WO2024024046A1 - 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 - Google Patents
順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024024046A1 WO2024024046A1 PCT/JP2022/029156 JP2022029156W WO2024024046A1 WO 2024024046 A1 WO2024024046 A1 WO 2024024046A1 JP 2022029156 W JP2022029156 W JP 2022029156W WO 2024024046 A1 WO2024024046 A1 WO 2024024046A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- lifter
- punching
- die
- steel plate
- strip
- Prior art date
Links
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 59
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 3
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 title 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 88
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 88
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 claims description 194
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 33
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 abstract description 12
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 124
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical group [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009751 slip forming Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D28/00—Shaping by press-cutting; Perforating
- B21D28/02—Punching blanks or articles with or without obtaining scrap; Notching
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D43/00—Feeding, positioning or storing devices combined with, or arranged in, or specially adapted for use in connection with, apparatus for working or processing sheet metal, metal tubes or metal profiles; Associations therewith of cutting devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B30—PRESSES
- B30B—PRESSES IN GENERAL
- B30B13/00—Methods of pressing not special to the use of presses of any one of the preceding main groups
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02K—DYNAMO-ELECTRIC MACHINES
- H02K15/00—Methods or apparatus specially adapted for manufacturing, assembling, maintaining or repairing of dynamo-electric machines
- H02K15/02—Methods or apparatus specially adapted for manufacturing, assembling, maintaining or repairing of dynamo-electric machines of stator or rotor bodies
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a progressive die for punching thin plate pieces from a strip-shaped thin steel plate that is intermittently conveyed, and a processing method using the same.
- Progressive molds have conventionally been known as manufacturing equipment for laminated iron cores used in motor cores, etc.
- a progressive die is provided with a plurality of stages in which necessary processing is sequentially performed on a strip-shaped thin steel plate (hoop material) made of an electromagnetic steel plate.
- punching of pilot holes (positioning holes), punching of internal shapes (internal shapes such as slots and teeth), formation of caulked portions, application of adhesive, etc. are performed as necessary.
- the shape of each thin plate piece constituting the laminated core is continuously formed in the strip-shaped thin steel plate conveyed through the progressive die.
- each thin plate piece may be manufactured in an independent state, and a predetermined number of these thin plate pieces may be laminated and fixed outside the progressive mold.
- a technique for stably transporting a strip-shaped thin steel plate includes, for example, a lower die formed by arranging multiple stages in parallel with punched holes, and an upper die that moves up and down in opposition to the lower die. It is known that a progressive press device is provided with a plurality of lifters around the punch hole of the lower die to raise the electromagnetic steel sheet from the top surface of the lower die when feeding the electromagnetic steel sheet (Patent Document (see 1).
- an aspect of the present invention provides a progressive die for punching thin plate pieces from a strip-shaped thin steel plate that is intermittently conveyed in a predetermined conveyance direction, the die for each of the thin plates in the strip-shaped thin steel plate being intermittently conveyed in a predetermined conveyance direction.
- a plurality of stages are provided, each of which performs a punching process into a portion corresponding to a piece, and the plurality of stages include an outline punching stage for punching the outline of the thin plate piece, and the outline punching stage includes a punch for punching the outline.
- the length in the transport direction of at least one of the one or more lifters is the maximum length of the plurality of openings formed in the strip-shaped thin steel plate by punching on the upstream side of the at least one lifter.
- the length of the opening in the transport direction is larger than the length of the opening.
- the length in the transport direction of the lifter that lifts the strip thin steel sheet from the surface of the die for external punching is longer than the length in the transport direction of the largest opening formed in the strip thin steel sheet by punching on the upstream side. Since the height is also large, it is possible to prevent the conveyance of the strip-shaped thin steel plate from being hindered by a lifter for lifting the strip-shaped thin steel plate.
- the length of the at least one lifter in the conveyance direction is preferably larger than the conveyance pitch of the strip-shaped thin steel plate.
- the length of the lifter in the conveying direction is larger than the conveying pitch, it becomes possible to always support the portion of the strip-shaped thin steel sheet other than the opening by the lifter, and as a result, the strip-shaped thin steel plate during conveyance. It is possible to suppress flapping.
- the at least one lifter is arranged downstream of the outer shape punching die in the conveying direction, and the length of the lifter in the conveying direction is equal to the length of the opening of the outer shape punching die in the conveying direction. It should be larger than the length of .
- the length in the transport direction of the lifter provided on the downstream side of the outline punching die is determined by the opening of the outline punching die (i.e., the opening formed in the strip-shaped thin steel plate by punching in the outline punching stage). (equivalent to ), it is possible to more effectively suppress the conveyance of the strip-shaped thin steel plate from being disturbed by the lifter disposed on the die for punching out the outer shape.
- the plurality of stages include an inner shape punching stage for punching the inner shape of the thin plate piece on the upstream side of the outer shape punching stage in the conveyance direction, and the inner shape punching stage includes a punch for punching the inner shape. and a die for punching an inner shape, the at least one lifter is disposed upstream of the die for punching an outer shape in the conveyance direction, and the length of the lifter in the conveyance direction is equal to the length of the die for punching an inner shape. It is preferable that the length of the opening is larger than the length of the opening in the transport direction.
- the length in the conveying direction of the lifter provided on the upstream side of the outer shape punching die is determined by the length of the opening of the inner shape punching die (i.e., the length of the lifter provided on the upstream side of the outer shape punching die). Since the lifter is larger than the opening (equivalent to the opening), it is possible to more effectively prevent the conveyance of the strip-shaped thin steel plate from being hindered by the lifter.
- the at least one lifter has a plurality of lifter segments that are divided so as to be continuous in the transport direction.
- the length of the lifter in the conveyance direction of the strip-shaped thin steel plate can be easily increased without affecting the operation of the lifter.
- the at least one lifter is arranged on the downstream side of the outline punching die in the conveyance direction, and the amount of lifting of the strip-shaped thin steel plate by each of the lifter segments is on the upstream side in the conveyance direction. It is preferable that the higher the lifter segment is located, the higher the lifter segment is set.
- the strip-shaped thin steel plate after being punched in the outline punching stage can be easily supported by the lifter disposed on the downstream side of the outline punching die.
- the at least one lifter is arranged upstream of the outline punching die in the transport direction, and the amount of lifting of the strip-shaped thin steel plate by each lifter segment is on the downstream side in the transport direction. It is preferable that the lower the lifter segment is located, the lower the lifter segment is set.
- the strip-shaped thin steel plate before being punched in the outline punching stage can be smoothly moved to the outline punching die side.
- the at least one lifter may include two or more lifters spaced apart in a direction perpendicular to the transport direction.
- interference between the strip-shaped thin steel plate and the die for punching the outer shape can be stably avoided while suppressing the transport of the strip-shaped thin steel plate from being hindered by the lifter.
- the lifting amount of the strip-shaped thin steel plate by one of the two lifters that lifts a portion closer to the center of the outer shape punching die in the direction perpendicular to the conveying direction is greater than the amount by which the other lifter lifts a portion closer to the center of the outer shape punching die. It is preferable that the amount of lifting of the strip-shaped thin steel plate is larger than the lifting amount of the strip-shaped thin steel plate.
- the lifting amount of the strip-shaped thin steel plate relative to the surface of the outer shape punching die is increased, and interference between the strip-shaped thin steel plate and the outer shape punching die can be more effectively avoided.
- the plurality of stages are respectively provided for two lines set to be lined up in the width direction of the strip-shaped thin steel plate.
- an aspect of the present invention is a processing method using a progressive die for punching a thin plate piece from a strip-shaped thin steel plate that is intermittently conveyed in a predetermined conveyance direction, A plurality of stages are provided in which a portion of the steel plate corresponding to each of the thin plate pieces is punched, and the plurality of stages include an outline punching stage for punching the outer shape of the thin plate piece, and the outline punching stage , when the strip-shaped thin steel plate is not conveyed, the strip-shaped thin steel plate is punched by an outline punch and an outline punching die, and when the belt-shaped thin steel plate is conveyed, one of the outline punching stages and stages adjacent thereto;
- the strip-shaped thin steel plate is lifted from the surface of the outline punching die by one or more lifters provided on at least one of the lifters, and the length of at least one of the one or more lifters in the conveying direction is The length is larger than the length in the transport direction of the largest opening among the plurality of opening
- the length in the transport direction of the lifter that lifts the strip thin steel sheet from the surface of the die for external punching is longer than the length in the transport direction of the largest opening formed in the strip thin steel sheet by punching on the upstream side. Since the height is also large, it is possible to prevent the conveyance of the strip-shaped thin steel plate from being hindered by a lifter for lifting the strip-shaped thin steel plate.
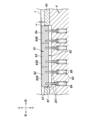
- FIG. 1 A schematic configuration diagram of a progressive mold 1 according to an embodiment Strip layout showing the outline of processing of hoop material F by progressive mold 1 shown in Fig. 1
- FIG. 1 A plan view of the lower die 4 showing the vicinity of the inner punching stage IV and the outer punching stage VI Enlarged view of main parts around outline punching stage VI (corresponding to the cross section taken along the IV-IV line in Figure 3)
- Cross-sectional view taken along line V-V in Figure 3 ((A) when hoop material F is transported, (B) when hoop material F is punched) VI-VI line sectional view in Figure 3 ((A) when hoop material F is transported, (B) when hoop material F is punched)
- FIG. 5 A diagram showing a modification of the lifter 65 shown in FIG. 6
- upstream and downstream respectively mean upstream (i.e., the start point side of transportation) and downstream (i.e., the end point side of transportation) in the transportation direction of the hoop material in the progressive mold. .
- a progressive mold 1 is used to manufacture a laminated core M in which a predetermined number of thin plate pieces W are laminated by processing a hoop material F (belt-shaped thin steel plate) made of an electromagnetic steel plate. It is a device.
- the laminated iron core M is used, for example, in a stator of a motor.
- the progressive die 1 while the hoop material F is intermittently conveyed in a predetermined conveyance direction (progressive conveyance direction indicated by the arrow in FIG. 1), parts corresponding to each thin plate piece W are sequentially punched out.
- the progressive mold 1 is provided with a plurality of stages I to VII along the conveyance direction of the hoop material F. In stages II, IV, and VI, the hoop material F is punched into portions corresponding to the respective thin plate pieces W, respectively.
- the progressive die 1 may be provided with a stage for providing a caulking portion (a caulking projection and a recess or hole into which it fits) for integrating the thin plate pieces W that overlap one above the other.
