WO2025041281A1 - 試験装置および試験方法 - Google Patents
試験装置および試験方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2025041281A1 WO2025041281A1 PCT/JP2023/030205 JP2023030205W WO2025041281A1 WO 2025041281 A1 WO2025041281 A1 WO 2025041281A1 JP 2023030205 W JP2023030205 W JP 2023030205W WO 2025041281 A1 WO2025041281 A1 WO 2025041281A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- under test
- device under
- voltage
- test
- measurement
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/28—Testing of electronic circuits, e.g. by signal tracer
Definitions
- the first measurement unit may measure a value corresponding to a current flowing through the device under test of the test subject in response to the application of the first voltage from the first power supply, or may measure a value corresponding to a voltage generated in the device under test of the test subject in response to the flow of the first current from the first power supply.
- 1 shows a test system 1 according to a first embodiment. The operation of the test device 2 will be described. 4 shows operational waveforms of the test device 2. 1 shows a test system 1A according to a second embodiment. 4 shows the operating waveforms of the test device 2A. 22 illustrates an example computer 2200 in which aspects of the present invention may be embodied, in whole or in part.
- First Embodiment 1 shows a test system 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the test system 1 includes a plurality of devices under test 10 and a test apparatus 2.
- the devices under test 10 are referred to as DUTs (Device Under Test).
- Each device under test 10 is an electronic device to be tested by the test apparatus 2.
- Each device under test 10 may be, for example, an integrated circuit including a semiconductor, a discrete semiconductor element, or another type of device.
- Each device under test 10 may have at least one connection terminal 101 that is connected to the test apparatus 2.
- Each device under test 10 may further have another connection terminal (not shown) that is connected to a ground voltage.
- Test device 2 The test apparatus 2 tests each device under test 10.
- the test apparatus 2 may test the quality of electrical static characteristics of each device under test 10 that has been connected in advance.
- the test apparatus 2 may sequentially switch between a device under test 10 as a test target among a plurality of devices under test 10 (in the present embodiment, n devices under test 10 (where n is a natural number of 2 or more) as an example).
- the order of the devices under test 10 may be set according to the connection positions to the test apparatus 2.
- the device under test 10 at one end may be the first device under test 10
- the device under test 10 at the other end may be the nth device under test 10.
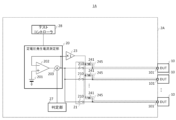
- the test device 2 has a constant voltage generating current measuring unit 20, a first switch unit 21, a second voltage source 23, a second switch unit 24, a constant current generating voltage measuring unit 25, a third switch unit 26, a judgment unit 27, and a test controller 28.
- the constant voltage generating current measuring section 20 measures a value corresponding to a current flowing through the device under test 10 in response to application of a constant voltage to the device under test 10.
- the constant voltage generating current measuring section 20 has a first voltage source 201, an amplifier 202, and a current sensor 203.
- the amplifier 202 is provided between the first voltage source 201 and the current sensor 203 to configure a voltage follower circuit.
- the output terminal of the amplifier 202 is connected to the current sensor 203, and is also connected to an inverting input terminal via the current sensor 203.
- the gain of the amplifier 202 may be 1 (0 dB), and the first voltage output from the first voltage source 201 may be output from the output terminal.
- the current sensor 203 is provided between the output terminal of the amplifier 202 and the first switch section 21.
- the current sensor 203 is an example of a first measurement section, and measures electrical characteristics of the device under test 10 in response to the first voltage source 201 being connected to the device under test 10.
- the current sensor 203 may measure a value corresponding to a current flowing through the device under test 10 in response to the application of a first voltage from the first voltage source 201.
- the current sensor 203 measures the current itself flowing between the output terminal of the amplifier 202 and the first switch section 21, but the measurement may be performed at another position, or another value corresponding to the current (for example, a voltage generated across a resistor in response to the current) may be measured.
- the current sensor 203 may supply the measurement value to the judgment section 27.
- the first switch section 21 is provided between the constant voltage generating current measuring section 20 and the n number of devices under test 10.
- the first switch section 21 connects the connection terminal 101 of the device under test 10 to be tested, among the connection terminals 101 of the n number of devices under test 10, to the first voltage source 201.
- the first switch section 21 may alternatively connect the connection terminal 101 of the device under test 10 to be tested to the first voltage source 201.
- the first switch section 21 may have n number of switches 210, one end of which is connected to the output terminal of the amplifier 202 in the constant voltage generating current measuring section 20 and the other end of which is connected to each of the connection terminals 101 of the n number of devices under test 10.
- the other end of the Nth switch 210 (where N is a natural number such that 1 ⁇ N ⁇ n) of the n number of switches 210 may be connected to the connection terminal 101 of the Nth device under test 10.
- Each switch 210 may be controlled by a test controller 28 described later.
- the second voltage source 23 outputs a second voltage of a predetermined magnitude.
- the second voltage source 23 may output the second voltage of a predetermined magnitude to the connection terminal 101 of at least one other device under test 10 other than the device under test 10 to be tested among the n devices under test 10.
- the second voltage source 23 according to the present embodiment may output the second voltage to at least one device under test 10 other than the device under test to be tested, in cooperation with the second switch section 24.
- the device under test 10 from which the second voltage is output may include, among the n devices under test 10, a device under test 10 that is measured by the current sensor 203 after the device under test 10 being tested, or may include a device under test 10 that is measured before the device under test 10 being tested, or may include a device under test 10 that is placed near the device under test 10 being tested.
- the device under test 10 from which the second voltage is output may be each of the n-1 devices under test 10 that are different from the device under test 10 being tested, among the n devices under test 10.
- the second voltage source 23 may output the second voltage in parallel with the measurement by the current sensor 203, and may output a voltage over the measurement period by the current sensor 203.
- the second voltage source 23 may be an amplifier that amplifies the first voltage output from the first voltage source 201 with a preset gain, and may output a voltage in parallel with the voltage output by the first voltage source 201.
- the amplifier as the second voltage source 23 may be connected to the amplifier 202 of the constant voltage generating current measuring unit 20 to form a voltage follower circuit, and may have a gain of 1 (0 dB).
- the second voltage may be a voltage for passing a current through a device under test 10 other than the test subject to settle the device under test 10 to a standby potential, that is, a standby voltage.
- the second voltage may be a voltage closer to the first voltage than the ground voltages of the n devices under test 10, and in this embodiment, as an example, may be a voltage the same magnitude as the first voltage.
- the current path flowing in the test apparatus 2 due to the voltage from the second voltage source 23 may be insulated from the path of the current flowing in the test apparatus 2 due to the voltage from the first voltage source 201.
- the second voltage source 23 is an amplifier, so the input side and the output side are insulated.
- the current path between the second voltage source 23 and each device under test 10 that is not the test subject, and the current path between the first voltage source 201 and the device under test 10 that is the test subject are separate paths that have no common parts and are insulated from each other.
- the second switch section 24 may connect the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 to the connection terminal 101 of the device under test 10 that is the subject of testing by the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 when the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 described below performs a measurement.
- the second switch section 24 may alternatively connect the device under test 10 that is the subject of testing to the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 when the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 performs a measurement.
- the second switch section 24 may have n switches 240, each having one end connected to the second voltage source 23 and the other end connected to each of the connection terminals 101 of the n devices under test 10. Of the n switches 240, the other end of the Nth switch 240 may be connected to the connection terminal 101 of the Nth device under test 10. Each switch 240 may be controlled by the test controller 28.
- the wiring from the Nth switch 240 to the Nth device under test 10 in the second switch section 24 and the wiring from the Nth switch 210 to the Nth device under test 10 in the first switch section 21 may have a common wiring portion.
- a noise removal filter such as a smoothing capacitor may be provided in the common wiring portion.
- a board-like interface for connecting between the test apparatus 2 and each device under test 10 may be provided between the n devices under test 10 and the n switches 210 and 240.
- the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 is an example of a second measuring section, and is connected between the second voltage source 23 and the second switch section 24.
- the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 measures a value corresponding to a voltage generated in the device under test 10 in response to a current of a predetermined magnitude being passed through the device under test 10.
- the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 may perform the measurement at a timing different from the measurement timing by the current sensor 203, and may perform the measurement in a state in which the device under test 10 to be tested by the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 and the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 are connected by the second switch section 24.
- the current of the predetermined magnitude may be set arbitrarily according to the characteristics of the device under test 10.
- the constant current generation voltage measuring section 25 may have a current source (not shown) that passes a constant current through the device under test 10 to be tested via the second switch section 24.
- the constant current generating voltage measuring section 25 may have a sensor (a voltage sensor, for example) not shown that measures a value corresponding to a voltage generated in the device under test 10 to be tested in response to a current from a current source and supplies the value to the judging section 27.
- the constant current generating voltage measuring section 25 may measure another value corresponding to the voltage (for example, a current flowing in response to a voltage) instead of the voltage itself generated in the device under test 10 to be tested.
- the third switch section 26 is provided between the second voltage source 23 and the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25, and the second switch section 24.
- the third switch section 26 has a switch 261 provided between the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 and the second switch section 24, and a switch 262 provided between the second voltage source 23 and the second switch section 24.
- the switch 261 may be turned on when the constant voltage generation current measurement section 20 performs measurement, that is, when the current sensor 203 performs measurement, and the switch 262 may be turned on when the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 performs measurement.
- the test controller 28 controls each section of the test apparatus 2 to execute a test on each device under test 10.
- the test controller 28 may cause the first voltage source 201 and the second voltage source 23 to output a voltage, and may cause the first switch section 21 and the second switch section 24 to switch the connection state between the first voltage source 201 and the second voltage source 23 and the device under test 10, respectively, to be measured by the current sensor 203.
- the test controller 28 may cause the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 to output a current, and may cause the second switch section 24 to switch the connection state between the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25 and the device under test 10, to be measured by the constant current generation voltage measurement section 25.
- the test controller 28 may be realized by software being executed by a processor or the like.
- the second voltage is output to the connection terminal 101 of the device under test 10 other than the test subject, so that the device under test 10 other than the test subject can be settled to a predetermined potential and put into a standby state for testing.
- a first voltage is applied to a defective device under test 10 to be tested, charge may move between the wiring from the first switch section 21 to the device under test 10 to be tested and the wiring from the first switch section 21 to the device under test 10 not to be tested through the capacitance between the wiring.
- the transfer of charge is eliminated in advance by outputting the second voltage, thereby lowering the impedance of the wiring to the device under test 10 other than the test subject, making it less susceptible to the effects of disturbances and coupling between the wiring, and putting the device under test 10 other than the test subject into a standby state for testing in advance. Furthermore, even if the device under test 10 is a capacitive load and needs to be charged in order to perform a test, the device under test 10 can be charged in advance by outputting the second voltage, and a device under test 10 other than the test subject can be placed in a standby state for testing. This makes it possible to speed up the start of testing for each device under test 10.
- the current path from the second voltage source 23 to the device under test 10 other than the test subject and the current path from the first voltage source 201 to the device under test 10 to be tested are separate paths, even when the current sensor 203 measures a value corresponding to a minute current, a non-minute current can be passed through the current path from the second voltage source 23 to the device under test 10 other than the test subject. Therefore, each device under test 10 can be put into a test standby state early.
- the second voltage is output in parallel with the measurement by the current sensor 203, a device under test 10 other than the device under test 10 under test can be put into a standby state while the device under test 10 under test is being tested. This makes it possible to reliably speed up the start of testing for each device under test 10.
- the second voltage source 23 is selectively connected to each of the connection terminals 101 of at least one device under test 10 other than the test subject, so that the second voltage can be applied to the device under test 10 other than the test subject while preventing the second voltage from being applied to the device under test 10 that is the test subject.
- the devices under test 10 to which the second voltage is applied include the device under test 10 that is to be measured next after the device under test 10 being tested. Therefore, the device under test 10 that is to be measured next can be placed in a test standby state, and the start of testing for that device under test 10 can be accelerated.
- the test apparatus 2 can be formed.
- the second voltage source 23 is an amplifier that amplifies the first voltage from the first voltage source 201, the input side and output side of the second voltage source 23 can be insulated. This makes it possible to prevent a decrease in measurement accuracy caused by the current from the first voltage source 201 flowing to the second voltage source 23 side.
- the second voltage is the same as the first voltage, a device under test 10 other than the test subject can be placed in a standby state so that testing can be performed immediately.
- the second voltage is closer to the first voltage than the ground voltage of the device under test 10
- a device under test 10 other than the test subject can be reliably placed in a standby state for testing.
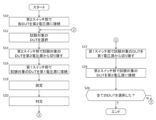
- (Operation of Test Apparatus 2) 2 shows the operation of the test apparatus 2. Note that this figure shows the operation of the test apparatus 2 relating to the measurement of the constant voltage generation current measurement section 20.
- the test apparatus 2 may test each device under test 10 by performing the processes of steps S10 to S26. In this operation, the first voltage source 201 and the second voltage source may continue to output voltages.
- the second switch section 24 connects the second voltage source 23 to the connection terminal 101 of at least one other device under test 10 (each device under test 10 is used as an example in this embodiment) that is different from the device under test 10 being tested. This allows a second voltage (a voltage having the same magnitude as the first voltage as an example in this embodiment) to be output to the connection terminal 101 of each device under test 10.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Testing Of Individual Semiconductor Devices (AREA)
- Testing Electric Properties And Detecting Electric Faults (AREA)
Abstract
予め定められた大きさの第1電圧、または、予め定めれらた大きさの第1電流を出力する第1電源と、複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のうち試験対象の被試験デバイスの接続端子を前記第1電源に対して接続する第1スイッチ部と、前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに接続されることに応じた当該試験対象の被試験デバイスの電気的特性を測定する第1測定部と、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち前記試験対象の被試験デバイスとは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの前記接続端子に対して予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力する第2電圧源と、を備える試験装置が提供される。
Description
本発明は、試験装置および試験方法に関する。
特許文献1,2には「本実施の形態においては、DUT50のある電気特性を測定する測定手段(SMU20)と、DUTの他の電気特性を測定する別の測定手段(LCRメータ22またはパルス発生器24)と、制御手段(コントローラ202)に接続され、微少電流検出手段を有している切替部12(ASU12P、12M)とが用いられる。そして、この切替部は、…DUT50に電気的に接続されている。また、この切替部12は、ケーブルによって幾つかの測定手段に電気的に接続されていて、測定手段または前記第2の測定手段のいずれと前記被測定素子とが電気的に接続されるかを前記制御手段(コントローラ202)からの制御信号に基づいて切り替える…」(段落0035)等と記載されている。
[先行技術文献]
[特許文献]
[特許文献1]特開2005-300495号公報
[特許文献2]特開2010-190768号公報
[先行技術文献]
[特許文献]
[特許文献1]特開2005-300495号公報
[特許文献2]特開2010-190768号公報
本発明の第1の態様においては、予め定められた大きさの第1電圧、または、予め定めれらた大きさの第1電流を出力する第1電源と、複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のうち試験対象の被試験デバイスの接続端子を前記第1電源に対して接続する第1スイッチ部と、前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに接続されることに応じた当該試験対象の被試験デバイスの電気的特性を測定する第1測定部と、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち前記試験対象の被試験デバイスとは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの前記接続端子に対して予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力する第2電圧源と、を備える試験装置が提供される。
上記の試験装置においては、前記第2電圧源と前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスとの間の電流経路、および、前記第1電源と前記試験対象の被試験デバイスとの間の電流経路は、互いに別々の経路であってよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第2電圧源は、前記第1測定部による測定と並行して電圧を出力してよい。
上記何れかの試験装置は、前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの接続端子のそれぞれに対して前記第2電圧源を選択的に接続する第2スイッチ部をさらに備えてよい。
上記の試験装置においては、前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスは、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち、前記第1測定部によって前記試験対象の被試験デバイスの次に測定が行われる被試験デバイスを含んでよい。
前記第2スイッチ部を備える上記何れかの試験装置は、前記第1測定部による測定タイミングとは異なるタイミングで、予め定められた大きさの電流が流されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイスに生じる電圧に応じた値を測定する第2測定部をさらに備え、前記第2測定部は、前記第2電圧源と、前記第2スイッチ部との間に接続され、前記第2スイッチ部は、前記第2測定部が測定を行うときに、前記第2測定部による試験対象の被試験デバイスに前記第2測定部を接続してよい。
上記何れかの試験装置は、前記第2電圧源と、前記複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のそれぞれとを接続した各配線に設けられた複数の抵抗をさらに備えてよい。
上記の試験装置においては、前記第1測定部は、前記第1スイッチ部が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスを前記第1電源に対して接続していない状態における測定値に応じて、前記第1スイッチ部が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスを前記第1電源に対して接続している状態における測定値を調整してよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、前記第2電圧源は、前記第1電源から出力される第1電圧を予め設定されたゲインで増幅するアンプであってよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、前記第2電圧は、前記第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧であってよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、前記第2電圧は、前記複数の被試験デバイスのグランド電圧よりも、前記第1電圧に近い電圧であってよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第2電圧源が前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスに流す電流は、前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに流す電流よりも大きくてよい。
上記何れかの試験装置は、前記第1測定部による測定結果に基づいて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスの良否を判定する判定部をさらに備え、前記判定部は、前記第1電源から前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに対して接続してから基準時間内に前記第1測定部による測定結果の値の変化速度が基準値以下とならないことに応じて、当該試験対象の被試験デバイスを不良と判定してよい。
上記何れかの試験装置においては、前記第1測定部は、前記第1電源から前記第1電圧が印加されることに応じて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに流れる電流に応じた値を測定するか、或いは、前記第1電源から前記第1電流が流されることに応じて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに生じる電圧に応じた値を測定してよい。
本発明の第2の態様においては、複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のうち試験対象の被試験デバイスの接続端子を、予め定められた大きさの第1電圧、または、予め定めれらた大きさの第1電流を出力する第1電源に対して接続すると共に、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち当該試験対象の被試験デバイスとは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの前記接続端子に対し、予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を第2電圧源から印加する段階と、前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに接続されることに応じた当該試験対象の被試験デバイスの電気的特性を測定する段階と、を備える試験方法が提供される。
なお、上記の発明の概要は、本発明の必要な特徴の全てを列挙したものではない。また、これらの特徴群のサブコンビネーションもまた、発明となりうる。
以下、発明の実施の形態を通じて本発明を説明するが、以下の実施形態は請求の範囲にかかる発明を限定するものではない。また、実施形態の中で説明されている特徴の組み合わせの全てが発明の解決手段に必須であるとは限らない。
<第1実施形態>
図1は、本実施形態に係る試験システム1を示す。試験システム1は、複数の被試験デバイス10と、試験装置2とを備える。なお、図中では被試験デバイス10をDUT(Device Under Test)として記載している。
図1は、本実施形態に係る試験システム1を示す。試験システム1は、複数の被試験デバイス10と、試験装置2とを備える。なお、図中では被試験デバイス10をDUT(Device Under Test)として記載している。
(被試験デバイス10)
各被試験デバイス10は、試験装置2によって試験されるエレクトロニクスデバイスである。各被試験デバイス10は、例えば半導体を含む集積回路であってもよいし、ディスクリート型の半導体素子であってもよいし、他の種類のデバイスであってもよい。
各被試験デバイス10は、試験装置2によって試験されるエレクトロニクスデバイスである。各被試験デバイス10は、例えば半導体を含む集積回路であってもよいし、ディスクリート型の半導体素子であってもよいし、他の種類のデバイスであってもよい。
各被試験デバイス10は、試験装置2と接続される少なくとも1つの接続端子101を有してよい。各被試験デバイス10は、グランド電圧に接続された他の接続端子(図示せず)をさらに有してもよい。
(試験装置2)
試験装置2は、各被試験デバイス10の試験を行う。試験装置2は、予め接続された各被試験デバイス10の電気的な静特性の良否を試験してよい。試験装置2は、複数の被試験デバイス10(本実施形態では一例としてn個(但しnは2以上の自然数)の被試験デバイス10)のうち、何れかの被試験デバイス10を試験対象として順次、切り替えて試験を行ってよい。被試験デバイス10の順番は、試験装置2に対する接続位置に従って設定されてよく、n個の被試験デバイス10が一列に並んで試験装置2と接続される場合には、一端の被試験デバイス10が第1の被試験デバイス10とされ、他端の被試験デバイス10が第nの被試験デバイス10とされてよい。
試験装置2は、各被試験デバイス10の試験を行う。試験装置2は、予め接続された各被試験デバイス10の電気的な静特性の良否を試験してよい。試験装置2は、複数の被試験デバイス10(本実施形態では一例としてn個(但しnは2以上の自然数)の被試験デバイス10)のうち、何れかの被試験デバイス10を試験対象として順次、切り替えて試験を行ってよい。被試験デバイス10の順番は、試験装置2に対する接続位置に従って設定されてよく、n個の被試験デバイス10が一列に並んで試験装置2と接続される場合には、一端の被試験デバイス10が第1の被試験デバイス10とされ、他端の被試験デバイス10が第nの被試験デバイス10とされてよい。
試験装置2は、定電圧発生電流測定部20と、第1スイッチ部21と、第2電圧源23と、第2スイッチ部24と、定電流発生電圧測定部25と、第3スイッチ部26と、判定部27と、テストコントローラ28とを有する。
((定電圧発生電流測定部20))
定電圧発生電流測定部20は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に定電圧を印加したことに応じて当該被試験デバイス10に流れる電流に応じた値を測定する。定電圧発生電流測定部20は、第1電圧源201と、アンプ202と、電流センサ203とを有する。
定電圧発生電流測定部20は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に定電圧を印加したことに応じて当該被試験デバイス10に流れる電流に応じた値を測定する。定電圧発生電流測定部20は、第1電圧源201と、アンプ202と、電流センサ203とを有する。
(((第1電圧源201)))
第1電圧源201は、第1電源の一例であり、予め定められた大きさの第1電圧を出力する。第1電圧源201は、アンプ202の非反転入力端子に第1電圧を供給してよい。第1電圧は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電流を流して測定を行うための電圧、つまり測定用の電圧であってよい。第1電圧の大きさは被試験デバイス10の特性に応じて任意に設定されてよい。本図では一例として、第1電圧源201をバッテリとして図示しているが、整流器やコンバータなど、他の装置であってもよい。
第1電圧源201は、第1電源の一例であり、予め定められた大きさの第1電圧を出力する。第1電圧源201は、アンプ202の非反転入力端子に第1電圧を供給してよい。第1電圧は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電流を流して測定を行うための電圧、つまり測定用の電圧であってよい。第1電圧の大きさは被試験デバイス10の特性に応じて任意に設定されてよい。本図では一例として、第1電圧源201をバッテリとして図示しているが、整流器やコンバータなど、他の装置であってもよい。
(((アンプ202)))
アンプ202は、第1電圧源201と電流センサ203との間に設けられてボルテージフォロワ回路を構成する。アンプ202の出力端子は電流センサ203に接続されるとともに、当該電流センサ203を介して反転入力端子に接続される。アンプ202のゲインは1(0dB)であってよく、第1電圧源201から出力される第1電圧を出力端子から出力してよい。
アンプ202は、第1電圧源201と電流センサ203との間に設けられてボルテージフォロワ回路を構成する。アンプ202の出力端子は電流センサ203に接続されるとともに、当該電流センサ203を介して反転入力端子に接続される。アンプ202のゲインは1(0dB)であってよく、第1電圧源201から出力される第1電圧を出力端子から出力してよい。
(((電流センサ203)))
電流センサ203は、アンプ202の出力端子と、第1スイッチ部21との間に設けられる。電流センサ203は、第1測定部の一例であり、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に接続されることに応じた当該被試験デバイス10の電気的特性を測定する。電流センサ203は、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流に応じた値を測定してよい。本実施形態では一例として、電流センサ203は、アンプ202の出力端子と第1スイッチ部21との間に流れる電流そのものを測定するが、他の位置で測定を行ってもよいし、電流に応じた他の値(例えば電流に応じて抵抗の両端に生じる電圧など)を測定してもよい。電流センサ203は、測定値を判定部27に供給してよい。
電流センサ203は、アンプ202の出力端子と、第1スイッチ部21との間に設けられる。電流センサ203は、第1測定部の一例であり、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に接続されることに応じた当該被試験デバイス10の電気的特性を測定する。電流センサ203は、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流に応じた値を測定してよい。本実施形態では一例として、電流センサ203は、アンプ202の出力端子と第1スイッチ部21との間に流れる電流そのものを測定するが、他の位置で測定を行ってもよいし、電流に応じた他の値(例えば電流に応じて抵抗の両端に生じる電圧など)を測定してもよい。電流センサ203は、測定値を判定部27に供給してよい。
((第1スイッチ部21))
第1スイッチ部21は、定電圧発生電流測定部20と、n個の被試験デバイス10との間に設けられる。第1スイッチ部21は、n個の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のうち試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第1電圧源201に対して接続する。第1スイッチ部21は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を択一的に第1電圧源201に接続してよい。第1スイッチ部21は、それぞれ一端が定電圧発生電流測定部20におけるアンプ202の出力端子に接続され、他端がn個の被試験デバイス10のそれぞれの接続端子101に接続されたn個のスイッチ210を有してよい。n個のスイッチ210のうち、第N(但しNは1≦N≦nの自然数)のスイッチ210の他端は、第Nの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に接続されてよい。各スイッチ210は、後述のテストコントローラ28によって制御されてよい。
第1スイッチ部21は、定電圧発生電流測定部20と、n個の被試験デバイス10との間に設けられる。第1スイッチ部21は、n個の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のうち試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第1電圧源201に対して接続する。第1スイッチ部21は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を択一的に第1電圧源201に接続してよい。第1スイッチ部21は、それぞれ一端が定電圧発生電流測定部20におけるアンプ202の出力端子に接続され、他端がn個の被試験デバイス10のそれぞれの接続端子101に接続されたn個のスイッチ210を有してよい。n個のスイッチ210のうち、第N(但しNは1≦N≦nの自然数)のスイッチ210の他端は、第Nの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に接続されてよい。各スイッチ210は、後述のテストコントローラ28によって制御されてよい。
((第2電圧源23))
第2電圧源23は、予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力する。第2電圧源23は、n個の被試験デバイス10のうち試験対象の被試験デバイス10とは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力してよい。本実施形態に係る第2電圧源23は、第2スイッチ部24と協働して、試験対象とは異なる少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10に第2電圧を出力してよい。
第2電圧源23は、予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力する。第2電圧源23は、n個の被試験デバイス10のうち試験対象の被試験デバイス10とは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力してよい。本実施形態に係る第2電圧源23は、第2スイッチ部24と協働して、試験対象とは異なる少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10に第2電圧を出力してよい。
第2電圧が出力される被試験デバイス10は、n個の被試験デバイス10のうち、電流センサ203によって試験対象の被試験デバイス10の次に測定が行われる被試験デバイス10を含んでもよいし、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の前に測定が行われた被試験デバイス10を含んでもよいし、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の近傍に配置された被試験デバイス10を含んでもよい。本実施形態では一例として、第2電圧が出力される被試験デバイス10は、n個の被試験デバイス10のうち、試験対象の被試験デバイス10とは異なるn-1個の各被試験デバイス10であってよい。
第2電圧源23は、電流センサ203による測定と並行して第2電圧を出力してよく、電流センサ203による測定期間に亘って電圧を出力してよい。第2電圧源23は、第1電圧源201から出力される第1電圧を予め設定されたゲインで増幅するアンプであってよく、第1電圧源201による電圧出力と並行して電圧を出力してよい。図1では図示を簡略化しているが、第2電圧源23としてのアンプは、定電圧発生電流測定部20のアンプ202に接続されてボルテージフォロワ回路を構成してよく、ゲインが1(0dB)であってよい。
第2電圧は、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10に電流を流して当該被試験デバイス10を待機電位にセトリングするための電圧、つまり待機用の電圧であってよい。第2電圧は、n個の被試験デバイス10のグランド電圧よりも第1電圧に近い電圧であってよく、本実施形態では一例として第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧であってよい。
第2電圧源23からの電圧によって試験装置2内を流れる電流経路は、第1電圧源201からの電圧によって試験装置2内を流れる電流の経路とは絶縁されてよい。本実施形態では一例として、第2電圧源23はアンプであるため、入力側と出力側とが絶縁されている。また、第2電圧源23と、試験対象ではない各被試験デバイス10との間の電流経路、および、第1電圧源201と試験対象の被試験デバイス10との間の電流経路は、互いに共通の部分を有さない別々の経路であり、絶縁されている。
((第2スイッチ部24))
第2スイッチ部24は、第2電圧源23と、n個の被試験デバイス10との間に設けられる。第2スイッチ部24は、定電圧発生電流測定部20が測定を行うときに、定電圧発生電流測定部20による試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のそれぞれに対して第2電圧源23を選択的に接続する。本実施形態では一例として、第2スイッチ部24は、試験対象ではないn-1個の各被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第2電圧源に接続してよい。
第2スイッチ部24は、第2電圧源23と、n個の被試験デバイス10との間に設けられる。第2スイッチ部24は、定電圧発生電流測定部20が測定を行うときに、定電圧発生電流測定部20による試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のそれぞれに対して第2電圧源23を選択的に接続する。本実施形態では一例として、第2スイッチ部24は、試験対象ではないn-1個の各被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第2電圧源に接続してよい。
第2スイッチ部24は、後述の定電流発生電圧測定部25が測定を行うときに、定電流発生電圧測定部25による試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に定電流発生電圧測定部25を接続してよい。第2スイッチ部24は、定電流発生電圧測定部25が測定を行うときに、試験対象の被試験デバイス10を択一的に定電流発生電圧測定部25に接続してよい。
第2スイッチ部24は、それぞれ一端が第2電圧源23に接続され、他端がn個の被試験デバイス10のそれぞれの接続端子101に接続されたn個のスイッチ240を有してよい。n個のスイッチ240のうち、第Nのスイッチ240の他端は、第Nの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に接続されてよい。各スイッチ240は、テストコントローラ28によって制御されてよい。
なお、第2スイッチ部24における第Nのスイッチ240から第Nの被試験デバイス10までの配線と、第1スイッチ部21における第Nのスイッチ210から第Nの被試験デバイス10までの配線とは、共通の配線部分を有してよい。当該共通の配線部分には、平滑コンデンサなどのノイズ除去フィルタが設けられてよい。また、n個の被試験デバイス10と、n個のスイッチ210,240との間には、試験装置2と各被試験デバイス10との間を接続するためのボード状のインターフェイスが設けられてもよい。
((定電流発生電圧測定部25))
定電流発生電圧測定部25は、第2測定部の一例であり、第2電圧源23と、第2スイッチ部24との間に接続される。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、予め定められた大きさの電流が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流されることに応じて当該被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧に応じた値を測定する。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、電流センサ203による測定タイミングとは異なるタイミングで測定を行ってよく、定電流発生電圧測定部25による試験対象の被試験デバイス10と当該定電流発生電圧測定部25とが第2スイッチ部24により接続された状態で測定を行ってよい。予め定められた大きさの電流は、被試験デバイス10の特性に応じて任意に設定されてよい。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、第2スイッチ部24を介して試験対象の被試験デバイス10に定電流を流す不図示の電流源を有してよい。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、電流源からの電流に応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧に応じた値を測定して判定部27に供給する不図示のセンサ(一例として電圧センサ)を有してよい。なお、定電流発生電圧測定部25は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧そのものではなく、当該電圧に応じた他の値(例えば電圧に応じて流れる電流など)を測定してもよい。
定電流発生電圧測定部25は、第2測定部の一例であり、第2電圧源23と、第2スイッチ部24との間に接続される。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、予め定められた大きさの電流が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流されることに応じて当該被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧に応じた値を測定する。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、電流センサ203による測定タイミングとは異なるタイミングで測定を行ってよく、定電流発生電圧測定部25による試験対象の被試験デバイス10と当該定電流発生電圧測定部25とが第2スイッチ部24により接続された状態で測定を行ってよい。予め定められた大きさの電流は、被試験デバイス10の特性に応じて任意に設定されてよい。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、第2スイッチ部24を介して試験対象の被試験デバイス10に定電流を流す不図示の電流源を有してよい。定電流発生電圧測定部25は、電流源からの電流に応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧に応じた値を測定して判定部27に供給する不図示のセンサ(一例として電圧センサ)を有してよい。なお、定電流発生電圧測定部25は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧そのものではなく、当該電圧に応じた他の値(例えば電圧に応じて流れる電流など)を測定してもよい。
((第3スイッチ部26))
第3スイッチ部26は、第2電圧源23および定電流発生電圧測定部25と、第2スイッチ部24との間に設けられる。第3スイッチ部26は、定電流発生電圧測定部25および第2スイッチ部24の間に設けられたスイッチ261と、第2電圧源23および第2スイッチ部24の間に設けられたスイッチ262とを有する。スイッチ261は、定電圧発生電流測定部20が測定を行う場合、つまり電流センサ203が測定を行う場合にオンとなってよく、スイッチ262は、定電流発生電圧測定部25が測定を行う場合にオンとなってよい。
第3スイッチ部26は、第2電圧源23および定電流発生電圧測定部25と、第2スイッチ部24との間に設けられる。第3スイッチ部26は、定電流発生電圧測定部25および第2スイッチ部24の間に設けられたスイッチ261と、第2電圧源23および第2スイッチ部24の間に設けられたスイッチ262とを有する。スイッチ261は、定電圧発生電流測定部20が測定を行う場合、つまり電流センサ203が測定を行う場合にオンとなってよく、スイッチ262は、定電流発生電圧測定部25が測定を行う場合にオンとなってよい。
((判定部27))
判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10の良否を判定する。本実施形態に係る判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20および定電流発生電圧測定部25による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10の良否を判定してよい。一例として、判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10が正常と判定され、かつ、定電流発生電圧測定部25による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10が正常と判定されることに応じて、当該被試験デバイス10を良好と判定し、他の場合には被試験デバイス10を不良と判定してよい。なお、判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果のみに基づいて被試験デバイス10の良否を判定してもよい。
判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10の良否を判定する。本実施形態に係る判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20および定電流発生電圧測定部25による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10の良否を判定してよい。一例として、判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10が正常と判定され、かつ、定電流発生電圧測定部25による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10が正常と判定されることに応じて、当該被試験デバイス10を良好と判定し、他の場合には被試験デバイス10を不良と判定してよい。なお、判定部27は、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定結果のみに基づいて被試験デバイス10の良否を判定してもよい。
((テストコントローラ28))
テストコントローラ28は、試験装置2の各部を制御して各被試験デバイス10に対する試験を実行する。例えば、テストコントローラ28は、第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から電圧を出力させつつ第1スイッチ部21および第2スイッチ部24によって第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23のそれぞれと被試験デバイス10との接続状態を切り替えて、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流を電流センサ203により測定させてよい。テストコントローラ28は、定電流発生電圧測定部25から電流を出力させつつ第2スイッチ部24によって当該定電流発生電圧測定部25と被試験デバイス10との接続状態を切り替えて、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧を定電流発生電圧測定部25に測定させてよい。なお、テストコントローラ28は、ソフトウェアがプロセッサ等で実行されることにより実現されてよい。
テストコントローラ28は、試験装置2の各部を制御して各被試験デバイス10に対する試験を実行する。例えば、テストコントローラ28は、第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から電圧を出力させつつ第1スイッチ部21および第2スイッチ部24によって第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23のそれぞれと被試験デバイス10との接続状態を切り替えて、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流を電流センサ203により測定させてよい。テストコントローラ28は、定電流発生電圧測定部25から電流を出力させつつ第2スイッチ部24によって当該定電流発生電圧測定部25と被試験デバイス10との接続状態を切り替えて、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧を定電流発生電圧測定部25に測定させてよい。なお、テストコントローラ28は、ソフトウェアがプロセッサ等で実行されることにより実現されてよい。
(試験装置2から得られる効果)
以上の試験装置2によれば、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧が出力されるので、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を予め定められた電位にセトリングし、試験の待機状態とすることができる。例えば、不良な試験対象の被試験デバイス10に第1電圧が印加されて試験が行われると、第1スイッチ部21から当該試験対象の被試験デバイス10までの配線と、第1スイッチ部21から試験対象ではない被試験デバイス10までの配線との間で、配線間の容量を通して電荷が移動しうる。このような場合であっても、第2電圧の出力によって予め電荷の移動を解消して試験対象とは別の当該被試験デバイス10までの配線のインピーダンスを下げ、外乱や配線間の結合の影響を受け難くすると共に、試験対象とは別の当該被試験デバイス10を予め試験の待機状態とすることができる。また、被試験デバイス10が容量性の負荷であり、試験を行うために被試験デバイス10に対して電荷のチャージを行う必要がある場合であっても、第2電圧の出力によって予め電荷のチャージを行い、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を試験の待機状態とすることができる。従って、各被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を早めることができる。
以上の試験装置2によれば、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧が出力されるので、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を予め定められた電位にセトリングし、試験の待機状態とすることができる。例えば、不良な試験対象の被試験デバイス10に第1電圧が印加されて試験が行われると、第1スイッチ部21から当該試験対象の被試験デバイス10までの配線と、第1スイッチ部21から試験対象ではない被試験デバイス10までの配線との間で、配線間の容量を通して電荷が移動しうる。このような場合であっても、第2電圧の出力によって予め電荷の移動を解消して試験対象とは別の当該被試験デバイス10までの配線のインピーダンスを下げ、外乱や配線間の結合の影響を受け難くすると共に、試験対象とは別の当該被試験デバイス10を予め試験の待機状態とすることができる。また、被試験デバイス10が容量性の負荷であり、試験を行うために被試験デバイス10に対して電荷のチャージを行う必要がある場合であっても、第2電圧の出力によって予め電荷のチャージを行い、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を試験の待機状態とすることができる。従って、各被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を早めることができる。
また、第2電圧源23から試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10までの電流経路、および、第1電圧源201から試験対象の被試験デバイス10までの電流経路は互いに別々の経路であるので、電流センサ203において微小電流に応じた値を測定する場合であっても、第2電圧源23から試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10までの電流経路に、微小ではない電流を流すことができる。従って、各被試験デバイス10を早期に試験の待機状態とすることができる。
また、電流センサ203による測定と並行して第2電圧が出力されるので、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対する試験中に、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を試験の待機状態とすることができる。従って、各被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を確実に早めることができる。
また、試験対象とは別の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のそれぞれに対して第2電圧源23が選択的に接続されるので、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対して第2電圧が印加されてしまうのを防止しつつ、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10に対して第2電圧を印加することができる。
また、第2電圧が印加される被試験デバイス10には、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の次に測定が行われる被試験デバイス10が含まれる。従って、次に測定が行われる被試験デバイス10を試験の待機状態とし、当該被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を早めることができる。
また、定電流発生電圧測定部25が第2電圧源23と第2スイッチ部24との間に接続されるので、定電流発生電圧測定部25と各被試験デバイスとの間の経路と、第2電圧源23と各被試験デバイス10との間の経路とを共通化することができる。また、定電流発生電圧測定部25と各被試験デバイス10との間の経路に第2電圧源23を接続することで、試験装置2を形成することができる。
また、第2電圧源23は第1電圧源201からの第1電圧を増幅するアンプであるので、第2電圧源23の入力側と出力側とを絶縁することができる。従って、第1電圧源201からの電流が第2電圧源23の側にも流れてしまうことによる測定精度の低下を防止することができる。
また、第2電圧は第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧であるので、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を、即座に試験を行うことができる待機状態とすることができる。
また、第2電圧は被試験デバイス10のグランド電圧よりも第1電圧に近い電圧であるので、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を、確実に試験の待機状態とすることができる。
(試験装置2の動作)
図2は、試験装置2の動作を示す。なお、本図では試験装置2の動作のうち、定電圧発生電流測定部20の測定に関する動作を示す。試験装置2は、ステップS10~26の処理を行うことにより各被試験デバイス10の試験を行ってよい。本動作においては第1電圧源201および第2電圧源が電圧を出力し続けてよい。
図2は、試験装置2の動作を示す。なお、本図では試験装置2の動作のうち、定電圧発生電流測定部20の測定に関する動作を示す。試験装置2は、ステップS10~26の処理を行うことにより各被試験デバイス10の試験を行ってよい。本動作においては第1電圧源201および第2電圧源が電圧を出力し続けてよい。
ステップS10において第2スイッチ部24は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10とは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10(本実施形態では一例として各被試験デバイス10)の接続端子101に対し、第2電圧源23を接続する。これにより各被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧(本実施形態では一例として第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧)が出力されてよい。
ステップS12においてテストコントローラ28は、n個の被試験デバイス10の何れかを試験対象の被試験デバイス10として選択する。テストコントローラ28は、ステップS12の処理ごとに、別々の被試験デバイス10を選択してよく、第1の被試験デバイス10~第nの被試験デバイス10を順に選択してよい。
ステップS14において第2スイッチ部24は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第2電圧源23から切り離す。これにより、試験対象の被試験デバイス10とは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10(本実施形態では一例として試験対象とは別の各被試験デバイス10)の接続端子101に対し、第2電圧源23が接続された状態となり、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧(本実施形態では一例として第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧)が出力されてよい。
ステップS16において第1スイッチ部21は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第1電圧源201に対して接続する。これにより、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第1電圧が出力されてよい。ステップS16の処理はステップS14の処理と同時に行われてもよい。
ステップS18において電流センサ203は、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に接続されることに応じた当該被試験デバイス10の電気的特性(本実施形態においては一例として試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流)を測定する。
ステップS20において判定部27は、電流センサ203による測定結果に基づいて試験対象の被試験デバイス10の良否を判定する。判定部27は、測定される電流の大きさが基準範囲内であることに応じて被試験デバイス10を良好と判定し、測定される電流の大きさが基準範囲外であることに応じて被試験デバイス10を不良と判定してよい。判定部27は、第1電圧源201を試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対して接続してから、つまりステップS16の処理が行われてから基準時間内に電流センサ203による測定結果の値の変化速度が基準値以下とならないことに応じて、当該試験対象の被試験デバイス10を不良と判定してよい。これにより、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流が安定しないことに応じて当該被試験デバイス10が不良と判定されてよい。基準時間は、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10に対して第2電圧源23から電圧を印加しない場合に、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電圧を印加してから被試験デバイス10の電位が安定するまでの時間よりも短くてよい。
ステップS22において第1スイッチ部21は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第1電圧源201から切り離す。
ステップS24において第2スイッチ部24は、試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を第2電圧源23に接続する。これにより各被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧が出力されてよい。ステップS24の処理はステップS22の処理と同時に行われてもよい。
ステップS26においてテストコントローラ28は、ステップS12においてn個の被試験デバイス10が全て選択されたか否かを判定する。被試験デバイス10が全て選択されていないと判定された場合(ステップS26;No)にはステップS12に処理が移行してよい。被試験デバイス10が全て選択されたと判定された場合(ステップS26;Yes)には動作が終了してよい。
以上の動作によれば、第1電圧源201を試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対して接続してから基準時間内に測定結果の値の変化速度が基準値以下とならないことに応じて、当該試験対象の被試験デバイス10が不良と判定される。従って、測定結果の値が安定するまで待つことなく基準時間の経過タイミングで試験対象の被試験デバイス10を不良と判定することができる。
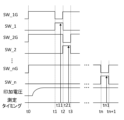
(動作波形)
図3は、試験装置2の動作波形を示す。なお、本図では試験装置2の動作のうち、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定動作の波形を示す。図中、横軸は時間を示す。「SW_1」~「SW_n」の動作波形は第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210~第nのスイッチ210に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「SW_1G」~「SW_nG」の動作波形は第2スイッチ部24における第1のスイッチ240~第nのスイッチ240に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「印加電圧」の動作波形は第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から出力される電圧を示す。測定タイミングは、電流センサ203による測定タイミングを示す。
図3は、試験装置2の動作波形を示す。なお、本図では試験装置2の動作のうち、定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定動作の波形を示す。図中、横軸は時間を示す。「SW_1」~「SW_n」の動作波形は第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210~第nのスイッチ210に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「SW_1G」~「SW_nG」の動作波形は第2スイッチ部24における第1のスイッチ240~第nのスイッチ240に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「印加電圧」の動作波形は第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から出力される電圧を示す。測定タイミングは、電流センサ203による測定タイミングを示す。
時点t0において第2スイッチ部24の各スイッチ240はオン状態となり、各被試験デバイス10と、第2電圧源23とをそれぞれ接続する。また、第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23が電圧の出力を開始する。これにより、各被試験デバイス10が待機電位となる。
時点t1において第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210のみがオン状態となり、第2スイッチ部24における第1のスイッチ240のみがオフ状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第1の被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点t11において当該電流が測定される。
続いて、時点t2において第1スイッチ部21における第2のスイッチ210のみがオン状態となり、第2スイッチ部24における第2のスイッチ240のみがオフ状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第2の被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点t21において当該電流が測定される。
以降、同様にして、時点tN(但し、ここではNは3≦N≦nの自然数)において第1スイッチ部21における第Nのスイッチ210のみがオン状態となり、第2スイッチ部24における第Nのスイッチ240のみがオフ状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第Nの被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点tN1において当該電流が測定される。
なお、以上の第1実施形態においては、試験装置2が定電流発生電圧測定部25、第3スイッチ部26、判定部27およびテストコントローラ28を有することとして説明したが、これらの何れかを有しなくてもよい。例えば、判定部27やテストコントローラ28は試験装置1の外部に設けられてもよい。試験装置2が定電流発生電圧測定部25を有しない場合には、第3スイッチ部26も有しなくてよい。
また、第1スイッチ部21および第2スイッチ部24は各被試験デバイス10を第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23の何れか一方に接続するよう接続を切り替えることとして説明したが、少なくとも1つの被試験デバイス10を一時的に第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23に接続してもよい。
<第2実施形態>
図4は、本実施形態に係る試験システム1Aを示す。なお、本実施形態に係る試験システム1Aにおいて、図1に示された試験システム1の構成と略同一のものには同一の符号を付け、説明を省略する。
図4は、本実施形態に係る試験システム1Aを示す。なお、本実施形態に係る試験システム1Aにおいて、図1に示された試験システム1の構成と略同一のものには同一の符号を付け、説明を省略する。
試験システム1Aの試験装置2Aは、第2スイッチ部24に代えて、第2電圧源23と、複数の被試験デバイス10(本実施形態では一例としてn個の被試験デバイス10)の接続端子101のそれぞれとを接続した各配線245(本実施形態では一例としてn個の配線245)に設けられた複数の抵抗241(本実施形態では一例としてn個の抵抗241)を有する。配線245と、第1電圧源201から被試験デバイス10までの電流経路とが共通部分を有する場合には、抵抗241は、配線245のうち、第1電圧源201から被試験デバイス10までの電流経路とは異なる部分に設けられてよい。
これにより、本実施形態における第2電圧源23は、測定対象の被試験デバイス10を含めてn個の被試験デバイス10のそれぞれに対して第2電圧を印加可能であってよい。但し、本実施形態に係る試験装置2Aでは、第1電圧に対する第2電圧の大きさの調整と、抵抗241の大きさの調整との少なくとも一方が予め行われることにより、試験対象の被試験デバイス10に接続された抵抗241には、第2電圧源23からの電圧に起因する電流が流れなくてよい。一例として、第2電圧は第1電圧と同じ大きさであってよい。n個の各抵抗241の抵抗値は互いに同じであってよい。
以上の試験装置2Aによれば、第2電圧源23と、n個の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のそれぞれとを接続した各配線245に抵抗241が設けられるので、試験対象とは別の各被試験デバイス10を試験の待機状態とすることができる。また、第1実施形態と異なり、第2スイッチ部24のスイッチングを行うことなく試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を待機電位にセトリングすることができるため、スイッチングのための構成や制御を省くことができる。また、第2電圧源23からの電圧に起因して試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電流が流れてしまうのを防止することができるため、測定精度の低下を防止することができる。
なお、以上の試験装置2Aは、ステップS10,S14、S24の処理を行わない点を除き、図2と同様にして定電圧発生電流測定部20による測定を行ってよい。また、ステップS18の処理において試験装置2Aの電流センサ203はキャリブレーションを行ってよい。例えば、電流センサ203は、第1スイッチ部21が試験対象の被試験デバイス10を第1電圧源201に対して接続していない状態における測定値に応じて、第1スイッチ部21が試験対象の被試験デバイス10を第1電圧源201に対して接続している状態における測定値を調整してよい。これにより、校正された正確な測定値を取得することができる。第1スイッチ部21が試験対象の被試験デバイス10を第1電圧源201に対して接続していない状態における電流の測定値は、配線245を電流が流れることに起因する測定誤差であってよく、試験対象の被試験デバイス10と第1電圧源201とが接続される前、或いは試験の開始前に予め測定されて試験装置2A内に記憶されてよい。電流センサ203は、第1スイッチ部21が試験対象の被試験デバイス10を第1電圧源201に対して接続している状態において電流センサ203が測定した実測値から当該測定誤差を引いて、校正された測定値を算出してよい。電流センサ203は、テストコントローラ28との協働によってキャリブレーションを行ってもよい。
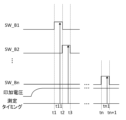
(動作波形)
図5は、試験装置2Aの動作波形を示す。図中、横軸は時間を示す。「SW_1」~「SW_n」の動作波形は第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210~第nのスイッチ210に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「印加電圧」の動作波形は第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から出力される電圧を示す。測定タイミングは、電流センサ203による測定タイミングを示す。
図5は、試験装置2Aの動作波形を示す。図中、横軸は時間を示す。「SW_1」~「SW_n」の動作波形は第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210~第nのスイッチ210に対する制御信号を示し、ハイレベルがオン、ローレベルがオフを示す。「印加電圧」の動作波形は第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23から出力される電圧を示す。測定タイミングは、電流センサ203による測定タイミングを示す。
本動作においては、予め第1電圧源201および第2電圧源23が電圧の出力を開始する。これにより、各被試験デバイス10が待機電位となる。
時点t1において第1スイッチ部21における第1のスイッチ210のみがオン状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第1の被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点t11において当該電流が測定される。
続いて、時点t2において第1スイッチ部21における第2のスイッチ210のみがオン状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第2の被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点t21において当該電流が測定される。
以降、同様にして、時点tN(但し、ここではNは3≦N≦nの自然数)において第1スイッチ部21における第Nのスイッチ210のみがオン状態となる。これにより、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10(ここでは第Nの被試験デバイス10)に電流が流れ、時点tN1において当該電流が測定される。
<変形例>
なお、上記の実施形態においては、第2電圧源23は第1電圧源201と同じ大きさの電圧を出力することとして説明したが、異なる大きさの電圧を出力してもよい。この場合であっても、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を予め定められた電位にセトリングし、試験の待機状態とすることができるため、各被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を早めることができる。
なお、上記の実施形態においては、第2電圧源23は第1電圧源201と同じ大きさの電圧を出力することとして説明したが、異なる大きさの電圧を出力してもよい。この場合であっても、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を予め定められた電位にセトリングし、試験の待機状態とすることができるため、各被試験デバイス10に対する試験の開始を早めることができる。
また、第2電圧源23を第1電圧源201から出力される第1電圧を増幅するアンプとして説明したが、第1電圧源201とは独立に電圧を出力するバッテリや整流器、コンバータなどであってもよい。
また、定電圧発生電流測定部20は、第1電圧源201と電流センサ203との間にゲイン1のアンプ202を有することとして説明したが、アンプ202を有しなくてもよい。また、第1電圧源201をバッテリや整流器、コンバータとして説明したが、これらに加えて出力電圧を第1電圧に増幅するアンプを有してもよい。第1電圧源201に具備されるアンプのゲインは、1より大きくてもよい。定電圧発生電流測定部20が第1電圧源201とは別にアンプ202を有しない場合には、第2電圧源23が試験対象とは別の各被試験デバイス10に流す電流は、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流す電流よりも大きくてよい。一例として、第2電圧源23から各被試験デバイス10までの電流経路の配線抵抗は、第1電圧源201から各被試験デバイス10までの電流経路の配線抵抗よりも小さくてよい。これにより、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を速やかに所望の電位に調整し、試験の待機状態とすることができる。
また、判定部27は第1電圧源201から試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対する電圧印加後の基準時間内に電流センサ203による測定値の変化速度が基準値以下とならないことに応じて、当該試験対象の被試験デバイス10を不良と判定することとして説明したが、他の手法で判定を行ってもよい。例えば、判定部27は、第1電圧源201から試験対象の被試験デバイス10に対する電圧印加が行われてから基準時間の経過後の測定値に基づいて判定を行ってよい。基準時間は、試験装置2,2Aの製造段階において複数の被試験デバイス10に仮試験を行った結果、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電圧を印加してから被試験デバイス10の電位が安定するまでの最長時間であってよい。基準時間は、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10に対して第2電圧源23から電圧を印加しない場合に、第1電圧源201が試験対象の被試験デバイス10に電圧を印加してから被試験デバイス10の電位が安定するまでの時間よりも短くてよい。
また、試験システム1,1Aは、第1電圧源201から第1電圧が印加されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に流れる電流に応じた値を測定する電流センサ203に代えて、定電流源から予め定められた大きさの第1電流が流されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイス10に生じる電圧に応じた値を測定するセンサ(一例として電圧センサ)を、第1測定部の一例として有してよい。この場合には、試験システム1,1Aは第1電圧源201に代えて第1電流を出力する定電流源を有してよく、第1スイッチ部21はn個の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101のうち試験対象の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101を定電流源に対して接続してよい。このような場合にも、電圧センサによる試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10の接続端子101に対して第2電圧源23から第2電圧が出力されるので、試験対象とは別の被試験デバイス10を予め定められた電位にセトリングし、試験の待機状態とすることができる。
本発明の様々な実施形態は、フローチャートおよびブロック図を参照して記載されてよく、ここにおいてブロックは、(1)操作が実行されるプロセスの段階または(2)操作を実行する役割を持つ装置のセクションを表わしてよい。特定の段階およびセクションが、専用回路、コンピュータ可読媒体上に格納されるコンピュータ可読命令と共に供給されるプログラマブル回路、および/またはコンピュータ可読媒体上に格納されるコンピュータ可読命令と共に供給されるプロセッサによって実装されてよい。専用回路は、デジタルおよび/またはアナログハードウェア回路を含んでよく、集積回路(IC)および/またはディスクリート回路を含んでよい。プログラマブル回路は、論理AND、論理OR、論理XOR、論理NAND、論理NOR、および他の論理操作、フリップフロップ、レジスタ、フィールドプログラマブルゲートアレイ(FPGA)、プログラマブルロジックアレイ(PLA)等のようなメモリ要素等を含む、再構成可能なハードウェア回路を含んでよい。
コンピュータ可読媒体は、適切なデバイスによって実行される命令を格納可能な任意の有形なデバイスを含んでよく、その結果、そこに格納される命令を有するコンピュータ可読媒体は、フローチャートまたはブロック図で指定された操作を実行するための手段を作成すべく実行され得る命令を含む、製品を備えることになる。コンピュータ可読媒体の例としては、電子記憶媒体、磁気記憶媒体、光記憶媒体、電磁記憶媒体、半導体記憶媒体等が含まれてよい。コンピュータ可読媒体のより具体的な例としては、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク、ディスケット、ハードディスク、ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)、リードオンリメモリ(ROM)、消去可能プログラマブルリードオンリメモリ(EPROMまたはフラッシュメモリ)、電気的消去可能プログラマブルリードオンリメモリ(EEPROM)、静的ランダムアクセスメモリ(SRAM)、コンパクトディスクリードオンリメモリ(CD-ROM)、デジタル多用途ディスク(DVD)、ブルーレイ(RTM)ディスク、メモリスティック、集積回路カード等が含まれてよい。
コンピュータ可読命令は、アセンブラ命令、命令セットアーキテクチャ(ISA)命令、マシン命令、マシン依存命令、マイクロコード、ファームウェア命令、状態設定データ、またはSmalltalk(登録商標)、JAVA(登録商標)、C++等のようなオブジェクト指向プログラミング言語、および「C」プログラミング言語または同様のプログラミング言語のような従来の手続型プログラミング言語を含む、1または複数のプログラミング言語の任意の組み合わせで記述されたソースコードまたはオブジェクトコードのいずれかを含んでよい。
コンピュータ可読命令は、汎用コンピュータ、特殊目的のコンピュータ、若しくは他のプログラム可能なデータ処理装置のプロセッサまたはプログラマブル回路に対し、ローカルにまたはローカルエリアネットワーク(LAN)、インターネット等のようなワイドエリアネットワーク(WAN)を介して提供され、フローチャートまたはブロック図で指定された操作を実行するための手段を作成すべく、コンピュータ可読命令を実行してよい。プロセッサの例としては、コンピュータプロセッサ、処理ユニット、マイクロプロセッサ、デジタル信号プロセッサ、コントローラ、マイクロコントローラ等を含む。
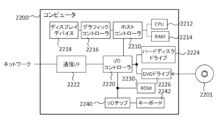
図6は、本発明の複数の態様が全体的または部分的に具現化されてよいコンピュータ2200の例を示す。コンピュータ2200にインストールされたプログラムは、コンピュータ2200に、本発明の実施形態に係る装置に関連付けられる操作または当該装置の1または複数のセクションとして機能させることができ、または当該操作または当該1または複数のセクションを実行させることができ、および/またはコンピュータ2200に、本発明の実施形態に係るプロセスまたは当該プロセスの段階を実行させることができる。そのようなプログラムは、コンピュータ2200に、本明細書に記載のフローチャートおよびブロック図のブロックのうちのいくつかまたはすべてに関連付けられた特定の操作を実行させるべく、CPU2212によって実行されてよい。
本実施形態によるコンピュータ2200は、CPU2212、RAM2214、グラフィックコントローラ2216、およびディスプレイデバイス2218を含み、それらはホストコントローラ2210によって相互に接続されている。コンピュータ2200はまた、通信インターフェイス2222、ハードディスクドライブ2224、DVD-ROMドライブ2226、およびICカードドライブのような入/出力ユニットを含み、それらは入/出力コントローラ2220を介してホストコントローラ2210に接続されている。コンピュータはまた、ROM2230およびキーボード2242のようなレガシの入/出力ユニットを含み、それらは入/出力チップ2240を介して入/出力コントローラ2220に接続されている。
CPU2212は、ROM2230およびRAM2214内に格納されたプログラムに従い動作し、それにより各ユニットを制御する。グラフィックコントローラ2216は、RAM2214内に提供されるフレームバッファ等またはそれ自体の中にCPU2212によって生成されたイメージデータを取得し、イメージデータがディスプレイデバイス2218上に表示されるようにする。
通信インターフェイス2222は、ネットワークを介して他の電子デバイスと通信する。ハードディスクドライブ2224は、コンピュータ2200内のCPU2212によって使用されるプログラムおよびデータを格納する。DVD-ROMドライブ2226は、プログラムまたはデータをDVD-ROM2201から読み取り、ハードディスクドライブ2224にRAM2214を介してプログラムまたはデータを提供する。ICカードドライブは、プログラムおよびデータをICカードから読み取り、および/またはプログラムおよびデータをICカードに書き込む。
ROM2230はその中に、アクティブ化時にコンピュータ2200によって実行されるブートプログラム等、および/またはコンピュータ2200のハードウェアに依存するプログラムを格納する。入/出力チップ2240はまた、様々な入/出力ユニットをパラレルポート、シリアルポート、キーボードポート、マウスポート等を介して、入/出力コントローラ2220に接続してよい。
プログラムが、DVD-ROM2201またはICカードのようなコンピュータ可読媒体によって提供される。プログラムは、コンピュータ可読媒体から読み取られ、コンピュータ可読媒体の例でもあるハードディスクドライブ2224、RAM2214、またはROM2230にインストールされ、CPU2212によって実行される。これらのプログラム内に記述される情報処理は、コンピュータ2200に読み取られ、プログラムと、上記様々なタイプのハードウェアリソースとの間の連携をもたらす。装置または方法が、コンピュータ2200の使用に従い情報の操作または処理を実現することによって構成されてよい。
例えば、通信がコンピュータ2200および外部デバイス間で実行される場合、CPU2212は、RAM2214にロードされた通信プログラムを実行し、通信プログラムに記述された処理に基づいて、通信インターフェイス2222に対し、通信処理を命令してよい。通信インターフェイス2222は、CPU2212の制御下、RAM2214、ハードディスクドライブ2224、DVD-ROM2201、またはICカードのような記録媒体内に提供される送信バッファ処理領域に格納された送信データを読み取り、読み取られた送信データをネットワークに送信し、またはネットワークから受信された受信データを記録媒体上に提供される受信バッファ処理領域等に書き込む。
また、CPU2212は、ハードディスクドライブ2224、DVD-ROMドライブ2226(DVD-ROM2201)、ICカード等のような外部記録媒体に格納されたファイルまたはデータベースの全部または必要な部分がRAM2214に読み取られるようにし、RAM2214上のデータに対し様々なタイプの処理を実行してよい。CPU2212は次に、処理されたデータを外部記録媒体にライトバックする。
様々なタイプのプログラム、データ、テーブル、およびデータベースのような様々なタイプの情報が記録媒体に格納され、情報処理を受けてよい。CPU2212は、RAM2214から読み取られたデータに対し、本開示の随所に記載され、プログラムの命令シーケンスによって指定される様々なタイプの操作、情報処理、条件判断、条件分岐、無条件分岐、情報の検索/置換等を含む、様々なタイプの処理を実行してよく、結果をRAM2214に対しライトバックする。また、CPU2212は、記録媒体内のファイル、データベース等における情報を検索してよい。例えば、各々が第2の属性の属性値に関連付けられた第1の属性の属性値を有する複数のエントリが記録媒体内に格納される場合、CPU2212は、第1の属性の属性値が指定される、条件に一致するエントリを当該複数のエントリの中から検索し、当該エントリ内に格納された第2の属性の属性値を読み取り、それにより予め定められた条件を満たす第1の属性に関連付けられた第2の属性の属性値を取得してよい。
上で説明したプログラムまたはソフトウェアモジュールは、コンピュータ2200上またはコンピュータ2200近傍のコンピュータ可読媒体に格納されてよい。また、専用通信ネットワークまたはインターネットに接続されたサーバーシステム内に提供されるハードディスクまたはRAMのような記録媒体が、コンピュータ可読媒体として使用可能であり、それによりプログラムを、ネットワークを介してコンピュータ2200に提供する。
以上、本発明を実施の形態を用いて説明したが、本発明の技術的範囲は上記実施の形態に記載の範囲には限定されない。上記実施の形態に、多様な変更または改良を加えることが可能であることが当業者に明らかである。その様な変更または改良を加えた形態も本発明の技術的範囲に含まれ得ることが、請求の範囲の記載から明らかである。
請求の範囲、明細書、および図面中において示した装置、システム、プログラム、および方法における動作、手順、ステップ、および段階等の各処理の実行順序は、特段「より前に」、「先立って」等と明示しておらず、また、前の処理の出力を後の処理で用いるのでない限り、任意の順序で実現しうることに留意すべきである。請求の範囲、明細書、および図面中の動作フローに関して、便宜上「まず、」、「次に、」等を用いて説明したとしても、この順で実施することが必須であることを意味するものではない。
1 試験システム
2 試験装置
10 被試験デバイス
20 定電圧発生電流測定部
21 第1スイッチ部
23 第2電圧源
24 第2スイッチ部
25 定電流発生電圧測定部
26 第3スイッチ部
27 判定部
28 テストコントローラ
101 接続端子
201 第1電圧源
202 アンプ
203 電流センサ
210 スイッチ
240 スイッチ
245 配線
261 スイッチ
262 スイッチ
2200 コンピュータ
2201 DVD-ROM
2210 ホストコントローラ
2212 CPU
2214 RAM
2216 グラフィックコントローラ
2218 ディスプレイデバイス
2220 入/出力コントローラ
2222 通信インターフェイス
2224 ハードディスクドライブ
2226 DVD-ROMドライブ
2230 ROM
2240 入/出力チップ
2242 キーボード
2 試験装置
10 被試験デバイス
20 定電圧発生電流測定部
21 第1スイッチ部
23 第2電圧源
24 第2スイッチ部
25 定電流発生電圧測定部
26 第3スイッチ部
27 判定部
28 テストコントローラ
101 接続端子
201 第1電圧源
202 アンプ
203 電流センサ
210 スイッチ
240 スイッチ
245 配線
261 スイッチ
262 スイッチ
2200 コンピュータ
2201 DVD-ROM
2210 ホストコントローラ
2212 CPU
2214 RAM
2216 グラフィックコントローラ
2218 ディスプレイデバイス
2220 入/出力コントローラ
2222 通信インターフェイス
2224 ハードディスクドライブ
2226 DVD-ROMドライブ
2230 ROM
2240 入/出力チップ
2242 キーボード
Claims (15)
- 予め定められた大きさの第1電圧、または、予め定めれらた大きさの第1電流を出力する第1電源と、
複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のうち試験対象の被試験デバイスの接続端子を前記第1電源に対して接続する第1スイッチ部と、
前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに接続されることに応じた当該試験対象の被試験デバイスの電気的特性を測定する第1測定部と、
前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち前記試験対象の被試験デバイスとは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの前記接続端子に対して予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を出力する第2電圧源と、
を備える試験装置。 - 前記第2電圧源と前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスとの間の電流経路、および、前記第1電源と前記試験対象の被試験デバイスとの間の電流経路は、互いに別々の経路である、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 前記第2電圧源は、前記第1測定部による測定と並行して電圧を出力する、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの接続端子のそれぞれに対して前記第2電圧源を選択的に接続する第2スイッチ部をさらに備える、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスは、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち、前記第1測定部によって前記試験対象の被試験デバイスの次に測定が行われる被試験デバイスを含む、請求項4に記載の試験装置。
- 前記第1測定部は、前記第1電源から前記第1電圧が印加されることに応じて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに流れる電流に応じた値を測定し、
当該試験装置は、前記第1測定部による測定タイミングとは異なるタイミングで、予め定められた大きさの電流が流されることに応じて試験対象の被試験デバイスに生じる電圧に応じた値を測定する第2測定部をさらに備え、
前記第2測定部は、前記第2電圧源と、前記第2スイッチ部との間に接続され、
前記第2スイッチ部は、前記第2測定部が測定を行うときに、前記第2測定部による試験対象の被試験デバイスに前記第2測定部を接続する、請求項4に記載の試験装置。 - 前記第2電圧源と、前記複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のそれぞれとを接続した各配線に設けられた複数の抵抗をさらに備える、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 前記第1測定部は、前記第1スイッチ部が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスを前記第1電源に対して接続していない状態における測定値に応じて、前記第1スイッチ部が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスを前記第1電源に対して接続している状態における測定値を調整する、請求項7に記載の試験装置。
- 前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、
前記第2電圧源は、前記第1電源から出力される第1電圧を予め設定されたゲインで増幅するアンプである、請求項1に記載の試験装置。 - 前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、
前記第2電圧は、前記第1電圧と同じ大きさの電圧である、請求項1に記載の試験装置。 - 前記第1電源は、予め定められた第1電圧を出力し、
前記第2電圧は、前記複数の被試験デバイスのグランド電圧よりも、前記第1電圧に近い電圧である、請求項1に記載の試験装置。 - 前記第2電圧源が前記他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスに流す電流は、前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに流す電流よりも大きい、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 前記第1測定部による測定結果に基づいて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスの良否を判定する判定部をさらに備え、
前記判定部は、前記第1電源を前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに対して接続してから基準時間内に前記第1測定部による測定結果の値の変化速度が基準値以下とならないことに応じて、当該試験対象の被試験デバイスを不良と判定する、請求項1に記載の試験装置。 - 前記第1測定部は、前記第1電源から前記第1電圧が印加されることに応じて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに流れる電流に応じた値を測定するか、或いは、前記第1電源から前記第1電流が流されることに応じて前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに生じる電圧に応じた値を測定する、請求項1に記載の試験装置。
- 複数の被試験デバイスの接続端子のうち試験対象の被試験デバイスの接続端子を、予め定められた大きさの第1電圧、または、予め定めれらた大きさの第1電流を出力する第1電源に対して接続すると共に、前記複数の被試験デバイスのうち当該試験対象の被試験デバイスとは異なる他の少なくとも1つの被試験デバイスの前記接続端子に対し、予め定められた大きさの第2電圧を第2電圧源から印加する段階と、
前記第1電源が前記試験対象の被試験デバイスに接続されることに応じた当該試験対象の被試験デバイスの電気的特性を測定する段階と、
を備える試験方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202380098510.4A CN121152976A (zh) | 2023-08-22 | 2023-08-22 | 试验装置及试验方法 |
| PCT/JP2023/030205 WO2025041281A1 (ja) | 2023-08-22 | 2023-08-22 | 試験装置および試験方法 |
| TW113119647A TW202509506A (zh) | 2023-08-22 | 2024-05-28 | 試驗裝置及試驗方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/030205 WO2025041281A1 (ja) | 2023-08-22 | 2023-08-22 | 試験装置および試験方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2025041281A1 true WO2025041281A1 (ja) | 2025-02-27 |
Family
ID=94731695
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/030205 Pending WO2025041281A1 (ja) | 2023-08-22 | 2023-08-22 | 試験装置および試験方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN121152976A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW202509506A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2025041281A1 (ja) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001041997A (ja) * | 1999-07-30 | 2001-02-16 | Advantest Corp | 電源電流測定装置 |
| JP2001242222A (ja) * | 2000-02-29 | 2001-09-07 | Ando Electric Co Ltd | テストボード試験装置、及びテストボード試験方法 |
| JP2002040098A (ja) * | 2000-07-24 | 2002-02-06 | Advantest Corp | 試験装置 |
| JP2005516226A (ja) * | 2002-01-30 | 2005-06-02 | フォームファクター,インコーポレイテッド | 被テスト集積回路用の予測適応電源 |
| JP2009025129A (ja) * | 2007-07-19 | 2009-02-05 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | 信号選択装置及び半導体試験装置 |
| WO2010029597A1 (ja) * | 2008-09-10 | 2010-03-18 | 株式会社アドバンテスト | 試験装置および回路システム |
| US20130214616A1 (en) * | 2012-02-21 | 2013-08-22 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Transmission line pulsing |
-
2023
- 2023-08-22 CN CN202380098510.4A patent/CN121152976A/zh active Pending
- 2023-08-22 WO PCT/JP2023/030205 patent/WO2025041281A1/ja active Pending
-
2024
- 2024-05-28 TW TW113119647A patent/TW202509506A/zh unknown
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001041997A (ja) * | 1999-07-30 | 2001-02-16 | Advantest Corp | 電源電流測定装置 |
| JP2001242222A (ja) * | 2000-02-29 | 2001-09-07 | Ando Electric Co Ltd | テストボード試験装置、及びテストボード試験方法 |
| JP2002040098A (ja) * | 2000-07-24 | 2002-02-06 | Advantest Corp | 試験装置 |
| JP2005516226A (ja) * | 2002-01-30 | 2005-06-02 | フォームファクター,インコーポレイテッド | 被テスト集積回路用の予測適応電源 |
| JP2009025129A (ja) * | 2007-07-19 | 2009-02-05 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | 信号選択装置及び半導体試験装置 |
| WO2010029597A1 (ja) * | 2008-09-10 | 2010-03-18 | 株式会社アドバンテスト | 試験装置および回路システム |
| US20130214616A1 (en) * | 2012-02-21 | 2013-08-22 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Transmission line pulsing |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW202509506A (zh) | 2025-03-01 |
| CN121152976A (zh) | 2025-12-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101489542B1 (ko) | 레거시 테스트 시스템의 동작 에뮬레이팅 | |
| US7818137B2 (en) | Characterization circuit for fast determination of device capacitance variation | |
| US9746520B2 (en) | Systems and methods mitigating temperature dependence of circuitry in electronic devices | |
| JPS60100065A (ja) | 電子回路の自動化テスト中にプログラムしたテスト信号を印加すると共にモニタする方法及び装置 | |
| KR20180137945A (ko) | 피시험 디바이스를 테스트하기 위한 프로세서 기반의 계측 방법 및 이를 이용한 계측 장치 | |
| JPH065261B2 (ja) | 電子デバイス又は回路テスト方法及び装置 | |
| EP1039389B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for adaptively learning test error sources to reduce the total number of test measurements required in real-time | |
| JP2539897B2 (ja) | 漏れ電流試験装置 | |
| JP2001099900A (ja) | 半導体集積回路の検査装置及びその検査方法並びにその検査プログラムを記録した記憶媒体 | |
| US4862069A (en) | Method of in-circuit testing | |
| CN111220901B (zh) | 运放测试系统和方法 | |
| WO2025041281A1 (ja) | 試験装置および試験方法 | |
| US11067623B2 (en) | Test system and method of operating the same | |
| CN107436379B (zh) | 用于测试模拟信号的系统 | |
| KR20260012766A (ko) | 시험 장치 및 시험 방법 | |
| JP2000165244A (ja) | 半導体集積回路装置 | |
| US20250216447A1 (en) | Procedure for making on-die-parametric measurements of circuit devices | |
| EP4653882A1 (en) | Method for determining at least one of a first contact resistance and a second contact resistance of a two-wire kelvin connection | |
| JPS6329277A (ja) | 論理集積回路の試験装置 | |
| JPH07183346A (ja) | 半導体テスト装置 | |
| JP4214361B2 (ja) | Ic試験装置及びその出力信号のタイミング調整方法 | |
| JPH11142489A (ja) | Lsi検査方法 | |
| JPS5951369A (ja) | 自動特性測定装置 | |
| JPH09101330A (ja) | プルアップ抵抗及びプルダウン抵抗の自動試験器 | |
| JPH04190175A (ja) | Ic試験装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 23949742 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1020257042130 Country of ref document: KR |