DE69908098T2 - Erdalkalimetalsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsmethode - Google Patents
Erdalkalimetalsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsmethode Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- DE69908098T2 DE69908098T2 DE69908098T DE69908098T DE69908098T2 DE 69908098 T2 DE69908098 T2 DE 69908098T2 DE 69908098 T DE69908098 T DE 69908098T DE 69908098 T DE69908098 T DE 69908098T DE 69908098 T2 DE69908098 T2 DE 69908098T2
- Authority
- DE
- Germany
- Prior art keywords
- alkaline earth
- alkyl aryl
- sulfonate
- aryl sulfonate
- sulfonate according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000010687 lubricating oil Substances 0.000 title claims description 28
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 title claims description 18
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 4
- -1 Alkaline earth metal sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 title description 58
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 title description 11
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 48
- 150000008055 alkyl aryl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 claims description 47
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 46
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N olefin Natural products CCCCCCCC=C JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 14
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M sulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)=O BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000004711 α-olefin Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000002199 base oil Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002518 antifoaming agent Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- WMYJOZQKDZZHAC-UHFFFAOYSA-H trizinc;dioxido-sulfanylidene-sulfido-$l^{5}-phosphane Chemical compound [Zn+2].[Zn+2].[Zn+2].[O-]P([O-])([S-])=S.[O-]P([O-])([S-])=S WMYJOZQKDZZHAC-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 claims description 6
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000040 hydrogen fluoride Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 24
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 18
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 13
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 11
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000006277 sulfonation reaction Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 9
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 description 7
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 125000001273 sulfonato group Chemical class [O-]S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 7
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 7
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bisulfite Chemical compound OS([O-])=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 6
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 5
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphur dioxide Chemical compound O=S=O RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 150000005840 aryl radicals Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 238000005227 gel permeation chromatography Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- AFFLGGQVNFXPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-decene Chemical compound CCCCCCCCC=C AFFLGGQVNFXPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000008733 Citrus aurantifolia Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000011941 Tilia x europaea Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 3
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004571 lime Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000010446 mineral oil Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen Substances N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000013049 sediment Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- BVUXDWXKPROUDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol Chemical compound CCC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 BVUXDWXKPROUDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 2
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000005228 aryl sulfonate group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- DKVNPHBNOWQYFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbamodithioic acid Chemical compound NC(S)=S DKVNPHBNOWQYFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000006471 dimerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012990 dithiocarbamate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001050 lubricating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002763 monocarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003345 natural gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011118 potassium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 2
- 238000004062 sedimentation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- AKEJUJNQAAGONA-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfur trioxide Chemical compound O=S(=O)=O AKEJUJNQAAGONA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000013638 trimer Substances 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N (z)-1-[(z)-octadec-9-enoxy]octadec-9-ene Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCOCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WJECKFZULSWXPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-didodecylbenzene Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1CCCCCCCCCCCC WJECKFZULSWXPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RUFPHBVGCFYCNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-naphthylamine Chemical class C1=CC=C2C(N)=CC=CC2=C1 RUFPHBVGCFYCNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KGRVJHAUYBGFFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2'-Methylenebis(4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=CC(C)=CC(CC=2C(=C(C=C(C)C=2)C(C)(C)C)O)=C1O KGRVJHAUYBGFFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OPLCSTZDXXUYDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 OPLCSTZDXXUYDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QHPKIUDQDCWRKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-ditert-butyl-4-[2-(3,5-ditert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=CC(C(C)(C)C=2C=C(C(O)=C(C=2)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 QHPKIUDQDCWRKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FUIQBJHUESBZNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(dimethylazaniumyl)methyl]phenolate Chemical compound CN(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1O FUIQBJHUESBZNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AKNMPWVTPUHKCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyclohexyl-6-[(3-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)methyl]-4-methylphenol Chemical compound OC=1C(C2CCCCC2)=CC(C)=CC=1CC(C=1O)=CC(C)=CC=1C1CCCCC1 AKNMPWVTPUHKCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MUHFRORXWCGZGE-KTKRTIGZSA-N 2-hydroxyethyl (z)-octadec-9-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCCO MUHFRORXWCGZGE-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFHKLSPMRRWLKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-4-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)sulfanyl-6-methylphenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C(O)C(C)=CC(SC=2C=C(C(O)=C(C)C=2)C(C)(C)C)=C1 YFHKLSPMRRWLKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BGWNOSDEHSHFFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-4-[(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)methylsulfanylmethyl]-6-methylphenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C(O)C(C)=CC(CSCC=2C=C(C(O)=C(C)C=2)C(C)(C)C)=C1 BGWNOSDEHSHFFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PFANXOISJYKQRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-4-[1-(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)butyl]-5-methylphenol Chemical compound C=1C(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C=C(C)C=1C(CCC)C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C=C1C PFANXOISJYKQRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MQWCQFCZUNBTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-6-(3-tert-butyl-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)sulfanyl-4-methylphenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=CC(C)=CC(SC=2C(=C(C=C(C)C=2)C(C)(C)C)O)=C1O MQWCQFCZUNBTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BKZXZGWHTRCFPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-6-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C1O BKZXZGWHTRCFPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MDWVSAYEQPLWMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-Methylenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol) Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=CC(CC=2C=C(C(O)=C(C=2)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C)=C1 MDWVSAYEQPLWMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acrylate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C=C NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 241000083700 Ambystoma tigrinum virus Species 0.000 description 1
- NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylhydroxytoluene Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KAOKYOBMEJBXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C(C)C)(C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)C)O)C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)C)O.C(C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)CCCCCCCCC)O)C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)CCCCCCCCC)O Chemical compound C(C(C)C)(C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)C)O)C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)C)O.C(C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)CCCCCCCCC)O)C1=C(C(=CC(=C1)C)CCCCCCCCC)O KAOKYOBMEJBXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Carbonate Chemical compound [O-]C([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- HBEMHMNHYDTVRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClC(CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC)(Cl)Cl Chemical compound ClC(CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC)(Cl)Cl HBEMHMNHYDTVRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005727 Friedel-Crafts reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M Methacrylate Chemical compound CC(=C)C([O-])=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- XQVWYOYUZDUNRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Phenyl-1-naphthylamine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=CC=C2C=1NC1=CC=CC=C1 XQVWYOYUZDUNRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Natural products C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WERKSKAQRVDLDW-ANOHMWSOSA-N [(2s,3r,4r,5r)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexyl] (z)-octadec-9-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO WERKSKAQRVDLDW-ANOHMWSOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AOZDHFFNBZAHJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-hexanoyloxy-2,2-bis(hexanoyloxymethyl)propyl] hexanoate Chemical compound CCCCCC(=O)OCC(COC(=O)CCCCC)(COC(=O)CCCCC)COC(=O)CCCCC AOZDHFFNBZAHJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N [C]1=CC=CC=C1 Chemical compound [C]1=CC=CC=C1 CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- OFHCOWSQAMBJIW-AVJTYSNKSA-N alfacalcidol Chemical compound C1(/[C@@H]2CC[C@@H]([C@]2(CCC1)C)[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)=C\C=C1\C[C@@H](O)C[C@H](O)C1=C OFHCOWSQAMBJIW-AVJTYSNKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002877 alkyl aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000004996 alkyl benzenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000005215 alkyl ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000008052 alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N barium atom Chemical compound [Ba] DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- SAOKZLXYCUGLFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate Chemical compound CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)CCCCC(=O)OCC(CC)CCCC SAOKZLXYCUGLFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005587 bubbling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000010354 butylated hydroxytoluene Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001733 carboxylic acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 description 1
- LMODBLQHQHXPEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibutylcarbamothioylsulfanylmethyl n,n-dibutylcarbamodithioate Chemical compound CCCCN(CCCC)C(=S)SCSC(=S)N(CCCC)CCCC LMODBLQHQHXPEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001991 dicarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HIKZOIYUQFYFBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N didodecyl decanedioate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCCCCCCCCCCCC HIKZOIYUQFYFBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GHKVUVOPHDYRJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N didodecyl hexanedioate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)CCCCC(=O)OCCCCCCCCCCCC GHKVUVOPHDYRJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000539 dimer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000118 dimethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LTYMSROWYAPPGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl sulfide Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1SC1=CC=CC=C1 LTYMSROWYAPPGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DMBHHRLKUKUOEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenylamine Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1NC1=CC=CC=C1 DMBHHRLKUKUOEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 1
- GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N divanadium pentaoxide Chemical compound O=[V](=O)O[V](=O)=O GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003974 emollient agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002191 fatty alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010720 hydraulic oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XJTQJERLRPWUGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodomethylbenzene Chemical compound ICC1=CC=CC=C1 XJTQJERLRPWUGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000006317 isomerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002734 metacrylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010755 mineral Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003607 modifier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000005673 monoalkenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000010705 motor oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010707 multi-grade lubricating oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002790 naphthalenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000006386 neutralization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002114 octoxynol-9 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000010422 painting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003014 phosphoric acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000006069 physical mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005862 polyol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000003077 polyols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920000259 polyoxyethylene lauryl ether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920005573 silicon-containing polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N strontium atom Chemical compound [Sr] CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000005846 sugar alcohols Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 125000000542 sulfonic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000003460 sulfonic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920006029 tetra-polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- MBBWTVUFIXOUBE-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc;dicarbamodithioate Chemical compound [Zn+2].NC([S-])=S.NC([S-])=S MBBWTVUFIXOUBE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M159/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being of unknown or incompletely defined constitution
