WO2021111669A1 - インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 - Google Patents
インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021111669A1 WO2021111669A1 PCT/JP2020/026424 JP2020026424W WO2021111669A1 WO 2021111669 A1 WO2021111669 A1 WO 2021111669A1 JP 2020026424 W JP2020026424 W JP 2020026424W WO 2021111669 A1 WO2021111669 A1 WO 2021111669A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- liquid level
- float
- cleaning
- level detection
- container
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 363
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 232
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 171
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 57
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002238 attenuated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000013361 beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000013011 mating Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J2/00—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed
- B41J2/005—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by bringing liquid or particles selectively into contact with a printing material
- B41J2/01—Ink jet
- B41J2/135—Nozzles
- B41J2/165—Prevention or detection of nozzle clogging, e.g. cleaning, capping or moistening for nozzles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J2/00—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed
- B41J2/005—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by bringing liquid or particles selectively into contact with a printing material
- B41J2/01—Ink jet
- B41J2/17—Ink jet characterised by ink handling
- B41J2/18—Ink recirculation systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an inkjet recording device, a cleaning unit of the inkjet recording device, and a liquid level detecting device.
- Patent Document 1 WO2015 / 114814
- a liquid level detection device for detecting a liquid level is provided in an auxiliary ink container for replenishing ink, and the liquid level detection signal detected by the liquid level detection device is used.
- an inkjet recording apparatus configured to replace an ink cartridge and replenish the ink in the auxiliary ink container when the ink in the auxiliary ink container falls below a predetermined liquid level.
- the auxiliary ink container for storing ink is prepared to replenish the ink container (main ink container) for storing the ink supplied to the print head with a required amount of ink.
- Patent Document 1 discloses two types of liquid level detection devices. That is, in the first liquid level detection device, a plurality of (specifically, four) electrode rods are installed in the container, an electric wire is connected to each electrode rod, and the liquid level detection signal is transmitted to the container by the electric wire. It is configured to be taken out to the outside (see the description in paragraphs 0034 to 0038 of Patent Document 1).
- the other liquid level detector has a stopper in the container at a position where the ink volume (liquid level) corresponds to the standard level amount, and float A that detects that the ink has reached the standard level, and the ink runs out.
- a float B for detecting such a situation is provided, and the liquid level detection signal detected using each of these floats is configured to be output to the outside of the container by an electric wire (paragraphs 0072 to paragraph 0072 to paragraph). See description in 0075).
- the liquid level detection signal detected by the detection unit arranged in the container is transmitted to the container by an electric wire. It is configured to output to the outside of. Therefore, if the container is to be removed, it is necessary to first remove the electric wire and then the container, which complicates the removal work of the container. Further, when mounting the container, it is necessary to mount the container at a predetermined position with an electrode rod, a float, or the like placed in the container, which further complicates the work. In addition, there are problems in these operations for making an electrically stable connection (preventing a short circuit, maintaining a good state of electrical contact).
- a print head is indispensable for printing. Since this print head is accompanied by very high-speed ink flight, it is unavoidable that stains are generated due to ink scattering or the like during use, and cleaning work for cleaning the print head is required from time to time.
- This cleaning unit for automatically cleaning the print head in the inkjet recording device.
- This cleaning unit is provided at the bottom of the cleaning tank, a cleaning tank in which the print head is set (accommodated) for cleaning, a cleaning nozzle for ejecting cleaning liquid toward the print head set in the cleaning tank, and cleaning. It is provided with a collection container for collecting the cleaning liquid after cleaning.
- a liquid level detection device for detecting the liquid level of the cleaning liquid in the collection container is provided, and the worker is notified that the cleaning liquid has reached a certain amount or more by using the detection signal of the liquid level detection device, and the worker informs the worker of the recovery container. Perform the work of removing and draining the cleaning liquid in the container. Then, the empty collection container is attached to the bottom of the washing tank again.
- an object of the present invention is to provide an inkjet recording device, a cleaning unit of the inkjet recording device, and a liquid level detecting device, which are easy to remove and attach the container and are effective for preventing the liquid from flowing out of the container. To do.
- the present invention provides a print head for printing, an ink container, and the ink that supplies the ink in the ink container to the print head and is not used for printing.
- An inkjet recording device having a path for collecting the ink in the ink container, a control unit for supplying the ink to the print head, and a control unit for controlling the printing operation of the print head, and can accommodate the print head.
- a cleaning tank having a space and a liquid outlet at the bottom, a cleaning nozzle that ejects and cleans the cleaning liquid toward the print head housed in the cleaning tank, and an outflow from the liquid outlet of the cleaning tank.
- a cleaning unit provided with a collection container for collecting the cleaning liquid to be printed and a first liquid level detecting device for detecting the liquid level of the cleaning liquid in the recovery container are provided, and the first liquid level detecting device is the recovery container.
- a first float that moves in accordance with the liquid level and a first holder that holds the first float are provided inside, and when the first float approaches the outside of the collection container, the said A first sensor that outputs a liquid level detection signal is installed, and the control unit is an ink-ink recording device that determines the mounting status of the collection container from the liquid level detection signal.
- a cleaning unit of an inkjet recording apparatus having a print head that prints with ink
- the cleaning unit has a space capable of accommodating the print head and a liquid outlet portion.
- a cleaning tank having a cleaning tank, a cleaning nozzle for ejecting and cleaning the cleaning liquid toward the print head housed in the cleaning tank, and a collection for collecting and cleaning the cleaning liquid flowing out from the liquid outlet portion of the cleaning tank.
- a container and a liquid level detection device for outputting a liquid level detection signal of the cleaning liquid in the recovery container are provided, and the liquid level detection device moves in the recovery container in accordance with the liquid level.
- a float and a holder for holding the float are provided, and a sensor that outputs the liquid level detection signal when the float is close to the collection container is installed outside the collection container, and the liquid level detection signal is transmitted. It is a cleaning unit of an inkjet recording apparatus, which is characterized in that the mounting state of the collection container is determined from the liquid level detection signal by using the liquid level detection signal.
- the present invention is a liquid level detecting device for detecting the liquid level of the liquid in the container, and the liquid level detecting device corresponds to the liquid level in the recovery container.
- a float that moves with the float and a holder that holds the float are provided, and a sensor that outputs the liquid level detection signal when the float approaches is installed outside the collection container.
- the liquid level detection device is characterized in that the mounting state of the collection container is determined from the liquid level detection signal using the detection signal.
- an inkjet recording device a cleaning unit of the inkjet recording device, and a liquid level detecting device, which are easy to remove and attach the container and are effective for preventing the liquid from flowing out of the container. Can be done.
- FIG. 1 It is a figure which shows the use situation of the inkjet recording apparatus in the Example of this invention. It is a figure which shows the schematic cross section of the inkjet recording apparatus main body in an Example. It is a figure which shows the schematic structure of the control part of the inkjet recording apparatus in an Example. It is a figure which shows the whole path composition of the inkjet recording apparatus in an Example. It is a block diagram of the head cleaning unit in an Example. It is a figure which shows the structure of the float of the liquid level detection apparatus in an Example. It is a figure which shows the exploded view of the float of the liquid level detection apparatus in an Example. It is sectional drawing of the cleaning unit in the state which set the print head. It is a figure which shows the state which detected that the cleaning liquid was almost full in the collection container in a cleaning unit. It is a figure which shows the state which removed the collection container in a cleaning unit.
- FIGS. 1 to 10 specific examples of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 10.
- the present invention is not limited to the examples described below. Further, in each of the following figures, the same device may be assigned the same number (reference numeral), and the description of the device already described may be omitted.
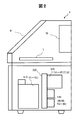
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a usage state of the inkjet recording device 100 in this embodiment.
- the inkjet recording apparatus 100 includes a main body 1, a main body 1, a print head 2 connected to the main body 1 via a conduit 5 (for a print head), a main body 1, and a cleaning unit. It is provided with a cleaning unit 3 connected by a conduit 6 for use.
- the inkjet recording device 100 is installed, for example, on a production line in a factory where food, beverages, and the like are produced.
- the main body 1 has a function of supplying ink for printing to the print head 2 and collecting ink not used by the print head 2. Further, the main body 1 is provided with an ink container for accommodating ink, an auxiliary ink container for replenishing the ink container with ink when the ink in the ink container is used for printing and becomes low, and also for ink and solvent. It has a built-in path for supply and recovery, and an on-off valve group (electromagnetic valve group) and a pump group provided in the middle of the path. Further, the main body 1 is operated by a control unit 7 (not shown in FIG.
- the main body 1 is installed in a place where the space required for regular maintenance work can be secured.
- the print head 2 is fixed to the print head fixing metal fitting 13 installed near the belt conveyor 11 and is close to the print objects 12A and 12B fed on the belt conveyor 11 in the direction of the arrow X. It is installed.
- the print target object 12A indicates a print target object before printing
- the print target object 12B indicates a print target object after printing.
- the print head 2 is equipped with parts such as a nozzle, a charging electrode, and a deflection electrode (not shown in FIG. 1) on the head base 16. Further, the print head 2 is provided with a protective cover 17 for the purpose of protecting these parts.
- the cleaning unit 3 provided for cleaning the print head 2 is attached in the vicinity of the belt conveyor 11 by a fixing jig 92 and a collating portion 93 for mating the fixing jig 92. ..
- the cleaning unit 3 includes a cleaning tank 71, a cleaning nozzle for cleaning the print head 2 set in the cleaning tank (not shown in FIG. 1), a collection container 4 for collecting the cleaning liquid, and the like.
- the conduit 6 is a conduit for supplying the cleaning liquid from the main body 1 to the cleaning unit 3.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a cross section of the main body 1 of the inkjet recording device in the embodiment.
- the container unit 510 is a portion that houses a container group (ink container 31, auxiliary ink container 32, solvent container 33).
- the flow path board 520 is a board portion that organizes flow paths (paths) and the like for supplying / recovering ink and supplying / recovering solvent.
- the pump unit 530 is a portion to which a group of pumps (pumps 34 to 35, 37, 38) provided in the middle of the path are attached.
- the solenoid valve unit 540 is a portion to which a solenoid valve group (solenoid valves 49, 50, 53 to 56) for opening and closing a flow path provided in the middle of the path is attached.
- a solenoid valve group solenoid valves 49, 50, 53 to 56
- the specific configuration of the pump group and the solenoid valve group will be described later.
- a control unit 7 is arranged on the upper part of the main body 1, and the control unit 7 executes control of the entire inkjet recording device 100.
- the specific configuration of the control unit 7 will be described later.
- An operation display unit 8 is provided on the upper part of the front surface of the main body 1.
- the operation display unit 8 has a configuration in which a touch panel for operation and a display device are integrally incorporated.
- the operation display unit may be provided with the operation unit and the display device separately.
- a power supply 70 for use in the inkjet recording device 100 is installed on the upper part of the main body 1.
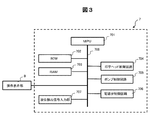
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of the control unit 7.
- the control unit 7 includes a microprocessing unit (MPU) 701, a read-only memory (ROM) 702 that stores a program for the operation of the MPU 701 and data / information necessary for the operation, and data of print contents. It also has a random access memory (RAM) 703 that stores data required for control, input signals, and the like.
- MPU microprocessing unit
- ROM read-only memory
- RAM random access memory
- control unit 7 has a print head control circuit 704 that controls the charging voltage and deflection voltage for driving the print head 2 and printing, various timings, and the like, and pump control for controlling the drive / stop of the pump group. It has a circuit 705 and a valve control circuit 706 that controls opening and closing of a solenoid valve group.
- the MPU 701 controls the print head control circuit 704, the pump control circuit 705, and the valve control circuit 706 to control the entire inkjet recording apparatus.
- control unit 7 in this embodiment has a liquid level detection signal input unit 707 for inputting a liquid level detection signal of each liquid level detection device.
- the liquid level detection signal input to the control unit 7 via the liquid level detection signal input unit 707 is temporarily stored in the RAM 703 and used for calculation, determination, control, and the like by the MPU.
- the MPU 701 recognizes that the liquid level in the container has reached a predetermined position by the liquid level detection signal, and further displays a warning regarding a cleaning operation or the like on the operation display unit 8. Further, using this liquid level detection signal, a control signal for controlling the liquid level to a predetermined value is calculated, and the related pump group and solenoid valve group are controlled via the pump control circuit 705 and the valve control circuit 706. To do.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an overall path configuration of the inkjet recording apparatus in this embodiment.
- the inkjet recording device 100 includes a main body 1, a printing head 2, a head cleaning unit 3, and conduits 5 and 6 connecting them.
- the main body 1 and the print head 2 are connected by a conduit 5, and the main body 1 and the head cleaning unit 3 are connected by a conduit 6.
- an ink supply path (paths 801 to 803) for supplying ink from the main body 1 to the print head 2 will be described.
- the main body 1 is provided with an ink container 31 that holds the circulating ink 68A.
