EP0202561B1 - Dispositif de repassage - Google Patents
Dispositif de repassage Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0202561B1 EP0202561B1 EP86106374A EP86106374A EP0202561B1 EP 0202561 B1 EP0202561 B1 EP 0202561B1 EP 86106374 A EP86106374 A EP 86106374A EP 86106374 A EP86106374 A EP 86106374A EP 0202561 B1 EP0202561 B1 EP 0202561B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- soleplate
- ironing device
- sole plate
- ironing
- air stream
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 238000010409 ironing Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 87
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 43
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 claims 4
- 239000003562 lightweight material Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 abstract description 40
- 230000008093 supporting effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 36
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 25
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 18
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000000396 iron Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000014676 Phragmites communis Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005339 levitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010025 steaming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000032258 transport Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037303 wrinkles Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06F—LAUNDERING, DRYING, IRONING, PRESSING OR FOLDING TEXTILE ARTICLES
- D06F75/00—Hand irons
- D06F75/30—Hand irons of special external shape or form
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for ironing a textile material lying on a base, in which an airflow generated by a blower and led via a flow channel to at least one outlet opening in the soleplate emerges from a soleplate of the ironing device.
- an iron which has a compressor which generates an air flow. Outlet openings for the air flow are provided on the underside of the ironing plate at the edge of the ironing plate.
- the air flow generated by the compressor flows in the iron through flow channels in which the air flow is heated.
- the hot air stream emerging from the outlet openings is deflected by the textile material placed on the base, flows radially away from the iron in all directions and serves to dry and smooth the textile material to be ironed. The warm air is thus distributed along the outline of the iron.
- the advantage that the drying effect of the warm air flow may achieve is reduced by the reduced pressure of the ironing plate on the textile material.
- the iron according to DE-OS-2 224 780 therefore requires significantly larger amounts of energy for ironing than a conventional iron.
- JP-GM-4 821 008 discloses a hair dryer which can also be used as an iron and has outlet openings in the ironing plate. Warm air flows from the outlet openings, which air is generated in that air is sucked in by a fan having a rotor via an opening provided on the front wall of the iron of the iron and is fed to the openings contained in the ironing plate via a first heating device. If the rotor is operated in the opposite direction of rotation and the device is not in contact with a textile material for the purpose of ironing, air flows in via the openings in the ironing plate, which is then heated in a second heating device and at the front of the Device opening emerges. With this direction of rotation of the rotor, the device serves as a hair dryer. Apart from the fact that this device is relatively complicated due to its two heating devices, it also remains in contact with the textile material to be ironed when ironing. h that the user has to exert considerable effort when ironing.
- the task was to design the ironing device from simple parts and inexpensive to assemble.
- blower is contained in a hair dryer which can be coupled to the soleplate and in that an edge bead directed onto the textile material is formed on the soleplate.
- the ironing device there is no direct contact with the textile material to be ironed over the entire sole plate.
- the ironing effect is therefore based on the flow of the air cushion carrying the ironing device and can therefore take place without contact heat.
- the air stream emerging from the outlet opening thus serves to carry the ironing device and to expel the moisture from the textile material. Furthermore, it is not necessary to process the sole plate particularly smoothly since the sliding friction between the soleplate and the textile material is eliminated. In addition, there is no risk of fire from the soleplate.
- the ironing device hovers on the air cushion, the weight of the iron is transferred to the textile material to be ironed via the large air cushion.
- the smoothing effect of the weight of the ironing device is not lost, although the adverse friction between the sole plate and textile material is avoided.
- the air flow is guided over long flow paths under the sole plate.
- the pressure of the air flow is selected so that a sufficient static pressure is established between the sole plate and the textile material, which is sufficient to lift the ironing device a certain distance from the textile material.
- the ironing device according to the invention has an edge bead on the soleplate.
- the edge bead creates a delimited storage space for the air flow under the sole plate.
- the edge bead hinders the outflow of the air flow and contributes to the fact that the air cushion or air cushion effect is increased at lower blower outputs.
- a warm air flow is used, whereby a similar effect is achieved as by a heavy, heat-storing soleplate of a conventional iron, although the soleplate can only be a simple, thin plastic or metal plate which forms an outflow channel for the warm air with the textile material placed on the base.
- a water vapor-containing air stream (claim 3).
- the outlet opening for the air flow is arranged in the central region of the sole plate. This results in large flow paths for the air flow from the central area to the edge of the soleplate. A large air cushion can be formed over the entire sole plate. Every part of the air flow is therefore forced to travel a certain distance from the central area of the sole plate to the edge of the sole plate, whereby the entire air flow is used to form a drying and stable air cushion.
- the outlet opening for the air flow is arranged on the edge of the soleplate and the direction of flow of the airflow is directed under the soleplate.
- the entire air flow is also used here to carry the ironing device.
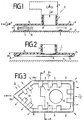
- Fig. 1 shows a first embodiment of an ironing device 1 according to the present invention in longitudinal section.
- An air flow WL is fed to the ironing device 1 by a blower 2.
- the air flow WL is guided via a tube 7 to an outlet opening 8 in a sole plate 6.
- the outlet opening 8 is arranged in the central region of the sole plate 6.
- the sole plate 6 thus extends from the outlet opening 8 to an edge 9 of the sole plate 6.
- the pressure and the air volume of the air flow WL generated by the blower 2 is selected such that the air flow WL has sufficient energy to exert the forces which lift the ironing device 1 by a certain amount "h" from the textile material to be ironed.
- the air flow WL thus forces itself between the sole plate 6 and the textile material 3 in all directions and thus forms a load-bearing air cushion 10 for the ironing device 1. That is, the ironing device 1 is caused by the continuously flowing air flow WL, which forms the air cushion 10 , carried. Furthermore, the air flow flows from the outlet opening 8 parallel to the textile material 3 beyond the edge 9 of the sole plate 6.
- the air cushion 10 is shown in the form of flow lines, which exert forces on the folds 5 of the textile material 3 and eliminate the folds 5.
- the flowing air cushion 10 absorbs the moisture contained in the textile material 3 and transports the moisture from a large area that extends beyond the surface of the sole plate 6. Since the outlet opening 8 is arranged in the central region of the sole plate 6, there are large outflow paths for the air flow WL, which is why the flowing air cushion 10 is made has sufficient time to absorb or entrain the moisture in the textile material 3.
- the weight of the ironing device 1 is transferred via the air cushion 10 to the textile material 3 to be ironed in the same way as when the sole plate 6 rests directly on the textile material 3 as in conventional ironing methods.
- the smoothing effect of the ironing device 1 is achieved via the sole plate 6 and the upstream air cushion 10, thereby helping to eliminate wrinkles 5.
- a major advantage of the ironing device 1 floating on the air cushion 10 or air cushion is that there is no friction between the sole plate 6 and the textile material 3.
- no high sliding requirements are placed on the underside of the soleplate 6, as in the case of conventional ironing boards of irons.
- the production of the sole plate 6 is therefore much easier and cheaper than with a conventional iron.
- the ironing device 1 can be moved much more easily due to the lower friction between the air molecules of the air cushion 10.
- the air flow WL is cold or heated.
- the blower 2 is a warm air blower.
- the elimination of the heating in the soleplate 6 additionally simplifies its manufacture.
- the air flow WL and especially as a warm air flow can have a water vapor content which is used for steaming in a known manner. Steam, water or moisture can also be supplied to nozzles (not shown) in the sole plate 6. Furthermore, it is possible to inject the steam into the blower 2 or in the area of the tube 7 as required.
- the outlet opening 8 is arranged in a position in the sole plate 6 at which the forces exerted by the air cushion 10 on the sole plate 6 counteract the tilting moments which originate from the ironing device 1 with respect to the outlet opening 8 as a fulcrum.
- the blower 2 indicated in FIG. 1 tilts the ironing device 1 counterclockwise as a result of the weight components extended to the left.
- the front section of the sole plate 6 is considerably longer than the rear section.
- the front section of the soleplate surface thus acts as a much longer lever than the rear section.
- the outlet opening 8 is therefore preferably on the longitudinal axis (x-axis) of the sole plate 6.
- the outlet opening 8 is arranged in the transverse direction of the sole plate 6 in a position such that the tilting moments about the longitudinal axis of the sole plate 6 (x-axis) are compensated.
- the edge 9 of the sole plate 6 has the same height h at all points in the floating state.
- the sole plate 6 together with the tube 7 is made of plastic, which are injection-molded in one piece. If the sole plate 6 has no heating, the sole plate can be made very thin - preferably 1 to 3 mm. The sole plate 6 can therefore be produced very easily and inexpensively than a conventional ironing board.
- the edge 9 of the sole plate 6 is rounded so that the edge 9 cannot damage the textile material when the edge 9 abuts, for example, upstanding folds 5.
- FIG. 2 shows an ironing device 1 with a sole plate 6, which preferably has a peripheral bead 11.
- the edge bead 11 also has outer rounded edges so as not to damage or better slide up the upstanding textile material edges.
- the inside 12 of the edge bead 11 is flattened with respect to the horizontally oriented sole plate 6 by an angle a directed downwards.
- a storage space for the air cushion 10 is formed by means of the edge bead 11, which is prevented from flowing out in comparison with FIG. 1.
- the outflowing air cushion 10 undergoes a change in direction by the angle a on the inside 12 of the edge bead 11, as a result of which the lifting and floating of the ironing device 1 is promoted as a result of the forces which result from the deflection of the air flow.
- the dynamic pressure or the static pressure is therefore increased in comparison with the exemplary embodiment from FIG. 1 with the same blower output by the edge bead 11. 2, the edge at the outlet opening 8 is rounded off for better and easier deflection of the air flow WL.
- the connection point at which the tube 7 is seated on the sole plate 6 is also reinforced.
- the sole plate 6 in the exemplary embodiments described so far and in the exemplary embodiments yet to be described runs parallel to the base in large areas, it is also possible to construct the sole plate 6 in a curved manner.
- the sole plate 6 can be concavely curved, for example.
- FIG. 3 shows the bracket device 1 from FIG. 2 in a view from below.
- the sole plate 6 has a tip on the front in a known manner.
- the remaining part of the soleplate is rectangular in the embodiment shown in FIG. 3.
- the sole plate 6 can have another suitable basic shape, depending on the application.
- the outlet opening 8 lies, as described above, on the longitudinal axis of the soleplate 6 (x-axis).
- the position of the outlet opening 8 on the longitudinal axis results from the previously described weight distribution and the resulting tilting moments about the y-axis shown in FIG. 3.
- the size of the outlet opening 8 is adapted to the air passage performance of the blower 2.
- the edge bead in FIG. 3 has openings 14.
- the air outlet at the edge bead 11 can be matched to the air throughput of the blower 2.
- the openings 14 also serve to blow larger folds 5 which are in front of the ironing device 1.
- the radial openings 14 are arranged symmetrically to the longitudinal axis of the sole plate 6, an opening 14 preferably being formed at the tip of the sole plate 6.
- the opening 14 formed at the tip of the sole plate 6 also serves to press larger folds 5 towards which the ironing device 1 is moved.
- the formation of the openings 14 in the edge bead 11 creates recesses between edge bead portions 13.
- the edge bead portions 13 are also flattened like the inside 12 of the edge bead 11 from FIG. 2.
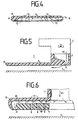
- FIG. 4 shows a section through the sole plate 6 from FIG. 3 along the bent section line AB.
- the section runs through the edge bead 11 including the edge bead portion 13 with the flattened inside.
- the cut at point B runs through a radial opening 14.
- the openings 14 can be comb-like incisions in the edge bead 11.
- the comb-like incisions can be formed when the edge bead 11 is sawn in from the underside of the sole plate 6.
- the number and size of the bores, slots and openings 14 make it possible to select the levitation height of the ironing device for a given air throughput of the blower 2.
- FIG. 5 shows a further exemplary embodiment of the invention.
- the ironing device 1 according to FIG. 5 differs from the ironing device according to FIG. 1 in that the outlet opening 8 for the air flow is arranged at the edge 9 of the sole plate 6, the direction of flow of the air flow being directed under the sole plate 6.
- the textile material 3 is not shown in Fig. 5 for better clarity. Because the air flow WL is directed under the sole plate 6, there is a very large outflow path. A large part of the air flow WL therefore flows through the entire sole plate 6 in its longitudinal direction at a sufficient flow speed. Although the air flow WL is blown from the edge 9 of the sole plate 6 under the sole plate, the entire air flow WL contributes to the construction of the air cushion 10.
- the sole plate 6 can also have the edge bead 11 described above, including the openings 14.
- the blower 2 can be a permanently integrated blower in all exemplary embodiments, which generates warm air, for example.
- the blower 2 is a hair dryer, which is coupled to the tube 7 via a sealing quick coupling.
- the hairdryer can also be used as an ironing device with the aid of the sole plate 6, which is particularly advantageous when traveling.
- guide webs for the air flow WL are perpendicular to the underside of the sole plate 6 and are aligned so that the air flow WL must run along a preferred flow path.
- exemplary embodiments are conceivable in which, starting from the outlet opening 8, 6 guide channels run in the longitudinal direction of the soleplate on the underside.
- the walls of the guide channels are preferably not higher than the edge bead 11, if one is provided.
- the walls of the guide channels can have interruptions or not directly abut the edge bead 11.
- the walls of the flow channels prevent the air cushion 10 from flowing off to the side (y direction) too easily.
- the ironing device 1 which floats on the air cushion 10, has a substantially better stability. That is, the ironing device 1 does not automatically change its parking position when the fan 2 is running and the ironing device 1 does not drift as quickly. Likewise, the air cushion does not collapse so quickly when the sole plate 1 protrudes laterally over an edge.
- webs extending transversely to the direction of flow can also be provided on the underside of the soleplate 6, which contribute to the swirling.
- Fig. 6 shows a further embodiment in which the air flow WL is blown from all sides from the edge under the sole plate 6.
- the sole plate 6 is connected to an outer wall 19 on the upper side via retaining webs 17.
- the height of the holding webs 17 thus determine the height of a flow channel between rule the outer wall 19 and the top of the sole plate 6.
- the air flow WL is guided over the tube into the flow channel 18, in which the air flow WL impacts the top of the sole plates 6 and is distributed radially to the flow channel 18 on all sides.
- the deflected air flow WL emerges at the outlet opening 8 running around the edge.
- the air flow emerging from the outlet opening 8 is in turn directed under the sole plate 6.
- individual flow channels 18 can also run between the outer wall 19 and the sole plate 6 to outlet openings 8, which are arranged at suitable locations on the edge of the ironing device 1. It is also possible to provide bores 16 in the sole plate 6 through which a portion of the air flow WL can emerge perpendicularly from the sole plate 6.
- a movement switch or vibration switch which detects whether the ironing device is in operation or has been switched off. By means of the switch, the blower 2 is then automatically switched off after a certain period of time when not in use. If the ironing device 1 is gripped in order to continue ironing, the switch detects the movement and lifting of the ironing device 1 from the parking space and immediately switches on the fan. The ironing device 1 is thus switched on again in the period in which the ironing device is moved from the parking space onto the material to be ironed.
- the ironing device according to the invention is thus much more energy efficient than conventional irons. It is also possible to provide a magnet at the parking space which influences a switch in the ironing device when the ironing device 1 is placed on the parking space.
- the switch sensitive to magnetic field strength is preferably a reed contact which can be easily accommodated and cast in, for example, the soleplate 6.
- the parking space of the ironing device 1 is adapted to the basic shape of the sole plate 6 and in the area in which the reed contact comes to rest when the ironing device 1 is switched off, a magnet is arranged.
- the magnet is a glued-on magnetic film.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Irons (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
- Beans For Foods Or Fodder (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
- Forging (AREA)
- Cleaning And De-Greasing Of Metallic Materials By Chemical Methods (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
- Auxiliary Devices For And Details Of Packaging Control (AREA)
- Seeds, Soups, And Other Foods (AREA)
- Formation And Processing Of Food Products (AREA)
- Load-Engaging Elements For Cranes (AREA)
Claims (14)
caractérisé
par le fait que le ventilateur (2) est contenu dans un sèche-cheveux pouvant être couplé à la plaque-semelle (6), et le fait qu'un bourrelet de bord (11), dirigé vers la matière textile (3), est aménagé sur la plaque-semelle (6).
caractérisé
par le fait que le courant d'air (WL) est échauffé par un dispositif chauffant agencé dans le sèche-cheveux (2).
caractérisé
par le fait que de l'humidité est apportée au courant d'air échauffé (WL).
caractérisé
par le fait que l'ouverte (8) pour la sortie du courant d'air (WL) est agencée dans la région médiane de la plaque-semelle (6).
caractérisé
par le fait que l'ouverture (8) pour la sortie du courant d'air (WL) est agencée au bord (9) de la plaque-semelle (6), et par le fait que la direction d'écoulement de sortie de l'ouverture de sortie (8) est dirigée en dessous de la plaque-semelle (6).
caractérisé
par le fait que l'ouverture de sortie (8) se trouve sur l'axe longitudinal X de la plaque-semelle (6).
caractérisé
par le fait que le côté dessus de la plaque-semelle (6) est plan, par le fait qu'il y est prévu un tube (7) pour le raccordement du sèche-cheveux (2), et par le fait que l'ouverte (8) pour la sortie du courant d'air (WL) présente sensiblement la même section droite que l'ouverture de sortie du sèche-cheveux (2).
caractérisé
par le fait que le bourrelet de bord (11) présente des arêtes arrondies.
caractérisé
par le fait que le côté interne (12) du bourrelet de bord (11) est aplati.
caractérisé
par le fait que le bourrelet de bord (11) présente des ajours radiaux (14).
caractérisé
par le fait que les ajours (14) sont agencés symétriquement à l'axe longitudinal X de la plaque-semelle (6).
caractérisé
par le fait que le sèche-cheveux (2) peut être raccordé à la plaque-semelle (6) par un raccord rapide étanche.
caractérisé
par le fait que la plaque-semelle (6) est en une matière légère, de préférence en matière plastique.
caractérisé
par le fait que la plaque-semelle (6) présente de préférence une épaisseur de 1 à 3 mm.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT86106374T ATE46930T1 (de) | 1985-05-22 | 1986-05-09 | Buegelvorrichtung. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19853518425 DE3518425A1 (de) | 1985-05-22 | 1985-05-22 | Verfahren zum buegeln und vorrichtung zum durchfuehren des verfahrens |
| DE3518425 | 1985-05-22 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0202561A2 EP0202561A2 (fr) | 1986-11-26 |
| EP0202561A3 EP0202561A3 (en) | 1987-08-05 |
| EP0202561B1 true EP0202561B1 (fr) | 1989-10-04 |
Family
ID=6271372
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86106374A Expired EP0202561B1 (fr) | 1985-05-22 | 1986-05-09 | Dispositif de repassage |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4685229A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0202561B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPS61272100A (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE46930T1 (fr) |
| BR (1) | BR8602269A (fr) |
| CA (1) | CA1268411A (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE3518425A1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES8703552A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4857706A (en) * | 1988-02-29 | 1989-08-15 | Diamond Paul J | Ironing accessory |
| US5170038A (en) * | 1991-07-23 | 1992-12-08 | Midori Co., Ltd. | Iron unit adapted to be used with hair dryers |
| US5333401A (en) * | 1993-02-01 | 1994-08-02 | Roberts Consolidated Industries, Inc. | Carpet seaming iron with air gap between cooling plates |
| US5787614A (en) * | 1993-03-30 | 1998-08-04 | Rowenta-Werke Gmbh | Electric steam iron with aerosol sprayer |
| DE19634870C1 (de) * | 1996-08-29 | 1997-10-16 | Rowenta Werke Gmbh | Dampfbügeleisen |
| DE20119767U1 (de) * | 2001-12-06 | 2002-02-21 | Chen, Shou Mao, Tah-Cha Township, Taichung | Mehrzweckhaartrockner |
| US6750747B2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2004-06-15 | Ljm Associates, Inc. | Proximity safety switch suitable for use in a hair dryer for disabling operation |
| US6784775B2 (en) * | 2002-08-29 | 2004-08-31 | Ljm Associates, Inc. | Proximity safety switch suitable for use in a hair dryer for disabling operation |
| FR2952385B1 (fr) * | 2009-11-12 | 2012-01-20 | Seb Sa | Fer a repasser comportant une semelle presentant un evidement muni de trous de sortie de vapeur |
| FR2952386B1 (fr) * | 2009-11-12 | 2011-10-28 | Seb Sa | Fer a repasser comportant une semelle presentant un evidement muni de trous de sortie de vapeur |
| US10883222B2 (en) * | 2017-09-12 | 2021-01-05 | Vivian Lou Lewis | Attachment to convert a standard handheld hair blow dryer into a device that can be used to iron clothing |
| DE202018104388U1 (de) | 2018-07-30 | 2018-09-03 | Brice Dupoyet | Bügeleisen für den häuslichen oder gewerblichen Gebrauch |
| FR3089525B1 (fr) | 2018-12-06 | 2020-12-25 | Guy Dupoyet | Fer à repasser à usage domestique ou professionnel |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2864185A (en) * | 1955-05-03 | 1958-12-16 | Hoover Co | Air floated iron |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE476394C (de) * | 1928-05-19 | 1929-05-16 | Joseph Schneider | Buegeleisen mit einem Verdampfungsraum und einem Luftheizraum |
| ES402122A1 (es) * | 1971-06-26 | 1975-03-01 | Azzolini | Perfeccionamientos en planchas electricas que suministran vapor y aire al tejido a planchar. |
| US3870309A (en) * | 1973-11-20 | 1975-03-11 | Joseph Donatien Leo Tessier | Sliding game piece having friction reduction air cushion |
| US3992009A (en) * | 1975-02-03 | 1976-11-16 | Trbovich Nicholas D | Air cushion game |
| US4233763A (en) * | 1978-08-21 | 1980-11-18 | Nesco Products, Inc. | Steam iron with low temperature soleplate |
| DE3115696C2 (de) * | 1981-04-18 | 1983-05-19 | Braun Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Elektrisches Bügeleisen |
| US4524263A (en) * | 1981-04-18 | 1985-06-18 | Braun Aktiengesellschaft | Electric travel iron using portable hair-dryer as the heat source |
| DE3202978C2 (de) * | 1982-01-29 | 1990-01-04 | Braun Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Elektrisches Bügeleisen |
| DD219228A1 (de) * | 1983-11-11 | 1985-02-27 | Elektrogeraete Ingbuero Veb | Elektrisches buegeleisen |
| DD221487A1 (de) * | 1984-02-16 | 1985-04-24 | Werkzeugmasch Heckert Veb | Elektrisches mehrzweckgeraet, insbesondere zum gebrauch als reisebuegeleisen und handluftdusche |
-
1985
- 1985-05-22 DE DE19853518425 patent/DE3518425A1/de active Granted
-
1986
- 1986-04-08 ES ES553766A patent/ES8703552A1/es not_active Expired
- 1986-05-09 AT AT86106374T patent/ATE46930T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1986-05-09 EP EP86106374A patent/EP0202561B1/fr not_active Expired
- 1986-05-09 DE DE8686106374T patent/DE3666057D1/de not_active Expired
- 1986-05-20 CA CA000509510A patent/CA1268411A/fr not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1986-05-20 BR BR8602269A patent/BR8602269A/pt unknown
- 1986-05-20 US US06/865,380 patent/US4685229A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1986-05-22 JP JP61116306A patent/JPS61272100A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2864185A (en) * | 1955-05-03 | 1958-12-16 | Hoover Co | Air floated iron |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE46930T1 (de) | 1989-10-15 |
| EP0202561A3 (en) | 1987-08-05 |
| DE3518425A1 (de) | 1986-11-27 |
| DE3518425C2 (fr) | 1988-03-10 |
| DE3666057D1 (en) | 1989-11-09 |
| US4685229A (en) | 1987-08-11 |
| ES553766A0 (es) | 1987-02-16 |
| JPS61272100A (ja) | 1986-12-02 |
| EP0202561A2 (fr) | 1986-11-26 |
| CA1268411A (fr) | 1990-05-01 |
| BR8602269A (pt) | 1987-01-21 |
| ES8703552A1 (es) | 1987-02-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0202561B1 (fr) | Dispositif de repassage | |
| DE69219707T2 (de) | Unterdruckdüsenanordnung zur Behandlung von Bahnen | |
| DE3807857C2 (fr) | ||
| DE3890457C2 (de) | Verfahren zum berührungsfreien Trocknen einer Papier- oder Kartonbahn | |
| DE3910898A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung in einem kombinationstrockner, der aus einer gasinfraanordnung und einer wirbelanordnung besteht | |
| EP0908551B1 (fr) | Fer à repasser à vapeur avec sortie de vapeur sur le devant et le côté du fer | |
| DE2836103C2 (de) | Luftdüse für einen Düsentrockner | |
| EP0298299B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour guider des bandes sans contact direct | |
| DE4029487A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum fuehren einer papierbahn in der streichmaschine | |
| DE19546046A1 (de) | Bogenführsystem für eine Druckmaschine | |
| DE2613963C2 (de) | Textilwärmebehandlungsvorrichtung insbesondere Spannrahmen | |
| EP0723522B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour le guidage en suspension dans l'air d'une bande en defilement | |
| DE69815120T2 (de) | Papier- oder pappemaschine mit einem saugkasten | |
| EP0658427B1 (fr) | Dispositif de séchage | |
| WO2008128887A1 (fr) | Lave-linge automatique apte au séchage | |
| DE3220076C2 (de) | Luftblaskasten für die Trockenpartie einer Papiermaschine | |
| DE3822624C2 (fr) | ||
| EP0130579B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour le traitement en continu par la chaleur, par exemple le séchage, de matière textile en bande ou ruban | |
| DE3115696C2 (de) | Elektrisches Bügeleisen | |
| DE1965719U (de) | Vorrichtung zum glaetten von flaechigen waeschestuecken. | |
| DE1034128B (de) | Trockenmaschine zum Trocknen von bahnfoermigem Gut, insbesondere Gewebespann- und Trockenmaschine | |
| EP0501400A1 (fr) | Dispositif de séchage pour le linge, en particulier pour vêtements | |
| DE4228453C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Beblasen einer textilen Warenbahn | |
| EP0437272A1 (fr) | Séchoir vertical | |
| DE883136C (de) | Gewebe-Trockenmaschine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870820 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19881018 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 46930 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19891015 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3666057 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19891109 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920423 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19920428 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19920430 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920505 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920507 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19920531 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19920619 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930509 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19930509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19930510 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19930531 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19930531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19931201 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930509 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19940131 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19940201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 86106374.1 Effective date: 19931210 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050509 |