leakage currents degraded, which in the series connected varistors 40, 41 be guided. Speaks one of the contact points, for example the contact point 61, before the other contact points have approached, the occurrence is impermissibly higher Overvoltages at this point of contact by the parallel switched varistor avoided.
- the Partial bodies 30 to 35 each formed as U and are such joined together, that the resistance body 3 is a meander forms.
- this meander are two each in the meander in pairs successive U against each other rotated by 180 ° and so pushed together, that each one of the legs of one of U is located between the thighs of the other U.
- the varistors can then by simple without additional spacers Insertion into the U contacted with the resistance body 3 become.
- a particularly good mechanical strength of the resistance body 3 is obtained when as in the embodiment according to Fig.5 is apparent, between the two sections at least one of the U, e.g. the part body 31 ', each one of Varistors, e.g. 41, and one leg each two in the resistance body adjacent and only by the varistor from each other spaced U, e.g. the part body 30 'and 32', arranged are.
- each one of Varistors e.g. 41
- one leg each two in the resistance body adjacent and only by the varistor from each other spaced U e.g. the part body 30 'and 32', arranged are.
- the mutually facing inner surfaces of superimposed legs of the U e.g. the partial body 31 'and Formed 32 'and 30' and 31 ', wedge-shaped bevelled, then can the resistance body 3 by mutual wedging the single U are made very easy.
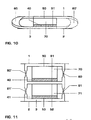
- FIGS. 4 and 11 show embodiments of the invention Resistance can be seen in which the resistor body is integrally formed.
- the contact resistance between the individual partial bodies deleted the resistance body 3 is characterized by a particularly low ohmic resistance.
- the Resistive bodies are produced in a casting process and can then the resistance by subsequent insertion of the Varistors and the optionally provided intermediate pieces 70th to 73 or 70, 71 in a particularly simple and cost-saving Be made way.
- the Widerstansisson 3 then forward open and closed pockets of semicircular Cross-section, in which in the manufacture of the resistor the individual varistors are inserted.
- the resistance body 3 may be formed as follows: as U with curved ( Figures 1 to 5) or straight connecting portion, as a double U with bent connecting sections ( Figure 2 with dash) or straight connecting sections, as Screw line (Fig.10), as a double or multiple screw line (Fig. 10 with dashes), as a meander ( Figures 3 to 5), as Double meander ( Figures 6 and 11) or garland or Double garland (stacking of several partial bodies, which are formed according to the part-body of Fig.10).
- the resistance body is a double U, double screw line, Formed double meander or double garland, so he can beside the point of 60 an additional parallel to this Contact point 60 'have ( Figures 2, 6, 10 and 11).
- One with resistor provided with such a resistor body 3 is characterized by high strength, greater current carrying capacity and ease of manufacture. At the same time, the PTC transition occurring thermal and mechanical forces evenly distributed throughout the resistance.
- Runs or run as in the embodiments according to the FIGS. 1 to 6 show the part containing the point of contact 60 or the contact points 60, 60 ', 61, ... containing parts of the U or the double U is bent, so when executing the PTC transition by strong local heating of the resistance body in the Range of points of contact generated due to mechanical force the spring effect of the legs of the U or double U attenuated on the part of the resistor body containing the varistors transfer. Will the contact points be predominantly horizontal Guided areas of the connecting parts of the U or double U guided, so is practically no vertical contact force of the resistance produces debilitating counterforce.
- the resistance can be particularly space-saving be formed.
- the resistance body 3 as a screw line, garland or Double or multiple garlands trained, so is a achieved particularly good cooling of the resistor, because then Ambient air constructed along the helical line Resistance body 3 is led into the interior of the resistor.
- the contact points 60, 60 ' are predominantly formed horizontally guided part of the resistor body.
- the resistance body can be other, but topological have similar shapes, which optionally to the Topology of the varistor or varistors are adjusted.
- the Varistor can take virtually any cross-sectional shapes and be designed, for example, round, rectangular or oval.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Thermistors And Varistors (AREA)
Claims (15)
- Résistance de limitation de courant avec deux électrodes de raccordement (1, 2) disposées en parallèle l'une par rapport à l'autre, avec un corps de résistance (3) contacté en surface par les électrodes de raccordement (1, 2) et présentant un comportement PTC et avec un premier varistor (40) se trouvant en contact électriquement conducteur avec le corps de résistance (3), caractérisée en ce que le corps de résistance (3) comporte deux premières faces de contact (50, 51) avec le premier varistor (40) ainsi qu'une première zone de réponse (60), qui est raccordée en parallèle avec le premier varistor (40) par les deux premières faces de contact (50, 51) et qui effectue une transition PTC au-dessus d'une valeur de seuil d'un courant circulant à travers la résistance.
- Résistance selon la revendication 1 avec au moins un deuxième varistor (41) pouvant être raccordé en série avec le premier varistor (40), caractérisée en ce que le corps de résistance (3) présente deux deuxièmes faces de contact (52, 53) ainsi qu'au moins une deuxième zone de réponse (61), qui est raccordée en parallèle avec le deuxième varistor (41) par l'intermédiaire des deux deuxièmes faces de contacts (52, 53) et qui effectue la transition PTC au-dessus de la valeur de seuil.
- Résistance selon l'une des revendications 1 ou 2, caractérisée en ce qu'une (50) des deux premières faces de contact est raccordée par une première pièce intermédiaire électriquement conductrice (70) à une face de contact du premier varistor (40).
- Résistance selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisée en ce que la surface de la section transversale du corps de résistance (3) dans la région de la première (60) et/ou de la au moins une deuxième zone de réponse (61) est plus petite que chacune des deux faces de contact entre le corps de résistance (3) et les deux électrodes de raccordement (1, 2).
- Résistance selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisée en ce que des portions du corps de résistance (3) menées parallèlement aux électrodes de raccordement (1, 2) contiennent chacune une des deux premières (50, 51) ou deuxièmes (52, 53) faces de contact, et en ce que la première (60) ou la au moins une deuxième zone de réponse (61) est formée dans une partie du corps de résistance (3) reliant deux de ces portions voisines.
- Résistance selon la revendication 5, caractérisée en ce que la première (60) et/ou la au moins une deuxième (61) zone de réponse contiennent des fentes (601) ou des encoches menées en direction des extrémités de la portion et sensiblement parallèles les unes aux autres.
- Résistance selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 6, caractérisée en ce que le corps de résistance (3) est formé d'un seul tenant.
- Résistance selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 6, caractérisée en ce que le corps de résistance (3) est composé de corps partiels (30, 31, ..., 34') comportant chacun deux portions orientées parallèlement aux électrodes de raccordement (1, 2) et au moins une partie reliant les deux portions.
- Résistance selon la revendication 8, caractérisée en ce qu'un des varistors (40) et au maximum une portion d'un corps partiel (31) voisin dans le corps de résistance (3) sont disposés entre les deux portions d'au moins un corps partiel (30).
- Résistance selon la revendication 9, caractérisée en ce qu'un des varistors (41) et chaque fois une portion de deux corps partiels (30', 32') voisins dans le corps de résistance (3) sont disposés entre les deux portions d'au moins un des corps partiels (31').
- Résistance selon la revendication 10, caractérisée en ce que les faces orientées l'une vers l'autre des deux portions des corps partiels (30', 31', ...) sont formées en oblique en forme de coin.
- Résistance selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 11, caractérisée en ce que le corps de résistance (3) est façonné en forme de U, de ligne hélicoïdale, de double U, de ligne hélicoïdale double ou multiple, de méandres, de guirlande, de méandres doubles ou multiples, ou de guirlande double ou multiple, etc.
- Résistance selon la revendication 12, caractérisée en ce que, lorsque l'on façonne le corps de résistance en forme de double U, de ligne hélicoïdale double, de méandres doubles ou de guirlande double, il est prévu à côté de la première (60) ou de la deuxième (61) zone de réponse au moins une zone de réponse supplémentaire (60', 61') raccordée en parallèle avec celle-ci.
- Résistance selon l'une des revendications 12 ou 13, caractérisée en ce que chaque partie du U ou du double U contenant une zone de réponse (60) est orientée perpendiculairement aux branches du U ou du double U.
- Résistance selon l'une des revendications 12 ou 13, caractérisée en ce que chaque partie du U ou du double U ou du U multiple contenant une zone de réponse (60) est courbée.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19612841 | 1996-03-30 | ||
| DE19612841A DE19612841A1 (de) | 1996-03-30 | 1996-03-30 | Strombegrenzender Widerstand mit PTC-Verhalten |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0798750A2 EP0798750A2 (fr) | 1997-10-01 |
| EP0798750A3 EP0798750A3 (fr) | 1998-12-02 |
| EP0798750B1 true EP0798750B1 (fr) | 2005-05-04 |
Family
ID=7790045
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97810116A Expired - Lifetime EP0798750B1 (fr) | 1996-03-30 | 1997-03-03 | Résistance de limitation de courant à comportement PTC |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5861795A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0798750B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPH1022109A (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19612841A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19833609A1 (de) | 1998-07-25 | 2000-01-27 | Abb Research Ltd | Elektrisches Bauteil mit einer Einschnürung in einem PTC-Polymerelement |
| EP1168378A1 (fr) * | 2000-06-19 | 2002-01-02 | Abb Research Ltd. | Procédé de production d'un dispositif PTC |
| US6411191B1 (en) | 2000-10-24 | 2002-06-25 | Eaton Corporation | Current-limiting device employing a non-uniform pressure distribution between one or more electrodes and a current-limiting material |
| DE10058908C1 (de) * | 2000-11-21 | 2002-08-08 | Siemens Ag | Anordnung zum Abbau von Überspannungen mit mehreren Varistoren |
| DE10144364A1 (de) | 2001-09-10 | 2003-04-03 | Epcos Ag | Elektrisches Vielschichtbauelement |
| US20090146042A1 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-11 | Jan Ihle | Mold comprising a ptc-ceramic |
| US20090148657A1 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-11 | Jan Ihle | Injection Molded PTC-Ceramics |
| US20090148802A1 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-11 | Jan Ihle | Process for heating a fluid and an injection molded molding |
| US20090145977A1 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-11 | Jan Ihle | Injection molded nozzle and injector comprising the injection molded nozzle |
| US9034210B2 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2015-05-19 | Epcos Ag | Feedstock and method for preparing the feedstock |
| US7973639B2 (en) * | 2007-12-05 | 2011-07-05 | Epcos Ag | PTC-resistor |
| CN117393253A (zh) | 2022-07-04 | 2024-01-12 | 国巨电子(中国)有限公司 | 抗浪涌电阻器及其制造方法 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3976854A (en) * | 1974-07-31 | 1976-08-24 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Constant-temperature heater |
| CH581377A5 (fr) * | 1975-02-11 | 1976-10-29 | Bbc Brown Boveri & Cie | |
| DE3204207C2 (de) * | 1982-02-08 | 1985-05-23 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | Elektrischer Widerstand mit einem keramischen PTC-Körper und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| US4780598A (en) * | 1984-07-10 | 1988-10-25 | Raychem Corporation | Composite circuit protection devices |
| US5064997A (en) * | 1984-07-10 | 1991-11-12 | Raychem Corporation | Composite circuit protection devices |
| JPH01158702A (ja) * | 1987-12-15 | 1989-06-21 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | 複合機能電子部品 |
| JPH01310509A (ja) * | 1988-06-09 | 1989-12-14 | Tdk Corp | 回路保護素子 |
| DE4142523A1 (de) * | 1991-12-21 | 1993-06-24 | Asea Brown Boveri | Widerstand mit ptc - verhalten |
| DE4221309A1 (de) * | 1992-06-29 | 1994-01-05 | Abb Research Ltd | Strombegrenzendes Element |
| DE4230848C1 (de) * | 1992-09-15 | 1993-12-23 | Siemens Matsushita Components | Vielfachkaltleiter |
| US5379022A (en) * | 1993-05-03 | 1995-01-03 | Fluke Corporation | Thermistor device with extended operating range |
-
1996
- 1996-03-30 DE DE19612841A patent/DE19612841A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-02-27 US US08/807,171 patent/US5861795A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-03-03 EP EP97810116A patent/EP0798750B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-03-03 DE DE59712291T patent/DE59712291D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-03-27 JP JP9075991A patent/JPH1022109A/ja active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0798750A3 (fr) | 1998-12-02 |
| US5861795A (en) | 1999-01-19 |
| EP0798750A2 (fr) | 1997-10-01 |
| DE59712291D1 (de) | 2005-06-09 |
| JPH1022109A (ja) | 1998-01-23 |
| DE19612841A1 (de) | 1997-10-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69103135T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum motor- und kurzschlussschutz. | |
| DE19727009B4 (de) | Strombegrenzender Widerstand mit PTC-Verhalten | |
| EP0798750B1 (fr) | Résistance de limitation de courant à comportement PTC | |
| DE202011000434U1 (de) | Elektrische Verbindung zwischen zwei Busbars aus ebenen Leitern und einer zwischen den Leitern angeordneten Isolationsschicht | |
| WO2012031963A2 (fr) | Composant résistance et procédé de fabrication d'un composant résistance | |
| EP0600222B1 (fr) | Dispositif pouvant supporter un courant de foudre, muni d'au moins deux éclateurs connectés en série | |
| EP0931321B1 (fr) | Groupe de contact comprenant un posistor | |
| DE2508845B2 (de) | Sicherungsleiste | |
| EP1728311A1 (fr) | Dispositif permettant de relier la gaine d'un bobinage electrique a un cable de terre et train a sustentation magnetique equipe dudit dispositif | |
| DE102021104410A1 (de) | Elektrische Heizvorrichtung | |
| EP2591488B1 (fr) | Régulateur bilame | |
| DE69509774T2 (de) | Überstromschutzvorrichtung für elektrische schaltungen | |
| WO2007036392A1 (fr) | Actionneur piezo-electrique a resistance protectrice | |
| WO2013182276A1 (fr) | Élément de contact pour varistor | |
| EP0254770B1 (fr) | Dispositif de contact électrique | |
| EP3270403B1 (fr) | Fusible | |
| DE4243314A1 (de) | Strombegrenzender Schalter | |
| WO2003028185A1 (fr) | Composant electrique | |
| DE102016217496B4 (de) | Einschaltwiderstandsanordnung | |
| DE1908152A1 (de) | Funkenstreckenanordnung fuer UEberschlagssicherung | |
| DE202017006764U1 (de) | Relais | |
| DE102018009112B4 (de) | Formgedächtnisaktor mit Schutzfunktion | |
| DE4316032C2 (de) | Widerstandsmaterial und daraus hergestellter Widerstand | |
| EP1128410A2 (fr) | Contact de commutation pour un démarreur | |
| DE102010040369B4 (de) | Trennbares Kontaktelement |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19990116 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: STRUEMPLER, RALF, DR. Inventor name: SKINDHOJ, JORGEN, DR. Inventor name: SCHUELER, CLAUS, DR. Inventor name: PELANEK, ZDENEK Inventor name: MAUTHE, GERHARD Inventor name: GREUTER, FELIX, DR. Inventor name: GLATZ-REICHENBACH, JOACHIM, DR. |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59712291 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20050609 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20050822 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20060207 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20100402 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20100322 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20100419 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20110303 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20111130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20111001 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59712291 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20111001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110303 |