- the ink container 31 is connected to the path 801 at a portion immersed in the ink 68A, and a viscosity measuring instrument 45 and a solenoid valve 49 for opening and closing the path for supplying ink are installed in the middle of the path 801. doing.
- the viscometer 45 is provided to measure the viscosity of the ink and is input to the control unit 7. Specifically, it is input and stored in the RAM 703.
- the control unit 7 executes control for maintaining the viscosity of the ink 68A within a predetermined value or a predetermined range by the viscosity detection signal.
- the path 801 is connected to the ink supply pump 34 installed in the path 802 and used for sucking and pumping the ink 68A via the merging path 901. Then, on the output side of the pump 34, it is connected to a filter 39 (for ink supply) that removes foreign matter mixed in the ink 68A.
- the filter 39 is connected to a pressure regulating valve 46 that adjusts the pressure to an appropriate pressure for printing the ink 68A pumped from the pump 34, and the pressure regulating valve 46 measures the pressure of the ink 68A supplied to the nozzle 21. It is connected to the sensor 47.
- the path 802 in which the pressure sensor 47 is arranged passes through the conduit 5 and is connected to the print head 2. Specifically, it is connected to a switching valve 26 for controlling whether or not to supply ink 68A to the nozzle 21.
- the switching valve 26 is connected to a nozzle 21 provided with a discharge port for ejecting ink 68A via a path 803.
- the switching valve 26 is a three-way solenoid valve, and the switching valve 26 is connected to the ink supply path 802 and the nozzle cleaning path 812, and supplies ink 68A and solvent 69A to the nozzle 21. Can be switched.
- the ink recovery path (path 804) of the inkjet recording apparatus 100 in this embodiment will be described.
- the gutter 25 is connected to path 804.
- the path 804 passes through the conduit 5 and is connected to a filter 40 (for ink recovery) that removes foreign matter mixed in the ink arranged in the main body 1, and the filter 40 opens and closes the path 804.
- the solenoid valve 50 (for ink recovery) that performs the above.
- the solenoid valve 50 is connected to a pump 35 (for collecting ink) that sucks the ink particles 68B captured by the gutter 25, and the pump 35 is connected to the ink container 31.
- the ink container 31 is connected to the path 805 in an upper space that does not come into contact with the ink 68A, and the path 805 has a configuration that communicates with the outside of the main body 1.
- the control unit 7 opens the solenoid valve 50 and executes the control to drive the pump 35, the ink particles 68B captured by the gutter 25 are collected in the ink container 31 via these. ..
- the main body 1 is provided with a solvent container 33 that holds (accommodates) the solvent 69A for supplying the solvent to the ink container 31 and for cleaning the nozzles and the head.
- the solvent container 33 is connected to the path 809 at a portion immersed in the solvent 69A, and a pump 37 used for sucking and pumping the solvent is arranged in the path 809. Then, the pump 37 is connected to the branch path 903 in order to change the supply destination of the solvent 69A according to the purpose.
- the branch path 903 is connected to the solenoid valve 53 for opening and closing the flow path arranged in the path 810 in the solvent replenishment path, and the solenoid valve 53 is connected to the ink container 31 by the path. There is.
- the solenoid valve 53 may be opened and the pump 37 may be driven.
- the supply (replenishment) of the solvent to the ink container 31 is performed in order to keep the ink viscosity within the predetermined value range when the ink viscosity detected by the viscometer 45 becomes higher than the predetermined value.
- the control unit 7 determines that the ink viscosity input from the viscometer 45 has become higher than the viscosity suitable for printing, the control unit 7 opens the electromagnetic valve 53 and drives the pump 37.
- the solvent 69A in the solvent container 33 is supplied to the ink container 31, and the viscosity of the ink 68A is controlled to be appropriate.
- the solvent container 33 is provided with a liquid level detecting device 33A for detecting whether or not the solvent 69A in the solvent container 33 has a liquid level within an appropriate range.
- the liquid level detection device 33A has a float 331 that moves up and down in response to fluctuations in the liquid level and a holder 332 that holds the float 331 inside the solvent container 33.
- the holder 332 suppresses the float 331 from moving other than moving up and down. Stoppers (indicated by triangles in the figure) are provided at the upper and lower positions of the holder 332. Specifically, in the holder 332, stoppers are provided at positions where the float 331 detects the minimum liquid level and at positions where the maximum liquid level is detected, respectively.
- the sensors 333 and 334 that detect the float 331 are arranged so as to output a liquid level detection signal when the float approaches (closes) the stopper.
- the two sensors 333 and 334 are attached to the support member 335 on the outside of the solvent container 33. That is, the sensor 333 on the bottom side of the solvent container 33 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 331 moves to the lower stopper due to the liquid level fluctuation and approaches.
- the sensor 334 on the upper side of the solvent container 33 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 331 moves upward and approaches the stopper on the upper side.
- the sensors 333 and 334 of the liquid level detection device 33A are installed outside the solvent container 33, and the electric wire (not shown) for transmitting the liquid level detection signal to the control unit 7 is wired outside the solvent container 33. Detachment work (removal and installation work) of the solvent container 33 becomes easy.
- the sensor 333 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 331 moves to a position where it contacts the lower stopper of the holder 332. Further, the sensor 334 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 331 moves to a position where it comes into contact with the upper stopper of the holder 332.
- the liquid level detection signal detected by the sensors 333 and 334 is input to the control unit 7. Specifically, it is stored in the RAM 703 via the liquid level detection signal input unit 707 of the control unit 7 (see FIG. 3).
- the control unit 7 determines that the solvent 69A in the solvent container 33 is not within the predetermined liquid level range by using this liquid level detection signal
- the solvent is displayed on the operation display unit 8. Display the residual state of, or display a warning that the solvent is insufficient.
- the MPU 701 determines the excess or deficiency of the solvent by using the liquid level detection signal stored in the RAM 703, and if the solvent is insufficient, the solvent is insufficient and it is necessary to replenish the solvent.
- a warning such as the presence is displayed on the screen of the operation display unit 8. This allows the operator to know that the solvent needs to be replenished.
- the main body 1 is provided with an auxiliary ink container 32 for holding the replenishment ink 68C.
- the auxiliary ink container 32 is connected to the ink replenishment path 811 at a portion immersed in the ink 68C.
- the path 811 is connected to the solenoid valve 54 that opens and closes the path, and the solenoid valve 54 is connected to the pump 34 installed in the path 802 and used for sucking and pumping the ink 68C via the merging path 901. Has been done.
- the ink 68C in the auxiliary ink container 32 is fed to the print head 2, passes through the ink recovery path including the path 804, the solenoid valve 50, and the pump 35 via the nozzle 21, the gutter 25, and the ink container 31. Is replenished to.
- the timing for replenishing the ink container 31 with the ink in the auxiliary ink container 32 is performed by using the liquid level detection value of the liquid level detection device 31A that detects the liquid level of the ink in the ink container 31. That is, the ink container 31 is provided with a liquid level detecting device 31A that detects whether or not the ink in the ink container 31 has reached a reference liquid level which is an appropriate amount.
- This liquid level detection device 31A has the same configuration as the above-mentioned liquid level detection device 33A. That is, inside the ink container 31, there is a float 311 that moves up and down in response to fluctuations in the liquid level, and a holder 312 that holds the float 311 and suppresses movement other than the vertical movement of the float. Similar to the transfer, stoppers are provided above and below the holder 312. Further, the sensors 313 and 314 of the liquid level detection device 31A are attached to the support member 315 on the outside of the ink container 31. The sensor 313 provided on the lower outside of the ink container 31 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 311 is close to the lower stopper of the holder.
- the sensor 314 provided on the outer upper side of the container outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 311 is close to the stopper on the upper side of the holder 312. Since the sensor 313 and the sensor 314 are arranged outside the ink container 31, the work of attaching / detaching (removing / attaching) the ink container 31 for inspection and cleaning becomes easy.
- the liquid level detection signal detected by the sensors 313 and 314 is stored in the RAM 703 via the liquid level detection signal input unit 707 of the control unit 7 (see FIG. 3).
- the control unit 7 uses this liquid level detection signal to control the amount of ink in the ink container 31 to be a predetermined amount. Specifically, when the liquid level of the ink in the ink container 31 drops to the liquid level detected by the sensor 313, the ink replenishment to the ink container 31 is started. When the control unit 7 inputs the detection signal of the sensor 313 of the liquid level detection device 31A, the control unit 7 starts ink replenishment. That is, since the control unit 7 can know from the liquid level detection signal of the sensor 313 that the amount of ink (ink liquid level) in the ink container 31 has decreased to a predetermined amount or less, the control unit 7 can know that the amount of ink in the auxiliary ink container 32 has decreased.
- Ink 68C is replenished from the path 811, the path 802, and the print head 2 to the ink container 31 via the path 804.
- the solenoid valve 54 provided in the middle of the path is opened to drive the pump 34
- the ink supplied in the print head 2 is captured by the gutter 25, and the solenoid valve 50 provided in the middle of the path 804 is captured.
- the ink 68C in the auxiliary ink container 32 is supplied (replenished) to the ink container 31.
- the control unit 7 ends this ink replenishment operation. The end is performed when the control unit 7 closes the solenoid valve 54 and stops the pump 34.
- a liquid level detecting device 32A for detecting the liquid level of the ink in the auxiliary ink container 32 is also provided.
- the liquid level detection signal detected by the liquid level detection device 32A is also input to the control unit 7.
- the control unit 7 can input this liquid level detection signal to know the ink liquid level in the auxiliary ink container 32.
- the liquid level detecting device 32A has the same configuration as the other liquid level detecting devices (31A, 32A) already described. That is, the liquid level detecting device 32A has a float 321 that moves up and down in response to the fluctuation of the liquid level inside the auxiliary ink container 32, and a holder 322 that suppresses the movement of the float 321 other than the vertical movement.
- Stoppers are provided above and below the holder 322. Further, in the liquid level detection device 32A, the sensors 323 and 324 are attached to the support member 325 on the outside of the auxiliary ink container 32. The sensor 323 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 321 is close to the lower stopper. The sensor 324 outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 321 is close to the upper stopper. The liquid level detection signal detected by the sensors 323 and 324 is stored in the RAM 703 as an electric signal via the liquid level detection signal input unit 707 of the control unit 7 (see FIG. 3).
- the control unit 7 can know from this liquid level detection signal that the ink 68C in the auxiliary ink container 32 has decreased to a liquid level outside the predetermined range, and can perform control to replenish the auxiliary ink. Alternatively, a warning that ink needs to be replenished in the auxiliary ink container 32 is displayed on the operation display unit 8.
- the nozzle cleaning path (path 809 and path 812)
- the pump 37 arranged on the path 809 is connected to the path 812 via the branch path 903.
- the path 812 is connected to a solenoid valve 55 (for cleaning the nozzle) for opening and closing the flow path.
- the solenoid valve 55 is connected to a filter 41 (for cleaning the nozzle) for removing foreign matter mixed in the solvent 69A.
- the filter 41 is provided in the print head 2 via a path 812 passing through the conduit 5, and is connected to a switching valve 26 for controlling whether or not to send the cleaning solvent 69A to the nozzle 21. ing.
- the cleaning unit 3 for cleaning the print head 2 has a cleaning tank 71 having an upper surface open and a storage space for inserting (setting) the print head 2, and a print head set in the cleaning tank 71.
- the solvent 69A contained in the solvent container 33 is used as the cleaning liquid used in the cleaning unit 3. Therefore, the solvent 69A of the solvent container 33 is connected to the path 809 at the immersed portion, and the pump 37 provided in the middle of the path 809 is connected to the path 821 via the branch path 903.
- the path 821 is connected to the cleaning nozzle 72 of the cleaning unit 3.
- a solenoid valve 56 for opening and closing the flow path is arranged on the path 822.
- the control unit 7 opens the solenoid valve 56 and controls to drive the pump 37, so that the solvent 69A in the solvent container 33 is used as a “cleaning liquid” and the cleaning nozzle 72 in the head cleaning unit 3 is used.
- the cleaning liquid may be supplied from a cleaning liquid supply device provided separately from the solvent in the solvent container of the main body 1.
- air can be ejected from the air nozzle 73 to dry the print head 2.
- the air nozzle 73 is connected to the path 825, and air can be injected into the cleaning tank 71 by driving a pump 38 provided in the middle of the path 825.
- the main body 1 and the cleaning unit are connected by a conduit 6.
- the collection container 4 is provided to accommodate the cleaning liquid 69B after cleaning, and when the cleaning liquid 69B in the container reaches a certain level or higher, the collection container 4 is removed and the cleaning liquid 69B is discharged.
- the collection container 4 emptied by the discharge of the cleaning liquid 69B is reattached to the bottom of the cleaning tank 71 in order to accommodate the cleaning liquid 69B.
- the liquid level detection device 4A is provided in the collection container 4 of the cleaning unit 3.