- the processing of the hoop material F by the progressive mold 1 is not limited to punching processing using a punch and die, but also processing that does not change the shape of the hoop material F (or the portion corresponding to each thin plate piece W) (for example, the upper and lower parts). (applying an adhesive to integrate the overlapping thin plate pieces W) may also be included.
- a plurality of stages I to VII are provided for the first and second lines 100 and 200, which are set to be lined up in the width direction (left and right direction) of the hoop material F. It is being That is, in the progressive mold 1, the hoop material F is processed in the same manner in the first and second lines 100 and 200, and thin plate pieces W having the same shape are formed. Note that the portion corresponding to each thin plate piece W corresponds to a portion of the hoop material F from which each thin plate piece W will be punched out later.
- the progressive mold 1 may have a configuration having only one line (for example, the first line 100).
- the progressive mold 1 includes an upper mold 3 and a lower mold 4 that are arranged to sandwich a hoop material F made of an electromagnetic steel plate vertically.
- the upper mold 3 has a plate-shaped upper holder 12 fixed to the lower surface of the upper ram (not shown) of the press machine. Thereby, the upper mold 3 can move in the vertical direction so as to approach the lower mold 4 and move away from the lower mold 4.
- a backing plate 16 and a punch plate 18 are attached to the lower part of the upper holder 12.
- the punch plate 18 fixes a pilot hole punch 20, a slot punch 21, an inner shape punch 22, and an outer shape punch 24 to the upper holder 12, respectively.
- the backing plate 16 prevents the processing force of each punch 20 , 21 , 22 , 24 from being applied directly to the upper holder 12 .
- a stripper 28 is attached below the upper holder 12.
- the stripper 28 is movable relative to the upper holder 12 in the vertical direction.
- the stripper 28 is suspended and supported by a hanging bolt (not shown), and its lowest position with respect to the upper holder 12 is set.
- the stripper 28 is constructed as a joined body of a stripper body 30 and a stripper plate 32, each of which has a plate shape.
- the lower surface 33 of the stripper plate 32 faces the upper surface of a die plate 40 and each of the dies 42, 43, 44, and 46, which will be described later.
- the stripper plate 32 has a lower surface 33 parallel to the upper surface of the die plate 40 and each die 42, 43, 44, 46.
- Punch insertion holes 34, 35, 36, and 38 are formed in the stripper plate 32, through which the punches 20, 21, 22, and 24 pass.
- the lower mold 4 has a plate-shaped lower holder 14 fixed to the upper surface of a lower bolster (not shown) of the press machine.
- the lower holder 14 is arranged to face the upper holder 12.
- a plate-shaped die plate 40 is attached to the upper surface of the lower holder 14.
- the die plate 40 has a pilot hole punching die 42, a slot punching die 43, an inner shape punching die 44, and an outer shape punching die 46 at positions corresponding to the punching stages I, II, IV, and VI, respectively. attached.
- the upper surfaces of the die plate 40 and each of the dies 42, 43, 44, and 46 are flush with each other, so these upper surfaces are hereinafter collectively referred to as the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4.
- the plurality of stages I-VII include a pilot hole punching stage I, a slot punching stage II, an idle stage III, an inner shape punching stage IV, an idle stage Va, Vb, and an outer shape punching stage VI. and Idol Stage VII.
- stages I to VII are arranged at predetermined intervals in the progressive direction (conveyance direction).
- the pilot hole punching stage I In the pilot hole punching stage I, slot punching stage II, inner shape punching stage IV, and outer shape punching stage VI, the pilot hole P for positioning is punched, the slot S is punched, and the inner shape Da of the thin plate piece W is punched. step, and a step of punching out the outer shape Db of the thin plate piece W.
- idle stages III, Va, Vb, and VII the hoop material F is idly fed. However, the idle stage Vb is set only on the line 200 side.
- pilot hole punching punch 20 and the pilot hole punching die 42 constitute a pair of tools for punching out the pilot hole P.
- Each pilot hole P is arranged near the left and right side edges of the hoop material F, respectively.
- a circular pilot hole P is punched out in the hoop material F each time a press operation is performed (that is, each time the hoop material F is transferred intermittently).
- the slot punching punch 21 and the slot punching die 43 constitute a pair of tools for respectively punching out the slots S formed in the thin plate piece W.
- the slots S are arranged at predetermined intervals in the circumferential direction and correspond to areas between a plurality of teeth formed on the thin plate piece W.
- a slot punch 21 and a slot punch die 43 are provided corresponding to each slot S.
- a slot S is punched out in the hoop material F for each press operation.
- the inner shape punching punch 22 and the inner shape punching die 44 constitute a pair of tools for punching out the inner shape Da of the thin plate piece W.
- the inner punching die 44 has a substantially annular shape.
- the inner shape punching die 44 is formed with an opening 44A (see FIG. 3) into which the inner shape punch 22 is inserted.
- a circular inner shape Da (including a portion defining the inner edges of the plurality of teeth) is punched out in the hoop material F each time the press operation is performed.
- the outer shape punching punch 24 and the outer shape punching die 46 constitute a pair of tools for punching the outer shape of the thin plate piece W.
- the outer shape punching die 46 has a substantially annular shape.
- the outer shape punching die 46 has an opening 46A (see FIG. 3) into which the outer shape punching punch 24 is inserted.
- lifters 63-66 (see FIG. 3) for lifting the hoop material F are provided around the outline punching stage VI. Lifters 63-66 may be provided on at least one of the profile punching stage VI and the stages adjacent thereto.
- the outer shape of the hoop material F is punched out with each press operation. By punching out this outer shape, the thin plate piece W is completed (that is, the processing on the hoop material F is completed).
- the stripper plate 32 descends together with the upper mold 3. At this time, the hoop material F is in a substantially stopped state (strictly speaking, including a case where it is not stopped) when not being conveyed.
- the descending stripper plate 32 presses the upper surface of the hoop material F downward with its lower surface 33. At this time, the hoop material F is held between the lower surface 33 of the stripper plate 32 and the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4.
- the stripper plate 32 rises together with the upper die 3.
- the pressure of the stripper plate 32 against the hoop material F is released, and the hoop material F is separated from the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4.
- the hoop material F is conveyed by a predetermined feed amount in the forward feed direction.
- the outline punching stage VI includes a structure for guiding the transport of the hoop material F (hereinafter referred to as a guide structure) and a structure for lifting the hoop material F when transporting the hoop material F. (hereinafter referred to as a lift-up structure).
- a guide structure for guiding the transport of the hoop material F
- a lift-up structure for lifting the hoop material F when transporting the hoop material F.
- the lift-up structure allows the displacement of the hoop material F due to its own weight (i.e., the distance from the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4) to be controlled or adjusted, regardless of the decrease in the rigidity of the hoop material F. can do.
- Each of the thin plate pieces W whose outer shape has been punched out is pushed into the die 46 by the punch 24 and stacked in order on the previously punched thin plate piece W.
- the plurality of thin plate pieces W stacked in the die 46 are integrated by vertically overlapping pieces by connection using caulking portions or adhesion using an adhesive.
- the thin plate piece W whose outer shape has been punched out may be laminated on the previously punched thin plate piece W after being rotated by a predetermined angle (for example, 90° C.).
- a squeeze ring having an inner diameter slightly smaller than the inner diameter of the die 46 may be provided below the die 46 in the lower die 4 .
- the squeeze ring applies a predetermined side pressure to the laminated thin plate pieces W moving downward.
- the progressive mold 1 may be manufactured with each thin plate piece W being independent (that is, not being fixed to each other). In that case, the manufactured thin plate pieces W are fixed (for example, welded) in a predetermined number of stacks outside the progressive mold 1.
- a plurality of left side guides 61A to 61F that guide the left edge of the hoop material F are provided around the inner punching stage IV and the outer punching stage VI.
- Right side guides 62A to 62E for guiding the right edge of the material F are provided.
- the left side guides 61A-61F are arranged along the left side edge of the lower mold 4 at predetermined intervals.
- the right side guides 62A to 62E are arranged along the right edge of the lower die 4 at predetermined intervals.
- Each of the left side guides 61A-61F and the right side guides 62A-62E is fixed to the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4 (the upper surface of the die plate 40).
- Each of the left side guides 61A-61F and the right side guides 62A-62E includes a vertical wall that rises from the upper surface 47 of the lower die 4 and has a surface facing the side edge of the hoop material F, and a vertical wall that extends downward from the top of the vertical wall. It has a horizontal wall (for example, see horizontal walls 110 and 111 shown in FIG. 5) that extends horizontally toward the center of the mold 4 in the left-right direction.
- the configuration (number, position, shape, etc.) of the left side guides 61A-61F can be changed as appropriate.
- similar side guides can be provided in stages other than the internal punching stage IV and the external punching stage VI.
- lifters 63 and 64 are provided downstream of the outer shape punching die 46.
- the lifter 63 extends in the front-rear direction (conveyance direction) in plan view.
- the center of the lifter 63 is arranged at a position that generally overlaps the center C of the corresponding outer shape punching die 46 in the left-right direction (direction perpendicular to the conveyance direction).
- the length L1 of the lifter 63 in the front-rear direction is set larger than the length G1 of the opening of the corresponding outer shape punching die 46 (on the first line 100 side) in the front-rear direction.
- the length L1 of the lifter 63 is set to be larger than the length in the front-back direction of the largest opening among the plurality of openings formed in the hoop material F on the upstream side (here, the length G1). be done.
- the lifter 63 will not fit into the opening. It is possible to prevent the lifter 63 from engaging (that is, being caught) with the periphery of the opening formed in the hoop material F by punching out the outer shape Db. As a result, it is possible to suppress the transportation of the hoop material F from being hindered by the lifter 63 for lifting the hoop material F on the downstream side of the outer shape punching die 46.
- the length G1 is set to be the same as the inner diameter of the die 46 for punching out the outer shape.
- the length G1 of the opening of the outer shape punching die 46 is approximately the same as the conveyance pitch X of the hoop material F.
- the length L1 of the lifter 63 is preferably set larger than the conveyance pitch X of the hoop material F.
- one lifter 63 has a lifter main body 71 that is retractably provided in the lower mold 4.
- the lifter main body 71 has a configuration in which it is divided into a plurality of parts in the front-rear direction.
- the lifter main body 71 has four lifter segments 72-75 that are continuous in the front-rear direction.
- the front and rear side surfaces of adjacent lifter segments are in sliding contact with each other.
- the front surface 72A (downstream side surface) of the lifter segment 72 and the rear surface 73A (upstream side surface) of the lifter segment 73 are in sliding contact with each other.
- the lifter segments 72 - 75 are accommodated in one lifter hole 77 that opens in the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4 .
- the lifter hole 77 has a concave shape.
- the lifter hole 77 extends from the upper surface 47 of the lower die 4 through the die plate 40 to the lower holder 14.
- Each of the lifter segments 72-75 is movable in the lifter hole 77 between a raised position (an advanced position where it advances upward) and a lowered position (a retreated position where it retreats downward).
- the lifter main body 71 is composed of a plurality of lifter segments 72 to 75 divided in the transport direction, so that the length of the lifter 63 in the transport direction of the hoop material F can be adjusted to affect the operation of the lifter 63. It can be easily increased without any problems.
- the upper part of the lifter segment 72 has an upper surface 72B that extends substantially parallel to the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4.
- the upper part of the lifter segment 72 presses the lower surface of the hoop material F by the urging force of the two lifter springs 79.
- An inclined portion 72C is formed on the rear side of the upper portion of the lifter segment 72 by chamfering the corner portion. This prevents the rear (upstream side) upper part of the lifter main body 71 from engaging with the peripheral edge of the opening formed in the hoop material F. As a result, smooth movement of the hoop material F in the transport direction can be prevented from being hindered by the lifter 63.
- Each lifter spring 79 is housed in a spring housing hole 80 formed in the lower die 4 (here, the lower holder 14). Each lifter spring 79 is connected to the lifter segment 72 via a connecting member 101, respectively.
- the lifter segments 73-75 have generally the same configuration as the lifter segment 72, so a detailed description thereof will be omitted. However, no inclined portion is formed on the upper surface of the lifter segments 73 and 74 located in the middle of the lifter main body 71. Further, on the front side of the upper surface of the lifter segment 75, an inclined portion 75C is formed by chamfering the corner portion. This prevents the front (downstream) upper part of the lifter main body 71 from engaging with the peripheral edge of the opening formed in the hoop material F. As a result, smooth movement of the hoop material F in the transport direction can be prevented from being hindered by the lifter 63.
- the other lifter segments 73 to 75 When transporting the hoop material F, the other lifter segments 73 to 75 operate in the same manner as the lifter segment 72. Each of the other lifter segments 73-75 is also located below the horizontal wall of the corresponding left side guide in its raised position.
- the hoop material F during transportation is lifted from the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4 by the lifter main body 71, so that the hoop material F and the peripheral part of the progressive mold 1 (here, the lower mold 4 Interference with the outer shape punching die 46) is avoided. Therefore, in the progressive die 1, it becomes possible to stably convey the hoop material F after the thin plate piece W has been punched out.
- the length L1 of the lifter 63 to be larger than the length G1 in the front-rear direction of the opening of the outer shape punching die 46, it is possible to prevent the transport of the hoop material F from being hindered by the lifter 63. Can be suppressed.
- lifter 64 extends generally parallel to lifter 63 in plan view.
- Lifter 64 is arranged on the left side of lifter 63. Similar to the lifter 63, the length L2 of the lifter 64 is set to be larger than the length G1 of the opening of the corresponding outer shape punching die 46 in the front-rear direction.
- the length L2 of the lifter 64 is preferably set larger than the conveyance pitch X. Note that the length L1 of the lifter 63 located closer to the center C of the outer shape punching die 46 in the width direction of the hoop material F is smaller than the length L2 of the lifter 64 located further away from the center C of the outer shape punching die 46. Set.
- the lifting position of the lifter body (that is, the lifting amount of the hoop material F) of the lifter 63 located on the center C side of the outer shape punching die 46 in the width direction of the hoop material F is from the center C of the outer shape punching die 46. It is preferable to set it larger (higher) than the raised position of the lifter main body 71 in the lifter 64 which is further away. Thereby, the amount of lifting of the hoop material F with respect to the surface of the outer shape punching die 46 is increased, and interference between the hoop material F and the outer shape punching die 46 can be more effectively avoided.
- the operation of the lifter 64 during transporting the hoop material F and when punching the hoop material F is similar to the operation of the lifter 63 described above.
- an example is shown in which two lifters 63 and two lifters 64 are provided on the downstream side of the outer shape punching die 46, but one of them may be omitted.
- the effect of suppressing the transport of the hoop material F from being hindered by the lifter is that the length of at least one lifter in the transport direction is set to be larger than the length G1 in the front-rear direction of the opening of the outer shape punching die 46.
- Such a lifter may be provided on at least one of the profile punching stage VI and the stage adjacent thereto.
- the lengths of some of the lifters in the transport direction are may be set smaller than the length G1.
- the same or smaller advance amount (raised position) as for the lifters 63 and 64 is set.
- a lifter 65 and a lifter 66 are provided upstream of the outer shape punching die 46.
- the lifter 65 extends in the front-rear direction in plan view.
- the lifter 65 is arranged at a position overlapping the center C of the corresponding outer shape punching die 46 in the left-right direction (direction perpendicular to the conveyance direction).
- the length L3 of the lifter 65 in the front-rear direction is set to be larger than the length G2 of the opening of the corresponding internal punching die 44 (on the second line 200 side) in the front-rear direction.
- the length L3 of the lifter 65 is set to be larger than the length in the front-rear direction (here, the length G2) of the largest opening among the plurality of openings formed in the hoop material F on the upstream side thereof. be done.
- the lifter 65 will not fit into the opening. It is possible to prevent the lifter 65 from engaging with the periphery of the opening formed in the hoop material F by punching the inner shape Da. As a result, it is possible to suppress the transportation of the hoop material F from being hindered by the lifter 65 for lifting the hoop material F on the upstream side of the outer shape punching die 46.
- the length G2 is set to be the same as the inner diameter of the inner punching die 44.
- the length L3 of the lifter 65 is set larger than the conveyance pitch X of the hoop material F.
- one lifter 65 has a lifter main body 81 that is provided so as to be retractable from the lower mold 4.
- the lifter main body 81 has a configuration in which it is divided into a plurality of parts in the front-rear direction.
- the lifter main body 81 has three lifter segments 82-84 that are continuous in the front-rear direction.
- the front and rear side surfaces of adjacent lifter segments are in sliding contact with each other.
- the front surface 82A (downstream side surface) of the lifter segment 82 and the rear surface 83A (upstream side surface) of the lifter segment 83 are in sliding contact with each other.
- the lifter segments 82 - 84 are accommodated in one lifter hole 87 that opens in the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4 .
- the lifter hole 87 has a concave shape.
- the lifter hole 87 extends from the upper surface 47 of the lower die 4 through the die plate 40 to the lower holder 14.
- Each of the lifter segments 82-84 is movable in the lifter hole 87 between a raised position (an advanced position where it advances upward) and a lowered position (a retreated position where it retreats downward).
- the lifter main body 81 is composed of a plurality of lifter segments 82 to 84 divided in the transport direction, so that the length of the lifter 65 in the transport direction of the hoop material F can be controlled to affect the operation of the lifter 65. It can be easily increased without any problems.
- the upper part of the lifter segment 82 has a horizontal surface 82B that extends substantially parallel to the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4.
- the upper part of the lifter segment 82 presses the lower surface of the hoop material F by the biasing force of the two lifter springs 89.
- An inclined portion 82C is formed on the rear side of the upper surface of the lifter segment 82 by chamfering the corners. This prevents the upper part of the rear side (upstream side) of the lifter main body 81 from engaging with the peripheral edge of the opening formed in the hoop material F. As a result, smooth movement of the hoop material F in the transport direction can be prevented from being hindered by the lifter 65.
- Each lifter spring 89 is housed in a spring housing hole 90 formed in the lower die 4 (here, the lower holder 14). Each lifter spring 89 is connected to the lifter segment 82 via a connecting member 201, respectively.
- the lifter segments 83 and 84 have the same configuration as the lifter segment 82, detailed description thereof will be omitted. However, no inclined portion is formed on the upper surface of the lifter segment 83 located in the middle of the lifter main body 81. Further, on the front side of the upper surface of the lifter segment 84, an inclined portion 84C is formed by chamfering the corner portion. This prevents the front (downstream) upper part of the lifter main body 81 from engaging with the peripheral edge of the opening formed in the hoop material F. As a result, smooth movement of the hoop material F in the transport direction can be prevented from being hindered by the lifter 65.
- the upper part of the lifter segment 82 is located below the corresponding right side guide 62C in its raised position. More specifically, the horizontal surface 82B (horizontal portion) of the lifter segment 82 is located below the position of the lower surface of the horizontal wall 210 of the right side guide 62C.
- the other lifter segments 83 and 84 When transporting the hoop material F, the other lifter segments 83 and 84 operate in the same manner as the lifter segment 82. Each of the other lifter segments 83, 84 is also located below the horizontal wall of the corresponding right side guide in its raised position.
- the hoop material F during transportation is in a state of being lifted from the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4 by the lifter main body 81, so that the hoop material F during transportation and the peripheral part of the progressive mold 1 (here, the bottom Interference with the outer shape punching die 46) in the mold 4 is avoided. Therefore, in the progressive die 1, it becomes possible to stably convey the hoop material F after the thin plate piece W has been punched out.
- the length L3 of the lifter 65 to be larger than the length G2 in the front-rear direction of the opening of the internal punching die 44, it is possible to prevent the lifter 65 from interfering with conveyance of the hoop material F. can.
- lifter 66 extends generally parallel to lifter 65 in plan view.
- Lifter 66 is arranged on the right side of lifter 65. Similar to the lifter 65, the length L4 of the lifter 66 is set to be larger than the length G2 of the opening of the corresponding internal punching die 44. However, it is more preferable that the length L4 of the lifter 66 is set larger than the conveyance pitch X of the hoop material F. Note that the length L3 of the lifter 65 located closer to the center C of the outer shape punching die 46 in the width direction of the hoop material F is larger than the length L4 of the lifter 66 located further away from the center C of the outer shape punching die 46. Set.
- the lifting position of the lifter body (that is, the lifting amount of the hoop material F) of the lifter 65 located on the center C side of the outer shape punching die 46 in the width direction of the hoop material F is from the center C of the outer shape punching die 46. It may be set larger (higher) than the raised position of the lifter body 81 of the lifter 66 that is farther away. Thereby, the amount of lifting of the hoop material F with respect to the surface of the outer shape punching die 46 is increased, and interference between the hoop material F and the outer shape punching die 46 can be more effectively avoided.
- the operations of the lifter 66 during conveyance of the hoop material F and during punching of the hoop material F are similar to the operations of the lifter 65 described above.
- an example is shown in which two lifters 65 and 66 are provided on the upstream side of the outer shape punching die 46, but one of them may be omitted.
- the effect of suppressing the transport of the hoop material F from being hindered by the lifters is that the length of at least one lifter in the transport direction is larger than the length G2 in the front-rear direction of the opening of the internal punching die 44. Obtained by setting.
- Such a lifter may be provided on at least one of the profile punching stage VI and the stage adjacent thereto.
- the lengths of some of the lifters in the conveyance direction are different from the front and back of the opening of the inner punching die 44. It may be set smaller than the length G2 in the direction.
- the lifting amount of the hoop material F by the lifter segments 72-75 is preferably set higher as the lifter segment is located on the upstream side in the transport direction.
- the upper surface of the lifter main body 71 is formed as an inclined surface that slopes upward toward the upstream side in the conveying direction with reference to the virtual line H indicating the horizontal direction (that is, the direction along the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4). has been done.
- the upper portions of lifter segments 72-75 have sloped upper surfaces 72B-75B, respectively, forming the upper surface of lifter body 71. Further, the ends of the upper surfaces 72B to 75B that are adjacent to each other are connected smoothly (at the same height) so that no step occurs.
- each of the upper portions of the lifter segments 72-75 may have a horizontal surface.
- the amount of advancement (or rising position) of the lifter segments 72-75 from the upper surface 47 of the lower die 4 is set to be smaller (or lower) in the order of the lifter segments 72, 73, 74, and 75. Ru.
- the amount of lifting of the hoop material F by the lifter segments that constitute the lifter 64 can also be changed in the same way as the lifter 63.
- the lifting amount of the hoop material F by the lifter segments 72-75 is set higher as the lifter segment is located on the more upstream side in the conveyance direction.
- the hoop material F can be easily supported by the lifter 63 disposed downstream of the die 46 for punching out the outer shape.
- the lifting amount of the hoop material F by the lifter segments 82-84 is preferably set to be higher as the lifter segment is located on the downstream side in the conveyance direction.
- the upper surface of the lifter main body 81 is formed as an inclined surface that slopes upward toward the downstream side in the conveying direction with reference to the virtual line H indicating the horizontal direction (that is, the direction along the upper surface 47 of the lower mold 4). has been done.
- the upper portions of lifter segments 82-84 have sloped upper surfaces 82B-84B, respectively, which constitute the upper surface of lifter body 81. Furthermore, the ends of the upper surfaces 82B-84B that are adjacent to each other are smoothly connected (at the same height) so that no step occurs.
- each of the upper portions of the lifter segments 82-84 may have a horizontal surface.
- the amount of advancement (or amount of rise) of the lifter segments 82-84 from the upper surface 47 of the lower die 4 is set to be larger (or higher) in the order of the lifter segments 82, 83, and 84.
- the amount of lifting of the hoop material F by the lifter segments that constitute the lifter 66 can also be changed in the same way as the lifter 65.
- the lifting amount of the hoop material F by the lifter segments 82-84 is set higher as the lifter segment is located on the more downstream side in the conveyance direction. F can be smoothly moved to the outer shape punching die 46 side.
- the shape of the thin plate piece W is not limited to that shown in the embodiment, and various changes can be made.
- lifters similar to the lifters 65 and 66 may be further provided upstream of the die 46 for punching out the outer shape.
- lifters similar to the lifters 63 and 64 may be further provided downstream of the outer shape punching die 46.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Press Drives And Press Lines (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】順送り金型において、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制する。 【解決手段】順送り金型1が、帯状薄鋼板Fへの打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される複数のステージI-VIIが設けられ、複数のステージI-VIIは、薄板片Wの外形Dbを打ち抜く外形打ち抜きステージVIを含み、外形打ち抜きステージVIは、外形打ち抜き用パンチ24、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46を含み、外形打ち抜きステージ及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つには、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の表面から帯状薄鋼板Fを持ち上げる1個以上のリフタ63-66が設けられ、リフタ63-66のうちの少なくとも1個のリフタの搬送方向の長さは、外形打ち抜きステージVI以外の他のステージでの打ち抜き加工によって帯状薄鋼板Fに形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口における搬送方向の長さよりも大きい、構成とする。
Description
本発明は、間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜くための順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法に関する。
従来、モータコア等に用いられる積層鉄心の製造装置として順送り金型が知られている。順送り金型では、電磁鋼板からなる帯状薄鋼板(フープ材)に対して必要な加工が順次実施される複数のステージが設けられる。各ステージでは、パイロット孔(位置決め用孔)の打ち抜きや、内形(スロット、ティース等の内部形状)の打ち抜き、かしめ部の形成、接着剤の塗布などが必要に応じて行われる。これにより、順送り金型内を搬送される帯状薄鋼板において、積層鉄心を構成する各薄板片の形状が連続的にかたちづくられる。最終的に帯状薄鋼板から外形を打ち抜かれた薄板片が、順送り金型において所定枚数積層された状態で固着されることによって積層鉄心が完成する。ただし、順送り金型において、各薄板片が独立した状態で製造され、順送り金型外において、それら薄板片が所定枚数積層された状態で固着されてもよい。
順送り金型内での帯状薄鋼板の搬送時には、順送り金型における周辺部との干渉(すなわち、意図しない当接や擦れなど)が生じないように、帯状薄鋼板の自重(重力)による変位(または変形)を適切に制御または調整する必要がある。
一方、順送り金型による積層鉄心の製造では、原材料の歩留まりの観点から薄板片が打ち抜かれた後の残材をより低減することが望ましい。残材を低減させるために帯状薄鋼板における薄板片に対応する部分の割合を増大させると、残材の剛性が低下し、残材の自重による変位(延いては、順送り金型における周辺部との干渉)が生じ易くなる。特に、帯状薄鋼板の厚さの低減や、帯状薄鋼板の幅の増大により、そのような自重による変位はより生じ易くなる。
帯状薄鋼板を安定して搬送するための技術としては、例えば、抜き穴を設けた複数のステージを複数並列配置してなる下型と、下型に対向して上下動する上型とを有する順送プレス装置において、下型の抜き穴の周囲には、電磁鋼板を送る際に電磁鋼板を下型の上面位置から上昇させるためのリフタが複数設けられたものが知られている(特許文献1参照)。
ところで、上述のような順送り金型において間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板には、各ステージにおいて種々の開口(内形の打ち抜き孔や、外形の打ち抜き孔など)が順次形成される。
本願発明者らが鋭意検討した結果、例えば、順送り金型に設けたリフタによって帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げる構成では、帯状薄鋼板の加工によって形成された開口の周縁にリフタが係合する(すなわち、引っ掛る)と、帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられる可能性があることを見出した。
しかしながら、上記特許文献1に記載されたような従来技術では、帯状薄鋼板の搬送がリフタによって妨げられ得ることについては全く考慮されていない。
本発明は、以上の背景に鑑み、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制可能な順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法を提供することを課題とする。
上記課題を解決するために本発明のある態様は、所定の搬送方向に間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜くための順送り金型であって、前記帯状薄鋼板において前記各薄板片に対応する部分への打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される複数のステージが設けられ、前記複数のステージは、前記薄板片の外形を打ち抜く外形打ち抜きステージを含み、前記外形打ち抜きステージは、外形打ち抜き用パンチ、外形打ち抜き用ダイを含み、前記外形打ち抜きステージ及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つには、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から前記帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げる1個以上のリフタが設けられ、前記1個以上のリフタのうちの少なくとも1個のリフタの前記搬送方向の長さは、当該少なくとも1個のリフタの上流側における打ち抜き加工によって前記帯状薄鋼板に形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口における前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい構成とする。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるリフタの搬送方向の長さが、その上流側における打ち抜き加工によって帯状薄鋼板に形成される最大の開口における搬送方向の長さよりも大きいため、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記帯状薄鋼板の搬送ピッチよりも大きいとよい。
この態様によれば、リフタの搬送方向の長さが、搬送ピッチよりも大きいため、帯状薄鋼板における開口以外の部分をリフタによって常時支持することが可能となり、その結果、搬送時の帯状薄鋼板のばたつきを抑制することができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に配置され、当該リフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの開口の前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きいとよい。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に設けられるリフタの搬送方向の長さが、外形打ち抜き用ダイの開口(すなわち、外形打ち抜きステージでの打ち抜き加工によって帯状薄鋼板に形成される開口に相当)よりも大きいため、外形打ち抜き用ダイに配置されたリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることをより効果的に抑制することができる。
上記の態様において、前記複数のステージは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜きステージの上流側において前記薄板片の内形を打ち抜く内形打ち抜きステージを含み、前記内形打ち抜きステージは、内形打ち抜き用パンチおよび内形打ち抜き用ダイを含み、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの上流側に配置され、当該リフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記内形打ち抜き用ダイの開口の前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きいとよい。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜き用ダイの上流側に設けられるリフタの搬送方向の長さが、内形打ち抜き用ダイの開口(すなわち、内形打ち抜きステージでの打ち抜き加工によって帯状薄鋼板に形成される開口に相当)よりも大きいため、リフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることをより効果的に抑制することができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向に連なるように分割された複数のリフタセグメントを有するとよい。
この態様によれば、帯状薄鋼板の搬送方向におけるリフタの長さを、リフタの動作に影響を及ぼすことなく容易に増大させることができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に配置され、前記各リフタセグメントによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、前記搬送方向においてより上流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されているとよい。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜きステージにおいて打ち抜き加工された後の帯状薄鋼板を、外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に配置されたリフタによって容易に支持することができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの上流側に配置され、前記各リフタセグメントによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、前記搬送方向においてより下流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より低く設定されているとよい。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜きステージにおいて打ち抜き加工される前の帯状薄鋼板を、外形打ち抜き用ダイ側に円滑に移動させることができる。
上記の態様において、前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向に直交する方向に間隔をおいて配置された2個またはそれ以上の前記リフタを含むとよい。
この態様によれば、リフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制しつつ、帯状薄鋼板と外形打ち抜き用ダイとの干渉を安定的に回避できる。
上記の態様において、前記2個のリフタのうち、前記搬送方向に直交する方向において、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの中心により近い部位を持ち上げる一方のリフタによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、他方のリフタによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量よりも大きいとよい。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面に対する帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量が高まり、帯状薄鋼板と外形打ち抜き用ダイとの干渉をより効果的に回避できる。
上記の態様において、前記複数のステージは、前記帯状薄鋼板の幅方向に並ぶように設定された2つのラインに対してそれぞれ設けられるとよい。
この態様によれば、1つの帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜く効率を高めつつ、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
上記課題を解決するために本発明のある態様は、所定の搬送方向に間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜くための順送り金型を用いた加工方法であって、前記帯状薄鋼板において前記各薄板片に対応する部分への打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される複数のステージが設けられ、前記複数のステージは、前記薄板片の外形を打ち抜く外形打ち抜きステージを含み、前記外形打ち抜きステージでは、前記帯状薄鋼板の非搬送時に、外形打ち抜き用パンチおよび外形打ち抜き用ダイによって前記帯状薄鋼板の打ち抜き加工が行われ、前記帯状薄鋼板の搬送時に、前記外形打ち抜きステージ及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つに設けられた1個以上のリフタによって前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から前記帯状薄鋼板が持ち上げられ、前記1個以上のリフタのうちの少なくとも1個のリフタの前記搬送方向の長さは、当該少なくとも1個のリフタの上流側における打ち抜き加工によって前記帯状薄鋼板に形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口における前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい構成とする。
この態様によれば、外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるリフタの搬送方向の長さが、その上流側における打ち抜き加工によって帯状薄鋼板に形成される最大の開口における搬送方向の長さよりも大きいため、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
以上の態様によれば、帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げるためのリフタによって帯状薄鋼板の搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、説明の便宜上、各図に矢印で示した上下、前後、左右によって方向を規定する。ただし、本発明に係る順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法は、必ずしもそれらの方向によって限定されない。なお、以下の説明において、用語「上流」および「下流」は、それぞれ順送り金型におけるフープ材の搬送方向における上流(すなわち、搬送の始点側)および下流(すなわち、搬送の終点側)を意味する。
図1に示すように、順送り金型1は、電磁鋼板からなるフープ材F(帯状薄鋼板)を加工することにより、所定枚数の薄板片Wが積層されてなる積層鉄心Mを製造するための装置である。積層鉄心Mは、例えば、モータの固定子に用いられる。
なお、順送り金型1では、フープ材Fが所定の搬送方向(図1中の矢印で示す順送り方向)に間欠的に搬送されながら、各薄板片Wに対応する部分が順次打ち抜き加工される。詳細は後述するが、順送り金型1には、フープ材Fの搬送方向に沿って複数のステージI-VIIが設けられている。ステージII、IV、及びVIでは、フープ材Fにおいて各薄板片Wに対応する部分への打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される。
順送り金型1では、上下に重なる薄板片Wを一体化させるためのかしめ部(かしめ突起およびそれが嵌まり込む凹部または孔)を設けるためのステージが設けられてもよい。また、順送り金型1によるフープ材Fに対する加工は、パンチ及びダイによる打ち抜き加工に限らず、例えば、フープ材F(または各薄板片Wに対応する部分)の形状を変更しない加工(例えば、上下に重なる薄板片Wを一体化させるための接着剤の塗布)が含まれてもよい。
本実施形態では、図2に示すように、フープ材Fの幅方向(左右方向)に並ぶように設定された第1及び第2ライン100、200に対し、それぞれ複数のステージI-VIIが設けられている。すなわち、順送り金型1では、第1及び第2ライン100、200においてフープ材Fに対して同様の加工がなされ、同一形状の薄板片Wが形成される。なお、各薄板片Wに対応する部分は、フープ材Fにおいて後に各薄板片Wが打ち抜かれる部分に相当する。順送り金型1は、1つのライン(例えば、第1ライン100)のみを有する構成であってもよい。
再び図1を参照して、順送り金型1は、電磁鋼板からなるフープ材Fを上下に挟み込むように配置された上型3及び下型4を備える。
上型3は、プレス機械の上部ラム(不図示)の下面に固定される板状の上側ホルダ12を有する。これにより、上型3は、下型4に近接および下型4と離間するように、上下方向に移動することが可能である。上型3において、上側ホルダ12の下部には、バッキングプレート16及びパンチプレート18が取り付けられている。パンチプレート18は、パイロット孔打ち抜き用パンチ20、スロット打ち抜き用パンチ21、内形打ち抜き用パンチ22、及び外形打ち抜き用パンチ24をそれぞれ上側ホルダ12に固定する。バッキングプレート16は、各パンチ20、21、22、24の加工力が上側ホルダ12に直接かかることを防止する。
上型3において、上側ホルダ12の下方には、ストリッパ28が取り付けられている。ストリッパ28は、上側ホルダ12に対して上下方向に相対変位可能である。ストリッパ28は、吊下げボルト(不図示)による吊り下げ支持によって上側ホルダ12に対する最降下位置が設定されている。ストリッパ28は、それぞれ板状をなすストリッパ本体30とストリッパプレート32との接合体として構成される。
ストリッパプレート32の下面33は、後述するダイプレート40及び各ダイ42、43、44、46の上面に対向する。換言すると、ストリッパプレート32は、ダイプレート40及び各ダイ42、43、44、46の上面と平行な下面33を有する。ストリッパプレート32には、各パンチ20、21、22、24が貫通するパンチ挿通孔34、35、36、38が形成されている。
下型4は、プレス機械の下部ボルスター(不図示)の上面に固定される板状の下側ホルダ14を有する。下側ホルダ14は、上側ホルダ12に対向するように配置される。下型4において、下側ホルダ14の上面には板状のダイプレート40が取り付けられている。ダイプレート40には、各打ち抜きステージI、II、IV、VIに対応する位置に、それぞれパイロット孔打ち抜き用ダイ42、スロット打ち抜き用ダイ43、内形打ち抜き用ダイ44、及び外形打ち抜き用ダイ46が取り付けられている。
なお、ダイプレート40、各ダイ42、43、44、46の上面は面一であるので、以降、これらの上面を総称して下型4の上面47と称する。
図2に示すように、複数のステージI-VIIは、パイロット孔打ち抜きステージIと、スロット打ち抜きステージII、アイドルステージIIIと、内形打ち抜きステージIVと、アイドルステージVa、Vbと、外形打ち抜きステージVIと、アイドルステージVIIと、を含む。順送り金型1において、各ステージI-VIIは、順送り方向(搬送方向)に所定の間隔をおいて配置される。
パイロット孔打ち抜きステージI、スロット打ち抜きステージII、内形打ち抜きステージIV、及び外形打ち抜きステージVIでは、それぞれ位置決め用のパイロット孔Pの打ち抜き工程、スロットSの打ち抜き工程、薄板片Wの内形Daの打ち抜き工程、及び薄板片Wの外形Dbの打ち抜き工程が行われる。アイドルステージIII、Va、Vb、VIIでは、フープ材Fの空送りが行われる。ただし、アイドルステージVbは、ライン200側にのみ設定されている。
パイロット孔打ち抜きステージIにおいて、パイロット孔打ち抜き用パンチ20及びパイロット孔打ち抜き用ダイ42は、パイロット孔Pを打ち抜くための一対の工具を構成する。各パイロット孔Pは、フープ材Fの左右の側縁の近傍にそれぞれ配置される。フープ材Fには、1回のプレス動作毎(すなわち、フープ材Fの1回の間欠移送毎)に円形のパイロット孔Pが打ち抜かれる。
スロット打ち抜きステージIIにおいて、スロット打ち抜き用パンチ21及びスロット打ち抜き用ダイ43は、薄板片Wに形成されるスロットSをそれぞれ打ち抜くための一対の工具を構成する。スロットSは、周方向に所定の間隔で配置されており、薄板片Wに形成される複数のティースの間の領域に相当する。スロット打ち抜き用パンチ21及びスロット打ち抜き用ダイ43は、各スロットSに対応して設けられる。フープ材Fには、1回のプレス動作毎にスロットSが打ち抜かれる。
内形打ち抜きステージIVにおいて、内形打ち抜き用パンチ22及び内形打ち抜き用ダイ44は、薄板片Wの内形Daを打ち抜くための一対の工具を構成する。内形打ち抜き用ダイ44は略円環状をなす。内形打ち抜き用ダイ44には、内形打ち抜き用パンチ22が挿入される開口44A(図3参照)が形成されている。フープ材Fには、1回のプレス動作毎に円形の内形Da(複数のティースの内縁を画定する部分を含む)が打ち抜かれる。
