EP0789339B1 - Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung - Google Patents
Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0789339B1 EP0789339B1 EP97100487A EP97100487A EP0789339B1 EP 0789339 B1 EP0789339 B1 EP 0789339B1 EP 97100487 A EP97100487 A EP 97100487A EP 97100487 A EP97100487 A EP 97100487A EP 0789339 B1 EP0789339 B1 EP 0789339B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- magnetic material
- soft magnetic
- security element
- layers
- radius
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000005347 demagnetization Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 241001295925 Gegenes Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009849 deactivation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005137 deposition process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005289 physical deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010025 steaming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/22—Electrical actuation
- G08B13/24—Electrical actuation by interference with electromagnetic field distribution
- G08B13/2402—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting
- G08B13/2405—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting characterised by the tag technology used
- G08B13/2408—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting characterised by the tag technology used using ferromagnetic tags
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/22—Electrical actuation
- G08B13/24—Electrical actuation by interference with electromagnetic field distribution
- G08B13/2402—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting
- G08B13/2428—Tag details
- G08B13/2434—Tag housing and attachment details
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/22—Electrical actuation
- G08B13/24—Electrical actuation by interference with electromagnetic field distribution
- G08B13/2402—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting
- G08B13/2428—Tag details
- G08B13/2437—Tag layered structure, processes for making layered tags
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/22—Electrical actuation
- G08B13/24—Electrical actuation by interference with electromagnetic field distribution
- G08B13/2402—Electronic Article Surveillance [EAS], i.e. systems using tags for detecting removal of a tagged item from a secure area, e.g. tags for detecting shoplifting
- G08B13/2428—Tag details
- G08B13/2437—Tag layered structure, processes for making layered tags
- G08B13/2442—Tag materials and material properties thereof, e.g. magnetic material details
Definitions
- the invention relates to a securing element in the preamble of Claim 1 specified Art.
- Elements of the aforementioned type are preferably in Electronic goods surveillance in department stores and bearings used.
- a particularly advantageous embodiment such an element is from DE 42 42nd 992 A1 became known.
- So-called "thin film” labels to secure preferably CDs described consist of a thin, in the ⁇ m range lying layer of soft magnetic material. The layer is e.g. by means of a physical deposition process onto a carrier substrate under vacuum conditions applied.
- Thin film labels show an anisotropic structure.
- Anisotropic means that the soft magnetic layer is made of of which the "thin film” labels are formed, one Preferred axis.
- the anisotropic structure makes itself felt In practice, this is noticeable in that the "Thin Film” label in response to a query field characteristic signal is maximum if query field and Preferred axis are aligned parallel to each other; the However, the signal disappears if the preferred axis and Query field are perpendicular to each other.
- EP 123 586 B proposes in addition to two query fields with frequencies f1 and f2 in the kHz range a field with one in the Hz range frequency in the query zone.
- the low frequency Query field causes the fuse element in the Clock of this field from saturation in one direction to Saturation is driven in the other direction.
- the characteristic signal therefore occurs periodically with the Frequency of the low-frequency field.
- An alternative solution has also become known, merely a query field in the kHz range to excite the Use security element, the characteristic signal of the fuse element in turn in time with a low-frequency field, which is the soft magnetic Material between the two saturations drifts, occurs.
- EP-A 0 567 080 is a securing element in the preamble of the claim 1 specified type known. It is an annular securing element, which in an annular groove provided in an optical information storage disc is glued in then closed by a coating covering the surface of the plate. The width of the annular securing element is reduced in at least two places, which are spaced about ninety degrees apart by at least two narrow switching ranges to form, which alternate with wide river collection areas. The overall orthogonal Relative orientation of the switching ranges ensures multidirectional detection of the fuse element in a query field.
- the invention is based, one out of a task securing element not simply connected surface to create its detection rate is comparable to the detection rate of a security element, that from a simply connected surface consists.
- the change is made in such a way that the given characteristic signal reduced to a pronounced peak is.
- the soft magnetic material from these areas completely or at least partially removed, that becomes characteristic Signal to a pronounced peak (or two symmetrically lying peaks) reduced.
- the soft magnetic is proposed Material along the legs of a triangular Area as well as in strip-shaped sections that parallel to one placed on the inner radius and the Base side of the triangle forming tangent are arranged, to remove. Removing the soft magnetic material from the desired areas, for example, by mechanical processing or by steaming away (e.g. by means of Laser).
- this is characteristic signal maximum when exciting magnetic field and preferred axis are parallel to each other; with vertical Position it disappears.
- the securing element from at least two layers of soft magnetic Material exists, with the preferred axes of the Were preferably at an angle of 360 ° / (2 • n) relative are turned towards each other; n denotes the in the formula Number of layers.
- Two layers are a concrete example of soft magnetic material called with their Preferred axes are perpendicular to each other.
- a semi-hard or hard magnetic material is usually arranged on or near the soft magnetic material.
- This so-called deactivator material is characterized by a high coercive force and a relatively low permeability. If the deactivator material is exposed to such a strong magnetic field that it is driven into saturation, it subsequently prevents the reaction of the soft magnetic material to the magnetic field in the interrogation zone.
- a layer of semi-hard or hard magnetic material is provided at least between two of the layers of the soft magnetic material.
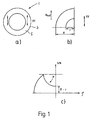
- Fig. 1a shows an electronic fuse element 1, the has the shape of a ring 5.
- a security element 1 is already known from DE 42 52 992 A1 become.
- the soft magnetic material 3 of the securing element 1 has an anisotropic structure a preferred axis XV is marked. For reasons of symmetry it suffices the ring section shown in Fig. 1b viewed from 90 °.
- the ring 5 has one inner radius r and an outer radius R.
- Fig. 1c is the reciprocal Demagnetization factor 1 / N over the radius ⁇ of the in Fig. 1b shown ring section.
- the reciprocal Demagnetization factor N is a first approximation proportional to the length of the securing element 1 in Direction of the external magnetic field hext.
- the magnetization curve shows a very pronounced plateau P, the can be interpreted to mean that a relative large volume fraction V of the ring 5 is almost constant Demagnetization factor N has. This means that a relatively large volume fraction V of the ring 5 at almost same strength of the external magnetic field hext is demagnetized.
- the reaction of the ring-shaped Securing element 1 on an external magnetic field is hext from the figures Fig. 2a to Fig. 2d can be seen.
- FIG. 2a shows a simplified illustration of a soft magnetic material 3 with different demagnetization factors N1, N2 in different volume ranges V1, V2.
- the arrow indicates the preferred axis XV of the soft magnetic material 3.
- the hysteresis curves assigned to the volume regions V1, V2 with different demagnetization factors N1, N2 can be seen in FIG. 2b.
- the fuse element 1 is excited in the non-linear regions of the hysteresis curves (-> transition between the linear and the saturated region) to emit a signal A (t). If the hysteresis curves are traversed at a constant rate in time, the two volume ranges V1, V2 contribute their contributions to the characteristic signal A (t) at different times.
- FIG. 2c A breakdown according to individual signals can be seen in FIG. 2c.
- FIG. 3a shows a section of an embodiment of the securing element 1 according to the invention, which are particularly good for Securing CDs is suitable.
- a designed securing element around the central opening of the Placed on CD there are no imbalances affecting the playback result influence negatively.
- This will be advantageous soft magnetic material by means of a deposition process manufactured under vacuum conditions. It goes without saying it is also possible to produce the material layers by punching them out.
- the securing element 1 has the shape of a ring 5 with the inner radius r and the outer radius R.
- the selected area 2 is not a soft magnetic material 3 to find: either the invention Securing elements 1 already with the broken one Ring shape or the soft magnetic material 2 is subsequently replaced by mechanical or chemical Treatment of the corresponding areas 2 removed.
- the configuration is to be regarded as particularly advantageous if that the selected areas 2 fold symmetrically with respect the preferred axis XV of the soft magnetic material 3.
- the selected areas are approximate the shape of an isosceles triangle, the base of which from a section of the inner ring radius (r) is formed and its opposite the base side Tip lies on the outer radius (R). This is explained in more detail with reference to FIG. 5.
- FIG. 3b shows the course of the reciprocal demagnetization factor 1 / N over the radius ⁇ of the ring section shown in Fig. 3a.
- Fig. 1c shows the No plateau curve here. It works particularly well different behavior of the known and the annular securing element 1 according to the invention in the Recognize diagram, which is plotted in Fig. 4.
- Fig. 4 is the magnetized volume fraction of the in Fig. 1b and in Fig. 3a shown security element 1 depending on the outer magnetic field hext plotted. While the familiar Securing element 1 a pronounced, unfavorable plateau has the corresponding embodiment of the Securing element 1 according to the invention a smooth Course.
- this also shows the characteristic Signal A (t) of the fuse element 1 according to the invention only one of these is provided by the detector device articles in the query zone that are not allowed assigned - a pronounced peak (or two symmetrical peaks, symmetrical by the two lying non-linear areas of the hysteresis curve derived).
- FIG. 5a shows a further embodiment of the invention Fuse element 1.
- Fuse element 1 it is soft magnetic material 3 not entirely, but only from certain sections of the selected areas 2 removed Service.
- a triangular shape has proven to be particularly favorable of the selected area 2, the Triangle symmetrical with respect to the preferred axis XV is arranged.
- the soft magnetic material 3 is in Area of the legs of the triangular area 2 and in striped sections removed parallel to a tangent to the inner circle, where the tangent forms the base of the triangle.
- FIG. 5b A diagram representation analogous to FIG. 4 for this Embodiment of the securing element 1 according to the invention can be seen in Fig. 5b.
- the invention shows Securing element 1 the desired smooth course without plateau.
- the characteristic signal A (t) of the Securing element 1 only the two occur symmetrically lying peaks 4 (Fig. 5c).
- the characteristic signal A (t) of an anisotropically applied soft magnetic material 3 is maximum if its Preferred axis XV is parallel to the external magnetic field Hext.
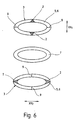
- FIG Securing element 1 two layers 6 of soft magnetic material 3 with its preferred axes XV approximately crossed over one another.
- This Overlay can be applied to any number of layers 6 expand, the optimal relative angular position of the 6 were to each other using the formula 360 ° / 2 • n (n indicates the number of layers 6) can be determined.
- n indicates the number of layers 6
- the in Fig. 6 illustrated embodiment is between the two Layers 6 of soft magnetic material 3 also one Layer 6 made of semi-hard or hard magnetic material 7 intended. This material 7 becomes saturated driven, the fuse element 1 is deactivated.
- the layers 6 of the soft magnetic material 3 in the two areas perpendicular to the selected ones Regions 2 each have a scratch 9 of length R-r. It has it turned out that the strength of the characteristic Signal A (t) of a ring 5 made of soft magnetic material 3 decreases from a certain size. This negative effect can by mechanical or chemical removal of the soft magnetic material 3 (e.g. by a scratch 9) in the area of the greatest linear expansion of the Remove securing element 1.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Burglar Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Financial Or Insurance-Related Operations Such As Payment And Settlement (AREA)
- Soft Magnetic Materials (AREA)
Description
Um eine Deaktivierung des erfindungsgemäßen Sicherungselementes zu ermöglichen, ist zumindest zwischen zwei der Lagen des weichmagnetischen Materials eine Lage aus halbhart- oder hartmagnetischem Material vorgesehen.
Die den Volumenbereichen V1, V2 mit unterschiedlichen Entmagnetisierungsfaktoren N1, N2 zugeordneten Hysteresekurven sind in Fig. 2b zu sehen. Wie allgemein bekannt, wird das Sicherungselement 1 in den nicht-linearen Bereichen der Hysteresekurven (--> Übergang zwischen dem linearen und dem gesättigten Bereich) zur Aussendung eines Signals A(t) angeregt. Werden die Hysteresekurven mit zeitlich konstanter Geschwindigkeit durchfahren, so steuern die beiden Volumenbereiche V1, V2 ihre Beiträge zu dem charakteristischen Signal A(t) zu verschiedenen Zeiten bei. Eine Aufschlüsselung nach Einzelsignalen ist aus der Fig. 2c ersichtlich. Das aus der Überlagerung der beiden Signale resultierende charakteristische Signal A(t) des ringförmigen Sicherungselementes 1 ist in Fig. 2d dargestellt. Aufgrund der von der üblichen Signalform abweichenden Form des charakteristischen Signals - das Signal weist ein ausgeprägtes Plateau P auf - wird das Sicherungselement 1 mit einer nicht einfach zusammenhängenden Fläche in den üblicherweise verwendeten Detektoreinrichtungen nicht als einem elektronisch gesicherten Artikel zugeordnet erkannt.
- 1
- Sicherungselement
- 2
- ausgewählter Bereich
- 3
- weichmagnetisches Material
- 4
- Peak
- 5
- Ring
- 6
- Lage
- 7
- halbhart- oder hartmagnetisches Material
- 8
- streifenförmiger Abschnitt
- 9
- Kratzer
- A(t)
- charakteristisches Signal
- ρ
- Radius
- r
- innerer Radius
- R
- äußerer Radius
- N
- Entmagnetisierungsfaktor
- XV
- Vorzugsachse
- Hext
- äußeres Magnetfeld
- V
- Volumenelement
- P
- Plateau
Claims (8)
- Sicherungselement zur elektronischen Artikelsicherung, bestehend aus einem anisotropen, durch eine Vorzugsachse ausgezeichneten magnetischen Material hoher Permeabilität und geringer Koerzitivkraft (weichmagnetisches Material), das die Form eines Rings mit einem äußeren Radius und einem inneren Radius aufweist und das bei Anlegen eines äußeren magnetischen Wechselfeldes ein charakteristisches Signal erzeugt, wobei das Signal maximal ist, wenn die Vorzugsachse des Sicherungselementes parallel zum äußeren magnetischen Wechselfeld ausgerichtet ist,
wobei das Sicherungselement zumindest zwei ausgewählte Bereiche aufweist, in denen der Entmagnetisierungsfaktor des weichmagnetischen Materials derart geändert ist, daß das charakteristische Signal (A(t)) eine vorgegebene Signalform aufweist, und wobei die ausgewählten Bereiche klappsymmetrisch bezüglich der Vorzugsachse des weichmagnetischen Materials liegen,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß ein ausgewählter Bereich (2) näherungsweise die Form eines gleichschenkligen Dreiecks aufweist, dessen Grundseite von einem Abschnitt des inneren Ringradius' (r) gebildet wird und dessen der Grundseite gegenüberliegende Spitze auf dem äußeren Radius (R) liegt. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das vorgegebene charakteristische Signal (A(t)) auf einen ausgeprägten Peak (4) reduziert ist. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß in den ausgewählten Bereichen (2) kein weichmagnetisches Material (3) vorhanden ist. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Entmagnetisierungsfaktor (N) in den ausgewählten Bereichen (2) durch Entfernen von weichmagnetischem Material (3) gezielt verändert ist. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 4,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das weichmagnetische Material (3) vorzugsweise entlang der Schenkel des dreieckförmigen Bereiches (2) und in streifenförmigen Abschnitten (8), die parallel zu einer an den inneren Radius (r) gelegten und die Grundseite des Dreiecks bildenden Tangente angeordnet sind, entfernt ist. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 1, 4 oder 5,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Sicherungselement (1) aus zumindest zwei Lagen (6) des weichmagnetischen Materials (3) besteht, wobei die Vorzugsachsen (XV) der Lagen (6) vorzugsweise um einen Winkel von 360°/(2•n) relativ zueinander gedreht sind, wobei n die Anzahl der Lagen (6) kennzeichnet. - Sicherungselement nach Anspruch 6,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß zumindest zwischen zwei der Lagen (6) des weichmagnetischen Materials (3) eine Lage (6) aus halbhartoder hartmagnetischem Material (7) vorgesehen ist. - Sicherungselement nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 7,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß es sich bei dem weichmagnetischen Material (3) um ein sog. Dünnschichtmaterial handelt.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19604114A DE19604114A1 (de) | 1996-02-06 | 1996-02-06 | Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung |
| DE19604114 | 1996-02-06 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0789339A2 EP0789339A2 (de) | 1997-08-13 |
| EP0789339A3 EP0789339A3 (de) | 1998-06-03 |
| EP0789339B1 true EP0789339B1 (de) | 2002-08-28 |
Family
ID=7784552
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97100487A Expired - Lifetime EP0789339B1 (de) | 1996-02-06 | 1997-01-15 | Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0789339B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE223097T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE19604114A1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2180826T3 (de) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19738309A1 (de) * | 1997-09-02 | 1999-03-04 | Meto International Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur Sicherung von Artikeln gegen Diebstahl, entsprechendes Herstellungsverfahren und Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens |
| DE19740442A1 (de) * | 1997-09-15 | 1999-03-18 | Meto International Gmbh | Deaktivierbares Sicherungselement für die elektronische Überwachung von Artikeln |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3471760D1 (en) | 1983-03-25 | 1988-07-07 | Fairchild Camera Instr Co | Tri-state driver circuit for automatic test equipment |
| US4967185A (en) * | 1989-08-08 | 1990-10-30 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Multi-directionally responsive, dual-status, magnetic article surveillance marker having continuous keeper |
| US5083112A (en) * | 1990-06-01 | 1992-01-21 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Multi-layer thin-film eas marker |
| US5347508A (en) * | 1992-04-22 | 1994-09-13 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Optical information storage disk for use with electronic article surveillance systems |
| DE4242992B4 (de) * | 1992-12-18 | 2004-01-29 | Meto International Gmbh | Anordnung zur Sicherung eines Artikels, insbesondere einer Aufzeichnungsplatte wie eine CD-Platte |
| AU667431B2 (en) * | 1993-06-11 | 1996-03-21 | Sensormatic Electronics Corporation | Multidirectional surveillance marker |
| US5401584A (en) * | 1993-09-10 | 1995-03-28 | Knogo Corporation | Surveillance marker and method of making same |
-
1996
- 1996-02-06 DE DE19604114A patent/DE19604114A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-01-15 DE DE59708026T patent/DE59708026D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-01-15 AT AT97100487T patent/ATE223097T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1997-01-15 EP EP97100487A patent/EP0789339B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-01-15 ES ES97100487T patent/ES2180826T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE223097T1 (de) | 2002-09-15 |
| DE59708026D1 (de) | 2002-10-02 |
| EP0789339A2 (de) | 1997-08-13 |
| ES2180826T3 (es) | 2003-02-16 |
| EP0789339A3 (de) | 1998-06-03 |
| DE19604114A1 (de) | 1997-08-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69322540T2 (de) | Optische Informationsspeicherplatte zur Verwendung in elektronischen Artikelüberwachungssystemen | |
| DE69111516T2 (de) | Dünnfilm-Vielschicht-Markierungsetikett für die Warenüberwachung. | |
| DE3784822T2 (de) | Zweistand-artikelueberwachungsetikett, magnetisch mit einem muster zu versehen. | |
| DE3509160C2 (de) | Markierungselement für ein System zur Überwachung von Gegenständen | |
| DE2732167C2 (de) | ||
| DE3837129C2 (de) | ||
| DE68925395T2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Identifikationssystem | |
| DE3942722B4 (de) | Ferromagnetische Fasern zur Verwendung in der elektronischen Artikelüberwachung und Verfahren zur Herstellung derselben | |
| DE69701480T2 (de) | Verfahren zum Schutz einer magnetischen Schicht auf einem photoempfindlichen Material | |
| EP0789339B1 (de) | Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung | |
| EP0789340B1 (de) | Sicherungselement für die elektronische Artikelsicherung | |
| DE3026482A1 (de) | Magnetischer markierstreifen | |
| EP0949598A2 (de) | Element für die elektronische Artikelsicherung | |
| DE69423135T2 (de) | Multirichtungsempfindliches Etikett für die Warenüberwachung | |
| DE3347466C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines magnetischen Aufzeichnungsmaterials | |
| EP0901100B1 (de) | Magnetisches Identifizierungselement | |
| DE3426178C2 (de) | ||
| DE3146932A1 (de) | "magnetoresistiver wandler zum auslesen eines aufzeichnungstraegers mit hoher informationsdichte" | |
| DE69613901T2 (de) | Magnetisches Antidiebstahletikett | |
| DE69804317T2 (de) | Sicherungselement für elektronische artikelsicherung | |
| DE3736024C1 (en) | Demagnetising device | |
| DE2403401A1 (de) | Magnetisierbares aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| DE19516474C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von magnetischen Aufzeichnungsmedien | |
| DE60010132T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines biegsamen Magnetbandes | |
| EP1138016B1 (de) | Markierungseinrichtung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE DE ES FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: METO INTERNATIONAL GMBH |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE DE ES FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19980901 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20010911 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE ES FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRE;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED.SCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020828 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 223097 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 20020915 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59708026 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20021002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20021128 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20021130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2180826 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20030530 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20031112 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20040224 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050131 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *METO INTERNATIONAL G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20050131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050801 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20050801 |
|
| NLXE | Nl: other communications concerning ep-patents (part 3 heading xe) |
Free format text: A REQUEST FOR RESTORATION TO THE PRIOR STATE (ARTICLE 23 OF THE PATENTS ACT 1995) HAS BEEN FILED ON 20051202 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *METO INTERNATIONAL G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20050131 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20100126 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20100205 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20100125 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20100127 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20110115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20110930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59708026 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20110802 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20120220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110116 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110802 |