- the liquid level detection device 4A includes a float 74 that can move up and down according to the liquid level in the collection container 4, and a holder 75 that holds the float 74. Further, on the outside of the collection container 4, a sensor 76 that outputs a liquid level detection signal when the float 74 moves up and down and approaches is installed.
- the sensor 76 and the electric wire 76A for transmitting the liquid level detection signal to the control unit 7 are provided outside the collection container 4, they do not hinder the removal or installation of the collection container 4.
- the liquid level detection device 4A used for the collection container is reduced. That is, in the case of the liquid level detection devices 31A, 32A, and 33A, two sensors are provided at the top and bottom. On the other hand, in the liquid level detecting device 4A, only one sensor 76 is provided.
- the liquid level detection device 4A is provided with a stopper 75A at an intermediate position of the holder 75, and limits the range of movement of the float 74 in the vertical direction from the intermediate position to the upper side. Then, the sensor 76 is arranged so as to output a liquid level detection signal when the float 74 is close to the stopper 75A.
- the position where the stopper 75A is provided in the holder 75 is an intermediate position between the upper and lower parts (a position below the liquid level for detecting the maximum capacity of the container, and above the position when there is no liquid in the container).
- Position The installation position of the stopper 75A is the position of the liquid level where the risk of the liquid in the container overflowing to the outside immediately in the operating state is considered to be small, considering the frequency of removing the container and discharging the cleaning liquid 69B in the container. To do.
- the position of the stopper 75A is preferably in the range of 50 to 90% when the liquid level position corresponding to the maximum volume is 100%.
- the reason why it is set to 50% is that if it is lower than that, the sensor 76 frequently outputs a liquid level detection signal, so that the collection container 4 is frequently removed and attached in order to discharge the cleaning liquid 69B. is there.
- 90% is set because when the control unit 7 warns the operation display unit 8, the cleaning liquid 69B may overflow if the worker is a little late in noticing the tendency. This is to secure a spare time.
- the float 74 does not move when the liquid level of the liquid (cleaning liquid 69B) in the collection container 4 is still low and below the position of the stopper 75A. Therefore, the sensor 76 continuously outputs the liquid level detection signal during the period when the float 74 does not move (in other words, during the period when the cleaning liquid 69B of the collection container 4 is low). Then, when the liquid level of the cleaning liquid 69B in the collection container 4 rises above the position of the stopper 75A and the float 74 moves upward, the sensor 76 stops the output of the liquid level detection signal.
- the liquid level detection signal by the sensor 76 is input to the control unit 7. Specifically, it is stored in the RAM 703 via the liquid level detection signal input unit 707 of the control unit 7 (see FIG. 3).
- the control unit 7 While the liquid level detection device continuously outputs the liquid level detection signal, the control unit 7 has a small amount of liquid (cleaning liquid 69B) in the collection container 4 (in other words, can still sufficiently store the cleaning liquid 69B). ) Can be judged. Further, the control unit 7 indicates that when the output of the liquid level detection signal disappears, the cleaning liquid 69B in the collection container is almost full (in other words, the collection container cannot contain the cleaning liquid 69B). I can judge. That is, when the liquid level detection signal is interrupted, the control unit 7 can display a warning on the operation display unit 8 instructing that the cleaning liquid 69B in the collection container 4 should be discharged.
- the control unit 7 issues a warning not to perform cleaning when the liquid level detection signal has disappeared (in this embodiment, it is displayed on the operation display unit 8). In this way, not only the liquid level is detected by using the liquid level detection signal of the liquid level detection device 4A, but also when there is a risk that the cleaning liquid 69B in the recovery container 4 may accumulate and overflow, or the recovery container 4 itself may be overwhelmed. It is possible to determine the case where the liquid is removed from the cleaning unit 3 and may flow out to the outside. In addition, the worker can be notified of this. Therefore, the control unit 7 displays an appropriate warning based on this determination. Alternatively, it is possible to control so that the cleaning operation by the cleaning unit is not performed.
- the liquid level detection device 4A installed in the collection container 4 is provided with a stopper 75A provided in the middle portion of the holder 75 and one sensor 76 for detecting the liquid level at that position.
- the liquid level detecting device 4A may have the same configuration as the other liquid level detecting devices 31A, 32A, 33A described above. That is, stoppers are provided at the detection positions of the lowest and maximum liquid levels to be detected, the float can be moved up and down between these two stoppers according to the fluctuation of the liquid level, and the upper and lower stoppers are provided on the outside of the container. It may be configured to have two sensors arranged to output a liquid level detection signal when the float is positioned. Even with such a configuration, when the upper sensor outputs a liquid level detection signal, it can be determined that the container is almost full of liquid and the amount of liquid that can be stored has decreased.
- the control unit 7 warns the operation display unit 8 that the collection container 4 should be removed and the cleaning liquid 69B should be discharged. As a result, the operator can remove the collection container 4 and discharge the cleaning liquid 69B inside.
- the control unit 7 determines that there is a high possibility that the collection container 4 has been removed after the operation of the upper sensor until the lower sensor operates (outputs the liquid level detection signal). be able to. In that case, the control unit 7 displays the warning as described above. Alternatively, during that period, it is possible to control so that the cleaning operation is not performed.
- the cleaning liquid 69B in the collection container 4 can be discharged.
- the cleaning liquid 69B may be discharged to the main body 1 side, or may be discharged to another container.
- a lid block 81 is installed above the cleaning tank 71.
- the lid block 81 has a print head insertion portion 81A, and the print head 2 can be inserted through the insertion portion 81A.
- a lid member 83 is provided on the lower surface of the insertion portion 81A, and is normally closed by the spring force of the lid hinge 82. This is to prevent dust and the like from entering the cleaning tank 71.
- Reference numeral 85 denotes a cover that protects the piping portion.
- the operator When cleaning the print head 2, the operator inserts the print head 2 into the cleaning tank 71. At this time, the lid member 83 closed by the spring force of the lid hinge 82 rotates (rotates clockwise in FIG. 5), and the print head 2 is set in the cleaning tank 71.
- the cleaning liquid sent by the path 822 flows into the cleaning nozzle 72 through the liquid joint 84.
- the filter 43 is provided in the middle of the path 822 to remove dust in the cleaning liquid.
- the cleaning nozzle 72 has two liquid discharge holes 72A and 72B in this embodiment in order to inject the cleaning liquid corresponding to the cleaning portion of the print head 2 to be cleaned.
- the air nozzle 73 provided for drying the print head 2 after cleaning is also provided with two air discharge holes 73A and 73B.
- a liquid outlet portion 71A is provided at the bottom portion of the cleaning tank 71, and also has a mounting portion 71B used when mounting the recovery container 4. From this liquid outlet portion 71A, the cleaning liquid 69B after cleaning is dropped (flowed down) into the recovery container 4 by gravity.
- the collection container 4 has a mounting portion 77A for mounting on the cleaning tank 71 at the upper end of the container 77. In this embodiment, both the mounting portions 71B and 77A are mounted by a screw structure. The removal of the collection container 4 can be carried out by the worker twisting the collection container 4 in the removal direction (for example, counterclockwise direction).
- the collection container 4 is attached by twisting in the attachment direction (for example, clockwise).
- the float 74 and the holder 75 are arranged in the collection container 4 among the components of the liquid level detection device 4A.
- the stopper 75A is formed at an intermediate position of the holder 75 so that the float 74 cannot move below the position of the stopper 75A.
- Reference numeral 75B is an upper stopper, which defines the maximum liquid level to be detected.
- 75C to 75F are openings provided to allow liquid to flow into the holder 75.
- a sensor 76 of the liquid level detection device 4A is installed on the outside of the collection container 4 so as to output a liquid level detection signal while the float 74 is present at the position of the stopper 75A.
- the float 74 in the liquid level detection device 4A uses a magnet type float in which a magnet 86 is installed as a detector inside, and the sensor 76 uses a liquid level detection signal (electrical signal) when the magnet 86 is in close proximity to the float 74. It is a magnet type proximity sensor that outputs.
- the detailed operation of the liquid level detection device 4A has already been described and will be omitted.
- a proximity sensor other than the magnet type sensor for example, another known proximity sensor such as a "high frequency transmission type proximity sensor” can be used.
- a metal is provided inside the float, and as a sensor outside the container, a high-frequency current is applied to the coil to generate a high-frequency magnetic field, and the float (metal) is generated in this high-frequency magnetic field as the liquid level changes.
- an induced current flows through the metal and the oscillation is attenuated (or stopped). Therefore, this can be realized by detecting this change in the oscillation state with the transmission state detection circuit and operating the output circuit.
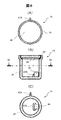
- FIGS. 6 and 7 are views showing the configuration of a float, in which FIG. 6A is a top view, FIG. 6B is a front sectional view, and FIG. 6C is a sectional view taken along line MM of FIG. 6B.
- FIG. 7 shows the components of the float as an exploded view.
- the float of the liquid level detection device for example, the float 74, includes a housing 87, a lid 89, a lid sealing member 88, a magnet 86, and a magnet fixing portion 87B for fixing the magnet 86.
- the housing 87 is configured to have an in-container positioning portion 87A for positioning the inside of the container.
- the lid fixing portion 87C is for fixing the lid 89 to the housing 87.
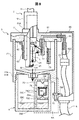
- FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view of the cleaning unit in a state where the print head 2 is set in the cleaning unit 3.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a state in which it is detected that the amount of liquid in the collection container 4 (the amount of the cleaning liquid 69B after cleaning) is almost full in the cleaning unit 3.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a state in which the collection container 4 is removed in the cleaning unit.
- the print head 2 when cleaning the print head 2, the print head 2 is set (inserted) in the cleaning unit 3.
- the protective cover 17 of the print head 2 is removed.
- a slide door is provided on the protective cover, and the slide door is slid at the time of insertion to expose the internal parts (nozzle, charging electrode, deflection electrode, etc.) of the print head 2 in the cleaning tank 71. For example, the trouble of removing the protective cover 17 can be saved.
- the cleaning nozzle 72 ejects the cleaning liquid toward the print head as indicated by arrows J and K to clean the print head. While cleaning the components such as the nozzle 21, the charging electrode 23, the deflection electrode 24, and the gutter 25 assembled inside the print head 2 with the cleaning liquid, the components such as the nozzle 21, the charging electrode 23, the deflection electrode 24, and the gutter 25 are washed down by gravity as shown by the arrow L.
- the cleaning liquid that has flowed down to the lower part of the cleaning tank 71 flows toward the collection container 4 as shown by the arrow M, and is stored inside the collection container 4. When the cleaning of the print head is completed, the print head is dried by the air nozzle 73.
- the cleaning liquid 69B after cleaning falls from the cleaning tank 71, and the liquid level of the cleaning liquid 69B in the collection container 4 rises.
- the liquid level is still low, and the liquid level detection device.
- the float 74 of 4A does not fluctuate, and the sensor 76 outputs a liquid level detection signal.
- This liquid level detection signal is taken into the control unit 7 via the electric wire 76A. While the sensor 76 is outputting the liquid level detection signal, the control unit 7 determines that the collection container 4 can still sufficiently contain the cleaning liquid 69B, and displays a warning for discharging the cleaning liquid 69B. Absent.
- the control unit 7 can detect (determine) that the amount of the cleaning liquid 69B that can be further stored in the collection container 4 is small and is almost full, so that the control unit 7 can display the operation in such a state.
- a warning is displayed in part 8. For example, it may be indicated that the collection container 4 should be removed and the cleaning liquid 69B contained therein should be discharged. Although the warning has only been described to be displayed on the operation display unit 8, the operator may be notified by a buzzer or voice.
- the control unit 7 can receive the liquid level detection signal from the sensor 76 and determine that the collection container 4 has been attached. Based on this determination, the control unit 7 erases the warning display displayed on the operation display unit 8. Alternatively, it is possible to display that the cleaning unit 3 is in an operable (cleanable) state, release the prohibited state of the cleaning operation, and control the cleaning to be permitted.
- the configuration of the liquid level detection device used in the inkjet recording device is such that a float that moves up and down due to fluctuations in the liquid level inside the container and the float outside the container are at predetermined positions. Since at least one sensor for detecting the proximity is provided, the container can be easily attached and detached. Further, in the case of the liquid level detection device described in this embodiment, it is possible to detect whether the container is removed or attached by the output state of the liquid level detection signal of the liquid level detection device. Further, since the liquid level detection device for detecting the liquid level in the collection container of the cleaning unit can be composed of at least one sensor, it is possible to realize a low-cost liquid level detection device having a simple structure. it can.
- Liquid discharge hole, 72B Liquid discharge hole, 73 ... Air nozzle, 73A ... Air discharge hole, 73B ... Air discharge hole, 74 ... Float, 75 ... Holder, 75A ..., stopper, 75B ... stopper, 75C-75F ... opening, 76 ... sensor, 76A ... electric wire, 77A ... mounting part, 81 ... lid block, 81A ... print head insertion part, 82 ... lid hinge, 83 ... lid member , 84 ... Liquid joint, 85 ... Cover, 86 ... Magnet, 87 ... Housing, 87A ... Container positioning part, 87B ... Magnet fixing part, 87C ... Lid fixing part, 88 ...