外形打ち抜きステージVIにおいて、外形打ち抜き用パンチ24及び外形打ち抜き用ダイ46は、薄板片Wの外形を打ち抜くための一対の工具を構成する。外形打ち抜き用ダイ46は略円環状をなす。外形打ち抜き用ダイ46には、外形打ち抜き用パンチ24が挿入される開口46A(図3参照)が形成されている。また、後に詳述するように、外形打ち抜きステージVIの周辺には、フープ材Fを持ち上げるためのリフタ63-66(図3参照)が設けられている。リフタ63-66は、外形打ち抜きステージVI及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つに設けられ得る。フープ材Fには、1回のプレス動作毎に外形が打ち抜かれる。この外形の打ち抜きによって薄板片Wが完成する(すなわち、フープ材Fに対する加工が終了する)。
外形打ち抜きステージVIでは、薄板片Wの外形の打ち抜き開始時に上型3が下降すると、ストリッパプレート32は、上型3と共に下降する。このとき、フープ材Fは非搬送時の実質的な停止状態(厳密には停止していない場合を含む)にある。下降するストリッパプレート32は、その下面33によってフープ材Fの上面を下方に向けて押圧する。このとき、フープ材Fは、ストリッパプレート32の下面33と、下型4の上面47との間に挟持された状態となる。
薄板片Wの外形の打ち抜き終了後に上型3が上昇すると、ストリッパプレート32は上型3と共に上昇する。これにより、フープ材Fに対するストリッパプレート32の押圧は解除され、フープ材Fは、下型4の上面47から離間した状態となる。この状態で、フープ材Fは、順送り方向に所定の送り量だけ搬送される。
なお、このようなストリッパプレート32の動作は、他のステージI-V、VIIにおいても同様である。
後に詳述するように、外形打ち抜きステージVIには、フープ材Fの搬送時にその搬送をガイドするための構造(以下、ガイド構造という。)と、フープ材Fの搬送時にフープ材Fを持ち上げるための構造(以下、リフトアップ構造という。)と、が設けられている。順送り金型1では、そのガイド構造により、フープ材Fの幅方向における過度の変位を抑制することができる。また、順送り金型1では、そのリフトアップ構造により、フープ材Fの剛性の低下に拘わらず、フープ材Fの自重による変位(すなわち、下型4の上面47からの離間距離)を制御または調整することができる。その結果、フープ材Fと、順送り金型1における周辺部との干渉(すなわち、意図しない当接や擦れなど)が生じることを抑制することができ、フープ材Fを安定的に搬送することが可能となる。
外形を打ち抜かれた各薄板片Wは、パンチ24によってダイ46内に押し込まれ、先に打ち抜かれた薄板片W上に順に積層される。ダイ46内に積層された複数の薄板片Wは、かしめ部による連結や接着剤による接着によって上下に重なり合うもの同士で一体化される。
なお、外形を打ち抜かれた薄板片Wは、所定の角度(例えば、90℃)回転した後に、先に打ち抜かれた薄板片W上に積層されてもよい。また、下型4におけるダイ46の下方には、ダイ46の内径より僅かに小さい内径を有するスクイズリングが設けられてもよい。スクイズリングは、下方に移動する積層状態の薄板片Wに対して所定の側圧を付与する。また、順送り金型1は、各薄板片Wを独立した状態で(すなわち、互いに固着されない状態で)製造してもよい。その場合、製造された薄板片Wは、順送り金型1外において、所定枚数積層された状態で固着(例えば、溶接)される。
外形打ち抜きステージVIにおいて、積層状態で互いに固着された所定枚数の薄板片Wは、積層鉄心Mとして、下側ホルダ14に形成された排出孔48の下部から取り出される。
次に、外形打ち抜きステージVIにおけるガイド構造およびリフトアップ構造について説明する。
図3及び図4に示すように、下型4において、内形打ち抜きステージIVおよび外形打ち抜きステージVIの周辺には、フープ材Fの左側縁をガイドする複数の左サイドガイド61A-61Fと、フープ材Fの右側縁をガイドする右サイドガイド62A-62Eと、が設けられている。
左サイドガイド61A-61Fは、下型4の左側縁に沿って所定の間隔をおいて配置されている。右サイドガイド62A-62Eは、下型4の右側縁に沿って所定の間隔をおいて配置されている。左サイドガイド61A-61Fおよび右サイドガイド62A-62Eの各々は、下型4の上面47(ダイプレート40の上面)に固定される。左サイドガイド61A-61Fおよび右サイドガイド62A-62Eの各々は、下型4の上面47から立ち上がり、かつフープ材Fの側縁に対向する面を有する縦壁と、その縦壁の上部から下型4の左右方向中央に向けて水平に延在する水平壁(例えば、図5に示された水平壁110、111を参照)とを有する。
なお、左サイドガイド61A-61Fの構成(数、位置、及び形状等)については、適宜変更することが可能である。右サイドガイド62A-62Eについても同様である。また、内形打ち抜きステージIVおよび外形打ち抜きステージVI以外の他のステージにおいても同様のサイドガイドを設けることができる。
図3に示すように、下型4の第1ライン100側において、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側には、リフタ63、64が設けられている。
リフタ63は、平面視において前後方向(搬送方向)に延在する。リフタ63の中心は、対応する外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cと左右方向(搬送方向に直交する方向)において概ね重なる位置に配置される。前後方向におけるリフタ63の長さL1は、対応する(すなわち、第1ライン100側における)外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の前後方向の長さG1よりも大きく設定される。換言すれば、リフタ63の長さL1は、その上流側においてフープ材Fに形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口の前後方向の長さ(ここでは、長さG1)よりも大きく設定される。
これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口がフープ材Fの搬送時にリフタ63上に重なる場合でも、リフタ63はその開口に嵌まり込むことはない。外形Dbの打ち抜きによってフープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁にリフタ63が係合する(すなわち、引っ掛かる)ことを回避できる。その結果、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側においてフープ材Fを持ち上げるためのリフタ63によってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。なお、本実施形態では、長さG1は、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の内径と同一に設定されている。
また、本実施形態では、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の長さG1は、フープ材Fの搬送ピッチXと略同一である。ただし、搬送ピッチXが長さG1よりも大きい場合、リフタ63の長さL1は、フープ材Fの搬送ピッチXよりも大きく設定されるとよい。これにより、搬送時のフープ材Fのばたつきを抑制することができる。
1個のリフタ63は、図5に示すように、下型4に出没可能に設けられたリフタ本体71を有する。リフタ本体71は、前後方向に複数に分割された形態を有する。本実施形態では、リフタ本体71は、前後方向に連なる4つのリフタセグメント72-75を有する。リフタセグメント72-75において、隣接するもの同士の前後方向の側面は、互いに摺接した状態にある。例えば、リフタセグメント72の前面72A(下流側の面)と、リフタセグメント73の後面73A(上流側の面)とは、互いに摺接する。リフタセグメント72-75は、下型4の上面47に開口する1つのリフタ用孔77に収容される。ここでは、リフタ用孔77は、凹状をなす。リフタ用孔77は、下型4の上面47からダイプレート40を貫通し、下側ホルダ14まで延在する。リフタセグメント72-75の各々は、リフタ用孔77において、上昇位置(上方に向けて進出する進出位置)と、下降位置(下方に向けて後退する後退位置)との間を移動可能である。
このように、リフタ本体71は、搬送方向に分割された複数のリフタセグメント72-75によって構成されるため、フープ材Fの搬送方向におけるリフタ63の長さを、リフタ63の動作に影響を及ぼすことなく容易に増大させることができる。
リフタセグメント72の上部は、下型4の上面47と略平行に延在する上面72Bを有する。リフタセグメント72の上部は、2つのリフタ用ばね79の付勢力によってフープ材Fの下面を押圧する。リフタセグメント72の上部の後側には、角部が面取りされることにより傾斜部72Cが形成されている。これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁部に、リフタ本体71の後側(上流側)の上部が係合することが防止される。その結果、フープ材Fの搬送方向への円滑な移動がリフタ63によって阻害されることを回避できる。
各リフタ用ばね79は、下型4(ここでは、下側ホルダ14)に形成されたばね収容孔80に収容される。各リフタ用ばね79は、それぞれ連結部材101を介してリフタセグメント72に接続される。
リフタセグメント73-75は、リフタセグメント72と概ね同様の構成を有するため、それらの詳細な説明は省略する。ただし、リフタ本体71の中間に位置するリフタセグメント73、74の上面には、傾斜部は形成されない。また、リフタセグメント75の上面の前側には、角部が面取りされることにより傾斜部75Cが形成されている。これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁部に、リフタ本体71の前側(下流側)の上部が係合することが防止される。その結果、フープ材Fの搬送方向への円滑な移動がリフタ63によって阻害されることを回避できる。
図5(A)に示すように、フープ材Fの搬送時には、フープ材Fに対するストリッパプレート32の押圧は解除されている。そこで、外形打ち抜きステージVI周辺では、リフタ本体71(すなわち、対応するリフタ用ばね79によってそれぞれ付勢されたリフタセグメント72-75)の上部によってフープ材Fが上方に持ち上げられる。
フープ材Fの搬送時において、他のリフタセグメント73-75は、リフタセグメント72と同様に動作する。他のリフタセグメント73-75の各々についても、その上昇位置において、対応する左サイドガイドの水平壁よりも下側に位置する。
このように、搬送時のフープ材Fは、リフタ本体71によって下型4の上面47から持ち上げられた状態にあるため、フープ材Fと順送り金型1における周辺部(ここでは、下型4における外形打ち抜き用ダイ46)との干渉が回避される。そのため、順送り金型1では、薄板片Wが打ち抜かれた後のフープ材Fを安定的に搬送することが可能となる。特に、上述のように、リフタ63の長さL1を、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の前後方向の長さG1よりも大きく設定することにより、リフタ63によってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
図5(B)に示すように、フープ材Fの打ち抜き時(非搬送時)には、その上面がストリッパプレート32の下面33によって下方に向けて押圧される。これにより、フープ材Fの下面は、下型4の上面47に当接した状態となる。例えば、リフタセグメント72は、2つのリフタ用ばね79の付勢力に抗する力で、フープ材Fの下面によって下方に押される。これにより、リフタセグメント72は、リフタ用孔77内に後退する(すなわち、後退位置まで移動する)。フープ材Fの打ち抜き時において、他のリフタセグメント73-75は、リフタセグメント72と同様に動作する。
再び図3を参照して、リフタ64は、平面視においてリフタ63と概ね平行に延在する。リフタ64は、リフタ63の左側に配置される。リフタ63と同様に、リフタ64の長さL2は、対応する外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の前後方向の長さG1よりも大きく設定される。搬送ピッチXが長さG1よりも大きい場合、リフタ64の長さL2は、搬送ピッチXよりも大きく設定されるとよい。なお、フープ材Fの幅方向において外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心C側に位置するリフタ63の長さL1は、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cからより離れたリフタ64の長さL2よりも小さく設定される。
また、フープ材Fの幅方向において外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心C側に位置するリフタ63におけるリフタ本体の上昇位置(すなわち、フープ材Fの持ち上げ量)は、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cからより離れたリフタ64におけるリフタ本体71の上昇位置よりも大きく(高く)設定されるとよい。これにより、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の表面に対するフープ材Fの持ち上げ量が高まり、フープ材Fと外形打ち抜き用ダイ46との干渉をより効果的に回避できる。
なお、フープ材Fの搬送時およびフープ材Fの打ち抜き時におけるリフタ64の動作は、上述のリフタ63の動作と同様である。また、本実施形態では、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側に2つのリフタ63およびリフタ64が設けられる例を示したが、それらの一方が省略されてもよい。さらに、リフタによってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制する効果は、少なくとも1個のリフタの搬送方向における長さが、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の前後方向の長さG1よりも大きく設定されることにより得られる。そのようなリフタは、外形打ち抜きステージVI及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つに設けられ得る。例えば、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側にリフタ63、64以外の複数のリフタが設けられた場合、それらの一部のリフタの搬送方向における長さは、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の開口の前後方向の長さG1よりも小さく設定されてもよい。その場合、搬送方向における長さがG1よりも小さく設定されたリフタについては、リフタ63、64と同一またはより小さい進出量(上昇位置)が設定されるとよい。
一方、下型4の第2ライン200側において、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側には、リフタ65およびリフタ66が設けられている。
リフタ65は、平面視において前後方向に延在する。リフタ65は、対応する外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cと左右方向(搬送方向に直交する方向)において重なる位置に配置される。前後方向におけるリフタ65の長さL3は、対応する(すなわち、第2ライン200側における)内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の開口の前後方向の長さG2よりも大きく設定される。換言すれば、リフタ65の長さL3は、その上流側においてフープ材Fに形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口の前後方向の長さ(ここでは、長さG2)よりも大きく設定される。
これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口がフープ材Fの搬送時にリフタ65上に重なる場合でも、リフタ65はその開口に嵌まり込むことはない。内形Daの打ち抜きによってフープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁にリフタ65が係合することを回避できる。その結果、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側においてフープ材Fを持ち上げるためのリフタ65によってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。なお、本実施形態では、長さG2は、内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の内径と同一に設定されている。また、リフタ65の長さL3は、フープ材Fの搬送ピッチXよりも大きく設定されることがより好ましい。
1個のリフタ65は、図6に示すように、下型4に出没可能に設けられたリフタ本体81を有する。リフタ本体81は、前後方向に複数に分割された形態を有する。ここでは、リフタ本体81は、前後方向に連なる3つのリフタセグメント82-84を有する。リフタセグメント82-84において、隣接するもの同士の前後方向の側面は、互いに摺接した状態にある。例えば、リフタセグメント82の前面82A(下流側の面)と、リフタセグメント83の後面83A(上流側の面)とは、互いに摺接する。リフタセグメント82-84は、下型4の上面47に開口する1つのリフタ用孔87に収容される。ここでは、リフタ用孔87は、凹状をなす。リフタ用孔87は、下型4の上面47からダイプレート40を貫通し、下側ホルダ14まで延在する。リフタセグメント82-84の各々は、リフタ用孔87において、上昇位置(上方に向けて進出する進出位置)と、下降位置(下方に向けて後退する後退位置)との間を移動可能である。
このように、リフタ本体81は、搬送方向に分割された複数のリフタセグメント82-84によって構成されるため、フープ材Fの搬送方向におけるリフタ65の長さを、リフタ65の動作に影響を及ぼすことなく容易に増大させることができる。
リフタセグメント82の上部は、下型4の上面47と略平行に延在する水平面82Bを有する。リフタセグメント82の上部は、2つのリフタ用ばね89の付勢力によってフープ材Fの下面を押圧する。リフタセグメント82の上面の後側には、角部が面取りされることにより傾斜部82Cが形成されている。これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁部に、リフタ本体81の後側(上流側)の上部が係合することが防止される。その結果、フープ材Fの搬送方向への円滑な移動がリフタ65によって阻害されることを回避できる。
各リフタ用ばね89は、下型4(ここでは、下側ホルダ14)に形成されたばね収容孔90に収容される。各リフタ用ばね89は、それぞれ連結部材201を介してリフタセグメント82に接続される。
リフタセグメント83、84は、リフタセグメント82と同様の構成を有するため、その詳細な説明は省略する。ただし、リフタ本体81の中間に位置するリフタセグメント83の上面には、傾斜部は形成されない。また、リフタセグメント84の上面の前側には、角部が面取りされることにより傾斜部84Cが形成されている。これにより、フープ材Fに形成された開口の周縁部に、リフタ本体81の前側(下流側)の上部が係合することが防止される。その結果、フープ材Fの搬送方向への円滑な移動がリフタ65によって阻害されることを回避できる。
図6(A)に示すように、フープ材Fの搬送時には、フープ材Fに対するストリッパプレート32の押圧は解除されている。そこで、外形打ち抜きステージVI周辺では、リフタ本体81(すなわち、対応するリフタ用ばね89によってそれぞれ付勢されたリフタセグメント82-84)の上部によってフープ材Fが上方に持ち上げられる。
このとき、例えば、リフタセグメント82の上部は、その上昇位置において、対応する右サイドガイド62Cよりも下側に位置する。より詳細には、リフタセグメント82の水平面82B(水平部)は、右サイドガイド62Cの水平壁210の下面の位置よりも下側に位置する。
フープ材Fの搬送時において、他のリフタセグメント83、84は、リフタセグメント82と同様に動作する。他のリフタセグメント83、84の各々についても、その上昇位置において、対応する右サイドガイドの水平壁よりも下側に位置する。
このように、搬送時のフープ材Fは、リフタ本体81によって下型4の上面47から持ち上げられた状態にあるため、搬送時のフープ材Fと順送り金型1における周辺部(ここでは、下型4における外形打ち抜き用ダイ46)との干渉が回避される。そのため、順送り金型1では、薄板片Wが打ち抜かれた後のフープ材Fを安定的に搬送することが可能となる。特に、リフタ65の長さL3を、内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の開口の前後方向の長さG2よりも大きく設定することにより、リフタ65によってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制することができる。
図6(B)に示すように、フープ材Fの打ち抜き時(非搬送時)には、その上面がストリッパプレート32の下面33によって下方に向けて押圧される。これにより、フープ材Fの下面は、下型4の上面47に当接した状態となる。また、例えば、リフタセグメント82は、2つのリフタ用ばね89の付勢力に抗する力で、フープ材Fの下面によって下方に押される。これにより、リフタセグメント82は、リフタ用孔87内に後退する(すなわち、後退位置まで移動する)。フープ材Fの打ち抜き時において、他のリフタセグメント83、84は、リフタセグメント82と同様に動作する。
再び図3を参照して、リフタ66は、平面視においてリフタ65と概ね平行に延在する。リフタ66は、リフタ65の右側に配置される。リフタ65と同様に、リフタ66の長さL4は、対応する内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の開口の長さG2よりも大きく設定される。ただし、リフタ66の長さL4は、フープ材Fの搬送ピッチXよりも大きく設定されることがより好ましい。なお、フープ材Fの幅方向において外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心C側に位置するリフタ65の長さL3は、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cからより離れたリフタ66の長さL4よりも大きく設定される。
また、フープ材Fの幅方向において外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心C側に位置するリフタ65におけるリフタ本体の上昇位置(すなわち、フープ材Fの持ち上げ量)は、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の中心Cからより離れたリフタ66のリフタ本体81の上昇位置よりも大きく(高く)設定されるとよい。これにより、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の表面に対するフープ材Fの持ち上げ量が高まり、フープ材Fと外形打ち抜き用ダイ46との干渉をより効果的に回避できる。
なお、フープ材Fの搬送時およびフープ材Fの打ち抜き時におけるリフタ66の動作は、上述のリフタ65の動作と同様である。また、本実施形態では、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側に2個のリフタ65およびリフタ66が設けられる例を示したが、それらの一方が省略されてもよい。さらに、リフタによってフープ材Fの搬送が妨げられることを抑制する効果は、少なくとも1個のリフタの搬送方向における長さが、内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の開口の前後方向の長さG2よりも大きく設定されることにより得られる。そのようなリフタは、外形打ち抜きステージVI及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つに設けられ得る。例えば、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側にリフタ65、66以外の複数のリフタが設けられた場合、それらの一部のリフタの搬送方向における長さは、内形打ち抜き用ダイ44の開口の前後方向の長さG2よりも小さく設定されてもよい。
次に、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側に設けられるリフタ63の変形例について説明する。
図7に示すように、リフタ63では、リフタセグメント72-75によるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量が、搬送方向において上流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されるとよい。
ここでは、リフタ本体71の上面は、水平方向を示す仮想線H(すなわち、下型4の上面47に沿う方向)を基準として、搬送方向の上流側に向けて上側に傾斜する傾斜面として形成されている。リフタセグメント72-75の上部は、それぞれリフタ本体71の上面を構成する傾斜した上面72B-75Bを有する。また、互いに隣接する上面72B-75Bの端部同士は、段差が生じないように滑らかに(同じ高さで)接続されている。
これに限らず、リフタセグメント72-75の上部がそれぞれ水平面を有する構成であってもよい。その場合、リフタセグメント72-75の、下型4の上面47からの進出量(または上昇位置)が、リフタセグメント72、73、74、75の順により小さく(またはより低く)なるように設定される。
なお、リフタ64を構成するリフタセグメントによるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量についても、リフタ63と同様に変更することが可能である。
このように、リフタセグメント72-75によるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量は、搬送方向においてより上流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されているため、外形打ち抜きステージVIにおいて打ち抜き加工された後のフープ材Fを、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側に配置されたリフタ63によって容易に支持することができる。
次に、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側に設けられるリフタ65の変形例について説明する。
図8に示すように、リフタ65では、リフタセグメント82-84によるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量が、搬送方向において下流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されるとよい。
ここでは、リフタ本体81の上面は、水平方向を示す仮想線H(すなわち、下型4の上面47に沿う方向)を基準として、搬送方向の下流側に向けて上側に傾斜する傾斜面として形成されている。リフタセグメント82-84の上部は、それぞれリフタ本体81の上面を構成する傾斜した上面82B-84Bを有する。また、互いに隣接する上面82B-84Bの端部同士は、段差が生じないように滑らかに(同じ高さで)接続されている。
これに限らず、リフタセグメント82-84の上部がそれぞれ水平面を有する構成であってもよい。その場合、リフタセグメント82-84の、下型4の上面47からの進出量(または上昇量)が、リフタセグメント82、83、84の順により大きく(またはより高く)なるように設定される。
なお、リフタ66を構成するリフタセグメントによるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量についても、リフタ65と同様に変更することが可能である。
このように、リフタセグメント82-84によるフープ材Fの持ち上げ量は、搬送方向においてより下流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されているため、外形打ち抜きステージVIにおいて打ち抜き加工されるフープ材Fを、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46側に円滑に移動させることができる。
以上、本発明を特定の実施形態に基づいて説明したが、これらの実施形態はあくまでも例示であって、本発明はこれらの実施形態によって限定されるものではない。上記実施形態に示した本発明に係る順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法の各構成要素は、必ずしも全てが必須ではなく、少なくとも本発明の範囲を逸脱しない限りにおいて適宜取捨選択することが可能である。
例えば、実施形態で示した順送り金型1に設けられる複数のステージについては、それらの一部を省略したり、新たに別のステージを付加したりすることができる。また、薄板片Wの形状については、実施形態に示したものに限らず、種々の変更が可能である。
また、第1ライン100側において、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の上流側にリフタ65、66と同様のリフタが更に設けられてもよい。或いは、第2ライン200側において、外形打ち抜き用ダイ46の下流側にリフタ63、64と同様のリフタが更に設けられてもよい。
1 :順送り金型
3 :上型
4 :下型
12 :上側ホルダ
14 :下側ホルダ
16 :バッキングプレート
18 :パンチプレート
20 :パイロット孔打ち抜き用パンチ
21 :スロット打ち抜き用パンチ
22 :内形打ち抜き用パンチ
24 :外形打ち抜き用パンチ
28 :ストリッパ
30 :ストリッパ本体
32 :ストリッパプレート
33 :下面
34 :パンチ挿通孔
35 :パンチ挿通孔
36 :パンチ挿通孔
38 :パンチ挿通孔
40 :ダイプレート
42 :パイロット孔打ち抜き用ダイ
43 :スロット打ち抜き用ダイ
44 :内形打ち抜き用ダイ
44A:開口
46 :外形打ち抜き用ダイ
46A:開口
47 :上面
48 :排出孔
61A-61F:左サイドガイド
62A-62E:右サイドガイド
63-66:リフタ
71 :リフタ本体
72-75:リフタセグメント
72A:前面
72B-75B:上面
72C:傾斜部
73A:後面
75C:傾斜部
77 :リフタ用孔
79 :リフタ用ばね
80 :ばね収容孔
81 :リフタ本体
82-84:リフタセグメント
82A:前面
82B-84B:上面
82C:傾斜部
83 :リフタセグメント
83A:後面
84 :リフタセグメント
84C:傾斜部
87 :リフタ用孔
89 :リフタ用ばね
90 :ばね収容孔
100:第1ライン
101:連結部材
110:水平壁
111:水平壁
200:第2ライン
201:連結部材
210:水平壁
C :中心
Da :内形
Db :外形
F :フープ材
H :水平方向を示す仮想線
M :積層鉄心
P :パイロット孔
S :スロット
W :薄板片
3 :上型
4 :下型
12 :上側ホルダ
14 :下側ホルダ
16 :バッキングプレート
18 :パンチプレート
20 :パイロット孔打ち抜き用パンチ
21 :スロット打ち抜き用パンチ
22 :内形打ち抜き用パンチ
24 :外形打ち抜き用パンチ
28 :ストリッパ
30 :ストリッパ本体
32 :ストリッパプレート
33 :下面
34 :パンチ挿通孔
35 :パンチ挿通孔
36 :パンチ挿通孔
38 :パンチ挿通孔
40 :ダイプレート
42 :パイロット孔打ち抜き用ダイ
43 :スロット打ち抜き用ダイ
44 :内形打ち抜き用ダイ
44A:開口
46 :外形打ち抜き用ダイ
46A:開口
47 :上面
48 :排出孔
61A-61F:左サイドガイド
62A-62E:右サイドガイド
63-66:リフタ
71 :リフタ本体
72-75:リフタセグメント
72A:前面
72B-75B:上面
72C:傾斜部
73A:後面
75C:傾斜部
77 :リフタ用孔
79 :リフタ用ばね
80 :ばね収容孔
81 :リフタ本体
82-84:リフタセグメント
82A:前面
82B-84B:上面
82C:傾斜部
83 :リフタセグメント
83A:後面
84 :リフタセグメント
84C:傾斜部
87 :リフタ用孔
89 :リフタ用ばね
90 :ばね収容孔
100:第1ライン
101:連結部材
110:水平壁
111:水平壁
200:第2ライン
201:連結部材
210:水平壁
C :中心
Da :内形
Db :外形
F :フープ材
H :水平方向を示す仮想線
M :積層鉄心
P :パイロット孔
S :スロット
W :薄板片
Claims (11)
- 所定の搬送方向に間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜くための順送り金型であって、
前記帯状薄鋼板において前記各薄板片に対応する部分への打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される複数のステージが設けられ、
前記複数のステージは、前記薄板片の外形を打ち抜く外形打ち抜きステージを含み、
前記外形打ち抜きステージは、外形打ち抜き用パンチ、外形打ち抜き用ダイを含み、
前記外形打ち抜きステージ及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つには、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から前記帯状薄鋼板を持ち上げる1個以上のリフタが設けられ、
前記1個以上のリフタのうちの少なくとも1個のリフタの前記搬送方向の長さは、当該少なくとも1個のリフタの上流側における打ち抜き加工によって前記帯状薄鋼板に形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口における前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい、順送り金型。 - 前記少なくとも1個のリフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記帯状薄鋼板の搬送ピッチよりも大きい、請求項1に記載の順送り金型。
- 前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に配置され、当該リフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの開口の前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい、請求項1または請求項2に記載の順送り金型。
- 前記複数のステージは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜きステージの上流側において前記薄板片の内形を打ち抜く内形打ち抜きステージを含み、
前記内形打ち抜きステージは、内形打ち抜き用パンチおよび内形打ち抜き用ダイを含み、
前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの上流側に配置され、当該リフタの搬送方向の長さは、前記内形打ち抜き用ダイの開口の前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい、請求項1から請求項3のいずれか1項に記載の順送り金型。 - 前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向に連なるように分割された複数のリフタセグメントを有する、請求項1から請求項4のいずれか1項に記載の順送り金型。
- 前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの下流側に配置され、
前記各リフタセグメントによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、前記搬送方向においてより上流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より高く設定されている、請求項5に記載の順送り金型。 - 前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向における前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの上流側に配置され、
前記各リフタセグメントによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、前記搬送方向においてより下流側に位置するリフタセグメントほど、より低く設定されている、請求項5に記載の順送り金型。 - 前記少なくとも1個のリフタは、前記搬送方向に直交する方向に間隔をおいて配置された2個またはそれ以上の前記リフタを含む、請求項1から請求項7のいずれか1項に記載の順送り金型。
- 前記2個のリフタのうち、前記搬送方向に直交する方向において、前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの中心により近い部位を持ち上げる一方のリフタによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量は、他方のリフタによる前記帯状薄鋼板の持ち上げ量よりも大きい、請求項8に記載の順送り金型。
- 前記複数のステージは、前記帯状薄鋼板の幅方向に並ぶように設定された2つのラインに対してそれぞれ設けられる、請求項1から請求項9のいずれか1項に記載の順送り金型。
- 所定の搬送方向に間欠的に搬送される帯状薄鋼板から薄板片を打ち抜くための順送り金型を用いた加工方法であって、
前記帯状薄鋼板において前記各薄板片に対応する部分への打ち抜き加工がそれぞれ実施される複数のステージが設けられ、
前記複数のステージは、前記薄板片の外形を打ち抜く外形打ち抜きステージを含み、
前記外形打ち抜きステージでは、前記帯状薄鋼板の非搬送時に、外形打ち抜き用パンチおよび外形打ち抜き用ダイによって前記帯状薄鋼板の打ち抜き加工が行われ、前記帯状薄鋼板の搬送時に、前記外形打ち抜きステージ及びそれに隣接するステージのうちの少なくとも1つに設けられた1個以上のリフタによって前記外形打ち抜き用ダイの表面から前記帯状薄鋼板が持ち上げられ、
前記1個以上のリフタのうちの少なくとも1個のリフタの前記搬送方向の長さは、当該少なくとも1個のリフタの上流側における打ち抜き加工によって前記帯状薄鋼板に形成される複数の開口のうちの最大の開口における前記搬送方向の長さよりも大きい、順送り金型を用いた加工方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/029156 WO2024024046A1 (ja) | 2022-07-28 | 2022-07-28 | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 |
| JP2022555802A JP7171975B1 (ja) | 2022-07-28 | 2022-07-28 | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/029156 WO2024024046A1 (ja) | 2022-07-28 | 2022-07-28 | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024024046A1 true WO2024024046A1 (ja) | 2024-02-01 |
Family
ID=84046001
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/029156 WO2024024046A1 (ja) | 2022-07-28 | 2022-07-28 | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7171975B1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2024024046A1 (ja) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59102222U (ja) * | 1982-12-24 | 1984-07-10 | 日産自動車株式会社 | プログレシブ加工用プレス型 |
| JPH0475728A (ja) * | 1990-07-13 | 1992-03-10 | Toshiba Corp | 順送プレス型装置における製品排出方法 |
| JP6245978B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-26 | 2017-12-13 | 株式会社三井ハイテック | 打ち抜き金型装置及びそれを用いた積層鉄心の製造方法 |
| JP2019166551A (ja) * | 2018-03-23 | 2019-10-03 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 加工装置 |
-
2022
- 2022-07-28 WO PCT/JP2022/029156 patent/WO2024024046A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2022-07-28 JP JP2022555802A patent/JP7171975B1/ja active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59102222U (ja) * | 1982-12-24 | 1984-07-10 | 日産自動車株式会社 | プログレシブ加工用プレス型 |
| JPH0475728A (ja) * | 1990-07-13 | 1992-03-10 | Toshiba Corp | 順送プレス型装置における製品排出方法 |
| JP6245978B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-26 | 2017-12-13 | 株式会社三井ハイテック | 打ち抜き金型装置及びそれを用いた積層鉄心の製造方法 |
| JP2019166551A (ja) * | 2018-03-23 | 2019-10-03 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 加工装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7171975B1 (ja) | 2022-11-15 |
| JPWO2024024046A1 (ja) | 2024-02-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4746914B2 (ja) | プレス方法およびプレス型 | |
| US9887038B2 (en) | Blanking die apparatus and method for manufacturing laminated iron core | |
| CN110709181B (zh) | 冲压成型品的制造方法以及冲压生产线 | |
| CN106238605A (zh) | 一种片材冲压装置 | |
| CN103785754A (zh) | 一种冷冲压拉延模具 | |
| JP2021159944A (ja) | 燃料電池用セパレータの製造方法、および燃料電池用セパレータの製造装置 | |
| JP2007190570A (ja) | プレス送り込み方法及びその設備 | |
| CN110138156B (zh) | 一种利用废片自扣方式制造散片电机铁芯方法 | |
| WO2024024046A1 (ja) | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 | |
| CN104014627B (zh) | 制造层叠至少两个母材的马达重量平衡芯的装置 | |
| US11642714B2 (en) | Progressive pressing method, progressive pressing device, manufacturing method for fuel cell separators and manufacturing apparatus for fuel cell separators | |
| WO2023199503A1 (ja) | 順送り金型およびこれを用いた加工方法 | |
| US9757786B2 (en) | Die apparatus and manufacturing method of metal product using die apparatus | |
| KR100591251B1 (ko) | 코어철심, 이를 성형,적층시키는 금형, 그 적층방법 | |
| JP2021159943A (ja) | 順送プレス装置および燃料電池用セパレータの製造装置 | |
| JP5796526B2 (ja) | 打ち抜き加工装置および打ち抜き加工方法 | |
| CN109562432B (zh) | 层叠铁芯的制造装置以及层叠铁芯的制造方法 | |
| US11583906B2 (en) | Manufacturing method for fuel cell separator, and manufacturing apparatus for fuel cell separator | |
| JP2024015464A (ja) | 積層鋼板製造装置、及び積層鋼板製造方法 | |
| JP4797455B2 (ja) | プレス順送金型装置およびモータ又はイグニッション用のコア | |
| JP2006205240A (ja) | 順送式のプレス成形装置 | |
| KR101875524B1 (ko) | 펜슬코어 제조장치 | |
| JP2005211935A (ja) | トランスファフィーダ | |
| CN221184361U (zh) | 高效自动冲裁装置 | |
| KR920008572B1 (ko) | 성형금형 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2022555802 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22953135 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |