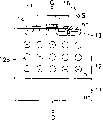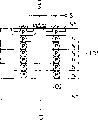CN1177373C - 半导体器件及其制造方法 - Google Patents
半导体器件及其制造方法Info
- Publication number
- CN1177373C CN1177373C CNB011165421A CN01116542A CN1177373C CN 1177373 C CN1177373 C CN 1177373C CN B011165421 A CNB011165421 A CN B011165421A CN 01116542 A CN01116542 A CN 01116542A CN 1177373 C CN1177373 C CN 1177373C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- mentioned
- semiconductor regions
- electrode
- forms
- semiconductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D30/00—Field-effect transistors [FET]
- H10D30/60—Insulated-gate field-effect transistors [IGFET]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/324—Thermal treatment for modifying the properties of semiconductor bodies, e.g. annealing, sintering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D30/00—Field-effect transistors [FET]
- H10D30/01—Manufacture or treatment
- H10D30/021—Manufacture or treatment of FETs having insulated gates [IGFET]
- H10D30/028—Manufacture or treatment of FETs having insulated gates [IGFET] of double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor [DMOS] FETs
- H10D30/0291—Manufacture or treatment of FETs having insulated gates [IGFET] of double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor [DMOS] FETs of vertical DMOS [VDMOS] FETs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D30/00—Field-effect transistors [FET]
- H10D30/60—Insulated-gate field-effect transistors [IGFET]
- H10D30/64—Double-diffused metal-oxide semiconductor [DMOS] FETs
- H10D30/66—Vertical DMOS [VDMOS] FETs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D62/00—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers
- H10D62/10—Shapes, relative sizes or dispositions of the regions of the semiconductor bodies; Shapes of the semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/113—Isolations within a component, i.e. internal isolations
- H10D62/115—Dielectric isolations, e.g. air gaps
- H10D62/116—Dielectric isolations, e.g. air gaps adjoining the input or output regions of field-effect devices, e.g. adjoining source or drain regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D64/00—Electrodes of devices having potential barriers
- H10D64/118—Electrodes comprising insulating layers having particular dielectric or electrostatic properties, e.g. having static charges
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D62/00—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers
- H10D62/80—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers characterised by the materials
- H10D62/83—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers characterised by the materials being Group IV materials, e.g. B-doped Si or undoped Ge
- H10D62/832—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers characterised by the materials being Group IV materials, e.g. B-doped Si or undoped Ge being Group IV materials comprising two or more elements, e.g. SiGe
- H10D62/8325—Silicon carbide
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Abstract
本发明的主要特征是,使得在功率MOS FET中,可以实现RESURF原理而无须控制杂质分布。例如,在外延生长Si的过程中,适宜地形成亚微米单位的沟槽。然后,采用借助于氢气退火促进表面原子的迁徙以使沟槽上部闭口的办法,形成空洞部分(12a)。接着,采用反复进行该工序的办法,在外延层(12)中制作成多个空洞部分(12a),变成为实现异质结的N缓冲器构造的构成。
Description
技术领域
本发明涉及半导体器件及其制造方法,特别是涉及要求耐高压的功率MOS FET(Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor,金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管)。
背景技术
近年来,市场对在电动汽车(EV)中使用的功率MOS FET提出了进一步小型化、节能化、低价格化的要求。
在这种要求强烈的功率MOS FET的领域内,作为对元件耐压与ON(导通)电阻之间的妥协进行改善的器件,例如人们知道具有图3所示的那样的构造的MOS FET。这种器件是一种采用在N漏层101中形成埋入多级的p埋入外延层102的办法,使得在降低N漏层101的电阻的同时,在反向偏置时使N漏层101的内部的P/N扩散层完全耗尽化的器件(RESURF(REduced SURface Field,简化表面场)原理)。
除此之外,人们还提出了在N漏层中形成叫做P柱状物/N条带的扩散层的构造等类似的构造。
[表1]
构造的定义
v:漏层(体积)
Γ(v):漏层内的有源杂质浓度
ni:硅的本征浓度(1011cm-3)
:PIN二极管的I层
的形式
其中,
r:漏层的微小的方向向量
P(
r):漏层内的P型有源杂质浓度
N(
r):漏层内的N型有源杂质浓度
Ecrit=2×105[V/cm]
Qcrit=1.5×1012[/cm2]
BVDSS:在给器件加上击穿电压时结的最大电场强度。
但是,在上述构造的MOS FET的情况下,存在着难于进行N漏层中杂质分布的控制的问题。
就是说,要想实现RESURF原理,就要求N漏层中的P型/N型的有源杂质的总和接近于~Ni,和在反向偏置时,在所有的区域内完全耗尽化,在所有的区域内电场强度E<Ecrit。
如上所述,在以往,尽管已经尝试着使高耐压化和低电阻化并存,但是,在RESURF原理的实现上仍然存在着难于进行N漏层中的杂质分布控制的问题。
发明内容
于是,本发明的目的是提供一种借助于异质结构造可以实现RESURF原理而无须控制N漏层中的杂质分布,且可以容易地使高耐压化和低导通电阻并存的半导体器件及其制造方法。
为了实现上述目的,本发明的半导体器件具备:第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个空洞部分。
此外,本发明的半导体器件具备:第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个多孔硅层。
此外,本发明的半导体器件具备:第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个电介质层。
再有,本发明的半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是具备下述工序:在第1半导体区域上边形成第1导电类型的第1外延层的第1工序;在该第1外延层的表面区域上形成多个沟槽的第2工序;采用借助于氢气退火使上述沟槽的上部分别闭口的办法形成多个空洞部分的第3工序;在形成了上述多个空洞部分的上述第1外延层上边形成第1导电类型的第2外延层的第4工序。
倘采用本发明的半导体器件的制造方法,结果就变成为可以把第2半导体区域的平均浓度控制为~Ni,而无须控制杂质分布。借助于此,可以使反向偏置时的第2半导体区域的内部电场有效降低到第2半导体区域不会产生雪崩的那种程度。
附图说明
图1的剖面图示出了本发明实施例1的功率MOS FET的概略构成。
图2的剖面图示出了本发明实施例2的功率MOS FET的概略构成。
图3是为了说明现有技术的问题而示出的功率MOS FET的概略构成。
以下,参看附图对本发明的实施例进行说明。
具体实施方式
(实施例1)
图1的剖面图示出了本发明的实施例1的功率MOS FET的概略构成。
就是说,图1所示的功率MOS FET的构造是:在n+型的硅衬底(第1导电类型的第1半导体区域)11上边形成将成为漏极(或集电极)区的n-型的外延层(第1导电类型的第2半导体区域)12,在该外延层12的表面区域上,选择性地形成将成为p基极区的p型杂质区(第2导电类型的第3半导体区域)13、13和将成为n+源极区的n+型杂质区(第1导电类型的第4半导体区域)14、14,上述外延层12被作成为混杂地设置多个空洞部分的异质结构造(异质结的N缓冲器构造)。
然后,中间存在着栅极氧化膜(栅极绝缘膜)15,在与上述p型杂质区13、13之间对应的上述外延层12的表面(沟道)上边设置由多晶硅构成的栅极电极16。
此外,在与上述n+型杂质区14、14之间对应的上述杂质区13的表面上边分别形成源极电极17,此外,上述硅衬底11的背面一侧变成为漏极电极。
上述外延层12被作成为形成了具有多个空洞部分12a的异质结的N缓冲器构造。
在这种情况下,例如,可以在生长用来形成上述外延层12的硅(Si)的过程中,在适宜地形成了亚微米单位的沟槽之后,为了促进表面原子的迁徙,采用借助于氢气退火使上述沟槽的上部闭口的办法形成上述空洞部分12a。然后,采用反复进行该工序的办法,就可以得到上述那样的内部制作有多个空洞部分12a而构成的外延层12。
在这里,以具有500V系列耐压的功率MOS FET为例,对于该外延层的形成方法进行说明。
例如,用单张式外延生长装置,首先,在n+型的硅衬底11上边,用大约1000℃的温度生长厚度10微米左右的n型杂质浓度为1×1010/cm3左右的Si膜,形成第1层的外延层(第1外延层)。
接着,在第1层的外延层的表面上边,形成膜厚大约5000的CVD氧化膜。
接着,用干法刻蚀使该CVD膜图形化,形成例如1mm见方左右那么大小的开口图形。在这种情况下,要把多个开口图形形成为使得开口面积比变成为30%以下。
接着,以已形成了多个开口图形的CVD膜为掩模,进行RIE等,在上述第1外延层的表面区域上,分别形成大约0.6微米见方、深度为大约1微米的沟槽。
接着,在除去了CVD膜之后,用上述外延生长装置,用800℃以上的温度进行氢还原处理,除去在上述第1外延层的表面上形成的自然氧化膜。这时,借助于表面原子的迁徙效应,使各个沟槽的上部(开口部分)闭口,形成多个空洞部分。
接着,用上述外延生长装置,约1000℃的温度生长厚度10微米左右的n型杂质浓度为1×1015/cm3左右的Si膜,在上述第1外延层上边,形成第2层的外延层(第2外延层)。
然后,在对该第2外延层反复实施了上边所说的各个工序之后,采用使第3层的外延层的形成与第2层的外延层的形成同样地进行的办法,作为具有500V系列耐压的功率MOS FET的外延层,就可以得到与图1不同的用2级构成制作成的多个空洞部分的外延层。
另外,空洞部分12a的大小、个数和位置等,可以根据所需要的器件的特性(器件耐压或导通电阻)来决定。
具有这样的空洞部分12a的外延层12的浓度,可以高到外延层的平均浓度的10倍左右或10倍以上。由于空洞部分12a的介电系数是Si的12倍,故绝缘破坏可以期待为Ecrit的100倍以上。
从微观上看,异质结的N缓冲器构造的外延层12中的I层,可以使电阻下降,同时使破坏电场强度上升。换句话说,SiC等的Ecrit可比拟于Si的10倍的新材料。
在这种情况下的构造,可以定义为下边要给出的表2所示。
[表2]
V’:V-Vhetero
Vhetero:位于漏层体积中的非Si区域(异质结区域)
ρ(V):非Si区域所具有的电荷分布
由此,变成为
或
因而可以扩展现有的RESURF原理。
因此,可以期待
Q’crit>Qcrit E’crit>Ecrit
如上所述,采用在体内形成空洞部分12a的办法,就可以把外延层12的平均浓度控制为~Ni而无须控制杂质分布。借助于此,就可以把反向偏置时体内的内部电场有效降低到Si自身不会产生雪崩的那种程度。因此,可以实现RESURF原理而不必进行复杂的杂质分布控制,可以使高耐压化与低导通电阻化并存。
(实施例2)
图2的剖面图示出了本发明的实施例2的功率MOS FET的概略构成。另外,在这里,是在外延层中混杂地设置多个电介质层以取代空洞部分的例子。
就是说,在这种情况下的外延层12’,例如被作成为在体内具有已形成了负的固定电荷(-)的多个电介质层12b的异质结的N缓冲器构造。
如上所述,即便是采用在外延层12’中形成电介质层12b的办法,也可以把外延层12’的平均浓度控制为~Ni。其结果是可以得到与上边所说的实施例1大体上同样的效果。
另外,不限于在体内形成空洞部分或电介质层的情况,例如即便是采用在外延层中设置多个多孔硅层(未画出来),借以实现异质结的N缓冲器构造的办法,也可以期待与上边所说的实施例1、2的情况下同样的效果。
如上所述,可以把外延层的平均浓度控制为~Ni而无须控制杂质分布。
就是说,作成为在体内形成空洞部分、多孔硅层或电介质层而构成异质结的N缓冲器构造。借助于此,就可以把反向偏置时的体内的内部电场有效降低到Si自身不会产生雪崩的那种程度。因此,可以实现RESURF原理而不必进行复杂的杂质分布控制,可以使高耐压化与低导通电阻化并存。
除此之外,在不改变本发明的要旨的范围内,可以进行种种变形实施是不言而喻的。
如以上所详述的那样,倘采用本发明,则可以提供可以用异质结构造实现RESURF原理而无须控制N漏层中的杂质分布,且可以容易地使高耐压化与低电阻化并存的半导体器件及其制造方法。
Claims (13)
1.一种半导体器件,具备:
第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;
在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;
在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;
在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;
中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;
在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;
在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,
其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个空洞部分。
2.权利要求1所述的半导体器件,其特征是:在生长上述第2半导体区域的过程中,在形成了多个沟槽之后,采用借助于氢气退火使上述沟槽的上部闭口的办法形成上述空洞部分。
3.一种半导体器件,具备:
第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;
在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;
在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;
在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;
中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;
在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;
在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,
其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个多孔硅层。
4.一种半导体器件,具备:
第1导电类型的第1半导体区域;
在上述第1半导体区域上边形成,杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域;
在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第2导电类型的第3半导体区域;
在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择地形成的第1导电类型的第4半导体区域;
中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成的栅极电极;
在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成的第1电极;
在上述第1半导体区域下边形成的第2电极,
其特征是:在上述第2半导体区域内设置多个电介质层。
5.权利要求4所述的半导体器件,其特征是:上述多个电介质层分别具有负的固定电荷。
6.权利要求1、3或4所述的半导体器件,其特征是:上述第4半导体区域的杂质浓度比上述第2半导体区域高。
7.权利要求1、3或4所述的半导体器件,其特征是:构成以上述第2半导体区域为漏极,以上述第3半导体区域为沟道,以上述第4半导体区域为源极,以上述第1电极为源极电极,以上述第2电极为漏极电极而形成的功率MOS FET。
8.权利要求1、3或4所述的半导体器件,其特征是:上述第1半导体区域是硅衬底,上述第2半导体区域是在上述硅衬底上边形成的外延层。
9.一种半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是具备下述工序:
在第1半导体区域上边形成第1导电类型的第1外延层的第1工序;
在该第1外延层的表面区域上形成多个沟槽的第2工序;
采用借助于氢气退火使上述沟槽的上部分别闭口的办法形成多个空洞部分的第3工序;
在形成了上述多个空洞部分的上述第1外延层上边形成第1导电类型的第2外延层的第4工序。
10.权利要求9所述的半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是:采用以规定的次数反复进行上述第2~第4的各个工序的办法,在上述第1半导体区域上边,形成具有上述多个空洞部分,且杂质浓度比上述第1半导体区域还低的第1导电类型的第2半导体区域。
11.权利要求10所述的半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是还具备下述工序:
在上述第2半导体区域的表面区域上选择性地形成第2导电类型的第3半导体区域的工序;
在上述第3半导体区域的表面区域上选择性地形成第1导电类型的第4半导体区域的工序;
中间存在着栅极绝缘膜、在上述第3半导体区域间的上述第2半导体区域的表面上形成栅极电极的工序;
在上述第4半导体区域间的上述第3半导体区域的表面上形成第1电极的工序;
在上述第1半导体区域的下边形成第2电极的工序。
12.权利要求11所述的半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是:上述第4半导体区域的杂质浓度比上述第2半导体区域高。
13.权利要求11所述的半导体器件的制造方法,其特征是:构成以上述第2半导体区域为漏极,以上述第3半导体区域为沟道,以上述第4半导体区域为源极,以上述第1电极为源极电极,以上述第2电极为漏极电极而形成的功率MOS FET。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP111039/2000 | 2000-04-12 | ||
| JP2000111039A JP4965756B2 (ja) | 2000-04-12 | 2000-04-12 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1317833A CN1317833A (zh) | 2001-10-17 |
| CN1177373C true CN1177373C (zh) | 2004-11-24 |
Family
ID=18623452
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB011165421A Expired - Fee Related CN1177373C (zh) | 2000-04-12 | 2001-04-12 | 半导体器件及其制造方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6476429B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP1146566A3 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP4965756B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR100398756B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1177373C (zh) |
| TW (1) | TW492058B (zh) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003007976A (ja) * | 2001-06-25 | 2003-01-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置及びモジュール装置 |
| US6686244B2 (en) * | 2002-03-21 | 2004-02-03 | General Semiconductor, Inc. | Power semiconductor device having a voltage sustaining region that includes doped columns formed with a single ion implantation step |
| JP3634830B2 (ja) * | 2002-09-25 | 2005-03-30 | 株式会社東芝 | 電力用半導体素子 |
| JP4209260B2 (ja) | 2003-06-04 | 2009-01-14 | Necエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP4813762B2 (ja) | 2003-12-25 | 2011-11-09 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2005322723A (ja) | 2004-05-07 | 2005-11-17 | Nec Electronics Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| EP1696490A1 (en) * | 2005-02-25 | 2006-08-30 | STMicroelectronics S.r.l. | Charge compensation semiconductor device and relative manufacturing process |
| JP4488984B2 (ja) * | 2005-08-25 | 2010-06-23 | 株式会社東芝 | ショットキーバリアダイオード |
| US7994573B2 (en) | 2007-12-14 | 2011-08-09 | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Structure and method for forming power devices with carbon-containing region |
| EP2286455B1 (en) * | 2008-05-28 | 2019-04-10 | Nexperia B.V. | Trench gate semiconductor device and method of manufacturing thereof |
| CN102456692A (zh) * | 2011-11-29 | 2012-05-16 | 上海华力微电子有限公司 | 异质结1t-dram单元结构及其制备方法 |
| JP2013175655A (ja) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-09-05 | Toshiba Corp | 電力用半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| KR101514537B1 (ko) * | 2013-08-09 | 2015-04-22 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 전력 반도체 소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP2017168720A (ja) * | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | 富士電機株式会社 | 炭化珪素半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6703666B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-31 | 2020-06-03 | 国立研究開発法人産業技術総合研究所 | 炭化珪素基体の製造方法 |
| US10720494B2 (en) * | 2018-01-22 | 2020-07-21 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Field-effect transistors with airgaps |
| CN109494246B (zh) * | 2018-10-12 | 2021-11-02 | 龙腾半导体有限公司 | 超结mosfet结构及其制造方法 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1019720B (zh) * | 1991-03-19 | 1992-12-30 | 电子科技大学 | 半导体功率器件 |
| DE4309764C2 (de) * | 1993-03-25 | 1997-01-30 | Siemens Ag | Leistungs-MOSFET |
| JPH06334503A (ja) * | 1993-05-24 | 1994-12-02 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 縦型misトランジスタ |
| JPH07231088A (ja) * | 1994-02-18 | 1995-08-29 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Mis形電界効果トランジスタ |
| JP3392665B2 (ja) | 1995-11-06 | 2003-03-31 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| US6037632A (en) * | 1995-11-06 | 2000-03-14 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Semiconductor device |
| EP0879481B1 (de) * | 1996-02-05 | 2002-05-02 | Infineon Technologies AG | Durch feldeffekt steuerbares halbleiterbauelement |
| JPH09270513A (ja) * | 1996-03-29 | 1997-10-14 | Toyota Central Res & Dev Lab Inc | 絶縁ゲート型半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JPH10284718A (ja) * | 1997-04-08 | 1998-10-23 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 絶縁ゲート型サイリスタ |
| DE19808348C1 (de) * | 1998-02-27 | 1999-06-24 | Siemens Ag | Durch Feldeffekt steuerbares Halbleiterbauelement |
| SE512259C2 (sv) * | 1998-03-23 | 2000-02-21 | Abb Research Ltd | Halvledaranordning bestående av dopad kiselkarbid vilken innefattar en pn-övergång som uppvisar åtminstone en ihålig defekt och förfarande för dess framställning |
| JP3762136B2 (ja) * | 1998-04-24 | 2006-04-05 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP3988262B2 (ja) * | 1998-07-24 | 2007-10-10 | 富士電機デバイステクノロジー株式会社 | 縦型超接合半導体素子およびその製造方法 |
| ATE386339T1 (de) * | 1998-11-18 | 2008-03-15 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleiterbauelement mit dielektrischen oder halbisolierenden abschirmstrukturen |
| JP4074051B2 (ja) * | 1999-08-31 | 2008-04-09 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体基板およびその製造方法 |
-
2000
- 2000-04-12 JP JP2000111039A patent/JP4965756B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2001
- 2001-04-11 TW TW090108654A patent/TW492058B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-04-11 US US09/832,208 patent/US6476429B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2001-04-12 CN CNB011165421A patent/CN1177373C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2001-04-12 EP EP01109330A patent/EP1146566A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2001-04-12 KR KR10-2001-0019561A patent/KR100398756B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1146566A2 (en) | 2001-10-17 |
| US6476429B2 (en) | 2002-11-05 |
| CN1317833A (zh) | 2001-10-17 |
| KR20010098551A (ko) | 2001-11-08 |
| US20020008258A1 (en) | 2002-01-24 |
| JP4965756B2 (ja) | 2012-07-04 |
| JP2001298189A (ja) | 2001-10-26 |
| KR100398756B1 (ko) | 2003-09-19 |
| EP1146566A3 (en) | 2008-04-09 |
| TW492058B (en) | 2002-06-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1177373C (zh) | 半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| CN100342505C (zh) | 高压半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| JP7263178B2 (ja) | 半導体装置、インバータ回路、駆動装置、車両、及び、昇降機 | |
| CN1317771C (zh) | 绝缘栅型半导体器件 | |
| JP5586887B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US6849880B1 (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| CN1215570C (zh) | Mos晶体管组件 | |
| CN1295795C (zh) | 电力半导体器件 | |
| CN1977386A (zh) | 碳化硅器件及其制造方法 | |
| CN1790714A (zh) | 半导体器件及制造其的方法 | |
| CN1726596A (zh) | 具有注入漏漂移区的沟槽金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管及其制造方法 | |
| CN1605119A (zh) | 有改善的较小正向电压损耗和较高截断能力的半导体结构 | |
| CN1528020A (zh) | 具有较低栅极电荷结构的沟槽mosfet | |
| CN1520616A (zh) | 具有防止基区穿通的横向延伸基区屏蔽区的功率半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| CN1815739A (zh) | 半导体器件及其制作方法 | |
| CN1468449A (zh) | 内含沟道型肖特基整流器的沟道型dmos晶体管 | |
| JP7278902B2 (ja) | 半導体装置、インバータ回路、駆動装置、車両、及び、昇降機 | |
| CN1260068A (zh) | 免闭锁功率金属氧化物半导体一双极型晶体管 | |
| CN1496587A (zh) | 横向结型场效应晶体管 | |
| CN1525575A (zh) | 高耐电压场效应型半导体设备 | |
| CN1763974A (zh) | 半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| CN116960178A (zh) | 碳化硅半导体功率晶体管及其制造方法 | |
| CN1819270A (zh) | 场效应晶体管和制造场效应晶体管的方法 | |
| CN104347614A (zh) | 功率半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| JP2023554134A (ja) | 炭化珪素パワーデバイスおよびその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20041124 Termination date: 20100412 |