- C10M159/12—Reaction products
- C10M159/20—Reaction mixtures having an excess of neutralising base, e.g. so-called overbasic or highly basic products
- C10M159/24—Reaction mixtures having an excess of neutralising base, e.g. so-called overbasic or highly basic products containing sulfonic radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M129/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing oxygen
- C10M129/02—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing oxygen having a carbon chain of less than 30 atoms
- C10M129/04—Hydroxy compounds
- C10M129/10—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M133/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing nitrogen
- C10M133/02—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing nitrogen having a carbon chain of less than 30 atoms
- C10M133/04—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M133/12—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M133/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing nitrogen
- C10M133/52—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing nitrogen having a carbon chain of 30 or more atoms
- C10M133/56—Amides; Imides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M137/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing phosphorus
- C10M137/02—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being an organic non-macromolecular compound containing phosphorus having no phosphorus-to-carbon bond
- C10M137/04—Phosphate esters
- C10M137/10—Thio derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M163/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being a mixture of a compound of unknown or incompletely defined constitution and a non-macromolecular compound, each of these compounds being essential
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2205/00—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2205/00—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2205/06—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions containing conjugated dienes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/02—Hydroxy compounds
- C10M2207/023—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/02—Hydroxy compounds
- C10M2207/023—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2207/024—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings having at least two phenol groups but no condensed ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/02—Hydroxy compounds
- C10M2207/023—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2207/026—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings with tertiary alkyl groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/02—Hydroxy compounds
- C10M2207/023—Hydroxy compounds having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2207/027—Neutral salts thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/10—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof
- C10M2207/12—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms
- C10M2207/125—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms having hydrocarbon chains of eight up to twenty-nine carbon atoms, i.e. fatty acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/10—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof
- C10M2207/12—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms
- C10M2207/129—Carboxylix acids; Neutral salts thereof having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms having hydrocarbon chains of thirty or more carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/26—Overbased carboxylic acid salts
- C10M2207/262—Overbased carboxylic acid salts derived from hydroxy substituted aromatic acids, e.g. salicylates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/28—Esters
- C10M2207/287—Partial esters
- C10M2207/289—Partial esters containing free hydroxy groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2209/00—Organic macromolecular compounds containing oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2209/02—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10M2209/08—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds containing monomers having an unsaturated radical bound to a carboxyl radical, e.g. acrylate type
- C10M2209/084—Acrylate; Methacrylate
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2209/00—Organic macromolecular compounds containing oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2209/10—Macromolecular compoundss obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10M2209/103—Polyethers, i.e. containing di- or higher polyoxyalkylene groups
- C10M2209/104—Polyethers, i.e. containing di- or higher polyoxyalkylene groups of alkylene oxides containing two carbon atoms only
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2215/064—Di- and triaryl amines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2215/064—Di- and triaryl amines
- C10M2215/065—Phenyl-Naphthyl amines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2215/066—Arylene diamines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2215/067—Polyaryl amine alkanes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/02—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines
- C10M2215/06—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C10M2215/068—Amines, e.g. polyalkylene polyamines; Quaternary amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings having amino groups bound to polycyclic aromatic ring systems, i.e. systems with three or more condensed rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/08—Amides [having hydrocarbon substituents containing less than thirty carbon atoms]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/08—Amides [having hydrocarbon substituents containing less than thirty carbon atoms]
- C10M2215/082—Amides [having hydrocarbon substituents containing less than thirty carbon atoms] containing hydroxyl groups; Alkoxylated derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/086—Imides [having hydrocarbon substituents containing less than thirty carbon atoms]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/22—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/22—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds
- C10M2215/221—Six-membered rings containing nitrogen and carbon only
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/22—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds
- C10M2215/225—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds the rings containing both nitrogen and oxygen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/22—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds
- C10M2215/225—Heterocyclic nitrogen compounds the rings containing both nitrogen and oxygen
- C10M2215/226—Morpholines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/24—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions having hydrocarbon substituents containing thirty or more carbon atoms, e.g. nitrogen derivatives of substituted succinic acid
- C10M2215/28—Amides; Imides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2215/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions
- C10M2215/24—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing nitrogen as ingredients in lubricant Compositions having hydrocarbon substituents containing thirty or more carbon atoms, e.g. nitrogen derivatives of substituted succinic acid
- C10M2215/30—Heterocyclic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/02—Sulfur-containing compounds obtained by sulfurisation with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds
- C10M2219/022—Sulfur-containing compounds obtained by sulfurisation with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds of hydrocarbons, e.g. olefines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/02—Sulfur-containing compounds obtained by sulfurisation with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds
- C10M2219/024—Sulfur-containing compounds obtained by sulfurisation with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds of esters, e.g. fats
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/04—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions containing sulfur-to-oxygen bonds, i.e. sulfones, sulfoxides
- C10M2219/046—Overbased sulfonic acid salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/06—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof
- C10M2219/062—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof having carbon-to-sulfur double bonds
- C10M2219/066—Thiocarbamic type compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/06—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof
- C10M2219/062—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof having carbon-to-sulfur double bonds
- C10M2219/066—Thiocarbamic type compounds
- C10M2219/068—Thiocarbamate metal salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2223/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2223/02—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions having no phosphorus-to-carbon bonds
- C10M2223/04—Phosphate esters
- C10M2223/045—Metal containing thio derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2223/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2223/02—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions having no phosphorus-to-carbon bonds
- C10M2223/04—Phosphate esters
- C10M2223/047—Thioderivatives not containing metallic elements
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2227/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing atoms of elements not provided for in groups C10M2203/00, C10M2207/00, C10M2211/00, C10M2215/00, C10M2219/00 or C10M2223/00 as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2227/06—Organic compounds derived from inorganic acids or metal salts
- C10M2227/061—Esters derived from boron
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2010/00—Metal present as such or in compounds
- C10N2010/04—Groups 2 or 12
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/04—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/04—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives
- C10N2040/042—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives for automatic transmissions
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/04—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives
- C10N2040/044—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives for manual transmissions
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/04—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives
- C10N2040/046—Oil-bath; Gear-boxes; Automatic transmissions; Traction drives for traction drives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/08—Hydraulic fluids, e.g. brake-fluids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/251—Alcohol-fuelled engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/252—Diesel engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/252—Diesel engines
- C10N2040/253—Small diesel engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/255—Gasoline engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/255—Gasoline engines
- C10N2040/28—Rotary engines
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Lubricants (AREA)
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Waschhilfsmittel/Dispersionszusatzstoffe für Schmieröle und Methoden zur Herstellung dieser Sulfonate.
- Allgemeiner Stand der Technik
- Im Stand der Technik sind Methoden zum Herstellen schwach oder stark überalkalisierter Sulfonate aus Sulfonsäure bekannt, die aus der Sulfonierung verschiedener Alkylarylkohlenwasserstoffen und einem Überschuß an Erdalkalibasen erhalten werden.
- Die Alkylarylkohlenwasserstoffe, die der Sulfonierungsreaktion unterzogen werden, werden über die Friedel-Craft-Reaktion verschiedener Arylwasserstoffe, insbesondere aromatischer, mit zwei verschiedenen Arten von Olefin erhalten:
-
- – Verzweigte Olefine, die durch die Oligo-Polymerisierung von Propylen zu C15 bis C42 Wasserkohlenstoffen, insbesondere Propylentetrapolymer, das zu einem C24 Olefin dimerisiert wurde, erhalten werden, und
- – Lineare Olefine, die durch die Oligo-Polymerisierung von Äthylen zu C14 bis C40 Wasserkohlenstoften erhalten werden.
- Es ist leicht, eine gute Dispersion im Medium der Erdalkalibase, die nicht in Form von Salz gebunden sind, zu erhalten, wenn die Sulfonsäure von einem Wasserstoff abgeleitet ist, der durch Alkylierung eines Arylwasserstoffs mit einem verzweigten Olefin erhalten wurde. Es ist schwierig, wenn die Alkylierung mit einem linearen Olefin durchgeführt wird. Es ist insbesondere schwierig für die Alkylierung eines Arylwasserstoffs, wenn ein hoher Anteil des Alkylarylwasserstoffs den Arylsubstiuenten an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests aufweist, aufgrund der Ausbildung einer Haut im Freien.
- Diese dürftige Dispersion ist insbesondere ausgeprägt, wenn das Medium außerdem einen hohen Anteil von Sulfonat enthält, d.h. wenn es einer niedrigen Basenzahl (zwischen 3 und 60), daher einem niedrigen Anteil an freiem Kalk und der Abwesenheit von Kohlendioxid und Karbonat entspricht.
- Tatsächlich weisen während der Alkylierungsreaktion mit Benzol oder einem anderen aromatischen oder Arylwasserstoff 25 Mol% des Alkylarylwasserstoffs den Arylsubstituenten an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests auf. Herkömmlicherweise ergeben Aromaten, die an der 2-Position der Alkylgruppe gebunden sind, die meiste Wasserabsorption.
- Bei der Alkylierungsreaktion von Aromaten unter Verwendung von normalen alpha Olefinen (NAO) gibt es drei konkurrierende Reaktionen. Dies sind (1) Isomerisierung der NAO, (2) Alkylierung der Aromaten mit dem Olefin und (3) Dimerisierung des Olefins.
- Bei Herstellung durch die Methode, die zum Beispiel im französischen Patent Nr. 2,564,830 beschrieben ist, führt dieser hohe Anteil an Alkylarylwasserstoff mit einem Arylradikal an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests zu einem Sulfonat, das hygroskopische Eigenschaften zeigt, so daß eine oberflächliche „Haut" ausgebildet wird. Diese „Haut" macht dieses Erzeugnis als einen Zusatzstoff für Schmieröl unannehmbar.
- Außerdem wird die Bildung dieser oberflächlichen Haut im allgemeinen von einer sehr geringen Filtrierungsrate, einer hohen Viskosität, einer niedrigen Kalziumeingliederung, einer Verschlechterung der Rostbeständigkeitsleistung und einem unerwünschten trüben Erscheinungsbild oder sogar von Sedimentation begleitet, wenn das derart hergestellte Sulfonat einem Standardschmieröl in einem Verhältnis von 10 Gewichtsprozent zugesetzt und zur Untersuchung gelagert wird.
- Der Anmelder hat chromatographische Analysen zum Identifizieren von jeden der verschiedenen Isomere durchgeführt, die sich durch die Position des Arylradikals am Kohlenstoffatom des linearen Alkylrests unterscheiden, und ihren jeweiligen Einfluß auf die Eigenschaften der entsprechenden Alkylarylsulfonate von Alkalinmetallen untersucht, die aus diesen verschiedenen Isomeren erhalten werden.
- Der Anmelder hat daher herausgefunden, daß er die oben angeführten Nachteile insoweit bewältigen könnte, als das Mol% des Arylwasserstoffs, im Unterschied zum Benzol, der den Arylsubstiuenten an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests aufweist, zwischen 0 und 13%, vorzugsweise zwischen 5 und 11% und insbesondere zwischen 7 und 10% aufweist.
- Diese Entdeckung war der Gegenstand des französischen Patents Nr. 2 731 427, das am 8. März 1995 vom Anmelder eingereicht wurde.
- Der Anmelder hatte jedoch keinen Erfolg beim Erhalten zufriedenstellender Resultate, wenn der Arylwasserstoff Benzol war, da er bis dahin nie imstande war, die Bildung der Haut bei Verwendung dieses aromatischen Wasserstoffs zu verhindern, auch wenn der Wasserstoff mit einem sehr langkettigen linearen Monoolefin alkyliert wurde, so daß das Mol% des Arylwasserstoffs mit dem Arylsubstituenten an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests zwischen 0 und 13% und vorzugsweise zwischen 5 und 11% und insbesondere zwischen 7 und 10% aufweist.
- Infolge intensiverer Studien hatte der Anmelder entdeckt, daß die oben angeführten Nachteile durch Verwendung einer Mischung aus Alkylarylsulfonaten von überalkalisierten Erdalkalimetallen bewältigt werden konnten, bestehend aus:
-
- (a) 50% bis 85% eines linearen Monoalkylphenylsulfonat, bei dem der lineare Alkylrest zwischen 14 und 40 Kohlenstoffatome enthält und zwischen 0 und 13 Mol% des Phenylsulfonatradikals des Erdalkalimetalls an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist, und
- (b) 15% bis 50% eines schweren Alkylarylsulfonats, ausgewählt aus:
- (i) Dialkylarylsulfonaten, wobei beide Alkylsubstituenten lineare Alkylreste sind, von denen die Summe der Kohlenstoffatome 16 bis 40 beträgt, oder
- (ii) Mono- oder Polyalkylarylsulfonate, wobei der Alkylsubstituent oder die Alkylsubstituenten verzweigte Ketten sind, wobei die Summe der Kohlenstoffatome 15 bis 48 Kohlenstoffatome beträgt.
- Diese Mischung von Alkylarylsulfonaten weist ein Maximum von 10 Mol% des Phenylsulfonatradikals des Erdalkalimetalls an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests gebunden auf. Diese Mischung weist nach dreitägiger Lagerung in einem offenen Gefäß bei Raumtemperatur keine Hautbildung auf. Es weist gute Kalziumeingliederung, eine niedrige Viskosität, gute Löslichkeit und gute Leistung auf.
- Diese Entdeckung war der Gegenstand des französischen Patents Nr. 2 752 838, das am 8. September 1996 vom Anmelder eingereicht wurde.
- Infolge intensiverer Studien hatte der Anmelder eine Mischung von Alkylphenylsulfonaten von Erdalkalimetallen mit niedriger Farbausbildung und auch nach dreitägiger Lagerung in einem offenen Gefäß bei Raumtemperatur keiner Hautbildung entdeckt. Diese Mischung besteht aus:
-
- (a) 20% bis 70% eines linearen Monoalkylphenylsulfonats, bei dem der lineare Monoalkylsubstituent 14 und 40 Kohlenstoffatome enthält und dessen Mol% an Phenylsulfonatradikal, das an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist, zwischen 10% und 25% aufweist, und
- (b) 30% bis 80% eines verzweigten Monoalkylphenylsulfats, bei dem der verzweigte Monoalkylsubstituent 14 bis 18 Kohlahnstoffatome enthält.
- Diese Erfindung war der Gegenstand der europäischen Patentanmeldung Nr. 976 810, die am 31. Juli 1998 vom Anmelder eingereicht wurde.
- Kurzdarstellung der Erfindung
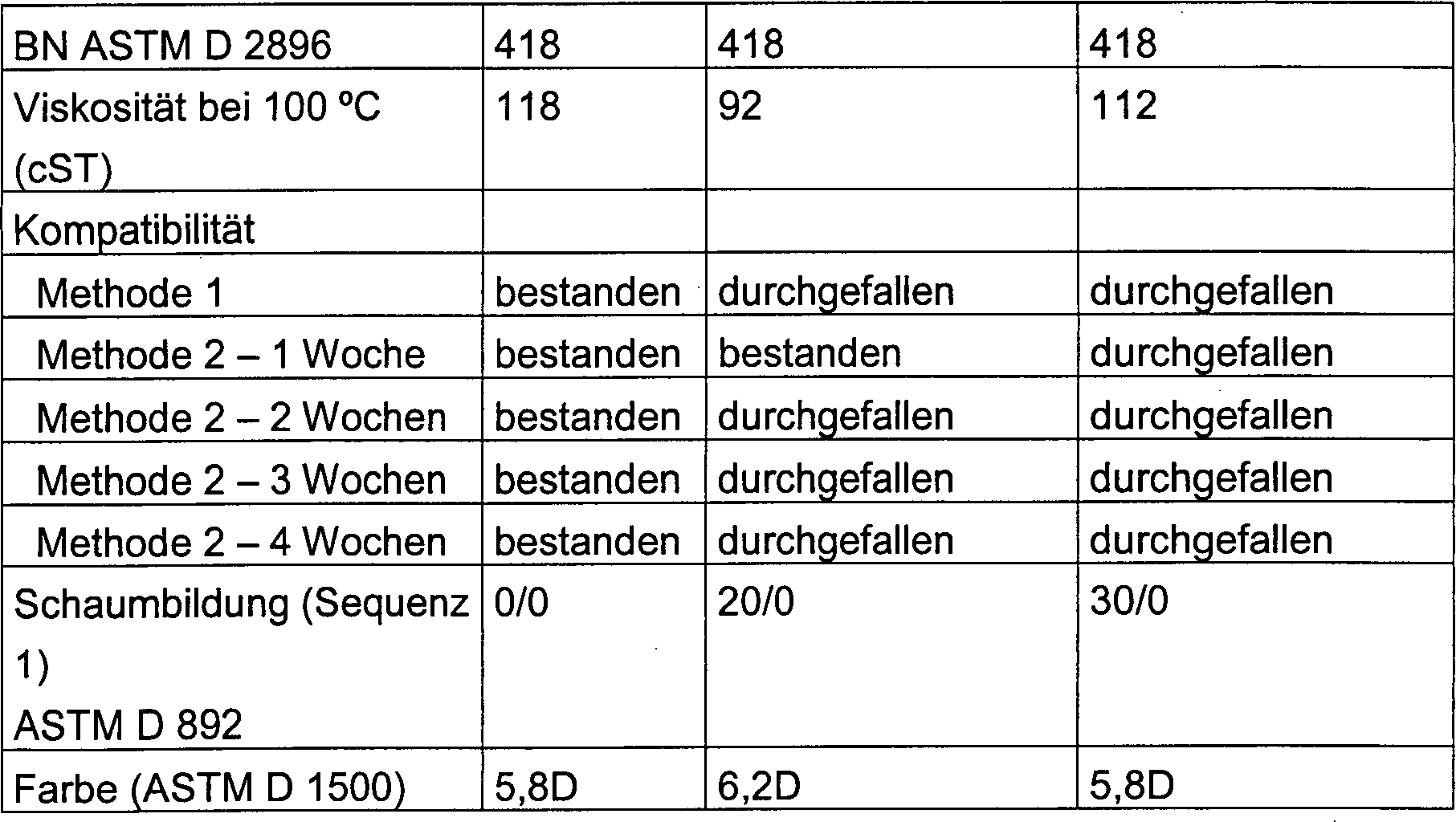
- Die vorliegende Erfindung stellt ein hochgradig alkalisch eingestelltes Erdalkaliarylsulfonat bereit, das erhöhte Kompatibilität und Löslichkeit bei niedriger Farb- und keiner Hautausbildung aufweist.
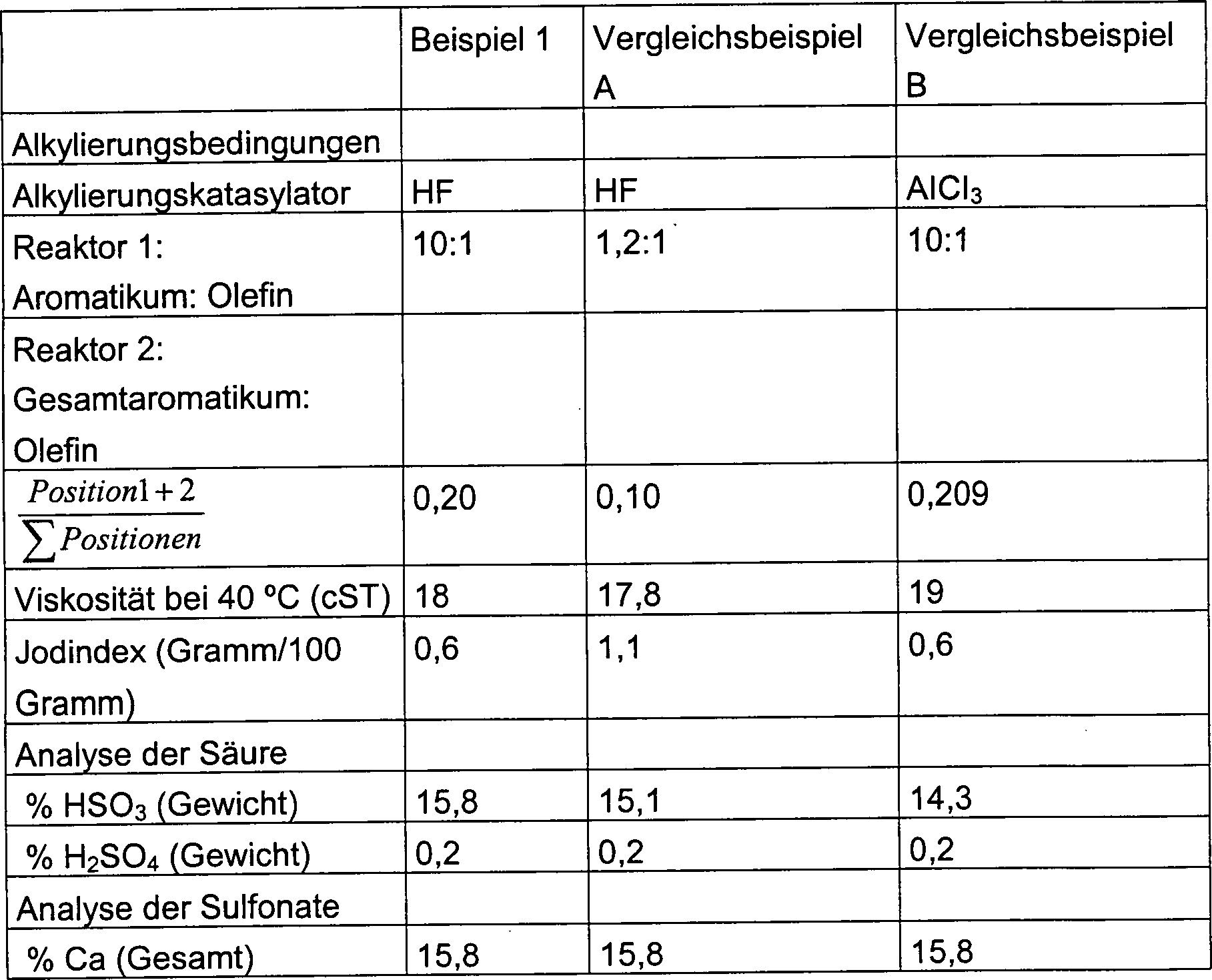
- Während wir herausgefunden haben, daß eine zu hohe Konzentration von linearen 1-Aryl oder 2-Aryl Alkylarylsulfonaten Hautbildung bei Sulfonaten bewirkt, haben wir herausgefunden, daß der höhere BN (mindestens 250 BN) Sulfonate weniger empfindlich auf den 2-Aryl Anteil in dem Alkylat macht, weil der 2-aryl Anteil durch die Salze verdünnt wird. Daher kann, wenn der BN hoch genug (mindestens 250) ist und das Arylradikal nicht Phenol ist, das Mol% an Arylsulfonatradikal, das an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist, zwischen 13% und 30% (vorzugsweise zwischen 15% und 25%) ohne Hautbildung aufweisen. Dieser hohe Molprozentsatz von 2-Aryl ergibt ein Sulfonat mit guten Wasserabsorptionseigenschaften.
- Der Alkylrest des Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonats ist eine lineare Kette, die zwischen 14 und 40 Kohlenstoffatome, vorzugsweise 20 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatome enthält.
- Vorzugsweise weist das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat ein Monoalkylatanteil von mindestens 87% und eine Jodzahl von mindestens 1,0 auf.
- Vorzugsweise leitet sich das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat von einem normalen C14-C40 alpha Olefin, vorzugsweise von einem C20-C24 alpha Olefin ab.
- Dieses Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat leitet sich vorzugsweise von einem Alkylat ab, welches durch Reaktion mit normalem alpha Olefin in Anwesenheit von Hydrogenfluorid, vorzugsweise in einem Einstufenreaktor, dargestellt wurde. Vorzugsweise wird das Alkylat in Anwesenheit von Methanol und Xylene, jedoch in Abwesenheit von Chlor dargestellt.
- Vorzugsweise wird das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat als ein Waschhilfsmittel/Dispersionszusatzstoff für Schmieröle verwendet. Eine Formulierung von Schmierölen würde einen Hauptanteil eines Basisöls mit Schmiermittelviskosität und einen Nebenanteil (vorzugsweise 0,5 bis 40%) des Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonats der vorliegenden Erfindung enthalten. Außerdem würde die Formulierung von Schmierölen typischerweise 0 bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels, 0 bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats, 0 bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers, 0 bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und 0 bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers enthalten.
- Diese Schmierölzusammensetzung kann durch Mischen eines Hauptanteils eines Basisöls mit Schmiermittelviskosität und 0,5 bis 40% eines Waschhilfsmittels bestehend aus dem Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat der vorlie genden Erfindung, vorzugsweise mit 0 bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels, 0 bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats, 0 bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers, 0 bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und 0 bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers hergestellt werden.
- Es kann ein Konzentrat bestehend aus ungefähr 10% bis 90% eines kompatiblen organischen, flüssigen Verdünnungsmittels und aus ungefähr 0,5% bis 90% des Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonats der vorliegenden Erfindung dargestellt werden.
- Kurze Beschreibung der Zeichnungen
- Um das Verstehen dieser Erfindung zu unterstützen, wird nun auf die beiliegenden Zeichnungen Bezug genommen. Die Zeichnungen sind nur beispielhaft und sollten nicht als die Erfindung beschränkend verstanden werden.
-
1 zeigt die Gelpermeations-Chromatographie für Beispiel 1 der vorliegenden Erfindung. -
2 zeigt die Gelpermeations-Chromatographie für Vergleichsbeispiel A. -
3 zeigt die Gelpermeations-Chromatographie für Vergleichsbeispiel B. - Detaillierte Beschreibung der Erfindung
- In ihrem allgemeinsten Aspekt beinhaltet die vorliegende Erfindung ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat, seine Verwendung als Waschhilfsmittel/Dispersionszusatzstoff für Schmieröle und Methoden zur Herstellung dieser Mischung.
- Vor der Behandlung der Erfindung im einzelnen werden die folgenden Ausdrücke definiert:
- Definitionen
- Wie hierin verwendet haben die folgenden Ausdrücke, außer bei ausdrücklicher gegenteiliger Angabe, die folgende Bedeutung:
- Der Ausdruck „Erdalkalimetall" bezeichnet Kalzium, Barium, Magnesium und Strontium.
- Der Ausdruck „Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat" bezeichnet ein Erdalkalimetallsalz einer Alkylarylsäure. Anders gesagt ist es ein Erdalkalimetallsalz eines Aryls, das durch (1) eine Alkylgruppe und (2) eine Sulfonsäuregruppe substituiert ist, die imstande ist, ein Metallsalz darzustellen.
- Der Ausdruck „das Mol% an Arylsulfonatradikal, welches an Position 1 oder 2 des Alkylrests gebunden ist" bezeichnet den Molprozentanteil aller Arylsulfonatradikalen, die an einen Alkylrest gebunden sind, welche an der 1. oder 2. Position des Alkylrests gebunden sind. Die 1. Position des linearen Alkylrests ist die Position am Ende der Kette. Die 2. Position des linearen Alkylrests ist die Position unmittelbar neben Position 1.
- Der Ausdruck „1-Aryl" bezeichnet ein Arylsulfonatradikal, das an einen linearen Alkylrest an der 1. Position des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist.
- Der Ausdruck „2-Aryl" bezeichnet ein Arylsulfonatradikal, das an einen linearen Alkylrest an der 2. Position des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist.
- Der Ausdruck „Monoalkylatanteil" ist der Gewichtsprozentanteil des Alkylats, das nicht Dialkylat ist [100 × Moloalkylat/(Moloalkylat + Dialkylat)].
- Der Ausdruck „Jodzahl" ist der Absorptionswert (Hüblzahl oder Wejszahl), der die Menge von Jod in Gramm, die unter bestimmten Bedingungen von 100 Gramm Fett oder Öl absorbiert wird. Er gibt die Menge vorhandener Doppelbindungen an.
- Der Ausdruck „Basiszahl" oder „BN" bezeichnet den Basisanteil, der Milligramm KOH in einem Gramm Probe entspricht. Höhere BN spiegeln daher alkalischere Erzeugnisse und daher eine größere Alkalinitätsreserve wider. Der BN einer Probe kann durch ASTM Test Nr. D2896 oder jedes andere entsprechende Verfahren bestimmt werden.
- Der Ausdruck „alkalisch eingestellte Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonate" bezeichnet eine Zusammensetzung, die einen Verdünner (z. B. Schmieröl) und Alkylarylsulfonat enthält, wobei zusätzliche Alkalinität durch einen stöchiometrischen Überschuß an einer Erdalkalimetallbase vorgesehen ist, auf Grundlage der erforderlichen Menge zum Reagieren mit dem säurereichen Anteil des Waschhilfsmittels. Es sollte in dem alkalisch eingestellten Waschhilfsmittel ausreichend Verdünner beinhaltet sein, um leichtes Handhaben bei sicheren Betriebstemperaturen zu ermöglichen.
- Der Ausdruck „hochgradig alkalisch eingestelltes Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat" bezeichnet ein alkalisch eingestelltes Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat mit einem BN von 250 oder mehr. Im allgemeinen ist eine Kohlendioxidbehandlung zum Erhalten alkalisch eingestellter Waschhilfsmittelzusammensetzungen mit hohem BN erforderlich. Es wird angenommen, daß dies eine kolloidale Metallbasisdispersion darstellt.
- Wenn nicht anders angegeben, sind alle Prozentsätze in Gewichtsprozent angegeben, sind alle Verhältnisse Molverhältnisse und alle Molmassen durchschnittliche Molmassen.
- Alkylarylsulfonate
- Die Alkylarylsulfonate der vorliegenden Erfindung sind hochgradig alkalisch eingestellte Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonate mit linearen Alkylgruppen und einem hohen Mol% des Arylsulfonatradikals, das an Position 1 oder 2 des linearen Alkylrests gebunden ist (13% bis 30%, vorzugsweise 15% bis 15%). Diese Alkylarylsulfonate weisen erhöhte Kompatibilität und erhöhte Löslichkeit bei niedriger Farb- und keiner Hautbildung auf.
- Es ist wesentlich, daß die Alkylarylsulfonate hochgradig alkalisch eingestellt sind (BN von mindestens 250), um den 2-Aryl Anteil ausreichend zu verdünnen, so daß es zu keiner Hautbildung kommt.
- Es ist ebenfalls wesentlich, daß da Arylradikal nicht Phenol ist, da hochgradig alkalisch eingestellte Alkylphenoxysulfonate mit einem hohen 2-Aryl Anteil zu viskos für leichte Handhabung zu sein pflegen. Vorzugsweise ist es ein Alkylbenzolsulfonat oder ein Alkyltoluolsulfonat.
- Der lineare Alkylrest enthält zwischen 14 und 40 Kohlenstoffatome, vorzugsweise 20 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatome. Vorzugsweise leitet sich das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat von einem normalen C14-C40 alpha Olefin, vorzugsweise von einem C20-C24 alpha Olefin ab.
- Vorzugsweise weist das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat ein Monoalkylatanteil von mindestens 87% und eine Jodzahl von mindestens 1.0 auf.
- Das französische Patent Nr. 2.564.830 an das Unternehmen Orogil, den vorherigen Namens des Zessionars, dessen entsprechende Anmeldung 1985 veröffentlicht wurde und das US-Patent Nr. 4,764,295 entspricht, beschreibt Alkylarylsulfonate von Erdalkalimetallen, die aus Alkylierung durch ein lineares Olefin erfolgen.
- Das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat kann aus einem Alkylat durch die Reaktion von Benzol und einem normalen alpha Olefin in Anwesenheit von Hydrogenfluorid, vorzugsweise in einem Einstufenreaktor, abgeleitet werden. Vorzugsweise wird das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat in Anwesenheit von Methanol und Xylene und in Abwesenheit von Chlor dargestellt.
- Vorzugsweise wird das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat in Verbindung mit einem anderen Waschhilfsmittel, vorzugsweise einem geschwefelten Erdalkalialkylarylphenat, verwendet.
- Sonstige Zusatzstoffkomgonenten
- Die folgenden Zusatzstoffkomponenten sind Beispiele für Komponenten, die vorteilhaft in Kombination mit der Mischung von Alkylarylsulfonaten von Erdalkalimetallen in den Zusammensetzungen der vorliegenden Erfindung Anwendung finden können:
-
- (1) Aschlose Dispersionsmittel: Alkylsuccinimide, mit anderen Verbindungen modifizierte Alkylsuccinimide und mit Borsäure, Alkenylbernsteinester modifizierte Alkylsuccinimide.
- (2) Waschhilfsmittel: geschwefelte oder ungeschwefelte Alkyle oder Alkylphenate, geschwefelte oder ungeschwefelte Metallsalze von Multihydroxyalkyl- oder aromatischen Alkylverbindungen, Alkyl- oder aromatische Alkenylhydroxysulfonate, geschwefelte oder ungeschwefelte Alkyloder Alkenylsalzylate, geschwefelte oder ungeschwefelte Alkyl- oder Alkenylnaphtenate, Metallsalze alkanoischer Säuren, Metallsalze einer Alkyl- oder Alkenylmehrfachsäure und chemischer und physischer Mischungen davon.
- (3) Oxidationshemmer:
- 1) Phenolartige (phenolische) Oxidationshemmer: 4,4'-methylenebis (2,6-di-tert-butylphenol), 4,4'-bis(2,6-di-tent-butylphenol), 4,4'bis(2-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol, 2,2'-(methylenebis(4-methyl-6-tertbutyl-phenol), 4,4'-butylidenebis(3-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol), 4,4'isopropylidenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol), 2,2'methylenebis(4methyl-6-nonylphenol)2,2'-isobutyliden-bis(4,6-dimethylphenol), 2,2'-methylenebis(4-methyl-6-cyclohexylphenol), 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol, 2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butylphenol, 2,6-di-tert-α-dimethylamin-pcresol, 2,6-di-tert-4-(N,N' dimethylaminomethylphenol), 4,4'thiobis(2-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol), 2,2'-thiobis(4-methyl-6-tertbutylphenol), bis(3-methyl-4-hydroxy-5-tert-butylbnzyl)-sulfid und bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hidroxybenzyl).
- 2) Diphenylaminartige Oxidationshemmer: alkyliertes Diphenylamin, Phenyl-α-Naphtylamin und alkyliertes α-Naphthylamin.
- 3) Sonstige Arten: Metalldithiokarbamat (z. B. Zinkdithiokarbamat) und Methylenebis (Dibutyldithiokarbamat).
- (4) Rosthemmer (Rostschutzmittel)
- 1) Nichtionische, oberflächenaktive Polyoxyethylenmittel: Polyoxyethylenlauryläther, Polyoxyethylennonphenyläther, Polyoxyethylenoctylphenyläther, Polyoxyethylenoktylstearyläther, Polyoxyethylenoleyläther, Polyoxyethylensorbitolmonostearat, Polyoxyethylensorbitolmonooleat und Polyethylenglykolmonooleat.
- 2) Sonstige Verbindungen: Stearinsäure und andere Fettsäuren, Diskarboxylsäuren, Metallseifen, Fettsäureaminsalze, Metallsalze schwerer Sulfonsäure, teilweise Karboxylsäureester von mehrwertigem Alkohol und Phosphorsäureester.
- (5) Demulgatoren: Zusatzprodukt von Alkylphenol und Ethylenoxid, Poloxyethylenalkyläther und polyoxyethylensorbitanester.
- (6) Höchstdruckmittel (EP-Mittel): Zinkdialkyldithiophosphat (Zn-DTP, primäre Alkylart und sekundäre Alkylart), geschwefelte Öle, Diphenylsulfid, Methyltrichlorostearat, chloriertes Naphtalen, Benzyljod, Fluoroalkylpolysiloxan und Bleinaphtenat.
- (7) Reibungsmodifizierer: Fettalkohol, Fettsäure, Amin, Boratester und andere Ester.
- (8) Multifunktionszusätze: geschwefeltes Oxymolybdändithiokarbamat, geschwefeltes Oxymolybdänorganophosphorodithionat, Oxymolybdänmonoglycerid, Oxymolybdändiethylat, Aminmolybdänkomplexverbindung und schwefelhaltige Molybdänkomplexverbindung.
- (9) Viskositätsindexerhöher: polymethancrylatartige Polymere, Ethylenpropylencopolymere, Styrolisoprencopolymere, hydrierte Styrolisoprencopolymere und dispergatorartige Viskositätsindexerhöher.
- (10) Pourpoint-Sinkmittel: Polymethylmethacrylat.
- (11) Schaumbildungshemmer: Methacrylatpolymere und Dimethylsilikonpolymere.
- Öl mit Schmierviskosität
- Das Öl mit Schmierviskosität, das in solchen Zusammensetzungen verwendet wird, kann Mineralöl oder synthetisches Öl mit einer Viskosität sein, die zur Verwendung im Kurbelgehäuse eines Verbrennungsmotors wie Benzinoder Dieselmotoren einschließlich PKW-, schwere Straßen- und Geländefahrzeug-, Eisenbahn-, Erdgas- und Schiffs- sowie Tauchkolben- und langsam laufende Kreuzkopfmotoren geeignet ist. Kurbelgehäuseschmieröle weisen gewöhnlich eine Viskosität von ungefähr 1300 cST bei 0°F (–18°C) bis 24 cST bei 210°F (99°C) auf. Die Schmieröle können von synthetischen oder natürlichen Quellen abgeleitet sein. Mineralöl zum Gebrauch als das Basisöl in dieser Erfindung beinhaltet paraffinhaltiges, naphthenisches und andere Öle, die gewöhnlich in Schmierölzusammensetzungen verwendet werden. Synthetische Öle beinhalten sowohl synthetische Kohlenwasserstofföle als auch synthetischen Ester. Nützliche synthetische Kohlenwasserstofföle beinhalten flüssige Polymere von alpha Olefinen mit der geeigneten Viskosität. Besonders nützlich sind die hydrierten Flüssigoligomere von C6 bis C12 alpha Olefinen, wie 1-decene Trimer. Gleichermaßen können Alkylbenzolamit geeigneter Viskosität, wie Didodecylbenzol verwendet werden. Nützliche synthetische Ester beinhalten die Ester sowohl der Monocarbonsäuren als auch der Polycarbonsäuren sowohl Monohydroxyalkanolen und Polyolen. Typische Beispiele sind Didodecyladipat, Pentaerythritoltetracaproat, di-2-ethylhexyladipat, Dilaurylsebacat und dergleichen. Komplexe Ester, die aus Mischungen von Mono- und Dicarboxylsäuren hergestellt sind, und Mono- und Dihydroxyalkanole können auch verwendet werden.
- Mischungen von Mineralölen mit synthetischen Ölen sind ebenfalls nützlich. Zum Beispiel ergeben Mischungen von 10% bis 25% hydriertes 1-decene Trimer mit 75% bis 90% 150 SUS (100°F) Mineralöl eine ausgezeichnete Schmierölbasis.
- Schmierölzusammensetzungen
- Die Zusatzstoffe, die durch das Verfahren der vorliegenden Erfindung verwendet werden, sind nützlich zum Übertragen von Wasch- und Dispergierungskrafteigenschaften auf das Schmieröl. Bei Anwendung auf diese Art und Weise reicht das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat von ungefähr 0,5% bis 40% der gesamten Schmiermittelzusammensetzung, vorzugsweise von 1% bis 25 der gesamten Schmiermittelzusammensetzung. Solche Schmierölzusammensetzungen sind im Kurbelwellengehäuse eines Verbrennungsmotors nützlich, wie Benzin- oder Dieselmotoren einschließlich PKW-, schwere Straßen- und Geländefahrzeug-, Eisenbahn-, Erdgas- und Schiffs- sowie Tauchkolben- und langsam laufende Kreuzkopfmotoren. Sie sind auch in Hydraulikanwendungen nützlich.
- Die Schmierölzusammensetzungen können in einer Methode zum Vermindern von Schmutzablagerungen im Motor, einer Methode zum Vermindern von Kolbenablagerungen oder beiden zur Anwendung kommen.
- Solche Schmierölzusammensetzungen setzen ein fertiggestelltes Schmieröl ein, das Einbereichs- oder Mehrbereichsöl sein kann. Mehrbereichsschmieröle werden durch Zusetzen von Vikositätsindexerhöhern (VI-Erhöhern) hergestellt. Typische VI-Erhöher sind Polyalkylmethacrylate, Ethylenpropylencopolymere, Styroldiencopolymere und dergleichen. Sogenannte Dispersant-VI-Erhöher, die Dispergier- sowie VI-modifizierende Eigenschaften aufweisen, können auch in solchen Formulierungen verwendet werden.
- In einer Ausführungsform könnte eine Schmierölzusammensetzung folgendes enthalten:
-
- (a) einen Hauptanteil eines Öls mit Schmiermittelviskosität;
- (b) 0,5% bis 40% eines Waschhilfsmittels, das bestehend aus dem Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat der vorliegenden Erfindung;
- (c) 0% bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels;
- (d) 0% bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats;
- (e) 0% bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers;
- (f) 0% bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und
- (g) 0% bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers.
- Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Schmierölzusammensetzung
- In einer Ausführungsform wird eine Schmierölzusammensetzung durch Mischen einer Mischung aus folgendem hergestellt:
-
- (a) einem Hauptanteil eines Öls mit Schmiermittelviskosität;
- (b) 0,5% bis 40% eines Waschhilfsmittels, das bestehend aus dem Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat der vorliegenden Erfindung, vorzugsweise außerdem umfassend ein geschwefeltes Alkylarylphenat;
- (c) 0% bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels;
- (d) 0% bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats;
- (e) 0% bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers;
- (f) 0% bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und
- (g) 0% bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers.
- Die Schmierölzusammensetzung, die durch diese Methode hergestellt ist, könnte sich leicht von der anfänglichen Mischung unterscheiden, da die Komponenten interagieren können. Die Komponenten können in jeder Reihenfolge und als Komponentenkombinationen gemischt werden.
- Zusatzstoffkonzentrate
- Zusatzstoffkonzentrate sind ebenfalls im Anwendungsgebiet dieser Erfindung beinhaltet. Die Konzentrate dieser Erfindung umfassen das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat der vorliegenden Erfindung mit mindestens einem der Zusätze, die oben offenbart sind. Typischerweise enthalten die Konzentrate ausreichend organischen Verdünner, um sie bei Versand und Lagerung leicht handhabbar u machen.
- 10% bis 90% des Konzentrats ist organischer Verdünner. 0,5% bis 90% Konzentrat beträgt die Mischung von Alkalialkylarylsulfonat von Erd alkalimetallen der vorliegenden Erfindung. Der Rest des Konzentrats besteht aus anderen Zusatzstoffen.
- Geeignete organische Verdünner, die verwendet werden können, beinhalten zum Beispiel 100N geläutertes Lösungsmittel, d. h. Cit-Con 100N, und wasserstoffbehandeltes N100, d. h. RLOP 100N und dergleichen. Der organische Verdünner weist vorzugsweise eine Viskosität von ungefähr 1 bis ungefähr 20 cST bei 100°C auf.
- Beispiele für Zusatzstoffpakete
- Nachstehend sind repräsentative Beispiele für Zusatzstoffpakete aufgeführt, die bei verschiedenen Anwendungen verwendet werden können. Diese repräsentativen Beispiele setzen die neuartigen Dispersionsmittel der vorliegenden Erfindung ein. Die folgenden Prozentsätze haben den aktiven Komponentenanteil ohne Weichmacheröl oder Verdünnungsöl zur Grundlage. Diese Beispiele sind zum Veranschaulichen der vorliegenden Erfindung vorgesehen, sollen sie jedoch nicht einschränken.
- Das unten angeführte Waschhilfsmittel kann entweder das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat der vorliegenden Erfindung allein oder in Kombination mit einem anderen Waschhilfsmittel sein.
- Beispiele
- Die Erfindung wird ferner durch folgende Beispiele veranschaulicht, die besonders vorteilhafte Methodenausführungsformen darstellen. Diese Beispiele sind zum Veranschaulichen der vorliegenden Erfindung vorgesehen, sollen sie jedoch nicht einschränken.
- Meßmethoden
- Die Beispiele enthalten Testergebnisse, die durch folgende Meßmethoden erhalten wurden:
- Viskosität bei 100°C in cST
- Die Viskosität wurde bei einer Temperatur von 100°C nach Verdünnung der Produktprobe zum Messen in 600 N Öl, bis eine Lösung mit einem Gesamtkalziumanteil von 15,5% erhalten wurde, gemessen. Die Viskosität wurde Methode ASTM D 445 folgend gemessen.
- Kompatibilität
- Zwei Methoden wurden zum Bewerten des Erscheinungsbilds und der Lagerungsstabilität der Zusatzstoffe und der entsprechenden Öle, die sie enthalten, angewendet.
- Methode Nr. 1: Accelerated Stability Storage Test (ASST)
- Verfahren:
-
- – Eine Mischung von 100 Gramm in einem Becher von 250 ml der folgenden Produkte darstellen:
- – Ein Phenat mit 250 BN in solcher Menge, daß der BN, der von dem Phenat kommt, in einer Mischung von 100 Gramm 35 ist.
- – Ein Sulfonat mit 400 BN (oder ein Sulfonat mit 320 BN) in solcher Menge, daß der BN, der von dem Sulfonat kommt, in einer Mischung von 100 Gramm 35 ist.
- – 35 Gramm Verdünneröl der Bezeichnung 150 Brightstock (von der Idemitsu Kosan Company).
- – Durch Zusetzen eines 500N Verdünneröls (von der Idemitsu Kosan Company) auf 100 Gramm auffüllen.
- – 30 Minuten lang bei 65°C mischen, dann das erhaltene Ö1 in ein Zentrifugenrohr einführen. 24 Stunden lang bei 100°C in einem Ofen belassen, dann 1 Stunde lang bei 4540 rpm zentrifugieren.
- – Den Sedimentanteil auslesen. Wenn der Sedimentanteil weniger als 0,05% des Öls beträgt, dann ist das Testergebnis „Bestanden", andernfalls „Durchgefallen".
- Methode Nr. 2: Kompatibilität/Löslichkeit in einem gebräuchlichen Basisöl mit der folgenden Zusammensetzung:
-
- – 20% Brightstock (von der Idemitsu Kosan Company)
- – 80% 500N (von der Idemitsu Kosan Company)
- Verfahren:
-
- – Dem gebräuchlichen Basisöl eine Menge von HOB Sulfonaten mit 400 BN zusetzen, um eine Lösung mit 100 m mol Kalzium pro Liter zu erhalten.
- – Das Basisöl und die Sulfonate unter Rühren für 30 Minuten bei einer Temperatur von 80°C mischen.
- – Das Öl in zwei Flaschen aufteilen, wobei eine bei Raumtemperatur und die andere bei einer Temperatur von 80°C gelagert wird.
- – Die Mischung gleich nach dem Mischen unter Verwendung eines Schaumtests (ASTM D 892) bewerten.
- – Das Erscheinungsbild jede Woche bewerten.
- Farbtest
- Vor dem Mischen wurde an dem Sulfonat ein Farbtest (ASTM D 1500) durchgeführt.
- Herstellungsverfahren
- Synthese der Alkylate
- Das Alkylat wurde in einer Alkilierungspilotanlage mit Fluorwasserstoffsäure synthetisiert, die aus zwei Reaktoren in Reihe von jeweils 1,150 Liter und einem 25-Liter-Sedimentierglas besteht, wobei die organische Phase von der Phase getrennt wurde, die die Fluorwasserstoffsäure enthielt, wobei die gesamte unterhaltene Ausrüstung unter einem Druck von ungefähr 5 × 105 Pa gehalten wurde.
- Die organische Phase wurde dann über ein Ventil beseitigt und auf atmosphärischen Druck ausgedehnt, und das Benzol wurde durch Toppen, das heißt durch Erhitzen auf 160°C bei atmosphärischem Druck, beseitigt.
- Nach der Beseitigung wurde die mineralische Phase durch Ätzkali neutralisiert.
- Die Reaktion wurde in entweder einem oder zwei Reaktoren ausgeführt:
-
- – Wenn nur ein Reaktor verwendet wurde, betrug das Benzol/Olefinmolverhältnis 10 : 1, was sehr hoch war, und der zweite Reaktor wurde umgangen.
- Wenn zwei Reaktoren verwendet wurden, war das Benzol/Olefinmolverhältnis relativ niedrig im ersten Reaktor, ungefähr 1 : 1 bis 1,5 : 1, und höher im zweiten Reaktor, ungefähr 2 : 1 bis 10 : 1. Außerdem lag das Verhältnis von Fluorwasserstoffsäure zu dem Olefin per Volumen ungefähr bei 1 : 1 im ersten Reaktor und bei 2 : 1 im zweiten Reaktor.
- Destillation der Alkylate
- Da Benzol durch ein lineares C20 bis C24 Olefin alkyliert wurde, gab es keine Darstellung einer Lichtbrechung. Daher war es ausreichend, ein Toppen des nicht reagierten Benzols und der restlichen Fluorwasserstoffsäure durchzuführen, um das entsprechende Alkalyt zu erhalten.
- Sulfonierung der Alkylate
- Die molare Proportion des Phenylradikals, das auf den Kohlenstoffatomen an Position 1 oder 2 des Alkylradikals substituiert wurde, wurde an dem Alkylat bestimmt, dann wurde das Alkylat der Sulfonierungsreaktion unterzogen.
- Die Sulfonierung wurde an dem Alkylat unter Verwendung von Schwefeltioxid (SO3) vorgenommen, das durch den Durchlauf einer Mischung aus Sauerstoff und Schwefeldioxid (SO2) durch einen Katalyseofen, der Vanadiumoxid (V2O5) enthielt, hergestellt wurde. Das Schwefeltrioxidgas wurde an der Oberseite eines Sulfonierungsreaktors (2 m lang und 1 cm im Durchmesser) in einen gleichlaufenden Alkalytstrom eingeleitet.
- Die resultierende Sulfonsäure wurde am Boden des Reaktors zurückgewonnen. Die Sulfonierungsbedingungen sind folgendermaßen:
-
- – Der SO3-Durchfluß wurde auf 76 Gramm/Stunde eingestellt.
- – Der Alkalytdurchfluß lag zwischen 300 und 450 Gramm/Stunde, abhängig von dem gewünschten Alkylatmolverhältnis, das zwischen 0,8 : 1 und 1,2 : 1 schwankte.
- – Die Sulfonierungstemperatur lag zwischen 50°C und 60°C.
- – Stickstoff wurde als Vektorgas zum Verdünnen das SO3 auf 4 Vol% verwendet.
- Nach der Sulfonierungsreaktion wurde die restliche Schwefelsäure durch Wärmebehandlung nach Verdünnung durch 10% 100 N Öl, Stickstoffsprudeln in einem Verhältnis von 10 Liter/Stunde pro Produktkilogramm und Rühren bei 85°C beseitigt, bis ein niedrigerer restlicher H2SO4-Anteil erhalten wurde (max. 0,5 Gew%).
- Überalkalisierung
- In diesem Schritt wurde dem Reaktionsprodukt hydrierter Kalk Ca(OH)2 in einem sehr hohen molaren Verhältnis von hydriertem Kalk zu Sulfonsäure zugesetzt, und das Produkt wurde zur Reaktion gebracht, um ein Endprodukt mit einem BN über 250 (vorzugsweise zwischen 300 und 430) gemäß dem Standard ASTM D 2896 zu erhalten.
- Um dies zu erreichen, wurde eine Menge Ca(OH)2 in hohem Übermaß zur stöchiometrischen Neutralisierung der reagierten Sulfonsäuremenge zugesetzt (0,5 Mol Ca(OH)2 pro Mol dieser Sulfonsäure).
- Das Kalkreagens war Methanol und das Lösungsmittel Xylene. Die Sättigung mit Kohlensäure wurde durch CO2 bei einer Temperatur zwischen 20°C und 55°C durchgeführt. Vor der Eliminierung des Lösungsmittels wurde das Sediment durch Zentrifugieren eliminiert.
- Die Leistungen, die durch die Alkylarylsulfonatmischungen der Erfindung erreicht werden, sind in der Tabelle am Ende der Beschreibung zusammengefasst.
- Beispiel 1
- Das Produkt der vorliegenden Erfindung wurde in einem Durchlaufreaktor mit Fluonrvasserstoffsäure hergestellt. Das Molarverhältnis Benzol : Olefin war 10 : 1.
- Vergleichsbeispiel A
- Ein Vergleichsprodukt wurde in zwei Stapelreaktoren mit Fluorwasserstoffsäure hergestellt. Das Molarverhältnis Benzol : Olefin war 1 : 2 : 1 im ersten Reaktor und 5 : 8 : 1 im zweiten Reaktor.
- Vergleichsbeispiel B
- Ein Vergleichsprodukt wurde in einem Stapelreaktor mit AlCl3 hergestellt. Das Molarverhältnis Benzol : Olefin war 10 : 1.
- In jedem der obigen Beispiele (1, A und B) war das Aromatikum Benzol, das Olefin war ein lineares C20-C24 Olefin, und die Bedingungen zum Erhalten von Alkylat sind Benzoltoppen.
- Gelpermeations-Chromatographieergebnisse
- Diese drei Produkte wurden durch eine Gelpermeations-Chromatographie analysiert, wie in
1 ,2 und3 gezeigt. Es erschienen drei Spitzen: - Das kleinste Molekül (Monoalkylat C20-C24) weist die längste Stehzeit auf. Das größte Molekül weist die kürzeste Stehzeit auf.
- In Beispiel 1 war das Produkt vorwiegend Monoalkylat (Stehzeit = 13,2 Minuten).
- Im Vergleichsbeispiel A kam ein höherer Dimerisationspegel während der Alkylierung (kleinerer Überschuß von Benzol im ersten Reaktor), ein leichtes Ansteigen der starken Spitze 2 (Stehzeit = 12,2 Minuten) und das Auftreten einer dritten Spitze (noch stärker bei 11,7 Minuten) vor.
- Im Vergleichsbeispiel B kam ein erheblicher Monoalkylatprozentsatzabfall und ein bedeutender Anstieg der dritten Spitze vor.
- Daher wies Beispiel 1 das niedrigste Schwereniveau (Dimer + Dialkylatmaterial) auf. Infolgedessen war das Sulfonierungsniveau das höchste (wodurch eine bedeutende Verbesserung bei der Umwandlung im Sulfonierungsschritt bewirkt ist).
- Während die vorliegende Erfindung unter Bezugnahme auf spezifische Ausführungsformen beschrieben wurde, ist diese Anmeldung jedoch dazu bestimmt, jene verschiedenen Änderungen und Ersetzungen abzudecken, die vom Fachmann ohne von Umfang und Wesen der Erfindung abzuweichen vorgenommen werden könnten.
Claims (12)
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat, welches einen BN von mindestens 250 aufweist und dessen Alkylrest eine lineare Kette von zwischen 14 und 40 Kohlenstoffatomen, vorzugsweise zwischen 20 und 24 Kohlenstoffatomen, darstellt und dessen Mol% an Arylsulfonatradikal, welches an Position 1 oder 2 des Alkylrestes gebunden ist, zwischen 13% und 30%, vorzugsweise zwischen 15% und 25%, aufweist.
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach Anspruch 1, bei welchem besagtes Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat zu mindestens 87% aus Monoalkylat besteht und eine Jodzahl von mindestens 1.0 aufweist.
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach den Ansprüchen 1 und 2, welches sich von einem normalen C14-C40 alpha Olefin, vorzugsweise von einem normalen C20-C24 Olefin, ableitet.
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach den Ansprüchen 1, 2 und 3, bei welchem sich das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat von einem Alkylat ableitet, welches durch Reaktion von Benzol mit normalem alpha Olefin in Anwesenheit von Hydrogenfluorid, vorzugsweise in einem Einstufenreaktor, dargestellt wurde.
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach Anspruch 4, bei welchem das Sulfonat in Anwesenheit von Methanol und Xylene dargestellt wird.
- Ein Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach einem der Ansprüche 4 oder 5, bei welchem das Sulfonat in Abwesenheit von Chlor dargestellt wird.
- Ein Waschhilfsmittel/Dispersionszusatzstoff für Schmieröle, welches eine erhöhte Löslichkeit in gebräuchlichen Basisölen, eine erhöhte Kompatibilität mit Phenolen in gebräuchlichen Basisölen und eine erhöhte Schaumleistung aufweist, wobei besagtes Waschhilfsmittel/besagter Dispersionszusatzstoff das Erdalkalialkyl-arylsulfonat nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6 enthält.
- Eine Formulierung von Schmierölen, welche das Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6 enthält.
- Eine Formulierung von Schmierölen bestehend aus: (a) einem Hauptanteil eines Basisöls mit Schmiermittelviskosität; (b) 0,5 bis 40% eines Waschhilfsmittels bestehend aus dem Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6 (c) 0 bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels; (d) 0 bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats; (e) 0 bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers; (f) 0 bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und (g) 0 bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers.
- Eine Methode zur Herstellung von Schmierölzusammensetzungen, bestehend aus der Mischung folgender Komponenten: (a) einem Hauptanteil eines Basisöls mit Schmiermittelviskosität; (b) 0,5 bis 40% eines Waschhilfsmittels bestehend aus dem Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonat nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6 (c) 0 bis 20% mindestens eines aschlosen Dispersionsmittels; (d) 0 bis 5% mindestens eines Zinkdithiophosphats; (e) 0 bis 10% mindestens eines Oxidationshemmers; (f) 0 bis 1% mindestens eines Schaumbildungshemmers; und (g) 0 bis 20% mindestens eines Viskositätsindexerhöhers.
- Eine Schmierölzusammensetzung hergestellt nach der unter Anspruch 10 dargestellten Methode.
- Ein Konzentrat bestehend aus 10 Gewichts% bis 90 Gewichts% eines kompatiblen organischen, flüssigen Verdünnungsmittels und 0,5 Gewichts% bis 90 Gewichts des Erdalkalialkylarylsulfonats nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99401417A EP1059301B1 (de) | 1999-06-10 | 1999-06-10 | Erdalkalimetalsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsmethode |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| DE69908098D1 DE69908098D1 (de) | 2003-06-26 |
| DE69908098T2 true DE69908098T2 (de) | 2004-04-08 |
Family
ID=8242007
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE69908098T Expired - Lifetime DE69908098T2 (de) | 1999-06-10 | 1999-06-10 | Erdalkalimetalsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsmethode |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6479440B1 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1059301B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5086508B2 (de) |
| AU (1) | AU5420900A (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2336689C (de) |
| DE (1) | DE69908098T2 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2000077015A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6564814B2 (en) * | 1997-05-23 | 2003-05-20 | Shelba F. Bowsman | Engine decarbonizing system |
| US6337310B1 (en) | 2000-06-02 | 2002-01-08 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Alkylbenzene from preisomerized NAO usable in LOB and HOB sulfonate |
| US7407919B2 (en) | 2001-11-05 | 2008-08-05 | The Lubrizol Corporation | Sulfonate detergent system for improved fuel economy |
| US6790813B2 (en) * | 2002-11-21 | 2004-09-14 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Oil compositions for improved fuel economy |
| US20050124510A1 (en) * | 2003-12-09 | 2005-06-09 | Costello Michael T. | Low sediment friction modifiers |
| US8618029B2 (en) * | 2003-12-22 | 2013-12-31 | Chevron Oronite S.A. | Overbased detergents for lubricating oil applications |
| US8188020B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2012-05-29 | Chevron Oronite S.A. | Lubricating oil composition containing an alkali metal detergent |
| US7635668B2 (en) * | 2004-03-16 | 2009-12-22 | The Lubrizol Corporation | Hydraulic composition containing a substantially nitrogen free dispersant |
| WO2006047091A2 (en) * | 2004-10-25 | 2006-05-04 | Huntsman Petrochemical Corporation | Fuel and oil detergents |
| US8293698B2 (en) * | 2005-07-20 | 2012-10-23 | Chevron Oronite S.A. | Alkylaryl sulfonate detergent mixture derived from linear olefins |
| US7435709B2 (en) * | 2005-09-01 | 2008-10-14 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Linear alkylphenol derived detergent substantially free of endocrine disruptive chemicals |
| US7449596B2 (en) * | 2005-12-21 | 2008-11-11 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Method of making a synthetic petroleum sulfonate |
| US8603956B2 (en) * | 2006-04-12 | 2013-12-10 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Super overbased polyalkenyl sulfonate and alkylaryl sulfonate composition and process for making the same |
| US20080119378A1 (en) | 2006-11-21 | 2008-05-22 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Functional fluids comprising alkyl toluene sulfonates |
| JP5027533B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-19 | 2012-09-19 | Jx日鉱日石エネルギー株式会社 | 潤滑油組成物 |
| JP5473236B2 (ja) * | 2008-03-10 | 2014-04-16 | Jx日鉱日石エネルギー株式会社 | 潤滑油組成物 |
| JP5465938B2 (ja) * | 2009-07-03 | 2014-04-09 | シェブロンジャパン株式会社 | 内燃機関用潤滑油組成物 |
| US8916726B2 (en) | 2011-03-30 | 2014-12-23 | Chevron Oronite Company Llc | Method for the preparation of low overbased alkyltoluene sulfonate |
| US9434906B2 (en) * | 2013-03-25 | 2016-09-06 | Chevron Oronite Company, Llc | Marine diesel engine lubricating oil compositions |
| WO2015067724A1 (en) * | 2013-11-06 | 2015-05-14 | Chevron Oronite Technology B.V. | Marine diesel cylinder lubricant oil compositions |
| SG11201603378WA (en) * | 2013-11-06 | 2016-05-30 | Chevron Oronite Technology Bv | Marine diesel cylinder lubricant oil compositions |
| KR20170078706A (ko) * | 2014-11-06 | 2017-07-07 | 셰브런 오로나이트 테크놀로지 비.브이. | 선박용 디젤 실린더 윤활유 조성물 |
| KR20170137709A (ko) * | 2015-01-26 | 2017-12-13 | 셰브런 오로나이트 테크놀로지 비.브이. | 선박용 디젤 엔진 윤활유 조성물 |
| CN114829558B (zh) * | 2019-12-20 | 2023-11-17 | 路博润公司 | 含有来源于腰果壳液的洗涤剂的润滑剂组合物 |
| CN112899059A (zh) * | 2021-02-25 | 2021-06-04 | 江苏澳润新材料有限公司 | 一种无氯低碱值磺酸钙清净剂及其制备方法 |
| EP4352188A1 (de) | 2021-06-10 | 2024-04-17 | Chevron Oronite Company LLC | Aminverstärktes waschmittel |
| US11845717B1 (en) | 2022-08-24 | 2023-12-19 | Chevron Phillips Chemical Company Lp | Isomerization of linear olefins with solid acid catalysts and primary esters |
| CN120981554A (zh) | 2023-03-13 | 2025-11-18 | 雪佛龙奥伦耐有限责任公司 | 后处理系统友好型发动机油制剂 |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1134608A (en) * | 1966-05-23 | 1968-11-27 | Chevron Res | Alkaline earth metal carbonate dispersions containing organic sulfonate dispersants |
| US4235810A (en) * | 1978-08-03 | 1980-11-25 | Exxon Research & Engineering Co. | Alkylates and sulphonic acids and sulphonates produced therefrom |
| FR2564830B1 (fr) * | 1984-05-25 | 1986-09-19 | Orogil | Procede de preparation d'alkylaryl sulfonates de metaux alcalino-terreux a partir d'acides alkylaryl sulfoniques lineaires et additifs detergents-dispersants pour huiles lubrifiantes ainsi obtenus |
| FR2588269B1 (fr) * | 1985-10-03 | 1988-02-05 | Elf France | Procede de preparation d'additifs surbases tres fluides et a basicite elevee et composition contenant lesdits additifs |
| FR2588268B1 (fr) * | 1985-10-03 | 1988-02-05 | Elf France | Procede de synthese d'additifs surbases par carbonatation sous pression constante d'anhydride carbonique |
| GB8723907D0 (en) * | 1987-10-12 | 1987-11-18 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Overbased metal sulphonate composition |
| EP0312315B1 (de) * | 1987-10-12 | 1991-12-11 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc. | Verwendung von einem überbasischen Magnesiumsulphonatgemische |
| JP2795469B2 (ja) * | 1989-07-07 | 1998-09-10 | 東燃株式会社 | 潤滑油組成物 |
| WO1995002709A2 (en) | 1993-07-15 | 1995-01-26 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | EXTENDED NITRIDE MATERIAL COMPRISING β-C3N¿4? |
| EP0645444A3 (de) * | 1993-09-27 | 1995-05-24 | Texaco Development Corp | Schmiermittel mit überbasischen Detergentien aus linearen Alkylaromaten. |
| WO1996010833A1 (en) | 1994-10-04 | 1996-04-11 | Philips Electronics N.V. | Method of adjusting the switch-gap in a reed switch |
| JP3476942B2 (ja) * | 1994-12-28 | 2003-12-10 | 東燃ゼネラル石油株式会社 | 潤滑油組成物 |
| FR2731427B1 (fr) * | 1995-03-08 | 1997-05-30 | Chevron Chem Sa | Alkylaryl-sulfonates lineaires isomerises, utiles comme additifs pour huiles lubrifiantes et hydocarbures alkylaryliques correspondants |
| CA2204461C (en) * | 1996-05-14 | 2006-07-04 | Thomas V. Harris | Process for producing an alkylated, non-oxygen-containing aromatic hydrocarbon |
| FR2752838B1 (fr) * | 1996-09-05 | 1998-12-04 | Chevron Chem Sa | Melange d'alkyl-aryl-sulfonates de metaux alcalino-terreux, son application comme additif pour huile lubrifiante et procedes de preparation |
| JP4632465B2 (ja) * | 1997-05-30 | 2011-02-16 | 東燃ゼネラル石油株式会社 | 潤滑油組成物 |
| EP0976810A1 (de) * | 1998-07-31 | 2000-02-02 | Chevron Chemical S.A. | Mischung von Erdalkalimetalalkylphenylsulfonaten, Ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsverfahren |
| US6204226B1 (en) * | 1999-06-03 | 2001-03-20 | Chevron Oronite S.A. | Mixture of alkyl-phenyl-sulfonates of alkaline earth metals, its application as an additive for lubricating oil, and methods of preparation |
-
1999
- 1999-06-10 DE DE69908098T patent/DE69908098T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-06-10 EP EP99401417A patent/EP1059301B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2000
- 2000-06-06 WO PCT/IB2000/000916 patent/WO2000077015A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2000-06-06 JP JP2001503872A patent/JP5086508B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-06-06 CA CA002336689A patent/CA2336689C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-06-06 AU AU54209/00A patent/AU5420900A/en not_active Abandoned
-
2001
- 2001-01-25 US US09/770,927 patent/US6479440B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1059301B1 (de) | 2003-05-21 |
| JP2003502452A (ja) | 2003-01-21 |
| DE69908098D1 (de) | 2003-06-26 |
| CA2336689C (en) | 2009-09-22 |
| WO2000077015A1 (en) | 2000-12-21 |
| JP5086508B2 (ja) | 2012-11-28 |
| AU5420900A (en) | 2001-01-02 |
| EP1059301A1 (de) | 2000-12-13 |
| CA2336689A1 (en) | 2000-12-21 |
| US6479440B1 (en) | 2002-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69908098T2 (de) | Erdalkalimetalsulfonate, ihre Verwendung als Schmierölzusatz und Herstellungsmethode | |
| DE69937721T2 (de) | Herstellung eines schwach überbasischen Alkylarylsulfonats | |
| DE69812873T2 (de) | Schwefel- und alkalimetalfreie Schmieröladditive | |
| DE2925784C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von hydrierten Olefinoligomeren und deren Verwendung in Schmierölmischungen | |
| DE69422184T2 (de) | Schmiermittelzusammensetzungen mit verbesserten antioxidationseigenschaften | |
| DE60203639T2 (de) | Schmiermittelzusammensetzung mit verbesserter Brennstoffersparnis | |
| DE69228677T2 (de) | Motorölzusammensetzung | |
| DE60124645T2 (de) | Niedrigviskose Schmiermittelzusammensetzungen | |
| DE69719113T2 (de) | Schwefelhaltige phenolische Antioxidationszusammensetzung, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, sowie sie enthaltende Petroleumprodukte | |
| DE60204784T2 (de) | Lineare verbindungen enthaltend phenol und salicylsäure-einheiten | |
| DE2941323A1 (de) | Schmieroelzubereitung | |
| DE69936203T2 (de) | Polyalphaolefine mit vervesserter oxidationsstabilität und verfahren zu deren herstellung | |
| DE69102172T2 (de) | Motorölzusammensetzung. | |
| US6444624B1 (en) | Lubricating oil composition | |
| DE1221226B (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von in Kohlenwasserstoffoelen loeslichen, basische Erdalkalimetallkomplexverbindungen der Carbon- und/oder Oelloeslichen organischen Sulfonsaeuren | |
| DE60000219T2 (de) | Schmiermittelzusammensetzungen zum Schmieren eines Schiffsdieselmotors | |
| DE2755225A1 (de) | Hochbasische sulfonate | |
| DE69211148T2 (de) | Verbesserte überbasische Carboxylate | |
| DE102009034983A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Vermindern von Asphaltenablagerung in einem Motor | |
| DE60310822T2 (de) | Methode zur Verbesserung der Reibungseigenschaften von funktionellen Flüssigkeiten | |
| JPH10265791A (ja) | 超中性ジアルキルジチオ燐酸亜鉛を含有する低灰潤滑油 | |
| DE2942826A1 (de) | Oelloesliche thio-bis(c tief 4 - bis c tief 10000 -hydrocarbyl-substituierte- c tief 4 - bis c tief 10 -dicarbonsaeurematerialien), verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und diese verbindungen enthaltende zubereitungen | |
| DE3529192C2 (de) | ||
| DE69531043T2 (de) | Überbasische alkyloxybenzolsulfonate als detergentien | |
| DE69433335T2 (de) | Molybdän enthaltende Reibung herabsetzende Zusätze |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8364 | No opposition during term of opposition |