EP0047383B1 - Tête magnétique multipiste et son procédé de fabrication - Google Patents
Tête magnétique multipiste et son procédé de fabrication Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0047383B1 EP0047383B1 EP81105738A EP81105738A EP0047383B1 EP 0047383 B1 EP0047383 B1 EP 0047383B1 EP 81105738 A EP81105738 A EP 81105738A EP 81105738 A EP81105738 A EP 81105738A EP 0047383 B1 EP0047383 B1 EP 0047383B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- magnetic
- substrate
- bonding
- pieces
- fingers
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B5/00—Recording by magnetisation or demagnetisation of a record carrier; Reproducing by magnetic means; Record carriers therefor
- G11B5/127—Structure or manufacture of heads, e.g. inductive
- G11B5/29—Structure or manufacture of unitary devices formed of plural heads for more than one track
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B5/00—Recording by magnetisation or demagnetisation of a record carrier; Reproducing by magnetic means; Record carriers therefor
- G11B5/127—Structure or manufacture of heads, e.g. inductive
- G11B5/29—Structure or manufacture of unitary devices formed of plural heads for more than one track
- G11B5/295—Manufacture
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T29/00—Metal working
- Y10T29/49—Method of mechanical manufacture
- Y10T29/49002—Electrical device making
- Y10T29/4902—Electromagnet, transformer or inductor
- Y10T29/49021—Magnetic recording reproducing transducer [e.g., tape head, core, etc.]
- Y10T29/49032—Fabricating head structure or component thereof
- Y10T29/49048—Machining magnetic material [e.g., grinding, etching, polishing]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T29/00—Metal working
- Y10T29/49—Method of mechanical manufacture
- Y10T29/49002—Electrical device making
- Y10T29/4902—Electromagnet, transformer or inductor
- Y10T29/49021—Magnetic recording reproducing transducer [e.g., tape head, core, etc.]
- Y10T29/49032—Fabricating head structure or component thereof
- Y10T29/49055—Fabricating head structure or component thereof with bond/laminating preformed parts, at least two magnetic
Definitions
- This invention relates to a multitrack magnetic head and a method of manufacture thereof.
- multitrack magnetic heads are formed by bonding single track modules, such as described in US-A-3,613,228, DE-A-2,032,354, FR-A-2,053,903 and GB-A-1,307,587. It is apparent that a multiplicity of modules must be properly aligned and have similar dimensions to result in precisely positioned tracks and accurately defined track widths, amongst other things. The steps of alignment, joinder and machining the several elements to precise predetermined dimensions are costly and time consuming. In addition, the resultant heads are not closely spaced to give a high data track density.
- the invention seeks to provide a multitrack magnetic head that affords high data track density, that minimizes the separation between data tracks recorded on a magnetic medium, and that allows improved track definition.
- the invention also seeks to provide a method of forming a multitrack magnetic head by which a reduction in manufacturing steps and savings in cost are realized.
- a multitrack magnetic head comprises a row of spaced magnetic blocks and a magnetic wafer bonded to the magnetic blocks to form transducing gaps filled with non-magnetic bonding, and is characterised in that one surface of a non-magnetic substrate is joined to the row of magnetic blocks thereby forming a closure section and an adjacent surface of the substrate is bonded to the magnetic wafer, the substrate, the row of magnetic blocks and the magnetic wafer forming a compact block in which the magnetic blocks are spaced and separated by non-magnetic bonding.
- the invention also provides an assembly from which said closure section may be cut, comprising a magnetic block and a non-magnetic bonding, characterised in that the magnetic block consists of a first magnetic piece having alternate slots and fingers, and a second magnetic piece having alternate slots and fingers, the fingers of the first and second magnetic pieces being interdigitated, with the fingers of one magnetic piece in the slots of the other magnetic piece, magnetic pieces being bonded together by non-magnetic bonding.
- the invention further provides a method of forming said closure section involving bonding a magnetic block to a non-magnetic substrate by non-magnetic bonding and slicing the magnetic block and the substrate, characterised by the steps of forming spaced slots and fingers in first and second magnetic pieces, aligning the magnetic pieces on a non-magnetic substrate with the fingers of the first and second magnetic pieces interdigitated, the fingers of one magnetic piece being in the slots of the other magnetic piece, bonding the magnetic pieces together and to the substrate by non-magnetic bonding, and slicing the substrate and pieces across the slots and fingers to form a closure section.
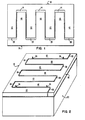
- a first ferrite comb piece 10 (Fig. 1) is formed with alternating fingers 12 and slots 14, and a second ferrite comb piece 16 is formed with similar but complementary alternating fingers 18 and slots 20.
- the number of slots 14 corresponds to the number of fingers 18, and the number of slots 20 corresponds to the number of fingers 12.
- the slots 14 and 20 are of the same dimensions, and are slightly larger in length and width than the fingers 12 and 18.
- the width of each slot is approximately 700 microns, and the width of each finger is about 500 microns.
- the depth or the height of the slots and fingers is about 1 mm, by way of example.
- the slots may be gang sawed or wire sawed individually, by well known techniques, so that the slots and fingers have substantially parallel sides, and the fingers of one piece closely fit with the slots of the other piece, so that the fingers are interdigitated and closely spaced.
- the ferrite pieces 10 and 16 are bonded together preferably by glass, and to a non- magnetic ceramic substrate 22, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
- metal wires or shims 24 are fixed securely between the ferrite pieces to act as spacers.
- the ferrite pieces 10 and 16 are positioned and aligned on the substrate prior to glass bonding. The alignment between the ferrite pieces is critical, whereas the alignment to the substrate is less significant.
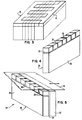
- the bonded assembly (Fig. 3) is sliced into closure sections 26 (Fig. 4), as shown by the dash lines in Fig. 3.
- Each closure section 26 consists of a row of magnetic ferrite blocks 28 supported by a nonmagnetic substrate 30.
- Alternate blocks 28 are parts of fingers 12 and 18, respectively.
- the ferrite blocks are joined together and to the nonmagnetic substrate 30 by glass bonding 33.
- the width of each ferrite block 28 determines the width of the data track, and the width of the glass bond 33 between adjacent ferrite blocks 28 establishes the separation distance between the data tracks.
- a ferrite wafer 32 having the same length and width as the closure section 26 is cemented to the section 26 to form a write head 38 (Fig. 5).
- a cement layer 34 between the wafer 32 and section 26 delineates the transducing gap that co-acts with a magnetic medium, such as a magnetic tape 36.
- Multiple tracks are recorded along the moving tape 36 that correspond in width to the width of each ferrite block 28 disposed on the substrate 30.
- a thicker cutting wheel that affords greater rigidity and less wobble may be used for cutting slots in ferrite, with the realization of accurate alignment and spacing of the multiple tracks.
- the use of a thicker cutting wheel can greatly improve tool life.
- the novel configuration and method allows a simplified, inexpensive approach to be employed for making multitrack magnetic heads.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Magnetic Heads (AREA)
Claims (15)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US06/183,559 US4366518A (en) | 1980-09-02 | 1980-09-02 | Multi-track head assembly |
| US183559 | 1994-01-19 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0047383A1 EP0047383A1 (fr) | 1982-03-17 |
| EP0047383B1 true EP0047383B1 (fr) | 1984-07-04 |
Family
ID=22673328
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP81105738A Expired EP0047383B1 (fr) | 1980-09-02 | 1981-07-21 | Tête magnétique multipiste et son procédé de fabrication |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4366518A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0047383B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPS5746316A (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3164561D1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4396967A (en) * | 1981-04-13 | 1983-08-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Multielement magnetic head assembly |
| US4797767A (en) * | 1986-11-20 | 1989-01-10 | American Magnetics Corporation | Digital magnetic head structure |
| US5211734A (en) * | 1989-03-31 | 1993-05-18 | Tdk Corporation | Method for making a magnetic head having surface-reinforced glass |
| US5055957A (en) * | 1989-06-19 | 1991-10-08 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method of making low wear glass for magnetic heads |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2785038A (en) * | 1952-06-02 | 1957-03-12 | Rca Corp | Magnetic transducer |
| US2840643A (en) * | 1955-04-04 | 1958-06-24 | Hughes Aircraft Co | Integral transformer electromagnetic transducer |
| NL253072A (fr) * | 1959-06-04 | |||
| US3354540A (en) * | 1961-04-07 | 1967-11-28 | Philips Corp | Method of manufacturing reliable magnetic heads having accurately predetermined dimensions |
| US3613228A (en) * | 1969-07-02 | 1971-10-19 | Ibm | Manufacture of multielement magnetic head assemblies |
| US3655923A (en) * | 1970-02-02 | 1972-04-11 | Ceramic Magnetics Inc | Preformed multiple track magnetic head assembly |
| US3943624A (en) * | 1975-01-24 | 1976-03-16 | U. S. Philips Corporation | Method of manufacturing a magnetic head |
| GB1529967A (en) * | 1977-04-28 | 1978-10-25 | Bicc Ltd | Magnetic cores |
-
1980
- 1980-09-02 US US06/183,559 patent/US4366518A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1981
- 1981-06-12 JP JP56089779A patent/JPS5746316A/ja active Granted
- 1981-07-21 EP EP81105738A patent/EP0047383B1/fr not_active Expired
- 1981-07-21 DE DE8181105738T patent/DE3164561D1/de not_active Expired
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPS5746316A (en) | 1982-03-16 |
| EP0047383A1 (fr) | 1982-03-17 |
| US4366518A (en) | 1982-12-28 |
| DE3164561D1 (en) | 1984-08-09 |
| JPS6333205B2 (fr) | 1988-07-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR920002579B1 (ko) | 고정자기 디스크 장치용 헤드 코아 슬라이더 및 그 제조방법 | |
| EP0140977B1 (fr) | Tete magnetique et son procede de fabrication | |
| US4914805A (en) | Method of manufacturing a magnetic head having a plurality of magnetic gaps | |
| EP0047383B1 (fr) | Tête magnétique multipiste et son procédé de fabrication | |
| EP0062739B1 (fr) | Assemblage de tête magnétique à éléments multiples et son procédé de fabrication | |
| EP0116451B1 (fr) | Structure de transducteur magnétique à largeur de piste réduite et procédé de fabrication | |
| EP0179269B1 (fr) | Tête magnétique | |
| US3557445A (en) | Method of fabricating slant cores | |
| US4831481A (en) | Composite magnetic head and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JPS62197908A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドの製造方法 | |
| JP2563246B2 (ja) | 磁気ヘツドの製造方法 | |
| JP2566599B2 (ja) | 複合型磁気ヘッドの製造方法 | |
| JPS63152003A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドの製造方法 | |
| JPH0378105A (ja) | マルチトラツク磁気ヘッド | |
| JPH03288306A (ja) | マルチチヤンネル磁気ヘツド及びその製造方法 | |
| JPH0377565B2 (fr) | ||
| JPH02177107A (ja) | マルチトラツク磁気ヘツド及びその製造方法 | |
| JPH0731781B2 (ja) | 磁気ギャップ形成方法 | |
| JPS6286527A (ja) | 浮上型磁気ヘツド | |
| JPS6192411A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドの製造方法 | |
| JPS6297111A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドとその製造方法 | |
| JPH0554314A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドの製造方法 | |
| JPS5827569B2 (ja) | 磁気ヘツドコアの製造方法 | |
| JPS63149807A (ja) | 磁気ヘツド用コア及びその製造方法 | |
| JPS62217409A (ja) | 磁気ヘツドおよびその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19820407 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB NL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19840704 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3164561 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19840809 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19910625 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19910723 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920624 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19930331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19930401 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930721 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930721 |