- Seal member 89 ... Lid, 89A ... Fixing part , 91 ... Fixing jig (for main body), 92 ... Fixing jig (for conveyor), 93 ... Containing part, 100 ... Inkjet recording device, 311 ... Float, 312 ... Holder, 313 ... Sensor, 314 ... Sensor , 315 ... Support member, 321 ... Float, 322 ... Holder, 323 ... Sensor, 324 ... Sensor, 325 ... Support member, 331 ... Float, 332 ... Holder, 333 ... Sensor, 334 ... Sensor, 335 ... Support member, 510 ... Container unit, 520 ... Flow path board, 530 ...
- Electromagnetic valve unit 701 ... Microprocessing unit (MPU), 702 ... Read-only memory (ROM), 703 ... Random access memory (RAM), 704 ... Printing Head control circuit, 705 ... Pump control circuit, Electromagnetic valve control circuit, 707 ... Liquid level detection signal input unit, 708 ... bus, 801 to 803 ... route, 804 ... route, 805 ... route, 809 ... route, 810 ... route, 811 ... route, 812 ... route, 821 ... route, 825 ... route, 901 ... confluence route, 903 ... branch route
Landscapes
- Ink Jet (AREA)
Abstract
本発明は、容器の取外しや取付けが容易であり液体流出を防止するために有効なインクジェット記録装置を提供する。 印字ヘッドと、インク容器と、インク容器内のインクを印字ヘッドに供給し、印字ヘッドの印字動作を制御する制御部とを有するインクジェット記録装置において、洗浄ユニットを設ける。洗浄ユニットは、洗浄槽と、洗浄ノズルと、洗浄液を回収する回収容器とを備え、さらに回収容器内の液位を検出する液位検出装置を備える。 この液位検出装置は、回収容器内に、液位に応じて移動するフロートと、そのフロートを保持するホルダーとを備え、回収容器の外側に、フロートが近接したときに液位検出信号を出力するセンサを設置した構成としている。 この構成により、回収容器を容易に取外すこと及び取付けることができる。また、回収容器が洗浄ユニットに取付けられているか否かを判断することができる。
Description
本発明は、インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置に関する。
本技術分野に関する技術として、WO2015/114814号公報(特許文献1)に記載の技術が知られている。
特許文献1(WO2015/114814公報)には、インクを補充する補助インク容器内に、液位を検出する液位検出装置を設け、この液位検出装置により検出された液位検出信号を用いて、補助インク容器内のインクが所定液位を下回った場合に、インクカートリッジを交換して、補助インク容器内にインクを補充するように構成されたインクジェット記録装置が開示されている。なお、インクを収納する補助インク容器は、印字ヘッドに供給するインクを収納するインク容器(主インク容器)に必要な量のインクを補充するために用意されている。この特許文献1では、二種類の液位検出装置が開示されている。すなわち、一つ目の液位検出装置は、容器内に複数本(具体的には4本)の電極棒を設置し、各電極棒に電線を接続して、電線により液位検出信号を容器外部に取出す構成になっている(特許文献1の段落0034~段落0038の記載参照)。
特許文献1(WO2015/114814公報)には、インクを補充する補助インク容器内に、液位を検出する液位検出装置を設け、この液位検出装置により検出された液位検出信号を用いて、補助インク容器内のインクが所定液位を下回った場合に、インクカートリッジを交換して、補助インク容器内にインクを補充するように構成されたインクジェット記録装置が開示されている。なお、インクを収納する補助インク容器は、印字ヘッドに供給するインクを収納するインク容器(主インク容器)に必要な量のインクを補充するために用意されている。この特許文献1では、二種類の液位検出装置が開示されている。すなわち、一つ目の液位検出装置は、容器内に複数本(具体的には4本)の電極棒を設置し、各電極棒に電線を接続して、電線により液位検出信号を容器外部に取出す構成になっている(特許文献1の段落0034~段落0038の記載参照)。
もう一つの液位検出装置は、容器内にインクの容量(液位)が標準レベルの量に該当する位置にストッパを有し、標準レベルになったことを検出するフロートAと、インクがなくなりそうになったことを検出するフロートBとを備え、これらの各フロートを用いて検出された液位検出信号は電線により容器の外部に出力されるような構成になっている(段落0072~段落0075の記載参照)。
特許文献1の技術は、いずれの液位検出装置においても、液位検出信号を容器外部に取出す(出力する)ために、容器内に配置した検出部が検出した液位検出信号を電線により容器の外部に出力するような構成になっている。そのため、もし、容器を取外す場合には、まず電線を取外してから容器の取外しを行う必要があり、容器の取外し作業は煩雑となる。また、容器を取付ける際には、容器内に電極棒やフロート等を入れた状態で容器を所定位置に取付ける必要があるため、更に作業は煩雑となる。また、これらの作業において電気的に安定した接続(短絡防止、電気的接触の良好な状態の維持)にするための問題も出てくる。
ところで、インクジェット記録装置では、印字を行うために印字ヘッドは必要不可欠である。この印字ヘッドは、非常に高速なインクの飛翔を伴うために使用中においてインクの飛散等により汚れが発生することは避けがたく、時々印字ヘッドを洗浄する洗浄作業が必要になる。
しかし、洗浄作業を手作業で行うのは手間がかかること、人手による洗浄では確実に洗浄が行われているかどうかが不明である。そのため、最近、インクジェット記録装置に印字ヘッドを自動的に洗浄する洗浄ユニットを設けることが検討され始めている。この洗浄ユニットは、印字ヘッドを洗浄のためにセット(収容)する洗浄槽と、洗浄槽内においてセットされた前記印字ヘッドに向け洗浄液を噴出し洗浄する洗浄ノズルと、洗浄槽の底部に設けられ洗浄後の前記洗浄液を回収する回収容器とを備えている。
このような洗浄ユニットでは、洗浄を何度か行う際にそのまま放置すると、洗浄液が回収容器から溢れ外部に流出する。そのため、回収容器内の洗浄液の液位を検出する液位検出装置を設け、液位検出装置の検出信号を用いて洗浄液が一定量以上になったことを作業員に知らせ、作業員は回収容器を取外して容器内の洗浄液を排出する作業を実施する。そして、空になった回収容器は、再び洗浄槽の底部に取付ける。然るに、このような回収容器の脱着作業(取外しや取付け作業)はかなりの頻度で行われるため、上述した特許文献1に記載されたような液位検出装置を用いると、容器の脱着作業が非常に煩雑となり実用的でない。また、洗浄ユニットにおいて、うっかり回収容器が洗浄槽から取外された状態で洗浄作業を実施すると、洗浄後の洗浄液が洗浄槽の底部から流出してしまい周囲を汚染することになる。そのため、通常、容器が装着されているかどうかを検知するための装置が別途必要となる。
そこで、本発明の目的は、容器の取外しや取付けが容易であり液体が容器外に流出することを防止するために有効なインクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット、および液位検出装置を提供することにある。
上述した目的を達成するために、本発明は、その一例を挙げると、印字を行う印字ヘッドと、インク容器と、前記インク容器内のインクを前記印字ヘッドに供給するとともに印字に使用しない前記インクを前記インク容器に回収するための経路と、前記印字ヘッドに前記インクを供給する制御と前記印字ヘッドの印字動作を制御する制御部とを有するインクジェット記録装置であって、前記印字ヘッドを収容可能な空間を有し下部に液出口部を有する洗浄槽と、前記洗浄槽内に収容された前記印字ヘッドに向けて洗浄液を噴出し洗浄する洗浄ノズルと、前記洗浄槽の前記液出口部から流出する洗浄液を回収する回収容器とを備えた洗浄ユニットと、前記回収容器内の前記洗浄液の液位を検出する第1液位検出装置とを設け、前記第1液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動する第1フロートと、前記第1フロートを保持する第1ホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記第1フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力する第1センサを設置した構成とし、前記制御部は、前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断するインクジェット記録装置である。
また、本発明の他の一例を挙げると、インクにより印字を行う印字ヘッドを有するインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットであって、前記洗浄ユニットは、前記印字ヘッドを収容可能な空間を有し液出口部を有する洗浄槽と、前記洗浄槽内に収容された前記印字ヘッドに向けて洗浄液を噴出し洗浄する洗浄ノズルと、前記洗浄槽の前記液出口部から流出する洗浄後の前記洗浄液を回収する回収容器と、前記回収容器内の前記洗浄液の液位検出信号を出力する液位検出装置とを備えており、前記液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動するフロートと、前記フロートを保持するホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力するセンサを設置した構成とし、前記液位検出信号を用いて前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットである。
また、本発明の他の一例を挙げると、容器内の液体の液位を検出するための液位検出装置であって、前記液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、液位に対応して移動するフロートと、前記フロートを保持するホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力するセンサを設置した構成とし、前記液位検出信号を用いて前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断することを特徴とする液位検出装置である。
本発明によれば、容器の取外しや取付けが容易であり液体が容器外に流出することを防止するために有効なインクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット、および液位検出装置を提供することができる。
以下、本発明の具体的な実施例を、図1~図10を用いて説明する。なお、本発明は、以下に説明する実施例に限定されるものではない。
また、以下の各図において、同一機器には同一番号(符号)を付し、すでに説明した機器の説明を省略する場合がある。
また、以下の各図において、同一機器には同一番号(符号)を付し、すでに説明した機器の説明を省略する場合がある。
(インクジェット記録装置の構成と使用状態)
最初に、本発明の実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の基本構成および使用状態について説明する。図1は、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の使用状態を示す図である。
最初に、本発明の実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の基本構成および使用状態について説明する。図1は、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の使用状態を示す図である。
まず、図1に示すように、本実施例に係るインクジェット記録装置100は、本体1と、本体1と導管5(印字ヘッド用)を介して接続された印字ヘッド2と、本体1と洗浄ユニット用の導管6により接続された洗浄ユニット3とを備える。
インクジェット記録装置100は、例えば、食品や飲料などが生産される工場内の生産ラインに据付けられる。本体1は、印字ヘッド2に印字用のインクを供給するとともに、印字ヘッド2で使用しなかったインクを回収する機能を有する。また、本体1は、インクを収容するインク容器、インク容器内のインクが印字に使用されて少なくなった場合にインクをインク容器に補充するための補助インク容器などを備え、またインクや溶剤の供給や回収を行うための経路と、その経路途中に設けた開閉弁群(電磁弁群)やポンプ群などを内蔵している。更に、本体1は、印字ヘッドにより印字を制御すること、インクや溶剤の供給、回収等を制御すること等のための制御部7(図1では図示せず)と、この制御部7に操作指令を与えるためおよび制御部7から送信されるインクジェット記録装置の各種状態を表示する操作表示部8とを備えている。本体1は定期的な保守作業などに必要なスペースが確保可能な場所に設置されている。
印字ヘッド2は、ベルトコンベア11の近傍に設置された印字ヘッド固定用金具13に固定され、ベルトコンベア11上を矢印Xの方向に給送される印字対象物12A、12Bに印字するために近接して設置されている。なお、印字対象物12Aは印字前の印字対象物を示し、印字対象物12Bは印字後の印字対象物を示す。また、印字ヘッド2は、ヘッドベース16上に、ノズル、帯電電極、偏向電極等(図1では図示せず)の部品を装備している。また、印字ヘッド2は、これらの部品を保護する目的で保護カバー17が取付けられている。
印字ヘッド2を洗浄するために設けられた洗浄ユニット3は、固定用治具92と、固定用治具92を篏合するための篏合部93により、ベルトコンベア11の近傍に取付けられている。なお、洗浄ユニット3は、洗浄槽71と、洗浄槽内にセットされた印字ヘッド2を洗浄するための洗浄ノズル(図1では図示せず)と、洗浄液を回収する回収容器4等を含む。導管6は、本体1から洗浄液を洗浄ユニット3に供給するための導管である。
(本体の構成)
次に、インクジェット記録装置100における本体1内の機器配置構成について説明する。図2は、実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置の本体1の断面を示す図である。
図2において、容器ユニット510は、容器群(インク容器31、補助インク容器32、溶剤容器33)を収納している部分である。流路ボード520は、インク供給・回収および溶剤の供給・回収等を行うための流路(経路)等をまとめているボード部分である。ポンプユニット530は、それらの経路途中に設けられるポンプ群(ポンプ34~35、37、38)を取付けている部分である。電磁弁ユニット540は、経路途中に設けられる流路開閉用の電磁弁群(電磁弁49,50、53~56)を取付けている部分である。なお、ポンプ群および電磁弁群の具体的な構成(図4参照)は後述する。
次に、インクジェット記録装置100における本体1内の機器配置構成について説明する。図2は、実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置の本体1の断面を示す図である。
図2において、容器ユニット510は、容器群(インク容器31、補助インク容器32、溶剤容器33)を収納している部分である。流路ボード520は、インク供給・回収および溶剤の供給・回収等を行うための流路(経路)等をまとめているボード部分である。ポンプユニット530は、それらの経路途中に設けられるポンプ群(ポンプ34~35、37、38)を取付けている部分である。電磁弁ユニット540は、経路途中に設けられる流路開閉用の電磁弁群(電磁弁49,50、53~56)を取付けている部分である。なお、ポンプ群および電磁弁群の具体的な構成(図4参照)は後述する。
また、本体1の上部には制御部7が配設されており、制御部7はインクジェット記録装置100全体の制御を実行する。制御部7の具体的な構成は後述する。本体1の前面上部には、操作表示部8が設けられている。操作表示部8は、この実施例では操作用のタッチパネルと表示装置を一体に組込んだ構成としている。もちろん、操作表示部は、操作部と表示装置とを別々に設けるものでも良い。また、本体1の上部にはインクジェット記録装置100において使用するための電源70が設置されている。
(制御部の構成)
次に、本発明の実施例における制御部7の構成について説明する。図3は、制御部7の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
図3において、制御部7は、マイクロプロセッシングユニット(MPU)701と、MPU701の動作のためのプログラムおよび動作に必要なデータ・情報を記憶するリードオンリーメモリ(ROM)702と、印字内容のデータや、制御に必要なデータや入力される信号等を記憶するランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)703とを有する。また、制御部7は、印字ヘッド2を駆動し印字するための帯電電圧や偏向電圧、各種タイミング等を制御する印字ヘッド制御回路704と、ポンプ群の駆動・停止の制御を行うためのポンプ制御回路705と、電磁弁群の開閉制御を行う弁制御回路706とを有する。MPU701は、印字ヘッド制御回路704、ポンプ制御回路705、弁制御回路706を制御して、インクジェット記録装置の全体を制御する。
次に、本発明の実施例における制御部7の構成について説明する。図3は、制御部7の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
図3において、制御部7は、マイクロプロセッシングユニット(MPU)701と、MPU701の動作のためのプログラムおよび動作に必要なデータ・情報を記憶するリードオンリーメモリ(ROM)702と、印字内容のデータや、制御に必要なデータや入力される信号等を記憶するランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)703とを有する。また、制御部7は、印字ヘッド2を駆動し印字するための帯電電圧や偏向電圧、各種タイミング等を制御する印字ヘッド制御回路704と、ポンプ群の駆動・停止の制御を行うためのポンプ制御回路705と、電磁弁群の開閉制御を行う弁制御回路706とを有する。MPU701は、印字ヘッド制御回路704、ポンプ制御回路705、弁制御回路706を制御して、インクジェット記録装置の全体を制御する。
更に、本実施例における制御部7は、各液位検出装置の液位検出信号を入力する液位検出信号入力部707を有する。この液位検出信号入力部707を介して制御部7に入力された液位検出信号は、一旦RAM703に記憶され、MPUによる演算・判断・制御などに使用される。MPU701は、この液位検出信号により、容器内の液位が所定位置に達したことを認識し、さらに洗浄動作などに関する警告などを操作表示部8に表示する。また、この液位検出信号を用いて、液位を所定値に制御するための制御信号を演算し、ポンプ制御回路705および弁制御回路706を介して、関連するポンプ群および電磁弁群を制御する。
(全体経路構成)
次に、本発明の実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の経路構成について説明する。
図4は、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置の全体経路構成を示す図である。図4において、インクジェット記録装置100は、本体1と、印字ヘッド2と、ヘッド洗浄ユニット3と、それらを結ぶ導管5,6とを備えている。本体1と印字ヘッド2との間は、導管5により接続され、本体1とヘッド洗浄ユニット3との間は導管6により接続される。
次に、本発明の実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の経路構成について説明する。
図4は、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置の全体経路構成を示す図である。図4において、インクジェット記録装置100は、本体1と、印字ヘッド2と、ヘッド洗浄ユニット3と、それらを結ぶ導管5,6とを備えている。本体1と印字ヘッド2との間は、導管5により接続され、本体1とヘッド洗浄ユニット3との間は導管6により接続される。
〔印字ヘッドへのインク供給〕
まず、本体1から印字ヘッド2に対してインクを供給するインク供給用の経路(経路801~803)について説明する。図4において、本体1には、循環するインク68Aを保持するインク容器31が備えられている。
インク容器31は、インク68Aに浸漬している部分で経路801に接続されており、経路801の途中には、粘度測定器45と、インク供給のための経路の開閉を行う電磁弁49を設置している。粘度測定器45は、インクの粘度を測定するために設けられ、制御部7に入力される。具体的には、RAM703に入力・記憶される。制御部7は、この粘度検出信号によりインク68Aの粘度を所定値あるいは所定範囲内に維持する制御を実行する。
まず、本体1から印字ヘッド2に対してインクを供給するインク供給用の経路(経路801~803)について説明する。図4において、本体1には、循環するインク68Aを保持するインク容器31が備えられている。
インク容器31は、インク68Aに浸漬している部分で経路801に接続されており、経路801の途中には、粘度測定器45と、インク供給のための経路の開閉を行う電磁弁49を設置している。粘度測定器45は、インクの粘度を測定するために設けられ、制御部7に入力される。具体的には、RAM703に入力・記憶される。制御部7は、この粘度検出信号によりインク68Aの粘度を所定値あるいは所定範囲内に維持する制御を実行する。
更に、経路801は、合流経路901を介して、経路802に設置されてインク68Aを吸引・圧送するために使用されるインク供給用のポンプ34に接続されている。そして、ポンプ34の出力側において、インク68A中に混入している異物を除去するフィルタ39(インク供給用)に接続されている。
フィルタ39は、ポンプ34から圧送されたインク68Aを印字するために適正な圧力に調整する調圧弁46に接続されており、調圧弁46はノズル21に供給されるインク68Aの圧力を測定する圧力センサ47に接続されている。圧力センサ47が配置された経路802は、導管5内を通過して印字ヘッド2に接続されている。具体的には、ノズル21にインク68Aを供給するかどうかを制御するための切替弁26に接続される。
切替弁26は、経路803を介して、インク68Aを吐出する吐出口を備えたノズル21に接続されている。なお、切替弁26は三方型電磁弁であり、切替弁26にはインク供給用の経路802とノズル洗浄用の経路812とが接続されており、ノズル21に対してインク68Aと溶剤69Aの供給を切替えることができる。ノズル21の吐出口の直進方向には、ノズル21で粒子化されたインク粒子68Bに対して所定の電荷量を付加する(印字内容に対応して電荷量が付与する)ための帯電電極23、印字に使用するインク粒子68Bを帯電量に対応して偏向させるための偏向電極24、および印字に使用されないために帯電・偏向されずに直進的に飛翔するインク粒子68Bを捕捉するためのガター25が配置されている。印字は、偏向電極24で偏向されたインク粒子68Bを被印字物に着弾させることで行われる。
〔印字ヘッドからのインク回収〕
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100のインク回収経路(経路804)について説明する。図4において、ガター25は、経路804に接続されている。そして、経路804は、導管5内を通過し、本体1内に配置されているインク中に混入している異物を除去するフィルタ40(インク回収用)と接続され、フィルタ40は経路804の開閉を行う電磁弁50(インク回収用)に接続されている。さらに、電磁弁50は、ガター25により捕捉されたインク粒子68Bを吸引するポンプ35(インク回収用)と接続されており、ポンプ35がインク容器31と接続されている。また、インク容器31は、インク68Aに接触しない上部の空間にて、経路805と接続されていて、経路805は本体1の外部と連通した構成をとっている。このような構成において、制御部7が電磁弁50を開き、ポンプ35を駆動する制御を実行することにより、ガター25により捕捉されたインク粒子68Bは、これらを介してインク容器31に回収される。
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100のインク回収経路(経路804)について説明する。図4において、ガター25は、経路804に接続されている。そして、経路804は、導管5内を通過し、本体1内に配置されているインク中に混入している異物を除去するフィルタ40(インク回収用)と接続され、フィルタ40は経路804の開閉を行う電磁弁50(インク回収用)に接続されている。さらに、電磁弁50は、ガター25により捕捉されたインク粒子68Bを吸引するポンプ35(インク回収用)と接続されており、ポンプ35がインク容器31と接続されている。また、インク容器31は、インク68Aに接触しない上部の空間にて、経路805と接続されていて、経路805は本体1の外部と連通した構成をとっている。このような構成において、制御部7が電磁弁50を開き、ポンプ35を駆動する制御を実行することにより、ガター25により捕捉されたインク粒子68Bは、これらを介してインク容器31に回収される。
〔溶剤補給経路〕
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の溶剤補給経路(経路809~810)について説明する。図4において、本体1には、インク容器31への溶剤供給や、ノズル洗浄やヘッド洗浄に使用するための溶剤69Aを保有(収容)する溶剤容器33が備えられている。溶剤容器33は、溶剤69Aに浸漬している部分で経路809に接続されており、経路809には溶剤を吸引、圧送するために使用されるポンプ37が配置されている。そして、ポンプ37は、目的に応じて溶剤69Aの供給先を変えるために分岐経路903に接続されている。分岐経路903は、溶剤補給経路においては経路810に配置された流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁53に接続されており、電磁弁53はインク容器31と経路により接続された構成となっている。
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の溶剤補給経路(経路809~810)について説明する。図4において、本体1には、インク容器31への溶剤供給や、ノズル洗浄やヘッド洗浄に使用するための溶剤69Aを保有(収容)する溶剤容器33が備えられている。溶剤容器33は、溶剤69Aに浸漬している部分で経路809に接続されており、経路809には溶剤を吸引、圧送するために使用されるポンプ37が配置されている。そして、ポンプ37は、目的に応じて溶剤69Aの供給先を変えるために分岐経路903に接続されている。分岐経路903は、溶剤補給経路においては経路810に配置された流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁53に接続されており、電磁弁53はインク容器31と経路により接続された構成となっている。
このような構成において、溶剤69Aをインク容器31に供給するには、電磁弁53を開き、ポンプ37を駆動すれば良い。インク容器31への溶剤の供給(補給)は、粘度測定器45が検出するインク粘度が所定値よりも高い状態になった場合に、インク粘度を所定値範囲内にするために行われる。具体的には、制御部7は、粘度測定器45から入力されたインク粘度が印字を行うに適切な粘度よりも高くなったことを判断すると、電磁弁53を開き、ポンプ37を駆動して、溶剤容器33内の溶剤69Aをインク容器31に供給し、インク68Aの粘度が適正になるように制御する。
この実施例では、溶剤容器33には、溶剤容器33内の溶剤69Aが適正な範囲内の液位であるかどうかを検出する液位検出装置33Aが備えられている。この液位検出装置33Aは、溶剤容器33の内側において、液位変動に対応して上下に移動するフロート331と、フロート331を保持するホルダー332とを有する。ホルダー332により、フロート331は上下動以外の移動をしないよう抑制されている。ホルダー332の上下位置にストッパ(図では三角形状で示している)を設けている。具体的には、ホルダー332において、フロート331が最小液位を検知する位置および最大液位を検知する位置に夫々ストッパを設けている。フロート331を検出するセンサ333と334は、このストッパにフロートが接近(近接)した場合に、液位検出信号を出力するように配設されている。ここで、2個のセンサ333と334は、溶剤容器33の外側において支持部材335に取付けられている。すなわち、溶剤容器33の底部側のセンサ333は、フロート331が液位変動により下方のストッパに移動して近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。溶剤容器33の上部側のセンサ334は、フロート331が上方に移動して上側のストッパに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。液位検出装置33Aのセンサ333と334を溶剤容器33の外部に設置し、液位検出信号を制御部7に送信する電線(図示せず)は溶剤容器33の外部に配線されているので、溶剤容器33の脱着作業(取外しや取付け作業)は容易になる。
センサ333は、フロート331がホルダー332の下側ストッパに接触する位置に移動した場合、液位検出信号を出力する。また、センサ334は、フロート331がホルダー332の上側ストッパに接触する位置に移動した場合、液位検出信号を出力する。このセンサ333および334により検出された液位検出信号は、制御部7に入力される。具体的には、制御部7の液位検出信号入力部707を経由し、RAM703に記憶される(図3参照)。
制御部7(具体的にはMPU701)は、この液位検出信号を用いて、溶剤容器33内の溶剤69Aが所定の液位の範囲内でないと判断した場合には、操作表示部8に溶剤の残留状態を表示したり、溶剤が不足している旨の警告を表示する。具体的には、MPU701が、RAM703に記憶されている液位検出信号を用いて溶剤の過不足を判断し、不足している場合には溶剤が不足していること、溶剤を補充する必要があることなどの警告を操作表示部8の画面に表示する。これにより、作業者は溶剤の補給が必要であることを知ることができる。
〔インク補給経路〕
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100のインク補給経路について説明する。図4において、本体1には、補充用のインク68Cを保持する補助インク容器32が備えられている。補助インク容器32は、インク68Cに浸漬している部分でインク補給のための経路811に接続されている。経路811は、経路の開閉を行う電磁弁54に接続されており、電磁弁54は合流経路901を介して、経路802に設置されてインク68Cを吸引、圧送するために使用するポンプ34に接続されている。そして、補助インク容器32内のインク68Cは、印字ヘッド2に送給され、ノズル21、ガター25を経由して、経路804、電磁弁50、ポンプ35からなるインク回収経路を通り、インク容器31に補充される。
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100のインク補給経路について説明する。図4において、本体1には、補充用のインク68Cを保持する補助インク容器32が備えられている。補助インク容器32は、インク68Cに浸漬している部分でインク補給のための経路811に接続されている。経路811は、経路の開閉を行う電磁弁54に接続されており、電磁弁54は合流経路901を介して、経路802に設置されてインク68Cを吸引、圧送するために使用するポンプ34に接続されている。そして、補助インク容器32内のインク68Cは、印字ヘッド2に送給され、ノズル21、ガター25を経由して、経路804、電磁弁50、ポンプ35からなるインク回収経路を通り、インク容器31に補充される。
補助インク容器32内のインクをインク容器31に補充するタイミングは、インク容器31内のインクの液位を検出する液位検出装置31Aの液位検出値を利用して行う。すなわち、インク容器31には、インク容器31内のインクが適正な量である基準液位に達しているか否かを検出する液位検出装置31Aが備えられている。
この液位検出装置31Aは、上述した液位検出装置33Aと同様の構成である。すなわち、インク容器31の内側には、液位変動に対応して上下に移動するフロート311と、フロート311を保持しフロートの上下動以外の移動を抑制するホルダー312とを有する。譲渡同様に、ホルダー312の上下にはストッパが設けられる。また、この液位検出装置31Aのセンサ313と314は、インク容器31の外側において支持部材315に取付けられている。インク容器31の外側の下側に設けたセンサ313は、フロート311がホルダーの下側ストッパに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。容器の外側の上側に設けたセンサ314は、フロート311がホルダー312の上側のストッパに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。センサ313およびセンサ314は、インク容器31の外側に配置されているので、点検や洗浄のためにインク容器31の脱着作業(取外したり取付ける作業)は容易になる。このセンサ313および314により検出された液位検出信号は、制御部7の液位検出信号入力部707を介して、RAM703に記憶される(図3参照)。
制御部7は、この液位検出信号を用いて、インク容器31内のインクが所定量になるように制御する。具体的には、インク容器31内のインクの液位が下がり、センサ313で検出される液位にまで下降した場合、インク容器31へのインクの補給が開始される。制御部7は、液位検出装置31Aのセンサ313の検出信号を入力すると、インク補充を開始する。すなわち、制御部7は、センサ313の液位検出信号からインク容器31内のインク量(インク液位)が所定量以下に減少していることを知ることができるので、補助インク容器32内のインク68Cを経路811、経路802、印字ヘッド2から、経路804を経由して、インク容器31に補給する。インク補給中は、経路途中に設けた電磁弁54を開動作し、ポンプ34を駆動し、印字ヘッド2内に供給されたインクをガター25で捕捉し、経路804の途中に設けた電磁弁50を開動作し、ポンプ35を駆動する。これにより、補助インク容器32内のインク68Cは、インク容器31に供給(補充)される。インク補充により液位が上昇し、液位検出装置31Aのセンサ314が液位検出信号を出力すると、制御部7は、このインク補充動作を終了する。終了は、制御部7が電磁弁54を閉、ポンプ34を停止することで行われる。
なお、この実施例では、補助インク容器32内のインクの液位を検出する液位検出装置32Aも設けている。この液位検出装置32Aにより検出された液位検出信号も、制御部7に入力される。制御部7は、この液位検出信号を入力し、補助インク容器32内のインク液位を知ることができる。液位検出装置32Aは、既に説明した他の液位検出装置(31A,32A)と同様の構成になっている。すなわち、液位検出装置32Aは、補助インク容器32の内側に液位変動に対応して上下に移動するフロート321と、フロート321の上下動以外の移動を抑制するホルダー322とを有する。ホルダー322の上下には、ストッパが設けられる。また、この液位検出装置32Aは、センサ323と324とを補助インク容器32の外側の支持部材325に取付けている。センサ323は、フロート321が下側のストッパに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。センサ324は、フロート321が上側のストッパに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力する。このセンサ323および324により検出された液位検出信号は、電気信号として、制御部7の液位検出信号入力部707を介して、RAM703に記憶される(図3参照)。
制御部7は、この液位検出信号により、補助インク容器32内のインク68Cが所定範囲外の液位まで減少したことを知ることができ、補助インクを補充する制御を実施することができる。あるいは、補助インク容器32内にインクを補充する必要がある旨の警告を操作表示部8に表示する。
〔ノズル洗浄〕
次に、ノズル洗浄経路(経路809及び経路812)について説明する。図4において、経路809に配置されたポンプ37は、分岐経路903を介して経路812に接続されている。経路812は、流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁55(ノズル洗浄用)に接続されている。そして、電磁弁55は、溶剤69A中に混入している異物を除去するためのフィルタ41(ノズル洗浄用)に接続されている。フィルタ41は、導管5内を通る経路812を介して印字ヘッド2内に備えられ、ノズル21に洗浄のための溶剤69Aを送るかどうかを制御するための切替弁26に接続された構成となっている。
次に、ノズル洗浄経路(経路809及び経路812)について説明する。図4において、経路809に配置されたポンプ37は、分岐経路903を介して経路812に接続されている。経路812は、流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁55(ノズル洗浄用)に接続されている。そして、電磁弁55は、溶剤69A中に混入している異物を除去するためのフィルタ41(ノズル洗浄用)に接続されている。フィルタ41は、導管5内を通る経路812を介して印字ヘッド2内に備えられ、ノズル21に洗浄のための溶剤69Aを送るかどうかを制御するための切替弁26に接続された構成となっている。
〔洗浄ユニット〕
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の洗浄ユニット3の基本構成について説明する。
図4において、印字ヘッド2を洗浄する洗浄ユニット3は、上面が開口し印字ヘッド2を挿入する(セットする)ための収容空間部を有する洗浄槽71と、洗浄槽71にセットされた印字ヘッド2を洗浄するために洗浄液を噴出する洗浄ノズル72と、洗浄後の印字ヘッド2を乾燥するために乾燥エアを噴出するエアノズル73と、洗浄槽71の底部に取付けられ洗浄槽の低部の開口から流出する(流れ落ちる)洗浄液69Bを回収する回収容器4とを備えている。洗浄ユニット3において使用する洗浄液は、この実施例では溶剤容器33に保有されている溶剤69Aを使用する。そのため、溶剤容器33の溶剤69Aは、浸漬している部分で経路809と繋がっており、経路809途中に設けたポンプ37は、分岐経路903を介して経路821に接続されている。経路821は、洗浄ユニット3の洗浄ノズル72と接続されている。経路822には、流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁56が配置されている。この構成により、制御部7は、電磁弁56を開動作し、ポンプ37を駆動する制御を行うことにより、溶剤容器33内の溶剤69Aを、「洗浄液」としてヘッド洗浄ユニット3内の洗浄ノズル72に供給することができる。なお、洗浄液は、本体1の溶剤容器の溶剤とは別に設けた、洗浄液供給装置から供給しても良い。
次に、本実施例におけるインクジェット記録装置100の洗浄ユニット3の基本構成について説明する。
図4において、印字ヘッド2を洗浄する洗浄ユニット3は、上面が開口し印字ヘッド2を挿入する(セットする)ための収容空間部を有する洗浄槽71と、洗浄槽71にセットされた印字ヘッド2を洗浄するために洗浄液を噴出する洗浄ノズル72と、洗浄後の印字ヘッド2を乾燥するために乾燥エアを噴出するエアノズル73と、洗浄槽71の底部に取付けられ洗浄槽の低部の開口から流出する(流れ落ちる)洗浄液69Bを回収する回収容器4とを備えている。洗浄ユニット3において使用する洗浄液は、この実施例では溶剤容器33に保有されている溶剤69Aを使用する。そのため、溶剤容器33の溶剤69Aは、浸漬している部分で経路809と繋がっており、経路809途中に設けたポンプ37は、分岐経路903を介して経路821に接続されている。経路821は、洗浄ユニット3の洗浄ノズル72と接続されている。経路822には、流路の開閉を行うための電磁弁56が配置されている。この構成により、制御部7は、電磁弁56を開動作し、ポンプ37を駆動する制御を行うことにより、溶剤容器33内の溶剤69Aを、「洗浄液」としてヘッド洗浄ユニット3内の洗浄ノズル72に供給することができる。なお、洗浄液は、本体1の溶剤容器の溶剤とは別に設けた、洗浄液供給装置から供給しても良い。
また、印字ヘッドの洗浄後には、エアノズル73からエアを噴出させ、印字ヘッド2の乾燥を行うことができる。エアノズル73は、経路825と接続されており、その経路825途中に設けたポンプ38を駆動することによりエアを洗浄槽71内に噴射することができる。なお、本体1と洗浄ユニットとの間は、導管6により接続される。回収容器4は、洗浄後の洗浄液69Bを収容するために設けられ、容器内の洗浄液69Bが一定以上の液位になった場合に、回収容器4を取外して洗浄液69Bを排出する。洗浄液69Bの排出により空になった回収容器4は、洗浄液69Bを収容するために、再び洗浄槽71の底部に取付ける。
この実施例においては、洗浄ユニット3の回収容器4に液位検出装置4Aが設けられている。液位検出装置4Aは、回収容器4内に液位に応じて上下に移動可能なフロート74と、このフロート74を保持するホルダー75とを備えている。また、回収容器4の外側には、フロート74が上下動して近接した場合に、液位検出信号を出力するセンサ76が設置される。ここで、センサ76および液位検出信号を制御部7に送信する電線76Aは回収容器4の外部に設けられているので、回収容器4の取外しや取付けの支障にはならない。
ところで、液位検出におけるセンサの数は、多数個設ければきめ細かく液位を検出することができる。しかし、センサの数が多くなるとその分液位検出装置が高価になる。そのため、この実施例では、回収容器に使用する液位検出装置4Aのセンサの数を少なくする工夫をしている。すなわち、液位検出装置31A,32A、33Aの場合は上下に2個のセンサを設けた構成にしている。これに対し、液位検出装置4Aでは、センサ76は1個しか設けていない。
液位検出装置4Aは、ホルダー75の中間位置にストッパ75Aを設け、フロート74の上下方向に移動する範囲を中間位置から上側への移動に制限する。そして、センサ76は、フロート74がこのストッパ75Aに近接した場合に液位検出信号を出力するように配設する。
ここで、ホルダー75におけるストッパ75Aが設けられる位置は、上下の中間位置(容器の最大容量を検出するに液位よりは下方の位置であり、容器内に液体が存在しない場合の位置よりも上方の位置)である。ストッパ75Aの設置位置は、容器を取外して容器内の洗浄液69Bを排出する頻度を考慮し、かつそのままの運転状態において直ちに容器内の液体が外部に溢れるリスクが小さいと考えられる液位の位置とする。好ましくは、ストッパ75Aの位置は、最大容量に対応する液位位置を100%とした場合に、その50~90%の範囲内の位置が好都合である。ここで、50%としたのは、それより低くするとセンサ76が頻繁に液位検出信号を出力するので、洗浄液69Bを排出するために回収容器4の取外しと取付けを行う頻度が多くなるためである。また、90%としたのは、制御部7が操作表示部8に警告した場合に、作業員がその傾向に気が付くのが少し遅れた場合に洗浄液69Bが溢れる恐れが出てくるため、多少の余裕時間を確保するためである。
このような液位検出装置4Aの構成では、フロート74は回収容器4内の液体(洗浄液69B)の液位がまだ少なくてストッパ75Aの位置より下側にある場合にはフロート74は動かない。したがって、センサ76は、フロート74が移動しない期間中(言いかえれば、回収容器4の洗浄液69Bが少ない期間中)において、継続して液位検出信号を出力し続けることになる。そして、回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bの液位がストッパ75Aの位置よりも上昇して、フロート74が上方に移動した場合に、センサ76は、液位検出信号の出力を停止する。このセンサ76による液位検出信号は、制御部7に入力される。具体的には、制御部7の液位検出信号入力部707を介して、RAM703に記憶される(図3参照)。
制御部7は、液位検出装置が液位検出信号を継続して出力している間は、回収容器4内の液体(洗浄液69B)が少ないこと(言いかえると、洗浄液69Bをまだ十分収容できること)を判断することができる。また、制御部7は、液位検出信号の出力が消失したときは回収容器内の洗浄液69Bがほぼ満杯になったこと(言いかえると、回収容器が洗浄液69Bを収容できなくなっていること)を判断できる。つまり、液位検出信号が途切れたときには、制御部7は、回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bを排出すべきことを指示する警告を操作表示部8に表示することが可能となる。また、液位検出装置4A(センサ76)は、回収容器4が取外されている(無い)ときにも、フロート74が近くにないことから、液位検出信号は消失する。そのため、制御部7は、液位検出信号が消失している場合には洗浄をしないように警告を発する(この実施例では、操作表示部8に表示する)。このように、液位検出装置4Aの液位検出信号を利用して、液位を検出するだけでなく、回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bがたまって溢れる恐れがある場合や、回収容器4自体が洗浄ユニット3から取外されて液体が外部に流出する恐れがある場合を判断することができる。また、そのことを作業員に知らせることができる。このため、制御部7は、この判断に基づき、適切な警告を表示する。あるいは、洗浄ユニットによる洗浄の動作を行わせないように制御することも可能となる。
ここで、この実施例では、回収容器4に設置される液位検出装置4Aを、ホルダー75の中間部にストッパ75Aを設け、その位置の液位を検出するセンサ76を1個設けたものを示した。しかし、液位検出装置4Aは、上述した他の液位検出装置31A,32A,33Aと同様の構成にすることもできる。すなわち、検出する最低の液位と最大の液位の検出位置にストッパを設け、フロートを液位の変動に応じてそれら両ストッパ間で上下に移動可能とし、容器の外部には上下のストッパにフロートが位置するときに液位検出信号を出力するように配置された2個のセンサを有する構成にしても良い。このような構成でも、上側のセンサが液位検出信号を出力した場合に、容器内に液体がほぼ満杯になり、収容できる液体量が少なくなったことを判断することができる。
すなわち、この上側のセンサの液位検出信号が出力された場合には、制御部7は回収容器4を取外して洗浄液69Bを排出すべきことを操作表示部8に警告表示する。これにより、作業者は、回収容器4を取外して、中の洗浄液69Bを排出することができる。
また、上側のセンサが動作した後に回収容器4を取外した場合には、上下のセンサは液位検出信号を出力しない。そして、その後、回収容器4が取付けられると(容器内の液体がなくなっているので)、下側のセンサが液位検出信号を出力する。したがって、制御部7は、上側のセンサの動作後に、下側のセンサが動作(液位検出信号を出力)するまでの間は、回収容器4が取外されている可能性が高いと判断することができる。その場合、制御部7は、上述したような警告を表示する。あるいは、その期間中は、洗浄動作を行わせないように制御することが可能となる。
なお、回収容器4内の液体を容器外に排出する機器(排出用の経路、経路途中に設けた電磁弁およびポンプ)を設置している場合には、関連機器(電磁弁及びポンプ)を駆動して回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bを排出することができる。その場合、洗浄液69Bの排出は、本体1側に回収するようにしても良いし、あるいは別の容器に排出することでも良い。
(洗浄ユニットの具体的な構成)
次に、図5により、洗浄ユニット3の具体的な構成について説明する。なお、以下では、図4に関して説明した内容と重複する説明は省略する場合がある。
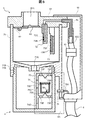
図5において、洗浄槽71の上部には蓋ブロック81が設置される。蓋ブロック81は、印字ヘッドの挿入部81Aを有し、この挿入部81Aにより印字ヘッド2を挿入することができる。挿入部81Aの下面には、蓋部材83が設けられ、蓋ヒンジ82のバネ力により通常は閉じられている。ゴミ等が洗浄槽71内に入るのを防ぐためである。85は、配管部分を保護するカバーである。
次に、図5により、洗浄ユニット3の具体的な構成について説明する。なお、以下では、図4に関して説明した内容と重複する説明は省略する場合がある。
図5において、洗浄槽71の上部には蓋ブロック81が設置される。蓋ブロック81は、印字ヘッドの挿入部81Aを有し、この挿入部81Aにより印字ヘッド2を挿入することができる。挿入部81Aの下面には、蓋部材83が設けられ、蓋ヒンジ82のバネ力により通常は閉じられている。ゴミ等が洗浄槽71内に入るのを防ぐためである。85は、配管部分を保護するカバーである。
印字ヘッド2を洗浄する場合、作業者は印字ヘッド2を洗浄槽71に挿入する。この際、蓋ヒンジ82によるバネ力で閉じられた蓋部材83が回動(図5では時計回りに回動)して、印字ヘッド2が洗浄槽71内にセットされる。経路822により送られる洗浄液は、液継手84を介して洗浄ノズル72に流入する。フィルタ43は、洗浄液内のごみを除去するために経路822の途中に設けられている。洗浄ノズル72は、洗浄する印字ヘッド2の洗浄部位に対応して洗浄液を噴射するために、この実施例では2つの液吐出穴72Aおよび72Bを有している。
また、洗浄後の印字ヘッド2を乾燥させるために設けたエアノズル73にも、2つのエア吐出穴73Aおよび73Bが設けられている。洗浄槽71の底の部分には液出口部71Aが設けられ、また回収容器4を取付ける際に使用する取付部71Bを有する。この液出口部71Aから、洗浄後の洗浄液69Bを重力により回収容器4に落下させる(流れ落ちる)ようにしている。回収容器4は、容器77の上側の端部に洗浄槽71に取付けるための取付部77Aを有している。この実施例では、取付部71B,77Aともにネジ構造による取付けとした。回収容器4の取外しは、作業員が回収容器4を取外し方向(例えば、反時計方向)にねじることにより実施できる。回収容器4の取付けは、取付方向(例えば、時計方向)にねじることにより行われる。すでに述べたように、回収容器4内には、液位検出装置4Aの構成要素の内、フロート74とホルダー75が配置されている。また、ストッパ75Aはホルダー75の中間位置に形成され、フロート74がそのストッパ75Aの位置より下側には移動できないようにしている。75Bは、上側のストッパであり、検出する最大液位を規定している。75C~75Fは、ホルダー75内に液体が流入可能にするために設けた開口である。回収容器4の外側には、液位検出装置4Aのセンサ76が設置され、フロート74がストッパ75Aの位置に存在する期間中、液位検出信号を出力するようにしている。なお、この液位検出装置4Aにおけるフロート74は、内部に検出体として磁石86を設置する磁石式フロートを用いており、センサ76はこの磁石86が近接したときに液位検出信号(電気信号)を出力する磁石方式の近接センサとしている。この液位検出装置4Aの詳細な動作は、既に説明したので省略する。
なお、この近接センサとしては、磁石式のセンサ以外の近接センサ、例えば「高周波発信方式の近接センサ」などその他の公知の近接センサを用いることができる。高周波発信方式の近接センサは、フロート内に金属を設け、容器外部にセンサとして、コイルに高周波電流を与えて高周波磁界を発生させておき、液位変化に伴いこの高周波磁界にフロート(金属)が接近すると金属中に誘導電流が流れて発振が減衰(又は停止)するので、この発振状態変化を発信状態検出回路で検出して出力回路を動作させることで実現できる。
次に、図6及び図7により、本実施例に用いる各液位検出装置の「フロート」の具体的な構成例を説明する。図6は、フロートの構成を示す図であり、図6の(A)は上面図、(B)は正面断面図、(C)は(B)のM-M断面を示す図である。図7は、フロートの構成部品を分解図として示している。
図6および図7において、液位検出装置のフロート、例えばフロート74は、ハウジング87と、蓋89と、蓋のシール部材88と、磁石86と、磁石86を固定する磁石固定部87Bとで構成される。なお、ハウジング87は、容器内の位置決めを行う容器内位置決め部87Aを有する構成としている。蓋固定部87Cは、蓋89をハウジング87に固定するためのものである。
(洗浄ユニットにおける洗浄動作)
次に、洗浄ユニット3の動作について、図8~図10により説明する。図8は、洗浄ユニット3に印字ヘッド2をセットした状態の洗浄ユニット断面図である。図9は、洗浄ユニット3において、回収容器4内の液体量(洗浄後の洗浄液69Bの収容量)がほぼ一杯になったことを検出した状態を示す図である。図10は、洗浄ユニットにおいて、回収容器4を取外した状態を示す図である。
次に、洗浄ユニット3の動作について、図8~図10により説明する。図8は、洗浄ユニット3に印字ヘッド2をセットした状態の洗浄ユニット断面図である。図9は、洗浄ユニット3において、回収容器4内の液体量(洗浄後の洗浄液69Bの収容量)がほぼ一杯になったことを検出した状態を示す図である。図10は、洗浄ユニットにおいて、回収容器4を取外した状態を示す図である。
図8において、印字ヘッド2を洗浄する際には、印字ヘッド2を洗浄ユニット3にセット(挿入)する。セット時には、印字ヘッド2の保護カバー17は外す。なお、保護カバーにスライド扉を設け、挿入の際にそのスライド扉をスライドして印字ヘッド2の内部の部品(ノズル、帯電電極、偏向電極、など)を洗浄槽71内で露出する構成にすれば、保護カバー17を取り外す手間が省ける。
洗浄は、そのセット後に開始される。洗浄ノズル72は、矢印J,Kで示すように洗浄液を印字ヘッドに向けて噴出し印字ヘッドを洗浄する。洗浄液により、印字ヘッド2の内部に組付けられたノズル21や帯電電極23、偏向電極24やガター25などの構成部品を洗浄しながら、矢印Lで示したように重力で下方に流れ落ちていく。洗浄槽71の下部に流れ落ちてきた洗浄液は、矢印Mに示したように回収容器4に向かって流れていき、回収容器4の内部に収容される。印字ヘッドの洗浄が終了すると、エアノズル73により、印字ヘッドを乾燥させる。
洗浄の実施により洗浄槽71から洗浄後の洗浄液69Bが落下し、回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bの液位が上昇するが、図8の場合はまだ液位が低い位置であり、液位検出装置4Aのフロート74は変動せず、センサ76は液位検出信号を出力している。この液位検出信号は、電線76Aを介して制御部7に取込まれる。制御部7は、センサ76が液位検出信号を出力している期間中は、回収容器4が洗浄液69Bをまだ十分に収容可能であると判断し、洗浄液69Bを排出するための警告表示は行わない。
回収容器4内に洗浄液69Bがほぼ満杯である場合、図9に示すような状態になる。すなわち、回収容器4内の液位上昇により、フロート74が浮上がり、センサ76は、液位検出信号を出力することができなくなっている。この場合、制御部7は、回収容器4内にさらに収容可能な洗浄液69Bの量は少なく、ほぼ満杯であることを検知(判断)することができるので、このような状態で制御部は操作表示部8に警告を表示する。例えば、回収容器4を取外して中の洗浄液69Bを排出すべきことを表示しても良い。なお、警告は、操作表示部8に表示することのみを述べてきたが、ブザーや音声で作業者に知らせても良い。表示に加えて、ブザーや音声等で警告するもできる。このような警告により、作業員は、図10に示すように、回収容器4を取外し、回収容器4内の洗浄液69Bを排出することができる。そして、空になった回収容器4を、再び洗浄槽71の底部に取付ける。液位検出装置のセンサを回収容器の外側に設置しているので、回収容器4の取外し、取付け作業は容易である。
回収容器4を取付けた場合、フロート74がストッパ75Aの位置にあるため、センサ76は液位検知信号の出力を開始する。制御部7は、センサ76からの液位検出信号を受信し、回収容器4が取付けられたことを判断することができる。この判断により、制御部7は、操作表示部8に表示していた警告表示を消去する。あるいは、洗浄ユニット3が動作可能(洗浄可能)な状態であることを表示することや、洗浄動作の禁止状態を解除し、洗浄を許可するよう制御することができる。
(実施例における効果)
以上説明したように、本発明の実施例によれば、インクジェット記録装置に用いる液位検出装置の構成を、容器内側に液位変動により上下動するフロートと、容器外側にそのフロートが所定位置に近接したことを検知する少なくとも1個のセンサを設ける構成としたので、容器の取付け及び取外しを簡単に実施することができる。また、この実施例で説明した液位検出装置の場合、液位検出装置の液位検出信号の出力状態により、容器が取外されているか取付けられているかを検知することができる。さらに、洗浄ユニットの回収容器内の液位を検出するに液位検出装置では、少なくとも1個のセンサで構成することができるので、構造が簡単で低コストの液位検出装置を実現することもできる。
以上説明したように、本発明の実施例によれば、インクジェット記録装置に用いる液位検出装置の構成を、容器内側に液位変動により上下動するフロートと、容器外側にそのフロートが所定位置に近接したことを検知する少なくとも1個のセンサを設ける構成としたので、容器の取付け及び取外しを簡単に実施することができる。また、この実施例で説明した液位検出装置の場合、液位検出装置の液位検出信号の出力状態により、容器が取外されているか取付けられているかを検知することができる。さらに、洗浄ユニットの回収容器内の液位を検出するに液位検出装置では、少なくとも1個のセンサで構成することができるので、構造が簡単で低コストの液位検出装置を実現することもできる。
以上、本発明の実施例について説明したが、本発明は上記した実施例に限定されるものではなく、本発明は様々な変形例が含まれる。また、上記した実施例は本発明を分かりやすく説明するために詳細に説明したものであり、必ずしも説明した全ての構成を備えるものに限定されない。
1…本体、2…印字ヘッド、3…洗浄ユニット、4…回収容器、4A…液位検出装置、5…導管、6…導管、7…制御部、8…操作表示部、11…ベルトコンベア、12A…印字対象物、12B…印字対象物、13…印字ヘッド固定用金具、16…ヘッドベース、17…保護カバー、21…ノズル、23…帯電電極、24…偏向電極、25…ガター、26…切替弁、31…インク容器、31A…液位検出装置、32…補助インク容器、32A…液位検出装置、33…溶剤容器、33A…液位検出装置、34…ポンプ、35…ポンプ、37…ポンプ、38…ポンプ、39…フィルタ、40…フィルタ、41…フィルタ、43…フィルタ、45…粘度測定器、46…調圧弁、47…圧力センサ、49…電磁弁、50…電磁弁、53…電磁弁、54…電磁弁、55…電磁弁、56…電磁弁、68A…インク、68B…インク粒子、68C…インク、69A…溶剤、69B…洗浄液、70…電源、71…洗浄槽、71A…液出口部、71B…取付部、72…洗浄ノズル、72A…液吐出穴、72B…液吐出穴、73…エアノズル、73A…エア吐出穴、73B…エア吐出穴、74…フロート、75…ホルダー、75A…、ストッパ、75B…ストッパ、75C~75F…開口、76…センサ、76A…電線、77A…取付部、81…蓋ブロック、81A…印字ヘッドの挿入部、82…蓋ヒンジ、83…蓋部材、84…液継手、85…カバー、86…磁石、87…ハウジング、87A…容器内位置決め部、87B…磁石固定部、87C…蓋固定部、88…シール部材、89…蓋、89A…固定部、91…固定用治具(本体用)、92…固定用治具(コンベア用)、93…篏合部、100…インクジェット記録装置、311…フロート、312…ホルダー、313…センサ、314…センサ、315…支持部材、321…フロート、322…ホルダー、323…センサ、324…センサ、325…支持部材、331…フロート、332…ホルダー、333…センサ、334…センサ、335…支持部材、510…容器ユニット、520…流路ボード、530…ポンプユニット、540…電磁弁ユニット、701…マイクロプロセッシングユニット(MPU)、702…リードオンリーメモリ(ROM)、703…ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)、704…印字ヘッド制御回路、705…ポンプ制御回路、電磁弁制御回路、707…液位検出信号入力部、708…バス、801~803…経路、804…経路、805…経路、809…経路、810…経路、811…経路、812…経路、821…経路、825…経路、901…合流経路、903…分岐経路
Claims (18)
- 印字を行う印字ヘッドと、インク容器と、前記インク容器内のインクを前記印字ヘッドに供給するとともに印字に使用しない前記インクを前記インク容器に回収するための経路と、前記印字ヘッドに前記インクを供給する制御と前記印字ヘッドの印字動作を制御する制御部とを有するインクジェット記録装置であって、
前記印字ヘッドを収容可能な空間を有し下部に液出口部を有する洗浄槽と、前記洗浄槽内に収容された前記印字ヘッドに向けて洗浄液を噴出し洗浄する洗浄ノズルと、前記洗浄槽の前記液出口部から流出する洗浄液を回収する回収容器とを備えた洗浄ユニットと、
前記回収容器内の前記洗浄液の液位を検出する第1液位検出装置とを設け、
前記第1液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動する第1フロートと、前記第1フロートを保持する第1ホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記第1フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力する第1センサを設置した構成とし、
前記制御部は、前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断するインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記第1ホルダーは、前記回収容器の液位の中間位置にストッパを備え、前記第1フロートを前記ストッパの上側に配置して中間位置以上の液位となった場合に前記第1フロートが上下動するように構成し、
前記第1センサは、前記第1フロートが前記中間位置に存在する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記第1センサは、少なくとも、前記第1フロートが最小液位を検知する位置または最大液位を検知する位置に近接する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記インク容器内の前記インクの液位を検出する第2液位検出装置を設け、
前記第2液位検出装置は、前記インク容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動する第2フロートと、前記第2フロートを保持する第2ホルダーを備えており、前記インク容器の外側に、前記第2フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力する第2センサを設置した構成とし、
前記制御部は、前記第2液位検出装置の前記液位検出信号を用いて前記インク容器内のインク量を所定範囲内に制御することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項4記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記第2センサは、少なくとも、前記第2フロートが最小液位を検知する位置または最大液位を検知する位置に近接する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記インク容器または前記洗浄ユニットに供給する溶剤を収容する溶剤容器を設け、
前記溶剤容器内の前記溶剤の液位を検出する第3液位検出装置を設け、
前記第3液位検出装置は、前記溶剤容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動する第3フロートと、前記第3フロートを保持する第3ホルダーを備えており、前記インク容器の外側に、前記第3フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力する第3センサを設置した構成とし、
前記制御部は、前記第3液位検出装置の前記液位検出信号を用いて前記溶剤容器内の溶剤量を所定範囲内に制御することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項6記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記第3センサは、少なくとも、前記第3フロートが最小液位を検知する位置または最大液位を検知する位置に近接する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記第1フロートは磁石を内蔵しており、前記第1センサは、前記第1フロートが近接したときに前記磁石により誘起される電流により前記液位検出信号を出力することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - 請求項1記載のインクジェット記録装置において、
前記制御部と接続される操作表示部を設け、
前記制御部は、前記回収容器が前記洗浄ユニットに取付けられていない場合には、前記操作表示部に警告情報を表示することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 - インクにより印字を行う印字ヘッドを有するインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットであって、
前記洗浄ユニットは、前記印字ヘッドを収容可能な空間を有し液出口部を有する洗浄槽と、前記洗浄槽内に収容された前記印字ヘッドに向けて洗浄液を噴出し洗浄する洗浄ノズルと、前記洗浄槽の前記液出口部から流出する洗浄後の前記洗浄液を回収する回収容器と、前記回収容器内の前記洗浄液の液位検出信号を出力する液位検出装置とを備えており、
前記液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、前記液位に対応して移動するフロートと、前記フロートを保持するホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力するセンサを設置した構成とし、
前記液位検出信号を用いて前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット。 - 請求項10記載のインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットにおいて、
前記ホルダーは、前記回収容器の液位の中間位置にストッパを備え、前記フロートを前記ストッパの上側に配置させて前記中間位置以上の液位となった場合に前記フロートが上下動するように構成し、
前記センサは、前記フロートが前記中間位置に存在する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット。 - 請求項10記載のインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットにおいて、
前記センサは、少なくとも、前記フロートが最小液位を検知する位置または最大液位を検知する位置に近接する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット。 - 請求項10記載のインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットにおいて、
前記フロートは磁石を内蔵しており、前記センサは、前記フロートが近接したときに前記磁石により誘起される電流により前記液位検出信号を出力することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットの洗浄ユニット。 - 請求項10記載のインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットにおいて、
前記液位検出信号を入力する制御部と、前記制御部と接続される操作表示部とを設け、
前記制御部は、前記回収容器が前記洗浄ユニットに取付けられていない場合には、前記操作表示部に警告情報を表示することを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニット。 - 容器内の液体の液位を検出するための液位検出装置であって、
前記液位検出装置は、前記回収容器内に、液位に対応して移動するフロートと、前記フロートを保持するホルダーとを備えており、前記回収容器の外側に、前記フロートが近接したときに前記液位検出信号を出力するセンサを設置した構成とし、
前記液位検出信号を用いて前記液位検出信号から前記回収容器の装着状況を判断することを特徴とする液位検出装置。 - 請求項15記載の液位検出装置において、
前記ホルダーは、前記回収容器の液位の中間位置にストッパを備え、前記フロートを前記ストッパの上側に配置させて中間位置以上の前記液位となった場合に前記フロートが上下動するように構成し、
前記センサは、前記フロートが前記中間位置に存在する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とする液位検出装置。 - 請求項15記載の液位検出装置において、
前記センサは、少なくとも、前記フロートが最小液位を検知する位置または最大液位を検知する位置に近接する場合に前記液位検出信号を出力するように設置していることを特徴とする液位検出装置。 - 請求項15記載の液位検出装置において、
前記フロートは磁石を内蔵しており、前記センサは、前記フロートが近接したときに前記磁石により誘起される電流により前記液位検出信号を出力することを特徴とする液位検出装置。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021562451A JP7364690B2 (ja) | 2019-12-04 | 2020-07-06 | インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 |
| JP2023173737A JP2023171955A (ja) | 2019-12-04 | 2023-10-05 | インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019219478 | 2019-12-04 | ||
| JP2019-219478 | 2019-12-04 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021111669A1 true WO2021111669A1 (ja) | 2021-06-10 |
Family
ID=76221874
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/026424 WO2021111669A1 (ja) | 2019-12-04 | 2020-07-06 | インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP7364690B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2021111669A1 (ja) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63122546A (ja) * | 1986-11-12 | 1988-05-26 | Hitachi Ltd | インクジエツト記録装置の記録部洗浄装置 |
| US5183066A (en) * | 1991-04-02 | 1993-02-02 | General Dynamics Corp., Air Defense Systems Division | Spray nozzle cleaning apparatus and method |
| JP2009241492A (ja) * | 2008-03-31 | 2009-10-22 | Brother Ind Ltd | インクカートリッジ、溝形成方法 |
| JP2011020353A (ja) * | 2009-07-16 | 2011-02-03 | Brother Industries Ltd | 液体供給装置 |
| JP2014028466A (ja) * | 2012-07-31 | 2014-02-13 | Brother Ind Ltd | 液体貯留装置 |
| JP2019171651A (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-10 | 株式会社日立産機システム | 洗浄装置、及びインクジェット記録装置 |
-
2020
- 2020-07-06 WO PCT/JP2020/026424 patent/WO2021111669A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2020-07-06 JP JP2021562451A patent/JP7364690B2/ja active Active
-
2023
- 2023-10-05 JP JP2023173737A patent/JP2023171955A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63122546A (ja) * | 1986-11-12 | 1988-05-26 | Hitachi Ltd | インクジエツト記録装置の記録部洗浄装置 |
| US5183066A (en) * | 1991-04-02 | 1993-02-02 | General Dynamics Corp., Air Defense Systems Division | Spray nozzle cleaning apparatus and method |
| JP2009241492A (ja) * | 2008-03-31 | 2009-10-22 | Brother Ind Ltd | インクカートリッジ、溝形成方法 |
| JP2011020353A (ja) * | 2009-07-16 | 2011-02-03 | Brother Industries Ltd | 液体供給装置 |
| JP2014028466A (ja) * | 2012-07-31 | 2014-02-13 | Brother Ind Ltd | 液体貯留装置 |
| JP2019171651A (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-10 | 株式会社日立産機システム | 洗浄装置、及びインクジェット記録装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2023171955A (ja) | 2023-12-05 |
| JP7364690B2 (ja) | 2023-10-18 |
| JPWO2021111669A1 (ja) | 2021-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021005890A1 (ja) | インクジェット記録装置およびインクジェット記録装置の制御方法 | |
| US7465044B2 (en) | Ink jet recording apparatus and liquid supply apparatus | |
| EP4241999A2 (en) | Inkjet recording device | |
| US8444242B2 (en) | Ink refilling device | |
| US9493009B2 (en) | Tank unit for supplying liquid to liquid jetting apparatus, and liquid jetting system including tank unit and liquid jetting apparatus | |
| JP2015047700A (ja) | 液体容器及びそれを備えたインクジェット記録装置 | |
| CN115570887A (zh) | 喷墨记录装置和打印头清洗装置 | |
| US20170028736A1 (en) | Lid for an ink reservoir with mixing function | |
| WO2021111669A1 (ja) | インクジェット記録装置、インクジェット記録装置の洗浄ユニットおよび液位検出装置 | |
| CN115135507B (zh) | 喷墨记录装置和喷墨记录装置的清洗方法 | |
| JP2021041606A (ja) | インクジェット記録装置 | |
| JP7229071B2 (ja) | 液体収容装置 | |
| CN111826899B (zh) | 洗衣机 | |
| WO2022097212A1 (ja) | インクジェット記録装置 | |
| JP2020121520A (ja) | 容器 | |
| JP2005001195A (ja) | インクジェット記録装置 | |
| CN111497450B (zh) | 具备罐主体和盖的罐 | |
| JP6879251B2 (ja) | 液体排出装置 | |
| JP2007190726A (ja) | マーキング装置 | |
| CN117320885A (zh) | 喷墨记录装置和喷墨记录系统 | |
| JP2017140734A (ja) | 液体供給装置、液体噴射装置 | |
| JP2022112283A (ja) | 流路監視装置 | |
| JP2019111787A (ja) | 液体排出装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20895143 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021562451 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20895143 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |